Recent advances on the complex and multifaceted T memory and effector immunity elicited to S. Typhi in humans
|
|
|
- Elijah Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recent advances on the complex and multifaceted T memory and effector immunity elicited to S. Typhi in humans Marcelo B. Sztein, M.D. Immunology Group Center for Vaccine Development University of Maryland 8th International Conference on Typhoid Fever and Other Invasive Salmonelloses Dhaka, Bangladesh March 1, 2013
2 Lack of known immunological correlates of protection in typhoid fever Ab to S. Typhi antigens (e.g., Vi, LPS O) are likely to play an important role in defense against typhoid bacilli when they are extracellular. In contrast, since S. Typhi persists intracellularly, thereby avoiding destruction by Ab and C, CMI is expected to be essential in eliminating S. Typhi from the infected cells. Both adaptive immune mechanisms (CMI & Ab) are expected to provide critical support to innate immunity in the mucosal microenvironment and elsewhere
3 Effector Ab responses to S. Typhi 1. Serum IgG and IgA Abs to S. Typhi antigens LPS O, flagella, Vi, OMPs, hsp, others? (Elisa) Opsonophagocytosis, ADCC, bactericidal (Functional) 2. IgG and IgA ASC to S. Typhi antigens in circulation LPS O, flagella, Vi, OMPs, others? 7-10 days after immunization (longevity in the gut and other tissues unknown) 3. Anti-S. Typhi specific secretory IgA (SIgA) in intestinal lavage fluids and stools of subjects exposed to S. Typhi 4. B memory cells (e.g., LPS, Vi)
4 Immunological correlates of protection in typhoid fever: Ab summary It is not known whether Ab to common S. Typhi antigens, particularly to O, H and Vi, particulalry those with defined functional activities, actually (1) Mediate protection, (2) Act in conjunction with other innate and adaptive responses or (3) Serve as a surrogate for the presence of other more dominant protective immune responses (e.g., CMI) that will eventually lead to the elimination of this intracellular bacteria from the host
5 Immunological correlates of protection in typhoid fever: Hypothesis Both CMI and Ab responses play central roles in protection in typhoid fever and are elicited following immunization with attenuated S. Typhi vaccine candidates
6 Vaccine Development The never ending search for the optimal balance Immunogenicity Reactogenicity What responses?
7 Attenuated S. Typhi vaccine strains Organism Strain Deletions Mutations Metabolic Pathways S. Typhi CVD 908 ΔaroC ΔaroD Biosynthesis of aromatic aa S. Typhi CVD htra aroc ΔaroC arod ΔaroD htra ΔhtrA S. CVD htra Typhi CVD ΔaroC guaba arod ΔaroD htra ( fragc of TT) ΔhtrA, viab Biosynthesis of aromatic aa heat - shock protein Biosynthesis of of aromatic guanine aa heat - shock protein Constitutively expresses Vi Chemical S. Typhi Ty21a Many mutagenesis
8 Key Effector CMI to S. Typhi in orally immunized subjects (1) Effector responses to S. Typhi-infected targets: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) activity ( 51 Cr-release assays; granzyme; CD107 staining by flow cytometry) IFNγ production (TNF-α, others) Mediated by both CD8 + (dominant) and CD4 + cells CD8+ CTL activity restricted by: Classical class Ia molecules (HLA-A, B, C) Non-classical class-ib molecules (HLA-E)
9 Key Effector CMI to S. Typhi in orally immunized subjects (2) Proliferation and predominant type-1 cytokine responses to soluble S. Typhi antigens (e.g., flagella) IFNγ, TNFα, IL-10 in the absence of IL-4, IL-5 & IL-6 IFNγ produced predominantly by CD4 + cells Homing to mucosal and non-mucosal tissues: IFN-γ production by central and effector memory T subsets that express, or not, the gut homing molecule integrin α 4 /β 7 Presence of long-term multifunctional HLA-E-restricted CD8 + cells co-expressing IFN-γ, TNF-α and CD107
