Allergens as triggers of pattern recognition receptors. Marsha Wills-Karp Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Baltimore, MD
|
|
|
- Naomi Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Allergens as triggers of pattern recognition receptors Marsha Wills-Karp Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Baltimore, MD
2 Allergic disorders are CD4+ Th2 Cell Driven IL-12 DC Allergens TSLP IL-33 IL-25 epithelium B IgE Y Y Mast cell IL-13 IL-4 IL-5 EOS Th1 Resistance Treg Tolerance Th2 ASTHMA AHR
3 Allergy/Asthma: A Central Conundrum Why do specific proteins out of a universe of antigens act as aeroallergens in susceptible hosts (in susceptible environments)? Why do such (innocuous) diverse proteins tend to generate effector T cell responses? adjuvanticity Why are effector T cell responses to these proteins tend to be Th2-polarized? Allergenicity
4 Allergens are derived from diverse sources which have diverse molecular structures Allergens derive from a variety of environmental sources such as: plants (trees, grasses) fungi (Alternaria alternata) arthropods (mites, cockroaches) mammals (cats, dogs, cows) As they are derived from complex living organisms they serve a broad range of functions in their respective hosts, from structural to enzymatic.
5 The common house dust mite contains many enzymatically active molecules several cysteine proteases (Der p 1, Der p 3) serine proteases (Der p 6, Der p 9) chitinases (Der p 15, Der p 18) lipid-binding molecules (Der p 2), structural molecules--tropomyosin (Der p 10)
6 Allergens may uniquely induce innate immune pathways There is currently no compelling evidence for common structural characteristics among the diverse T and B cell epitopes. Other factors such as the size, glycosylation status, resistance to proteolysis, and enzymatic activity, have been suggested to play an important role in allergenicity. However, none of these factors have been consistently linked with allergenic potential. Recent studies suggest that allergens are linked by their ability to stimulate innate immune pathways
7 Steps in the initiation of allergic inflammation Allergens PRR Viruses Pollutants Recruitment Activation Th2 Allergy Asthma PAMP DC DC PRRs PRR MHC CD80 CD86 Signal 1 Signal 2 Cytokines Signal 3 TCR CD28 CTLA4 Naïve T Cell IL-6 TGFB Treg Th17 Th1 Tolerance Infections Severe Asthma Intracellular Pathogens
8 Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are recognized by pattern recognition receptors PAMPs (signal 3) Invariant structures shared by classes of pathogens PRR Inborn Germ-line encoded Genetically determined specificities for pathogens Passed onto progeny Cytokines
9 Human Pattern Recognition Receptors Toll-like receptors (membrane bound) Types TLR1-10, CD14 Recognizes Microbial membranes and nuclei acids C-type lectin receptors Dectin 1, 2, collectins, SP-A and SP-D Microbial glucans, mannan NOD-like receptors NOD1,2, cryopyrin Microbial components RIG-I receptors Anti-microbial peptides (secreted) Defensins, cathelicidin dsrna Microbial membranes
10 Toll-like Receptors and Agonists PAM 3 CysK 4 19 kda Mtb lipoprotein AraLAM Lipoarabinomannan PAM 2 CysK 4 P.gingivalis LPS L.interrogans LPS (?2/1, 2/2, 2/6?) LTA Zymosan MALP-2 dsrna Enterobacterial LPS chlamydial HSP60 VSV-G MMTV-G Flagellin ssrna CpG DNA T. Gondii prophilin UPEC??? LRR TIR TLR2/1 TLR2/6 TLR3 TLR4 TLR5 TLR7 TLR8 hu TLR9 TLR10 hu TLR11 (mouse) TLR12/13 (mouse)
11 TLR4 LBP LPS CD14 MD-2 LRR cc TIR
12 TLR4 LBP LPS CD14 MD-2 LRR cc TIR
13 LPS doesn t bind TLR4 directly CD14 and MD-2 act as a bridge between LPS and TLR4 TLR4 LBP LPS TLR4 MD-2 multimerization CD14 LRR cc TIR
14 TLR4 Signaling Pathways Proinflammatory cytokines Type I and II IFN s
15 Structural Comparison of a Homology Model of MD-2 with the Crystal Structure of Der p 2 MD-2 Der p 2 belongs to MD-2-like lipid binding family Der p 2 Gruber A, JBC (2004)
16 Allergens-House dust mites Dust mites are major source of aeroallergens for patients with allergic asthma highest rates of skin test positivity among allergens in atopic patients Dust mites contain many allergenic peptides Der p 1 (cysteine protease) Der p 2, Der f 2 ( major group II allergens )
