Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report
|
|
|
- Maria Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik Kassel ggmbh, Kassel, Germany 2 Exponent, Philadelphia, PA, USA Address all correspondence to Prof. Dr. med. Werner E. Siebert, Orthopädische Klinik Kassel ggmbh, Wilhelmshoher Allee 345, D Kassel Germany; Tel.: ; Fax: ; wsiebert@okkassel.de. ABSTRACT: An acetabular cup made of a compliant polycarbonate-urethane material has been introduced as an alternative bearing solution. This case study examines the use of this acetabular cup in a single patient at 12 months. The cup had minimal loss of with the most being in the superior area (approximately 10%) and minimal loss of weight (2.4%). On the back side was evidence of abrasive macroscopic wear on one side of the implanted component in the area of directional loading from the head to the acetabulum. On the front side, the wear rate was determined to be minimal (less than 15 mm 3 per year), meaning that most of the change in and weight was caused on the back side. The retrieved synovial fluid appeared normal in color and volume at the time of revision. The histology of the tissue taken showed minimal wear particles and minimal reactivity, confirming that the patient did not have any signs of synovitis. The analysis of the cup confirms the preclinically determined low wear articulation and biocompatibility of polycarbonateurethane as a weight-bearing material. In summary, the surgical findings, data reviewed, and images taken from this case report warrant further study. KEY WORDS: PCU, total hip arthroplasty, alternative bearing, tribology, hip replacement, active implants, polycarbonate urethane /08 $ by Begell House, Inc. 69
2 70 W. SIEBERT ET AL. I. INTRODUCTION Hip arthroplasty is currently the standard care for the treatment of arthritic degenerative disease and fracture of the hip. Today three types of bearing surfaces are prevalent in the hip arthroplasty field: ceramics, metals, and polymers. Each of these bearing surfaces is associated with particular strengths and controversies. Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) has historically been known to produce elevated wear rates, associated with inflammatory bone loss in certain patients. Hard-on-hard bearings, including ceramic and metal bearings, were introduced with the goal to reduce clinical wear rates to below the osteolysis threshold observed with historical polyethylene. However, ceramic bearings have been known, in rare cases, to squeak and to potentially fracture, and metal-on-metal systems release metallic ions into the body, for which the long-term human health risks remain unknown. Many attempts to improve current hip bearing systems, particularly UHMWPE, have been investigated, ranging from carbon-fiber reinforcement, high-pressure crystallization, and elevated doses of cross-linking, as well as, most recently, the addition of vitamin E. While each of these changes has been performed to reduce wear and improve oxidation resistance, each has introduced new controversies into the material and performance characteristics for novel orthopedic bearing materials. Currently, the scientific community has not yet reached consensus as to which of the currently available bearing surface options are optimal for total hip replacement. Polycarbonate urethane (PCU) has been evaluated extensively over the past decade as a new weight-bearing joint system. 1 7 In 2006, a human clinical study was begun in Europe to evaluate the use of polycarbonate urethane as a new weight-bearing material for total hip arthroplasty in patients with femoral neck fractures. This report describes the case and retrieval analysis of a polycarbonateurethane cup from that study. II. PATIENT INFORMATION In February, 2006, a 70-year-old female (165 cm tall, weighing 58 kg) patient with Parkinson s disease experienced a femoral neck fracture of her left hip. This patient, referred to hereafter and in the study as patient AI #001, had multiple comorbidities, including osteoporosis, and a history of L4-S1 fusion for symptomatic spondylolisthesis. After obtaining informed consent to participate in an Ethics Committee approved study, the patient was implanted with a 52 mm diameter cup made of a soft (80A hardness), compliant polycarbonate-urethane material. (TriboFit Acetabular Buffer Catalog No , Active Implants Corp, Memphis, Tennessee). The surgical procedure consisted of removing the acetabular articular cartilage and exposing the bone. An approximately 2 mm groove was cut into the bony bed