Neurotransmitters. Mohammad Nusier. Hadeel AL-Momani. Biochemistry. 1 P a g e
|
|
|
- Jasmine Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neurotransmitters Mohammad Nusier Hadeel AL-Momani 1 P a g e Biochemistry #2
2 Date : 15/2/2016 \ Lecture #2 biochemistry \ Lecture #17 CNS \ Subject : Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters 1- Excitatory : 2-Inhibitory: 1.Acetylcholine 2. chatecholamines ( Dopamine, E, NE ) 1.Glycine* (acts in spinal cord & brain stem) 2.GABA* (acts in all other parts of brain) 3.Taurine * Major ones The biogenic amines: indolamines 1. Serotonin 2. Histamine The amino acid transmitters: "GGG" 1. Glutamate 2. GABA 3. Glycine Acetylcholine Synthesized in terminals from acetyl CoA (found everywhere) and choline (from blood and recycled ACh, but not synthesized in neurons) Synthesizing enzyme = CAT (choline acetyl transferase) Acetyl CoA + Choline Acetyl Choline (Ach) Inactivated = by ACHesterase; ACh is not taken up into neurons (only degradation ) Used by somatic motor neurons within CNS Two major subtypes of receptors = nicotinic (nachr) and muscarinic (machr), each of which has its own subtypes. 2 P a g e
3 Nicotinic Receptor type directly gated channels for Na + and K + Places striate muscle (N 1 ) postganglionic neurons (N 2 ); CNS Muscarinic linked to 2 nd messengers visceral smooth, cardiac muscle, glands, postganglionic neurons, CNS Dopamine Is a biogenic amine & specifically a catecholamine, so it shares a pathway with NE & EPI Synthesized from tyrosine (Tyr is from the essential AA Phenyl alanine "Phe") Rate limiting enzyme is tyrosine hydroxylase Carbidopa "drug" blocks conversion of DOPA (dihydroxyphenylalanine) to dopamine by dopa decarboxylase, but cannot cross the BBB >> the difference btw DOPA & Dopamine is the carboxyl group >> if u remove it.. DOPA will become Dopamine. Inactivation of DOPA: either by Reuptake (blocked by cocaine); or Degradation by COMT 1 (extracellular) and by MAO 2 (intracellular) A major Metabolite for DOPA degradation : HVA (homovanillic acid) which shows up in CSF >> look for this metabolite level in the lab to looking for specific disorders!. So far, there are 5 subtypes known, all 2 nd messenger-linked. DA"dopamine" is important in mood disorders, schizophrenia, basal ganglia function. Parkinson's results from loss of DA neurons in basal ganglia. Norepinephrine Shares pathway with other catecholamines (Dopamine) Used in CNS (locus coeruleus and lateral tegmental nuclei of brainstem) and by most post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons 1 catechol-o-methyl transferase.. 2 monoamine oxidase 3 P a g e
4 Inactivation = reuptake (blocked by cocaine); or degradation by COMT in (extracellular) space and by MAO (intracellular) At least 4 subtypes, all 2 nd messenger-linked. (b1,b2 both increase camp, a2 decreases camp, að1 acts through PLC)>> PLC >> phospholipase C system. Agonists include Ephedrine, Phenylephrine (a), Isoproterenol (b)>> "EPI" Antagonists include phentolamine (a), propranolol (b) >> "PP" A transmitter in a few brain stem neurons an adrenal neurohormone.. ** synthesis of catecholamines:: Epinephrine From the pic above : -focus on the enzymes which are responsible for tyrosine development into Dopamine -Focus on the difference btw DOPA & DA DO U REMMEBER?! -focus on Dopamine β- hydroxylase & its requirement ( ascorbic acid + oxygen ). 4 P a g e
5 -focus on the difference btw NE & E which is "methyl" group only.. & this converting done by Phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase enzyme, which convert Adenosyl methionine into Adenosyl homocysteine. ** Catecholamine Metabolites from "degradation ": MAO "intracellular " & COMT "extrcellular " >> intermediates >> mandelic acid "which have diagnostic value for some neurological disorders.. OoooH, how can I memorize this 8arf?? " Joke :P " it's احفظ بصمت **focus on : if MAO did the first step, so the 2 nd step for COMT.. & vise versa. ** all of the following are intermediates for E & NE except :?? HVA : is very important metabolite for Dopamine "also have diagnostic value for some neurological disorders". **focus on : if MAO did the first step, so the 2 nd step for COMT.. & vise versa. ** all of the following are intermediates / metabolites for Dopamine except :?? "**" this sign >> the doctor did't say them.. they are only for Nerds :P the doctor only concentrated on the final result for the metabolism & "MAO, COMT " enzymes. بقية الصفحة للخرابيش! 5 P a g e
