Toll-like Receptor Signaling During Infection and Inflammation Prof. Luke O Neill
|
|
|
- Clyde Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid arthritis Osteoarthritis Asthma Multiple sclerosis Crohn s disease Ulcerative Colitis Several types of anti-inflammatory drugs Newer drugs: Enbrel, Remicade, Rituxin, Tosilimumab New findings: Innate Immunity A starting point: a Russian, Mechnikov Nobel Prize for Medicine 1908 shared with Ehrlich for work on immunity Acceptance speech, December 11 th 1908: I will enlarge on the resistance of the body to disease and show you the practical value of pure research Animal organisms are very complex so I chose lower animals with very simple organisation to observe immunity Research should concentrate on the conditions capable of strengthening the phagocytic reaction 3 1
2 An Irishman and inflammation: Almroth Wright, founding father of innate immunity Firm advocate of stimulating the phagocytes Discoverer of opsonisation Wikipedia: Wright proposed that logic should be part of medical training but his idea was never adopted 4 Up to 1990s+: focus on the Ag Inflammation Inflammatory mediators and cytokines: e.g., IL1, TNF, IL6, IL12, IL8, etc. Macrophage Ag 5 Pathogens MHC/Ag presentation Co-stimulation Adaptive immunity: T and B cells 6 2
3 Our understanding of immunological recognition by clonally distributed receptors is approaching an asymptote Our knowledge of T and B cells mechanisms is approaching an asymptote Why do we use adjuvants? To be quite honest the answer is not known IL1 is required for priming and clonal expansion of T cells. One role for adjuvants is to induce IL1 The system predominantly discriminates infectious non-self from non-infectious self by means of a system of pattern recognition receptors..a new immunology that integrates innate and induced immunology Providing explanations for...induced second signals, the myriad of T cell surface molecules and A role for receptors that recognise patterns of microbial structures. This will require a rediscovery of microbiology by immunologists 7 Approaching the asymptote? evolution and revolution in immunology Cold Spring Harbour Symposia on Quantitative Biology 1989, 54: parts to the pathogen Inflammation Inflammatory mediators and cytokines: e.g., IL1, TNF, IL6, IL12, IL8, etc. Pattern recognition receptors Dendritic cell 8 PAMPs Ag Pathogens MHC/Ag presentation Co-stimulation Adaptive immunity: T and B cells Pentraxins Innate immunity 2009: 7 families of PRRs Phosphocholines Bacterial cell walls (e.g., LPS) Flagellin Fungal cell wall (e.g., Zymosan) LRR Toll-like receptors Bacterial surface Fungal surface (mannose) Fungal cell wall (beta-glucan) CRD MBL TIR ITAM Dectins Microbial genomes (dsrna, ssrna, dsdna) Endosome Toll-like receptors Bacterial cell wall fragments Bacterial toxins Uric acid Flagellin Viruses Potassium efflux ROS Lysosome disruption NOD-like receptors LRR NACHT CARD - PYRIN 9 Viral RNA RIG-I-like receptors Helicase CARD HIN200 family DNA HIN200 Pyrin 3
4 AIM2 Vaccinia PYRIN NALP3 Innate immunity to viruses 2010 Influenza Adenovirus MVA, EMCV PYRIN RIG-I Rabies VSV CARDs MAVS EBV, HSV Adenovirus RNA Pol III MDA5 Vaccinia EMCV MVA CARDs NOD2 RSV PYRIN CARD Innate immunity to viruses 2010 HSV, others? ASC CARD PYRIN TRAF3 K63 Uq NEMO STING IKKe TBK1 DDX3?? DAI DNARs? CMV Caspase 1 NF-kB IRF3/7 10 IL1β Pro-IL1β IFNβ 11 The sea urchin: 222 TLRs : NF-kappaBand p38 as key IL1 signals 12 4
5 13 Sims JE and Dower S, IL-1R family 1994 Eur Cyt Network 5, Toll! 14 Wild-type larvae Toll mutant Amazing Wild Weird Great Brilliant Cool Bodacious Superb Corky Mad Wow Go h-iontach The mouldy fly Toll-deficient Drosophila 15 Jules Hoffman and colleagues,
6 IL-1 receptor family The Toll / IL-1R superfamily in humans (a) Immunoglobulin domain sub-group: IL-1RI-like TIR domain Ig domain Leucine-rich repeat domain Death domain IL-1RI IL-1RAcP IL-18R IL-18RAcP ST2 IL-1Rrp2 IL-1RAPL TIGGIR1 SIGGIR (b) Leucine rich-repeat sub-group: TLRs TLR1 TLR2 TLR3 TLR4 TLR5 TLR6 TLR7 TLR8 TLR9 TLR10 (c) Adapter sub-group MyD88 Mal Trif Tram SARM 17 NOD-like receptors, RIGI-like receptors, C-type lectin receptors IL-1 IL-18 IL-33 (with AcP) IL-1F6,8 and 9 (with AcP) Orphans Partners TLR2 for blp blps, Zymosan dsrna LPS, F protein, hsp60, FN frags Flagellin Partners TLR2 for MALP-2 Imiquimod Imiquimod CpG DNA Pan-adapter Adapter for TLR2 and TLR4 Adapter for TLR3 Adapter for TLR4 Inhibitor of Trif? Toll-like receptors: how do we know they are important? Genetic variation and disease Therapeutic intervention in disease models 18 6