around the circumference of the acetabulum. It should be noted that during implantation, a blade broke in the grooving instrument and the patient had to be rereamed and regrooved for an implant that was one size larger. The polycarbonate-urethane cup was inserted by elastically snapping the cup into position using finger pressure. After positioning the acetabular component, a 46 mm Smith & Nephew cobalt-chrome modular head and stem were implanted. At six months postoperatively, she had a 120 deg range of motion in flexion, 30 deg abduction, 10 deg adduction, and 10 deg of internal and 40 deg of external rotation. At nine months postoperatively, she had a 105 deg range of motion in flexion, 35 deg abduction, 20 deg adduction, and 35 deg of internal and 30 deg of external rotation, all essentially equal to the unoperated right hip. Immediately after surgery, the patient developed a urinary tract infection, followed by a case of gastroenteritis, and was readmitted for a case of toxic hepatopathia. At the three-month follow-up visit, the patient complained of gastrointestinal pain. Nine months after surgery, the patient continued to experience pain and, among other considerations, was evaluated for possible hip infection symptoms, although the blood work was negative. An aspirate of the hip was taken, and little synovial fluid could be obtained. Because the blood work was negative, and it took three weeks for anything to grow out of the tissue aspirate, it was believed at the time that the positive culture was caused by sample contamination. Since the patient continued to complain of hip pain, a revision of the left hip Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants
3 ANALYSIS OF A POLYCARBONATE-URETHANE ACETABULAR CUP 71 was scheduled and performed 12 months after the initial implantation. At the time of revision, a normal amount of minimal synovial fluid was present (~1 ml) and its color appeared typical. A sample of the fluid was checked for infection and none was present. Histological analysis of tissue taken at the time of surgery confirmed that the patient s hip was not infected. During revision, the acetabular cup was found to be intact and well fixed to the acetabular bone. After removal of the cup, histological samples were taken adjacent to the back side of the cup. Because the cartilage and bone removed during the original surgery was minimal, the patient was revised to an identically sized 52 mm (outer diameter) metal shell with a UHMWPE component. After the revision surgery, the patient s hip pain persisted, and was attributed to her spine pathology. III. WEIGHT MEASUREMENT REPORT OF RETRIEVED CUP Weight measurements were taken of the retrieved cup and were compared to a reference weight determined by the average of three unused cups from the same production batch. The reference weight average was grams. The retrieved buffer was cleaned and found to weigh grams. Therefore, by assuming that the average weight on a dry unimplanted cup was representative of the starting weight of the implanted cup, the weight loss of the retrieved buffer cup can be calculated to be approximately grams or 2.1%. IV. HISTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS An independent pathologist analyzed the histological samples from this case report (Fig. 1). With the use of an H&E stain, 120 histological slides from eight locations of the acetabulum were created with only one location having any polycarbonate-urethane particles found. V. WEAR ANALYSIS The articulating surface of the polycarbonate-urethane cup retrieval appeared smooth and glossy, with minimal macroscopic wear. Evidence of macroscopic back-side abrasion was present on the back side of the retrieved cup the superior medial side in the area of loading (Fig. 2). ATR-FTIR confirmed that the white discoloration on the back side of the buffer was not a deposit of any heavy element, but was instead a protein deposit. A micro-ct analysis revealed that the bearing surface wear rate for the retrieval was less than 15 mm 3 per year. FIGURE 1. Histology slides from patient AI #001 showing little adverse reaction to particulate debris. Volume 18, Number 1, 2008