6 Synthesized from tryptophan Serotonin (5HT = 5-hydroxytryptamine) Rate-limiting enzyme = tryptophan hydroxylase Inactivation = reuptake into terminals, degradation by MAO The raphe nuclei of the brain stem are the major source of 5HT raphe nuclei are midline, i.e. unpaired nuclei Many subtypes, many actions Mostly 2 nd messenger-gated ion channels, but at least one direct channel receptor Many anti-depressants are targeted at 5-HT neurons (the popular prozac)>> prolong serotonin action " pleasure hormone action" From pic.>> ** Synthesis of Serotonin by Two processes : 1- Hydroxylation : by hydroxylase >> 5HT 2- Decarboxylation : by decarboxylase >> serotonin ** the source of hydroxyle group in the first step is : Tetrahydrobiopterin.. histamine : A local hormone and a hypothalamic transmitter. At least three receptor subtypes known so far. Synthesized from histidine (amino acid). **The histadine is converted to histamine by Decarboxylase enzyme. 6 P a g e
7 Glutamate Mediates fast excitatory communication in the CNS (direct channel-linked) Acts through : 1) 3 direct ligand-gated channel receptor types: NMDA, AMPA and kainate (KA) receptors* 2) 2 or more types of metabotropic (G-protein linked) receptors: ACPD and L-AP4* G- protein linked >> phosphorlate certain enzymes which lead to inhibition or activation certain activity in the cells. NOTE"*" : The names reflect their different pharmacological profiles, but physiologically, in the body, they all bind glutamate ; ex : NMDA receptor channels admit Ca ++ which is an important 2 nd messenger GLU (Glutamate ) is an abundant amino acid in the brain "one of the most abundant AA in the brain ", maybe 30% of which is transmitter. Inactivation = reuptake by glial cells, or by conversion to glutamine then it will return to neuron terminal (where it can be reconverted to GLU) --> the difference btw glutamine & glutamate is an amide group only.. Glu is synthesized by 3 methods: 1- Deamination of Glutamine by glutamase "removal of amide group " 2- Amination of alpha ketoglutarate by Glu dehydrogenase ( utilizing free ammonia and then move the amide group to the alpha ketoglutarate ) 3- Transamination of alpha ketoglutarate by transaminase ( utilizing attached amide group from other AA ) **the difference between Amination &transamination is that the Source of amide group. 7 P a g e
8 Major inhibitory transmitter in the CNS 8 P a g e GABA Altered GABAergic function may play a role in many clinical situations (e.g. basal ganglia disorders, seizure disorders, schizophrenia, sleep disorders) & have a big role in epilepsy. Synthesized from glutamate by GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase), requires Vit B6 as cofactor so, B6 deficiency can lead to loss of synaptic transmission. P.s : Glutmate "excitatory " GABA "inhibitory ". Inactivation = reuptake by nerve terminals for reuse by glia, where it undergoes conversion to glutamine, then return to neuron terminal (where it can be reconverted to Glu and then to GABA) >> as Glutamate inactivation. At least two major receptor subtypes: 1- GABA A is a direct-gated Cl - channel 2- GABA B is G-protein linked, inhibited by K + permeability, Ca ++ influx (especially as presynaptic inhibition), which will camp. Benzodiazepines (Valium) and, probably, neurosteroids bind to GABA A receptor, increase GABA effect >> they increase the inhibitory effect. Agonists: Muscimol (A), baclofen (B) >> in math science "-ve X +ve = -ve " so the agonist increase the " vitiy" >> the inhibition. Antagonists: Bicuculline (A) >> in math science " ve X ve = +ve " so the antagonists decrease the "-vitiy " >> the inhibition. Glycine The other inhibitory transmitter in the CNS Receptor is direct ligand-gated Cl - channel Used by Renshaw cells (inhibitory interneurons in spinal cord, supplying recurrent inhibition) Antagonist = strychnine >> the inhibition.
