Role of Diffusion weighted and Contrast enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentiating Activity of Ankylosing Spondylitis
|
|
|
- Julie Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Role of Diffusion weighted and Contrast enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentiating Activity of Ankylosing Spondylitis Ying Hua Zhao 1, Yan Yan Cao 2, Qun Zhang 3, Ying Jie Mei 4, Ji Jie Xiao 1, Shao Yong Hu 1, Wei Li 1, Shao Lin Li 1 1 Department of Radiology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Orthopaedic Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou, Guangdong , China 2 Department of Rheumatology, Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong , China 3 Department of Rheumatology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Orthopaedic Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou, Guangdong , China 4 Department of MR Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, Guangdong , China Ying Hua Zhao and Yan Yan Cao contributed equally to this study. Abstract Background: Previous studies showed that combining apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value with the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) index value might provide a reliable evaluation of the activity of ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and that contrast enhanced (CE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is unnecessary. However, the results were based on confirming only a small random sample. This study aimed to assess the role of CE MRI in differentiating the disease activity of AS by comparing ADC value with a large sample. Methods: A total of 115 patients with AS were enrolled in accordance with Bath AS Disease Activity Index and laboratory indices, and 115 patients were divided into two groups, including active group (n = 69) and inactive group (n = 46). SPARCC, ΔSI, and ADC values were obtained from the short tau inversion recovery (STIR), diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), and CE MRI, respectively. One way analysis of variance and receiver operating characteristic analysis were performed for all parameters. Results: The optimal cutoff values (with sensitivity, specificity, respective area under the curve, positive likelihood ratio, and negative likelihood ratio) for the differentiation between active and inactive groups are as follows: SPARCC = 6 (72.06%, 82.61%, 0.836, 4.14, 0.34); ΔSI (%) = 153 (80.6%, 84.78%, 0.819, 5.3, 0.23); ADC value = mm 2 /s (72.73%, 81.82%, 0.786, 4, 0.33). No statistical differences were found among the predictive values of SPARCC, ΔSI, and ADC. Multivariate analysis showed no significant difference between the combination of SPARCC and ADC values with and without ΔSI. Conclusions: Using large sample, we concluded that the combination of STIR and DWI would play significant roles in assessing the disease activity, and CE MRI sequence is not routinely used in imaging of AS to avoid renal fibrosis and aggravation of kidney disease. Key words: Activity; Ankylosing Spondylitis; Diffusion weighted Imaging; Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that mainly affects the spine, causing lower back pain, and presents as a persistent alternation of active and inactive stages. [1] Bone marrow edema (BME) of sacroiliitis has been considered to be used to diagnose AS and to be the important indicator of different AS stages. [2] In general, the more accurate of active and inactive changes are distinguished; the better treatment on patients could be achieved. [3] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is increasingly utilized to observe Quick Response Code: Access this article online Website: DOI: / the activity of sacroiliitis through quantifying BME of sacroiliitis in patients with AS, [4 8] which is more sensitive Address for correspondence: Prof. Shao Lin Li, Department of Radiology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Orthopaedic Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou, Guangdong , China E Mail: lishaolin1963@163.com This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms. For reprints contact: reprints@medknow.com 2017 Chinese Medical Journal Produced by Wolters Kluwer Medknow Received: Edited by: Yi Cui How to cite this article: Zhao YH, Cao YY, Zhang Q, Mei YJ, Xiao JJ, Hu SY, Li W, Li SL. Role of Diffusion-weighted and Contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentiating Activity of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Chin Med J 2017;130: Chinese Medical Journal June 5, 2017 Volume 130 Issue
2 than other modalities in monitoring the activity of AS. [7,8] Recommended sequences for MRI of the sacroiliac joint included turbo spin echo (TSE), T1 weighted (T1W) with fat saturation (FS) pre and post contrast, short tau inversion recovery (STIR), and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI). However, all of MRI sequences for evaluation of AS used to detect the activity of AS could result in the scan time prolonged and inconvenient, and the application of contrast agent might lead to myelofibrosis or aggravate existing kidney disease. The previous studies showed that the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) MRI index, combined with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values, is a validated semiquantitative measure of sacroiliac inflammation [9] and that contrast enhancement (ΔSI) based on postcontrast T1W FS was not be needed. [10] However, the conclusion was only testified by a small sample. The aim of this study was to compare SPARCC and ADC with and without ΔSI in discriminating active from inactive AS in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, and negative likelihood ratio