Glossary. Springer International Publishing AG 2017 A.H. Elgazzar, Orthopedic Nuclear Medicine, DOI /
|
|
|
- Christian Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glossary Ankylosing spondylitis The most common type of spondyloarthropathies with chronic inflammatory changes leading to stiffening and fusion (ankylosis) of the spine and sacroiliac with a strong genetic predisposition associated with HLA B27. Other joints, such as hips, knees, and shoulders, are involved in approximately 30% of patients. Apophysis An accessory secondary ossification center that develops late and forms a protrusion from the growing bone where tendons and ligaments insert or originate. Avulsion Complete separation of tendons or ligaments, with or without a portion of bone and/or cartilage. Behçet s syndrome An uncommon disorder characterized by recurrent oral and genital ulceration, uveitis, or retinal vasculitis, cutaneous pustules, or erythema nodosum and synovitis. The disease is more common in Mediterranean countries and Japan than in the United States. Bone contusion (bone bruise) A term describing microfractures of trabecular bone together with edema or hemorrhage within the marrow. Brodie s abscess An intraosseous abscess in the cortex that becomes walled off by reactive bone. Calciphylaxis Soft tissue calcification in response to administration of an agent after induction of a hypersensitive state. Calcinosis cutis A term used to describe a group of disorders in which calcium deposits form in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and connective tissue sheaths around the muscles but not within the muscles. Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis This term has emerged as a global term to describe a group of autoinflammatory bone diseases, including chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO), synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome, and diffuse sclerosing osteitis (DSO). These disease entities are sterile bone lesions that may include associated systemic and dermatologic manifestations. Costochondritis (Tietze s syndrome) A common painful condition that affects the costochondral junction, usually in young patients, and is self-limiting. The etiology remains unknown, although trauma and infection have been proposed. It can affect any rib, but the first and second ribs are most commonly involved. Complex regional pain syndrome type I (reflex sympathetic dystrophy) A pain syndrome that usually develops after an initiating noxious event with no identifiable major nerve injury, is not limited to the distribution of a single peripheral nerve, and is disproportional to the inciting event or expected healing response. CPPD Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease, also called pseudogout and chondrocalcinosis: a type of crystal deposition arthropathy with such crystals deposited in cartilage, synovium, tendons, and ligaments. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) Also known as Forestier s disease or senile ankylosing hyperostosis; is a common progressive noninflammatory bone and enthesis disorder of unknown etiology affecting the Springer International Publishing AG 2017 A.H. Elgazzar, Orthopedic Nuclear Medicine, DOI /
2 418 Glossary elderly population (up to 30% of men older than the age of 50 years). It is characterized by calcification and ossification of the spinal and various extraspinal soft tissues, mainly entheses, ligaments, and joint capsules. Dystrophic calcification A type of soft tissue calcification that occurs in the setting of normal serum calcium and phosphate levels and occurs in damaged, inflamed, neoplastic, or necrotic tissue. Endochondral ossification Most of the skeleton forms by this type of ossification, where a preexisting cartilage forms first and then undergoes ossification. Enteropathic arthropathies Arthropathies associated with inflammatory bowel diseases, including ulcerative colitis, Crohn s disease, Whipple s disease, intestinal bypass surgery, and celiac disease. Entheses The sites of insertion of tendons, ligaments, and articular capsule to bone. Enthesopathy A pathologic process affecting entheses particularly trauma and/or inflammation resulting in regional periosteal reaction with osteoblastic bone activity. Fibrous dysplasia A benign bone disorder characterized by the presence in the fibrous tissue in lesions of trabeculae of non- lamellar bone (woven bone) which remains essentially unchanged. Flare pattern on bone scan An initial apparent deterioration of primary or some or all metastatic lesions on the bone scan, followed by improvement usually accompanying successful treatment. Fracture delayed union Delay of fracture union beyond the expected time (usually 9 months). Fracture nonunion Complete cessation of repair process of a fracture. Fracture A break in the continuity of a bone. Gout A metabolic disorder that results in hyperuricemia and leads to deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in various sites in the body, especially joint cartilage. Heterotopic ossification A specific type of soft tissue calcification that may or may not follow trauma and is due to a complex pathogenetic mechanism believed to be due to transformation of certain primitive cells of mesenchymal origin in the connective tissue septa within muscles into bone-forming cells. Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy A form of periostitis that may be painful and may be associated with clubbing of fingers and toes, sweating, and thickening of skin. It may be primary or may follow a variety of pathologic conditions, predominantly intrathoracic, and is characterized by periosteal new bone formation. Impingement syndromes A group of painful conditions caused by friction of joint tissue, which include bone impingement, soft tissue impingement, and entrapment neuropathy, depending on the type of tissue involved. Inflammation A complex nonspecific tissue reaction to injury caused by many agents such as living agents such as bacteria and viruses, leading to infection, or nonliving agents, including chemical, physical, and immunologic factors or radiation. Intramembranous ossification Occurs through the transformation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts, seen in flat bones of the skull, part of the mandible, and part of the clavicle. Involucrum A layer of new bone formation around the site of skeletal infection formed secondary to the body s response to that infection. Lisfranc injury Fracture or fracture- dislocation of tarsometatarsal joints. Malunion Healing of a bone in a nonanatomic orientation. Mandibular condylar hyperplasia A unilateral developmental abnormality of the mandible leading to asymmetry in condyles that may result in facial asymmetry. Metastatic calcification The type of soft tissue calcification that involves viable undamaged normal tissue as a result of hypercalcemia and/or hyperphosphatemia associated with increased calcium phosphate product locally or systematically. Myositis ossificans progressiva The congenital and rare form of heterotopic ossification. Osteochondritis dissecans Transchondral fracture with fragmentation and separation of portions of cartilage or cartilage and bone; most prevalent in adolescents.
