MRI identifies plantar plate pathology in the forefoot of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Cora Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
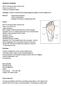
1 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: DOI /s ORIGINAL ARTICLE MRI identifies plantar plate pathology in the forefoot of patients with rheumatoid arthritis Heidi J. Siddle & Richard J. Hodgson & Anthony C. Redmond & Andrew J. Grainger & Richard J. Wakefield & David A. Pickles & Elizabeth M. A. Hensor & Philip S. Helliwell Received: 7 September 2011 / Revised: 10 November 2011 / Accepted: 20 November 2011 / Published online: 7 December 2011 # The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract Previous cadaveric studies have suggested that forefoot deformities at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) might result from the failure of the ligamentous system and displacement of the plantar plates. This study aimed to examine the relationship between plantar plate pathology and the rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAM- RIS) of the lesser (second to fifth) MTP joints in patients with RA using high-resolution 3 T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In 24 patients with RA, the forefoot was imaged using 3 T MRI. Proton density fat-suppressed, T2- weighted fat-suppressed and T1-weighted post gadolinium sequences were acquired through 96 lesser MTP joints. H. J. Siddle (*) : A. C. Redmond : R. J. Wakefield : E. M. A. Hensor : P. S. Helliwell Division of Musculoskeletal Disease, Leeds Institute of Molecular Medicine, University of Leeds, 2nd Floor Chapel Allerton Hospital, Chapeltown Road, Leeds LS7 4SA, UK h.siddle@leeds.ac.uk R. J. Hodgson : A. C. Redmond : A. J. Grainger : R. J. Wakefield NIHR Leeds Musculoskeletal Biomedical Research Unit, Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Chapel Allerton Hospital, Chapeltown Road, Leeds LS7 4SA, UK A. J. Grainger Department of Radiology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Chapel Allerton Hospital, Chapeltown Road, Leeds LS7 4SA, UK D. A. Pickles Department of Rheumatology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Chapel Allerton Hospital, Chapeltown Road, Leeds LS7 4SA, UK Images were scored for synovitis, bone marrow oedema and bone erosion using the RAMRIS system and the plantar plates were assessed for pathology. Seventeen females and 7 males with a mean age of 55.5 years (range 37 71) and disease duration of 10.6 years (range ) took part in the study. Plantar plate pathology was most frequently demonstrated on MRI at the fifth MTP joint. An association was demonstrated between plantar plate pathology and RAMRIS-reported synovitis, bone marrow oedema and bone erosion at the fourth and fifth MTP joints. In patients with RA, 3 T MRI demonstrates that plantar plate pathology at the lesser MTP joints is associated with features of disease severity. Plantar plate pathology is more common at the fourth and fifth MTP joints in subjects with RA in contrast to the predilection for the second MTP reported previously in subjects without RA. Keywords Forefoot. Magnetic resonance imaging. Metatarsophalangeal joint. Plantar plate. RAMRIS. Rheumatoid arthritis Introduction The foot is commonly involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), particularly at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints [1, 2]. On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) synovitis, erosion and bone oedema are well recognised in the foot but the plantar plate is seldom routinely visualised. In RA the function of the plantar plate in forefoot deformity is poorly understood. The plantar plate (Fig. 1) is the major distal attachment of the plantar fascia, inserting into the proximal phalanx. Proximally it attaches to the metatarsal shaft with the two collateral ligaments providing the most substantial attachment of
2 622 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: Fig. 1 a Sagittal illustration through the lesser MTP joint, the plantar plate (short arrow) inserts into the proximal phalanx (P) and the flexor tendon (long arrow) lies adjacent to the plantar plate. b Short axis illustration through the forefoot, proximally the plantar plate (PP) attaches to the metatarsal shaft (MT) with the two collateral ligaments (CL) providing the most substantial attachment of the plantar plate to the metatarsal. The dorsal interosseous tendon (I) with the accessory CL insert into the dorsal aspect of the plantar plate. The flexor tendon sheath (FT) lies immediately plantar to the plantar plate and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament (TML) runs between the metatarsals attaching to the plantar plates the plantar plate to the metatarsal. The flexor tendon sheath, which encompasses the flexor digitorum longus and brevis tendons lies immediately plantar to the plantar plate and is adherent to the outer borders of the plantar surface of the plate. The plate is a fibrocartilaginous structure which together with the deep transverse metatarsal ligament has an important role in maintaining the structural integrity of the MTP joints [3]. During walking, the forces imposed as the toes push off cause repeated hyperextension of the MTP joint, and it has been postulated that this may predispose the plantar plates to attenuation or rupture [3]. Degeneration or loss of function of the plantar plate is a potential mechanism through which the characteristic forefoot deformity may develop in patients with RA.