4 72 W. SIEBERT ET AL. FIGURE 2. Photographic documentation of patient AI #001 retrieval (left) and unimplanted control (right). VI. ANALYSIS OF RETRIEVED CUP The implants were examined using optical microscopy to determine the regions of minimal and maximal adhesive abrasive wear, which could be used to establish the anterior-posterior orientation of the components. By knowing the side on which the implant was located in vivo, the medial-lateral orientation could also be established. With the use of a quadrant system, and mass were measured in triplicate for each zone (Table 1). VII. SURFACE ASSESSMENT The components were visually examined under a stereomicroscope for evidence of wear and or macro- or microfatigue damage (Fig. 2). An abbreviated variant of the Hood method 8 was used to evaluate each face of the components for the presence and/ or absence of damage modes (e.g., plastic deformation, scratching, burnishing, pitting, delamination, abrasion) typically observed in retrieved UHM- TABLE 1. Average Dimensions and Mass Compared to Unimplanted Control Liner ID# Superior Inferior Medial Lateral Mass (g) AI # ± ± ± ± ± Control #1 2.8 ± ± Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants
5 ANALYSIS OF A POLYCARBONATE-URETHANE ACETABULAR CUP 73 TABLE 2. Damage Mode Scale Damage score Extent of damage 0 Absence of damage mode 1 10% coverage of wear surface % coverage of wear surface 3 50% coverage of wear surface Note: This damage scoring method is an assessment of the extent but not the severity of the damage that occurred in vivo. WPE orthopedic implants. 8 Each damage mode was graded on a 0 3 scale (Table 2). Based on this scoring method and the six modes of damage described above, the maximum damage score that an implant could possible receive would be 18. With the use of the nomenclature established above to identify each quadrant of the components, a wear score was assigned. Table 3 summarizes the values for retrieval for patient AI #001. These values indicate that relative to UHMWPE retrievals, this cup had very mild abrasive, burnishing, and scratching scores. The surface topography of the articulating surface of one retrieved and one control acetabular liner were measured using white-light interferometry (WLI) using a NewView 5000 Model 5032 equipped with advanced texture analysis software, MetroPro (Zygo, Middlefield, Connecticut). Nine measurements were taken on each retrieved component and six measurements were taken on the control component. Table 4 shows the average values for roughness (Ra) and waviness (Wa). The waviness represents the low-frequency features, and the roughness represents the high-frequency features. IX. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS We have presented a case report of a retrieved polycarbonate-urethane (PCU) acetabular cup that had been implanted for 12 months in a human. Overall, the surgical findings, data, and images collected from this case report were encouraging and similar to what was found in sheep 1 and predicted in TABLE 3. Totaled Wear Scores by Quadrant Liner ID Superior Medial Lateral Inferior Average AI # VIII. WHITE-LIGHT INTERFEROMETRY laboratory studies. 2,5 7 The cup had minimal loss of with the most being in the superior area (approximately 10%) and minimal loss of weight (2.4%). On the back side was evidence of abrasive macroscopic wear on one side of the implanted component in the area of directional loading from the head to the acetabulum. On the front side, the wear rate was determined to be minimal (less than 15 mm 3 per year), meaning that most of the change in and weight was caused on the back side. This volumetric wear rate compares favorably TABLE 4. White-Light Interferometry Measurements (Average ± Standard Deviation) AI #001 Control #1 R a (μm) ± ± Wa (μm) ± ± Volume 18, Number 1, 2008
6 74 W. SIEBERT ET AL. with that of standard UHMWPE retrievals found in the literature. Schmalzried et al. 9 and Jasty et al. 10 reported in vivo volumetric wear rates of 36 and 35 mm 3 per year, respectively. The articulating surface had a marked reduction in the surface roughness by a factor of about 2; the same reduction as was found with the identical articulating material after implanted for three years in hip of sheep. 4 The synovial fluid appeared normal in color and volume at the time of revision. The histology of the tissue taken showed minimal wear particles and minimal reactivity, confirming that the patient did not have any signs of synovitis. All of these findings indicate that the material was well tolerated by the body. The fact that the acetabular component could be easily revised with an identically sized component was viewed as a positive feature of this new type of hip replacement system. Although this retrieval is only from one patient, the analysis of the cup confirms the preclinically determined low wear articulation and biocompatibility of polycarbonate urethane as a weight-bearing material. 