3 Glossary Osteomalacia Abnormal mineralization of bone with a decrease in bone density secondary to lack of both calcium and phosphorus with no decrease in the amount of osteoid (bone formation). Osteomyelitis A term applied to skeletal infection when it involves the bone marrow. Osteopetrosis A rare inherited metabolic bone disease characterized by a generalized increase in skeletal mass due to a congenital defect in the development or function of the osteoclasts, leading to defective bone resorption. Osteoporosis Reduction of bone tissue amount increasing the likelihood of fractures. Oxalosis Deposition of calcium oxalate crystals that leads to arthropathy. Pathologic fracture A fracture at a site of preexisting abnormalities that weaken bone. Patellofemoral stress syndrome (patellofemoral pain syndrome) A common musculoskeletal disorder believed to be due to abnormal motion or pressure between the patella and femur secondary to chondromalacia and malalignment, but overuse is currently believed to be the most important etiology. It causes pain, sometimes sharp and acute. Plantar fasciitis (calcaneal periosteitis) An inflammatory condition that can occur as an isolated entity, e.g., secondary to occupation or degenerative, or may accompany spondyloarthropathies. Podagra A term describing affection of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe in gout, the most typical finding of gouty arthritis. Progressive diaphyseal dysplasia (Camurati- Engelmann disease) Rare autosomal dominant hereditary disorder characterized by progressive bone formation along the periosteal and endosteal surfaces of long bones and sometimes the skull with widening of bones. It is usually manifested in childhood but can present later. It may cause pain, muscle weakness, and occasionally deafness. Pseudarthrosis A gap between the fracture bone ends containing a space filled with fluid. Also termed false joint. Reactive arthritis (Reiter s disease) A syndrome characterized by a combination of nongonococcal urethritis, arthritis, and conjunctivitis. 419 Renal osteodystrophy A metabolic condition of the bone associated with chronic renal failure. Rheumatoid arthritis An autoimmune disease causing inflammation of connective tissue, mainly in the joints, with synovial inflammatory response triggered by immune complexes in the blood and synovial tissue through activation of plasma protein complement. This inflammation spreads from the synovial membrane to the articular cartilage, the joint capsule, and the surrounding tendons and ligaments, leading to pain, loss of function, and joint deformity. SAPHO syndrome A syndrome characterized by synovitis, acne, palmoplantar pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis. The small and large joints of the feet, ankles, knees, hips, right sacroiliac joints, and shoulders are affected by the synovitis. Scheuermann disease A destructive form of osteochondrosis with erosions of the end plates of two adjacent vertebrae and anterior wedging of thoracic vertebrae. Schmorl s node Herniation of nucleus pulposus upward or downward through the cartilaginous and bony end plate into the body of an adjacent vertebra. Usually involves the inferior end plate of the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebral bodies. Involvement of both the inferior and the superior end plates is not uncommon. Septic tenosynovitis An inflammatory condition affecting generally the flexor tendons of the hands and feet of diabetic patients and resulting from penetrating injuries or spread of infection from a contiguous focus of infection. Sequestrum Segmental bone necrosis that develops when normal blood supply to the bone is interrupted by the edema and ischemia produced by the inflammation. Shin splints Periosteal elevation with reactive bone formation secondary to extreme tension on muscles or muscle groups inserting on bones. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis Displacement of the femoral head from the femoral neck at the site of the growth plate during growth. Spondyloarthropathies A group of seronegative arthropathies formerly called rheumatoid
4 420 variants that share common clinical and radiographic features with characteristic involvement of the sacroiliac joints, the spine, and, to various degrees, the peripheral joints, are linked to HLA B27 histocompatibility antigen, and include ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis (Reiter s disease), and enteropathic spondylitis. Spondylolysis A loss of continuity of bone of the neuroarch of the vertebra due to stress or trauma. Spondylolisthesis Forward movement of one vertebra on another, usually as a result of fracture of the neuroarch. Sprains Tears of ligaments. Strains Tears of tendons. Stress fracture A pathologic condition of bone due to repeated episodes of stress, each less forceful than that needed to cause acute fracture of the bony cortex. Synovial joints Specialized joints that are found mainly in the appendicular skeleton and allow free motion. Tarsal coalition Fusion of the talus and calcaneus or of the navicular and calcaneus due to failure of normal segmentation of their ossification centers during embryogenesis. Glossary Toddler s fracture Fracture in preschool children which is typically a non-displaced spiral fracture of the mid-tibia but also includes fractures of other bones, such as the fibula, calcaneus, talus, metatarsal, and cuboid bones. Transient synovitis A joint inflammation of unknown origin and self-limiting course affecting most frequently boys between 5 and 10 years of age. It was previously known as toxic synovitis and affects preferentially the hip or knee and subsides without antibiotics. T-score A parameter used to express bone mineral density by relating an individual s bone density to the mean BMD of healthy young adults, matched for gender and ethnic group. Tumoral calcinosis A type of soft tissue calcification characterized by large, calcified, periarticular soft tissue masses of calcium phosphate near the large joints such as the hip, the shoulder, and the elbow, in addition to the wrist, hands, and feet. Woven bone Immature non-lamellar bone that is later normally converted to lamellar bone. Z-score A parameter used to express bone mineral density by comparing the bone density value of an individual to the mean value expected for his/her age group.