9 GABA is synthesis from decarboxylation of glutamate ; which need Vit6 cofactor. So Vit 6 deficiency leads to loss of synaptic transmission. Receptors A & B play a role in Epilepsy. Glycine- about 1/2 of neurons in spinal cord use glycine receptors similar to GABAa receptors & both of them are rapidly reuptake by glia & neuron after they exert their action. Hyperglycinemia- defect in glycine uptake and removal leads to severe mental retardation. ** Both GABA and glycine are rapidly taken up by glia and neurons. ** GABA & Glysine : Most inhibitory neurons use one or the other & Inhibits the ability to fire action potentials. Similar to glutamate: excitatory NT Functions in fewer pathways Aspartate Made from oxaloacetate by tranamination reaction ; why?bcz the oxaloacetate is α - ketoacid for aspartate! Aspartate can't pass through BBB Nitric Oxide Effects: vasodilatation, neurotransmission (penile erection), killing tumor cells and parasites Made from arginine by NO-synthase NO activates guanylate cyclase: increase cgmp: activates protein kinases Can cross membranes BBB (bcz it's gas). 9 P a g e
10 This pic illustrate " Synthesis, Release, and Reuptake of GABA and Glycine".. Vesicular transporters regulate the amount and type of neurotransmitters requestered into synaptic vesicles. We have two examples for neurological disorders that related to neurotransmitters : 1-Phenylketonuria (PKU) : Phenylalanine cause mental retardation ; and it's one of the tests that done in neonatal screening.and the treatment is very easy by restrict the Phenylalanine in the diet. This is one of the most common inborn errors of metabolism which affects cerebral activity, affecting approximately 1 out of 20,000 infants. The genetic defect is a lack of phenylalanine hydroxylase and leads to increased concentrations of phenylalanine. The neurochemical mechanisms involve tyrosine and tryptophan pathways. Fortunately, the disorder can be treated in many cases by diet restriction 2- Tay Sachs Disease : This is a lipid-storage disorder transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait. The metabolic defect is a deficiency of the hexosaminidase found in lysosomes involved in ganglioside degradation. Its absence causes lipids and proteins to accumulate in membranous cytoplasmic bodies. There is no established therapy;the treatment is only symptomatic, although recent research has searched for a means of enzyme replacement. % 99 من أطباء امعامل ينصحون مرضامه ابستخدام امساليدات.. امرصاحة أان ثعبت من امكويب بيست لك امتوفيق ع ون (; هذا امتفريغ برعاية )كوجليت \ س ينسوداين \ سيجنل ) معلش إلنه لكهم حاصلني عىل رضا %99 من أطباء السنان ابمعامل :3 Done By your sister : Hadeel Izzat AL-Momani & Checked by : Alanood Albustanji 10 P a g e
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Objectives. 1. Outline the criteria that need to be met before a molecule can be classified as neurotransmitter
 Neurotransmitters Objectives 1. Outline the criteria that need to be met before a molecule can be classified as neurotransmitter 2. Identify the major neurotransmitter types 3. Mechanism of action of important
Neurotransmitters Objectives 1. Outline the criteria that need to be met before a molecule can be classified as neurotransmitter 2. Identify the major neurotransmitter types 3. Mechanism of action of important
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters
 Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Brain Neurotransmitters
 Brain Neurotransmitters * Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane * Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane * Binds to and
Brain Neurotransmitters * Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane * Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane * Binds to and
Dania Ahmad. Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad. Faisal I. Mohammed