3 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: Cadaveric studies of the feet in RA have suggested that forefoot deformities in RA might result from failure of the complex ligamentous system and the dynamic effect of displacement of the plantar plates [4]. However, the structures involved, the potential mechanisms by which changes occur and the relationship between synovial, bone and plantar plate abnormalities have not been clearly identified in patients with RA. MRI has been used to identify the plantar plate and visualise tears in normal subjects [5] but has not been used at high field strengths to image the plantar plate in patients with RA. The rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS) allows semiquantative, standardised assessment of inflammatory and destructive changes in RA [6, 7] and has excellent interreader and intrareader reliability in the assessment of the forefoot (MTP joints) in patients with RA [8]. Furthermore the relationship between plantar plate pathology, synovitis and bone change in patients with RA has not been reported previously. The aim of this study was to use MRI to investigate the relationship between plantar plate pathology and RAMRIS in the lesser (second to fifth) MTP joints in patients with RA. Materials and methods Recruitment of patients Local ethical approval was received and written consent obtained from all participants. Consecutive patients diagnosed with RA, according to the 1987 American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for RA [9] (data were acquired prior to 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria [10]), and presenting to a specialist rheumatology foot clinic were invited to take part in the study. Patients were recruited between August and December The first MTP joint was not studied because of the different anatomy and pattern of pathological changes compared to the lesser MTP joints. Patients were excluded if they had a diagnosis of diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, peripheral neuropathy, a history of forefoot surgery or contraindications to having a MRI scan or intravenous contrast. Clinical measures Demographic data and current medication were recorded for each patient. In order to quantify current disease activity, a disease activity score (DAS 44) which includes the MTP joints was used. A tender and swollen joint count was performed by an experienced research nurse (DAP) and inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)) were obtained in order to establish a current disease activity score (DAS 44 (CRP) and DAS 44 (ESR)). Platto s Structural Index was completed to assess the forefoot structural deformity present [11], the index score includes the presence or absence of hallux valgus and fifth MTP joint exostosis, and the number of cock/hammer/claw toes present (0 5) and subluxed MTP joints (0 5). MRI protocol The forefoot was imaged using a 3-T Verio scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with an extremity radio frequency coil. Intermediate-weighted fat-suppressed sagittal (Fast spin echo, repetition time (TR) 03,500 ms, echo time (TE) ms, mm in-plane resolution, 3 mm slice thickness) and T2-weighted fat-suppressed short and long axis images (Fast spin echo, TR03,100 4,300 ms, TE ms, mm in-plane resolution, 3 mm slice thickness) were acquired through the lesser MTP joints. 3D VIBE post contrast images (TR09 ms, TE=5 ms, flip-angle=30degrees, mm resolution) were acquired after the administration of 0.1 mmol/kg intravenous contrast agent (Gd-DOTA, Guerbert, France) together with pre and post contrast T1 weighted fat-supressed images (spin-echo, TR=900 ms, TE=16ms, mm inplane resolution) if the patient was able to tolerate further time in the scanner. Images were scored for synovitis (0 3), bone marrow oedema (0 3) and bone erosion (0 10) at each lesser MTP joint, respectively (Fig. 2), using the RAMRIS defined by the outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials group [6 8]. RAMRIS has demonstrated excellent reliability in assessment of the forefoot in patients with RA [8]. Plantar plate pathology (Figs. 3 and 4) was defined from sagittal and axial MR images as the absence of (failure to visualise) the plantar plate, or a full-width or partial-width tear, including failure to visualise the medial or lateral distal insertions. MR images were read by two experienced musculoskeletal radiologists (RJH and AJG) and consensus was reached. Statistical methods In order to identify associations between RAMRIS and the odds of plantar plate pathology at the lesser MTP joints in patients with RA, proximal and distal bone oedema scores and proximal and distal bone erosion scores were summated to give a total bone oedema score and a total bone erosion score per lesser MTP joint. These were then coded into three score categories (0, 1 and >2). Comparison of a multilevel model containing only plantar plate pathology status and controlling for clustering at the patient level with a singlelevel model that did not control for clustering gave some indication that substantive cluster effects were present,
4 624 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: Fig. 2 Images through the MTP joints of a patient with RA showing synovitis, bone marrow oedema and bone erosion. a Long axis T2-weighted fatsuppressed image showing extensive bone marrow oedema (white arrows). b Sagittal post contrast T1-weighted image showing synovitis (black arrow). The plantar plate is absent and synovitis extends from the joint to the flexor tendon. c Long axis and d short axis reconstructions from T1-weighted post contrast 3D VIBE images, again showing synovitis (black arrows) and erosion of the metatarsal heads (black arrowheads) given that the sample size was small and the likelihood ratio test is conservative (chi-bar02.07, p00.075). Therefore, multilevel modelling was used to explore the association between RAMRIS and the odds of plantar plate pathology. Multilevel binary logistic regression models were constructed in which plantar plate pathology was the outcome and either the synovitis, bone oedema or bone oedema score was the primary predictor at the joint level. Odds ratios were also calculated for the third to fifth MTP joints relative to the second MTP joint. The forefoot Platto Structural Index score was included as a patient (foot)-level contextual factor. Results Demographic and disease characteristics Twenty-seven patients were approached to take part in the study; 24 patients with RA (17 females and 7 males) met the inclusion criteria and took part in the study. Patients mean (SD) age was 55.5 (10.5) (range 37 71) years and disease duration was 10.6 (8.6) (range ) years. Eighteen patients were rheumatoid factor positive, the mean (SD) DAS44 (CRP) and DAS44 (ESR) were 2.5 (0.8) and 2.6 (0.9), respectively. Twenty-three patients were taking a disease modifying antirheumatic drug, 15 patients (63%) were taking a biologic therapy and 1 patient was taking oral steroids. The median (range) forefoot Platto Structural Index score was 8.0 (2 12). There was some evidence that MTP joints from feet with a forefoot Platto Structural Index scores above the median of the distribution (>8) were more likely to show plantar plate pathology [24/48 (50.0%)] than those from feet with lower scores [14/48 (29.2%)]. Platto index ( 8, >8) was therefore included in each multilevel model as a level 2 contextual factor. No statistically significant associations were found between forefoot Platto Structural Index score and plantar plate pathology. Plantar plate pathology seen on MRI At the patient level, one or more lesser plantar plates were absent in nine (38%) patients. All the lesser plantar plates