10 Detailed CMI studies to S. Typhi-infected autologous cells in Ty21 vaccinees 1. Define the kinetics of CMI to S. Typhi-infected autologous cells elicited by Ty21a in humans 2. Study IL-17A responses elicited in Ty21a vaccinees IL-17A is a pro-inflammatory cytokine produced by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Recently shown to play a key role in mucosal immunity Measure the multi-functionality of T cell responses following Ty21a immunization
11 CMI to S. Typhi-infected autologous cells in Ty21 vaccinees: Multi-functional T cells Why study multi-functionality of the T cell responses following Ty21a immunization? Studies have shown that multifunctional T cells, those producing 2 or more cytokines simultaneously, might be critical effectors in protection from infection in animals and humans (e.g., HIV, Mtb) Technological advances and unsupervised flow ctyometry analysis packages enable the study of all possible combinations of many cytokines to define multi-functional CD8+ T cell subsets
12 Experimental Design: In vitro stimulation with S. Typhi-infected targets Target Cells Autologous EBV-LCL, AEH, blasts Effector cells Ex vivo PBMC collected before and 1, 2, 4, 8, 10, 14, 21, 28, 60, 90, 180, 360 days after Ty21a immunizaiton CD8+ T effectors (CTL, cytokines) CD4+ T effectors (cytokines) S. Typhi infection Others? + γ-irradiation hrs Flow cytometry (Tm subsets, CD107a, IFN-γ, TNF-α, MIP-1β, IL-17A, IL-2, etc)
13 Experimental Design: Flow cytometry gating TABLE 1. Cell phenotypes Phenotype "Dump" channel Dead cells Monocytes B cells EBV-LCL T cell subset Marker Yevid CD14 CD19 CD45 Naïve CD45RA + CD62L + Central memory (T CM ) CD45RA - CD62L + Effector memory (T EM ) CD45RA - CD62L - Effector memory (T EMRA ) CD45RA + CD62L - SSC-A Sequential gating strategy Lymphocytes Singlets No Gate Gate: R1 R1 : 19% R1: 43.89% FSC-A FSC-A R2: 95.28% R2 : 92% FSC-H Live T cells Gate: R1&R2 R201: 75.70% R3 : 75% Yevid-CD14-CD19-CD45 Degranulation (CTL) LAMP-1 Cytokines/chemokines CD107a IFN-γ TNF-α IL-2 IL-17A MIP-1β CD8 CD8 PerCP-Cy5-5-A live CD8+ T cells Gate: R1&R2&R3 R4: 23.47% R4 : 24% CD3 BV650-A CD3 CD62-L CD8+ subsets Gate: R1&R2&R3&R4 R6: 13.17% R7: 56.02% R8: 15.53% R9: 8.56% T CM T N T EM T EMRA CD45-RA CD107a/b IFN-γ TNF-α IL-2 IL-17A MIP-1β
14 IL-17A PerCP-Cy5-5-A TNFa APC-Alexa700-A Tcm 0.18% TNFa APC-Alexa700-A Tn R36: 0.01% Tn 0.01% TNFa APC-Alexa700-A MIP1b APC-A Temra 9.60% IL-2 PE-Cy7-A TNFa APC-Alexa700-A R33: 14.33% Temra 14.33% IFN-γ IFNg APC-Cy7-A MIP1b APC-A R38: 15.70% Temra 15.70% IL-2 Tem R28: 9.60% IFNg APC-Cy7-A Temra 6.40% R37: 26.81% 26.81% Tem 23.39% Tem 14.55% MIP1b APC-A Tcm IFNg APC-Cy7-A R35: 0.18% 0.00% MIP1b APC-A IFNg APC-Cy7-A IL-2 PE-Cy7-A IL-17A Tn 0.00% 0.06% R34: 8.51% total8.51% Temra 2.29% IFNg APC-Cy7-A IL-10 FITC-A Tem 9.53% IL-17A PerCP-Cy5-5-A IL-10 IL-2 PE-Cy7-A R29: 7.42% total 7.42% R27: 14.55% 0.30% Temra R13: 0 Tn0.06% Tem 3.88% Tcm 0.08% IL-17A PerCP-Cy5-5-A R17: 3.88% IL-10 FITC-A IL-2 PE-Cy7-A 0.22% Tem Tcm 0.05% R16: 0.00% R12: 0 IL-17A PerCP-Cy5-5-A 0.00% Tn IL-10 FITC-A IL-2 PE-Cy7-A 0.00% R11: 0 total 4.65% IL-17A PerCP-Cy5-5-A Tcm 0.02% IL-10 FITC-A CD69 Tn CD8+ TEMRA R10: % CD8+ TEM Tcm CD8+ TN IL-10 FITC-A CD8+ TCM 0.08% total 3.04% total 1.24% Total CD8+ R9: 0.0 total Cytokines/chemokines are secreted primarily from the CD8+ TEM & TEMRA subsets TNFa APC-Alexa700-A TNF-α MIP1b APC-A MIP-1β
15 IL-17A is secreted by CD8+ T EM cells in response to Ty21a immunization in humans 5 53s 5 54s % positive cells % positive cells Days post immunization Days post immunization 5 50s % positive cells IL-17A Days post immunization
