Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis
|
|
|
- Beverly Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
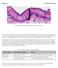
1 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis P. C. MAUDGAL AND L. MISSOTTEN From the Eye Research Laboratory of the Department of Ophthalmology. Catholic University of Leuven, Belgium SUMMARY Iii-vivo corneal replicas were made in 20 cases of patients with superficial dendritic ulcers of the cornea. Histopathological study of the replicas and superficial epithelial cells showed that the dendrites are composed of rounded epithelial cells and variable sized syncytia containing bizarre shaped nuclei. Pseudopodia-like processes containing DNA and some RNA extend from the syncytia into the surrounding epithelial cells, which on coming into contact with these processes become rounded and liquefied to give rise to another syncytium. The epithelial cells adjacent to the dendrite are elongated and usually orientated parallel to the long axis of the lesion. Surrounding the terminal bulbs, they are disposed in an arcuate fashion. These cells show C-mitotic lesions, intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusion bodies, and polykaryocyte formation. Microscopic examination of the corneal replicas shows the intranuclear lesions and rounding of cells up to about 2 mm away from the dendritic ulcers. These areas appear normal on clinical examination. The corneal scrapings of herpetic dendritic ulcers have been studied by Thygeson (1958) and Naib et al. (1967). These authors have described the giant polykaryocytes in the scrapings to be characteristic of herpes simplex keratitis. As the scrapings destroy the exact histological detail owing to the crumpling of cells this method does not provide a full histological picture. We have developed an in-vivo corneal replica technique to study the histopathology of superficial keratitis (Maudgal, 1976; Maudgal and Missotten, 1977; Missotten and Maudgal, 1977). With this technique we have been able to study the replication and maturation stages of the herpes virus and the formation of disseminating inclusion bodies in experimental herpes simplex keratitis in rabbits (Maudgal, 1976). In this paper we report the histopathology of human superficial dendritic lesions studied by the in-vivo corneal replica technique. Subjects and methods In-vivo collodion corneal replicas were made in 20 patients diagnosed clinically to have superficial herpetic dendritic keratitis in 1 eye. The technique of making a corneal replica in vivo and preparing flat mounts has been described previously (Missotten Address for reprints: Professor L. Missotten, Oogziekten, A.Z. St. Rafael, Kapucijnenvoer 7, 3000 Leuven, Belgium and Maudgal, 1977). The replicas were examined by phase-contrast microscopy. After dissolving the collodion membrane in acetone the flat mounts of superficial epithelial cells were studied by phasecontrast and oblique-illumination microscopy. Later the flat mounts were stained by haematoxylin and eosin, acridine orange, and Love's toluidine blue ammonium molybdate (TBM) method (Pearse, 1968) and studied by light microscopy. Results Phase-contrast microscopy of the replicas and the flat mounts of superficial epithelial cells shows that the dendritic ulcers (Fig. 1) are made up of different sized rounded epithelial cells many of which form varying sized syncytia (Figs. 2, 3, 4). The nodular areas in the dendrites and the terminal bulbs of the finger-like projections contain larger syncytia and a larger number of rounded cells. Our observations under oblique-illumination microscopy of unstained specimens and the light microscopy of stained preparations suggest that the syncytia are produced by fusion of cells. At the borders of the syncytium partly fused cells are seen (Figs. 3, 4). Bizarre shaped nuclei are present in the syncytial masses. Most of them are small and rounded or irregular and elongated. In the haematoxylin-eosin stained flat mounts the nuclei are represented by faint basophilic masses in some parts 46