by a large sample. Our results will direct at profiting from the elimination of redundant sequences, increasing patient comfort, and decreasing cost savings. Methods Ethical approval This prospective study was reviewed by the Ethics Committee in our hospital, and the approval with written informed consent was obtained from each participant. Participants According to the criteria of the modified New York classification criteria for AS, [11] 115 patients were diagnosed with AS who underwent MRI of the sacroiliac joints from May 2011 to September 2014 (99 male, 16 female; mean age, 27.2 years, range years). Patients with cardiac pacemakers, metallic implants, or pregnancy for the past 6 months were excluded from the study. Within a 2 week interval, MRI and laboratory inflammatory markers were achieved. The criteria of clinical and laboratory tests were served as the standard for determining the active and inactive group, including Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C reactive protein (CRP). These criteria for active and inactive groups are as follows: [12] (1) active group: BASDAI average score 6, a score between 4 and 6 with ESR 20 mm/h (Westergren method), or CRP 3 mg/l; (2) inactive group: BASDAI average score <4.0 or a score between 4 and 6 with ESR <20 mm/h or CRP <3 mg/l. The patients were differentiated into 69 patients with active AS (mean age, 27.2 years; range, years; symptom duration 4.57 ± 4.38 years) and 46 with inactive AS (mean age, 33.2 years; range, years; symptom duration 5.5 ± 5.34 years). The active group was significantly different from inactive group in ESR and CRP (F = 38.93, P < and F = 15.72, P = 0.003), whereas there was no significant difference in BASDAI (F = 0.045, P = 0.834). Magnetic resonance imaging techniques All patients underwent MRI of bilateral sacroiliac joints using a 1.5 T MR system (Philips Healthcare, Netherlands). Imaging sequences included as shown in Table 1: (a) coronal oblique (parallel to the long axis of the sacrum) T1W TSE with spectral presaturation with inversion recovery (SPIR), (b) coronal oblique T2 weighted (T2W) TSE, (c) STIR, and (d) DWI. Two b values were used in DWI: 0 and 800 s/mm 2. Before and after gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist, Schering, Germany) was injected into the right brachiocephalic vein, coronal oblique T1W TSE SPIR were performed with the contrast agent administrated with 0.1 mmol/kg body weight at a rate of 2.0 ml/s. The oblique coronal T1W TSE SPIR scan was finished within 1 min after intravenous injection. All MR images were collected with bilateral sacroiliac joints coverage. Scoring method of Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada The scoring method is shown in Figure 1c. Scoring sacroiliac joints were limited to the synovial section of the joints through these coronal slices, and then six consecutive coronal slices were consistently overviewed. Therefore, slices 4 9 were typically scored. Of the 12 acquisition images, 6 were obtained from posterior to anterior. Each sacroiliac joint was divided into 4 quadrants: upper sacral, lower sacral, upper iliac, and lower iliac. The dichotomous basis was used to score the presence of increased signal on T2W imaging (T2WI) STIR, in each of these four quadrants. A score of 1 stands for increased signal and a score of 0 was normal. If there was a lesion showing intense signal on each Table 1: Imaging parameters T2W TSE, T1W TSE SPAIR, T2W STIR, and DWI_2b Parameters T2W TSE T1W TSE SPIR T2W STIR DWI_2b TR/TE (ms) 4830/ /20 Shortest/ /52 Echo train length (n) FOV (mm) /250 Matrix Slices (n) Thickness/gap (mm) 6/1 6/1 3/1 6/1 NSA SENSE factor T1W TSE: T1 weighted turbo spin echo; SPIR: Spectral presaturation inversion recovery; T2W TSE: T2 weighted turbo spin echo; STIR: Short tau inversion recovery; DWI: Diffusion weighted imaging; TR/TE: Repetition time/echo time; FOV: Field of view; NSA: Number of signal average Chinese Medical Journal June 5, 2017 Volume 130 Issue 11
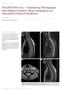
3 a b c d Figure 1: A 27 year old male ankylosing spondylitis patient with lumbosacral pain and morning stiffness for over 6 months. Focal lesions of bone marrow edema are shown in left anterior edge of ilium (white arrow). Coronal (a) spectral presaturation with inversion recovery T1 weighted magnetic resonance and coronal (b) T2 weighted magnetic resonance images show isointense. Coronal (c) short tau inversion recovery T2 weighted magnetic resonance (Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada scoring method shown), coronal (d) postcontrast spectral presaturation with inversion recovery T1 weighted magnetic resonance images and axial (e) apparent diffusion coefficient maps (b = 0, 800 mm 2 /s) show hyperintense. The apparent diffusion coefficient value for the indicated region of interest is mm 2 /s. e sacroiliac joint, the maximum score for the abnormal signal was 8 scores of a coronal slice on sacroiliac joints. Similarly, the depth associated with any part of a joint receives a score of 1, and maximum scores were added up to 24 on the depth of sacroiliac joint. The depth and the increased signal were the referents of BME that extends away from the joint space. The use of the depth and the intensity was reserved for clearly positive cases. The maximum scores were 72 that was obtained by being repeated for each consecutive coronal slice. [13] Signal enhancement (ΔSI) A region of interest (ROI) was used to quantitatively measure the changes in signal enhancement (ΔSI) of the lesion before and after the injection of gadopentetate dimeglumine. The signal enhancement (percentage of signal intensity increase) was calculated according to the enhancement formula: [1] ΔSI = (SIc