Genotypic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii Strains Associated with Human Toxoplasmosis in Spain: Direct Analysis from Clinical Samples
|
|
|
- Mae Owens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2001, p Vol. 39, No /01/$ DOI: /JCM Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Genotypic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii Strains Associated with Human Toxoplasmosis in Spain: Direct Analysis from Clinical Samples ISABEL FUENTES,* JOSE M. RUBIO, CARMEN RAMÍREZ, AND JORGE ALVAR Servicio de Parasitología, Centro Nacional de Microbiología, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Majadahonda, Madrid, Spain Received 8 September 2000/Returned for modification 20 November 2000/Accepted 26 January 2001 Genetic analysis of the SAG2 locus was performed to determine the prevalence of the different genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii (strain types I, II, and III) associated with human toxoplasmosis in Spain. This determination was made directly from primary clinical samples, obviating the previous process of isolation in mice or cell culture. A total of 34 isolates of T. gondii, collected from immunocompromised patients and congenital infection cases, were analyzed. Restriction fragment length polymorphism in PCR-amplified SAG2 products was used to group strains into one of the three genotypes of T. gondii. Complete characterization of the SAG2 gene was successful in 76.5% of the cases, demonstrating the feasibility of direct genotype analysis from clinical samples of different origins. Strains of T. gondii type II were the most prevalent in immunocompromised patients, with 52% of cases, while strains of type I were present in 75% of the congenital infection cases. These data differ from previous reports that show type II strains to be mostly associated with all kinds of human toxoplasmosis. These differences might be an effect of selection in the process of culture and isolation of the samples performed by other researchers prior to strain characterization. The protozoan Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that infects humans and a broad spectrum of vertebrate hosts. The transmission of T. gondii occurs by ingestion of oocysts shed from feline feces, by ingestion of T. gondii cysts from chronically infected tissues, or by vertical transmission (23). Between 15 and 85% of the world adult human population is chronically infected with T. gondii depending on geographical location (4). Toxoplasmosis has variable outcomes in the host. Immunocompetent infected individuals show mild symptoms or may remain asymptomatic, while infection in congenitally infected children and in immunocompromised persons (AIDS patients, organ transplant recipients, and cancer patients) causes high rates of morbidity and mortality (15). The progression and severity of the disease differ in patients due to several variables, including host and parasite genetics (8, 21). It is wellknown that the virulence of T. gondii differs in animals, depending on the T. gondii strain (16). The identification of a possible correlation between the severity or type of disease and strain genotyping might be very important for determination of the correct treatment and the possible outcome of the disease in each human case (21). Genetic analysis of strains indicates that the propagation of T. gondii is primarily by clonal, asexual, or uniparental sexual reproduction, while sexual recombination between different strains of the parasite is exceptional in natural populations (20). * Corresponding author. Mailing address: Servicio de Parasitología, Centro Nacional de Microbiología, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Cra. Majadahonda-Pozuelo Km 2, Majadahonda, Madrid, Spain. Phone: , ext Fax: T. gondii strains have been subdivided in two or three major groupings using different methods of characterization, such as isoenzyme electrophoresis, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), PCR, or random amplified polymorphism DNA (2, 3, 9, 12, 20). Howe and Sibley (14), analyzing six independent single-copy loci by PCR-RFLPs, described three clonal lineages, named types I, II, and III, which correspond to the genetic analysis of the polymorphic surface antigen 2 locus (SAG2) (12). Several reports analyzing samples isolated in mice or in vitro cultures show that type II is the most prevalent genotype (3, 12, 14, 18 20). The genetic analysis of T. gondii based on amplification of the SAG2 locus requires small amounts of DNA, thus allowing it to be used directly on clinical samples. The aim of this work was to determine the lineage types of T. gondii associated with human toxoplasmosis in Spain. For this purpose, genetic analysis of the SAG2 locus for amplification of the DNA obtained directly from clinical samples was performed, obviating the previous process of isolation in mice or cell culture. MATERIALS AND METHODS Clinical samples. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood, aqueous humor, and lung and brain biopsy samples were obtained from immunocompromised patients with toxoplasmosis, along with amniotic fluid, blood, and urine samples from pregnant women and abortion ascitic fluid and blood samples from newborn babies with congenital infections. A total of 34 samples from 33 patients, 20 immunocompromised patients and 13 infants with congenital infections, with different pathologies were included in the study (see Table 1). Samples of CSF (0.5 ml) and urine and amniotic fluid (2 to 5 ml) were concentrated by centrifugation at 1,800 g for 10 min, and the pellets were stored at 20 C. The rest of the samples were stored at 4 C, until analyzed. Experimental samples. The following representative strain types of T. gondii were used for standardization and as controls of PCR assays: strain RH (type I), strains Beverly and Me49 (type II), and strain C56 (type III) (14). Parasites were grown and maintained by bioassay in mice, and samples of chronically infected mouse brain were used as positive controls in PCR assays and genotype analysis. 1566
