Animal Reproduction. Review for test #3. # lectures for cumulative test # 03 book
|
|
|
- Debra Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) , 27 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture slides: Meetings 01-02: Introduction to Animal Reproduction (2) Meetings 03-04: Reproductive Structures and their Functions (2) Meetings 05-07: The HPG axis and its Liposoluble and Watersoluble Hormones (3) Meetings 08-09: The Neuroendocrine Control of Male and Female Puberty Onset (2) Meetings 10-11: REVIEW AND TEST #1 Meetings 12-17: Female and Male Reproduction and Techniques for their Control (6) Meetings 18-19: REVIEW AND TEST #2 Meetings 20-21: Reproductive Behavior and the Spermatozoa in the Female Tract (2) Meetings 22-23: Embryogenesis, Placentation, Parturition and Lactation (3) Meetings 24-25: Puerperium, Lactation and Reproductive Ageing (2) Meeting 26 Reproductive Pathology and Case Studies (1) Meetings 27-28: REVIEW AND TEST #3 There are not intended to be the sole source for studying the course material!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Slides are good to review the course material after you have study your course textbook Slides are a good indicator of the relative importance of lecture topics (see slide # per topic) Group slides by titles when using them to review course material. Match lectures and text. # lectures for cumulative test # 03 book 20 Reproductive behavior Spermatozoa in female tract: transport, capacitation, fertilization Early embriogenesis and maternal recognition of pregnancy Placentation, the endocrinology of gestation and parturition The puerperium and lactation Reproductive aging and the role of biological clocks in senescence Reproductive pathology: case studies as a tool to study reproductive failure 27 REVIEW material from lecture # 20 through lecture # EXAM # 01 - material from lecture # 01 through lecture # Page 1
2 See review # 1 As indicated in lectures and in the course outline students can review their tests during office hours, starting a week after the test was taken. Remember that all tests are cumulative and that questions are seldom repeated See review # 2 As indicated in lectures and in the course outline students can review their tests during office hours, starting a week after the test was taken. Remember that all tests are cumulative and that questions are seldom repeated Page 2
3 Neuro-endocrine inputs to the GnRH neurons can influence reproductive behaviors The flehmen response: olfactory cues provided by pheromones stimulate the vomeronasal organ Page 3
4 Steps in penile erection as they relate to cavernous blood pressure and contraction of the bulbospongious and ischiocavernosus muscles Major steps in ejaculation Page 4
5 Novel females and a change of location has a positive effect on mounting behavior Steps in sexual preparation resulting in transport of spermatozoa from tail of epididymis into pelvic urethra Page 5
6 Events following deposition of spermatozoa in female tract Conceptual version of the main steps in mammalian capacitation Page 6
7 Hyperactive motility 2 Binding to zona pelucida 3 Acrosomal reaction 4 Penetration of zona pelucida 5 Sperm oocyte membrane fusion 6 Sperm engulfed 7 Decondensation of sperm nucleus 8 Formation of male pronucleus Post - capacitation sequence of events leading to fertilization Overview of early embryogenesis and anatomical sections of the reproductive tube where it occurs Page 7
8 Pre-attachment development of the embryo Development of extra-embryonic membranes Page 8
9 IFN-t from conceptus prevents luteolysis (cow, ewe) E2 reroutes PGF2a to prevents luteolysis (sow) Page 9
10 direct follicular aspiration transvaginal aspiration in mare aspirated oocyte Oocytes placed in culture vessel with capacitated spermatozoa Embryos cultured to the appropiate stage for transfer Embryos transferred to recipient female Oocyte collection from ovarian follicles for in vitro fertilization epitheliochorial hemochorial endotheliochorial Placental classification based on separation between fetal and maternal blood supplies Page 10
11 Luteal P4 output during the first half of gestation in the mare Estrogen and P4 profiles during gestation Page 11
12 Cascade of events prompted by fetal cortisol Pressure on the cervix causes oxytocin release and subsequent myometrial contractions Page 12
13 Major events from parturition to subsequent conception Changes in the mammary gland as a function of reproductive stage Page 13
14 The anatomy and physiology of milk ejection A biological clock located in the SCN is involved in eliciting a preovulatory surge of LH. This clock mechanism starts failing in middle age animals, before a failure in ovulation occurs. Page 14
15 SCN is responsible for the precise timing of the LH surge: SCN lesions eliminates the ovarian cycle (behavior & LH surge). The LH surge maintains its exact relationship to the locomotor activity in a constant light environment, suggesting they are controlled by the same circadian mechanism. Lengthening / shortening of activity cycle by pharmacological treatment or light entrainment alters the estrous behavior and the LH surge. Pentobarbital in proestrous AM temporarily blocks the LH surge, which occurs at precisely the normal time the next day. Light sensors in retina project to the SCN and from there, through the superior cervical ganglion to the pineal gland. The latter secretes melatonin in response to darkness, which entrains the SCN, the main biological clock in brain. Young LHRH=GnRH Middle- Aged A biological clock located in the SCN is involved in eliciting a preovulatory surge of LH. This clock mechanism starts failing in middle age animals, before a failure in ovulation occurs. Page 15