SI)/SI 100, [1] where SI and SIc are the precontrast and the postcontrast signal intensities, respectively. Image postprocessing and regions of interest All indices were obtained on Extended MR Workspace (Philips Healthcare, Netherlands). For ADC and ΔSI values, ROIs were drawn on each lesion along the inside of the contour (approximately 1 mm). Examples are shown in Figure 1d and 1e. Lesion ROIs were set as large as possible; the lower and upper levels of lesions were excluded to minimize contamination from surrounding tissues. Blood vessels, sclerosis, and cystic areas were avoided. We took four lesions for every patient. If there were more than four lesions, we choose four obvious lesions. Oppositely, if there were <4 lesions, we choose all of these lesions, and then the average of the measurements was taken and the mean ROI area turned out to be 46 mm 2 (range, mm 2 ). Two independent observers (each with 10 year experience in bone MRI diagnosis) measured all indices; these observers were blinded between each other and also to the clinical data. Statistical analysis All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics version 13.0 for Windows (IIBM, Armonk, New York,US), except for the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) comparison that was completed by MedCalc statistical software (MedCalc Software, Acacialaan 22, B 8400 Ostend, Belgium). The data variability for the 2 different observers was derived by the intraclass correlation coefficient being calculated. The data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Levene s test was used to investigate the homogeneity of variance. Dunnett s T3 and Bonferroni s methods for heterogeneity of variance and post hoc Scheffe s method for homogeneity of variance were performed. All indices were compared using one way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Using curve analyses, the differentiation was obtained to assess the utility of the parameters from active and inactive AS. To account for multiple comparisons, we would compare the precision of ROC curves from different mix parameters, and P values would be based on Bonferroni correction. There was statistical significance with P values of <0.01. To analyze the differences between ROC curves, stepwise regression analysis has been used. Results Patient characteristics and magnetic resonance imaging Of 115 patients, acute subchondral BME was detected in 75 patients (active 68 vs. inactive 7). T1WI TSE SPIR showed hypointense or isointense lesions in bones of the bilateral sacroiliac joint. Hyperintense lesions in affected areas were shown on coronal oblique T2WI STIR, contrast enhanced (CE) MRI, DWI, and ADC map [Figure 1]. Furthermore, 38 of the patients had erosions in bilateral or only unilateral sacroiliac joints surfaces (active 12 vs. inactive 26), showing uneven and moth eaten bone destruction of bone cortex on the sacroiliac joint. Chinese Medical Journal June 5, 2017 Volume 130 Issue
4 Twenty six of the patients had sclerosis either on bilateral or only unilateral sacroiliac joints subchondral bones (active 11 vs. inactive 15), showing patchy hypointense in bones of the sacroiliac joints on MR images. Sixty eight of the patients had fat deposition in the sacroiliac joints (active 32 vs. inactive 36), of which T2WI showed hyperintense lesions in bilateral or only unilateral sacroiliac joints and hypointense lesions in affected areas were seen on coronal oblique T2WI STIR, CE MRI, T1WI TSE SPIR, DWI, and ADC map [Figure 2]. All indices analysis between active and inactive group A kappa value (κ) showed good agreement with 0.86 for SPARCC and ΔSI and with 0.85 for ADC value among interobserver. The ranges of all indices of the active and inactive AS patients are described in Table 2. The mean ± SD values of the active and inactive group with respect to all indices are as follows: for the active group: ADC value = 1.34 ± mm 2 /s, ΔSI (%) = 247 ± 161, SPARCC = ± 14.8; for the inactive group, all measures were lower: ADC value = 0.9 ± mm 2 /s, ΔSI (%) = 122 ± 65, SPARCC = 3.86 ± SPARCC, ΔSI, and ADC values in the inactive group were lower than these in the active, and ANOVA indicated that there were significant differences in ADC, ΔSI, and SPARCC values between the active and inactive group (P < 0.001). Dunnett s T3 method indicated that all indices in active AS were higher than those in inactive AS. Table 3 shows the ROC curve analysis of the two groups. The optimal cutoff Table 2: Test of all indices between the active and inactive groups by ANOVA Items Active group Inactive group P ΔSI (%) 247 ± ± 65* <0.05 SPARCC ± ± 5.09* <0.05 ADC value (10 3 mm 2 /s) 1.34 ± ± 0.43* <0.05 *P<0.05 vs. active group. ANOVA: One way analysis of variance; ΔSI: Signal enhancement; SPARCC: Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Index values; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient. values (with respective area under the curve, sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, and negative likelihood ratio) between active and inactive AS patients were ADC value = mm 2 /s (0.786, 72.73%, 81.82%, 4, 0.33), ΔSI (%) = 153 (0.819, 80.6%, 84.78%, 5.3, 0.23), and SPARCC = 6 (0.836, 72.06%, 82.61%, 4.14, 0.34) [Figure 3]. Although, according to the ROC curves, ΔSI was the most reliable predictor for differentiating active from inactive AS patients, there were no significant differences among SPARCC, ADC, and ΔSI values. The specificity of ΔSI (80.6%) was highest among all indices between the active and inactive groups. Using any multivariate model, although the combination of SPARCC, ADC, and ΔSI values had the highest ROC (0.878, P = ) compared with SPARCC alone, there was no statistical significance between the