1,3,4 Also, it is unknown whether the rereaming and regrooving had any significant effect on the outcome. Continued evaluation of this new material for use in hip replacement surgery in humans is warranted. REFERENCES 1. Carbone A, Howie DW, McGee M, Field J, Pearcy M, Smith N, Jones E. Aging performance of a compliant layer bearing acetabular prosthesis in an ovine hip arthroplasty model. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6): Dowson D, Fisher J, Jin ZM, Auger DD, Jobbins B. Design considerations for cushion form bearings in artificial hip joints. Proc IMech E Part H. 1991;205: Khan I, Smith N, Jones E, Finch DS, Cameron RE. Analysis and evaluation of a biomedical polycarbonate urethane tested in an in vitro study and an ovine arthroplasty model. Part I: material selection and evaluation. Biomaterials. 2005;26: Khan I, Smith N, Jones E, Finch DS, Cameron RE. Analysis and evaluation of a biomedical polycarbonate urethane tested in an in vitro study and an ovine arthroplasty model. Part II: in vivo investigation. Biomaterials. 2005;26: Scholes SC, Unsworth A, Blamey JM, Burgess IC, Jones E, Smith N. Design aspects of compliant, soft layer bearings for an experimental hip prostesis. Proc. IMechE. Part H. 2005;219: Scholes SC, Burgess IC, Marsden HR, Unsworth A, Jones E, Smith N, Compliant layer acetabular cups: Friction testing of a new range of materials and designs for a new generation of prosthesis that mimics the natural joint. Proc. IMechE. Part H. 2006;220: Schwartz CJ, Bahadur S. Development and testing of a novel joint wear simulator and investigation of the viability of an elastomeric polyurethane for total-joint arthroplasty devices. Wear. 2006;262(3-4): Hood RW, Wright TM, Burstein AH. Retrieval analysis of total knee prostheses: a method and its application to 48 total condylar prostheses. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983; 17: Schmalzried TP, Kwong LM, Jasty M, Sedlacek RC, Haire TC, O Connor DO, Bragdon CR, Kabo JM, Malcolm AJ. The mechanism of loosening of cemented acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. Analysis of specimens retrieved at autopsy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 274: Jasty M, Goetz DD, Bragdon CR, Lee KR, Hanson AE, Elder JR, Harris WH. Wear of polyethylene acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. An analysis of one hundred and twenty-eight components retrieved at autopsy or revision operations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79A: Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants
Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate Urethane: A Case Report
 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 75 83 (2008) Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate Urethane: A Case Report B. Wippermann,
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 75 83 (2008) Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate Urethane: A Case Report B. Wippermann,
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval
 Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction. Effects on Polyethylene Wear
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
Long-term Wear Evaluation of an Artificial Medial Meniscus Implant
 Long-term Wear Evaluation of an Artificial Medial Meniscus Implant Jonathan J. Elsner, PhD, Maoz Shemesh, MSc, Adaya Shefy-Peleg, MSc, Eyal Zylberberg, BSc, Eran Linder-Ganz, PhD. Active Implants, Netanya,
Long-term Wear Evaluation of an Artificial Medial Meniscus Implant Jonathan J. Elsner, PhD, Maoz Shemesh, MSc, Adaya Shefy-Peleg, MSc, Eyal Zylberberg, BSc, Eran Linder-Ganz, PhD. Active Implants, Netanya,
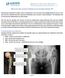
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation
 An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil
 Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil M.M.Souza 1, R.M. Trommer 2, M.M.Maru 2, C.R.M.Roesler 3, W.S.Barros 1, M.S. Dutra 3 1 Dimensional Metrology Laboratory, Inmetro. Brazil;
Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil M.M.Souza 1, R.M. Trommer 2, M.M.Maru 2, C.R.M.Roesler 3, W.S.Barros 1, M.S. Dutra 3 1 Dimensional Metrology Laboratory, Inmetro. Brazil;
Product Information. *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System
 APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code
 BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
Allofit /Allofit -S Alloclassic Acetabular Cup System
 Allofit /Allofit -S Alloclassic Acetabular Cup System Product Information Convincing Primary Stability The Allofit acetabular cup was developed in 1993. The goal was to create a reliable implant that was