16 Kinetics of net CD8+ T EM responses to stimulation with S. Typhi-infected autologous cells in Ty21a vaccinees % positive cells s IL-10 IL-17A IL-2 IFN-γ TNF-α MIP-1β Days post immunization Immunization
17 IL-17A+ multifunctional CD8+ T EM following exposure to S. Typhi-infected autologous cells 4 53s IL-17A+ IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ IL-17A+ IL-2+ IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ IL-17A+ IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ MIP-1β+ IL-17A+ IL-2+ IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ MIP-1β+ % positive cells Days post immunization
18 Conclusions (I) Ty21a-immunized volunteers exhibited CD8+ T EM and T EMRA cell responses following stimulation with S. Typhi-infected autologous EBV-LCL. Multifunctional CD8+ T cells are present in response to Ty21a immunization. Multifunctional T cells have been reported to correlate with lack of disease progression in HIV, have been identified as a potential correlate of protection for Leishmania major immunization in a mouse model, etc.
19 Conclusions (II) This is the first demonstration of IL-17A production in response to Ty21a immunization IL-17A secreting cells have been shown to play a role in mucosal immunity IL-17A is secreted from multifunctional cells that coproduce IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and/or MIP-1β There is heterogeneity in the kinetics of the immune responses to Ty21a immunization. Bi-phasic & tri-phasic responses to S. Typhi-infected autologous EBV-LCL are typical. Thus, evaluating a single time point may fail to accurately evaluate responsiveness
20 S. Typhi Peyer s Patch CD8 M Ag uptake & presentation Mesenteric lymph nodes T H 1 T & B activation M cells B act ASC Ab B M T act DC T H 2 GALT Lumen Epithelium T CD8 H 1 Proliferation PC T H 2 Th1 T H 1 cytokine B pattern: IFN-γ,TNF-α, IL-10, IFN-γ IL-17, T H 2 B FDC IL-4, IL-5, IL-6 Lamina CD8 T PC B H 1 CTL [classical class Ia- and Propria class Ib (HLA-E)-restricted] B T M [ T EM T IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 Cytokines EMRA T (e.g., CM ] IFN-γ, TNF-α) Other Chemokines tissues Biliary tract, other organs? Thoracic duct Bacteremia Immune cells path? S. Typhi path Peripheral circulation IELs CD8 CD8 T EM T EMRA T CM expressing [or not] integrin α4/β7 M S-IgA LPLs Common Mucosal Immune System? RES spleen, liver, bone marrow, LN, intracellular replication
21 The question remains: Which of these complex and heterogeneous CMI responses, if any, are associated with protection from typhoid fever?
22 To answer this question, and to better understand typhoid disease, we recently initiated a collaboration with Dr. Pollard and his team at Oxford who have reestablished a human challenge model with wild-type S. Typhi
23 Multiphasic kinetics of CMI responses by CD8+ T EM to S. Typhi-infected AEH-cells (HLA-E-restriction) This volunteer (Ox6) did not develop typhoid fever (No TD) CD107a IFN-γ TNF-α ABX 5 ABX 8 ABX % positive cells IL-2 IL-17 MIP-1β ABX 0.25 ABX 6 ABX Days post-challenge ABX : antibiotics
24 Multifunctional CD8+ T EM to S. Typhi-inf B- LCL in wild-type S. Typhi-challenged subjects Peak d No TD: Ox4 Ox6 Ox7 Ox8 Ox12 mean TD: Ox3 Ox5 Ox9 Ox10 Ox11 mean % positive cells % positive cells CD107a IFN-γ TNF-α IL-2 IL-17A MIP-1β CD107a IFN-γ TNF-α IL-2 IL-17A MIP-1β
25 Mass cytometry Mass cytometry (CyTOF), a transformational flow cytometry technology to measure human immune responses by simultaneously evaluating >35 parameters/cell
26 S. Typhi appears to be such an effective pathogen, at least in part, by being exquisitely stealth. Thus, identifying the effective immunological CoP among a sea of nonprotective or downregulatory immunity might hold the key for the development of more effective vaccines.