17 Is there functional homology between MD-2 and Der p 2?
18 Der p 2 reconstitutes TLR4 signaling MD-2 deficient HEK293 cells * E.V Der p 2-HA IL-8 (pg/ml) TLR4 + CD Der p 2 binds LPS and CD14 Trompette, Nature, ng/ml E.coli LPS
19 All sequenced MD-2 contain a conserved tyrosine (Tyr 102) at a site functionally Amino acid 91 important in Der p 2 sequence, for TLR4 aa102 in MD-2 sequences signaling tyrosine Human MD-2 88 PKRKEVICRGSDDDYSFCRALKGETVNTTISFSFKGIKFSKGKYKCVV 135 Chimpanzee MD-2 88 PKRKEVICRGSDDDYSFCRALKGETVNTTISFSFKGIKFSKGKYKCVV 135 Macaca MD-2 88 PKRKEVICRGSDDDYSFCRALKGETVNTTVSFSFKGIKFSKGKYKCVV 135 Murine MD-2 88 PKRKEVLCHGHDDDYSFCRALKGETVNTSIPFSFEGILFPKGHYRCVA 135 Rat MD-2 88 PKRKEIVCHGYDDDYSFCRALKGEAVNTAIPFSFDGILFPKGHHRCVA 135 Hamster MD-2 88 PTRKEIICHGYDDNYSFCKALKGETVNTVVPFSFKGILFPKGQYRCVA 135 Rabbit MD-2 88 PKRKEIICKGSDDVYSFCRALKGETVNTTVPFSFKGIRLSKGQYRCVV 135 Pig MD-2 88 PMRKEVICREYGGDYSFCGALKGETVNTTIPFSFQGIRFSPGQYHCVV 135 Bovine MD-2 88 PMRKEVICREYGGDYSFCGALKGETVNTTIPFSFQGIRFSPGQYHCVV 135 Equine MD-2 88 PMRKEVICRGSDDDYSFCRALKGETVNTTVSFSFRGMRFPKGRYSCIA 135 Human MD-1 95 LNFSYPICEAALPKFSFCGRRKGEQIYYAGPVNNPEFTIPQGEYQVLL 142 Chimpanzee MD-1 95 LNFSYPICEAALPKFSFCGRRKGEHCYFAGPSPRVSSFVHQGEYQVLL 142 Macaca MD-1 95 LNFSYPICEVALPKFSFCGRRKGEQIYYAGPVNNPEFTIPQGEYQVLL 142 Murine MD-1 95 LNYSYPLCEEDQPKFSFCGRRKGEQIYYAGPVNNPGLDVPQGEYQLLL 142 Pig MD-1 92 LNLSYPICEADLPKFSFCGRRKGEQIYYAGPVNNLGFEFPTGEYQVLL 139 Chicken MD-1 90 LSYSETLCGPGLSKLIFCGKKKGEHLYYEGPITLGIKEIPQGDYTITA 137 Der gi# p 2 82 PGIDPNACH-----YMKCPLVKGQQYDIKYTWNVP-KIAPKSE-NVVV 122
20 Mutation of Y91A impairs the ability of Der p 2 to modulate TLR4 signaling E. V ( L P S - m o c k ) D e r p 2 - H A * Y 9 1 A D e r p 2 - H A IL-8 (pg/ml) NO MD-2 0 T L R C D n g / m l E. c o l i L P S
21 Cell number (x 1000) TLR4-dependent induction of experimental allergic asthma by Der p 2 BAL Cell Number *** ** NS W.T. TLR4 -/- Cell number (x 1000) NS NS ** NS *** ** *** *** Macrophages Neutrophils Eosinophils Lymphocytes NS NS Total IgE (ng/ml) 250 * W.T. (LPS) W.T. (rder p 2/LPS) WT/Der p2 TLR4-KO (LPS) TLR4-KO (rder p 2/LPS) TLR4-/- Der p2 Total IgE (ng/ml) NS W.T. TLR4 -/- W.T. TLR4KO Et Trompette, Nature, 2009
22 Der p 2 activates TLR4 Der p 2 binds LPS signaling Der p 2 interacts directly with the TLR4 complex, facilitating LPS signaling Der p 2 drives Th2 inflammation in the airway in a TLR4-dependent fashion by mimicking MD-2 Der p 2 can drive airway Th2 inflammation in the absence of MD-2 These findings are consistent with other studies demonstrating a role for TLR4 signaling in type-2- mediated inflammation (Hammad, 2009; Tan, 2009)
23 Is this phenomenon generalizable? Numerous other ML family members are allergens A large number of defined major allergens are lipid-binding proteins Der f 2 also binds LPS (Ichikawa S, Genes Cells, 14:1055, 2009). Der p 7 binds to the lipoprotein polymixin B (Mueller, JACI, 125: , 2010).
