Schlüsselwörter Dopamintransporter-Szintigrafie, 123 I-Ioflupan, FP-CIT, DaTSCAN, semi-quantitative Analyse, Referenzregion, globale Skalierung
|
|
|
- Sheryl Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article 1 Global scaling for semi-quantitative analysis in FP-CIT SPECT D. Kupitz 1 *; I. Apostolova 1 *; C. Lange 2 ; G. Ulrich 1 ; H. Amthauer 1 ; W. Brenner 2 ; R. Buchert 2 1 Radiologie und Nuklearmedizin, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität, Magdeburg, Germany; 2 Nuklearmedizin, Universitätsmedizin Charité Berlin, Germany Keywords Dopamine transporter scintigraphy, 123 I- ioflupane, FP-CIT, DaTSCAN, semi-quantitative analysis, reference region, global scaling Summary Semi-quantitative characterization of dopamine transporter availability from single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) with 123 I-ioflupane (FP-CIT) is based on uptake ratios relative to a reference region. The aim of this study was to evaluate the whole brain as reference region for semiquantitative analysis of FP-CIT SPECT. The rationale was that this might reduce statistical noise associated with the estimation of non-displaceable FP-CIT uptake. Patients, methods: 150 FP-CIT SPECTs were categorized as neuro degenerative or non-neurodegenerative by an expert. Semi-quantitative analysis of specific binding ratios (SBR) was performed with a custom-made tool based on the Statistical Parametric Mapping software package using predefined regions of interest (ROIs) in the anatomical space of the Montreal Neurological Institute. The following reference regions were compared: predefined ROIs for frontal and and whole brain (without striata, thalamus and brainstem). Tracer uptake in the reference region was characterized by the mean, median or 75th percentile of its voxel intensities. The area (AUC) under the receiver operating Correspondence to: Ralph Buchert, PhD Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin Department of Nuclear Medicine Charitéplatz 1, Berlin, Germany Tel. +49/(0)30/ Fax +49/(0)30/ * These authors contributed equally. characteristic curve was used as performance measure. Results: The highest AUC of was achieved by the SBR of the putamen with the 75 th percentile in the whole brain as reference. The lowest AUC for the putamen SBR of was obtained with the mean in the as reference. Conclusion: We recommend the 75 th percentile in the whole brain as reference for semi-quantitative analysis in FP-CIT SPECT. This combination provided the best agreement of the semi-quantitative analysis with visual evaluation of the SPECT images by an expert and, therefore, is appropriate to support less experienced physicians. Schlüsselwörter Dopamintransporter-Szintigrafie, 123 I-Ioflupan, FP-CIT, DaTSCAN, semi-quantitative Analyse, Referenzregion, globale Skalierung Zusammenfassung Die semi-quantitative Charakterisierung der Verfügbarkeit von Dopamintransportern bei der Einzel-Photonen-Emissions-Tomographie (SPECT) mit 123 I-Ioflupan (FP-CIT) basiert auf dem Vergleich des Uptakes in striatalen Regionen mit einer Referenzregion. Ziel dieser Studie war die Evaluierung des gesamten Gehirns als Referenzregion für die semi-quantitative Analyse bei der FP-CIT SPECT. Die Rationale hierfür war, dass dies zu einer Reduktion des Globale Skalierung des Tracer-Uptakes für die semi- quantitative Analyse in der FP-CIT SPECT Nuklearmedizin 2014;53:- received: April 4, 2014 accepted in revised form: August 25, 2014 epub ahead of print: September 11, 2014 statistischen Fehlers bei der Bestimmung der unspezifischen FP-CIT-Aufnahme führen könnte. Patienten, Methoden: 150 FP-CIT SPECTs wurden retrospektiv eingeschlossen und mittels visueller Beurteilung durch einen erfahrenen Befunder als neurodegenerativ oder nicht neurodegenerativ kategorisiert. Für den benutzerunabhängigen Vergleich der verschiedenen Referenzregionen wurden semi-quantitative Analysen von SBR (specific binding ratios) vollautomatisch mit einem eigenen Tool durchgeführt, welches Routinen des Statistical Parametric Mapping Software- Pakets und im anatomischen Raum des Montreal Neurological Institutes vordefinierte ROIs (regions of interest) verwendet. Es wurden folgende Referenzregionen miteinander verglichen: ROIs für den Frontal- und Okzipitallappen, sowie das gesamte Gehirn (ohne Striatum, Thalamus und Hirnstamm). Der Tracer Uptake in der Referenzregion wurde durch den Mittelwert, Median oder das 75. Perzentil der Voxelintensitäten in der Referenzregion charakterisiert. Die Fläche (AUC) unter der Receiver Operating Characteristic Kurve für die Differenzierung von neurodegenerativ und nicht neurodegenerativ wurde als Maß für das diagnostische Potential der semi-quantitativen Analyse verwendet. Ergebnisse: Die größte AUC (0,973) erzielte das SBR des Putamens mit dem 75. Perzentil im gesamten Gehirn als Referenzwert. Die kleinste AUC (0,937) für das Putamen SBR ergab sich mit dem Mittelwert des Frontallappens als Referenz. Schlussfolgerung: Wir empfehlen die Verwendung des 75. Perzentils im gesamten Gehirn als Referenz für die semi-quantitative Analyse von FP-CIT SPECTs. Dieser Referenzwert scheint zur besten Übereinstimmung von semi-quantitativer Analyse mit visueller Beurteilung der SPECT Bilder durch einen erfahrenen Experten zu führen und ist daher für die Unterstützung weniger erfahrener Befunder besonders geeignet. Schattauer 2014 Nuklearmedizin 6/2014
2 2 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) with N-ω-fluoro - propyl-2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(4-123 I-iodo - phenyl)nortropane (FP-CIT) is widely used for the differentiation of Parkinsonian syndromes (PS) with presynaptic dopaminergic loss (referred to as neurodegenerative PS) versus PS without such loss (non-neurodegenerative PS) (4, 6, 11, 12, 19, 21, 24). FP-CIT is registered for this indication in both the United States and in Europe. Guidelines for the diagnosis of Parkinson s disease recommend FP-CIT SPECT with the highest evidence level, particularly in the presence of significant diagnostic uncertainty such as parkinsonism associated with neuroleptic exposure and atypical tremor manifestations such as isolated unilateral postural tremor (3). In Europe, FP-CIT is also registered for the differentiation between dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer s disease (27). The interpretation of FP-CIT SPECT is based on visual assessment of the SPECT images. Visual analysis can be supported by semi-quantitative analysis of FP-CIT uptake in the striatum (8, 9, 13, 15, 20, 22, 29). Semi-quantitative analysis can be useful in follow-up studies and in borderline cases with mild reduction of FP-CIT uptake, particularly for less experienced raters. Semiquantitative analysis of FP-CIT SPECT usually is performed as pseudo-equilibrium analysis, to be more specific, by determination of the so-called specific binding ratio SBR according to the following formula SBR = (C ROI : C REF ) 1 (1), where C ROI and C REF and are the total tracer concentration in the region of interest and the reference region, respectively, during pseudo-equilibrium (in case of FP-CIT 3 6 h post injection). It is evident from this formula that the choice of an adequate reference region is important for reliable determination of the SBR. A pivotal requirement for the reference region is that it is void of the specific binding site or shows only very low concentrations. Considering the dopamine transporter (DAT), Hall and co-workers, using autoradiography with the highly selective DAT ligand 125 I-PE2I in normal post mortem human brains, found high DAT density in the striatum (10). Distinct DAT density was also found in the substantia nigra in the brainstem (about 50% of the level in the striatum). Other brain structures including thalamus, hippocampus, cerebellum and neocortical regions showed no or very low DAT density. According to these findings, all brain regions except striatum and brainstem (substantia nigra) appear appropriate as reference region in FP-CIT SPECT. However, very often the reference region is restricted to the (8, 9) or, less often, to the or the cerebellum (15). This restriction to a smaller than necessary reference region might result in increased test-retest and inter-subject variability of the SBR, not only due to increased statistical noise of C REF, but also due to variability in the identification (segmentation) of the reference region in each individual scan. In the, inter-subject variability might be further increased by particularly large unspecific uptake in white matter (10). Increased inter-subject variability reduces the statistical power of the SBR to detect alterations of DAT availability. This loss of diagnostic power might be reduced by increasing the spatial extent of the reference region. In the present study we propose and evaluate the largest possible reference region for FP-CIT SPECT, the whole brain without the striatum and the brainstem. The thalamus was also excluded from the reference region, because it shows rather high density of serotonin transporters (14) to which FP-CIT also binds with non-negligible affinity (28). A first step towards the use of the whole brain without striatum as reference region in FP-CIT SPECT has been described by Tossici-Bolt and co-workers who used a 44 mm thick transaxial slice centred at the highest striatal FP-CIT uptake for semiquantitative analyses (23). The whole brain (with exclusion of the striata) enclosed in this slab was used as reference region. The present study extends the so-called 2-dimensional method of these authors to a fully 3-dimensional approach by using a 3-dimensional region of interest (ROI) for the whole brain without striatum, thalamus and brainstem as reference region. In the following we abbreviate whole brain without striatum, thalamus and brainstem by (= all regions of the whole brain which show only non-displaceable FP-CIT uptake). 150 consecutive patients from clinical routine were included retrospectively for comparison of with occipital or as reference region in semiquantitative analysis. All patients had been referred to FP-CIT SPECT because of a clinically uncertain Parkinsonian syndrome. The mean, the median and the 75 th percentile of all voxel values within the reference region were compared for characterization of the FP-CIT uptake in the reference region. The rationale for the median instead of the mean was to exclude voxels in cerebrospinal fluid, and that the median might be less sensitive to moderate (disease-related) intensity changes. The rationale for the 75 th percentile was that it might be more representative of grey matter voxels than the median (50 th percentile). The latter is expected to represent both grey and white matter. In order to avoid operator-dependence and potential bias in the semi-quantitative analyses, a custom made, SPM-based software tool for fully automated analysis of FP-CIT SPECTs was used, similar to a tool previously developed by our group for fully automated analysis of dopamine receptor SPECT with 123 I-IBZM (7). Patients, material, methods Patients 150 consecutive patients who had been referred to the Department of Nuclear Medicine of the university medical centre Magdeburg, Germany, between August 2012 and September 2013 for FP-CIT SPECT because of an unclear Parkinsonian syndrome (PS) were recruited retrospectively. No further inclusion or exclusion criteria were applied. Patients were categorized as either neurodegenerative or non-neurodegenerative PS by an experienced physician (I.A.) based on visual inspection of the SPECT images using the rating scale described by Benamer and co-workers (2). Nuklearmedizin 6/2014 Schattauer 2014