16 How could nutrition, stress, social cues and clocks affect the LH surge??? Q Possible influence of metabolic signals on GnRH neurons from glucose sensing neurons inputing GnRH neurons. Comments on your weekly questions Page 16
17 Comments on your weekly questions Comments on your weekly questions Page 17
18 Animal Reproduction, test #03, JP Advis, 2012 Name Student ID Web ID (*) Seat Note: all the above info also goes in the scantron, with the web ID and seat in the upper right corner FOR ALL QUESTIONS SELECT THE BEST ANSWER FOR THE OPTIONS GIVEN (*) Your WEB ID is a 5-digit number YOU choose Since there are two versions for each test, you must return both the questions and your scantron sheets Page 18
Animal Reproduction. Spermatozoa in female tract. # lectures for cumulative test # 03 book
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 21 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 21 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction. Reproductive Cyclicity. # lectures for cumulative test # 02 book 12. Reproductive cyclicity: terminology and basic concepts
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 14 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 14 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction. Overview of Male Reproduction. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction. Reproductive Cyclicity. # lectures for cumulative test # 02 book 12. Reproductive cyclicity: terminology and basic concepts
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 15 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 15 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase
 Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
Human Sexuality Exam II Review Material Gametogenesis: Oogenesis 1. Be able to characterize the menstrual cycle from the perspective of the ovary a. Follicular phase b. Luteal phase 2. Know the relative
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23
 AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013
 VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013 Credits-3 Coordinator: Patrick M., DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACT Department of Clinical Sciences Office: Equine Reproduction Laboratory Phone: 491-8626 email: pmccue@colostate.edu
VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013 Credits-3 Coordinator: Patrick M., DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACT Department of Clinical Sciences Office: Equine Reproduction Laboratory Phone: 491-8626 email: pmccue@colostate.edu
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Lecture 3. Reproductive Endocrinology. (Sep 30, 2008)
 Lecture 3 Reproductive Endocrinology (Sep 30, 2008) Major achievements that speed up the development: 1. The anterior pituitary controls the function of the gonads. 2. Gonads produce steroid hormones that
Lecture 3 Reproductive Endocrinology (Sep 30, 2008) Major achievements that speed up the development: 1. The anterior pituitary controls the function of the gonads. 2. Gonads produce steroid hormones that
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Cell to Cell Communication
 Review #1 08 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Review #1 08 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Learning Outcome
 Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Ch 20: Reproduction. Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition
 Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
The Sex Hormones & Reproductive Systems (6)
 The Sex Hormones & Reproductive Systems (6) The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Lumen) Sperm Scrotum ~300 lobules Sertoli cell Leydig cell Testosterone Testes : - produce sperm cells
The Sex Hormones & Reproductive Systems (6) The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Lumen) Sperm Scrotum ~300 lobules Sertoli cell Leydig cell Testosterone Testes : - produce sperm cells
Physiology of Male Reproductive System
 Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Physiology of Male Reproductive System the anterior pituitary gland serves as the primary control of reproductive function at puberty Ant Pituitary secretes FSH & large amounts of LH (ICSH) FSH & LH cause
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
2. Which of the following factors does not contribute to ion selectivity?
 General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Menstrual Cycle. Last example of how a circle works. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)!!
 The goal of these lectures is to discuss how control system is formed and operates. For this, basic physiology associated with the control the menstrual cycle will be used. The sections for this lecture
The goal of these lectures is to discuss how control system is formed and operates. For this, basic physiology associated with the control the menstrual cycle will be used. The sections for this lecture
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
CASE 41. What is the pathophysiologic cause of her amenorrhea? Which cells in the ovary secrete estrogen?
 CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction 1 Terms Anestrus Artificial insemination Castration Cervix Copulation Diestrus Egg Ejaculation Estrous cycle Estrus Fertilization
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction 1 Terms Anestrus Artificial insemination Castration Cervix Copulation Diestrus Egg Ejaculation Estrous cycle Estrus Fertilization
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho. REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5
 Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
BIOL 439: Endocrinology
 1 Biol 439-01 (Call # 15034) Michael Chen, Ph.D. Biol Sci 247 (323) 343-2084 MW 4:20-6:00 pm Biol Sci. 120 mchen@calstatela.edu Office hours: TWR: 2:00-4:00 pm BIOL 439: Endocrinology This course provides
1 Biol 439-01 (Call # 15034) Michael Chen, Ph.D. Biol Sci 247 (323) 343-2084 MW 4:20-6:00 pm Biol Sci. 120 mchen@calstatela.edu Office hours: TWR: 2:00-4:00 pm BIOL 439: Endocrinology This course provides
HORMONES & REPRODUCTION OUTLINE
 1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach
 Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (848) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered:
Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (848) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 04 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered:
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Course: Animal Production. Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson. Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to:
 Course: Animal Production Unit Title: Hormones TEKS: 130.3 (C)(6)(A) Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Define what hormones
Course: Animal Production Unit Title: Hormones TEKS: 130.3 (C)(6)(A) Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Define what hormones
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Cell to Cell Communication
 Review #1 15 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Review #1 15 Review using OPAL figures Review using class web PDF Preview of test #1 Cell to Cell Communication 1 Communication Strategies endocrine neurocrine paracrine autocrine Endocrine System Overview
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Female Reproductive Physiology. Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF
 Female Reproductive Physiology Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF REFERENCE Lew, R, Natural History of ovarian function including assessment of ovarian reserve
Female Reproductive Physiology Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF REFERENCE Lew, R, Natural History of ovarian function including assessment of ovarian reserve
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46. Fission. Budding. Parthenogenesis. Fragmentation 11/27/2017
 Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Sow Reproduction and Seasonal Infertility. Darlington Pig Discussion Group 13 th March 2014 Richard Bull
 Sow Reproduction and Seasonal Infertility Darlington Pig Discussion Group 13 th March 2014 Richard Bull Richard Bull Taurus Concepts Ltd Sow Reproduction Endogenous Hormones Gland Hormone Function Hypothalamus
Sow Reproduction and Seasonal Infertility Darlington Pig Discussion Group 13 th March 2014 Richard Bull Richard Bull Taurus Concepts Ltd Sow Reproduction Endogenous Hormones Gland Hormone Function Hypothalamus
Endocrine Glands. Endocrine glands
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
Reproduction. Introduction
 Reproduction The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual diferentiation to adult reproductive function). 26 The sections for this
Reproduction The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual diferentiation to adult reproductive function). 26 The sections for this
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Biological Rhythms. Today s lecture
 Biological Rhythms (a review of general endocrinology) 35 Neuroendocrine control: homeostatic responses and biological rhythms. A role for anticipation or feed-forward mechanisms or scheduled events. Biological
Biological Rhythms (a review of general endocrinology) 35 Neuroendocrine control: homeostatic responses and biological rhythms. A role for anticipation or feed-forward mechanisms or scheduled events. Biological
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Hypothalamus. Small, central, & essential.
 Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Stage 4 - Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
 WELCOME Stage 4 - Ovarian Cancer Symptoms University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad,
WELCOME Stage 4 - Ovarian Cancer Symptoms University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad,
GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH)
 GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH) Naturally occurring hormone, produced by the hypothalamus and transferred to the anterior pituitary gland in the hypophyseal
GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH) Naturally occurring hormone, produced by the hypothalamus and transferred to the anterior pituitary gland in the hypophyseal
Female Reproductive System. Justin D. Vidal
 Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Written exam Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS. Exam date: Time: 09:00-11:00. Important information:
 Written exam 2016 Course title: Program: Semester: Reproductive endocrinology Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS 4 semester Exam date: 06-06-16 Time: 09:00-11:00 Evaluation form 7-point scale Important information:
Written exam 2016 Course title: Program: Semester: Reproductive endocrinology Bachelor in Medicine/MedIS 4 semester Exam date: 06-06-16 Time: 09:00-11:00 Evaluation form 7-point scale Important information:
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark)
 1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Timing of A.I. Swine AI 9/6/12
 Breeding Herd Education Series 20 Timely, relevant & convenient learning Thank you for participating in SowBridge 20. To start this presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or the down or right
Breeding Herd Education Series 20 Timely, relevant & convenient learning Thank you for participating in SowBridge 20. To start this presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or the down or right
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction
 Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review Rachel Ledden Paper for Bachelors in Science January 20, 2018
 Running head: 1 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review Rachel Ledden Paper for Bachelors in Science January 20, 2018 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review 2 The reproductive cycle
Running head: 1 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review Rachel Ledden Paper for Bachelors in Science January 20, 2018 Female reproductive cycle: A Comprehensive Review 2 The reproductive cycle
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction
 Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems!
 Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
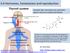
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