5 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: Fig. 3 a Sagittal intermediateweighted and b short axis T1- weighted fat suppressed images through the second MTP joint of a patient with RA showing an intact plantar plate (arrow), deep to the flexor tendon (long arrow). Small amount of high signal is seen at the insertion of the plantar plate into the proximal phalanx centrally (arrowhead), a common finding. (Cystic change is noted in first metatarsal head). c Sagittal intermediate-weighted and d short axis T2-weighted fatsuppressed images through the second MTP joint of a patient with RA. There is dislocation of the joint and the plantar plate is not visualised. There is bone marrow oedema (open arrow). On short axis section, fluid can be seen tracking from the joint around the flexor tendon sheath (arrow) were absent in one patient. Tears in one or more lesser plantar plates were identified in 14 (58%) patients. At the joint level, 16/96 (17%) plantar plates were absent and tears were observed in 22 (28%) of the 80 remaining plantar plates. All tears were located distally in the plantar plates. Five (23%) were full-width tears and the majority (94%) of partial tears were situated on the medial aspect of the plantar plate. Table 1 shows the number of patients with plantar plate, bone and synovial pathology at each lesser MTP joint. The fifth MTP joint was the most common site for all types of pathology. The associations between plantar plate pathology and features of RA disease at each lesser MTP joint are given in Table 2. RAMRIS synovitis and plantar plate pathology No substantive or statistically significant interactions were found between the RAMRIS synovitis categories and the four lesser MTP joints, indicating that the association between plantar plate pathology and RAMRIS synovitis score category was consistent across the four lesser MTP joints (and vice versa). Plantar plate pathology was more prevalent in the fourth MTP joint [OR09.44 (1.55 to 57.53), p00.015] and fifth MTP joint [OR (4.31 to ), p00.001] relative to the second MTP joint but the third MTP joint did not significantly differ from the second MTP joint [OR (0.30 to. 9.77), p00.538]. The odds of plantar plate pathology were increased in joints with synovitis grade 2 or above relative to those where synovitis was absent [OR (1.01 to ), p00.049] but odds for joints with grade 1 synovitis did not differ to a statistically significant degree [OR06.07 (0.72 to 51.12), p00.097]. The model as a whole was significantly better than the null model (Wald chi-square015.18, p00.019). RAMRIS bone oedema and plantar plate pathology No substantive or statistically significant interactions were found between MTP joint and the RAMRIS bone oedema categories and the four lesser MTP joints, indicating that the differences in prevalence of plantar plate pathology across the MTP joints were consistent. It also indicated that the association between plantar plate pathology and RAMRIS bone oedema score category was consistent across the four lesser MTP joints (and vice versa). Within any given bone oedema score, plantar plate pathology was more prevalent at the fourth MTP joint [OR (1.57 to 81.74), p00.016] and the fifth MTP joint [OR (3.96 to ), p ] compared to the second MTP joint. However, plantar
6 626 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: Fig. 4 a and b (adjacent slices) Sagittal intermediate-weighted, c short axis T2-weighted fatsuppressed and d short axis T1 fat suppressed images through the second MTP joint demonstrating atear(between arrowheads) of the plantar plate (arrow). The flexor tendon (long arrow) is adjacent to the bone distally without interposed plantar plate. There is extensive bone marrow oedema (open arrow) plate pathology was not significantly more prevalent at the third MTP joint [OR02.47 (0.40 to 15.41), p00.332]. In any given lesser MTP joints, odds of plantar plate pathology were increased in joints with bone oedema score of 2 or above [OR09.86 (1.61 to 60.40), p00.013] relative to those where bone oedema was absent (score 0). MTP joints with a score of 1 did not differ significantly [OR02.04 (0.30 to 13.98), p00.469]. The model as a whole was significantly better than the null model (Wald Chi-square014.07, p ). RAMRIS bone erosion and plantar plate pathology No substantive or statistically significant interactions were found between MTP joint and the RAMRIS erosion categories. At any given erosion category, plantar plate pathology was more prevalent at the fourth MTP joint [OR (2.21 to ), p00.009] and fifth MTP joint [OR (4.84 to ), p00.002] compared to the second MTP joint. However, plantar plate pathology was not significantly more prevalent at the third MTP joint [OR01.75 Table 1 Number of patients with pathology at each lesser MTP joint (n024 patients, n096 joints) MTP 2 MTP 3 MTP 4 MTP 5 Total N of PP absent N of PP tears Synovitis Bone oedema (proximal) Bone oedema (distal) Bone erosion (proximal) Bone erosion (distal)
7 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: Table 2 Associations between plantar plate pathology and features of RA disease at the lesser MTP joints RAMRIS n (%) with plantar plate pathology Adjusted OR (95% CI) p Synovitis Platto score 8 14/48 (29.2%) Reference >8 24/48 (50.0%) 4.88 (0.65 to 36.33) Synovitis Absent (0) 6/24 (25.0%) Reference Score 1 24/59 (40.7%) 6.07 (0.72 to 51.12) Score 2 8/13 (61.5%) (1.01 to ) MTP 2 4/24 (16.7%) Reference 3 6/24 (25.0%) 1.72 (0.30 to 9.77) /24 (45.8%) 9.44 (1.55 to 57.53) /24 (70.8%) (4.31 to ) Bone oedema Platto score 8 14/48 (29.2%) Reference >8 24/48 (50.0%) 3.16 (0.55 to 18.19) Oedema Absent (0) 4/30 (13.3%) Reference Score 1 9/22 (40.9%) 2.04 (0.30 to 13.98) Score 2 25/44 (56.8%) 9.86 (1.61 to 60.40) MTP 2 4/24 (16.7%) Reference 3 6/24 (25.0%) 2.47 (0.40 to 15.41) /24 (45.8%) (1.57 to 81.74) /24 (70.8%) (3.96 to ) Bone erosion Platto score 8 14/48 (29.2%) Reference >8 24/48 (50.0%) 6.14 (0.67 to 56.31) Erosion Absent (0) 3/28 (10.7%) Reference Score 1 6/22 (27.3%) (1.18 to ) Score 2 29/46 (63.0%) (6.19 to ) MTP 2 4/24 (16.7%) Reference 3 6/24 (25.0%) 1.75 (0.25 to 12.15) /24 (45.8%) (2.21 to ) /24 (70.8%) (4.84 to ) (0.25 to 12.15), p00.572]. Odds of plantar plate pathology were increased in joints with an erosion score of 1 [OR (1.18 to ), p00.037] or 2 or more [OR (6.19 to ), p00.001] relative to those where erosions absent (score 0). The model as a whole performed significantly better than the null model (Wald chi-square013.02, p00.043). Discussion This is the first exploratory study to use MRI to investigate plantar plate pathology at the lesser MTP joints in patients with RA. The study has demonstrated that plantar plate pathology is common in RA and provides evidence for an association with synovitis, bone oedema and bone erosion at the lesser MTP joints. Patients with RA and RAMRIS-reported synovitis, bone oedema and bone erosion were more likely to have plantar plate pathology present at the fourth and fifth MTP joints compared to the second MTP joint. This is supported by the frequency of plantar plate pathology seen at the fifth MTP joint, known to be the commonest site of erosive change in the forefoot [12 14]. The current findings are in contrast to previous studies of plantar plates of healthy subjects in which plantar plate tears have been reported to most commonly occur at the second MTP joint, with significantly fewer being reported in the fifth plantar plate [15]. Furthermore, the odds of plantar plate pathology were increased in joints with synovitis and bone oedema score 2 or above and with erosions score 1 or greater, relative to those where RAMRIS scores were 0. The plantar plate is a complex structure and in previous studies visualisation has been limited by the spatial resolution obtained [5]. This study used 3 T MRI with an