3 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT 3 Fig. 1 Predefined standard masks for the regions of interest (caudate, putamen) and the different reference regions in the anatomical space of the Montreal Neurological Institute. The whole brain mask excludes caudate, putamen, thalamus and brainstem (it includes the frontal and the ) fro: ; cau: caudate; put: putamen; wb: whole brain; occ: ; tha: thamalus The visual evaluation was performed blinded for both clinical information and the results of the semi-quantitative analysis. 66 patients were categorized as nonneurodegenerative PS (36 women, age 67.8 ± 12.8 years, years), 84 patients as neurodegenerative PS (29 women, age 68.1 ± 11.8 years, years). This categorization was used as ground truth. The study protocol had been approved by the local Clinical Institutional Review Board (reference number 02/14, RAD241) and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. SPECT acquisition SPECT data had been acquired with a dual head gamma camera E.CAM 7957 (Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with low-energy, high-resolution fanbeam collimators (focal distance 417 mm). The acquisition had started 3 hours after intravenous injection of MBq FP-CIT following blocking of the thyroid gland by oral administration of perchlorate. A matrix was used and an energy window with a width of ± 10% was centred at the photopeak of 123 I at 159 kev. The collimator-patient distance ranged between 16.5 and 18.0 cm. Each camera head covered 180 of a circular orbit in step and shoot mode with 60 angular views at steps of 3. The duration of the acquisition at each step was 40 s resulting in a total acquisition time of about 40 min. Transversal SPECT images were reconstructed by the filtered backprojection algorithm implemented in the scanner software (esoft 3.5) with a Butterworth filter (cutoff cm -1 ). Attenuation correction was performed by Changs method with a linear attenuation coefficient of 0.11 cm -1. No scatter correction was applied. The size of the reconstructed voxels was mm3. Semi-quantitative analyses Semi-quantitative analyses were performed fully automatically using a custom made, SPM-based software tool for the analysis of FP-CIT SPECT. The tool is similar to a tool previously developed by our group for fully automated analysis of dopamine receptor SPECT with 123 I-IBZM (7). The SPM tool first stereotactically normalizes the patient s FP-CIT SPECT to a custom made FP-CIT template in the anatomical space of the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) ( Fig. 1). The normalization routine of SPM8 is used for this purpose, including both affine transformation and warping (parameter settings: source image smoothing: 16 mm, source weighting image: none, template image smoothing: 0 mm, template weighting image: none, affine regularization: MNI space, non-linear frequency cut-off: 25, non-linear iterations: 12, non-linear regularization: 1, intensity modulation: preserve intensities of original image, voxel size: mm 3, bounding box: [ ; ], interpolation: tri-linear, wrapping: none). The fully automated ROI analysis performed by the tool is based on standard ROIs predefined as masks in MNI space ( Fig. 1). The whole brain was defined by the standard SPM8 brain mask. Thalamus and brainstem were removed from the whole brain mask using the ROIs for thalamus and brainstem (union of midbrain, pons and medulla) defined in the Wake Forest University (WFU) pickatlas (TDLobes, TDLabels) (17). The masks for occipital and were created from the corresponding ROIs of the WFU pickatlas (TDLobes), too. ROIs for caudate and putamen were defined manually in one hemisphere and then mirrored to the other. These ROIs are much bigger than caudate and putamen in order to guarantee that the actual caudate and putamen are completely included in the standard ROIs in each individual patient, independent of some residual anatomical inter-subject variability after stereotactical normalization. Mean FP-CIT uptake in the caudate and in the putamen was obtained by hottest voxel analysis within the large ROIs, separately in left and right hemisphere. The number of hottest voxels to be averaged was fixed to a total volume of 5 ml for the caudate and 10 ml for the putamen. The total volume of 15 ml for caudate and putamen is compatible with the normal range of the striatum volume in healthy subjects (1). In case of severely reduced FP-CIT uptake in the putamen, for example, manual definition of the putamen ROI tends to de- Schattauer 2014 Nuklearmedizin 6/2014
4 4 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT Tab. 1 Results of the semi-quantitative analysis: specific binding ratio in caudate and putamen, putamen-to-caudate ratio and left-right asymmetry (in %) in caudate and putamen for all combinations of reference region and characteristic value. Given are the mean value ± 1 standard deviation in the group of patients with neurodegenerative Parkinsonian syndrome (PS) and the group with non-neurodegenerative PS. For the specific binding ratio and the putamento-caudate ratio the minimum over both hemispheres was used. Parkinsonian syndrome reference region specific binding ratio caudate putamen characteristic putamen-to-caudate ratio left/right asymmetry caudate putamen neuro - degenerative (n = 84) mean BRASS 1.52 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± th percentile 1.49 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 15.9 median 1.86 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 13.3 non-neuro - degenerative (n = 66) mean BRASS 2.53 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± th percentile 2.18 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 5.2 median 2.62 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 4.7 : all regions of the whole brain which show only non-displaceable FP-CIT uptake lineate the regions with more or less conserved FP-CIT uptake. This results in overestimation of the FP-CIT uptake in the whole putamen (underestimation of the reduction) which in turn reduces the sensitivity for detection of reduced uptake. This limitation of manual ROI definition is avoided by the fully automated hottest voxel approach by using a fixed number of hottest voxels (stereotactical normalization is expected to eliminate inter-subject differences in the volume of the striatum and its subregions to a large extent, justifying the use of the same fixed striatal volume in all patients). FP-CIT uptake in the reference region was characterized either by the mean or by the median or by the 75 th percentile of the voxel values within the reference region. Specific binding ratios (SBR) were computed as the ratio of FP-CIT uptake in the region of interest (caudate, putamen) to the characteristic uptake in the reference region minus 1 (equation 1). This was done for each combination of reference region ( or or ) and characteristic value (mean or median or 75 th percentile), resulting in a total of nine SBRs for each region of interest. These nine SBRs for each region of interest were computed for all 150 patients fully automatically within a single batch processing session within a few minutes on a standard personal computer. The cerebellum, which is also used as reference region by some groups, was not considered in the present study, because it was not completely within the field-of-view of SPECT imaging in some patients (with short neck). For the as reference region, incomplete coverage of the brain by the SPECT field-of-view was taken into account by restricting the computation of the characteristic value (mean, median, 75 th percentile) to voxels with non-zero intensity. Semi-quantitative analysis was also performed with the commercially available brain analysis software BRASS (version 3.5, Hermes Medical Solutions, Stockholm, Sweden) (25). SPECT raw data were reconstructed iteratively on a Scivis workstation (Scivis-GmbH) with ReSPECT 2.5 software. BRASS stereotactically normalizes the patient s FP-CIT SPECT to an integrated template and then performes the ROI analyses. FP-CIT uptake is characterized by the mean value both in the region of interest (caudate, putamen) and in the reference region (). SBRs are Nuklearmedizin 6/2014 Schattauer 2014