5 A Achilles tendinitis, 183 Acute chest syndrome, 205, 207 Acute fracture, scintigraphic appearance, scintigraphic imaging battered child syndrome, growth plate injuries, , 162, 163 Lisfranc fracture, 157, 160, 161 Osgood-Schlatter disease, osteochondritis dissecans, rib fracture, scaphoid bone fracture, , 159 Scheuermann s disease, 165 slipped capital femoral epiphysis, sternal fracture, tarsal coalition, 164 toddler s injury, scintigraphic role, Acute inflammation, 38 40, 286, 339 Aluminum toxicity, 131, 132 Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC), Angiogenesis, 27, 39 Ankle synoviorthesis, 405 Ankle trauma, 358 Ankylosing spondylitis, 297, 298, 406 Antibiotics, 38, 45, 69, 300, 316 Apophysis, 2 4, 182, 192, 207 Atrophic non-union, 153, 179, 180 Avulsion injury, 153, , 182, 183 B Baker s cyst, , 295, 401 Basal cell carcinomas, 132, 325 Batson s venous plexus, 228, 230 Battered child syndrome, Behçet s syndrome, 282, 299 Body habitus, 21, 30, 31, 111, 113 Bone anatomy blood supply, 6, 7 cellular level, 5 6 features, 6 9 gross level, 4 molecular level, 6 tissue level, 4 5 development, 2 3 function, 7 metabolism, 7, Bone disease classification, 13 diagnosis F-18 FDG, 18 F-18 sodium fluoride, 18 In-111 oxine leukocytes, 17 lamellar bone, 15 scintigraphic-pathological correlation, 18 Tc-99m sestamibi, 17 Tc-99m sulfur colloid, 18 thallium-201, 17 imaging modalities, 14 Bone expansion, 128, 231, 232 Bone hemangiomas, 222, 245, 247, 248 Bone marrow active hematopoietic marrow, 310 alterations, 311 blood flow, 308 composition, 308 conversion, 310, 311 distribution, 308, 309 elements, 308 function of, 308 histologic section, 307, 308 imaging of, pre-and postnatal hematopoiesis, 308, 309 radionuclide therapy, 410 reconversion, 310, 311 Springer International Publishing AG 2017 A.H. Elgazzar, Orthopedic Nuclear Medicine, DOI /
6 422 Bone marrow (cont.) red marrow, 310 scintigraphy diabetic foot osteomyelitis diagnosis, F-FLT, 314 Gaucher s disease, IM-WPRT, 318 indium-111 chloride, 313 Paget s disease, 319 prosthetic joint infection diagnosis, sickle cell disease, 317, 318 Tc-99m MAb, 312, 313 Tc-99m SC SPECT, 318 Tc-99m sulfur colloid whole-body scan, Tc-99M-WBC, tumors and extension, 320 yellow marrow, 310 Bone marrow edema syndrome, 88, 200 Bone mass density (BMD), 109, Bone matrix, 5 7, 19, 111, 193, 388, 389 Bone modeling units (BMU), 10 Bone, remodeling healing, 152 osteoporosis, 109, 110 Paget s disease, phases, Bone resorption, 1, 5, , 110, 116, 117, 132, 227, 256 Bone scan acquisition, bone imaging radiopharmaceuticals, diagnostic errors sources history and physical examination, 30 interpretation, patient, 30 radiopharmaceuticals, technique, 31, 33 examination, 21 imaging time, instrumentation, of joint disorders, 282 patient history, 21 patient preparation, positioning, 23, post-imaging, scintigraphic methods, Bone turnover, 10, 120 Breast cancer combined F-18 NaF and F-18 FDG PET/CT, F-18 FDG PET/CT study, 259, 260 incidence of, 257 PET imaging, Tc-99m MDP bone scan, 258 Tc-99m MDP SPECT/CT study, Brodie s abscess, 42, 43, 45 C Café-au-lait pigmentation, 128 Caffey s disease. See Infantile cortical hyperostosis Caffey-Silverman syndrome. See Infantile cortical hyperostosis Calcinosis cutis, Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) deposition disease, , 344 Callus, 151 Camurati-Engelmann disease, 134, 136 Cancer-related bone pain treatment clinical response, contraindications, 394 current indications, 394 hemibody irradiation, 389 inflammatory and neuropathic mechanisms, 388 mechanism of action, pain relief, 389 palliative option, 389 precautions and radiation safety, radiopharmaceuticals, 390 dosimetric features, 393 hematological effects, 393 Lu-177, 392 phosphorus-32 orthophosphate, 391 radium-223 dichloride, 392 Re-188-HEDP, 392 Re-188-(V)DMSA, 392 rhenium-186 ethylene hydroxy diphosphonate, 391 Sm-153-EDTMP, 391 strontium-89 chloride, 389, 391 therapeutic response, 394 tin-117m diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, Carcinoid tumor, 268 Cardiac calcinosis, 323 Carpal tunnel syndrome, 184 Cartilaginous joint, 12 Cellulitis, 56 58, 61, 66 c-fos proto-oncogenes, 102, 104 Chondrogenic tumors, Chondrosarcoma, Chordoma, Chronic active osteomyelitis, 42, 62, 73, 75 80, Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO), 86 Circulatory disorders. See Osteonecrosis Closed fracture, 148 Cold lesions, 252, Collagenic tumors, 220 Combined F-18 NaF and F-18 FDG PET/CT breast cancer, lung cancer, soft tissue and bone disease staging, 376 Combined modality, 63 65
7 423 Compact bone, 5, 10, 110, 114 Complex regional pain syndrome-1 acute phase, 123 atrophic phase, 123 bone scan, 124, 126 diagnosis, 124 dystrophic phase, 123 histopathological changes, 123 pathophysiology, 123 scintigraphic patterns, Composite Severity (CSI), 67 Compression fractures, 349, Computed tomography (CT), 51 Congenital disorders, 13, 132, 133 Correlative imaging, 14. See also Individual disease conditions Costochondritis, 299 Coupling, Paget s disease, 104 Coupling signal, in bone remodeling, 10, 11, 104 CRMO. See Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO) Crush syndrome, 345 Crystal deposition arthropathies CPPD deposition disease, Gouty arthritis, Cushing s syndrome, 111, 128 D Delayed union, 152 Diabetic foot osteomyelitis, 47, 48, 63 69, , 362, 373 Diaphysis, 2, 3, 5, 7, 131, 136, 170, 199, 217, 220 Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), Diffuse metastases, Diffuse sclerosing osteitis (DSO), 86 Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), 112 Dysbaric osteonecrosis, 206 Dysprosium-165, 400 Dystrophic calcification arterial calcium deposits, 325, 328 in breast cancer, causes of, 324 in lung cancer, 325, 326 mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, 325, 327 Tc-99m MDP image, 325, 328 E Ectopic calcification, 131, 153, 344 Elbow synoviorthesis, 404 Endochondral ossification, 2, 153, 157, 206, 333 Enteropathic spondylitis, 298, 299 Enthesopathies, 183 Epiphyseal osteomyelitis, 84 Epiphysis, 2, 3, 5, 84 Erbium-169 citrate, 399 Escherichia coli, 43, 44 Estimated radiation absorbed dose, 17, 18 Ewing s sarcoma imaging, 245, 246 origin, 220 sites of involvement, 220, 222 Expansion, bone, 18 Extraction efficiency, 19 F Falx cerebri calcification, 134 Feet fracture, 172 Femoral head bone lesion, 254 multifocal osteonecrosis, osteonecrosis, 194 in adults, in children, Femoral neck fracture, F-18 FDG PET/CT breast cancer, 259, 260 chronic active osteomyelitis, 75, clinical uses, 372 combined F-18 NaF and, diabetic foot osteomyelitis, 373 metastatic bone disease, 372 osteogenic sarcoma, 270 post-arthroplastic infections, primary and metastatic tumors, 372 prostate cancer, 262 radiation absorbed dose, 18 spondylodiscitis, 72, 373 uptake, 235, 242 Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. See Myositis ossificans progressiva Fibrosarcoma, 220 Fibrous dysplasia bone scan, CT scan, 131 etiology, 128 FDG PET, 131 MRI, 131 radiographic findings, 128 Fibrous joint, 12 Flare phenomenon, 256 Fluoride toxicity, 131 Foot trauma, 358 Fracture acute, classification, 148 fatigue, , 170, 173, 174 healing,
8 424 Fracture (cont.) mal-union, 153 non-union atrophic, 153 hypertrophic, 153 scintigraphic evaluation bone graft viability, fracture healing, 179, 180 metallic implants removal, spondylolisthesis, 150, 152 spondylolysis, 150, 151 stress, Freiberg s disease, F-18 sodium fluoride PET/CT, bone imaging, 20 clinical use, 374 combined F-18 FDG PET/CT, low back pain, 294 lung cancer, 263 multiple fractures, 170 radiation absorbed dose, 18 thyroid cancer, 265 Full width at half maximum (FWHM), 27 G Gallium-67 citrate imaging, 60 chronic osteomyelitis, 73, 75 radiation absorbed dose, 17 in vertebral osteomyelitis, Gallium-68-PET/CT, 63, 378 Gallium-68 PSMA PET/CT, 378, 381 Gamma cameras, 22, 53, 84, 250, 391 Garre s sclerosing osteomyelitis, 88 Gastrointestinal tumors, 266, 268 Gaucher s disease, Giant cell tumors, Gleason s score, 261 Gorlin s syndrome, 132, 134, 135 Gouty arthritis, Granulation tissue, 151, 193, 289, 404 Growth hormone, 10 Growth plate injuries, 155, , 162, 163 Gynecological tumors, 266 H Haemophilus influenzae, 288 Hardcastle syndrome. See Medullary diaphyseal sclerosis Healing bone graft, fracture, inflammation, 40 Hemangioma. See bone hemangioma Heterotopic bone formation acquired form, 331 complications, 333 correlative imaging, 339 definition, 331 fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, 333 hereditary form, 331 heterotopic ossification, 331 hypervascularity, 333 incidence, 331 myositis ossificans, 331, 332 myositis ossificans progressiva, 339, 342 pathogenesis, 332 prevalence, 332 progressive osseous heteroplasia, 333, scintigraphic evaluation gallium-67 uptake, 339, 341 immature heterotopic bone formation, indium-labeled WBC studies, pathological conditions, 337, 339 serial bone scans, 334, 335 SPECT/CT, 335, Tc-99m MDP bone scan, 337, 338, 341 three-phase bone scans, 335, 336 SPECT/CT imaging, 364, tumoral calcinosis, 331, tumoral calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease, 344 High turnover disorder, 10, 120 Hip arthroplasty, 48, 80, 199, 301, 331, 337 Hip synoviorthesis, 404 Hodgkin s lymphoma, 41, 266, 320 Holmium-166 ferric hydroxide, 400 Hungry bone syndrome, 117 Hyperparathyroidism bone scan, hypocalcemia, 117 primary, 116 secondary, tertiary, 117 Hyperthyroidism, 131 Hypertrophic neuroarthropathy, 47, 296 Hypertrophic non-union, 153 Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy lung cancer, 127, 128 pathological condition, 127 primary, 127 scintigraphic patterns, secondary, 127 Hypervitaminosis A, 131 Hypocalcemia, 115, 116, 119, 120, 232 Hypothyroidism, 131 I IGF. See Insulin growth factor (IGF) Iliac crest, 3, 182 Immunoscintigraphy, Impingement syndrome, In-111 antimyosin, 182 Incomplete fracture, 148 Indium-111 labeled leukocytes in diabetic foot infection, in periprosthetic infection, radiation absorbed dose, 17
9 in vertebral osteomyelitis, 70 Infantile cortical hyperostosis, 88, 89, 136 Infantile osteomyelitis, Infectious arthritis, 48 49, 85, 288 Inflammation acute cancer patients, 41 cellular changes, healing, 40 vascular changes, chronic, 40 classification, 38 definition, 38 Inflammatory joint disease infectious (see Infectious arthritis) noninfectious crystal deposition arthropathies, neuroarthropathy, 296 rheumatoid arthritis, sacroiliitis, , 296 spondyloarthropathies, Insulin growth factor (IGF), 10 Intensity-modulated whole-pelvic radiation therapy (IM-WPRT), 318 International Committee for Standards in Bone Measurement (ICSBM), 113 Intramembranous ossification, 2, 3, 153 Involucrum, 42, 43, 51 Irregular bones, 6 Ischial tuberosity, 2 J Joints anatomy, 11, 13 classification, 12 disease classification, 13 inflammatory disease, 13 noninflammatory disease, 13 physiology, 11, 13 types, 12 Joint disorder Behçet s syndrome, 299 classification, costochondritis, 299 CPPD, gouty arthritis, infectious arthritis, 288 neuroarthropathy, 296 osteoarthritis, periarticular soft tissue