2 VOL. 39, 2001 GENOTYPIC CHARACTERIZATION OF T. GONDII STRAINS 1567 Isolation of DNA. DNA extraction from blood and paraffin-embedded tissues was performed using Wizard and Dexat genomic DNA purification kits (Promega, Madison, Wis.) in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. The rest of the samples were incubated in 100- l portions of lysis buffer (10 mm Tris-HCl [ph 8.3], 1.5 mm MgCl 2, 50 mm KCl, 0.1 mg of gelatin per ml, 0.5% Tween 20, 20 g of proteinase K) at 55 C, with shaking for 90 min. After inactivating the proteinase K at 94 C for 10 min, the suspension was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant, which contained the DNA, was moved to a new tube. Detection of T. gondii by PCR. T. gondii infections were initially confirmed by nested PCR amplification of the repetitive and conserved gene B1 (1, 6). Genotype analysis. The lineage type was determined by restriction fragment of the amplified SAG2 gene of T. gondii using two nested PCRs separately amplifying the 5 and 3 ends of the gene (12). The PCR mix for the nested reactions consisted of 75 mm Tris-HCl (ph 9.0), 50 mm KCl, 20 mm (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4, 2 mm MgCl 2, 0.001% bovine serum albumin, 200 M each of the four deoxynucleoside triphosphates, 0.5 pmol of each primer, 1 U of DNA polymerase (Biotools, Madrid, Spain), and, as a template, 1 to 20 l of extracted sample DNA for the first reactions and 5 l of a 1:100 dilution of the products of the first amplifications for the second reactions, in a final volume of 50 l. All the PCRs were performed in a 2400 GeneAmp PCR system thermal cycler (Perkin-Elmer, Norwalk, Conn.). The first step of amplification was 5 min of denaturation at 94 C. This step was followed by 40 cycles, with 1 cycle consisting of 45 s at 94 C, 45 s at the annealing temperature for each pair of primers, and 60 s at 72 C. The final cycle was followed by an extension step of 10 min at 72 C. The 5 end was amplified using primers SAG2F4 (5 -GACCTCGAACAGG AACAC-3 ) and SAG2R4 (5 -GCATCAACAGTCTTCGTTGC-3 ) in the first amplification, at an annealing temperature of 60 C. In the second reaction, the internal primers SAG2F (5 -GAAATGTTTCAGGTTGCTGC-3 ) and SAG2R2 (5 -GCAAGAGCGAACTTGAACAC-3 ) were used, with 58 C as the annealing temperature. Amplification of the 3 end was performed with primers SAG2F3 (5 -TCTG TTCTCCGAAGTGACTCC-3 ) and SAG2R3 (5 -TCAAAGCGTGCATTATC GC-3 ) for the first amplification at an annealing temperature of 58 C and with the internal primers SAG2F2 (5 -ATTCTCATGCCTCCGCTTC-3 ) and SAG2R (5 -AACGTTTCACGAAGGCACAC-3 ) for the second amplification at an annealing temperature of 55 C. The 5 -end amplification is expected to yield a product of 241 bp, while the 3 -end amplification must give a product of 221 bp in both cases for any strains of T. gondii. In order to avoid possible contamination, several measures, such as separate space to set up PCRs, filter tips, etc., were taken, as well as different negative controls (no DNA, uninfected blood, and extracted no DNA), and positive controls from different strains of T. gondii were used in order to locate any possible contamination. The amplified products were purified with Bioclean Purification Columns (Biotools) and digested with Sau3AI (5 -end products) and with HhaI (3 -end products). The PCR products and the restriction fragments were analyzed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Restriction digestion of 5 -end-amplified products with Sau3AI distinguished the type III strain from type I and II strains and digestion of the 3 -end-amplified fragments with HhaI differentiated type I and III strains. Controls for lineage types were prepared from RH (type I), Beverly (type II), Me49 (type II), and C56 (type III) strains of T. gondii. In those cases in which some of the samples were seen to be inhibited in the nested PCR, the rest of the reaction mix of the first amplification process was recovered and cleaned using the Bioclean Purification Columns (Biotools), in accordance with the manufacturer s protocol, and 5 l of the elute was used as a template in the nested PCR. The method used for the characterization of T. gondii strains implied digestion with restriction enzymes of the fragments amplified. The acquisition of digested and nondigested products from the same purification set means that the products obtained are not due to any contamination in the purification or amplification process. RESULTS A collection of 34 samples from 33 patients (15 immunosuppressed human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]-positive patients, 5 immunosuppressed HIV-negative patients, 5 pregnant women, and 8 newborn babies) were analyzed in order to characterize the genotype of T. gondii present in each sample (Table 1). The isolation of DNA was carried out directly from the samples without previous isolation in culture or mice. Genetic analysis was performed by PCR-RFLP at the SAG2 loci of T. gondii. Previously, all the samples were confirmed for the presence of the parasite by nested PCR of the B1 T. gondii gene. In all the samples, as well as in the four reference strains, the nested PCR rendered the expected fragment of 97 bp, while all the negative controls, including uninfected samples of mouse brain and human blood, were negative. Amplification of both ends of the SAG2 gene was successful in the four reference strains and in 26 of 34 clinical samples (76.5%). In another six cases (18%), only the 3 end of the SAG2 gene was amplified, and in the other two (6%), only the 5 end was amplified (Table 1). Nine of these fragments were obtained by purification and new nested amplification of previously inhibited PCR. In another nine cases, this strategy did not work and the method was impossible to repeat, as new samples were not available. The patterns of digestion of the four reference strains corresponded to the expected results. The RH strain was characterized as genotype I because the 3 - and 5 -end-amplified fragments of the SAG2 gene were undigested with the corresponding restriction enzymes. The Beverly and Me49 strains were characterized as genotype II since the 3 -end fragments of the SAG2 gene were digested with HhaI while the 5 -end fragments were undigested. The C56 strain was characterized as genotype III because the 3 -end fragments of the SAG2 gene were undigested while the 5 -end fragments were digested by Sau3AI. Figure 1 shows the digestion patterns of the various strains studied. Genotyping of the 25 fully studied samples rendered the following results: 10 of type I (40%), 10 of type II (40%), and 5 of type III (20%). The eight strains which were partially characterized resulted in two of type I or II (non-type III) and six of type I or III (non-type II). The two brain biopsy samples from the same patient (patient 14 IHIV ) rendered the same result, type III (Tables 1 and 2). Of the samples from the 17 immunosuppressed patients that were fully characterized, four (23.5%) were type I, nine (53%) were type II, and the other four (23.5%) were type III. The other three immunosuppressed patients were infected in two cases by non-type III strains of T. gondii, and the third was infected by a non-type II strain. On the other hand, of the eight samples from congenital toxoplasmosis cases that were fully characterized, six (75%) were type I, while one (12.5%) was type II and one (12.5%) was type III. The other five samples from newborn babies for which total characterization was not possible were infected by non-type II strains (Tables 1 and 2). In general, there is no clear correlation between strain genotype and symptomatology. In immunocompromised patients, the three genotypes produce symptomatology related to neurological diseases, associated in several cases with pneumonia and other related lung diseases; in two cases, with strain type II, the patients show eye diseases without other associated symptoms. In the cases of congenital toxoplasmosis in which it was possible to follow up on the patients, there was not a clear association between disease and the genotype of T. gondii. The two newborn patients that presented strain types II and III and