2 Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis of the syncytia where nuclear outlines cannot be seen (Fig. 5). TBM staining and the acridine orange staining show the dispersal of nuclear DNA into the cytoplasm from these nuclei. In other areas increase in the size of nuclei (Fig. 6), granular changes in the nuclei, and intranuclear inclusions may be seen (Fig. 7). The intranuclear inclusions are basophilic and are usually surrounded by an area of rarefaction Fig. 2 Part oj a dendritic ulcer showing syncytia and rounded epithelial cells in the lesion. Elongated cells are arranged in an arcuate fashion round the terminal bulbs andfill the spaces between the finger-like projections. Phase-contrast microscopy of the replica (x 133) of the nucleoplasm. Sometimes clumping and fragmentation of the nuclear chromatin are seen. Nuclear fragments may be found scattered in the syncytial masses. Similar lesions may be seen in the nuclei of rounded cells, which are quite often very large. The rounded epithelial cells and the liquefying cells possess variable amount of cytoplasm. It may be present only in the form of a marginal strip Fig. 1 Photo-montage of a aeal pa_.iet replica from a having typical dendritic ulcer. Nodes and terminal bulbs are evident. Note the elongated cells surrounding the lesion. Bright circular dots are artefacts. Phase-contrast microscopy, obi. (x 10) 47
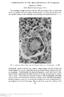
3 48 Fig. 4 Partly fusel rounded epithelial cells are seen at the margin ofa syncytium in a dendritic ulcer. Oblique-illumination microscopy (x 390) P. C. Maudgal and L. Missotten Fig. 3 Part of a syncytium in a dendritic ulcer. At the margin of the syncytium partly fused and rounded epithelial cells are seen. Note the pseudopodia-like processes extending from the syncytium to some cells. Phase-contrast microscopy ( x 400) Fig. 5 Part of a syncytium in a dendritic ulcer. Nuclear details are not visible in the fused cells above. Bizarre nuclei, and nuclear fragments are seen in the syncytium below. (H and E. x 480)
4 Histopathology of hitman suiperficial herpes simplex keratitis Fig. 6 Part of a syncytium in a dendritic ulcer. Large cells with large nuclei are seen. Note clumping and rarefaction of nuclear chromatin in some nuclei. Some nuclear fragments are lying in the syncytium. (1- and E. x 480) 4 ' Sometimes rounded ghost cells are seen in the debris (Fig. 10). They contain strongly eosinophilic cyto-...plasm and basophilic stellate nuclear material in the centre. In the area of necrosis vacuolation of the... & -- cytoplasm is frequently seen. From the rounded cells and syncytia pseudopda Ij;;9Xi S like processes are seen extending towards the surrounding cells (Figs. 3, 4, 7, 9) which are in 4f- contact me, with other rounded cells. In some areas such rounded cells have also become liquefied and partly 4 2._ or wholly fused to form a syncytium. The pseudo- "~*"- \ ~' podia-like processes may be very thin and may extend across a few cells before contacting another... Fig. 7 A large epithelial cell (upper right) showing intranuclear inclusion. Central dense area of clumped chromatin is surrounded by a ring of rarefaction. The elongated cell (upper middle) shows granularinn change in the nucleus and is connected by a pseudopodia-like process to the small syncytium below. Some rounded cells are also seen. (H and E. x 395) round the nuclei or on the contrary in very large amount, quite out of proportion to the size of the nucleus (Figs. 8, 9). The acridine orange staining \\~ shows an increase in the quantity of RNA in the cytoplasm of these cells as compared to the penipheral normal cells. The presence of green fluorescence of DNA is often encountered in the cytoplasm. Fig. 8 Two large cells containing small nuclei at the In the areas of necrosis the cytoplasm may be border of a syncytium. The rounded epithelial cell totally lost where faintly stained and deformed or below and to the right shows intranuclear granules. fragmented nuclei are seen in the debris (Fig. 9). (Hand E. x 390) 49
5 so Fig. 10 A ghost cell showing stellate nucleus. (HandE. x1130) cell at their tip. They contain RNA and DNA as seen by acridine orange staining. The 3 to 4 rows of the epithelial cells immediately adjacent to the dendritic lesion are elongated and orientated parallel to the lesion. The area between the 2 finger-like processes may be occupied by such elongated cells (Figs. 1, 2). Around the terminal bulb these cells are disposed in an arcuate fashion. Some of these cells show liquefaction and rounding. In these cells C-mitotic lesions (Fig. 11) and intranuclear inclusions may be seen. Fusion of the cells is often present. The fusing cells may possess elongated nuclei, which are displaced towards the area of contact. The cytoplasmic inclusions (Fig. 12) are often situated near to the nuclei. They are faintly eosinophilic rounded areas containing basophilic granules. The epithelial cells peripheral to the elongated cells P. C. Maudgal and L. Missotten Fig. 9 Pseudopodia-like processes extending from the syncytial mass above (partly shown) to the 2 rounded epithelial cells below. Some of the rounded cells contain scanty cytoplasm. To the left is an area ofnecrosis. (H and E. x 470) appear oedematous and larger and show stronger fluorescence for RNA in the cytoplasm and DNA in the nuclei. Some of them also show intranuclear inclusions. Such