Allofit /Allofit -S Alloclassic Acetabular Cup System Product Information Convincing Primary Stability The Allofit acetabular cup was developed in 1993. The goal was to create a reliable implant that was
Design Rationale and Clinical Review of a New Compliant Bearing Material for Acetabular Reconstruction
 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA Design Rationale and Clinical Review of a New Compliant Bearing Material for Acetabular Reconstruction Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc)*;
Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA Design Rationale and Clinical Review of a New Compliant Bearing Material for Acetabular Reconstruction Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc)*;
Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
Failure Analysis of Retrieved Polyethylene Insert in Total Knee Replacement
 Failure Analysis of Retrieved Polyethylene Insert in Total Knee Replacement DAN GRECU 1, IULIAN ANTONIAC 2*, OCTAVIAN TRANTE 2, MARIUS NICULESCU 3, OLIVERA LUPESCU 4 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy
Failure Analysis of Retrieved Polyethylene Insert in Total Knee Replacement DAN GRECU 1, IULIAN ANTONIAC 2*, OCTAVIAN TRANTE 2, MARIUS NICULESCU 3, OLIVERA LUPESCU 4 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 EMPIRICAL TESTING CORP. 4628 Northpark Drive Colorado Springs, CO 80918 Dawn Lissy Phone: 719 264 9937 dlissy@empiricaltesting.com MECHANICAL Valid To: January
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 EMPIRICAL TESTING CORP. 4628 Northpark Drive Colorado Springs, CO 80918 Dawn Lissy Phone: 719 264 9937 dlissy@empiricaltesting.com MECHANICAL Valid To: January
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique. *smith&nephew TANDEM. Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System
 Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
StelKast Acetabular. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications. Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems
 StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Long-Term Evaluation of a Compliant Cushion Form Acetabular Bearing for Hip Joint Replacement: A 20 Million Cycles Wear Simulation
 Long-Term Evaluation of a Compliant Cushion Form Acetabular Bearing for Hip Joint Replacement: A 20 Million Cycles Wear Simulation Jonathan J. Elsner, 1 Maoz Shemesh, 1 Yoav Mezape, 1 Mario Levenshtein,
Long-Term Evaluation of a Compliant Cushion Form Acetabular Bearing for Hip Joint Replacement: A 20 Million Cycles Wear Simulation Jonathan J. Elsner, 1 Maoz Shemesh, 1 Yoav Mezape, 1 Mario Levenshtein,
MicroSeal Total Hip Acetabular System. Like Nothing Else
 MicroSeal Total Hip Acetabular System Like Nothing Else Like Nothing Else Unique Patented Sealing and Locking Design The MicroSeal design features: Locking/Sealing mechanisms work together to minimize
MicroSeal Total Hip Acetabular System Like Nothing Else Like Nothing Else Unique Patented Sealing and Locking Design The MicroSeal design features: Locking/Sealing mechanisms work together to minimize
Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
CERAMIC-ON-METAL. References: Cat No: version 2
 CERAMIC-ON-METAL References: 1. Beaule, P. E., et al. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J.Bone Joint Surg (2002). 84-A: 256-63. 2. Jolles, B.
CERAMIC-ON-METAL References: 1. Beaule, P. E., et al. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J.Bone Joint Surg (2002). 84-A: 256-63. 2. Jolles, B.
TriboFit Hip System. Issue 3 - August 2013 English
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Observations on retrieved articular surfaces of total knee prostheses. Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands
 Chapter 11 Observations on retrieved articular surfaces of total knee prostheses Eric H. Garling 1, Henk K. Koerten 2, Edward R. Valstar 1,3, Rob G.H.H. Nelissen 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
Chapter 11 Observations on retrieved articular surfaces of total knee prostheses Eric H. Garling 1, Henk K. Koerten 2, Edward R. Valstar 1,3, Rob G.H.H. Nelissen 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
LEGION Total Knee System. Exceptional Durability
 LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
Reaching new heights. Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple.
 Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
ESC. Enhanced Stability Liners. Design Rationale & Surgical Technique
 ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of?