3 1568 FUENTES ET AL. J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. TABLE 1. Patients, clinical symptoms, origin of samples and genotype of different T. gondii strains characterized in this study Patient group and designation a Clinical symptoms b Sample Nested PCR RFLP result c SAG2-3 SAG2-5 Type Immunocompromised 1 IHIV NS CSF I 2 IHIV NS CSF I 3 IHIV GS, cachexia Blood I 4 IHIV No data Blood I 5 IHIV NS CSF II 6 IHIV NS CSF II 7 IHIV NS CSF NA II 8 IHIV NS Brain (from biopsy) II 9 IHIV NS CSF II 10 IHIV NS Brain (from biopsy) II 11 IHIV PS, fever Lung (from biopsy) II 12 IHIV Eye disease Vitreous humor II 13 IHIV Eye disease Vitreous humor II 14 IHIV NS, PS, retinochoroiditis CSF III 15 IHIV NS 2 brain samples (from biopsies) III 16 IHIV NS Blood III 17 IHIV NS CSF III 18 IHIV NS CSF NA non-iii 19 IHIV NS CSF NA non-iii 20 IHIV NS CSF NA non-ii Congenital infection 1 Cmaternal No data on newborn Amniotic fluid I 2 Cmaternal No data on newborn Amniotic fluid I 3 Cmaternal No data on newborn Amniotic fluid I 4 Cmaternal No data on newborn Maternal urine I 5 Cnewborn CC, VD, chorioretinitis Blood I 6 Cnewborn Abortion, cardiopathy Abortion ascitic fluid I 7 Cnewborn Newborn asymptomatic Blood II 8 Cnewborn Newborn asymptomatic Blood III 9 Cnewborn No data on newborn Blood NA non-ii 10 Cnewborn No data on newborn Blood NA non-ii 11 Cnewborn Newborn asymptomatic Blood NA non-ii 12 Cnewborn Newborn asymptomatic Blood NA non-ii 13 Cmaternal No data on newborn Maternal blood NA non-ii a The patient designations indicate the HIV status and time of diagnosis of congenital infection as follows: IHIV, immunocompromised HIV-positive patient; IHIV, immunocompromised HIV-negative patient; Cmaternal, maternal diagnosis of congenital infection; Cnewborn, newborn diagnosis of congenital infection. b Abbreviations; NS, neurological symptoms; GS, general symptoms; PS, pulmonary symptons; CC, cerebral calcifications; VD, ventricle dilation. c SAG2-3 and SAG2-5, 3 - and 5 -end-amplified fragments of SAG2;, product amplified digested;, product amplified not digested; NA, product not amplified; non-iii, non-type III; non-ii, non-type II. the three non-type II cases that were not fully characterized were asymptomatic, while of the two patients with genotype I, one was aborted and the other was seriously ill. DISCUSSION The main objective of this report has been to show the possibility of characterizing the different T. gondii genotypes directly from clinical samples, since the acquisition, isolation, and maintenance of strains are difficult and require a long period of time, besides preventing artificial prevalence of strains associated with enrichment of parasite prior to diagnosis in the culture process. Fifty-nine of 68 (86.8%) PCR fragments (3 end and 5 end amplified of the 34 clinical samples) were amplified directly from the clinical samples. Nine of these fragments were obtained after cleaning the first PCR mix and repeating the nested PCR; in another nine cases, this strategy did not work, and total characterization of eight strains was not possible. Total characterization of the SAG2 gene was successful in 26 of 34 clinical samples (76.5%). These results show that it is possible to use direct characterization not only to save time but also, and most importantly, because at least partial characterization was possible with all the samples. When using indirect characterization by previous growth of the parasite in cell culture or in mice, only 40% of the samples are able to grow (11). Moreover, the use of direct characterization also avoids misleading results due to artificial selection in relation to the culture process (5). This direct process of genotyping allows material kept frozen or in other adverse culture conditions to be characterized. The frequencies of the genotypes of the strains fully studied were 40% of type I, 40% of type II, and 20% of type III (Table 2). In other reports, the type II genotype is the most prevalent in humans with toxoplasmosis, with values of between 70 and 81% (3, 7, 12, 14, 20), but our data suggest that these differences are not so high, especially when it is considered that at least 64% of the individuals in our study, including these individuals without total genotyping characterization, carried nontype II strains.
4 VOL. 39, 2001 GENOTYPIC CHARACTERIZATION OF T. GONDII STRAINS 1569 FIG. 1. Agarose gel electrophoresis analysis of SAG2 PCR amplification products and restriction digests from T. gondii-infected clinical samples. (A) Sau3AI restriction analysis of the 5 amplification products and (B) HhaI restriction analysis of the 3 amplification products. Lane I, DNA from strain RH (type I); lane II, DNA from strain Beverly (type II); lane III, DNA from strain C56 (type III). Lanes 1 to 8 contain strains from clinical samples as follows: lane 1, CSF from patient 1 IHIV (type I); lane 2, CSF from patient 5 IHIV (type II); lane 3, blood from patient 7 Cnewborn (type II); lane 4, blood from patient 5 Cnewborn (type I); lane 5, CSF from patient 14 IHIV (type III); lane 6, vitreous humor from patient 12 IHIV (type II); lane 7, blood from patient 8 Cnewborn (type III); lane 8, brain (from biopsy) from patient 8 IHIV (type II). Lane M, molecular weight markers. There are other differences observed, depending on the risk group infected; while Howe et al. (12) reported that the 13 cases of congenital toxoplasmosis studied were all type II, we found in the same number of congenital infection cases that only 8% were type II, while 46% were type I, a further 8% were type III, and 38% were non-type II. In the immunocompromised patients, we found a maximum of 55% of infection by T. gondii type II, including two individuals characterized as nontype III, in contrast to the 76% found by Howe et al. (12). There are two possible explanations for these differences. The epidemiological prevalence and the route of transmission may be very different in Spain and France, where most studies were performed. The use of cell culture or mice to isolate and grow the parasites from the clinical samples, as has been the case in previous reports, might produce sensitive variations in the observed genotyping frequencies due to an effect of differential selection of the strains. In general, there is no clear correlation between strain genotype and symptomatology. In AIDS and other immunocompromised patients, the three genotypes produce symptomatology related to neurological diseases. The low level of gamma interferon and other factors related to the immune system in these patients might increase the possibility of reactivation of the infective forms of the parasite, especially of type II, due to the high potential to develop bradyzoite stages, increasing the formation of cysts in the brain (8), as shown in other studies carried out in experimental immunocompromised mice where genotype II increased the number of cysts