7 Mal S180L and disease Mal is a signalling adapter used by TLR2 and TLR4 Mal S180L heterozygotes have half the risk of malaria (3 populations), TB (3 out of 5 populations), pneumococcal pneumonia, Chagas disease and severe sepsis Mal S180L heterozygotes have a 3 fold decreased risk of SLE 19 When did Mal L180 arise in humans? 20 World distribution of MAL S180L in human populations Abbreviations: Sp, Spain; IRL, Ireland; UK, United Kingdom; Ge, Germany; Ro, Romania; Gr, Greece; Tu, Turkey; Ga, Gambia; Ma, Mali; Ta,Tanzania; Ke, Kenya; Ti, Trio Indians of Suriname; Isr, Israel; In, India; Ch, China; Pa, Papua New Guinea, Sp Irl UK Ge Ro Gr Tu SS SL LL Ga Ma Ta Ke Ti 21 Isr In Ch Pa 7
8 Worldwide human relationships inferred from genome-wide patterns of variation JZ Li et al., Science, 319, Superimposing Mal variants: S/L S/S L/L Native America Asia India Europe 22 Africa Middle East The leucine mutation probably occurred 8,000 years ago in the Middle East S/L S/S S/S S/L 80,000 yr S/L S/S S/S 23 Malaria, IPD, TB, Sepsis, SLE TLR2 TLR2 TLR2 MAL S180 MAL S180 MAL S180 MAL L180 MAL L180 MAL L180 Strong signal Modulated signal No signal Hyper-inflammation (TNF + IL-1) Increased risk of pathology/disease 24 Inflammation Lower risk of disease Less inflammation: Infection/Disease/Death 8
9 Columbus in the Americas, 1492: a family that split 67,000 years ago reunited Mal S/S Mal S/L 25 Death from infections How do TLRs work? 26 Toll-like receptors Microbial products Products of inflamed tissues 10 TLRs MyD88 Mal Trif Tram Modulation of immune and inflammatory genes Immune and inflammatory effector mechanisms 27 9
10 TLR4: ignition followed by acceleration Ignition LPS TLR4 NF-κB Pro-inflammatory gene expression IL1/TNF Acceleration Receptor for LPS from gram negative bacteria kills 600,000 people per year in Europe (septic shock 50% mortality) Most powerful immune response stimulator (half of immunology!) Implicated in many inflammatory pathologies, for example 28 TLRs in disease: allergy House dust mite allergen (Der p2) induces asthma via TLR4 triggering of airway structural cells; Hammad H et al., Nat Med (2009) 15, TLR4-MAPK-NF-κB interaction network 30 10
11 Golgi Recycling if empty of ligand TLR4 subcellular signalling LPS Plasma membrane PIP2 Mal MyD88 NF-κB No PIP2 Myr Tram Early endosome EEA1 Late endosome Rab7 E.R. Myr Tram Trif Myr Tram TAG Myr Tram TAG 31 IRF3 OFF Degraded TLR9 subcellular signalling DNA Plasma membrane DNA phagosome E.R. Unc93b Golgi endolysosome DNA MyD88 TLR9 cleaved (active) 32 Ewald SE et al., (2008) Nature 456, NF-κB 33 Summary Innate immunity involves at least 7 families of receptors for microbial products TLRs are the founder family and are involved in recognition of most pathogens NLRs, RLRs and CLRs are also very important, with respective roles in Summary anti-bacterial, anti-viral and anti-fungal responses Complex signalling pathways are activated by each family, leading to induction of host defense effector mechanisms There is great therapeutic potential in the targeting of these receptors for immune and inflammatory diseases 11
12 34 12
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Basic immunology. Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
MICR2209. Innate Immunity. Dr Allison Imrie
 MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 3: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Introduction to Toll-like
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 3: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Introduction to Toll-like
The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition
 International Immunology, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 317 337 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp017 ª The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2009. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