 What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Instrumentation Options
 Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
Effect of Femoral Head Size to Contact Stress at Pure Titanium Femoral Ball Head Outer Surface of Hip Joint Implant
 Effect of Femoral Head Size to Contact Stress at Pure Titanium Femoral Ball Head Outer Surface of Hip Joint Implant Agung Setyo Darmawan, Waluyo Adi Siswanto, Haryanti Samekto Faculty of Mechanical and
Effect of Femoral Head Size to Contact Stress at Pure Titanium Femoral Ball Head Outer Surface of Hip Joint Implant Agung Setyo Darmawan, Waluyo Adi Siswanto, Haryanti Samekto Faculty of Mechanical and
39 year old, 260 lb. park ranger. TKA in situ: 4 Years. First reported Metal-backed, non-modular PCA knee. 16% incidence. Modular metalbacked
 Designer (Royalty income) - DePuy A Johnson & Johnson Company Consultant on Knee Products for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics General Research Funding Inova Health System and the U.S. Army Medical Research
Designer (Royalty income) - DePuy A Johnson & Johnson Company Consultant on Knee Products for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics General Research Funding Inova Health System and the U.S. Army Medical Research
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Impingement in THA. Georgi I. Wassilew. Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C.
 Georgi I. Wassilew Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C. Perka Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Orthoload club, Berlin Reasons for revision in THA Reason
Georgi I. Wassilew Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C. Perka Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Orthoload club, Berlin Reasons for revision in THA Reason
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility
 PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners. Design Rationale Surgical Technique
 Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 7206-12 First edition 2016-10-01 Implants for surgery Partial and total hip joint prostheses Part 12: Deformation test method for acetabular shells Implants chirurgicaux Prothèses
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 7206-12 First edition 2016-10-01 Implants for surgery Partial and total hip joint prostheses Part 12: Deformation test method for acetabular shells Implants chirurgicaux Prothèses
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Zimmer TM. Continuum Acetabular System. Bringing together proven technologies.
 Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
I want that next-generation knee
 I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
6.1 Hip Joint Simulators: State of the Art
 Tribology 171 6.1 Hip Joint Simulators: State of the Art S. Affatato, W. Leardini and M. Zavalloni Abstract Wear and simulator testing are complicated tasks. Controlled wear testing should not be routinely
Tribology 171 6.1 Hip Joint Simulators: State of the Art S. Affatato, W. Leardini and M. Zavalloni Abstract Wear and simulator testing are complicated tasks. Controlled wear testing should not be routinely
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
 Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY
 FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT:
 THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement
 CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health
CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence.
 RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
Peggers Super Summaries: THR and Revision Concepts
 Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Implants for surgery Partial and total hip joint prostheses. Part 12: Deformation test method for acetabular shells
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 7206-12 First edition 2016-10-01 Implants for surgery Partial and total hip joint prostheses Part 12: Deformation test method for acetabular shells Implants chirurgicaux Prothèses
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 7206-12 First edition 2016-10-01 Implants for surgery Partial and total hip joint prostheses Part 12: Deformation test method for acetabular shells Implants chirurgicaux Prothèses
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Manza Cup HA SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
 1 PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING. Preoperative assessment of the appropriate size and position of the acetabular component will provide intraoperative guidance for acetabular reaming. To determine the acetabluar
1 PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING. Preoperative assessment of the appropriate size and position of the acetabular component will provide intraoperative guidance for acetabular reaming. To determine the acetabluar
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene
 MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
Progeny Hip Stem. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications
 Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Enhancing Stability and Increasing Range of Motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique
Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Enhancing Stability and Increasing Range of Motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis*
 Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Hip Resurfacing System
 Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System
 GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
R3think your options. For US distribution only.