formed in the brain compared to type I (10, 21). The number of congenital cases studied does not allow any clear correlation between symptoms and genotype to be observed, although in the cases where follow-up was possible the newborn patients that presented strain types II and III and the three cases with non-type II strains that were not fully characterized were asymptomatic, while patients with genotype I were seriously ill or were aborted. The type I genotype is considered to be the most virulent type, with a high level of parasitemia (14, 17). This might imply an increase in the risk of transplacental transmission, producing serious symptoms in the fetus or newborn. Thus, if this correlation is true, the three congenital asymptomatic cases with genotyping non-type II might be included in type III, a less virulent genotype; however, a larger number of studied cases would be necessary to prove this correlation hypothesis. These results demonstrate that molecular epidemiological studies on T. gondii may be performed directly from infectedtissue samples. The nested genotyping PCR used here is a fast and highly sensitive method and may be used directly on clinical samples, avoiding the time-consuming techniques required to grow the parasite and avoiding the possible loss of samples or strain selection during culture. These studies are important, as they will provide a better understanding of epidemiology and association between parasite genotypes and human toxoplasmosis, if studies with a larger number of samples confirm the results obtained, especially in cases of congenital toxoplasmosis infection where treatment might be improved. TABLE 2. Strain types of T. gondii found in human toxoplasmosis cases in Spain Patient group No. (%) of strain type Type I Type II Type III Non-type III Non-type II Immunocompromised 4 (24) 9 (52) 4 (24) 2 1 Congenital infection 6 (75) 1 (12.5) 1 (12.5) 5 Total 10 (40) 10 (40) 5 (20) 2 6
5 1570 FUENTES ET AL. J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported in part by the Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (grant 96/ ) from the Spanish Ministry of Health. J. M. Rubio was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship by the Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain. We thank Antonio Martínez (Madrid Complutense University) and Begoña Díez (University of the Basque Country) for supplying reference T. gondii strains and Agustin Benito (Instituto de Salud Carlos III) and Ana Arraztio for helpful comments on the manuscript. REFERENCES 1. Burg, J. L., C. M. Grober, P. Pouletty, and J. Boothroyd Direct and sensitive detection of a pathogenic protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii, by polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 27: Cristina, N., M. L. Dardé, C. Boudin, G. Tavernier, M. Pestre-Alexandre, and P. Ambroise-Thomas A DNA fingerprinting method for individual characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains: combination with isoenzymatic characters for determination of linkage groups. Parasitol. Res. 81: Dardé, M. L., Bouteille, and M. Pestre-Alexandre Isoenzyme analysis of 35 Toxoplasma gondii isolates and the biological and epidemiological implications. J. Parasitol. 78: Dubey, J. P., and C. P. Beattie Toxoplasmosis of animals and man. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Fla. 5. Frenkel, J. K., and P. Ambroise-Thomas Genomic drift of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol. Res. 83: Fuentes, I., M. Rodriguez, C. J. Domingo, F. del Castillo, T. Juncosa, and J. Alvar Urine sample used for congenital toxoplasmosis diagnosis by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34: Gross, U Toxoplasma gondii research in Europe. Parasitol. Today 12: Gross, U., M. C. Kempf, F. Seeber, C. G. K. Luder, R. Lugert, and W. Bohne Reactivation of chronic toxoplasmosis: is there a link to strain-specific differences in the parasite? Behring Inst. Mitt. 99: Guo, Z. G., and A. M. Johnson Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strain by random amplified polymorphic DNA polymerase chain reaction. Parasitology 111: Guo, Z. G., and A. M. Johnson DNA polymorphisms associated with murine virulence of Toxoplasma gondii identified by RAPD-PCR. J. Biol. Chem. 11: Hitt, J. A., and G. A. Filice Detection of Toxoplasma gondii parasitemia by gene amplification, cell culture, and mouse inoculation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30: Howe, D. K., S. Honore, F. Derouin, and L. D. Sibley Determination of genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from patients with toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35: Howe, D. K., and L. D. Sibley Toxoplasma gondii: analysis of different laboratory stocks of the RH strain reveals genetic heterogeneity. Exp. Parasitol. 78: Howe, D. K., and L. D. Sibley Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J. Infect. Dis. 172: Ho-Yen, D. O Immunocompromised patients, p In D. O. Ho-Yen and A. W. L. Joss (ed.), Human toxoplasmosis. Oxford University Press, Oxford, United Kingdom. 16. Johnson, A. M Speculation on possible life cycle for the clonal lineages in the genus Toxoplasma. Parasitol. Today 13: Lüder, C. G. K., and U. Gross Toxoplasmosis: from clinics to basic science. Parasitol. Today 14: Mondragon, R., D. K. Howe, J. P. Dubey, and L. D. Sibley Genotypic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from pigs. J. Parasitol. 84: Owen, M. R., and A. J. Trees Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii associated with abortion in sheep. J. Parasitol. 85: Sibley, L. D., and J. C. Boothroyd Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 359: Suzuki, Y., S. Y. Wong, F. C. Grumet, J. Fessel, J. G. Montoya, A. R. Zolopa, A. Portmore, F. Schumacher-Perdreau, M. Schrappe, S. Koppen, B. Ruf, B. W. Brown, and J. S. Remington Evidence for genetic regulation of susceptibility to toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS patients. J. Infect. Dis. 173: Tibayrenc, M Population genetics of parasitic protozoa and other microorganisms. Adv. Parasitol. 36: Wong, S. Y., and J. Remington Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 18: Downloaded from on April 17, 2018 by guest
Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016
 TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
Toxoplasma gondii. Definitive Host adult forms sexual reproduction. Intermediate Host immature forms asexual reproduction
 Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Coccidia. Eucoccidioside
 Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 September 2006 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi: /jcm
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 September 2006 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01786-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 September 2006 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01786-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Detection of Toxoplasma Parasitemia by PCR: Does it Correlate with IgG and IgM Antibody Titers?