 16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
Review of Neurochemistry
 Review of Neurochemistry UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR III SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 CEREBRAL METABOLISM What are some
Review of Neurochemistry UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR III SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 CEREBRAL METABOLISM What are some
Karam Darwish. Saleh Fayez AL-jbour. Diala
 1 Karam Darwish Saleh Fayez AL-jbour Diala Neurotransmitters Note: anything written with the italic font and present between brackets is from the slides. A neurotransmitter is a chemical substance that
1 Karam Darwish Saleh Fayez AL-jbour Diala Neurotransmitters Note: anything written with the italic font and present between brackets is from the slides. A neurotransmitter is a chemical substance that
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors
 Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 1: Dopamine and Norepinephrine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Overview of Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Criteria for defining a
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 1: Dopamine and Norepinephrine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Overview of Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Criteria for defining a
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs. ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani
 Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Omar Ismail. Dana Almanzalji. Faisal Mohammad
 11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
Advanced Neurotransmitters & Neuroglia
 Advanced Neurotransmitters & Neuroglia Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD Lundbeck, LLC. February
Advanced Neurotransmitters & Neuroglia Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD Lundbeck, LLC. February
Brain Neurotransmitters
 Brain Neurotransmitters Brain neurotransmitters Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane
Brain Neurotransmitters Brain neurotransmitters Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
I. OVERVIEW DIRECT. Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of
 THE CHOLINERGIC NEURON 1 I. OVERVIEW DIRECT Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of ACTING neuron involved in their mechanism of action.
THE CHOLINERGIC NEURON 1 I. OVERVIEW DIRECT Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of ACTING neuron involved in their mechanism of action.
Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work
 Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work with Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified
Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work with Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
 PSY 302 Lecture 6: The Neurotransmitters (continued) September 12, 2017 Notes by: Desiree Acetylcholine (ACh) CoA + Acetate Acetyl-CoA (mitochondria) (food, vinegar) + Choline ChAT CoA + ACh (lipids, foods)
PSY 302 Lecture 6: The Neurotransmitters (continued) September 12, 2017 Notes by: Desiree Acetylcholine (ACh) CoA + Acetate Acetyl-CoA (mitochondria) (food, vinegar) + Choline ChAT CoA + ACh (lipids, foods)
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Lujain Hamdan. Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
Mohammad Tarek. Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions
 The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions Lobes in a lateral view of left hemisphere Atlas Fig.2-11 The Insula The Hidden Lobe Atlas Fig. 2-11 Atlas Fig. 2-39 Lobes in a lateral view of left
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions Lobes in a lateral view of left hemisphere Atlas Fig.2-11 The Insula The Hidden Lobe Atlas Fig. 2-11 Atlas Fig. 2-39 Lobes in a lateral view of left
Synapses and Neurotransmitters.