24 Why do we respond to and mount a Th2 immune response to Der p 2? Der p 2 likely serves a host defense role in the mite It is unlikely that mammalian host responses are intentionally directed against the harmless mite Likely a case of mistaken identity-host response likely evolved to protect against bacterial infection The question remains as to why TLR4 signaling can drive both Th1 and Th2 immune responses?
25 TLR4 Signaling Drives Th2 Immune Responses Through Induction of TSLP Der p 2 TSLP TLR4 Ozone induced inflammation is also TLR4-dependent Ragweed induced AHR is TLR4- dependent Jagged-1 DC OX40L Hammad, 2009; Tan, 2009 Th2
26 Other PAMPs contained in HDM Chitin β-glucans --- Carbohydrate moieties
27 C-type lectin receptor (CLRs) Carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) Ligands are not present in mammalian cells Calcium dependent binding No signaling domains- -couple with stimulatory (ITAMs) & inhibitory (ITIMs)
28 Carbohydrate recognition in Th2 responses Glucans are a diverse class of naturally occurring glucose polymers, which can be short or long, branched or unbranched, exist as α or β isomers, and be soluble or particulate. Native but not deglycosylated Ara h 1, a peanut glycoallergen has been shown to activate human monocyte derived DC and induce IL-4 and IL-13- secreting Th2 cells (Shreffler et al, 2006).
29 Dust mite-induced CCL20 is β glycan dependent CCL20 (pg/ml) * Der p 1 and Der p 2 *p<0.05 Don t vs. Ctrl +p<0.05 Induce CCL20 vs. HDM + * + Nathan, Nathan, JACI, 2009
30 Dectin-1-2, β-glucan receptors, signaling pathways Yeast TLR2 TLR6 Yeast Y Y P SYK P Y Y MyD88 Y Y P Respiratory burst IL-10 phagocytosis TNF Derived from Brown, G Nat Immunol 2006
31 Dust mite & Aspergillus allergens are recognized by Dectin-2, release of LTC4 Mouse bone marrow derived mast cells Barrett NA et al. J Immunol., 2009.
32 Activation of the lectin pathways of complement activation Like other PRR, the complement system can be activated by hard-wired PRRS such as the mannose binding lectin (MBL) that has evolved to recognize danger motifs. Consistent with a role for lectins in driving Th2 immune responses, blockade of the mannose receptor, an endocytic C-type lectin receptor, significantly reduced Der p 1 uptake by DCs (Royer, 2010). Fed d 1 is a ligand of the mannose receptor and MR deficient mice have attenuated allergic responses to Fed d 1 (Emara, 2011).
33 Allergens induce complement factor 3 gene expression in AEC PBS HDM C3 leads to preferential uptake of Ag by mdcs Der p 1 containing proteases cleave C3 into its active fragment, C3a. SNPs in C3 are associated with asthma
34 Protease Containing Allergens Can Activate Several Innate Immune Cells Leading to Type 2 Immunity papain OxL Papain ROS OxL TLR4 TRIF Epithelium ROS OxL mdc TLR4 TRIF Sokol, 2008; Hammad, 2010, Tang, TSLPR Reduced IL-12 OX40L Jagged-1 TSLP CCL7 Naïve CD4+ T Cell TSLPR IL-4 TSLP Basophil Th2
35 Danger Associated Molecular Patterns Alum-NLR (Eisenbarth, 2008) ATP-(Idzko, 2007) Uric acid-(kool, 2011)
36 The danger sensor TFF2 drives Th2 immunity to allergens PBS HDM
37 Blockade of IL-33 in TFF2-treated macrophages abrogates T H 2 OVA TFF2 sirna Th2 cytokines GATA-3,Tbet IL-33 si RNA Control si RNA Wills-Karp, JEM, 2012
38 Allergens are recognized by and activate type 2 immune responses through a constellation of PRRs HDM β- glycan CLR? HDM Ara h 1 Candida albicans LPS RSV Der p 2 Ragweed DEP TLR4?? NOD1/2 CR Der p 1 Grass Fungal PAR2 HDM RSV Der p1 Ara h1 Bla g 2 Can f 1 Der p 2 MBL HDM CCL20 CCR6 Dectin-2 DC-SIGN TSLP TSLPR TSLP TSLP Jagged-1 OX40 Reduced IL-12 C3a C3ar MR ATP Uric acid TFF2 IL33
39 CONCLUSIONS Allergens possess the ability to induce a variety of innate immune pathways (particularly in the mucosal epithelium) which override the otherwise tolerogenic environment. Much more needs to be learned about the full spectrum of innate immune pathways activated by different classes of allergens Genetic differences in innate immune pathways may underlie susceptibility to allergic diseases Modulation of these pathways holds promise for screening for sensitizing abilities and the development of therapeutics aimed at preventing allergic sensitization
40 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CCHMC Ian Lewkowich Stephane Lajoie Amy Nathan Yusuke Suzuki Krista Dienger Alyssa Sproles Vanessa Saunders DeBroski Herbert CHRIS KARP A. Trompette