 Detection of Toxoplasma Parasitemia by : Does it Correlate with IgG and IgM Antibody Titers? Behzad Haghpanah 1, Mansoor Salehi 2, Shahram Sadri 1 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, 2 Department
Detection of Toxoplasma Parasitemia by : Does it Correlate with IgG and IgM Antibody Titers? Behzad Haghpanah 1, Mansoor Salehi 2, Shahram Sadri 1 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, 2 Department
Hepatitis B Virus Genemer
 Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Short Video. shows/monsters-inside- me/videos/toxoplasma-parasite/
 The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Molecular diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis: comparing markers that determine Toxoplasma gondii by PCR in peripheral blood from HIV-infected patients Authors Rafael Tonini Mesquita 1
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Molecular diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis: comparing markers that determine Toxoplasma gondii by PCR in peripheral blood from HIV-infected patients Authors Rafael Tonini Mesquita 1
Toxoplasma gondii. Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK
 Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Extra-intestinal coccidians
 Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer. Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment
 Product Manual Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2002-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in
Product Manual Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2002-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in
Pappas G. (2009) Int J Parasitol. 39:
 Genetic modifications within TLR4and TLR9genes contribute into congenital toxoplasmosis and cytomegalydevelopment Wioletta Wujcicka 1, Jan Wilczyński 1,2, Dorota Nowakowska 1,2 1 Department of Fetal-Maternal
Genetic modifications within TLR4and TLR9genes contribute into congenital toxoplasmosis and cytomegalydevelopment Wioletta Wujcicka 1, Jan Wilczyński 1,2, Dorota Nowakowska 1,2 1 Department of Fetal-Maternal
Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum in chickensbn from industrial farms in Kerman province
 Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014: 100-104 Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum
Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014: 100-104 Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum
Toxoplasmosis Objective :
 Toxoplasmosis Objective : Describe the Life cycle Mention the Infective stages Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis List the Lab.Diagnosis Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Show the relationship between
Toxoplasmosis Objective : Describe the Life cycle Mention the Infective stages Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis List the Lab.Diagnosis Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Show the relationship between
Human toxoplasmosis in Europe. Parasitology, Paris Descartes University, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France
 Human toxoplasmosis in Europe Prof Jean Dupouy-Camet Parasitology, Paris Descartes University, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France Toxoplasma gondii, discovered in 1908, by Nicolle at Institut Pasteur de Tunis,
Human toxoplasmosis in Europe Prof Jean Dupouy-Camet Parasitology, Paris Descartes University, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France Toxoplasma gondii, discovered in 1908, by Nicolle at Institut Pasteur de Tunis,
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
 3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology & Microbial Genomics September 24-26, 2014 Valencia, Spain Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology & Microbial Genomics September 24-26, 2014 Valencia, Spain Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran
 Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran Gholamreza Hatam 1*, Azra Shamseddin 2, Farhoud Nikouee 3 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, School of Medicine, Shiraz
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran Gholamreza Hatam 1*, Azra Shamseddin 2, Farhoud Nikouee 3 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, School of Medicine, Shiraz
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections
 Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis
 Product Manual HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures for clinical purposes Catalog
Product Manual HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures for clinical purposes Catalog
Product # Kit Components
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
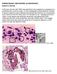 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit
 Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR
 IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR Zulhainan Hamzah 1, Songsak Petmitr 2, Mathirut Mungthin 3 and Porntip Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr 1 1 Department
IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR Zulhainan Hamzah 1, Songsak Petmitr 2, Mathirut Mungthin 3 and Porntip Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr 1 1 Department
Toxoplasmosis. Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy
 Toxoplasmosis Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy Human Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease Caused by Coccidian
Toxoplasmosis Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy Human Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease Caused by Coccidian
Dorota Nowakowska, 1,2 Iris Colón, 3,4 Jack S. Remington, 4,5 Michael Grigg, 6 Elzbieta Golab, 7 J. Wilczynski, 2 and L.
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 1382 1389 Vol. 44, No. 4 0095-1137/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.44.4.1382 1389.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 1382 1389 Vol. 44, No. 4 0095-1137/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.44.4.1382 1389.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP36300
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cytomegalovirus (CMV) End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP36300 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cytomegalovirus (CMV) End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP36300 Product
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit
 Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
HIV-1 Viral Load Real Time (RG)
 -1 Viral Load Real Time (RG) Real Time RT-PCR type 1 RNA quantification assay MSP Reg. pending Valdense 3616. 11700. Montevideo. Uruguay. phone (598) 2 336 83 01. Fax (598) 2 336 71 60. Info@atgen.com.uy
-1 Viral Load Real Time (RG) Real Time RT-PCR type 1 RNA quantification assay MSP Reg. pending Valdense 3616. 11700. Montevideo. Uruguay. phone (598) 2 336 83 01. Fax (598) 2 336 71 60. Info@atgen.com.uy
SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS
 SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS Pages with reference to book, From 183 To 186 Mughisuddin Ahmed ( Department of Pathology, Dow Medical College and Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah
SURVEILLANCE OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN DIFFERENT GROUPS Pages with reference to book, From 183 To 186 Mughisuddin Ahmed ( Department of Pathology, Dow Medical College and Basic Medical Sciences Institute, Jinnah
Norgen s HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit was developed and validated to be used with the following PCR instruments: Qiagen Rotor-Gene Q BioRad T1000 Cycler
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product# 33840 Product Insert Intended
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product# 33840 Product Insert Intended
TELEFAX. Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory (TSL) DATE: TO: FAX: FROM:
 TELEFAX DATE: TO: FAX: FROM: Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory RE: SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS AND TESTING INFORMATION (effective 1/15/16) THIS TRANSMISSION CONSISTS OF 16 PAGES INCLUDING THIS COVER PAGE. IF THERE
TELEFAX DATE: TO: FAX: FROM: Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory RE: SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS AND TESTING INFORMATION (effective 1/15/16) THIS TRANSMISSION CONSISTS OF 16 PAGES INCLUDING THIS COVER PAGE. IF THERE
Toxoplasma gondii IgM (Toxo IgM)
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND
 Research Article CODEN: IJPRNK B. V. Ramana, IJPRBS, 2013; Volume 2(4): 253-258 ISSN: 2277-8713 IJPRBS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMAC CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE SEROPREVALENCE OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS
Research Article CODEN: IJPRNK B. V. Ramana, IJPRBS, 2013; Volume 2(4): 253-258 ISSN: 2277-8713 IJPRBS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMAC CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE SEROPREVALENCE OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS
Product Manual. Omni-Array Sense Strand mrna Amplification Kit, 2 ng to 100 ng Version Catalog No.: Reactions
 Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
Innovation in Diagnostics. ToRCH. A complete line of kits for an accurate diagnosis INFECTIOUS ID DISEASES
 Innovation in Diagnostics ToRCH A complete line of kits for an accurate diagnosis INFECTIOUS ID DISEASES EN TOXOPLASMOSIS Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by with the obligate intracellular
Innovation in Diagnostics ToRCH A complete line of kits for an accurate diagnosis INFECTIOUS ID DISEASES EN TOXOPLASMOSIS Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by with the obligate intracellular
Comparison of the efficiency of two commercial kits ELFA and Western blot in estimating the phase of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women
 Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2016, Vol 23, No 4, 570 575 www.aaem.pl ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the efficiency of two commercial kits ELFA and Western blot in estimating the phase
Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2016, Vol 23, No 4, 570 575 www.aaem.pl ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the efficiency of two commercial kits ELFA and Western blot in estimating the phase
Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran
 Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran Aliehsan Heidari, Manizheh Nourian, Hossein Keshavarz Associate Prof. Dept.
Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran Aliehsan Heidari, Manizheh Nourian, Hossein Keshavarz Associate Prof. Dept.
Norgen s HIV proviral DNA PCR Kit was developed and validated to be used with the following PCR instruments: Qiagen Rotor-Gene Q BioRad icycler
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product # 33840 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product # 33840 Product Insert Background Information
Toxoplasmosis Seroepidemiology in Serum of Suspected Patients Attending Medical Lab, in 2013
 Journal of Community Health Research. 2015;4(1):47-54. Original Article Toxoplasmosis Seroepidemiology in Serum of Suspected Patients Attending Medical Lab, in 2013 Ali Fattahi Bafghi 1, Roya Anvari 2,
Journal of Community Health Research. 2015;4(1):47-54. Original Article Toxoplasmosis Seroepidemiology in Serum of Suspected Patients Attending Medical Lab, in 2013 Ali Fattahi Bafghi 1, Roya Anvari 2,
INFLUENCE OF SOME NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC TOXINS CHARACTERISTIC FOR FUSARIUM FUNGUS ON IZOPEROXIDASES IN SOME WHEAT GENOTYPES
 INFLUENCE OF SOME NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC TOXINS CHARACTERISTIC FOR FUSARIUM FUNGUS ON IZOPEROXIDASES IN SOME WHEAT GENOTYPES Ioana Hagima and Mariana Ittu ABSTRACT Analyses of izoperoxidase activity in
INFLUENCE OF SOME NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC TOXINS CHARACTERISTIC FOR FUSARIUM FUNGUS ON IZOPEROXIDASES IN SOME WHEAT GENOTYPES Ioana Hagima and Mariana Ittu ABSTRACT Analyses of izoperoxidase activity in
Convención Internacional de Salud, Cuba Salud 2018
 BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF Toxoplasma gondii IN SAMPLES FROM FREE- RANGE CHICKENS (Gallus gallus domesticus) FROM RURAL HOLDINGS IN ESPÍRITO SANTO STATE, BRAZIL 1 Cerqueira Buery, Julyana; 1 Ribeiro Ferreira,
BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF Toxoplasma gondii IN SAMPLES FROM FREE- RANGE CHICKENS (Gallus gallus domesticus) FROM RURAL HOLDINGS IN ESPÍRITO SANTO STATE, BRAZIL 1 Cerqueira Buery, Julyana; 1 Ribeiro Ferreira,
CHEMILUMINESCENCE ENZYME IMMUNOASSAY (CLIA) Toxoplasma IgG. Cat # (20-25 C Room temp.) Volume
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Kit Components Product # EP42720 (24 preps) MDx 2X PCR Master Mix 350 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Primer Mix 70 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Positive
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4 Related Products..
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol
 IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-85) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED
IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-85) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED
Ocular Toxoplasmosis Uveitis course Antalya Miles Stanford Medical Eye Unit St Thomas Hospital London
 Ocular Toxoplasmosis Uveitis course Antalya 2013 Miles Stanford Medical Eye Unit St Thomas Hospital London Toxoplasma gondii Obligate, intracellular, apicomplexan protozoan Infects > 1/3 world population
Ocular Toxoplasmosis Uveitis course Antalya 2013 Miles Stanford Medical Eye Unit St Thomas Hospital London Toxoplasma gondii Obligate, intracellular, apicomplexan protozoan Infects > 1/3 world population
Diversity and Frequencies of HLA Class I and Class II Genes of an East African Population
 Open Journal of Genetics, 2014, 4, 99-124 Published Online April 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojgen http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojgen.2014.42013 Diversity and Frequencies of HLA Class I and
Open Journal of Genetics, 2014, 4, 99-124 Published Online April 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojgen http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojgen.2014.42013 Diversity and Frequencies of HLA Class I and
Purification of viral nucleic acid from serum, plasma, cell-free biological fluids MACHEREY- NAGEL
 Purification of viral nucleic acid from serum, plasma, cell-free biological fluids Purification of viral nucleic acid from serum, plasma, cell-free biological fluids viral RNA: viral DNA: NucleoSpin RNA
Purification of viral nucleic acid from serum, plasma, cell-free biological fluids Purification of viral nucleic acid from serum, plasma, cell-free biological fluids viral RNA: viral DNA: NucleoSpin RNA
Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
 August 2011 Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 June
August 2011 Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 June
IVF Michigan, Rochester Hills, Michigan, and Reproductive Genetics Institute, Chicago, Illinois
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
Congenital CMV infection. Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 Congenital CMV infection Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Congenital CMV infection Approximately 0.15 2% of live births
Congenital CMV infection Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Congenital CMV infection Approximately 0.15 2% of live births
XCF TM COMPLETE Exosome and cfdna Isolation Kit (for Serum & Plasma)
 XCF TM COMPLETE Exosome and cfdna Isolation Kit (for Serum & Plasma) Cat# XCF100A-1 User Manual Store kit components at +4ºC and +25ºC Version 1 2/2/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product.
XCF TM COMPLETE Exosome and cfdna Isolation Kit (for Serum & Plasma) Cat# XCF100A-1 User Manual Store kit components at +4ºC and +25ºC Version 1 2/2/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product.
PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS Yaowalark Sukthana 1, Phuangphet Waree 1, Emsri Pongponratn 2, Urai Chaisri 2 and Mario Riganti 2
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS Yaowalark Sukthana 1, Phuangphet Waree 1, Emsri Pongponratn 2, Urai Chaisri 2 and Mario Riganti 2
PREDICTIVE VALUE OF LATEX AGGLUTINATION TEST IN SEROLOGICAL SCREENING FOR TOXOPLASMA GONDII
 PREDICTIVE VALUE OF LATEX AGGLUTINATION TEST IN SEROLOGICAL SCREENING FOR TOXOPLASMA GONDII Yaowalark Sukthana, Thaiyooth Chintana, Waraporn Supatanapong, Chutatip Siripan, Amorn Lekkla and Rachatawan
PREDICTIVE VALUE OF LATEX AGGLUTINATION TEST IN SEROLOGICAL SCREENING FOR TOXOPLASMA GONDII Yaowalark Sukthana, Thaiyooth Chintana, Waraporn Supatanapong, Chutatip Siripan, Amorn Lekkla and Rachatawan
الحترمونا من خري الدعاء
 الحترمونا من خري الدعاء Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could be true or
الحترمونا من خري الدعاء Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could be true or
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. D4076 Highlights High-quality DNA, including cell-free, is easily and robustly purified from up to 10 ml of serum/plasma, up to 1 ml amniotic
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. D4076 Highlights High-quality DNA, including cell-free, is easily and robustly purified from up to 10 ml of serum/plasma, up to 1 ml amniotic
International Conference on Parasitology August 24-26, 2015 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
 International Conference on Parasitology August 24-26, 2015 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA SYMPOSIA THE CHALLENGE OF PARASITES AND IMMUNOSUPRESSION: FROM DIAGNOSIS TO TREATMENT from the bench to the bed
International Conference on Parasitology August 24-26, 2015 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA SYMPOSIA THE CHALLENGE OF PARASITES AND IMMUNOSUPRESSION: FROM DIAGNOSIS TO TREATMENT from the bench to the bed
Pelagia Research Library. European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(10):1-5
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(10):1-5 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Molecular diagnosis of human immuno deficiency virus (HIV)
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(10):1-5 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Molecular diagnosis of human immuno deficiency virus (HIV)
New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions
 New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions Javier Moreno Immunoparasitology Unit WHO Collaborative Center for Leishmaniasis Centro Nacional de Microbiología INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS
New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions Javier Moreno Immunoparasitology Unit WHO Collaborative Center for Leishmaniasis Centro Nacional de Microbiología INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS
Toxoplasmosis: Summary of evidences, a Research line
 Toxoplasmosis: Summary of evidences, a Research line José G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School
Toxoplasmosis: Summary of evidences, a Research line José G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School
Absence of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus in Patients with Pulmonary
 Online Data Supplement Absence of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Cornelia Henke-Gendo, Michael Mengel, Marius M. Hoeper, Khaled Alkharsah, Thomas
Online Data Supplement Absence of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Cornelia Henke-Gendo, Michael Mengel, Marius M. Hoeper, Khaled Alkharsah, Thomas
Seroepidemiological study of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the rural area Okcheon-gun, Korea
 251 The Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 38, No. 4, 251-256, December 2000 Seroepidemiological study of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the rural area Okcheon-gun, Korea Young-Ha LEE*, Hyung-Jun NOH,
251 The Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 38, No. 4, 251-256, December 2000 Seroepidemiological study of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the rural area Okcheon-gun, Korea Young-Ha LEE*, Hyung-Jun NOH,
(b) Describe the role of antigen presentation in the body s specific immune response to infection by viruses. (4)
 1 The human body responds to infection by viruses in a number of ways. The non-specific response involves interferon. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation to the cells of the immune
1 The human body responds to infection by viruses in a number of ways. The non-specific response involves interferon. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation to the cells of the immune
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
Report of the 1 st NRL proficiency testing on Detection of anti-toxoplasma IgG in ovine serum samples. March - April, 2015
 Report of the 1 st NRL proficiency testing on Detection of anti-toxoplasma IgG in ovine serum samples March - April, 2015 page 1 of 12 Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope 3 3 Time frame 3 4 Test
Report of the 1 st NRL proficiency testing on Detection of anti-toxoplasma IgG in ovine serum samples March - April, 2015 page 1 of 12 Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope 3 3 Time frame 3 4 Test
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff
 Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff Aize Kijlstra Rome 2009 Toxoplasmosis is a neglected disease entity Disease burden is similar to salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis
Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff Aize Kijlstra Rome 2009 Toxoplasmosis is a neglected disease entity Disease burden is similar to salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis
in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares
 Influence of Probiotics on Microflora in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares Katie Barnhart Research Advisors: Dr. Kimberly Cole and Dr. John Mark Reddish Department of
Influence of Probiotics on Microflora in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares Katie Barnhart Research Advisors: Dr. Kimberly Cole and Dr. John Mark Reddish Department of
Urine - Based CMV PCR Detection Kit Product # 36300
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Urine - Based CMV PCR Detection Kit Product # 36300 Product Insert
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Urine - Based CMV PCR Detection Kit Product # 36300 Product Insert
Department of Immunology, The Todd Centre, 31 Taylor St, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow G4 ONR
 Studies on a murine model of congenital toxoplasmosis: vertical disease transmission only occurs in BALB/c mice infected for the first time during pregnancy 19 C. W. ROBERTS and]. ALEXANDER* Department
Studies on a murine model of congenital toxoplasmosis: vertical disease transmission only occurs in BALB/c mice infected for the first time during pregnancy 19 C. W. ROBERTS and]. ALEXANDER* Department
Real-time molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis by direct genotyping. of smear-positive clinical specimens
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 29 February 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00132-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Real-time molecular
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 29 February 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00132-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Real-time molecular
International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Journal Home Page: http://www.ijmhs.net ISSN:2277-4505 Case Report Submandibular Swelling- Not a Cat s Play!!! Rajeshwara. K.V* 1, Clement R.S. D Souza
International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Journal Home Page: http://www.ijmhs.net ISSN:2277-4505 Case Report Submandibular Swelling- Not a Cat s Play!!! Rajeshwara. K.V* 1, Clement R.S. D Souza
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TOXOPLASMOSIS ENCEPHALITIS
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TOXOPLASMOSIS ENCEPHALITIS Full title of guideline Guideline for the management of toxoplasmosis encephalitis Author Dr P Venkatesan (ID consultant) Division and specialty
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TOXOPLASMOSIS ENCEPHALITIS Full title of guideline Guideline for the management of toxoplasmosis encephalitis Author Dr P Venkatesan (ID consultant) Division and specialty
Evaluation of Four Commercial Systems for the Diagnosis of Epstein-Barr Virus Primary Infections