cells may be found up to 2 mm away from the dendritic ulcer. These areas do not show any abnormality on clinical biomicroscopy. In the replicas of the patients having diffuse epithelial oedema but no fluorescein staining clinically, rounding and liquefication of the cells is seen in extensive areas. Discussion The human dendritic corneal ulcers of herpes simplex origin have been clinically described to contain swollen epithelial cells (Duke-Elder, 1965). In the corneal scrapings from the dendritic keratitis giant polynucleate cells have been described (Thygeson, 1958; Naib et al., 1967). Rounding of the epithelial cells and their degeneration and clumping of the nuclear chromatin have been reported by Hudson et al. (1976) in experimental herpes keratitis. Our investigation shows that the dendritic lesions are made up of variable sized syncytia and rounded epithelial cells. The syncytia are formed by the fusion of rounded and liquefied cells. It may be speculated that the giant polykaryocytes described by Thygeson (1958) and Naib et al. (1967) could be parts of such syncytia broken down during the scraping or preparation of the slide. The granular particles seen in the nuclei of some cells resemble the A granules or maturing virus particles described by Love and Wildy (1963) and demonstrated in experimental herpes simplex keratitis in rabbits by
6 Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis Fig. 12 Cytoplasmic inclusion seen in an elongated epithelial cell surrounding the dendritic ulcer. H and E stain ( x 970) Maudgal (1976). The presence of green fluorescence for DNA in the cytoplasm of some cells may be related to the release of these virus particles into the cytoplasm. The degenerating cells contain either swollen or small deformed nuclei. The nuclei in the syncytia are bizarre shaped. The nuclear chromatin may be clumped or fragmented. Fragments of the nuclear material may be found scattered in the syncytial masses. It is not possible to confirm if these nuclear fragments contain virus particles. Balloon degeneration of the nuclei was not seen, although many rounded cells contain swollen nuclei. The cells adjacent to the syncytia may show intranuclear C-mitotic lesion or a colchicine-like effect, demonstrated by Love and Wildy (1963) in HeLa cell cultures infected by the herpes simplex virus. However, as the superficial epithelial cells are at the stage of being shed off and relatively metabolically inactive, this lesion is only infrequently seen. The basophilic granules in the cytoplasmic inclusions may be the maturing virus particles. The acridine orange staining shows an increase in the cytoplasmic RNA and nuclear DNA in the epithelial cells. It is known that in a productive infection with the herpes viruses the synthesis of cell-specific proteins ceases and virus-specific proteins are synthesised (Kaplan et al., 1975). The increase in the ribonucleoproteins could be due to the stimulation of the cell activity by the virus. Fig. 11 An epithelial cell adjacent to the syncytium showing C-mitotic intranuclear lesion. Phase-contrast microscopy ( x 1200) 51
7 52 The superficial epithelial cells surrounding the dendritic lesions are elongated and orientated parallel to the long axis of the lesion and in an arcuate pattern around the terminal bulbs. Their shape and arrangement may be due to the mechanical effect of displacement by the large masses of syncytia and swollen rounded cells. Scattered pathological cells may be found about 2 mm away from the dendrites. Larger areas of involvement are seen in the cases showing epithelial oedema. It is interesting to note that such areas do not stain with fluorescein and appear clinically normal. Lack of leucocytes in the replica specimens is noteworthy. Some rounded cells of lymphocyte size are seen, but their staining characteristics and cytological details show that they are degenerating rounded epithelial cells. References Duke-Elder, S. (1965). System of Ophthalmology, Vol. 8, Diseases of the outer eye. Kimpton: London. Hudson, J. B., Hollenberg, M. J., Wilkie, J. S., and Lewis, P. C. Maudgal and L. Missotten B. J. (1976). Ultra structural study of lesions induced in rabbit cornea by herpes simplex virus 1 and 2. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 133, Kaplan, A. S., Erickson, J. S., and Ben-Porat, T. (1975). Excretion of specific glycoproteins by cells infected with herpes simplex virus, Types 1 and 2. Progress in Medical Virology, 21, Love, R., and Wildy, P. (1963). Cytochemical studies of nucleo-proteins of HeLa cells infected with herpes virus. Journal of Cell Biology, 17, Maudgal, P. C. (1976). The epithelial response in keratitis sicca and keratitis herpetica (an experimental and clinical study). Thesis for D.Sc. (Ophth.), University of Louvain. Maudgal, P. C., and Missotten, L. (1977). The corneal replica technique. Read before the Belgian Society of Ophthalmology, February (in press). Missotten, L., and Maudgal, P. C. (1977). The corneal replica technique used to study the superficial corneal epithelium in vivo. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 84, Naib, Z., Clepper, A., and Elliot, S. (1967). Exfoliative cytology as an aid in the diagnosis of ophthalmic lesions. Acta cytologica, 11, Pearse, G. A. E. (1968). Histochemistry: Theoretical and Applied, Part I. Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh. Thygeson, P. (1958). Cytological observations on herpetic keratitis. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 45, Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 January Downloaded from on 20 November 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Effect of Viruses on Tissue Culture
 Pan American Society for Clinical Virology presents Effect of Viruses on Tissue Culture CDC Slide Set Provided by the National Laboratory Training Network* *Reproduced and distributed with permission Normal
Pan American Society for Clinical Virology presents Effect of Viruses on Tissue Culture CDC Slide Set Provided by the National Laboratory Training Network* *Reproduced and distributed with permission Normal
Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus
 244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Microscopic Anatomy of Inferior Medullary Velum Of Cerebellum
 32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
morphologically typical to be distinct from particulate chromatin, whereas SEX OF NUCLEI IN OCULAR TISSUES*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 362. SEX OF NUCLEI IN OCULAR TISSUES* BY CHRISTOPHER PEDLER AND NORMAN ASHTON Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London BARR AND BERnTAM (1949),
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 362. SEX OF NUCLEI IN OCULAR TISSUES* BY CHRISTOPHER PEDLER AND NORMAN ASHTON Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London BARR AND BERnTAM (1949),
Pathogenesis of viral infection
 Pathogenesis of viral infection Viral Pathogenesis Viral pathogenesis is the process by which a viral infection leads to disease. Viral pathogenesis is an abnormal situation of no value to the virus. The
Pathogenesis of viral infection Viral Pathogenesis Viral pathogenesis is the process by which a viral infection leads to disease. Viral pathogenesis is an abnormal situation of no value to the virus. The
H erpes simplex virus infection of the
 Herpes simplex keratitis An experimental study Samuel J. Kimura, Victor Diaz-Bonnet, and Masao Okumoto The incidence of complicated herpes simplex keratitis appears to have increased and the important
Herpes simplex keratitis An experimental study Samuel J. Kimura, Victor Diaz-Bonnet, and Masao Okumoto The incidence of complicated herpes simplex keratitis appears to have increased and the important
Changes in the normal anatomy. In some sections a fairly normal. (entropion). Obliteration of glands and occasionally a cyst were
 234 THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY PAGET'S DISEASE OF THE EYELID ASSOCIATED WITH CARCINOMA BY DR. A. HAGEDOORN (UNIVERSITY EYE HOSPITAL, AMSTERDAM) IN September, 1929, B. P., a woman aged 56 years
234 THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY PAGET'S DISEASE OF THE EYELID ASSOCIATED WITH CARCINOMA BY DR. A. HAGEDOORN (UNIVERSITY EYE HOSPITAL, AMSTERDAM) IN September, 1929, B. P., a woman aged 56 years
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Yara shwabkeh. Osama Alkhader. Heba Kalbouneh
 2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF LATE PHASE FLUORESCENCE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 519 821 HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF LATE PHASE FLUORESCENCE IN THE RABBIT FUNDUS*t BY A. W. SOLLOM AND I. A. R. BROWN Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital MANY different explanations
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 519 821 HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF LATE PHASE FLUORESCENCE IN THE RABBIT FUNDUS*t BY A. W. SOLLOM AND I. A. R. BROWN Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital MANY different explanations
Corneal blood staining after hyphaema
 Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Cytoplasmic changes Nuclear changes
 The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
Cytological and immunohistochemical study of the limbal form of vernal keratoconjunctivitis by the replica technique
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1987, 71, 867-872 Cytological and immunohistochemical study of the limbal form of vernal keratoconjunctivitis by the replica technique AHMED M ABU EL ASRAR,' KAREL GEBOES,2