combination of SPARCC and ADC values with and without ΔSI to differentiate active AS from inactive AS [Table 4]. Discussion In this study, we studied the sensitivity and specificity of SPARCC, ΔSI, and ADC values which detected the activity of AS. We found that T2W STIR, DWI, and CE MRI could offer good differentiation between the active and inactive AS, and that SPARCC, ΔSI, and ADC values in the active AS were all significantly higher than those in inactive AS. In general, BME was considered as a product of an inflammatory reaction of bone marrow in AS. [14] Respectively, the excessive water in bone marrow can cause SPARCC to increase; the increased blood flow and capillary permeability lead to an increase of ΔSI. [15] ADC value reflects the Brownian motion of water molecules in a biologic system. [16] Water movement in the inflammatory lesions was increased in acute AS, leading to high local ADC value. [17] Our multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that combining ADC value with SPARCC could slightly improve the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for active AS, but further combining ΔSI with SPARCC and ADC value a b c d Figure 2: A 57 year old male with lumbosacral pain for 4 years. Blurring edges are seen in the bilateral sacroiliac joints representing cartilage erosion and bone sclerosis (star). Bone fusion and fat deposition are shown in sacroiliac joint (white arrow). Coronal (a) spectral presaturation with inversion recovery T1 weighted magnetic resonance, coronal (c) short tau inversion recovery T2 weighted magnetic resonance, coronal (d) postcontrast spectral presaturation with inversion recovery T1 weighted magnetic resonance images and axial (e) apparent diffusion coefficient maps (b = 0, 800 mm 2 /s) show hypointense, and coronal (b) T2 weighted magnetic resonance images shows hyperintense. e 1306 Chinese Medical Journal June 5, 2017 Volume 130 Issue 11
5 Table 3: Optimal cutoff values for the active and inactive group under 95% CI according to ROC curves analysis with respective P values from comparison of ROC curves Items Cutoff value Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) LR AUC Positive Negative SPARCC ( ) ( ) 4.14 ( ) 0.34 ( ) ( ) ADC value mm 2 /s ( ) ( ) 4.00 ( ) 0.33 ( ) ( ) ΔSI (%) ( ) ( ) 5.3 ( ) 0.23 ( ) ( ) All P>0.05. CI: Confidence interval; LR: Likelihood ratio; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under the curve; ΔSI: Contrast enhancement; SPARCC: Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Index values; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient. Table 4: Multivariate logistic regression analysis showing all the multivariate models with P values against SPARCC between active and inactive group Items Models AUC 95% CI P Univariate SPARCC Multivariate SPARCC/ * ADC value Multivariate SPARCC/ΔSI/ ADC value All multivariate vs. univariate SPARCC: *P>0.05 vs. SPARCC; P>0.05 vs. SPARCC. ΔSI: Contrast enhancement; SPARCC: Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Index values; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; SPARCC/ADC value: The combination of SPARCC and ADC values; SPARCC/ΔSI/ADC value: The combination of SPARCC, ADC, and ΔSI values; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval. Figure 3: Comparisons of receiver operating characteristic curves of apparent diffusion coefficient value, ΔSI, and Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada for the active and inactive group. The receiver operating characteristic curves demonstrated Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada had the highest area under the curve, followed by ΔSI and, while apparent diffusion coefficient value had a lower area under the curve. could not significantly increase the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for the activity of AS in our study included 115 patients. However, Althoff et al. reported that although the role of T2W STIR and CE MRI are comparable in identifying the activity of AS, administration of contrast agents may be beneficial for inexperienced MRI readers or detecting early AS with minimal changes. [10] However, some studies using small sample had shown that DWI and CE MRI had similar diagnostic value, and that CE MRI does not contribute significant additional information as compared to DWI, [17 20] which is consistent with our results. Altogether, we conclude that STIR combined with DWI MRI should be used in MRI examination to detect the activity of AS, and that CE MRI was unnecessary. Because a contrast agent is administered, there is a risk of renal fibrosis induction and aggravation of inactive kidney disease, such as renal amyloidosis, IgA nephropathy, and other kidney diseases associated with AS, [21-23] Therefore, for assessing the activity of definite AS, CE MRI can be eliminated from MRI protocols, to avoid risks associated with contrast agent administrations and to save both cost and time. Three limitations need to be taken into account: First, MRI of normal bone marrow is known to be strongly influenced by age and fat content. [24] Therefore, we only included young patients to exclude significant effects of yellow bone marrow on our data. Second, synovitis and soft tissue inflammation were not studied, which were also regarded as presentations of active AS. [25] Third, there were errors in the specific inclusion criteria and measurement. These will be further studied in the next step. Financial support and sponsorship This work was supported by the public welfare research and capacity building of science and technology projects of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2014A , 2014A ) and the National Scientific Foundation of China (No ). Conflicts of interest There are no conflicts of interest. References 1. Shen K, Yang CL, Yin G, Xie QB. Sacroiliitis and spondylitis with sternoclavicular hyperostosis: SAPHO or an ankylosing spondylitis variant? Chin Med J 2016;129: doi: / Benton N, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, McQueen FM. MRI of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis can be used to predict functional outcome at 6 years. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63: doi: /ard Osman MS, Maksymowych WP. An update on the use of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in the treatment of ankylosing Chinese Medical Journal June 5, 2017 Volume 130 Issue