5 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT 5 Tab. 2 Area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC) for the differentiation of neurodegenerative versus non-neurodegenerative Parkinsonian syndrome by the semi-quantitative measures of FP-CIT uptake as function of the reference region and the value used to characterize FP-CIT uptake in the reference region. The 95%-confidence interval of the AUC is given in square brackets. characteristic reference region specific binding ratio caudate putamen putamen-to-caudate ratio left/right asymmetry caudate putamen BRASS [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] mean [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 75 th percentile [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] median [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] : all regions of the whole brain which show only non-displaceable FP-CIT uptake computed as described above. It should be noted that, because of the use of a different reconstruction algorithm by the BRASS software, observed differences between results from BRASS and results obtained with the custom made SPM tool described above are a mixed effect of image reconstruction, ROI definition and characteristic value. The putamen-to-caudate ratio in both hemispheres and left/right asymmetry were considered in addition to SBRs: asym(%) = 200 abs[(sbr left SBR right ) : (SBR left + SBR right ) Statistical analyses Statistical analyses used the minimum over both hemispheres for SBRs and the putamen-to-caudate ratio in each patient. Univariate analysis of variance was performed with the SBR as dependent variable and the following variables as fixed factors: group (neurodegenerative vs non-neurodegenerative PS), region of interest (caudate, putamen), reference region (, occipital lobe, ) and type of characteristic value within the reference region (mean, median, 75 th percentile). Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to evaluate the impact of the reference region and the characteristic value on the power of the semiquantitative measures for differentiation between non-neurodegenerative and neuro degenerative PS. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was used as performance measure. (Maximum) diagnostic accuracy was determined by the point on the ROC curve closest to the upper left corner. Univariate and ROC analyses were performed with SPSS (version 19, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Results The processing quality of the fully automatic analysis of the FP-CIT SPECTs with the custom-made SPM tool was supervised by visual inspection of a 12 mm thick transversal slab through the striatum after stereotactical normalization (7). The latter is the critical processing step. However, stereotactical normalization worked properly in all cases, although no patient was excluded based on technical constraints such as poor quality of the SPECT image. Results of the semi-quantitative analysis are summarized ( Tab. 1). Univariate analysis of variance revealed a highly significant effect (p < ) on the SBR for all considered factors, i.e. group (lower SBR in neurodegenerative than in non-neurodegenerative PS), region of interest (lower SBR in putamen than in caudate), reference region (lowest SBR for ) and type of characteristic value within the reference region (lowest SBR for 75 th percentile). In addition, the following inter - actions had a significant effect on the SBR group: region of interest (p < , smaller putamen-to-caudate ratio in neuro - degenerative PS), reference region (p = 0.038, smallest group difference with as reference region) and reference region characteristic (p = 0.018, reduction of SBR with occipital lobe as reference region compared to and more pronounced for mean and median than for 75 th percentile). The results of the ROC analyses for the differentiation between neurodegenerative and non-neurodegenerative PS by the semi-quantitative measures are summarized ( Tab. 2). ROC curves for the SBR in caudate and putamen are shown Fig. 2. The semi-quantitative measures obtained by the custom-made SPM tool provided very similar diagnostic accuracy as the semiquantitative values provided by the BRASS software ( Tab. 2). Concerning the impact of the reference region and the characteristic value, the largest AUC of was achieved by the putamen SBR (minimum Schattauer 2014 Nuklearmedizin 6/2014
6 6 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT Fig. 2 Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves for the differentiation of neurodegenerative versus non-neurodegenerative Parkinsonian syndrome by the SBR of the caudate (left) and the putamen (right). Each coloured line represents a given combination of reference region and characteristic value of FP-CIT uptake in the reference region as specified in the legend. : whole brain (wb) without striatum, thalamus and brainstem; occ: : fro: ; 75 th perc.: 75 th percentile of left and right hemisphere) with the 75 th percentile in the whole brain as reference (maximum accuracy: 133 of 150 patients classified correctly, i.e. 88.7%). Using the occipital or as reference region (with the 75 th percentile) resulted in small reduction of the diagnostic accuracy of the putamen SBR (accuracy 87.3% and 86.7%). The effect of the characteristic value, i.e. mean vs. median vs. 75 th percentile, was also small (with whole brain as reference 88.7% accuracy for 75 th percentile and median, 85.3% for mean). The AUC was much smaller for the putamen-to-caudate ratio and the left/right asymmetries than for the SBRs (Tab. 2). Discussion The aim of our study was to evaluate the whole brain without striatum, thalamus and brainstem () as reference region for semi-quantitative analysis of FP-CIT SPECT. The choice of the reference region might be considered a technical aspect, but, as is evident from equation (1), the computation of the SBR is as sensitive to errors in the estimation of the FP-CIT uptake in the reference region (C REF ) as it is sensitive to errors in the estimation of the FP-CIT uptake in the region of interest (C ROI ). Thus, the choice of the reference region can have a significant impact on the error of the SBR, and, as direct consequence, on the diagnostic value of semiquantitative analysis. Increased variability of the SBR results in decreased statistical power for the detection of disease-related alterations of DAT availability. The is the largest possible reference region for FP-CIT SPECT, because the reference region must not contain the binding site of interest (the dopamine transporter) or other specific binding sites (the serotonin transporter), or at very low concentrations only. The rationale for choosing the largest possible reference region is that this might reduce the error of the estimation of the FP-CIT uptake in the reference region by decreased statistical noise of the mean (or other characteristic values) in an spatially increased reference region (larger sample size), and decreased error in the identification of the reference region (placement of the ROI) in each individual patient. In this study, the use of as reference region resulted in only a small improvement of the agreement between semiquantitative analysis and visual expert reading compared to the, although the effect on the SBRs itself was much larger ( Tab. 1) and highly significant statistically. The fact that the impact on the agreement was small suggests that neither the statistical error nor the error of the ROI placement was strongly reduced by the whole brain compared to the occipital lobe as reference. The lack of an effect on the statistical error might in part be explained by the rather large FP-CIT doses of MBq used in the patients included in this study. The effect of the reference region on the statistical quality of the estimate of the FP-CIT uptake in the reference region might be larger at lower FP-CIT doses, particularly in combination with the use of single-head SPECT systems. The guidelines of the (American) Society of Nuclear Medicine for FP-CIT SPECT recommend a dosage of MBq (9), in agreement with the prescribing information of the manufacturer. The European Association of Nuclear Medicine recommends MBq (9). The lack of an effect of the reference region on the error of the placement of the ROI might be explained by the fact that the semi-quantitative analysis was performed fully automatically using stereotactical normalization of each individual patient s SPECT image and predefined standard masks for the considered reference regions. Stereotactical normalization worked properly in all 150 cases, independent of the FP- CIT uptake in the striatum, although there were no inclusion or exclusion criteria with respect to the image quality of the SPECT images. This indicates the robustness of the method, which is an important prerequisite for its routine use in everyday clinical patient care. Successful stereotactical normalization and the use of predefined ROI masks for the reference regions eliminate errors of the identification of the reference region by manual placement (both intraand inter-rater errors) (26). The benefit of the whole brain as reference region, therefore, might be larger in case of manual ROI placement. Concerning the characteristic value used for the description of FP-CIT uptake in the reference region, a percentile might be less sensitive to some disease-related (or physiological) local alterations of tracer uptake in the reference region. This effect may have been observed in the present study to some extent with the whole brain as reference region: the AUC under the Nuklearmedizin 6/2014 Schattauer 2014