syndrome, 301 DISH, plantar fasciitis, septic bursitis, 302 septic tenosynovitis, 302 rheumatoid arthritis, sacroiliitis, , 296 SAPHO syndrome, spondyloarthropathies, ankylosing spondylitis, 297, 298 enteropathic spondylitis, 299 psoriatic arthritis, 297 reactive arthritis, synovitis renal transplant, 300 transient, 300 K Kaposi s sarcoma, 268 Klebsiella pneumoniae, 43, 70 Knee arthroplasty, 48, 81, 317 Knee impingement syndromes, 184 Knee prosthesis, 48, 77, 82, 83, 361, 373 Knee, spontaneous osteonecrosis, 201 primary, 203 secondary, 203 stage I, stage II, 203 stage III, 203 stage IV, Knee synoviorthesis, 405 Kohler s disease, 208, 209 L Lamellar bone, 2, 15 16, 55, 227, 333, 389 Laminin, 7 Legg-Calve-Perthes disease, Legg-Perthes disease, 119, 196 Lesser trochanter, 4, 182 Ligament injuries, 153 Ligament tears, 183 Lisfranc fracture, 157 Lung cancer, Lu-177 somatostatin analogues, 387 Lutetium-177 ethylenediaminetetramethylene phosphonic acid (Lu-177 EDTMP), M Maffucci syndrome, 218 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), diabetic foot osteomyelitis, in vertebral osteomyelitis, 70, 72 Malignant fibrous histiocytoma, 132 Malignant hypercalcemia, Matrix size, 27, 28 McCune-Albright syndrome, 128 Medullary diaphyseal sclerosis, 132, 134 Meniscal tears, 183 Metabolic disorders, 13 Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG), 16, 213, , 388, 409 Metallic implants, removal, Metaphysis, 2, 3, 5 7, 44, 45, 49, 57, 59, 115, 157, 159, 167, 204, 217, 220, 236
10 426 Metastatic bone disease bone resorption, 227 definition, 225 detection modalities, 249 distribution of, FDG PET, F-18 PET, 250 generalized/metabolic consequences, hematogenous spread, 227 intraspinal spread, 227 local consequences, lymphatic spread, 227 mixed osteolytic/osteoblastic bone metastases, 228, 230 osteoblastic bone metastases, 226, 230 osteolytic bone metastases, 226, 230 PET, 213, 249 radiopharmaceuticals, 214 reactive bone formation, 227 scintigraphic patterns cold lesions, diffuse pattern, flare pattern, 256 solitary lesion, symmetrical pattern, 257 typical pattern, 251, 252 sequential events, tumors spreading, sources, 230 SPECT/CT, 249 stromal bone formation, 227 therapeutic response, 213 Metastatic calcification causes of, 325, 328 chronic renal failure, 328, 329 Metastatic prostate carcinoma, 408 Mineral homeostasis, 7 Multifocal osteomyelitis, Multifocal osteonecrosis, Multi-phase bone scanning, 51, 55 56, 64 Muscle stress, 33 Myelogenic tumors Ewing s sarcoma, myeloma, 220, 221 Myeloma imaging, origin, 220 photomicrograph, 220, 221 radionuclide therapy, sites of involvement, 220, 221 Myoglobulinuria, 345 Myositis ossificans progressiva, 339, 342 N NaF PET/MR, 378 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Necrotic bone, 47, 193, 205 Neonatal osteomyelitis, 40, 57, 58, 84 Neoplastic diseases metastasis (see Metastatic bone disease) primary bone tumors (see Primary bone tumors) SPECT/CT benign tumors, 353 heterotopic bone formation, 364, 366 infections, osteoarthritis, osteonecrosis, sacroiliitis, 364 skeletal metastases, trauma, Neuroarthropathy, 296 Neuroblastoma, , Neutrophils, 38, 39, 42, 53, 286 Nonbacterial osteomyelitis, 86 Non-Hodgkin s lymphoma, 41, 254, 324 Noninfectious inflammatory conditions infantile cortical hyperostosis, 88 osteitis condensans ilii, 88 osteitis condensans of the clavicle, osteitis pubis, 88 sternoclavicular hyperostosis, 88 Noninflammatory joint disease, 13, 282, 288 Nonneoplastic diseases, SPECT/CT imaging ankle and foot trauma, 358 compression fractures, 357, 358 diabetic foot osteomyelitis, 362 heterotopic bone formation, osteoarthritis, osteochondritis dissecans, 360 osteonecrosis, rib fractures, 357 sacroiliitis, 364, 365 soft tissue infection, 362 spinal fusion, spondylolysis, 357 tarsal coalition, 360 wrist and hand trauma, 360 Nutrient arteries, 6 O Oblique fracture, 148 Ollier disease, 218 Oncogenic osteomalacia, 232 Open fracture, 148 Osgood-Schlatter disease, , 208 Ossification centers, 2, 3, 164, 206, 208 Osteitis condensans ilii, 88 Osteitis condensans of the clavicle, 88, 90 Osteitis deformans. See Paget s disease Osteitis fibrosa, Osteitis pubis, 91 Osteoarthritis, Baker s cyst, commonly involved joints, 288, 290 degree of uptake, 292, 293 extrinsic repair, 289 F-18 NaF PET/CT study, 293, 296 intrinsic repair, 291
11 pathological characteristics, primary, secondary, 291 Tc99m MDP bone scan, , 297 Osteoblast, 2 Osteoblastoma, 215, 235, 238 Osteocalcin, 7 Osteochondritis dissicans. See Transchondral fractures Osteochondroma blood pool activity, 236, 240 bone scintigraphy, 238, 244 MRI, 238 radiographic appearance, 238 Osteochondroses, Osteoclast, 1, 5, 7, 10 Osteocyte, 7 Osteogenic sarcoma bone marrow involvement, 216 F-18 FDG PET study, 270, 273 imaging, , origin, 216 sites of involvement, 216, 217 whole-body bone scan, 268 Osteogenic tumors origin, 215 osteoblastoma, 216 osteogenic sarcoma, 216, 217 osteoid osteoma, 215, 216 Osteoid osteoma imaging, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, 215 origin, 215 prostaglandins levels, 215 sites of involvement, 215, 216 Osteomalacia, Osteomyelitis, 338, 362. See also Skeletal infections acute hematogenous, 43 algorithm, 85 Brodie s abscess, 42, 43 chronic, 42, classification, CRMO, 86 definition, 41 diabetic foot, 47, epiphyseal, 84 Garre s sclerosing, 88 imaging, and infectious arthritis, vs. infectious arthritis, 85 metaphysis, 44 neonatal, 84 nonbacterial, 86 organisms, 43, 44 periprosthetic infections, 48 posttraumatic, sequestrum, 42, 43 