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1987, 71, 867-872 Cytological and immunohistochemical study of the limbal form of vernal keratoconjunctivitis by the replica technique AHMED M ABU EL ASRAR,' KAREL GEBOES,2
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY. Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia
 August 1969 Volume 8, Number 4 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia 7?. M. H. Pinkerton and David M. Robertson A case of dysproteinemia with corneal and conjunctival
August 1969 Volume 8, Number 4 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia 7?. M. H. Pinkerton and David M. Robertson A case of dysproteinemia with corneal and conjunctival
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Disease caused by herpes simplex virus
 Recurrence of herpes simplex virus in rabbit eyes: Results of a three-year study Peter R. Laibson and Sidney Kibrick Spontaneous reactivation of herpes simplex virus in rabbit ocular tissue was found on
Recurrence of herpes simplex virus in rabbit eyes: Results of a three-year study Peter R. Laibson and Sidney Kibrick Spontaneous reactivation of herpes simplex virus in rabbit ocular tissue was found on
Characterization of changes observed in the corneal endothelium with the specular microscope
 Characterization of changes observed in the corneal endothelium with the specular microscope Emil S. Sherrard The specular microscope reveals little of the internal features of the corneal endothelium,
Characterization of changes observed in the corneal endothelium with the specular microscope Emil S. Sherrard The specular microscope reveals little of the internal features of the corneal endothelium,
IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS.
 CULTIVATION IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS. (From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Pr~AT~ LXXVII. The growth of malignant
CULTIVATION IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS. (From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Pr~AT~ LXXVII. The growth of malignant
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
A pitfall in the cytodiagnosis of sputum of asthmatics
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 84 A pitfall in the cytodiagnosis of sputum of asthmatics BERNARD NAYLOR AND CONSTANTINE RAILEY' From the Department ofpathology, the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan,
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 84 A pitfall in the cytodiagnosis of sputum of asthmatics BERNARD NAYLOR AND CONSTANTINE RAILEY' From the Department ofpathology, the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan,
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors
 Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Microscopic Sediment Epithelial Cells
 Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS. photocoagulation of the rabbit's retina.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Differential Staining of Ocular Goblet Cells
 Eye (1989) 3, 840--844 Differential Staining of Ocular Goblet Cells G. G. W. ADAMS and P. N. DILLY London Summary Millipore filters were used to obtain sheets of cells from the ocular surface. Using Periodic
Eye (1989) 3, 840--844 Differential Staining of Ocular Goblet Cells G. G. W. ADAMS and P. N. DILLY London Summary Millipore filters were used to obtain sheets of cells from the ocular surface. Using Periodic
BY N. N. SOODt AND V. J. MARMION- St. Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 609. SUPERFICIAL HERPETIC KERATITIS TREATED WITH 5-IODO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE* BY N. N. SOODt AND V. J. MARMION- St. Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool THE results of treating herpetic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 609. SUPERFICIAL HERPETIC KERATITIS TREATED WITH 5-IODO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE* BY N. N. SOODt AND V. J. MARMION- St. Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool THE results of treating herpetic
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes
 Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Olfactory mucosa in herpes simplex encephalitis
 g;i Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1979, 42, 983-987 Olfactory mucosa in herpes simplex encephalitis J. A. TWOMEY, CHRISTINE M. BARKER, G. ROBINSON, AND D. A. HOWELL From the Departments
g;i Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1979, 42, 983-987 Olfactory mucosa in herpes simplex encephalitis J. A. TWOMEY, CHRISTINE M. BARKER, G. ROBINSON, AND D. A. HOWELL From the Departments