International Immunology, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 317 337 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp017 ª The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2009. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis
 The Open Inflammation Journal, 2011, 4, (Suppl 1-M5) 31-48 31 Open Access Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley Doughty* Division of Critical
The Open Inflammation Journal, 2011, 4, (Suppl 1-M5) 31-48 31 Open Access Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley Doughty* Division of Critical
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
1. TLR. TLR Toll-like receptors. Toll Toll-like receptor, TLR TLR TLR TLR. type I TLR TLR. Toll
 54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
State of the Art. Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung CONTENTS AT A GLANCE COMMENTARY 1.
 State of the Art Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung Bastian Opitz 1, Vincent van Laak 1, Julia Eitel 1, and Norbert Suttorp 1 1 Department of Internal Medicine/Infectious
State of the Art Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung Bastian Opitz 1, Vincent van Laak 1, Julia Eitel 1, and Norbert Suttorp 1 1 Department of Internal Medicine/Infectious
Inflammation - Molecular events
 Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection
 Viruses 2011, 3, 920-940; doi:10.3390/v3060920 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Review Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection Mikayla
Viruses 2011, 3, 920-940; doi:10.3390/v3060920 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Review Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection Mikayla
Relative sizes of infectious agents
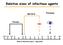 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Innate immunity. Monika Raulf. Lecture Tasks of the immune system. Body protection against damaging influences
 Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity
 Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Allergens as triggers of pattern recognition receptors. Marsha Wills-Karp Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Baltimore, MD
 Allergens as triggers of pattern recognition receptors Marsha Wills-Karp Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Baltimore, MD Allergic disorders are CD4+ Th2 Cell Driven IL-12 DC Allergens TSLP
Allergens as triggers of pattern recognition receptors Marsha Wills-Karp Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Baltimore, MD Allergic disorders are CD4+ Th2 Cell Driven IL-12 DC Allergens TSLP
The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors
 The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors Taro Kawai 1,2 & Shizuo Akira 1,2 The discovery of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) as components that recognize conserved
The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors Taro Kawai 1,2 & Shizuo Akira 1,2 The discovery of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) as components that recognize conserved
Test Bank for The Immune System 4th Edition by Parham
 Test Bank for The Immune System 4th Edition by Parham CHAPTER 3: INNATE IMMUNITY: THE INDUCED RESPONSE TO INFECTION 3 1 C-type lectins are so called because of the role of in facilitating receptor:ligand
Test Bank for The Immune System 4th Edition by Parham CHAPTER 3: INNATE IMMUNITY: THE INDUCED RESPONSE TO INFECTION 3 1 C-type lectins are so called because of the role of in facilitating receptor:ligand
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS
 Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections
 REVIEW Andrea K. PERRY et al The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections Andrea K. PERRY 1*, Gang CHEN 2,*, Dahai ZHENG 2,*, Hong TANG 2, Genhong CHENG 1,2,** 1 Department of
REVIEW Andrea K. PERRY et al The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections Andrea K. PERRY 1*, Gang CHEN 2,*, Dahai ZHENG 2,*, Hong TANG 2, Genhong CHENG 1,2,** 1 Department of
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Eat Dirt: Why Cleanliness is Bad for Asthma
 Eat Dirt: Why Cleanliness is Bad for Asthma Joel N. Kline MD MSc Professor, Pulmonary Medicine Director: UI Adult Asthma Center Director, Clinical Research ICTS University of Iowa Iowa City, IA 1 Disclosures:
Eat Dirt: Why Cleanliness is Bad for Asthma Joel N. Kline MD MSc Professor, Pulmonary Medicine Director: UI Adult Asthma Center Director, Clinical Research ICTS University of Iowa Iowa City, IA 1 Disclosures:
PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of TLR-4. By Christina, Ania and Xiaofu
 PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of TLR-4 By Christina, Ania and Xiaofu Introduction Macrophage PAMP Bacteria LPS Gram -ve LTA Gram +ve activation Clearance Macrophage PAMP Bacteria
PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of TLR-4 By Christina, Ania and Xiaofu Introduction Macrophage PAMP Bacteria LPS Gram -ve LTA Gram +ve activation Clearance Macrophage PAMP Bacteria
Role of TLR- / NLR-signaling and the associated cytokines involved in recruitment of neutrophils in murine models of Staphylococcus aureus infection
 Virulence ISSN: 2150-5594 (Print) 2150-5608 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/kvir20 Role of TLR- / NLR-signaling and the associated cytokines involved in recruitment of neutrophils
Virulence ISSN: 2150-5594 (Print) 2150-5608 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/kvir20 Role of TLR- / NLR-signaling and the associated cytokines involved in recruitment of neutrophils
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官. The Immune System. KE, Yuehai 柯越海. Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院
 生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官 The Immune System KE, Yuehai 柯越海 Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院 Outlines The Immune System 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Immune
生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官 The Immune System KE, Yuehai 柯越海 Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院 Outlines The Immune System 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Immune
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER. Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma
 INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
A Tale of Two SNPS: Polymorphism Analysis of Toll-like Receptor (TLR) Adapter Proteins: A Dissertation
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms GSBS Dissertations and Theses Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 5-16-2011 A Tale of Two SNPS: Polymorphism Analysis of Toll-like Receptor
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms GSBS Dissertations and Theses Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 5-16-2011 A Tale of Two SNPS: Polymorphism Analysis of Toll-like Receptor
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Effect of Mold Constituents on
 Effect of Mold Constituents on Innate Immune Responses (Alphabet Soup for Fungal Exposure) Charles S. Barnes, Ph.D. Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics The Fungal (fifth) Kingdom Fungi include mold,
Effect of Mold Constituents on Innate Immune Responses (Alphabet Soup for Fungal Exposure) Charles S. Barnes, Ph.D. Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics The Fungal (fifth) Kingdom Fungi include mold,
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Interferon Induction by RNA Viruses and Antagonism by Viral Pathogens
 Viruses 2014, 6, 4999-5027; doi:10.3390/v6124999 Review OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Interferon Induction by RNA Viruses and Antagonism by Viral Pathogens Yuchen Nan
Viruses 2014, 6, 4999-5027; doi:10.3390/v6124999 Review OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Interferon Induction by RNA Viruses and Antagonism by Viral Pathogens Yuchen Nan
Innate Immunity in Transplantation. Innate and Adapative Immunity
 Innate Immunity in Transplantation M. Sue Leffell, PhD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Innate and Adapative Immunity Innate or natural defense mechanisms phylogenetically older; present in
Innate Immunity in Transplantation M. Sue Leffell, PhD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Innate and Adapative Immunity Innate or natural defense mechanisms phylogenetically older; present in
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription (-) TLR2 PGN MDP. MyD88 IRAK ECSIT TRAF6 NIK. Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IKK.