27 Identification of the precise immunological correlates of protection (either mechanistic or non-mechanistic), can significantly advance the development of broad spectrum vaccines for enteric fevers (e.g., S. Paratyphi A, S. Paratyphi B)
28 Acknowledgements Center Vaccine Development, UMB Immunology Group Monica McArthur Stephanie Fresnay Franklin Toapanta Rosangela Mezghanni Rezwan Wahid Cathy Storrer Regina Harley Clinical studies Myron Levine Robin Barnes CVD Oxford Team Andrew J Pollard Claire Jones Claire Waddington Thomas Darton Christoph Blohmke Gordon Dougan Jeremy Farrar Paul Langford Brian Angus Derrick Crook Stephen Lockhart Supported by grants U19 AI (UMB-CCHI) and R01 AI-36525
Immune response and correlates of protection against typhoid
 Immune response and correlates of protection against typhoid Marcelo B. Sztein, M.D. Immunology Group Center for Vaccine Development University of Maryland Correlates of enteric vaccine-induced protection
Immune response and correlates of protection against typhoid Marcelo B. Sztein, M.D. Immunology Group Center for Vaccine Development University of Maryland Correlates of enteric vaccine-induced protection
Exploring S. Typhi-Specific HLA-E Restricted Immune Responses in Pediatric and Adult Ty21a Recipients
 Exploring S. Typhi-Specific HLA-E Restricted Immune Responses in Pediatric and Adult Ty21a Recipients Mark Rudolph PhD Candidate- University of Maryland Graduate Program in Life Sciences Institute for
Exploring S. Typhi-Specific HLA-E Restricted Immune Responses in Pediatric and Adult Ty21a Recipients Mark Rudolph PhD Candidate- University of Maryland Graduate Program in Life Sciences Institute for
x Lymphocyte count /µl CD8+ count/µl 800 Calculated
 % Lymphocyte in CBC A. 50 40 30 20 10 Lymphocyte count /µl B. x10 3 2.5 1.5 C. 50 D. 1000 % CD3+CD8+ Cells 40 30 20 Calculated CD8+ count/µl 800 600 400 200 10 0 #61 #63 #64 #65 #68 #71 #72 #75 Figure
% Lymphocyte in CBC A. 50 40 30 20 10 Lymphocyte count /µl B. x10 3 2.5 1.5 C. 50 D. 1000 % CD3+CD8+ Cells 40 30 20 Calculated CD8+ count/µl 800 600 400 200 10 0 #61 #63 #64 #65 #68 #71 #72 #75 Figure
Live oral vaccine approaches to typhoid and paratyphoid vaccines
 Live oral vaccine approaches to typhoid and paratyphoid vaccines Myron M. (Mike) Levine, M.D., D.T.P.H. Center for Vaccine Development. University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA 8 th
Live oral vaccine approaches to typhoid and paratyphoid vaccines Myron M. (Mike) Levine, M.D., D.T.P.H. Center for Vaccine Development. University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA 8 th
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Systemic and Terminal Ileum Mucosal Immunity Elicited by Oral Immunization With the Ty21a Typhoid Vaccine in Humans
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Systemic and Terminal Ileum Mucosal Immunity Elicited by Oral Immunization With the Ty21a Typhoid Vaccine in Humans Jayaum S. Booth, 1,2 Seema A. Patil, 3,4 Leyla Ghazi, 3,4 Robin Barnes,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Systemic and Terminal Ileum Mucosal Immunity Elicited by Oral Immunization With the Ty21a Typhoid Vaccine in Humans Jayaum S. Booth, 1,2 Seema A. Patil, 3,4 Leyla Ghazi, 3,4 Robin Barnes,
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Long-term persistence of T cell memory in Italian vaccinees
 Long-term persistence of T cell memory in Italian vaccinees Mario (Mago) Clerici Head, Department of Medical Sciences and Biotechnologies Head, Doctorate School in Molecular Medicine University of Milano
Long-term persistence of T cell memory in Italian vaccinees Mario (Mago) Clerici Head, Department of Medical Sciences and Biotechnologies Head, Doctorate School in Molecular Medicine University of Milano
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
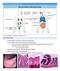 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder I Nakaya, Kousik
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-19 T H 2 response to cysteine-proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS mediated signaling Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-19 T H 2 response to cysteine-proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS mediated signaling Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Shigella Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development
 Shigella Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development Ryan Ranallo, Ph.D. Department of Enteric Infections Division of Communicable Diseases and Immunology Walter Reed Army Institute of Research Causes of Travelers
Shigella Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development Ryan Ranallo, Ph.D. Department of Enteric Infections Division of Communicable Diseases and Immunology Walter Reed Army Institute of Research Causes of Travelers