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma
 Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Condition: Herpes Simplex Keratitis
 Condition: Herpes Simplex Keratitis Description: Herpes simplex infection is very common but usually remains latent. When the virus is reactivated it travels along the trigeminal nerve to cause local infection
Condition: Herpes Simplex Keratitis Description: Herpes simplex infection is very common but usually remains latent. When the virus is reactivated it travels along the trigeminal nerve to cause local infection
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: 2. A. Skeletal muscle tissue ("striated muscle tissue")
 1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Chapter 21 Outline. General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements
 Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Introduction. 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology. FLUIDS, Part 1. Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT
 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
Acute hepatitis due to Herpes simplex virus in an adult
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 60-66 Acute hepatitis due to Herpes simplex virus in an adult T. H. FLEWETT, R. G. F. PARKER, AND W. M. PHILIP From East Birmingham Hospital, Birmingham SYNOPSIS A case is described
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 60-66 Acute hepatitis due to Herpes simplex virus in an adult T. H. FLEWETT, R. G. F. PARKER, AND W. M. PHILIP From East Birmingham Hospital, Birmingham SYNOPSIS A case is described
Acta Medica Okayama. Studies on diagnosis of leukemia by tissue culture. Kiyoshi Hiraki APRIL Volume 12, Issue Article 8
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 12, Issue 1 1958 Article 8 APRIL 1958 Studies on diagnosis of leukemia by tissue culture Kiyoshi Hiraki Okayama University, Copyright c 1999 OKAYAMA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL SCHOOL.
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 12, Issue 1 1958 Article 8 APRIL 1958 Studies on diagnosis of leukemia by tissue culture Kiyoshi Hiraki Okayama University, Copyright c 1999 OKAYAMA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL SCHOOL.
Cytology Report Format
 Squamous Precursor Lesions and Malignancies In Pap Test Dina R. Mody, MD, FCAP Director of Cytology The Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Weill Medical College
Squamous Precursor Lesions and Malignancies In Pap Test Dina R. Mody, MD, FCAP Director of Cytology The Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Weill Medical College
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module. 1) Connective tissue
 D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
 Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus Helena M. Tabery Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus In Vivo Morphology in the Human Cornea
Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus Helena M. Tabery Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus In Vivo Morphology in the Human Cornea
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
 Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
Sheet #7. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
ANNEX II: Atlas of histopathological lesions of Isolated Chicken Eyes
 ANNEX II: Atlas of histopathological lesions of Isolated Chicken Eyes (from Triskelion, Zeist, The Netherlands) 1. Introduction... 1 2. Semi-quantitative microscopic evaluation of the cornea... 1 3. Histopathology
ANNEX II: Atlas of histopathological lesions of Isolated Chicken Eyes (from Triskelion, Zeist, The Netherlands) 1. Introduction... 1 2. Semi-quantitative microscopic evaluation of the cornea... 1 3. Histopathology
Morphological Changes in Productive and Abortive Infection by Feline Herpesvirus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1970, p. 617-623 Copyright ( ) 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 5, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Morphological Changes in Productive and Abortive Infection by Feline Herpesvirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1970, p. 617-623 Copyright ( ) 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 5, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Morphological Changes in Productive and Abortive Infection by Feline Herpesvirus
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS
 THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
NEUROGLIAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE HUMAN
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 601. NEUROGLIAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE HUMAN RETINAL CAPILLARY NETWORK* BY C. A. ERSKINE School of Anatomy, Trinity College, Dublin THE investigation described in this paper