7 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT 7 ROC curve for the differentiation between neurodegenerative and non-neurodegenerative PS by the putamen SBR increased from for the mean value to for the median and for the 75 th percentile. Although the impact of reference region and characteristic value separately appears rather small in the present study, the total difference between the best combination (75 th percentile in the whole brain) and the worst (mean or median in ) was already rather sizable: AUC versus Diagnostic accuracy was 88.7% versus 84.7%, i. e. the best combination provided 4 % better accuracy than the worst. This appears a relevant improvement, particularly when taking into account that the diagnostic accuracy of 84.7% for the worst combination was already rather good, i. e. there was not very much space for improvement. The diagnostic value of the SBR was slightly smaller for the caudate than for the putamen ( Tab. 2). This is in agreement with the temporal progress of neurodegeneration in Parkinson s disease which affects the (posterior) putamen first (5, 13, 18). The diagnostic value of the secondary semi-quantitative measures putamen-tocaudate ratio and left/right asymmetries was considerably smaller than that of the primary SBR measures ( Tab. 2). Combining the putamen SBR with the putamen-to-caudate ratio and the left/right asymmetries by binary linear regression also did not improve the diagnostic power compared to the putamen SBR alone. This suggests that putamen-to-caudate ratio and left/right asymmetries provide no or very little additional information to improve the power of semi-quantitative analysis in FP-CIT SPECT in clinical routine. In this study, visual analysis of the SPECT images by an expert was used as gold standard for the evaluation of semiquantitative analysis. The rationale for this was that semi-quantitative analysis might support less experienced readers of FP-CIT SPECT so that they might achieve similar diagnostic performance as experts. However, best agreement between semi-quantitative analysis and the visual expert rating was 88.7%, i. e. there was disagreement in 11.3% of the cases. Most of these were borderline cases with rather mild reduction of striatal FP-CIT uptake. It would be very interesting to clarify these cases, i. e. to check whether visual or semi-quantitative analysis was correct. However, this requires a reliable ground truth, clinical follow-up over a period of 2 years, for example, which was not available. Conclusion We recommend the 75 th percentile in the whole brain (without striatum, thalamus and brainstem) as reference for semiquantitative analysis in FP-CIT SPECT. This combination provides slightly better agreement of the semi-quantitative analysis with visual evaluation of the SPECT images by an expert compared to the mean FP- CIT uptake in a smaller reference region such as the. We hypothesize that the improvement by the 75 th percentile in the whole brain is particularly large in case of low statistical image quality (low FP-CIT dose) and/or manual placement of ROIs. However, it should be mentioned that the impact of the different semi-quantitative analysis methods tested in the present study on the diagnostic accuracy was rather small, which underlines the robustness of FP-CIT SPECT. It also suggests that it probably is more important that the analysis is always done the same way than using a particular method. Conflict of interest The authors declare that that they have no conflicts of interest. References 1. Aylward EH, Li Q, Habbak QR et al. Basal ganglia volume in adults with Down syndrome. Psychiatry Res 1997; 74: Benamer TS, Patterson J, Grosset DG et al. Accurate differentiation of parkinsonism and essential tremor using visual assessment of [ 123 I]-FP-CIT SPECT imaging: the [ 123 I]-FP-CIT study group. Movement disorders 2000; 15: Berardelli A, Wenning GK, Antonini A et al. EFNS/MDS-ES/ENS [corrected] recommendations for the diagnosis of Parkinson s disease. Eur J Neurol 2013; 20: Berding G, Brucke T, Odin P et al. [ 123 I]beta-CIT SPECT imaging of dopamine and serotonin transporters in Parkinson s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nuklearmedizin 2003; 42: Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O et al. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci 1973; 20: Booij J, Tissingh G, Boer GJ et al. [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT shows a pronounced decline of striatal dopamine transporter labelling in early and advanced Parkinson s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 1997; 62: Buchert R, Berding G, Wilke F et al. IBZM tool: a fully automated expert system for the evaluation of IBZM SPECT studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006; 33: Darcourt J, Booij J, Tatsch K et al. EANM procedure guidelines for brain neurotransmission SPECT using 123 I-labelled dopamine transporter ligands, version 2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010; 37: Djang DS, Janssen MJ, Bohnen N et al. SNM practice guideline for dopamine transporter imaging with 123 I-ioflupane SPECT 1.0. J Nucl Med 2012; 53: Hall H, Halldin C, Guilloteau D et al. Visualization of the dopamine transporter in the human brain postmortem with the new selective ligand [ 125 I]PE2I. NeuroImage 1999; 9: Hesse SOC, Meyer PT, Roessler A et al. Is there a role for I-123-FP-CIT SPECT in the management of suspected Parkinsons disease? J Nucl Med 2003; 44 (5 Suppl): Innis RB, Seibyl JP, Scanley BE et al. Single photon emission computed tomographic imaging demonstrates loss of striatal dopamine transporters in Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: Kahraman D, Eggers C, Holstein A et al. 123 I-FP- CIT SPECT imaging of the dopaminergic state. Visual assessment of dopaminergic degeneration patterns reflects quantitative 2D operator-dependent and 3D operator-independent techniques. Nuklearmedizin 2012; 51: Kish SJ, Furukawa Y, Chang LJ et al. Regional distribution of serotonin transporter protein in postmortem human brain: is the cerebellum a SERTfree brain region? Nucl Med Biol 2005; 32: Koch W, Hornung J, Hamann C et al. Equipmentindependent reference values for dopamine transporter imaging with 123 I-FP-CIT. Nuklearmedizin 2007; 46: Koch W, Radau PE, Hamann C, Tatsch K. Clinical testing of an optimized software solution for an automated, observer-independent evaluation of dopamine transporter SPECT studies. J Nucl Med 2005; 46: Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH. An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fmri data sets. NeuroImage 2003; 19: Oh M, Kim JS, Kim JY et al. Subregional patterns of preferential striatal dopamine transporter loss differ in Parkinson disease, progressive supranu- Schattauer 2014 Nuklearmedizin 6/2014
8 8 D. Kupitz et al.: Global scaling in FP-CIT SPECT clear palsy, and multiple-system atrophy. J Nucl Med 2012; 53: Seibyl JP, Marek KL, Quinlan D et al. Decreased single-photon emission computed tomographic [ 123 I]beta-CIT striatal uptake correlates with symptom severity in Parkinson s disease. Ann Neurol 1995; 38: Soderlund TA, Dickson JC, Prvulovich E et al. Value of semiquantitative analysis for clinical reporting of 123 I-2-beta-carbomethoxy-3beta- (4-iodophenyl)-N-(3-fluoropropyl)nortropane SPECT studies. J Nucl Med 2013; 54: Tatsch K, Poepperl G. Nigrostriatal dopamine terminal imaging with dopamine transporter SPECT: an update. J Nucl Med 2013; 54: Tatsch K, Poepperl G. Quantitative approaches to dopaminergic brain imaging. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2012; 56: Tossici-Bolt L, Hoffmann SM, Kemp PM et al. Quantification of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT brain images: an accurate technique for measurement of the specific binding ratio. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006; 33: Van Laere K, Everaert L, Annemans L et al. The cost effectiveness of 123 I-FP-CIT SPECT imaging in patients with an uncertain clinical diagnosis of parkinsonism. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008; 35: Varrone A, Dickson JC, Tossici-Bolt L et al. European multicentre database of healthy controls for [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT (ENC-DAT): age-related effects, gender differences and evaluation of different methods of analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013; 40: Verhoeff NP, Kapucu O, Sokole-Busemann E et al. Estimation of dopamine D2 receptor binding potential in the striatum with iodine-123-ibzm SPECT: technical and interobserver variability. J Nucl Med 1993; 34: Walker Z, Costa DC, Walker RW et al. Differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer s disease using a dopaminergic presynaptic ligand. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 2002; 73: Ziebell M, Holm-Hansen S, Thomsen G et al. Serotonin transporters in dopamine transporter imaging: a head-to-head comparison of dopamine transporter SPECT radioligands 123 I-FP-CIT and 123 I-PE2I. J Nucl Med 2010; 51: Zubal IG, Early M, Yuan O et al. Optimized, automated striatal uptake analysis applied to SPECT brain scans of Parkinson s disease patients. J Nucl Med 2007; 48: Nuklearmedizin 6/2014 Schattauer 2014
NUCLEAR MEDICINE. Keywords I-123-ioflupane. Attenuation correction. Chang. Contour delineation. Stereotactical normalization.
 DOI 10.1007/s00330-015-3667-6 NUCLEAR MEDICINE Robust, fully automatic delineation of the head contour by stereotactical normalization for attenuation correction according to Chang in dopamine transporter
DOI 10.1007/s00330-015-3667-6 NUCLEAR MEDICINE Robust, fully automatic delineation of the head contour by stereotactical normalization for attenuation correction according to Chang in dopamine transporter
SPECT Dopamin Transporter lmaging Agent
 SPECT Dopamin Transporter lmaging Agent Product Summary Product Name DATrace-123 Injection Active Ingredient Action Mechanism DATrace-123 is used as a radiopharmaceutical for the SPECT imaging of Dopamine
SPECT Dopamin Transporter lmaging Agent Product Summary Product Name DATrace-123 Injection Active Ingredient Action Mechanism DATrace-123 is used as a radiopharmaceutical for the SPECT imaging of Dopamine
Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
 Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Page: 1 of 14 Photon Emission Computed Tomography Description Dopamine transporter imaging with single photon emission computed tomography (DAT-SPECT) is being evaluated
Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Page: 1 of 14 Photon Emission Computed Tomography Description Dopamine transporter imaging with single photon emission computed tomography (DAT-SPECT) is being evaluated
CT-Based Attenuation Correction in I-123-Ioflupane SPECT
 CT-Based Attenuation Correction in I-123-Ioflupane SPECT Catharina Lange 1, Anita Seese 2, Sarah Schwarzenböck 3, Karen Steinhoff 2, Bert Umland-Seidler 4, Bernd J. Krause 3, Winfried Brenner 1, Osama
CT-Based Attenuation Correction in I-123-Ioflupane SPECT Catharina Lange 1, Anita Seese 2, Sarah Schwarzenböck 3, Karen Steinhoff 2, Bert Umland-Seidler 4, Bernd J. Krause 3, Winfried Brenner 1, Osama
Short communication. dwk&:key words: Parkinson s disease Single-photon emission tomography Dopamine transporter imaging Aging. Materials and methods
 Short communication [ 123 I]β-CIT single-photon emission tomography in Parkinson s disease reveals a smaller decline in dopamine transporters with age than in controls G. Tissingh 1, P. Bergmans 1, J.