6 spondylitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2017;13: doi: / x Bollow M, Braun J, Hamm B, Eggens U, Schilling A, König H, et al. Early sacroiliitis in patients with spondyloarthropathy: Evaluation with dynamic gadolinium enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 1995;194: doi: /radiology Mok CC, Li OC, Chan KL, Ho LY, Hui PK. Effect of golimumab and pamidronate on clinical efficacy and MRI inflammation in axial spondyloarthritis: A 48 week open randomized trial. Scand J Rheumatol 2015;44: doi: / Li EK, Griffith JF, Lee VW, Wang YX, Li TK, Lee KK, et al. Short term efficacy of combination methotrexate and infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A clinical and magnetic resonance imaging correlation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47: doi: / rheumatology/ken Lambert RG, Bakker PA, van der Heijde D, Weber U, Rudwaleit M, Hermann KG, et al. Defining active sacroiliitis on MRI for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: Update by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75: doi: / annrheumdis Ostergaard M, Poggenborg RP, Axelsen MB, Pedersen SJ. Magnetic resonance imaging in spondyloarthritis How to quantify findings and measure response. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2010;24: doi: /j.berh Gaspersic N, Sersa I, Jevtic V, Tomsic M, Praprotnik S. Monitoring ankylosing spondylitis therapy by dynamic contrast enhanced and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Skeletal Radiol 2008;37: doi: /s Althoff CE, Feist E, Burova E, Eshed I, Bollow M, Hamm B, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of active sacroiliitis: Do we really need gadolinium? Eur J Radiol 2009;71: doi: /j.ejrad van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27: Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: The Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index. J Rheumatol 1994;21: Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D, Dhillon SS, Williams M, Stone M, et al. Spondyloarthritis research consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of sacroiliac joint inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 2005;53: doi: /art Appel H, Loddenkemper C, Miossec P. Rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis Pathology of acute inflammation. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2009;27 4 Suppl 55:S Gordon Y, Partovi S, Müller Eschner M, Amarteifio E, Bäuerle T, Weber MA, et al. Dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: Fundamentals and application to the evaluation of the peripheral perfusion. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 2014;4: doi: /j.issn Le Bihan D, Delannoy J, Levin RL. Temperature mapping with MR imaging of molecular diffusion: Application to hyperthermia. Radiology 1989;171: doi: /radiology Bozgeyik Z, Ozgocmen S, Kocakoc E. Role of diffusion weighted MRI in the detection of early active sacroiliitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008;191: doi: /AJR Gezmis E, Donmez FY, Agildere M. Diagnosis of early sacroiliitis in seronegative spondyloarthropathies by DWI and correlation of clinical and laboratory findings with ADC values. Eur J Radiol 2013;82: doi: /j.ejrad Sanal HT, Yilmaz S, Kalyoncu U, Cinar M, Simsek I, Erdem H, et al. Value of DWI in visual assessment of activity of sacroiliitis in longstanding ankylosing spondylitis patients. Skeletal Radiol 2013;42: doi: /s Wick MC, Grundtman C, Weiss RJ, Gruber J, Kastlunger M, Jaschke W, et al. The time averaged inflammatory disease activity estimates the progression of erosions in MRI of the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 2012;31: doi: /s Resorlu M, Gokmen F, Resorlu H, Adam G, Aylanc N, Akbal A, et al. Prospective evaluation of the renal morphology and vascular resistance in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Med Ultrason 2015;17: doi: /mu dyr. 22. Gönüllü E, Bilge NS, Cansu DU, Bekmez M, Musmul A, Akçar N, et al. Risk factors for urolithiasis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective case control study. Urolithiasis 2016;1-5. doi: /s Braun J, Bollow M, Eggens U, König H, Distler A, Sieper J. Use of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with fast imaging in the detection of early and advanced sacroiliitis in spondylarthropathy patients. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37: doi: / art Dawson KL, Moore SG, Rowland JM. Age related marrow changes in the pelvis: MR and anatomic findings. Radiology 1992;183: doi: /radiology Jee WH, McCauley TR, Lee SH, Kim SH, Im SA, Ha KY. Sacroiliitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Association of MR findings with disease activity. Magn Reson Imaging 2004;22: doi: /j.mri Chinese Medical Journal June 5, 2017 Volume 130 Issue 11
MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis
 MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
Department of Radiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark; 4. Key words MRI, sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis, axial spondyloarthritis.
 Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium Canada scoring system
 Cui et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2016) 18:38 DOI 10.1186/s13075-016-0916-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis
Cui et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2016) 18:38 DOI 10.1186/s13075-016-0916-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis
Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in children: frequency of findings and interobserver reliability
 Pediatric Radiology (2018) 48:1621 1628 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4185-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in children: frequency of findings and interobserver reliability
Pediatric Radiology (2018) 48:1621 1628 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4185-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in children: frequency of findings and interobserver reliability
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
Feasibility and reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac joint inflammation score in children
 Weiss et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1543-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Feasibility and reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac
Weiss et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1543-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Feasibility and reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Association of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient With Maturity in Adolescent Sacroiliac Joints
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Association of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient With Maturity in Adolescent Sacroiliac Joints Timothy J.P. Bray, MBBChir, MA, 1,2 * Kanimozhi Vendhan, MBBS, MD, 1 James Roberts, BMBS,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Association of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient With Maturity in Adolescent Sacroiliac Joints Timothy J.P. Bray, MBBChir, MA, 1,2 * Kanimozhi Vendhan, MBBS, MD, 1 James Roberts, BMBS,
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies
 Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis
 Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis Poster No.: C-1836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. E. Banegas Illescas, C. López Menéndez, M. L.
Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis Poster No.: C-1836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. E. Banegas Illescas, C. López Menéndez, M. L.
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions
 Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
UPDATE ON MRI OF SPONDYLOARTHRITIS. PART ONE: THE SACRO-ILIAC JOINT
 JR TR, 2014, 97: 222-227. UPDTE ON MRI OF SPONDYLORTHRITIS. PRT ONE: THE SCRO-ILIC JOINT.C. Vande erg, P. Omoumi,. Larbi, F. Lecouvet, J. Malghem 1 In recent years, there has been an increased trend toward
JR TR, 2014, 97: 222-227. UPDTE ON MRI OF SPONDYLORTHRITIS. PRT ONE: THE SCRO-ILIC JOINT.C. Vande erg, P. Omoumi,. Larbi, F. Lecouvet, J. Malghem 1 In recent years, there has been an increased trend toward
The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint
 i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
Jian Qin, Jianzhong Zhu, Yue Zhang, Changqin Li* DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis
 Open Med. 2016; 11:52-58 Research Article Open Access Jian Qin, Jianzhong Zhu, Yue Zhang, Changqin Li* DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis DOI 10.1515/med-2016-0011
Open Med. 2016; 11:52-58 Research Article Open Access Jian Qin, Jianzhong Zhu, Yue Zhang, Changqin Li* DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis DOI 10.1515/med-2016-0011
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Active (acute) inflammation on MRI highly suggestive of sacroiliitis associated with SpA
 MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
A nkylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common chronic
 1046 EXTENDED REPORT Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems
1046 EXTENDED REPORT Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems
Numerous studies have demonstrated that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive for detection of
 Reducing Invasiveness, Duration, and Cost of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Omitting Intravenous Contrast Injection Does It Change the Assessment of Inflammatory and Destructive
Reducing Invasiveness, Duration, and Cost of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Omitting Intravenous Contrast Injection Does It Change the Assessment of Inflammatory and Destructive
5/4/2018. Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis. Learning Objectives. Outcome Measures Clinical Outcome Assessments
 Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis Marina N Magrey MD Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives What are outcome measures
Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis Marina N Magrey MD Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives What are outcome measures
The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
MRI in imaging of rheumatic diseases: an overview for clinicians
 MRI in imaging of rheumatic diseases: an overview for clinicians I. Eshed 1, K.G.A. Hermann 2 1 Department of Radiology, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel; 2 Department of Radiology, Charité -
MRI in imaging of rheumatic diseases: an overview for clinicians I. Eshed 1, K.G.A. Hermann 2 1 Department of Radiology, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel; 2 Department of Radiology, Charité -
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Introduction SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE
 Skeletal Radiol (2017) 46:633 639 DOI 10.1007/s00256-017-2581-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Prevalence and clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional vertebra (LSTV) in a young back pain population with
Skeletal Radiol (2017) 46:633 639 DOI 10.1007/s00256-017-2581-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Prevalence and clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional vertebra (LSTV) in a young back pain population with
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation
 Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
A mong the inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway;
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 70, No. 7, July 2018, pp 1042 1048 DOI 10.1002/art.40475 2018 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 70, No. 7, July 2018, pp 1042 1048 DOI 10.1002/art.40475 2018 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40654 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stomp, W. Title: MR imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis : techniques and applications
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40654 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Stomp, W. Title: MR imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis : techniques and applications
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Curr Opin Rheumatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 20.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
M Bollow, T Fischer, H Reiβhauer, M Backhaus, J Sieper, B Hamm, J Braun
 Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:135 140 135 Radiology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany M Bollow T Fischer B Hamm Pathology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University H Reiβhauer Rheumatology and
Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:135 140 135 Radiology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany M Bollow T Fischer B Hamm Pathology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University H Reiβhauer Rheumatology and
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis W. Wojciechowski 1,2, Z. Tabor 3, A. Urbanik 2 1 Medical Centre
Assessing synovitis based on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI and EULAR-OMERACT scores of the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis W. Wojciechowski 1,2, Z. Tabor 3, A. Urbanik 2 1 Medical Centre
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Walter P. Maksymowych, Robert G. Lambert, L. Steven Brown and Aileen L. Pangan
 The Journal of Rheumatology Defining the Minimally Important Change for the SpondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada Spine and Sacroiliac Joint Magnetic Resonance Imaging Indices for Ankylosing
The Journal of Rheumatology Defining the Minimally Important Change for the SpondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada Spine and Sacroiliac Joint Magnetic Resonance Imaging Indices for Ankylosing
Key words Ankylosing spondylitis, radiographic scoring methods, intra- and interobserver reliability, BASRI, msasss.
 Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score F. Salaffi 1, M.
Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score F. Salaffi 1, M.
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor
 Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice
 Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 7, Issue 1, JanuaryMarch 2014, pp.7883 Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice Popescu C* **, Trandafir M*, Bădică AM*, Morar F*, Predeţeanu
Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 7, Issue 1, JanuaryMarch 2014, pp.7883 Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice Popescu C* **, Trandafir M*, Bădică AM*, Morar F*, Predeţeanu
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
The Clinical Usefulness of Multidetector Computed Tomography of the Sacroiliac Joint for Evaluating Spondyloarthropathies
 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:171-177, 2007 The Clinical Usefulness of Multidetector Computed Tomography of the Sacroiliac Joint for Evaluating Spondyloarthropathies You-Hyun Lee, M.D.,
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:171-177, 2007 The Clinical Usefulness of Multidetector Computed Tomography of the Sacroiliac Joint for Evaluating Spondyloarthropathies You-Hyun Lee, M.D.,
THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G)
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:66-71 THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G) S. D. JONES, A. STEINER,* S. L. GARRETT and A. CALIN Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:66-71 THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G) S. D. JONES, A. STEINER,* S. L. GARRETT and A. CALIN Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,
Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Determined Early Sacroiliitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 4, April 2009, pp 946 954 DOI 10.1002/art.24408 2009, American College of Rheumatology Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 4, April 2009, pp 946 954 DOI 10.1002/art.24408 2009, American College of Rheumatology Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With
2016 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis. Online supplementary material
 2016 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis Online supplementary material 1. Introduction A systematic literature review (SLR) was performed to inform the
2016 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis Online supplementary material 1. Introduction A systematic literature review (SLR) was performed to inform the
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies
 Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
The follow-up of uterine fibroids treated with HIFU: role of DWI and Dynamic contrast-study MRI
 The follow-up of uterine fibroids treated with HIFU: role of DWI and Dynamic contrast-study MRI Poster No.: C-1137 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit V. Zampa, V. Vallini,
The follow-up of uterine fibroids treated with HIFU: role of DWI and Dynamic contrast-study MRI Poster No.: C-1137 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit V. Zampa, V. Vallini,
Unilateral Sacroiliitis: Differential Diagnosis Between Infectious Sacroiliitis and Spondyloarthritis Based on MRI Findings
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kang et al. Use of MRI to Differentiate Infectious Sacroiliitis From Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yusuhn Kang 1 Sung Hwan Hong Ji
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kang et al. Use of MRI to Differentiate Infectious Sacroiliitis From Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yusuhn Kang 1 Sung Hwan Hong Ji
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Netherlands, Atrium Medical Center, Heerlen, the Netherlands. Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine DIMED, University of Padova, Italy
 DR. SOFIA RAMIRO (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-8899-9087) Article type : Full Length Is it useful to repeat MRI of the sacroiliac joints after three months or one year in the diagnostic process of patients with
DR. SOFIA RAMIRO (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-8899-9087) Article type : Full Length Is it useful to repeat MRI of the sacroiliac joints after three months or one year in the diagnostic process of patients with
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Quantifying bone marrow inflammatory edema in the spine and sacroiliac joints with thresholding
 Chronaiou et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:497 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1861-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Quantifying bone marrow inflammatory edema in the spine and sacroiliac joints with
Chronaiou et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:497 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1861-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Quantifying bone marrow inflammatory edema in the spine and sacroiliac joints with
The effect of two golimumab doses on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis: results through 4 years of the GO-RAISE trial
 Handling editor Tore K Kvien 1 Department of Rheumatology, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical School, Berlin, Germany 3 Division of Arthritis & Rheumatic
Handling editor Tore K Kvien 1 Department of Rheumatology, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical School, Berlin, Germany 3 Division of Arthritis & Rheumatic
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses
 The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
A simplified version of Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 DOI 10.1007/s10067-012-2056-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A simplified version of Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis Fernando A. Sommerfleck & Emilce E.
DOI 10.1007/s10067-012-2056-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A simplified version of Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis Fernando A. Sommerfleck & Emilce E.
Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis
 C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the
 Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2978 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2978 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Serum sclerostin as a possible biomarker in ankylosing spondylitis: a casecontrol
 Serum sclerostin as a possible biomarker in ankylosing spondylitis: a casecontrol study Fabio Massimo Perrotta 1, MD, Fulvia Ceccarelli 2, MD, PhD, Cristiana Barbati 2, PhD, Tania Colasanti 2, PhD, Antonia
Serum sclerostin as a possible biomarker in ankylosing spondylitis: a casecontrol study Fabio Massimo Perrotta 1, MD, Fulvia Ceccarelli 2, MD, PhD, Cristiana Barbati 2, PhD, Tania Colasanti 2, PhD, Antonia
Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis?
 Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis? Dr. Omar Azmat*, Dr. Zaid Jibri, Dr. Vimarsha Swami, Dr. Babak Maghdoori, Dr. Kent Greep,
Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis? Dr. Omar Azmat*, Dr. Zaid Jibri, Dr. Vimarsha Swami, Dr. Babak Maghdoori, Dr. Kent Greep,
Assessment and multiparametric functional MRI evaluation of Arthritis
 Assessment and multiparametric functional MRI evaluation of Arthritis 1 2 3 4 T. Martin Noguerol, MD 1 ; A. Luna, MD 1 M. Gomez Cabrera 3, MD; J Vilanova 2, MD, PhD; M. Romero Rivera MD 3 ; F Caro Mateo
Assessment and multiparametric functional MRI evaluation of Arthritis 1 2 3 4 T. Martin Noguerol, MD 1 ; A. Luna, MD 1 M. Gomez Cabrera 3, MD; J Vilanova 2, MD, PhD; M. Romero Rivera MD 3 ; F Caro Mateo
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Emergency Abdominal MRI Protocols
 2018 SPR Annual Meeting & Postgraduate Course May 15-19, 2018 Nashville, Tennessee Emergency Abdominal MRI Protocols Unni Udayasankar MD Associate Professor Department of Medical Imaging University of
2018 SPR Annual Meeting & Postgraduate Course May 15-19, 2018 Nashville, Tennessee Emergency Abdominal MRI Protocols Unni Udayasankar MD Associate Professor Department of Medical Imaging University of
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
BRIEF REPORT. Denis Poddubnyy, 1 Hildrun Haibel, 1 J urgen Braun, 2 Martin Rudwaleit, 3 and Joachim Sieper 1
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 9, September 2015, pp 2369 2375 DOI 10.1002/art.39225 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Clinical Course Over Two Years in Patients With Early
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 9, September 2015, pp 2369 2375 DOI 10.1002/art.39225 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Clinical Course Over Two Years in Patients With Early
Journal of Ningxia Medical University. Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI b 500 s / mm s / mm 2
 786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
I n 1995, the ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 38, no. 8
 The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 38, no. 8 Serum MMP-3 Level as a Biomarker for Monitoring and Predicting Response to Etanercept Treatment in Ankylosing Spondylitis SUZANNE ARENDS, EVELINE van der VEER,
The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 38, no. 8 Serum MMP-3 Level as a Biomarker for Monitoring and Predicting Response to Etanercept Treatment in Ankylosing Spondylitis SUZANNE ARENDS, EVELINE van der VEER,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis
 REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany
REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany
醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 肌肉骨骼磁振造影. 本週課程內容 General Technical Considerations 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line
 Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line August 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line August 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
6/6/2017. Spondyloarthritis and Osteopathic Primary Care: Facts and Challenges. Progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis Classic Disease
 1 Outline Talk 1 Introduction of spondyloarthritis (SpA) Clinical case challenge The problem of low back pain (LBP) in primary care and in osteopathic primary care Talk 2 What is SpA today? How many people
1 Outline Talk 1 Introduction of spondyloarthritis (SpA) Clinical case challenge The problem of low back pain (LBP) in primary care and in osteopathic primary care Talk 2 What is SpA today? How many people
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Sacroiliac joint infection
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
Low bone mineral density predicts the formation of new syndesmophytes in patients with axial spondyloarthritis
 Kim et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:231 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1731-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Low bone mineral density predicts the formation of new syndesmophytes in patients
Kim et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:231 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1731-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Low bone mineral density predicts the formation of new syndesmophytes in patients
Muhammad Haroon 1* Oliver FitzGerald 4. , Muddassar Ahmad 1, Muhammad Nouman Baig 2, Olivia Mason 3, John Rice 2 and
 Haroon et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:73 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1565-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Inflammatory back pain in psoriatic arthritis is significantly more responsive to corticosteroids
Haroon et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:73 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1565-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Inflammatory back pain in psoriatic arthritis is significantly more responsive to corticosteroids
Spondyloarthropathy: diagnostic imaging criteria for the detection of sacroiliitis
 Pictorial Essay Castro Jr MR et al. / Diagnostic imaging in sacroiliitis Spondyloarthropathy: diagnostic imaging criteria for the detection of sacroiliitis Espondiloartropatias: critérios de ressonância
Pictorial Essay Castro Jr MR et al. / Diagnostic imaging in sacroiliitis Spondyloarthropathy: diagnostic imaging criteria for the detection of sacroiliitis Espondiloartropatias: critérios de ressonância
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma
 Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma Fuad Julardžija*,
Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma Fuad Julardžija*,
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis to predict rheumatoid arthritis development?
 Dakkak et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1845-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis
Dakkak et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1845-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE What is the additional value of MRI of the foot to the hand in undifferentiated arthritis
adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott)
 adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott) 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott) 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study
 EXTENDED REPORT Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study Walter P Maksymowych, 1 Maxime Dougados, 2 Désirée van
EXTENDED REPORT Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study Walter P Maksymowych, 1 Maxime Dougados, 2 Désirée van