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Gp96-Ig-SIV VACCINES INDUCE PREDOMINANT IMMUNE RESPONSES AT MUCOSAL SITES
 Gp96-Ig-SIV VACCINES INDUCE PREDOMINANT IMMUNE RESPONSES AT MUCOSAL SITES Natasa Strbo M.D. Ph.D. Paris, AIDS Vaccine 29 October 19 22 Why is cell secreted gp96 Ig vaccine approach innovative and unconventional?
Gp96-Ig-SIV VACCINES INDUCE PREDOMINANT IMMUNE RESPONSES AT MUCOSAL SITES Natasa Strbo M.D. Ph.D. Paris, AIDS Vaccine 29 October 19 22 Why is cell secreted gp96 Ig vaccine approach innovative and unconventional?
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity
 Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
Challenges of Integrating Mucosal Immune Assays into HIV Vaccine Trials KAVI
 Challenges of Integrating Mucosal Immune Assays into HIV Vaccine Trials Omu Anzala, MBChB, PhD KAVI University of Nairobi Outline Why mucosal immunology Experience from Kenya Challenges The way forward
Challenges of Integrating Mucosal Immune Assays into HIV Vaccine Trials Omu Anzala, MBChB, PhD KAVI University of Nairobi Outline Why mucosal immunology Experience from Kenya Challenges The way forward
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation
 Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation William Warren, Ph.D. VaxDesign Corporation Orlando, FL 32826 wwarren@vaxdesign.com www.vaxdesign.com 1 MIMIC Technology Overview
Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation William Warren, Ph.D. VaxDesign Corporation Orlando, FL 32826 wwarren@vaxdesign.com www.vaxdesign.com 1 MIMIC Technology Overview
Nutrition & Gut Immunity
 Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
What to Measure, How to Measure It
 Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institutes of Health Monitoring Memory T-cells: What to Measure, How to Measure It Pratip K.
Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institutes of Health Monitoring Memory T-cells: What to Measure, How to Measure It Pratip K.
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections
 NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections Amy Chung Dr. Ivan Stratov Prof. Stephen Kent ADCC process consists of Target cell QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) FcγR decompressor
NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections Amy Chung Dr. Ivan Stratov Prof. Stephen Kent ADCC process consists of Target cell QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) FcγR decompressor
Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology
 By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy
 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Basis of Immunology and
 Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties
 Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Lymphocyte Migration to/from the Gut Tissue-specific markers of enteric vaccines immunogenicity
 Correlates of enteric vaccine-induced protection Fondation Mérieux, March 21-23, 2016 Lymphocyte Migration to/from the Gut Tissue-specific markers of enteric vaccines immunogenicity Quantitative aspects
Correlates of enteric vaccine-induced protection Fondation Mérieux, March 21-23, 2016 Lymphocyte Migration to/from the Gut Tissue-specific markers of enteric vaccines immunogenicity Quantitative aspects
Cytotoxicity assays. Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1. Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
 Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences
 The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
A TOLLIP DEFICIENCY ALLELE, RS , IS ASSOCIATED WITH LNCRNA TOLLIP-AS1 EXPRESSION, T-CELL MEMORY PHENOTYPE, AND INCREASED TB SUSCEPTIBILITY
 A TOLLIP DEFICIENCY ALLELE, RS5743854, IS ASSOCIATED WITH LNCRNA TOLLIP-AS EXPRESSION, T-CELL MEMORY PHENOTYPE, AND INCREASED TB SUSCEPTIBILITY February 2, 208 5th Global Forum on TB Vaccines MULTIPLE
A TOLLIP DEFICIENCY ALLELE, RS5743854, IS ASSOCIATED WITH LNCRNA TOLLIP-AS EXPRESSION, T-CELL MEMORY PHENOTYPE, AND INCREASED TB SUSCEPTIBILITY February 2, 208 5th Global Forum on TB Vaccines MULTIPLE
C. Incorrect! MHC class I molecules are not involved in the process of bridging in ADCC.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection
 Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection Moriah J. Castleman, Ph.D. Laboratory of Dr. Cara Wilson University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection Moriah J. Castleman, Ph.D. Laboratory of Dr. Cara Wilson University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy
 Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Third line of Defense. Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization!
 Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Vaccine Delivery and TLR Ligands Influence the Quality of T cell Responses in NHP. Robert A. Seder, M.D. Vaccine Research Center NIAID, NIH
 Vaccine Delivery and TLR Ligands Influence the Quality of T cell Responses in NHP Robert A. Seder, M.D. Vaccine Research Center NIAID, NIH Vaccines Against HIV, Malaria and Tuberculosis Will Require Neutralizing
Vaccine Delivery and TLR Ligands Influence the Quality of T cell Responses in NHP Robert A. Seder, M.D. Vaccine Research Center NIAID, NIH Vaccines Against HIV, Malaria and Tuberculosis Will Require Neutralizing
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies
 NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry Detection of Cytokines, Transcription Factors, and Phosphoprotein by Flow Cytometry Presented by Erika O Donnell, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-14876-00 Outline Basic principles
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry Detection of Cytokines, Transcription Factors, and Phosphoprotein by Flow Cytometry Presented by Erika O Donnell, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-14876-00 Outline Basic principles
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection
 Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Chapter 13: Cytokines
 Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Adaptive Immune System
 Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Immunobiology 7. The Humoral Immune Response
 Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein)
 Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay
 Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
Immune Surveillance. Immune Surveillance. Immune Surveillance. Neutrophil granulocytes Macrophages. M-cells
 he immune system is everywhere Some organs have developed strategies towards the immune system to keep it out or to put it under control Immune privileged organs: Brain Eye estis hyroid gland Humoral immunity
he immune system is everywhere Some organs have developed strategies towards the immune system to keep it out or to put it under control Immune privileged organs: Brain Eye estis hyroid gland Humoral immunity
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Supplementalgfigureg1gSchematicgdiagramgofgtumor1modellingg
 SChinjectionh F:LuchLCLsh IVhinjectionh T:cellsh Monitorhforhtumorh growthhandhxeno: reactivehgvhd GVLgexperimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse Xeno1reactiveg experimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse IVhinjectionh 5xh,N^6
SChinjectionh F:LuchLCLsh IVhinjectionh T:cellsh Monitorhforhtumorh growthhandhxeno: reactivehgvhd GVLgexperimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse Xeno1reactiveg experimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse IVhinjectionh 5xh,N^6
Supplementary Table 1: Summary of Reactogenicity Events by Group and Time of Onset in Entebbe
 Supplementary Table 1: Summary of Reactogenicity Events by Group and Time of Onset in Group A (n=39) B (n=11) A (n=39) B (n=11) Onset Post-Vaccination Event 3 Minutes 3-14 days Pain 5 (13%) 1 (1%) 6 (15%)
Supplementary Table 1: Summary of Reactogenicity Events by Group and Time of Onset in Group A (n=39) B (n=11) A (n=39) B (n=11) Onset Post-Vaccination Event 3 Minutes 3-14 days Pain 5 (13%) 1 (1%) 6 (15%)
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
VMC-221: Veterinary Immunology and Serology (1+1) Question Bank
 VMC-221: Veterinary Immunology and Serology (1+1) Objective type Questions Question Bank Q. No. 1 - Fill up the blanks with correct words 1. The British physician, who developed the first vaccine against
VMC-221: Veterinary Immunology and Serology (1+1) Objective type Questions Question Bank Q. No. 1 - Fill up the blanks with correct words 1. The British physician, who developed the first vaccine against
supplemental Figure 1
 supplemental Figure 1 A T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv B T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv C T cell BW1/6 anti-cea CDζ CH/CH scfv supplemental Figure 1.79.9.87
supplemental Figure 1 A T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv B T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv C T cell BW1/6 anti-cea CDζ CH/CH scfv supplemental Figure 1.79.9.87
Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria. T cell subsets
 Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria Role of T cells in anti-bacterial host responses. Dr. C. Piccirillo Department of Microbiology & Immunology McGill University T cell subsets MHC I and II -restricted cells
Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria Role of T cells in anti-bacterial host responses. Dr. C. Piccirillo Department of Microbiology & Immunology McGill University T cell subsets MHC I and II -restricted cells
Monocyte subsets in health and disease. Marion Frankenberger
 Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Online supplement. Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated
 Online supplement Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages Abdullah Al Tarique*, Jayden Logan *, Emma Thomas *, Patrick G Holt *, Peter
Online supplement Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages Abdullah Al Tarique*, Jayden Logan *, Emma Thomas *, Patrick G Holt *, Peter
B cell activation and antibody production. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
IOM Immunization Safety Review 11/12/2001. Immunological Competition and the Infant Immune Response to Vaccines
 IOM Immunization Safety Review 11/12/2001 Immunological Competition and the Infant Immune Response to Vaccines Richard Insel University of Rochester Goals Neonatal and Infant Immune System Broad Effects
IOM Immunization Safety Review 11/12/2001 Immunological Competition and the Infant Immune Response to Vaccines Richard Insel University of Rochester Goals Neonatal and Infant Immune System Broad Effects
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 16 THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The adaptive immune system protects us from many infections The adaptive immune system has memory so we are not infected by the same pathogen
CHAPTER 16 THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The adaptive immune system protects us from many infections The adaptive immune system has memory so we are not infected by the same pathogen
UNISEC Universal Influenza Vaccines Secured
 UNISEC Universal Influenza Vaccines Secured Partners in the UNISEC Consortium UNISEC has been made possible by contributions from the European Commission DG-Research and the European member states Project
UNISEC Universal Influenza Vaccines Secured Partners in the UNISEC Consortium UNISEC has been made possible by contributions from the European Commission DG-Research and the European member states Project
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Evidence review on the immunogenicity, efficacy/effectiveness and safety of typhoid conjugate vaccines
 Evidence review on the immunogenicity, efficacy/effectiveness and safety of typhoid conjugate vaccines SAGE meeting, Geneva, 17-19 October, 2017 Myron M. (Mike) Levine, MD, DTPH Grollman Distinguished
Evidence review on the immunogenicity, efficacy/effectiveness and safety of typhoid conjugate vaccines SAGE meeting, Geneva, 17-19 October, 2017 Myron M. (Mike) Levine, MD, DTPH Grollman Distinguished
Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity
 Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM:
 RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
Estimating primate effector T cell responses to DNA vaccination
 Estimating primate effector T cell responses to DNA vaccination Oct 22 nd, 21 Devon J. Shedlock, PhD th Vaccine Renaissance Conference Estimating vaccineinduced effector T cell responses Vaccineinduced
Estimating primate effector T cell responses to DNA vaccination Oct 22 nd, 21 Devon J. Shedlock, PhD th Vaccine Renaissance Conference Estimating vaccineinduced effector T cell responses Vaccineinduced
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces
 Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
Immune system. Self/non-self recognition. Memory. The state of protection from infectious disease. Acceptance vs rejection
 Immune system The state of protection from infectious disease Self/non-self recognition 自我 非我 Acceptance vs rejection Memory 疫苗 2 Microbes Commensal Microbes 共生菌 Normal flora: usually confined to certain
Immune system The state of protection from infectious disease Self/non-self recognition 自我 非我 Acceptance vs rejection Memory 疫苗 2 Microbes Commensal Microbes 共生菌 Normal flora: usually confined to certain
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
Anti-infectious Immunity
 Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