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Loai.physiology@yahoo.com Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Loai.physiology@yahoo.com Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Autonomic Nervous System. Introduction
 Autonomic Nervous System Introduction 1 The nervous system is divided into: 1- the central nervous system (CNS; the brain and spinal cord) 2- the peripheral nervous system (PNS; neuronal tissues outside
Autonomic Nervous System Introduction 1 The nervous system is divided into: 1- the central nervous system (CNS; the brain and spinal cord) 2- the peripheral nervous system (PNS; neuronal tissues outside
Synaptic transmission
 Michael J. Fox Hollywood actor John Nash Nobel prize laureate 1994 Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital sisth@mahidol.ac.th www.ps.si.mahidol.ac.th
Michael J. Fox Hollywood actor John Nash Nobel prize laureate 1994 Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital sisth@mahidol.ac.th www.ps.si.mahidol.ac.th
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC
 BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC Days: MWF, 12-1, room 201! Same old details! Ollieʼs Office hours:! Fri 1.30-4.30pm (may change)! room 3308 Biosciences! Lindsayʼs
BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC Days: MWF, 12-1, room 201! Same old details! Ollieʼs Office hours:! Fri 1.30-4.30pm (may change)! room 3308 Biosciences! Lindsayʼs
Lojayn Salah. Razan Aburumman. Faisal Muhammad
 20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
CONVERSION OF AMINO ACIDS TO SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 CONVERSION OF AMINO ACIDS TO SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU In addition to serving as building blocks for proteins, amino acids are precursors of many nitrogen-containing
CONVERSION OF AMINO ACIDS TO SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU In addition to serving as building blocks for proteins, amino acids are precursors of many nitrogen-containing
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions
 The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions The Cerebral cortex consists of 2 cerebral hemisphere and each hemisphere consists of 5 lobes (frontal, parietal,temporal,occipital,insular lobe which
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions The Cerebral cortex consists of 2 cerebral hemisphere and each hemisphere consists of 5 lobes (frontal, parietal,temporal,occipital,insular lobe which
Rick Gilmore :16:57
 260-2017-02-13 Rick Gilmore 2017-02-13 10:16:57 Prelude Prelude https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/mah_nà_mah_nà Today s Topics Neurotransmitters Quiz 2 on Friday. Review Exam 1 on Friday. The influx of which
260-2017-02-13 Rick Gilmore 2017-02-13 10:16:57 Prelude Prelude https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/mah_nà_mah_nà Today s Topics Neurotransmitters Quiz 2 on Friday. Review Exam 1 on Friday. The influx of which
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Neurotransmitters Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Exocytosis ~20 Amino Acids Used for Protein Synthesis Non-essential (Our bodies can make them) Alanine (A) Arginine (R) Asparagine (N) Aspartate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Neurotransmitters Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Exocytosis ~20 Amino Acids Used for Protein Synthesis Non-essential (Our bodies can make them) Alanine (A) Arginine (R) Asparagine (N) Aspartate
Introduction to CNS 1
 Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
11/10/16. Neurotransmitters and their Receptors. Professor Abercrombie, Chapter 6, Neuroscience, 4 th ed, D. Purves et el.
 Chapter 6, Neuroscience, 4 th ed, D. Purves et el. Neurotransmitters and their Receptors Professor Abercrombie, 2016 Events from neurotransmitter release to postsynaptic excitation or inhibition Sequence
Chapter 6, Neuroscience, 4 th ed, D. Purves et el. Neurotransmitters and their Receptors Professor Abercrombie, 2016 Events from neurotransmitter release to postsynaptic excitation or inhibition Sequence
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
Autonomic Nervous System
 ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
9.98 Neuropharmacology January (IAP) 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.98 Neuropharmacology January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Neuropharmacology: The
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.98 Neuropharmacology January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Neuropharmacology: The
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones
 Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones 1 Chemical Communication Terms and definitions: Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another
Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones 1 Chemical Communication Terms and definitions: Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II
 BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
Chapter 4. Psychopharmacology. Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2004
 Chapter 4 Psychopharmacology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of
Chapter 4 Psychopharmacology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?!
 Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Laith Khreisat. Ahmad Ali Massad. Faisal Muhammad
 21 Laith Khreisat Ahmad Ali Massad Faisal Muhammad * Note: I tried my best to include everything mentioned in the slides, but feel free to refer back to them in case I missed anything. * Last time we talked
21 Laith Khreisat Ahmad Ali Massad Faisal Muhammad * Note: I tried my best to include everything mentioned in the slides, but feel free to refer back to them in case I missed anything. * Last time we talked
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES. Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I.