41 Uric acid activates several innate immune pathways resulting in IL-1β cytokine
42 Zaki, MH, Trends Immunol 2011.
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
The role of mucosal innate immunity in allergic rhinitis Ji-Hwan Ryu
 The role of mucosal innate immunity in allergic rhinitis Ji-Hwan Ryu Research Center for Human Natural Defense system College of Medicine Yonsei University Mucosal epithelium in innate immunity Mucosal
The role of mucosal innate immunity in allergic rhinitis Ji-Hwan Ryu Research Center for Human Natural Defense system College of Medicine Yonsei University Mucosal epithelium in innate immunity Mucosal
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells
 Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS
 Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Innate immunity. Monika Raulf. Lecture Tasks of the immune system. Body protection against damaging influences
 Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Basic immunology. Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Introduction to Immune System
 Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Immunology for the Rheumatologist
 Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Eat Dirt: Why Cleanliness is Bad for Asthma
 Eat Dirt: Why Cleanliness is Bad for Asthma Joel N. Kline MD MSc Professor, Pulmonary Medicine Director: UI Adult Asthma Center Director, Clinical Research ICTS University of Iowa Iowa City, IA 1 Disclosures:
Eat Dirt: Why Cleanliness is Bad for Asthma Joel N. Kline MD MSc Professor, Pulmonary Medicine Director: UI Adult Asthma Center Director, Clinical Research ICTS University of Iowa Iowa City, IA 1 Disclosures:
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Lung Disease in Pediatrics: is it all in the Genes?
 Lung Disease in Pediatrics: is it all in the Genes? Jay K. Kolls, M.D. Chair, Department of Genetics LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA Children s s Hospital of Pittsburgh Severe combined immunodeficiency
Lung Disease in Pediatrics: is it all in the Genes? Jay K. Kolls, M.D. Chair, Department of Genetics LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA Children s s Hospital of Pittsburgh Severe combined immunodeficiency
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release. Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation. Neutrophils & Innate Defense
 Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Innate Immunity. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Allergic rhinitis (Hay fever) Asthma Anaphylaxis Urticaria Atopic dermatitis
 Hypersensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Immune Response IgE Disease Example Ragweed hay fever IgG Cytotoxic Immune complex T Cell Hemolytic anemia Serum sickness Poison ivy IgE-mediated Diseases
Hypersensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Immune Response IgE Disease Example Ragweed hay fever IgG Cytotoxic Immune complex T Cell Hemolytic anemia Serum sickness Poison ivy IgE-mediated Diseases
Relative sizes of infectious agents
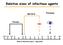 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Basic Immunology. Lecture 16th. Complement system
 Basic Immunology Lecture 16th Complement system Components: Inactive factors in the serum and body fluids which can activate each other in an enzyme cascade Cell surface receptors (CR) for binding the
Basic Immunology Lecture 16th Complement system Components: Inactive factors in the serum and body fluids which can activate each other in an enzyme cascade Cell surface receptors (CR) for binding the
Innate Immunity in Transplantation. Innate and Adapative Immunity
 Innate Immunity in Transplantation M. Sue Leffell, PhD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Innate and Adapative Immunity Innate or natural defense mechanisms phylogenetically older; present in
Innate Immunity in Transplantation M. Sue Leffell, PhD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Innate and Adapative Immunity Innate or natural defense mechanisms phylogenetically older; present in
Biochemistry of the immune system. B. Sopko
 Biochemistry of the immune system B. Sopko Content The innate immune system Introduction Cells Immediate Innate Immunity Early Induced Innate Immunity Adaptive immunity Introduction Humoral Immunity Cell-Mediated
Biochemistry of the immune system B. Sopko Content The innate immune system Introduction Cells Immediate Innate Immunity Early Induced Innate Immunity Adaptive immunity Introduction Humoral Immunity Cell-Mediated
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD. Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany
 Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
The role of dendritic cells in asthma
 Mechanisms of allergic diseases Series editors: Joshua A. Boyce, MD, Fred Finkelman, MD, William T. Shearer, MD, and Donata Vercelli, MD The role of dendritic cells in asthma Michelle Ann Gill, MD, PhD
Mechanisms of allergic diseases Series editors: Joshua A. Boyce, MD, Fred Finkelman, MD, William T. Shearer, MD, and Donata Vercelli, MD The role of dendritic cells in asthma Michelle Ann Gill, MD, PhD
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Complement. History. Chapter 7. Complement Components. Complement Pathways. Pathways of complement activation