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 601. NEUROGLIAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE HUMAN RETINAL CAPILLARY NETWORK* BY C. A. ERSKINE School of Anatomy, Trinity College, Dublin THE investigation described in this paper
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A. Pathological Case Report
 Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material
 Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION
 GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
(Iteceived for publication December 3, 1915)
 TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
The ultrastructure of the egg and
 The ultrastructure of the egg and central cell of Petunia J.L. van Went Botanisch Laboratorium, Universiteit, Nijmegen SUMMARY The egg and central cell of Petunia hybrida undergo a number of changes and
The ultrastructure of the egg and central cell of Petunia J.L. van Went Botanisch Laboratorium, Universiteit, Nijmegen SUMMARY The egg and central cell of Petunia hybrida undergo a number of changes and
Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 294-299 Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma C R PAYNE, P G I STOVIN, V BARKER, S McVITTIE, AND J E STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 294-299 Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma C R PAYNE, P G I STOVIN, V BARKER, S McVITTIE, AND J E STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard,
Infra-red transillumination stereophotography of the iris in Fuchs's heterochromic cyclitis
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 110-115 Infra-red transillumination stereophotography of the iris in Fuchs's heterochromic cyclitis M. SAARI, I. VUORRE, AND H. NIEMINEN From the University
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 110-115 Infra-red transillumination stereophotography of the iris in Fuchs's heterochromic cyclitis M. SAARI, I. VUORRE, AND H. NIEMINEN From the University
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man
 Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Epidemiological and clinical features of primary herpes simplex virus ocular infection
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1985, 69, 2-6 Epidemiological and clinical features of primary herpes simplex virus ocular infection S DAROUGAR, M S WISHART, AND N D VISWALINGAM From the Subdepartment
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1985, 69, 2-6 Epidemiological and clinical features of primary herpes simplex virus ocular infection S DAROUGAR, M S WISHART, AND N D VISWALINGAM From the Subdepartment
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Relationship between limbal incisions. angle. and the structures of the anterior chamber
 Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Graefe's Archive. Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Autoradiographic Studies and Mitosis of Heart Muscle Cells in Experimental Cardiac Hypertrophy
 Tohoku J. exp. Med., 1970, 102, 159-167 Autoradiographic Studies and Mitosis of Heart Muscle Cells in Experimental Cardiac Hypertrophy RIKURO SASAKI, TOSHIAKI MORISHITA, SHIZUKA ICHIKAWA and SHOICHI YAMAGATA
Tohoku J. exp. Med., 1970, 102, 159-167 Autoradiographic Studies and Mitosis of Heart Muscle Cells in Experimental Cardiac Hypertrophy RIKURO SASAKI, TOSHIAKI MORISHITA, SHIZUKA ICHIKAWA and SHOICHI YAMAGATA
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook
 Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
(Plates LXVIII-LXXI)
 [GANN, 54, 481-486; December, 1963] UDC 616.155.392-076.4:578.69 VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLES IN HUMAN CHLOROLEUKEMIA CELLS (Plates LXVIII-LXXI) Zensuke OTA, Shin-ya SUZUKI, and Satoru HIGASHI (Department of Internal
[GANN, 54, 481-486; December, 1963] UDC 616.155.392-076.4:578.69 VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLES IN HUMAN CHLOROLEUKEMIA CELLS (Plates LXVIII-LXXI) Zensuke OTA, Shin-ya SUZUKI, and Satoru HIGASHI (Department of Internal
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Evaluation of corneal endothelium and keratic precipitates by specular microscopy in anterior uveitis
 Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:1367 1371 1367 Department of Ophthalmology, B Floor, South Block, University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK C T Pillai H S Dua A Azuara-Blanco A R Sarhan
Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:1367 1371 1367 Department of Ophthalmology, B Floor, South Block, University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK C T Pillai H S Dua A Azuara-Blanco A R Sarhan
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