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
Session ID: 1001 June 14, 2012
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
BMS 153: Neuroscience The chemical synapse + neurotransmitters- lectures Dr Pen Rashbass
 BMS 153: Neuroscience The chemical synapse + neurotransmitters- lectures 12-14 Dr Pen Rashbass (p.rashbass@shef.ac.uk) THESE NOTES ARE MEANT TO BE SUPPLEMENTAL TO YOUR LECTURES/OWN READING THEY DO NOT
BMS 153: Neuroscience The chemical synapse + neurotransmitters- lectures 12-14 Dr Pen Rashbass (p.rashbass@shef.ac.uk) THESE NOTES ARE MEANT TO BE SUPPLEMENTAL TO YOUR LECTURES/OWN READING THEY DO NOT
Abdulrahman Nidal. Ameen Alsaras. Faisal I. Mohammed
 13 Abdulrahman Nidal Ameen Alsaras Faisal I. Mohammed Recall that Acetyl Choline is synthesized from the reaction between Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) with Choline under the presence of Choline acetyltransferase
13 Abdulrahman Nidal Ameen Alsaras Faisal I. Mohammed Recall that Acetyl Choline is synthesized from the reaction between Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) with Choline under the presence of Choline acetyltransferase
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 6 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Transmission at Synapses NeuroPhysiology TextBook Readings Pages 408 through 420 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 6 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Transmission at Synapses NeuroPhysiology TextBook Readings Pages 408 through 420 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
PROTEIN METABOLISM: SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACIDS CATABOLISM AND SYNTHESIS
 PROTEIN METABOLISM: SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACIDS CATABOLISM AND SYNTHESIS SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACID CATABOLISM After removing of amino group the carbon skeletons of amino acids are transformed into metabolic
PROTEIN METABOLISM: SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACIDS CATABOLISM AND SYNTHESIS SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACID CATABOLISM After removing of amino group the carbon skeletons of amino acids are transformed into metabolic
Antidepressants and Sedatives. David G. Standaert, M.D., Ph.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Antidepressants and Sedatives David G. Standaert, M.D., Ph.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Depression A frequent problem, affecting up to 5% of the population Common presentations
Antidepressants and Sedatives David G. Standaert, M.D., Ph.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Depression A frequent problem, affecting up to 5% of the population Common presentations
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Neurochemistry 2. Loewi s experiment
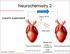 Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters?
 Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters? In molecular terms, neurotransmitters are molecules that ( ) and of neurons by, for example, increasing or decreasing enzymatic activity or altering
Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters? In molecular terms, neurotransmitters are molecules that ( ) and of neurons by, for example, increasing or decreasing enzymatic activity or altering
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Biopsychology 2012 sec 003 (Dr. Campeau)
 Biopsychology 2012 sec 003 (Dr. Campeau) Study Guide for First Midterm What are some fun facts about the human brain? - there are approximately 100 billion neurons in the brain; - each neuron makes between
Biopsychology 2012 sec 003 (Dr. Campeau) Study Guide for First Midterm What are some fun facts about the human brain? - there are approximately 100 billion neurons in the brain; - each neuron makes between
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]](/thumbs/86/94924826.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Amino acid metabolism II
 Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission. BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Neuroscience 2015
 Biochemistry of neurotransmitters Dr. Mamoun Ahram Neuroscience 2015 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed, pp. 908-918 http://what-whenhow.com/neuroscience/neurotransmitters-theneuron-part-1/
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters Dr. Mamoun Ahram Neuroscience 2015 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed, pp. 908-918 http://what-whenhow.com/neuroscience/neurotransmitters-theneuron-part-1/
Conversionofaminoacidsto specializedproducts
 Conversionofaminoacidsto specializedproducts α-nitrogen atom of amino acids is a primary source for many nitrogenous compounds: Heme Purines and pyrimidines Hormones Neurotransmitters Biologically active