sickle cell disease, 47, 84 vascular communication, 44, 45 vertebral, Osteonecrosis adults, femoral head blood pool imaging, 199 F-18 PET/CT, 200 MRI, pinhole scintigraphy, 200 SPECT, 199, 200 spontaneous, causes, 191, 192 children, femoral head, dysbaric, 206 knee, multifocal, osteochondroses, pathophysiology, post-traumatic, 195 scintigraphic features, scintigraphic staging, sickle cell disease, SPECT/CT slices and MIP images, 369, 370 Tc-99m MDP and labeled WBC SPECT/CT study, Osteonectin, 7 Osteopenia, 11, 109, 112, 114, 154 Osteopetrosis, 132, 133 Osteoporosis BMD, 112, 113 causes, 110 classification, 110 densitometry, 111, 113, 115 diagnosis, 114 DXA, 112 etiology, 110 femur, 113 multiple fragile fractures, 111, 112 peak bone mass, 109, 110 prevalence, 109 remodeling, 109, 110 risk factors, 111 senile, 110 T-score, 112, 113 Z-score, 112, 113 Osteoporosis circumscripta, 106, 108 Oteochondritis dissecans, 360 P Pachydermoperiostosis, 126 Paget s disease, 319 bone remodeling, bone resorption, diagnosis bone densitometry, 106 bone scanning, In-111 white blood cell, 107, 108 MRI, 106 radiograph, 106, 107 etiology, 102 genetic factors,
12 428 Paget s disease (cont.) incidence, 102 initial phase, 104 lytic phase, mixed phase, 105 pain, 105 sarcomatous degeneration, 105 sclerotic/burned-out phase, 105 skeletal distribution, 104 treatment, 109 vascular calcification, 105 Pancreatitis, 192, 199 Papillary thyroid carcinoma, 356 Paramyxovirus, 102 Parathormone, 10 Pars interarticularis, , 357 Pathological fracture, 105, 148, 218, 220, 231, 249, 394 Pelvic fracture, Periarticular soft tissue syndromes causes, 301 DISH, plantar fasciitis, septic bursitis, 302 septic tenosynovitis, 302 SPECT/CT, 302 standard radiography, 301 ultrasonography, 301 Periosteal new bone formation, 231 Periosteum, 2, 3, 5, 7, 41, 42, 84, 105, 136, 150, 151, 164, 169, 183, 216, 222, 297 Periprosthetic infection, 48, Phosphorus-32 chromic sulfate, Phosphorus-32 orthophosphate, 391 Pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS), Pinhole collimator, 22 23, 57, 150, 200, 296 Pixel size, 27, 28 Plantar fasciitis, Poliomyelitis, 90 Positron emission tomography (PET), in chronic osteomyelitis, 77 combined F-18 NaF and F-18 FDG PET/CT, 376, , F-18 FDG PET/CT, F-18 sodium fluoride PET/CT, Ga-68-citrate PET/CT, 372, 378 Ga-68 PSMA PET/CT, 378 in vertebral osteomyelitis, 72 Post-poliomyelitis syndrome, 90 Primary bone tumors, 13, 14 ABC, bone hemangiomas, 222 chondrogenic tumors, chordoma, collagenic tumors, 220 CT, 213 F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose study, 232, 234, 235 giant cell tumors, MRI, 213, myelogenic tumors, origin and classification, 215 osteogenic tumors, PET, radiopharmaceuticals, 214 Tc-99m MDP bone scan, 233, 234 Tc-99m MIBI, 232, 235 T1-201 scintigraphy, 232, 234 Primary osteogenic sarcoma, Procallus, 151 Progressive diaphyseal dysplasia. See Camurati- Engelmann disease Progressive osseous heteroplasia, 333, Prostate cancer, 259, , 269 Prosthetic joint infection, 316, 317 Proteoglycans, 7 Pseudofractures, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 43, 44, 70 Psoriatic arthritis, PVNS. See Pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS) R Radiation exposure, 15, 18, 19, 200, 400 Radioactive gold, 400 Radionuclide synovectomy advantages, 397 ankle synoviorthesis, 405 arthritis, contraindications, 401 elbow synoviorthesis, 404 hemophilia, 402, 404, 405 hip synoviorthesis, 403 indications, 401 knee synoviorthesis, 405 mechanism of action, 400 patient preparation, 401 radiopharmaceuticals, choice of, 398, dysprosium-165, 400 Er-169 colloid, 399 holmium-166 ferric hydroxide, 400 intra-articular administration, 397 phosphorus-32 chromic sulfate, radioactive gold, 400 Re-186 colloid, 399 rhenium-188 colloid, 400 samarium-153 hydroxyapatite, 400 yttrium-90 colloid, shoulder synoviorthesis, 403 side effects post-therapeutic regional inflammatory reaction, 406 radiation sickness, 407 radiopharmaceutical leakage, 406 somatic and genetic effects, treatment protocol, 402 Radionuclide therapy
13 advantage, 388 bone marrow ablation, 40 cancer-related bone pain, long-term consequences, 388 metastatic prostate carcinoma, 408 multiple myeloma, neuroblastoma treatment, primary osteogenic sarcoma treatment, radionuclide synovectomy, therapeutic applications, 388 Radiopharmaceuticals bone imaging diagnostic errors, F-18 sodium fluoride, 20 Tc-99m diphosphonates, 19, 20 for cancer treatment, for infection imaging, for intra-articular therapy, 397 radionuclide synovectomy, for tumor imaging, 214 Radium-223 dichloride, 392 Region of interest (ROI), 113 Reiter s disease, Renal cell carcinoma, Renal osteodystrophy, 10 bone scans, clinical presentation, 120 high turnover form, 120 Legg-Perthes disease, 119 low turnover form, 120 scintigraphic findings, skeletal changes, Tc99m MIBI, 121 Tc99m pentavalent DMSA, 121 vitamind, 119 Rhabdomyolysis, 345 Rhenium-186 ethylene hydroxy diphosphonate, 391 sulfide, 399 Rhenium-188 colloid, 400 Rhenium-188-hydroxyethylidine diphosphonate (Re-188-HEDP), 392 Rhenium-188-labeled dimercaptosuccinic acid complex (DMSA), 392 Rheumatoid arthritis bone scan, 284, 285 labeled leukocytes, 285 pathological changes, 283 radiograph, 283, 284 radionuclide synovectomy, Tc-99m-anti-E-selectin-Fab scintigraphy, 285 Tc-99m HDP, 284, 285 Tc99m-labeled anti-tnf mab, 285 Tc-99m MDP, 284 Tc-99m polyclonal HIG, 284 Rib fractures, , 172, Rickets, Rotator cuff impingement syndrome, S Sacral fractures, Sacroiliitis, , 296, 364, 365 Salmonella, 44, 47 