 D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Immunity to Microbes. Cellular and Molecular Immunology (7 th : Chap 15)
 Immunity to Microbes Cellular and Molecular Immunology (7 th : Chap 15) Infection Entry of the microbe Invasion and colonization of host tissues, Evasion of host immunity Tissue injury or functional impairment
Immunity to Microbes Cellular and Molecular Immunology (7 th : Chap 15) Infection Entry of the microbe Invasion and colonization of host tissues, Evasion of host immunity Tissue injury or functional impairment
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Innate Immunity Depends on Toll-Like Receptors
 Innate Immunity Depends on Toll-Like Receptors From flies to mammals, these proteins provide a first-line defense and are implicated in infectious and autoimmune diseases William Check omething about the
Innate Immunity Depends on Toll-Like Receptors From flies to mammals, these proteins provide a first-line defense and are implicated in infectious and autoimmune diseases William Check omething about the
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Immunology: an overview Lecture
 Slide #2: Immunology is sometimes regarded as part of microbiology department because it started there as an investigation of ways used to prevent against infectious agents (e.g. microorganisms ). However
Slide #2: Immunology is sometimes regarded as part of microbiology department because it started there as an investigation of ways used to prevent against infectious agents (e.g. microorganisms ). However
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Where are we heading?
 Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Two signal models in innate immunity
 Mary F. Fontana Russell E. Vance Two signal models in innate immunity Authors address Mary F. Fontana 1, Russell E. Vance 1 1 Division of Immunology & Pathogenesis, Department of Molecular & Cell Biology,
Mary F. Fontana Russell E. Vance Two signal models in innate immunity Authors address Mary F. Fontana 1, Russell E. Vance 1 1 Division of Immunology & Pathogenesis, Department of Molecular & Cell Biology,
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Microbial recognition and the immune response Dr. Dana Philpott
 Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Nucleic Acid Detection in Anti-Viral Responses and Autoimmunity
 Nucleic Acid Detection in Anti-Viral Responses and Autoimmunity Rebecca Lynn Brunette A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy University
Nucleic Acid Detection in Anti-Viral Responses and Autoimmunity Rebecca Lynn Brunette A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy University
Overview: The immune responses of animals can be divided into innate immunity and acquired immunity.
 GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately
 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity. Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity)
 Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity) : ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY: AN OVERVIEW OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Adaptive Immunity
Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity) : ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY: AN OVERVIEW OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Adaptive Immunity
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Innate pathogen recognition in the kidney: Toll-like receptors, NOD-like receptors, and RIG-like helicases
 BACTERIAL WALL COMPONENTS A group of cell surface TLRs and cytosolic NLRs recognize bacterial cell wall components (Table 1). A major cell wall component of all bacteria is peptidoglycan (PG), whereas
BACTERIAL WALL COMPONENTS A group of cell surface TLRs and cytosolic NLRs recognize bacterial cell wall components (Table 1). A major cell wall component of all bacteria is peptidoglycan (PG), whereas
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Defense mechanism against pathogens
 Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
In other words. how to prevent David from killing Goliath. Tammy Rickabaugh, Ph.D. January 14, 2014
 In other words. how to prevent David from killing Goliath Tammy Rickabaugh, Ph.D. January 14, 2014 2011 Nobel Prize in Medicine IMMUNOLOGISTS!!!!!!! Bruce A. Beutler Jules A. Hoffman Ralph M. Steinman
In other words. how to prevent David from killing Goliath Tammy Rickabaugh, Ph.D. January 14, 2014 2011 Nobel Prize in Medicine IMMUNOLOGISTS!!!!!!! Bruce A. Beutler Jules A. Hoffman Ralph M. Steinman
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation
 Leading Edge Review Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation Osamu Takeuchi 1,2 and Shizuo Akira 1,2, * 1 Laboratory of Host Defense, WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center 2 Research Institute
Leading Edge Review Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation Osamu Takeuchi 1,2 and Shizuo Akira 1,2, * 1 Laboratory of Host Defense, WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center 2 Research Institute
TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Kingston H.G. Mills
 TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity Kingston H.G. Mills Immunology Research Centre and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland Abstract Autoimmune disease can
TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity Kingston H.G. Mills Immunology Research Centre and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland Abstract Autoimmune disease can
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