Short communication [ 123 I]β-CIT single-photon emission tomography in Parkinson s disease reveals a smaller decline in dopamine transporters with age than in controls G. Tissingh 1, P. Bergmans 1, J.
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 30, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): May 20, 2014 Effective Date: August 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT
Original Issue Date (Created): July 30, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): May 20, 2014 Effective Date: August 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT
Imaging of the dopaminergic system with SPECT has
 Clinical Testing of an Optimized Software Solution for an Automated, Observer-Independent Evaluation of Dopamine Transporter SPECT Studies Walter Koch, MD 1 ; Perry E. Radau, PhD 2 ; Christine Hamann,
Clinical Testing of an Optimized Software Solution for an Automated, Observer-Independent Evaluation of Dopamine Transporter SPECT Studies Walter Koch, MD 1 ; Perry E. Radau, PhD 2 ; Christine Hamann,
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed. Tomography
 Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: dopamine_transporter_imaging_with_single_photon_emission_computed_tomography
Corporate Medical Policy Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: dopamine_transporter_imaging_with_single_photon_emission_computed_tomography
Clinical evaluation of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT scans on the novel brain-dedicated InSPira HD SPECT system: a head-to-head comparison
![Clinical evaluation of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT scans on the novel brain-dedicated InSPira HD SPECT system: a head-to-head comparison Clinical evaluation of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT scans on the novel brain-dedicated InSPira HD SPECT system: a head-to-head comparison](/thumbs/85/91877268.jpg) Adriaanse et al. EJNMMI Research (2018) 8:85 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-018-0436-y SHORT COMMUNICATION Clinical evaluation of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT scans on the novel brain-dedicated InSPira HD SPECT
Adriaanse et al. EJNMMI Research (2018) 8:85 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-018-0436-y SHORT COMMUNICATION Clinical evaluation of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT scans on the novel brain-dedicated InSPira HD SPECT
Creation and validation of an I-123 FP-CIT template for statistical image analysis using high-resolution SPECT for parkinsonian patients
 Ann Nucl Med (2016) 30:477 483 DOI 10.1007/s12149-016-1085-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Creation and validation of an I- FP-CIT template for statistical image analysis using high-resolution SPECT for parkinsonian
Ann Nucl Med (2016) 30:477 483 DOI 10.1007/s12149-016-1085-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Creation and validation of an I- FP-CIT template for statistical image analysis using high-resolution SPECT for parkinsonian
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2018 Related Policies: 6.01.06 Miscellaneous (Noncardiac, Nononcologic) Applications of Positron Emission Tomography 6.01.55 β-amyloid Imaging With
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2018 Related Policies: 6.01.06 Miscellaneous (Noncardiac, Nononcologic) Applications of Positron Emission Tomography 6.01.55 β-amyloid Imaging With
Optimized, Automated Striatal Uptake Analysis Applied to SPECT Brain Scans of Parkinson s Disease Patients
 Optimized, Automated Striatal Uptake Analysis Applied to SPECT Brain Scans of Parkinson s Disease Patients I. George Zubal, Michele Early, Olive Yuan, Danna Jennings, Kenneth Marek, and John P. Seibyl
Optimized, Automated Striatal Uptake Analysis Applied to SPECT Brain Scans of Parkinson s Disease Patients I. George Zubal, Michele Early, Olive Yuan, Danna Jennings, Kenneth Marek, and John P. Seibyl
I-123 SPECT: task groups
 I-123 SPECT: task groups Literature Review: Seibyl Claim Formulation Clinical Image Acquisition & Processing: Dewaraja Phantoms/ DRO: Dickson & Zimmerman Quantitative & Image Analysis: Seibyl & Miyaoka
I-123 SPECT: task groups Literature Review: Seibyl Claim Formulation Clinical Image Acquisition & Processing: Dewaraja Phantoms/ DRO: Dickson & Zimmerman Quantitative & Image Analysis: Seibyl & Miyaoka
Clinical Study Serotonin Transporter Availability in Early Stage Parkinson s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy
 ISRN Neurology, Article ID 345132, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/345132 Clinical Study Serotonin Transporter Availability in Early Stage Parkinson s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy S. R. Suwijn,
ISRN Neurology, Article ID 345132, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/345132 Clinical Study Serotonin Transporter Availability in Early Stage Parkinson s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy S. R. Suwijn,
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed. Tomography
 Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Impact of CT based attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of DaTSCAN ( 123 I-Ioflupane) imaging in diagnosis of extrapyramidal diseases
 Nuclear Medicine Review 2008 Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 53 58 Copyright 2008 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Impact of CT based attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of DaTSCAN ( 123 I-Ioflupane) imaging
Nuclear Medicine Review 2008 Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 53 58 Copyright 2008 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Impact of CT based attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of DaTSCAN ( 123 I-Ioflupane) imaging
SPECT imaging of the presynaptic dopaminergic terminal
 Journal of Nuclear Medicine, published on March 14, 2013 as doi:10.2967/jnumed.112.110106 Value of Semiquantitative Analysis for Clinical Reporting of I-2-b-Carbomethoxy-3b-(4-iodophenyl)-N-(3-Fluoropropyl)
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, published on March 14, 2013 as doi:10.2967/jnumed.112.110106 Value of Semiquantitative Analysis for Clinical Reporting of I-2-b-Carbomethoxy-3b-(4-iodophenyl)-N-(3-Fluoropropyl)
T he main symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson s disease
 1211 PAPER How useful is [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT in clinical practice? J Eerola, P J Tienari, S Kaakkola, P Nikkinen, J Launes... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Johanna
1211 PAPER How useful is [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT in clinical practice? J Eerola, P J Tienari, S Kaakkola, P Nikkinen, J Launes... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Johanna
Volume Quantification of 123I-DaTSCAN Imaging by MatLab for the Differentiation and Grading of Parkinsonism and Essential Tremor
 Volume Quantification of 123I-DaTSCAN Imaging by MatLab for the Differentiation and Grading of Parkinsonism and Essential Tremor Maria Lyra, John Striligas, Maria Gavrilleli, Nefeli Lagopati Radiation
Volume Quantification of 123I-DaTSCAN Imaging by MatLab for the Differentiation and Grading of Parkinsonism and Essential Tremor Maria Lyra, John Striligas, Maria Gavrilleli, Nefeli Lagopati Radiation
Views and Reviews. [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes ABSTRACT
![Views and Reviews. [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes ABSTRACT Views and Reviews. [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes ABSTRACT](/thumbs/76/73233066.jpg) Views and Reviews [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes Robert A. Hauser, MD, Donald G. Grosset, MD From the Departments of Neurology, Molecular
Views and Reviews [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes Robert A. Hauser, MD, Donald G. Grosset, MD From the Departments of Neurology, Molecular
Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson s disease
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders
 Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Dopamine transporter imaging 123 I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) SPET in differential diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia and young-onset Parkinson s disease
 Dopamine transporter imaging I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) SPET in differential diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia and young-onset Parkinson s disease Leposava D. Brajkovic 1 MD Marina V. Svetel 2, MD, PhD Vladimir
Dopamine transporter imaging I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) SPET in differential diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia and young-onset Parkinson s disease Leposava D. Brajkovic 1 MD Marina V. Svetel 2, MD, PhD Vladimir
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines. John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge
 Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge Why do we undertake brain imaging in AD and other dementias? Exclude other causes
Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge Why do we undertake brain imaging in AD and other dementias? Exclude other causes
Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique in Epilepsy Subjects
 22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique
22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Dopamine Transporter Loss Visualized With FP-CIT SPECT in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopamine Transporter Loss Visualized With FP-CIT SPECT in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia With Lewy Bodies John T. O Brien, DM, MRCPysch; Sean Colloby, MPhil; John Fenwick,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopamine Transporter Loss Visualized With FP-CIT SPECT in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia With Lewy Bodies John T. O Brien, DM, MRCPysch; Sean Colloby, MPhil; John Fenwick,
Interpreting 123 I ioflupane dopamine transporter scans using hybrid scores
 Nichols et al. European Journal of Hybrid Imaging (2018) 2:10 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41824-018-0028-0 European Journal of Hybrid Imaging ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Interpreting 123 I ioflupane dopamine
Nichols et al. European Journal of Hybrid Imaging (2018) 2:10 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41824-018-0028-0 European Journal of Hybrid Imaging ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Interpreting 123 I ioflupane dopamine
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
 Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana,
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana,
IBZM SPECT and FDG PET in the differential diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndromes Comparison with respect to inter-rater agreement
 Original article Schattauer 2010 139 IBZM SPECT and FDG PET in the differential diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndromes Comparison with respect to inter-rater agreement T. Derlin 1 ; W. Afzal 1 ; F. Wilke
Original article Schattauer 2010 139 IBZM SPECT and FDG PET in the differential diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndromes Comparison with respect to inter-rater agreement T. Derlin 1 ; W. Afzal 1 ; F. Wilke
Brain neurotransmission SPECT is currently devoted
 Quantitative Accuracy of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission Imaging with I SPECT Marine Soret, MSc 1 ; Pierre Malick Koulibaly, PhD 2 ; Jacques Darcourt, MD, PhD 2 ;Sébastien Hapdey, PhD 1 ; and Irène Buvat,
Quantitative Accuracy of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission Imaging with I SPECT Marine Soret, MSc 1 ; Pierre Malick Koulibaly, PhD 2 ; Jacques Darcourt, MD, PhD 2 ;Sébastien Hapdey, PhD 1 ; and Irène Buvat,
New semiquantitative assessment of 123 I-FP-CIT by an anatomical standardization method
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 20, No. 7, 477 484, 2006 New semiquantitative assessment of 123 I-FP-CIT by an anatomical standardization method Seiko TAKADA,* Mana YOSHIMURA,* Hiroaki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 20, No. 7, 477 484, 2006 New semiquantitative assessment of 123 I-FP-CIT by an anatomical standardization method Seiko TAKADA,* Mana YOSHIMURA,* Hiroaki
D ementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is the second most
 134 PAPER Differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer s disease using a dopaminergic presynaptic ligand Z Walker, D C Costa, RWHWalker, K Shaw, S Gacinovic, T Stevens, G Livingston, P Ince,
134 PAPER Differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer s disease using a dopaminergic presynaptic ligand Z Walker, D C Costa, RWHWalker, K Shaw, S Gacinovic, T Stevens, G Livingston, P Ince,
Update on functional brain imaging in Movement Disorders
 Update on functional brain imaging in Movement Disorders Mario Masellis, MSc, MD, FRCPC, PhD Assistant Professor & Clinician-Scientist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre University of Toronto 53 rd CNSF
Update on functional brain imaging in Movement Disorders Mario Masellis, MSc, MD, FRCPC, PhD Assistant Professor & Clinician-Scientist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre University of Toronto 53 rd CNSF
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Van Laere K, Vanhee A, Verschueren J, et al. Value of 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online March
Supplementary Online Content Van Laere K, Vanhee A, Verschueren J, et al. Value of 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online March
Brain imaging for the diagnosis of people with suspected dementia
 Why do we undertake brain imaging in dementia? Brain imaging for the diagnosis of people with suspected dementia Not just because guidelines tell us to! Exclude other causes for dementia Help confirm diagnosis
Why do we undertake brain imaging in dementia? Brain imaging for the diagnosis of people with suspected dementia Not just because guidelines tell us to! Exclude other causes for dementia Help confirm diagnosis
Photon Attenuation Correction in Misregistered Cardiac PET/CT
 Photon Attenuation Correction in Misregistered Cardiac PET/CT A. Martinez-Möller 1,2, N. Navab 2, M. Schwaiger 1, S. G. Nekolla 1 1 Nuklearmedizinische Klinik der TU München 2 Computer Assisted Medical
Photon Attenuation Correction in Misregistered Cardiac PET/CT A. Martinez-Möller 1,2, N. Navab 2, M. Schwaiger 1, S. G. Nekolla 1 1 Nuklearmedizinische Klinik der TU München 2 Computer Assisted Medical
GE Healthcare. Protocol Manual. Abnormal Scan. Normal Scan. Period-Shaped. Comma-Shaped
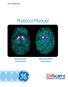 GE Healthcare Protocol Manual Normal Scan Comma-Shaped Abnormal Scan Period-Shaped 1 Contents Section 1: Introduction... 4 1.1 Scope 1.2 What is DaTscan? Section 2: Image Acquisition, Interpretation, and
GE Healthcare Protocol Manual Normal Scan Comma-Shaped Abnormal Scan Period-Shaped 1 Contents Section 1: Introduction... 4 1.1 Scope 1.2 What is DaTscan? Section 2: Image Acquisition, Interpretation, and
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123 I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123 I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data Implications of Putaminal Findings and Age Barbara Palumbo, MD, Mario Luca Fravolini,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123 I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data Implications of Putaminal Findings and Age Barbara Palumbo, MD, Mario Luca Fravolini,
CADA computer-aided DaTSCAN analysis
 Augimeri et al. EJNMMI Physics (2016) 3:4 DOI 10.1186/s40658-016-0140-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access CADA computer-aided DaTSCAN analysis Antonio Augimeri 1, Andrea Cherubini 1*, Giuseppe Lucio Cascini
Augimeri et al. EJNMMI Physics (2016) 3:4 DOI 10.1186/s40658-016-0140-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access CADA computer-aided DaTSCAN analysis Antonio Augimeri 1, Andrea Cherubini 1*, Giuseppe Lucio Cascini
GE Healthcare. Protocol Manual. Abnormal Scan. Normal Scan. Period-Shaped. Comma-Shaped
 GE Healthcare Protocol Manual Normal Scan Comma-Shaped Abnormal Scan Period-Shaped Contents Section 1: Introduction... 4 1.1 Scope 1.2 What is DaTscan? Section 2: Image Acquisition, Interpretation, and
GE Healthcare Protocol Manual Normal Scan Comma-Shaped Abnormal Scan Period-Shaped Contents Section 1: Introduction... 4 1.1 Scope 1.2 What is DaTscan? Section 2: Image Acquisition, Interpretation, and
Dual-isotope imaging ( 123 I/ 99m Tc) has potential clinical
 Absolute Activity Quantitation in Simultaneous I/ Tc Brain SPECT Georges El Fakhri, Stephen C. Moore, Philippe Maksud, André Aurengo, and Marie Foley Kijewski Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School
Absolute Activity Quantitation in Simultaneous I/ Tc Brain SPECT Georges El Fakhri, Stephen C. Moore, Philippe Maksud, André Aurengo, and Marie Foley Kijewski Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School
Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET
 Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET M. Soret, C. Riddell, S. Hapdey, and I. Buvat Abstract-- The influence of tumor diameter, tumor-tobackground activity ratio, attenuation, spatial resolution,
Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET M. Soret, C. Riddell, S. Hapdey, and I. Buvat Abstract-- The influence of tumor diameter, tumor-tobackground activity ratio, attenuation, spatial resolution,
Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment using Image Differences and Clinical Features
 Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment using Image Differences and Clinical Features L I N L I S C H O O L O F C O M P U T I N G C L E M S O N U N I V E R S I T Y Copyright notice Many of the images in
Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment using Image Differences and Clinical Features L I N L I S C H O O L O F C O M P U T I N G C L E M S O N U N I V E R S I T Y Copyright notice Many of the images in
Chapter 6. Hester Gietema Cornelia Schaefer-Prokop Willem Mali Gerard Groenewegen Mathias Prokop. Accepted for publication in Radiology
 Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Jauhar S, Nour MM, Veronese M, et al. A test of the transdiagnostic dopamine hypothesis of psychosis using positron emission tomographic imaging in bipolar affective disorder
Supplementary Online Content Jauhar S, Nour MM, Veronese M, et al. A test of the transdiagnostic dopamine hypothesis of psychosis using positron emission tomographic imaging in bipolar affective disorder