8 628 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: optimised protocol and careful positioning of the MTP joints to allow better visualisation of the plantar plates and more sensitive differentiation of pathology [16]. In this cohort of patients with a relatively low disease activity (DAS ), it appears that plantar plate pathology may be associated with current synovitis at the fourth and fifth MTP joints. However, only joints with a synovitis score of 2 or more had significantly higher odds of plantar plate pathology relative to joints without synovitis. This is not surprising as severity of synovitis may increase and decrease over time [17] while this study assesses synovitis at a single time point, providing no estimate of the average level of synovitis over time. This study suggests the possibility that plantar plate pathology could have been caused by higher levels of synovitis in the past, as has been suggested as a mechanism for bone erosion [18]. This study has not demonstrated an association between plantar plate pathology and forefoot deformity, measured using the forefoot Platto Structural Index. However, Platto s Structural index incorporates deformity at the first MTP joint, which was excluded in the assessment of plantar plate pathology. Furthermore, the Platto Index is a clinicianreported, subjective measurement and therefore potential for error occurs, particularly in reporting of subluxation at the MTP joints. The results of this study are limited by the relatively small sample size (n024) (and resulting large confidence intervals for the odds ratios). However, the patient demographics and disease characteristics are typical of this population of patients [19]. The small numbers in this study limited the ability to conduct a full multivariable analysis. As such it was not possible to evaluate whether RAMRISreported synovitis, bone oedema and bone erosion were related to plantar plate pathology independently of each other. Plantar plate pathology appears common in this group of patients with RA presenting to a specialist rheumatology foot clinic (79.2% of patients), raising the possibility that plantar plate pathology may contribute to pain at the lesser MTP joints [4]. This study did not assess the relationship between forefoot pain and plantar plate pathology, and therefore further work is needed to establish whether there is a correlation between pain at individual MTP joints and plantar plate pathology at the same joint. Although the results suggest an association between bone oedema and erosion and plantar plate pathology, no causative mechanism for this can be inferred from this crosssectional study. It may be that altered biomechanics or mechanical effects due to plantar plate abnormalities cause bone changes such as oedema. Alternatively, bone irregularity due to erosion may lead to plantar plate tears. Another possible explanation could be the existence of a common cause for both bone and plantar plate pathology, such as past synovitis. Longitudinal follow-up studies of patients with RA and forefoot pain and deformity would help elucidate this. However, the current work will allow formal powering of larger studies to further investigate the role of the plantar plate in forefoot pain and disease progression in RA. In conclusion, in this small exploratory study, plantar plate pathology appears to be associated with RAMRISreported synovitis, bone oedema and bone erosions at the lesser MTP joints of patients with RA. Plantar plate pathology was more common at the fourth and fifth MTP joints in people with RA, in contrast to the predilection for the second MTP reported previously in people without RA [15]. Refined MRI protocols allow for improved assessment of the progression of plantar plate pathology and should underpin future longitudinal studies. Acknowledgments The authors would like to thank Carole Burnett and Robert Evans from the NIHR Leeds Musculoskeletal Biomedical Research Unit for conducting the patient MRIs and William Davys for producing the illustrations in Fig. 1. HJS is funded by Arthritis Research UK (grant reference number 18007). Disclosures None. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited. References 1. Vidigal E, Jacoby RK, Dixon AS, Ratliff AH, Kirkup J (1975) The foot in chronic rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 34(4): Grondal L, Tengstrand B, Nordmark B, Wretenberg P, Stark A (2008) The foot: still the most important reason for walking incapacity in rheumatoid arthritis: distribution of symptomatic joints in 1,000 RA patients. Acta Orthop 79(2): Johnston RB 3rd, Smith J, Daniels T, Johnston RB 3rd, Smith J, Daniels T (1994) The plantar plate of the lesser toes: an anatomical study in human cadavers. Foot Ankle Int 15(5): Stainsby GD (1997) Pathological anatomy and dynamic effect of the displaced plantar plate and the importance of the integrity of the plantar plate-deep transverse metatarsal ligament tie-bar. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 79(1): Yao L, Do HM, Cracchiolo A, Farahani K, Yao L, Do HM, Cracchiolo A, Farahani K (1994) Plantar plate of the foot: findings on conventional arthrography and MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 163(3): Ostergaard M, Peterfy C, Conaghan P, McQueen F, Bird P, Ejbjerg B, Shnier R, O Connor P, Klarlund M, Emery P, Genant H, Lassere M, Edmonds J (2003) OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol 30: Ostergaard M, Edmonds J, McQueen F, Peterfy C, Lassere M, Ejbjerg B, Bird P, Emery P, Genant H, Conaghan P (2005) An
9 Clin Rheumatol (2012) 31: introduction to the EULAR-OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 1):i3 i7 8. Baan H, Bezooijen R, Avenarius JK, Dubbeldam R, Drossaers- Bakker WK, van de Laar MA (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging of the rheumatic foot according to the RAMRIS system is reliable. J Rheumatol 38(6): Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3): Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Menard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovsky J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 69(9): Platto MJ, O Connell PG, Hicks JE, Gerber LH (1991) The relationship of pain and deformity of the rheumatoid foot to gait and an index of functional ambulation. J Rheumatol 18 (1): Hulsmans HM, Jacobs JW, van der Heijde DM, van Albada-Kuipers GA, Schenk Y, Bijlsma JW (2000) The course of radiologic damage during the first six years of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43 (9): Boutry N, Lardé A, Lapegue F, Solau-Gervais E, Flipo RM, Cotten A (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging appearance of the hands and feet in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 30 (4): van der Leeden M, Steultjens MP, Ursum J, Dahmen R, Roorda LD, Schaardenburg DV, Dekker J (2008) Prevalence and course of forefoot impairments and walking disability in the first eight years of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59(11): Gregg J, Silberstein M, Schneider T, Marks P (2006) Sonographic and MRI evaluation of the plantar plate: a prospective study. Eur Radiol 16(12): Siddle HJ, Redmond AC, Helliwell PS, Wakefield RJ, O Connor PJ, Hodgson RJ (2010) High resolution MRI of asymptomatic plantar plate under flexion and extension: implications for understanding normal structure and diagnosing tears. Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB 2010, Stockholm, Sweden 17. Verstappen SM, Poole AR, Ionescu M, King LE, Abrahamowicz M, Hofman DM, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP (2006) Radiographic joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with differences in cartilage turnover and can be predicted by serum biomarkers: an evaluation from 1 to 4 years after diagnosis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(1):R Jansen LM, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van Schaardenburg D, Bezemer PD, Dijkmans BA (2001) Predictors of radiographic joint damage in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 60(10): Symmons D, Turner G, Webb R, Asten P, Barrett E, Lunt M, Scott D, Silman A (2002) The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United Kingdom: new estimates for a new century. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41(7):
The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint
 i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
Sewerin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:104
 Sewerin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:104 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Advantages of a combined rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS) for hand and feet: does the
Sewerin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:104 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Advantages of a combined rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS) for hand and feet: does the
This is a repository copy of The prevalence of tenosynovitis of the interosseous tendons of the hand in patients with rheumatoid arthritis..