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 444 448 Vol. 18, No. 3 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.00486-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation of
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 444 448 Vol. 18, No. 3 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.00486-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation of
Usefulness of Seminested Multiplex PCR in Surveillance of Imported Malaria in Spain
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1999, p. 3260 3264 Vol. 37, No. 10 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Usefulness of Seminested Multiplex
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1999, p. 3260 3264 Vol. 37, No. 10 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Usefulness of Seminested Multiplex
Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment
 For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 10(7), 815 828 (2012)
For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 10(7), 815 828 (2012)
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals. Taniawati Supali. Department of Parasitology
 Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
AIDS - Knowledge and Dogma. Conditions for the Emergence and Decline of Scientific Theories Congress, July 16/ , Vienna, Austria
 AIDS - Knowledge and Dogma Conditions for the Emergence and Decline of Scientific Theories Congress, July 16/17 2010, Vienna, Austria Reliability of PCR to detect genetic sequences from HIV Juan Manuel
AIDS - Knowledge and Dogma Conditions for the Emergence and Decline of Scientific Theories Congress, July 16/17 2010, Vienna, Austria Reliability of PCR to detect genetic sequences from HIV Juan Manuel
X/01/$ DOI: /JVI Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2001, p. 3753 3765 Vol. 75, No. 8 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3753 3765.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Route of Simian
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2001, p. 3753 3765 Vol. 75, No. 8 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3753 3765.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Route of Simian
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual
 Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
Table of Contents (continued)
 Emerging Molecular and Immunohematology Blood Typing, Grouping And Infectious Disease NAT Screening Assays And Companies Developing New Technologies and Products Table of Contents 1. Blood Typing and Grouping
Emerging Molecular and Immunohematology Blood Typing, Grouping And Infectious Disease NAT Screening Assays And Companies Developing New Technologies and Products Table of Contents 1. Blood Typing and Grouping
VIDAS Test for Avidity of Toxoplasma-Specific Immunoglobulin G for Confirmatory Testing of Pregnant Women
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 2002, p. 2504 2508 Vol. 40, No. 7 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2504 2508.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 2002, p. 2504 2508 Vol. 40, No. 7 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2504 2508.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Ocular Toxoplasmosis - A Laboratory View. Chatterton JMW* Evans R. Ho-Yen DO
 Ocular Toxoplasmosis - A Laboratory View Chatterton JMW* Evans R Ho-Yen DO Scottish Toxoplasma Reference Laboratory Microbiology Department Raigmore Hospital Inverness IV UJ * corresponding author Introduction
Ocular Toxoplasmosis - A Laboratory View Chatterton JMW* Evans R Ho-Yen DO Scottish Toxoplasma Reference Laboratory Microbiology Department Raigmore Hospital Inverness IV UJ * corresponding author Introduction
1. Toxoplasma gondii:
 Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Reliable screening for early diagnosis
 Elecsys TORCH panel Reliable screening for early diagnosis Toxoplasmosis Rubella HSV CMV Toxoplasmosis The safe and sure approach to Toxo screening Ultrasensitive Toxo IgM optimized to detect all potential
Elecsys TORCH panel Reliable screening for early diagnosis Toxoplasmosis Rubella HSV CMV Toxoplasmosis The safe and sure approach to Toxo screening Ultrasensitive Toxo IgM optimized to detect all potential
Toxoplasmosis. Seminar. For personal use. Only reproduce with permission from The Lancet Publishing Group.
 Seminar Toxoplasmosis J G Montoya, O Liesenfeld Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that infects up to a third of the world s population. Infection is mainly acquired by ingestion of food or water
Seminar Toxoplasmosis J G Montoya, O Liesenfeld Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that infects up to a third of the world s population. Infection is mainly acquired by ingestion of food or water
Contents. The ACMSF s approach to its work Human cases: prevalence Burden of disease
 Contents Summary 1-6 1. Background 1.1-1.5 The ACMSF s approach to its work 1.4-1.5 2. Introduction 2.1-2.4 3. The organism 3.1-3.9 4. Human toxoplasmosis: clinical disease 4.1-4.4 5. Human cases: prevalence
Contents Summary 1-6 1. Background 1.1-1.5 The ACMSF s approach to its work 1.4-1.5 2. Introduction 2.1-2.4 3. The organism 3.1-3.9 4. Human toxoplasmosis: clinical disease 4.1-4.4 5. Human cases: prevalence
Human Rotavirus A. genesig Advanced Kit. Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests. Primerdesign Ltd. For general laboratory and research use only
 TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
Human Rotavirus A. genesig Standard Kit. Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests. Primerdesign Ltd. For general laboratory and research use only
 TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
RealLine Mycoplasma genitalium Str-Format
 Instructions for use ASSAY KIT FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM DNA BY REAL-TIME PCR METHOD In vitro Diagnostics () VBD4396 96 Tests valid from December 2018 Rev06_1218_EN Page 1
Instructions for use ASSAY KIT FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM DNA BY REAL-TIME PCR METHOD In vitro Diagnostics () VBD4396 96 Tests valid from December 2018 Rev06_1218_EN Page 1
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
 Supplement Article Congenital Toxoplasmosis James B. McAuley Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois Corresponding Author: James B. McAuley, MD, MPH, 1653 W. Congress Parkway, Chicago, IL 60612.
Supplement Article Congenital Toxoplasmosis James B. McAuley Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois Corresponding Author: James B. McAuley, MD, MPH, 1653 W. Congress Parkway, Chicago, IL 60612.
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Bioresearch Communications Volume 05, Issue 01, January 2019 Journal Homepage:
 Bioresearch Communications Volume 05, Issue 01, January 2019 Journal Homepage: www.bioresearchcommunications.com Review Article Parasitic Disease of Human Taibur Rahman* and Tanzina Tarannum 1 Department
Bioresearch Communications Volume 05, Issue 01, January 2019 Journal Homepage: www.bioresearchcommunications.com Review Article Parasitic Disease of Human Taibur Rahman* and Tanzina Tarannum 1 Department
Research Article Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Patients of Intensive Care Unit in China: A Hospital Based Study
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 908217, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/908217 Research Article Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Patients of Intensive Care
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 908217, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/908217 Research Article Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Patients of Intensive Care
Ultrastructural Studies on Plasmodium vivax
 Characterization of Human Malaria Parasites Ultrastructural Studies on Plasmodium vivax For the first time a detailed ultrastructural study was carried out on P. vivax. Fine structural analysis of growth
Characterization of Human Malaria Parasites Ultrastructural Studies on Plasmodium vivax For the first time a detailed ultrastructural study was carried out on P. vivax. Fine structural analysis of growth
doi: /s
 doi: 10.1007/s10528-008-9185-3 Lack of association of the HbE variant with protection from cerebral malaria in Thailand Izumi Naka 1, Jun Ohashi 1, Pornlada Nuchnoi 2, Hathairad Hananantachai 2, Sornchai
doi: 10.1007/s10528-008-9185-3 Lack of association of the HbE variant with protection from cerebral malaria in Thailand Izumi Naka 1, Jun Ohashi 1, Pornlada Nuchnoi 2, Hathairad Hananantachai 2, Sornchai