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Nuclear neurology. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear neurology Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine To refresh your memory Brain has a high rate of oxidative metabolism. It has no reserves either of oxygen or of glucose and has a very limited
Nuclear neurology Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine To refresh your memory Brain has a high rate of oxidative metabolism. It has no reserves either of oxygen or of glucose and has a very limited
Il ruolo di nuove tecniche di imaging per la diagnosi precoce di demenza
 Parma, 23 maggio 2017 Il ruolo di nuove tecniche di imaging per la diagnosi precoce di demenza Livia Ruffini SC Medicina Nucleare Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma PET AND SPECT STUDIES OF THE
Parma, 23 maggio 2017 Il ruolo di nuove tecniche di imaging per la diagnosi precoce di demenza Livia Ruffini SC Medicina Nucleare Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma PET AND SPECT STUDIES OF THE
The current diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson s disease
 Sensitivity and Specificity of Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Differentiating Patients with Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease from Healthy Subjects Yi-Hsin Weng, MD 1 ; Tzu-Chen Yen, PhD 2 ; Min-Chi Chen, PhD
Sensitivity and Specificity of Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Differentiating Patients with Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease from Healthy Subjects Yi-Hsin Weng, MD 1 ; Tzu-Chen Yen, PhD 2 ; Min-Chi Chen, PhD
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics
 Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/26921 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Doan, Nhat Trung Title: Quantitative analysis of human brain MR images at ultrahigh
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/26921 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Doan, Nhat Trung Title: Quantitative analysis of human brain MR images at ultrahigh
Round table: Moderator; Fereshteh Sedaghat, MD, PhD Brain Mapping in Dementias and Non-invasive Neurostimulation
 Round table: Moderator; Fereshteh Sedaghat, MD, PhD Brain Mapping in Dementias and Non-invasive Neurostimulation 1. Reflection of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Dementias by Molecular Imaging, PET
Round table: Moderator; Fereshteh Sedaghat, MD, PhD Brain Mapping in Dementias and Non-invasive Neurostimulation 1. Reflection of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Dementias by Molecular Imaging, PET
Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype
 MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
FDG-PET e parkinsonismi
 Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using Linear Discriminative Analysis and Quadratic Discriminative Analysis
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
Neuro degenerative PET image from FDG, amyloid to Tau
 Neuro degenerative PET image from FDG, amyloid to Tau Kun Ju Lin ( ) MD, Ph.D Department of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital ( ) Department of Medical Imaging
Neuro degenerative PET image from FDG, amyloid to Tau Kun Ju Lin ( ) MD, Ph.D Department of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital ( ) Department of Medical Imaging
MRI-Guided Partial Volume Correction in Brain PET Imaging: Comparison of Five Algorithms
 MRI-Guided Partial Volume Correction in Brain PET Imaging: Comparison of Five Algorithms Gaël Boivin 1, Vassilis Genoud 1, Habib Zaidi 1,* 1. Division of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Geneva
MRI-Guided Partial Volume Correction in Brain PET Imaging: Comparison of Five Algorithms Gaël Boivin 1, Vassilis Genoud 1, Habib Zaidi 1,* 1. Division of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Geneva
Brain SPECT has become an important diagnostic and
 CONTINUING EDUCATION Technical Overview of Brain SPECT Imaging: Improving Acquisition and Processing of Data* Gina N. Morano, CNMT, RT(N) 1 ; and John P. Seibyl, MD 2 1 Molecular NeuroImaging, LLC, New
CONTINUING EDUCATION Technical Overview of Brain SPECT Imaging: Improving Acquisition and Processing of Data* Gina N. Morano, CNMT, RT(N) 1 ; and John P. Seibyl, MD 2 1 Molecular NeuroImaging, LLC, New
Establishing On-Site Reference Values for 123 I-FP-CIT SPECT (DaTSCAN ) Using a Cohort of Individuals with Non-Degenerative Conditions
 Published in which should be cited to refer to this work. Establishing On-Site Reference Values for 123 I-FP-CIT SPECT (DaTSCAN ) Using a Cohort of Individuals with Non-Degenerative Conditions Nicolas
Published in which should be cited to refer to this work. Establishing On-Site Reference Values for 123 I-FP-CIT SPECT (DaTSCAN ) Using a Cohort of Individuals with Non-Degenerative Conditions Nicolas
Austin Radiological Association BRAIN AMYLOID STUDY (F-18-Florbetapir)
 Austin Radiological Association BRAIN AMYLOID STUDY (F-18-Florbetapir) Overview The Brain Amyloid Study with F-18-florbetapir depicts the extracellular deposition of B- amyloid (Aβ) peptides (or plaques
Austin Radiological Association BRAIN AMYLOID STUDY (F-18-Florbetapir) Overview The Brain Amyloid Study with F-18-florbetapir depicts the extracellular deposition of B- amyloid (Aβ) peptides (or plaques
Cortical hypoperfusion in Parkinson's disease assessed with arterial spin labeling MRI
 Cortical hypoperfusion in Parkinson's disease assessed with arterial spin labeling MRI Poster No.: C-0609 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Aoki, K. Kamagata, Y. Motoi, K. Kamiya,
Cortical hypoperfusion in Parkinson's disease assessed with arterial spin labeling MRI Poster No.: C-0609 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Aoki, K. Kamagata, Y. Motoi, K. Kamiya,
Chapter Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease
 Chapter Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease 4 Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson's
Chapter Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease 4 Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson's
EU Regulation of in vivo Diagnostics Regulatory Assessment of Diagnostic Agents. 2 nd Regulatory Workshop University of Pretoria 9 th October, 2014
 EU Regulation of in vivo Diagnostics Regulatory Assessment of Diagnostic Agents 2 nd Regulatory Workshop University of Pretoria 9 th October, 2014 Diagnostic Agents Any pharmaceutical product used as
EU Regulation of in vivo Diagnostics Regulatory Assessment of Diagnostic Agents 2 nd Regulatory Workshop University of Pretoria 9 th October, 2014 Diagnostic Agents Any pharmaceutical product used as
responsiveness HMPAO SPECT in Parkinson's disease before and after levodopa: correlation with dopaminergic (SSmTc HMPAO) as a tracer in 21 patients
 18 1ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:18-185 Department of Neurology H S Markus A J Lees Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London,
18 1ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:18-185 Department of Neurology H S Markus A J Lees Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London,
Review of Longitudinal MRI Analysis for Brain Tumors. Elsa Angelini 17 Nov. 2006
 Review of Longitudinal MRI Analysis for Brain Tumors Elsa Angelini 17 Nov. 2006 MRI Difference maps «Longitudinal study of brain morphometrics using quantitative MRI and difference analysis», Liu,Lemieux,
Review of Longitudinal MRI Analysis for Brain Tumors Elsa Angelini 17 Nov. 2006 MRI Difference maps «Longitudinal study of brain morphometrics using quantitative MRI and difference analysis», Liu,Lemieux,
Application of Pattern Recognition Framework for Quantification of Parkinson s Disease in DAT SPECT Imaging
 Application of Pattern Recognition Framework for Quantification of Parkinson s Disease in DAT SPECT Imaging Saurabh Jain, Yousef Salimpour, Laurent Younes, Gwenn Smith, Zoltan Mari, Vesna Sossi, Arman
Application of Pattern Recognition Framework for Quantification of Parkinson s Disease in DAT SPECT Imaging Saurabh Jain, Yousef Salimpour, Laurent Younes, Gwenn Smith, Zoltan Mari, Vesna Sossi, Arman
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Computer-aided diagnosis for ( 123 I)FP-CIT imaging: impact on clinical reporting
 Taylor et al. EJNMMI Research (2018) 8:36 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-018-0393-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Computer-aided diagnosis for ( 123 I)FP-CIT imaging: impact on clinical reporting Jonathan
Taylor et al. EJNMMI Research (2018) 8:36 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-018-0393-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Computer-aided diagnosis for ( 123 I)FP-CIT imaging: impact on clinical reporting Jonathan
Dose Calibration for DaTscan
 GE Healthcare Dose Calibration for DaTscan Please review the simple steps below to learn how to properly calibrate your dose of DaTscan. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reading DaTscan in the Dose Calibrator 1. Place
GE Healthcare Dose Calibration for DaTscan Please review the simple steps below to learn how to properly calibrate your dose of DaTscan. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reading DaTscan in the Dose Calibrator 1. Place
CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM
 Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics
 Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
years; baseline off-state Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor ratings 24.6 ± 6.8).