 This is a repository copy of The prevalence of tenosynovitis of the interosseous tendons of the hand in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/0/
This is a repository copy of The prevalence of tenosynovitis of the interosseous tendons of the hand in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/0/
Numerous studies have demonstrated that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive for detection of
 Reducing Invasiveness, Duration, and Cost of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Omitting Intravenous Contrast Injection Does It Change the Assessment of Inflammatory and Destructive
Reducing Invasiveness, Duration, and Cost of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Omitting Intravenous Contrast Injection Does It Change the Assessment of Inflammatory and Destructive
What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis to predict rheumatoid arthritis development?
 Dakkak et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1845-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis
Dakkak et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1845-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis
S tructural joint damage, a major outcome in
 i3 An introduction to the EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas M Østergaard, J Edmonds, F McQueen, C Peterfy, M Lassere, B Ejbjerg, P Bird, P Emery, H Genant, P Conaghan... This
i3 An introduction to the EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas M Østergaard, J Edmonds, F McQueen, C Peterfy, M Lassere, B Ejbjerg, P Bird, P Emery, H Genant, P Conaghan... This
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System
 Precision. Insight. Innovation. White Paper: An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System At left: Volume of synovitis in the hand and wrist. Areas of enhancement
Precision. Insight. Innovation. White Paper: An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System At left: Volume of synovitis in the hand and wrist. Areas of enhancement
Dynamic high-resolution ultrasound (DHRUS) and MRI of plantar plate: role in diagnostic iter
 Dynamic high-resolution ultrasound (DHRUS) and MRI of plantar plate: role in diagnostic iter Poster No.: C-1003 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Saporiti, S. Migone, V. Prono, R.
Dynamic high-resolution ultrasound (DHRUS) and MRI of plantar plate: role in diagnostic iter Poster No.: C-1003 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Saporiti, S. Migone, V. Prono, R.
Aoyagi, Kiyoshi; Eguchi, Katsumi; K
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Combination of MRI-detected bone ma arthritis classification criteria i rheumatoid arthritis Tamai, Mami; Kita, Junko; Nakashima Horai, Yoshiro; Okada,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Combination of MRI-detected bone ma arthritis classification criteria i rheumatoid arthritis Tamai, Mami; Kita, Junko; Nakashima Horai, Yoshiro; Okada,
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
Targeted Ultrasound of the Fifth Metatarsophalangeal Joint in an Early Inflammatory Arthritis Cohort
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 61, No. 7, July 15, 2009, pp 1004 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.24564 2009, American College of Rheumatology CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE FIELD Targeted Ultrasound
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 61, No. 7, July 15, 2009, pp 1004 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.24564 2009, American College of Rheumatology CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE FIELD Targeted Ultrasound
Early diagnosis of Rheumatoid
 26 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Detection of Destructive Changes in Small Joints of Hands in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
26 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Detection of Destructive Changes in Small Joints of Hands in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40654 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stomp, W. Title: MR imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis : techniques and applications
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40654 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stomp, W. Title: MR imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis : techniques and applications
Plantar forefoot pressures in psoriatic arthritis-related dactylitis: an exploratory study
 Clin Rheumatol (2016) 35:2333 2338 DOI 10.1007/s10067-016-3304-z BRIEF REPORT Plantar forefoot pressures in psoriatic arthritis-related dactylitis: an exploratory study Richard A. Wilkins 1,2 & Heidi J.
Clin Rheumatol (2016) 35:2333 2338 DOI 10.1007/s10067-016-3304-z BRIEF REPORT Plantar forefoot pressures in psoriatic arthritis-related dactylitis: an exploratory study Richard A. Wilkins 1,2 & Heidi J.
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months.
 Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Lesser MTP joints Arthroscopy: Anatomical Description and Comparative Dissection
 Lesser MTP joints Arthroscopy: Anatomical Description and Comparative Dissection Caio Nery, MD Michael Coughlin, MD Daniel Baumfeld, MD Fernando Raduan, MD Carla Chertman, MD Disclosure Caio Nery, M.D.
Lesser MTP joints Arthroscopy: Anatomical Description and Comparative Dissection Caio Nery, MD Michael Coughlin, MD Daniel Baumfeld, MD Fernando Raduan, MD Carla Chertman, MD Disclosure Caio Nery, M.D.
Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detected Tenosynovitis in the Hand and Wrist in Early Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 4, April 2015, pp 869 876 DOI 10.1002/art.39000 2015, American College of Rheumatology Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detected Tenosynovitis in the Hand
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 4, April 2015, pp 869 876 DOI 10.1002/art.39000 2015, American College of Rheumatology Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detected Tenosynovitis in the Hand
LESSER MTPJ INSTABILITY- SURGICAL OPTIONS REFERENCES
 LESSER MTPJ INSTABILITY- SURGICAL OPTIONS REFERENCES Prepared by: Richard T. Bouché, DPM Seattle, WA FDL TENDON TRANSFER -Iglesias MEL, Vallejo RB, Jules KT, et al.: Meta-analysis of flexor tendon transfer
LESSER MTPJ INSTABILITY- SURGICAL OPTIONS REFERENCES Prepared by: Richard T. Bouché, DPM Seattle, WA FDL TENDON TRANSFER -Iglesias MEL, Vallejo RB, Jules KT, et al.: Meta-analysis of flexor tendon transfer
Immanuel Krankenhaus Berlin, Medical Centre for Rheumatology Berlin - Buch; 2
 Low-field MRI versus ultrasound: which is more sensitive in detecting inflammation and bone damage in MCP and MTP joints in mild or moderate rheumatoid arthritis? W.A. Schmidt 1, B. Schicke 2, B. Ostendorf
Low-field MRI versus ultrasound: which is more sensitive in detecting inflammation and bone damage in MCP and MTP joints in mild or moderate rheumatoid arthritis? W.A. Schmidt 1, B. Schicke 2, B. Ostendorf
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Weil osteotomy and flexor to extensor transfer for irreparable plantar plate tear: prospective study
 Weil osteotomy and flexor to extensor transfer for irreparable plantar plate tear: prospective study Daniel Baumfeld, MD Fernando Raduan, MD Fernanda Catena, MD Tania Mann, MD Caio Nery, MD Disclosure
Weil osteotomy and flexor to extensor transfer for irreparable plantar plate tear: prospective study Daniel Baumfeld, MD Fernando Raduan, MD Fernanda Catena, MD Tania Mann, MD Caio Nery, MD Disclosure
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation. Disclosures. Outline. Joint Effusion. Suprapatellar recess
 Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
The new ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA: how are the new criteria performing in the clinic?
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2012;51:vi10 vi15 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes280 The new ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA: how are the new criteria performing in the clinic? Vivian P. Bykerk 1,2 and
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2012;51:vi10 vi15 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes280 The new ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA: how are the new criteria performing in the clinic? Vivian P. Bykerk 1,2 and
Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: AReview of MRI and Sonographic Findings
 outry et al. MRI and Sonography of Rheumatoid rthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Nathalie outry 1 Mélanie Morel 1 René-Marc Flipo 2 Xavier Demondion 1,3 nne Cotten 1 outry N, Morel M, Flipo
outry et al. MRI and Sonography of Rheumatoid rthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Nathalie outry 1 Mélanie Morel 1 René-Marc Flipo 2 Xavier Demondion 1,3 nne Cotten 1 outry N, Morel M, Flipo
Key Indexing Terms: PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OMERACT
 The OMERACT Psoriatic Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (PsAMRIS): Definitions of Key Pathologies, Suggested MRI Sequences, and Preliminary Scoring System for PsA Hands MIKKEL ØSTERGAARD,
The OMERACT Psoriatic Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (PsAMRIS): Definitions of Key Pathologies, Suggested MRI Sequences, and Preliminary Scoring System for PsA Hands MIKKEL ØSTERGAARD,
Early Diagnosis. Instability of the lesser MTP joints (Crossover 2 nd toe deformity) -my 25 year journey- Progressive MTP joint subluxation
 Instability of the lesser MTP joints (Crossover 2 nd toe deformity) -my 25 year journey- Conflicts of interest Arthrex- consultant Arthrex- royalties Elsevier-book royalties Michael J Coughlin, M.D. Early
Instability of the lesser MTP joints (Crossover 2 nd toe deformity) -my 25 year journey- Conflicts of interest Arthrex- consultant Arthrex- royalties Elsevier-book royalties Michael J Coughlin, M.D. Early
Burwood Road, Concord Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Turf Toe Injury By Todd Gothelf Foot, Ankle, Shoulder History
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Turf Toe Injury By Todd Gothelf Foot, Ankle, Shoulder History
17/10/2017. Foot and Ankle
 17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
PASIG MONTHLY CITATION BLAST: No.44 September 2009
 PASIG MONTHLY CITATION BLAST: No.44 September 2009 Dear PASIG members: Many of us have been busy conducting our annual pre-season screening of both professional and student dancers. Dance/USA now has over
PASIG MONTHLY CITATION BLAST: No.44 September 2009 Dear PASIG members: Many of us have been busy conducting our annual pre-season screening of both professional and student dancers. Dance/USA now has over
Case Iselin's disease in a Thai boxer.