Samarium-153 ethylenediaminetetramethylene phosphonate (Sm-153-EDTMP), 91 Samarium-153 hydroxyapatite, 400 SAPHO syndrome. See Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome Sarcomatous degeneration, 105 Scaphoid fracture, Scheuermann s disease, 165 Schmorl s node, , 179 Sclerosing osteomyelitis. See Garre s sclerosing osteomyelitis Senile osteoporosis, 110 Septic arthritis. See Infectious arthritis Sequestrum, 42, 43, 51 Short bones, 6 Shoulder synoviorthesis, 403 Sickle cell disease, 315, 317 osteomyelitis, 50, 87 osteonecrosis, , 317 Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) clinical uses, 350 diabetic foot osteomyelitis, 65, 66 gallium-67, 64 in neoplastic diseases benign tumors, 353 skeletal metastases, in nonneoplastic diseases ankle and foot trauma, compression fractures, 357 diabetic foot osteomyelitis, 362 heterotopic bone formation, osteoarthritis, osteochondritis dissecans, 360 osteonecrosis, rib fractures, 357 sacroiliitis, 364, 365 soft tissue infection, 362 spinal fusion, spondylolysis, 357, 359 tarsal coalition, 360 wrist and hand trauma, 360 in osteonecrosis, spine infections, 350 in spondylolisthesis, 152 in spondylolysis, 150, 152 Skeletal infections. See also Osteomyelitis combined modality, 63 diagnostic imaging, 49 follow-up, 85 morphologic imaging modalities CT, 51 MRI, 51 standard radiographs, ultrasonography, 50
14 430 Skeletal infections (cont.) scintigraphic methods bone scanning, gallium-67 citrate imaging, 60 immunoscintigraphy, 61 labeled leukocyte imaging, PET imaging, 62 radiopharmaceuticals, Skeletal muscle injury, 150, 182 Slipped capital femoral epiphysis, 119, 159, , 196, 197, 201, 207 Soft tissue calcification, 183 calcinosis cutis, dystrophic calcification, heterotopic bone formation, metastatic calcification, 325, 328, 329 Solitary bone lesion FDG PET, 252 incidence of malignancy, 252, 253 Tc-99m bone scan, 250, 252 T1-201 uptake, 253, 254 Spinal fusion, Spiral fracture, 148, 163 Spondyloarthropathies ankylosing spondylitis, 297, 298 causes, 296 enteropathic spondylitis, 299 MRI, 296 psoriatic arthritis, 297 Reiter s disease, sacroiliitis, 296, 297 SPECT/CT, 296 Spondylodiscitis, 373. See Vertebral osteomyelitis Spondylolisthesis, 152 Spondylolysis, 150, 357, 359 Spongy bone, 1, 4 6 Sprains, 153 Sprengel s deformity, 134 Staphylococcus aureus, 43, 44, 47, 288 Stasis, 39 Steatopygia, 31, 113, 116 Sternoclavicular hyperostosis, 88 Sternum fracture, variants, Strains, 153 Stress fracture, scintigraphic appearance, scintigraphic diagnosis feet, 172 femur, pelvic fracture, rib fracture, 172 Schmorl s node, , 179 tibia, 172 vertebral fracture, scintigraphic role, 168 Strontium-89 chloride, 389, 391 Symmetrical metastases, 257 Symphysis pubis, 4, 12, 36, 208 Synarthroses, 12 Synovial joint, 11 13, 290, 406 Synovitis PVNS, 301 in renal transplantation, transient synovitis, 300 Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome, 86, T Tarsal coalition, 164, 360 Tc-99m diphosphonates administered activity, 20 bone uptake, 20 colon activity, 33 compounds, 19 skeletal accumulation, 19 utilization, 20 Tc99m-hexamethyl propyleneamine oxime labeled leukocytes, 53 56, 62 63, 68 diabetic foot osteomyelitis, 67, 69 Tc-99m-labeled human non-specific polyclonal immunoglobulin G, 53 Tc99m sestamibi, 17 Tc-99m sulfur colloid, 17, 66, 81, 82, 84, 313, 315, 319 Tendon injuries, 153 Tenosynovitis, 302 Tentorium cerebelli calcification, 134 TGF-B. See Transforming growth factor-b (TGF-B) Thallium-201, 1, 17, 86, 214, 232, 233, 243, 254, 265 Thyroid cancer, Tibia fracture, 172 Tibial tuberosity avulsion injury. See Osgood-Schlatter disease Tietze s syndrome, 299 Tin-117m diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, Toddler s fracture, Total hip arthroplasty (THA), 301, 331, 332, 337, 366 Transchondral fracture, 148, 155, Transforming growth factor-b (TGF-B), 10 Transient synovitis degree of uptake, 300 etiology, 300 three-phase bone scanning, 300 Transverse fracture, 148 Traumatic disorders, 13 Trochanteric bursitis, Tumoral calcinosis, 331, Tumoral calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease, 344 Tumors and infection, differentiation, Tuning fork test (TFT), 172 U Ultrasonography, 51, 301, 401 United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission, 397
15 431 V Vascularity, 18 Vascular permeability, 38 Vasodilation, 38 Vertebral fracture, Vertebral osteomyelitis, 44, 46, 70 77, 373 Vitamin-D, 7, 10, 19. See also Hypervitaminosis D W Woven bone, 2, 15, 19, 28, 55 Wrist and hand trauma, 360 Y Yttrium-90 colloid,
MUSCULOSKELETAL STUDY GUIDE
 MUSCULOSKELETAL STUDY GUIDE The following pages summarize potential content for the Certifying and Maintenance Examinations in the Musculoskeletal section. The subject matter that may be used for a test
MUSCULOSKELETAL STUDY GUIDE The following pages summarize potential content for the Certifying and Maintenance Examinations in the Musculoskeletal section. The subject matter that may be used for a test
Nuclear Medicine: Manuals. Nuclear Medicine. Nuclear imaging. Emission imaging: study types. Bone scintigraphy - technique
 Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS. CMS Clinical Concepts
 CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
Musculoskeletal Disorders. Fractures. Types of Fractures BIO 375. Pathophysiology
 Musculoskeletal Disorders BIO 375 Pathophysiology Fractures A fracture is a break in the rigid structure and continuity of a bone The fracture may be: Complete fracture Incomplete fracture Open fracture