 R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene. Clinical Value Dossier - APAC
 Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report
 Syracuse University SURFACE Biomedical and Chemical Engineering College of Engineering and Computer Science 1997 Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report R T. Trousdale
Syracuse University SURFACE Biomedical and Chemical Engineering College of Engineering and Computer Science 1997 Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report R T. Trousdale
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Ceramic Femoral Heads and Acetabular Cup Liners
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT
 ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success. Zimmer Natural-Knee II System
 Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Wear 268 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Wear. journal homepage:
 Wear 268 (2010) 617 621 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Wear journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/wear Wear comparison between a dual mobility total hip prosthesis and a typical modular
Wear 268 (2010) 617 621 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Wear journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/wear Wear comparison between a dual mobility total hip prosthesis and a typical modular
Activity Level and Wear in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 16 No. 4 2001 Activity Level and Wear in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Study of Autopsy Retrieved Specimens Carlos J. Lavernia, MD,* Rafael J. Sierra, MD,* David S. Hungerford,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 16 No. 4 2001 Activity Level and Wear in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Study of Autopsy Retrieved Specimens Carlos J. Lavernia, MD,* Rafael J. Sierra, MD,* David S. Hungerford,
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
Disclosure. Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table. History 11/3/2015
 Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table J. Masonis, M.D. OrthoCarolina Hip & Knee Center Chief Adult Hip & Knee reconstruction Carolinas Medical Center Disclosure Consultant & Design Smith & Nephew Zimmer
Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table J. Masonis, M.D. OrthoCarolina Hip & Knee Center Chief Adult Hip & Knee reconstruction Carolinas Medical Center Disclosure Consultant & Design Smith & Nephew Zimmer
Dual Mobility Cups. Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium
 Dual Mobility Cups Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium Introduction Indications Limitations Conclusions All good things in life come from France Gilles Bousquet 1979 + Rambert (SERF) Inventions Bousquet
Dual Mobility Cups Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium Introduction Indications Limitations Conclusions All good things in life come from France Gilles Bousquet 1979 + Rambert (SERF) Inventions Bousquet
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX
 HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX HIP IMPLANTS TOTAL HIPS Ultra High Demand (metal on metal) Femur, ingrowth Femoral head, metal Acetabular shell, ingrowth Acetabular liner,
HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX HIP IMPLANTS TOTAL HIPS Ultra High Demand (metal on metal) Femur, ingrowth Femoral head, metal Acetabular shell, ingrowth Acetabular liner,
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces
 Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
PMMA Spacer. X-ray Marker
 Full TM Cup 2.5 mm cement thickness PMMA Spacer Uniform 2.5 mm cement thickness; the cement mantle is built within the outer dimension of acetabular cup. Cup O.D. 20 o lipped Prevent joint dislocation
Full TM Cup 2.5 mm cement thickness PMMA Spacer Uniform 2.5 mm cement thickness; the cement mantle is built within the outer dimension of acetabular cup. Cup O.D. 20 o lipped Prevent joint dislocation
Partial hip resurfacing is considered investigational/not medically necessary for all other indications not listed above.
 Subject: Policy #: Current Effective Date: 11/13/2006 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 09/14/2006 Description/Scope Hip resurfacing can be categorized in two ways: as a partial (hemi) hip resurfacing
Subject: Policy #: Current Effective Date: 11/13/2006 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 09/14/2006 Description/Scope Hip resurfacing can be categorized in two ways: as a partial (hemi) hip resurfacing
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe
 1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 3 2000 The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty Motoi Yamaguchi, MD, PhD,* Toshihiro Akisue, MD, PhD,* Thomas W. Bauer, MD, PhD,* and Yasushi
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 3 2000 The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty Motoi Yamaguchi, MD, PhD,* Toshihiro Akisue, MD, PhD,* Thomas W. Bauer, MD, PhD,* and Yasushi
Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements.
 Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements. P. Bills*, L. Blunt*, G. Chakrabarty** *University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK **West
Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements. P. Bills*, L. Blunt*, G. Chakrabarty** *University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK **West
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
*smith&nephew CONTOUR
 Surgical Technique *smith&nephew CONTOUR Acetabular Rings CONTOUR Acetabular Rings Surgical technique completed in conjunction with Joseph Schatzker MD, BSc (Med.), FRCS (C) Allan E. Gross, MD, FRCS (C)
Surgical Technique *smith&nephew CONTOUR Acetabular Rings CONTOUR Acetabular Rings Surgical technique completed in conjunction with Joseph Schatzker MD, BSc (Med.), FRCS (C) Allan E. Gross, MD, FRCS (C)