 History Chapter 7 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
History Chapter 7 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Innate microbial sensors and their relevance to allergy
 Clinical reviews in allergy and immunology Series editors: Donald Y. M. Leung, MD, PhD, and Dennis K. Ledford, MD Innate microbial sensors and their relevance to allergy Andrew H. Liu, MD Denver, Colo
Clinical reviews in allergy and immunology Series editors: Donald Y. M. Leung, MD, PhD, and Dennis K. Ledford, MD Innate microbial sensors and their relevance to allergy Andrew H. Liu, MD Denver, Colo
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER. Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma
 INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
Determinants of Food Allergy Persistence and Severity
 Determinants of Persistence and Severity What determines sensitization? Bert Ruiter, Wayne Shreffler Immunology Institute and Jaffe Institute Mount Sinai School of Medicine Functional of a Unique Allergy-Immunology
Determinants of Persistence and Severity What determines sensitization? Bert Ruiter, Wayne Shreffler Immunology Institute and Jaffe Institute Mount Sinai School of Medicine Functional of a Unique Allergy-Immunology
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
MICR2209. Innate Immunity. Dr Allison Imrie
 MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Introduction. A system of soluble enzymes and proteins. Complement components: C1 to C9, B, D and P
 Complement Introduction A system of soluble enzymes and proteins Complement components: C1 to C9, B, D and P When activated, each component is split into small and large (major) fragments a b *A horizontal
Complement Introduction A system of soluble enzymes and proteins Complement components: C1 to C9, B, D and P When activated, each component is split into small and large (major) fragments a b *A horizontal
SINGLE CHOICE. 5. The gamma invariant chain binds to this molecule during its intracytoplasmic transport. A TCR B BCR C MHC II D MHC I E FcγR
 A Name: Group: SINGLE CHOICE 1. Which is the most important ligand of TLR5? A endospore B flagellin C polysaccharide capsule D DNA E pilus 2. The antibody-binding site is formed primarily by... A the constant
A Name: Group: SINGLE CHOICE 1. Which is the most important ligand of TLR5? A endospore B flagellin C polysaccharide capsule D DNA E pilus 2. The antibody-binding site is formed primarily by... A the constant
Toll-like Receptor Signaling During Infection and Inflammation Prof. Luke O Neill
 Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid
Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官. The Immune System. KE, Yuehai 柯越海. Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院
 生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官 The Immune System KE, Yuehai 柯越海 Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院 Outlines The Immune System 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Immune
生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官 The Immune System KE, Yuehai 柯越海 Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院 Outlines The Immune System 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Immune
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
History. Chapter 13. Complement Components. Complement Pathways
 History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
Immunology Lecture 4. Clinical Relevance of the Immune System
 Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
History. Chapter 13. Complement Components. Complement Pathways
 History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade
 Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade Bryan L. Martin, DO, MMAS, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FACOI, FACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics President, American College of Allergy,
Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade Bryan L. Martin, DO, MMAS, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FACOI, FACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics President, American College of Allergy,
Signaling through Fc RIII is required for optimal T helper type (Th)2 responses and Th2-mediated airway inflammation
 Signaling through Fc RIII is required for optimal T helper type (Th)2 responses and Th2-mediated airway inflammation Hozefa S. Bandukwala, 1 Bryan S. Clay, 1 Jiankun Tong, 2 Purvi D. Mody, 1 Judy L. Cannon,
Signaling through Fc RIII is required for optimal T helper type (Th)2 responses and Th2-mediated airway inflammation Hozefa S. Bandukwala, 1 Bryan S. Clay, 1 Jiankun Tong, 2 Purvi D. Mody, 1 Judy L. Cannon,
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES:
 Dr Mohammed Al- ani THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: When you finish this section, you should be able to: 1. Describe the effects of complement activation. 2. Outline the Classical, Mannan-Binding (MB)
Dr Mohammed Al- ani THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: When you finish this section, you should be able to: 1. Describe the effects of complement activation. 2. Outline the Classical, Mannan-Binding (MB)
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