 Case 13609 Iselin's disease in a Thai boxer. Joris De Win 1, 3, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 4, Els Goossens3 1: Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation; University Ghent (UGent), Belgium; Email:de_win_joris@hotmail.com
Case 13609 Iselin's disease in a Thai boxer. Joris De Win 1, 3, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 4, Els Goossens3 1: Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation; University Ghent (UGent), Belgium; Email:de_win_joris@hotmail.com
J. van Aken* H. van Dongen* S. le Cessie F.C. Breedveld T.W.J. Huizinga. * both authors contributed equally
 CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2978 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2978 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Role of Ultrasound and MRI in Detection of Hand and Wrist Joints Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Comparative Study
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, September: 615-620, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Ultrasound and MRI in Detection of Hand and Wrist Joints Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, September: 615-620, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Ultrasound and MRI in Detection of Hand and Wrist Joints Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients,
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Ankle Tendons in Athletes. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis W. Wojciechowski 1,2, Z. Tabor 3, A. Urbanik 2 1 Medical Centre
Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis W. Wojciechowski 1,2, Z. Tabor 3, A. Urbanik 2 1 Medical Centre
Patient Outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Patient Outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on patients quality of life A small qualitative study involving 25 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden looked at the
Patient Outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on patients quality of life A small qualitative study involving 25 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden looked at the
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS
 RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve. Lumbar radiculopathy Instability MTPJ joint or inflammatory MPJ
 MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
Disclosures. Ultrasonography. Conventional radiography (XR) Magnetic resonance imaging. Conventional CT 10/27/2013
 What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
 Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Impact of midfoot and Hindfoot involvement on functional disability in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Jeong et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:365 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1726-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Impact of midfoot and Hindfoot involvement on functional disability in Korean patients with rheumatoid
Jeong et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:365 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1726-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Impact of midfoot and Hindfoot involvement on functional disability in Korean patients with rheumatoid
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients
 Gout on CT: a symmetric arthropathy. Anthony J Doyle (corresponding author) Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients with gout using computed tomography (CT) and
Gout on CT: a symmetric arthropathy. Anthony J Doyle (corresponding author) Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients with gout using computed tomography (CT) and
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound
 Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Low field dedicated magnetic resonance imaging in untreated rheumatoid arthritis of recent onset
 770 Department of Internal Medicine C, Section of Rheumatology, Odense University, Denmark H Lindegaard P Junker Department of Radiology, Sønderborg Hospital J Vallø Graasten Gigthospital K Hørslev-Petersen
770 Department of Internal Medicine C, Section of Rheumatology, Odense University, Denmark H Lindegaard P Junker Department of Radiology, Sønderborg Hospital J Vallø Graasten Gigthospital K Hørslev-Petersen
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Ultrasound Versus MRI
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Rowbotham and Grainger Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Emma L. Rowbotham 1 Andrew J. Grainger Rowbotham EL, Grainger AJ Keywords: erosions,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Rowbotham and Grainger Imaging Rheumatoid Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Emma L. Rowbotham 1 Andrew J. Grainger Rowbotham EL, Grainger AJ Keywords: erosions,
Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging Studies
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Diagnostic values of DAS28 and DAS28-squeeze in evaluating Rheumatoid Arthritis disease
 Diagnostic values of DAS28 and DAS28-squeeze in evaluating Rheumatoid Arthritis disease David Santosa 1, Rudy Hidayat 2, Marcel Prasetyo, Pringgodigdo Nugroho 4 1 Departement, Medical Faculty of University
Diagnostic values of DAS28 and DAS28-squeeze in evaluating Rheumatoid Arthritis disease David Santosa 1, Rudy Hidayat 2, Marcel Prasetyo, Pringgodigdo Nugroho 4 1 Departement, Medical Faculty of University
An Explanation for the Apparent Dissociation Between Clinical Remission and Continued Structural Deterioration in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 10, October 2008, pp 2958 2967 DOI 10.1002/art.23945 2008, American College of Rheumatology An Explanation for the Apparent Dissociation Between Clinical Remission and
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 10, October 2008, pp 2958 2967 DOI 10.1002/art.23945 2008, American College of Rheumatology An Explanation for the Apparent Dissociation Between Clinical Remission and
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Citation for final published version:
 This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/97756/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted
This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/97756/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Review. Structural progression in rheumatoid arthritis remission: can MRI predict it? Frederique Gandjbakhch*1 & Violaine Foltz1
 Structural in rheumatoid arthritis remission: can MRI predict it? Remission has become an achievable goal in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) thanks to a large choice of drug therapies and improvement of treatment
Structural in rheumatoid arthritis remission: can MRI predict it? Remission has become an achievable goal in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) thanks to a large choice of drug therapies and improvement of treatment
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
T he ability to predict accurately prognosis at presentation
 555 EXTENDED REPORT MRI of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis can be used to predict functional outcome at 6 years N Benton, N Stewart, J Crabbe, E Robinson, S Yeoman, F M McQueen... See end of article
555 EXTENDED REPORT MRI of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis can be used to predict functional outcome at 6 years N Benton, N Stewart, J Crabbe, E Robinson, S Yeoman, F M McQueen... See end of article
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Clinical and Radiographic Examinations Do Not Correlate with MRI Determined Plantar plate or Collateral Ligament Tears of the Second MTP joint
 Clinical and Radiographic Examinations Do Not Correlate with MRI Determined Plantar plate or Collateral Ligament Tears of the Second MTP joint Brad D. Blankenhorn, MD Xan F. Courville, MD Julia Crimm,
Clinical and Radiographic Examinations Do Not Correlate with MRI Determined Plantar plate or Collateral Ligament Tears of the Second MTP joint Brad D. Blankenhorn, MD Xan F. Courville, MD Julia Crimm,
The long-term impact of early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis on radiographic progression: a population-based cohort study
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2011;50:1106 1110 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq424 Advance Access publication 21 January 2011 Concise report The long-term impact of early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis on
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2011;50:1106 1110 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq424 Advance Access publication 21 January 2011 Concise report The long-term impact of early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis on
Foot and Ankle Surgeon (To the poor and ignomious)
 Foot and Ankle Surgeon (To the poor and ignomious) www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Plantar plate repair A game changer John P.
Foot and Ankle Surgeon (To the poor and ignomious) www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Plantar plate repair A game changer John P.
Relationship between Foot Pain/Deformities and Risk of Fall in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between Foot Pain/Deformities and Risk of Fall in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis H Guler 1, MT Yildizgoren 1, N Ustun 1, A Balci 2, S Karazincir 2, C Ozer 3, AD Turhanoglu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between Foot Pain/Deformities and Risk of Fall in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis H Guler 1, MT Yildizgoren 1, N Ustun 1, A Balci 2, S Karazincir 2, C Ozer 3, AD Turhanoglu
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Preventing the Progression From Undifferentiated Arthritis to Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Clinical and Economic Implications
 n report n Preventing the Progression From Undifferentiated Arthritis to Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Clinical and Economic Implications Michael H. Schiff, MD Introduction Over the past few years, the management
n report n Preventing the Progression From Undifferentiated Arthritis to Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Clinical and Economic Implications Michael H. Schiff, MD Introduction Over the past few years, the management
1 Relationship between degenerative change in the sesamoid-metatarsal joint and 2 displacement of the sesamoids in patients with hallux valgus 3 4
 1 Relationship between degenerative change in the sesamoid-metatarsal joint and 2 displacement of the sesamoids in patients with hallux valgus 3 4 Abstract 5 Background: To treat a patient with hallux
1 Relationship between degenerative change in the sesamoid-metatarsal joint and 2 displacement of the sesamoids in patients with hallux valgus 3 4 Abstract 5 Background: To treat a patient with hallux
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
The plantar aponeurosis
 Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Dynamic high resolution sonography (d-hrus) of the foot: a detailed didactic approach.