Musculoskeletal Disorders BIO 375 Pathophysiology Fractures A fracture is a break in the rigid structure and continuity of a bone The fracture may be: Complete fracture Incomplete fracture Open fracture
The Child With a Limp
 KID WITH A LIMP Common in ED, common in Exams Differential diagnosis is very wide Most causes benign, but mustn't miss Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Fractures / NAI SUFE (older, heavier children) The
KID WITH A LIMP Common in ED, common in Exams Differential diagnosis is very wide Most causes benign, but mustn't miss Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Fractures / NAI SUFE (older, heavier children) The
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
From 2015/2016 Batch
 Department of & Nuclear February 7, 2018 Medical Imaging Module 04 th Year 1 st and 2 nd Semesters From 2015/2016 Batch Topic Objectives Time Dept. T / L Activity Comments Understand the principles of
Department of & Nuclear February 7, 2018 Medical Imaging Module 04 th Year 1 st and 2 nd Semesters From 2015/2016 Batch Topic Objectives Time Dept. T / L Activity Comments Understand the principles of
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Introduction. Physiology. Classification of Bones. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Skeletal System and Joint Movements.
 Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses. Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital
 Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS. Ms. Doshi
 CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
Notes: The Skeletal System
 Date: Notes: The Skeletal System Humans have an endoskeleton that develops from of the mesoderm. Composed of o o o : connects bone-to-bone o : connects muscle-to-bone Functions: o o o o Divided into two
Date: Notes: The Skeletal System Humans have an endoskeleton that develops from of the mesoderm. Composed of o o o : connects bone-to-bone o : connects muscle-to-bone Functions: o o o o Divided into two
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Chapter 6
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
ABOS Part I Certification Examination Blueprint
 2017 ABOS Part I Certification Examination Blueprint www.abos.org Table of Contents General Principles 12-14% Biostatistics/epidemiology 1-3% Legal/ethical 0.5-1% Basic Science Principles 9-11% Spine 13-15%
2017 ABOS Part I Certification Examination Blueprint www.abos.org Table of Contents General Principles 12-14% Biostatistics/epidemiology 1-3% Legal/ethical 0.5-1% Basic Science Principles 9-11% Spine 13-15%
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
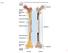 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI
 UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
DISEASE OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS BONES. Determines body size and shape. Mechanical support for movement. Protect vital organs
 https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ca/human_skeleton_front_en.svg/220px-human_skeleton_front_en.svg.png DISEASE OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Thanisa Sanmanee, M.D. FUNCTIONS Determines
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ca/human_skeleton_front_en.svg/220px-human_skeleton_front_en.svg.png DISEASE OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Thanisa Sanmanee, M.D. FUNCTIONS Determines
Mousa Al-Abadi. Abd. Kharabsheh. Rand Abu Anzeh
 7 Mousa Al-Abadi Abd. Kharabsheh Rand Abu Anzeh 1 Recap The histological appearance of Giant cell tumor of bone shows only multi-nucleated giant cells. The histological appearance of Aneurysmal bone cyst
7 Mousa Al-Abadi Abd. Kharabsheh Rand Abu Anzeh 1 Recap The histological appearance of Giant cell tumor of bone shows only multi-nucleated giant cells. The histological appearance of Aneurysmal bone cyst
Contents. copyrighted material by PRO-ED, Inc. Chapter 1. Chapter 2. Chapter 3. Chapter 4. Chapter 5. Conditions in Athletic Injuries
 Acknowledgments xiii Introduction to the First Edition xv Introduction to the Second Edition xvii Chapter 1 Conditions in Athletic Injuries Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear 2 Biceps Tendon Strain
Acknowledgments xiii Introduction to the First Edition xv Introduction to the Second Edition xvii Chapter 1 Conditions in Athletic Injuries Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear 2 Biceps Tendon Strain
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Topics. Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities. Detection of Infection. Role of Imaging in Extremity Infection. Detection of Infection
 Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
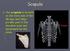 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Imaging the musculoskeletal system. An Introduction
 Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Medical English. -Musculoskeletal System- Professor & Director, Department of Orthopaedics Chung Shan Medical University
 Medical English -Musculoskeletal System- Ko-Hsiu Lu, M.D., Ph.D. Professor & Director, Department of Orthopaedics Chung Shan Medical University Chairman, Department of Orthopaedics Chung Shan Medical University
Medical English -Musculoskeletal System- Ko-Hsiu Lu, M.D., Ph.D. Professor & Director, Department of Orthopaedics Chung Shan Medical University Chairman, Department of Orthopaedics Chung Shan Medical University
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching.
 Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