Conversionofaminoacidsto specializedproducts α-nitrogen atom of amino acids is a primary source for many nitrogenous compounds: Heme Purines and pyrimidines Hormones Neurotransmitters Biologically active
BIOL Week 6. Nervous System. Transmission at Synapses
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Recreational Chemistry
 Recreational Chemistry Well I'm fading away And I can't find the way to the door So I'll sit here on my bed all day While I'm whiling away The best part of a day on the floor I'll sit here on my head all
Recreational Chemistry Well I'm fading away And I can't find the way to the door So I'll sit here on my bed all day While I'm whiling away The best part of a day on the floor I'll sit here on my head all
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Notes are online at The Neuron
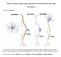 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Ch 9. The Autonomic Nervous System
 Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Biochemistry of Neurotransmitters. Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan CNS
 Biochemistry of Neurotransmitters Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan CNS References Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed, pp. 908-918 http://what-whenhow.com/neuroscience/neurotransmitters-theneuron-part-1/ What
Biochemistry of Neurotransmitters Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan CNS References Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed, pp. 908-918 http://what-whenhow.com/neuroscience/neurotransmitters-theneuron-part-1/ What
COGS 269. Lecture 1 Spring 2018
 COGS 269 Lecture 1 Spring 2018 Psychological Experience Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience Dissociation experiments (patients with brain damage) Neuroimaging experiments Computational modeling Brain damage
COGS 269 Lecture 1 Spring 2018 Psychological Experience Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience Dissociation experiments (patients with brain damage) Neuroimaging experiments Computational modeling Brain damage
Neurotransmitters 1. Types of Neurotransmitters 1) small, nitrogen-containing molecules: 2) neuroactive peptides
 Neurotransmitters 1. Types of Neurotransmitters Two general types: 1) small, nitrogen-containing molecules: Amino acids glutamate, aspartate, GABA, glycine Monoamines dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine,
Neurotransmitters 1. Types of Neurotransmitters Two general types: 1) small, nitrogen-containing molecules: Amino acids glutamate, aspartate, GABA, glycine Monoamines dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine,
Nervous System 2. Quick Video
 Nervous System 2 McMurray/Tarshish Intro Psych Quick Video https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=4gdjcd68sge 1 10/16/15 Divisions of Nervous System Nervous system divisions CNS PNS Sensory (in) Motor (out)
Nervous System 2 McMurray/Tarshish Intro Psych Quick Video https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=4gdjcd68sge 1 10/16/15 Divisions of Nervous System Nervous system divisions CNS PNS Sensory (in) Motor (out)
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
HISTAMINE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 HISTAMINE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer INTRODUCTION: Histamine is a biogenic amine, with a imidazoline ring and act as a neurotransmitter. It is involved in local immune responses as well as regulating
HISTAMINE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer INTRODUCTION: Histamine is a biogenic amine, with a imidazoline ring and act as a neurotransmitter. It is involved in local immune responses as well as regulating
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neurophysiology and Neurochemistry in PsychoGeriatrics
 Tel Aviv University Sackler Faculty of Medicine CME in Psychiatry Neurophysiology and Neurochemistry in PsychoGeriatrics Nicola Maggio, MD, PhD Sackler Faculty of Medicine Tel Aviv University Department
Tel Aviv University Sackler Faculty of Medicine CME in Psychiatry Neurophysiology and Neurochemistry in PsychoGeriatrics Nicola Maggio, MD, PhD Sackler Faculty of Medicine Tel Aviv University Department
NEUROTRANSMITTERS. Contraction of muscles to move our bodies Release hormones Psychological states of thinking and emotions
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS NEURONS Neurons don t actually touch Separated by a tiny fluid-filled gap called a synapse Neural impulses must be ferried across the synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
NEUROTRANSMITTERS NEURONS Neurons don t actually touch Separated by a tiny fluid-filled gap called a synapse Neural impulses must be ferried across the synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