 Jourdain et al. 1 Supplemental Data Supplemental Methods Subjects We studied 28 PD subjects (20 men and 8 women; age 61.0 ± 9.6 (mean ± SD) years; duration 8.7 ± 9.6 years; baseline off-state Unified Parkinson
Jourdain et al. 1 Supplemental Data Supplemental Methods Subjects We studied 28 PD subjects (20 men and 8 women; age 61.0 ± 9.6 (mean ± SD) years; duration 8.7 ± 9.6 years; baseline off-state Unified Parkinson
QIBA Profile: Quantifying Dopamine Transporters with 123 Iodine Labeled Ioflupane in Neurodegenerative Diseases
 5 QIBA Profile: Quantifying Dopamine Transporters with 123 Iodine Labeled Ioflupane in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Short Title: SPECT dopamine transporters) 10 Stage: Version 1.1 for Conformance Testing
5 QIBA Profile: Quantifying Dopamine Transporters with 123 Iodine Labeled Ioflupane in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Short Title: SPECT dopamine transporters) 10 Stage: Version 1.1 for Conformance Testing
Parkinsonism in corticobasal syndrome may not be primarily due to presynaptic dopaminergic deficiency
 Neurology Asia 2015; 20(1) : 23 27 Parkinsonism in corticobasal syndrome may not be primarily due to presynaptic dopaminergic deficiency 1 Ji Young Yun MD, 2 Jong-Min Kim MD, PhD, 3 Han-Joon Kim MD PhD,
Neurology Asia 2015; 20(1) : 23 27 Parkinsonism in corticobasal syndrome may not be primarily due to presynaptic dopaminergic deficiency 1 Ji Young Yun MD, 2 Jong-Min Kim MD, PhD, 3 Han-Joon Kim MD PhD,
DOWNLOAD PDF DOPAMINERGIC IMAGING IN PARKINSONS DISEASE : SPECT CHRISTOPH SCHERFLER AND WERNER POEWE
 Chapter 1 : Imaging Approaches to Parkinson Disease The diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) can often be made on clinical grounds with a high degree of accuracy particularly in cases with
Chapter 1 : Imaging Approaches to Parkinson Disease The diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) can often be made on clinical grounds with a high degree of accuracy particularly in cases with
Imaging in epilepsy: Ictal perfusion SPECT and SISCOM
 Imaging in epilepsy: Ictal perfusion SPECT and SISCOM Patrick Dupont Laboratory for Cognitive Neurology Laboratory for Epilepsy Research Medical Imaging Research Center KU Leuven, Belgium E-mail: Patrick.Dupont@med.kuleuven.be
Imaging in epilepsy: Ictal perfusion SPECT and SISCOM Patrick Dupont Laboratory for Cognitive Neurology Laboratory for Epilepsy Research Medical Imaging Research Center KU Leuven, Belgium E-mail: Patrick.Dupont@med.kuleuven.be
Personal Space Regulation by the Human Amygdala. California Institute of Technology
 Personal Space Regulation by the Human Amygdala Daniel P. Kennedy 1, Jan Gläscher 1, J. Michael Tyszka 2 & Ralph Adolphs 1,2 1 Division of Humanities and Social Sciences 2 Division of Biology California
Personal Space Regulation by the Human Amygdala Daniel P. Kennedy 1, Jan Gläscher 1, J. Michael Tyszka 2 & Ralph Adolphs 1,2 1 Division of Humanities and Social Sciences 2 Division of Biology California
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D, et al. Prediction of individual response to electroconvulsive therapy via machine learning on structural magnetic resonance imaging data. JAMA
Supplementary Online Content Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D, et al. Prediction of individual response to electroconvulsive therapy via machine learning on structural magnetic resonance imaging data. JAMA
TW Hamilton, EP Ficaro, TA Mitchell, JN Kritzman, JR Corbett University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor, MI
 Accuracy and Variability of of 3D-MSPECT for Estimating the Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction as as a Function of of Gating Frames and Reconstruction Filters TW Hamilton, EP Ficaro, TA Mitchell, JN Kritzman,
Accuracy and Variability of of 3D-MSPECT for Estimating the Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction as as a Function of of Gating Frames and Reconstruction Filters TW Hamilton, EP Ficaro, TA Mitchell, JN Kritzman,
L ecografia cerebrale: accuratezza diagnostica Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torino
 L ecografia cerebrale: accuratezza diagnostica Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torino Ecografia cerebrale: l accuratezza diagnostica. Lo studio NOBIS Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torinorin Normal
L ecografia cerebrale: accuratezza diagnostica Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torino Ecografia cerebrale: l accuratezza diagnostica. Lo studio NOBIS Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torinorin Normal
SPECT and PET Imaging: DaT Scan, Cerebral Blood Flow and Epilepsy
 SPECT and PET Imaging: DaT Scan, Cerebral Blood Flow and Epilepsy Dana Mathews Ph.D. M.D. Division of Nuclear Medicine Department of Radiology The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Financial
SPECT and PET Imaging: DaT Scan, Cerebral Blood Flow and Epilepsy Dana Mathews Ph.D. M.D. Division of Nuclear Medicine Department of Radiology The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Financial
Accurate discrimination of Alzheimer s disease from other dementia and/or normal subjects using SPECT specific volume analysis
 Accurate discrimination of Alzheimer s disease from other dementia and/or normal subjects using SPECT specific volume analysis Hitoshi Iyatomi a, Jun Hashimoto b, Fumihito Yoshii c, Toshiki Kazama b, Shuichi
Accurate discrimination of Alzheimer s disease from other dementia and/or normal subjects using SPECT specific volume analysis Hitoshi Iyatomi a, Jun Hashimoto b, Fumihito Yoshii c, Toshiki Kazama b, Shuichi
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is the second most
 The F-FDG PET Cingulate Island Sign and Comparison to 123 I-b-CIT SPECT for Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies Seok Ming Lim 1, Andrew Katsifis 2, Victor L. Villemagne 1,3, Rene Best 1, Gareth Jones
The F-FDG PET Cingulate Island Sign and Comparison to 123 I-b-CIT SPECT for Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies Seok Ming Lim 1, Andrew Katsifis 2, Victor L. Villemagne 1,3, Rene Best 1, Gareth Jones
X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT
 Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
8/10/2016. PET/CT Radiomics for Tumor. Anatomic Tumor Response Assessment in CT or MRI. Metabolic Tumor Response Assessment in FDG-PET
 PET/CT Radiomics for Tumor Response Evaluation August 1, 2016 Wei Lu, PhD Department of Medical Physics www.mskcc.org Department of Radiation Oncology www.umaryland.edu Anatomic Tumor Response Assessment
PET/CT Radiomics for Tumor Response Evaluation August 1, 2016 Wei Lu, PhD Department of Medical Physics www.mskcc.org Department of Radiation Oncology www.umaryland.edu Anatomic Tumor Response Assessment
Draft agreed by Scientific Advice Working Party 26 October Adopted by CHMP for release for consultation 09 November
 29 May 2018 EMA/CHMP/SAWP/765041/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Qualification opinion on dopamine transporter imaging as an enrichment biomarker for Parkinson s disease clinical
29 May 2018 EMA/CHMP/SAWP/765041/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Qualification opinion on dopamine transporter imaging as an enrichment biomarker for Parkinson s disease clinical
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Revised criteria for the clinical diagnosis of dementia with Lewy. Dementia with Lewy bodies. (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)
 Dementia with Lewy bodies First described: Okazaki H, 1961, Diffuse intracytoplasmic ganglionic inclusions (Lewy type) associated with progressive dementia and quadriparesis in flexion. J Neuropathol Exp
Dementia with Lewy bodies First described: Okazaki H, 1961, Diffuse intracytoplasmic ganglionic inclusions (Lewy type) associated with progressive dementia and quadriparesis in flexion. J Neuropathol Exp
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Animals. Male C57Bl/6 mice (n=27) were obtained from Charles River (Sulzfeld, Germany) and
 Supplemental Methods Animals. Male C57Bl/6 mice (n=27) were obtained from Charles River (Sulzfeld, Germany) and housed in groups of 5-10 in individually ventilated BCU cages within a temperature controlled
Supplemental Methods Animals. Male C57Bl/6 mice (n=27) were obtained from Charles River (Sulzfeld, Germany) and housed in groups of 5-10 in individually ventilated BCU cages within a temperature controlled
doi: /brain/aws253 Brain 2012: 135; Left hemispheric predominance of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson s disease
 doi:10.1093/brain/aws253 Brain 2012: 135; 3348 3354 3348 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Left hemispheric predominance of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson s disease Christoph Scherfler, 1 Klaus Seppi,
doi:10.1093/brain/aws253 Brain 2012: 135; 3348 3354 3348 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Left hemispheric predominance of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson s disease Christoph Scherfler, 1 Klaus Seppi,
Brain Perfusion SPECT
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Brain Perfusion SPECT Primary Indications: Brain perfusion SPECT is most commonly performed (1) to aid in identification of the epileptogenic focus in patients
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 5 Brain Perfusion SPECT Primary Indications: Brain perfusion SPECT is most commonly performed (1) to aid in identification of the epileptogenic focus in patients
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease
 Supplemental informations Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease Stéphanie Lefebvre, PhD^1,2, Guillaume Baille, MD^4, Renaud Jardri MD, PhD 1,2 Lucie Plomhause, PhD
Supplemental informations Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease Stéphanie Lefebvre, PhD^1,2, Guillaume Baille, MD^4, Renaud Jardri MD, PhD 1,2 Lucie Plomhause, PhD
Statistical parametric mapping with 18 F-dopa PET shows bilaterally reduced striatal and nigral dopaminergic function in early Parkinson s disease
 754 MRC Cyclotron Unit, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK P K Morrish J S Rakshi T Uema D L Bailey D J Brooks Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London, UK J Ashburner K J Friston D J Brooks Department
754 MRC Cyclotron Unit, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK P K Morrish J S Rakshi T Uema D L Bailey D J Brooks Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London, UK J Ashburner K J Friston D J Brooks Department
ABSTRACT. I-FP-CIT; 123 I-MIBG; Parkinson s disease; combined analysis
 Yonago Acta Medica 2018;61:117 127 Original Article The Utility of the Combined Use of 123 I-FP-CIT and 123 I-MIBG Myocardial Scintigraphy in Differentiating Parkinson s Disease from Other Parkinsonian
Yonago Acta Medica 2018;61:117 127 Original Article The Utility of the Combined Use of 123 I-FP-CIT and 123 I-MIBG Myocardial Scintigraphy in Differentiating Parkinson s Disease from Other Parkinsonian