 Dynamic high resolution sonography (d-hrus) of the foot: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-1871 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Perugin Bernardi, A. Arcidiacono, A. Corazza,
Dynamic high resolution sonography (d-hrus) of the foot: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-1871 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Perugin Bernardi, A. Arcidiacono, A. Corazza,
OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 3: An International Multicenter Reliability Study Using the RA-MRI Score
 2002-945-1 OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 3: An International Multicenter Reliability Study Using the RA-MRI Score MARISSA LASSERE, FIONA McQUEEN, MIKKEL ØSTERGAARD,
2002-945-1 OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 3: An International Multicenter Reliability Study Using the RA-MRI Score MARISSA LASSERE, FIONA McQUEEN, MIKKEL ØSTERGAARD,
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lateral ankle ligaments and peroneal tendons in a group of asymptomatic patients
 Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lateral ankle ligaments and peroneal tendons in a group of asymptomatic patients Abstract: Background: The role of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in patients with
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lateral ankle ligaments and peroneal tendons in a group of asymptomatic patients Abstract: Background: The role of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in patients with
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Summary of OMERACT 6 MR Imaging Module
 2002-949-1 OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Summary of OMERACT 6 MR Imaging Module FIONA McQUEEN, MARISSA LASSERE, JOHN EDMONDS, PHILIP CONAGHAN, CHARLES PETERFY, PAUL BIRD,
2002-949-1 OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Summary of OMERACT 6 MR Imaging Module FIONA McQUEEN, MARISSA LASSERE, JOHN EDMONDS, PHILIP CONAGHAN, CHARLES PETERFY, PAUL BIRD,
REPORTING SERVICE: XR
 REPORTING SERVICE: XR Report number: VETCT-70603 Report date: 04/04/2017 Referring Veterinarian: xxxxx Referring Practice: xxxxx Email address: xxxxx Owner: xxxx Patient: xxxx Species: Equine Breed: Belgian
REPORTING SERVICE: XR Report number: VETCT-70603 Report date: 04/04/2017 Referring Veterinarian: xxxxx Referring Practice: xxxxx Email address: xxxxx Owner: xxxx Patient: xxxx Species: Equine Breed: Belgian
Tomosynthesis of the Wrist and Hand in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Comparison With Radiography and MRI
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Aoki et al. Imaging of the Wrist and Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masami Fujii 1 Yoshiko Yamashita 1
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Aoki et al. Imaging of the Wrist and Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masami Fujii 1 Yoshiko Yamashita 1
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
New Radiographic Parameter Assessing Hindfoot Alignment in Stage II Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 New Radiographic Parameter Assessing Hindfoot Alignment in Stage II Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Emilie Williamson, BS; Jeremy Chan, MD; Jayme C Burket, PhD; Jonathan T Deland, MD; Scott Ellis, MD
New Radiographic Parameter Assessing Hindfoot Alignment in Stage II Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Emilie Williamson, BS; Jeremy Chan, MD; Jayme C Burket, PhD; Jonathan T Deland, MD; Scott Ellis, MD
Newer classification criteria 2010:How adequate is this to classify Rheumatoid Arthritis?
 Newer classification criteria 2010:How adequate is this to classify Rheumatoid Arthritis? DR MD MATIUR RAHMAN MBBS, MD, FCPS, FACR, Fellow APLAR Associate Professor, Medicine SSMC & Mitford Hospital New
Newer classification criteria 2010:How adequate is this to classify Rheumatoid Arthritis? DR MD MATIUR RAHMAN MBBS, MD, FCPS, FACR, Fellow APLAR Associate Professor, Medicine SSMC & Mitford Hospital New
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Section 6: Preoperative Planning
 Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology. Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Metatarsophalangeal joint instability of the lesser toes: review and surgical technique
 SA Orthopaedic Journal Winter 2014 Vol 13 No 2 Page 35 Metatarsophalangeal joint instability of the lesser toes: review and surgical technique James R. Jastifer, MD Michael J. Coughlin, MD St Alphonsus
SA Orthopaedic Journal Winter 2014 Vol 13 No 2 Page 35 Metatarsophalangeal joint instability of the lesser toes: review and surgical technique James R. Jastifer, MD Michael J. Coughlin, MD St Alphonsus
ARD Online First, published on July 21, 2011 as /ard Extended report
 ARD Online First, published on July 21, 2011 as 10.1136/ard.2010.146068 Extended report An additional supplementary table is published online only. To view this fi le please visit the journal online (
ARD Online First, published on July 21, 2011 as 10.1136/ard.2010.146068 Extended report An additional supplementary table is published online only. To view this fi le please visit the journal online (
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
MRI in Patients with Forefoot Pain Involving the Metatarsal Region
 MRI in Patients with Forefoot Pain Involving the Metatarsal Region Poster No.: C-0151 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Vukojevi#, M. Mustapic, D. Marjan; Zagreb/HR
MRI in Patients with Forefoot Pain Involving the Metatarsal Region Poster No.: C-0151 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Vukojevi#, M. Mustapic, D. Marjan; Zagreb/HR
Tenosynovitis of the flexor tendons of the hand detected by MRI: an early indicator of rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatology Advance Access published May 27, 2009 Rheumatology 2009; 1 of 5 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep136 Tenosynovitis of the flexor tendons of the hand detected by MRI: an early indicator of rheumatoid
Rheumatology Advance Access published May 27, 2009 Rheumatology 2009; 1 of 5 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep136 Tenosynovitis of the flexor tendons of the hand detected by MRI: an early indicator of rheumatoid
