Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement
|
|
|
- Chester Blair
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
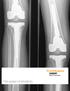
1 CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health Sciences Centre, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada We present a case of early retrieval of an Oxinium femoral head and corresponding polyethylene liner where there was significant surface damage to the head and polyethylene. The implants were retrieved at the time of revision surgery to correct leglength discrepancy just 48 hours after the primary hip replacement. Appropriate analysis of the retrieved femoral head demonstrated loss of the Oxinium layer with exposure of the underlying substrate and transfer of titanium from the acetabular shell at the time of a reduction of the index total hip replacement. In addition, the level of damage to the polyethylene was extensive despite only 48 hours in situ. The purpose of this report is to highlight the care that is required at the time of reduction, especially with these hard femoral counter-faces such as Oxinium. To our knowledge, the damage occurring at the time of reduction has not been previously reported following the retrieval of an otherwise well-functioning hip replacement. R. W. McCalden, MD, MPhil(Edin), FRCSC, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Associate Professor K. D. Charron, Mechanical Engineering Technologist (MET) University of Western Ontario, London Health Sciences Centre, 339 Windermere Road, London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5A5. R. D. Davidson, Metallurgical Technologist, Manager Scientific Operations Surface Science Western The University of Western Ontario, Research and Development Park Convergence Centre, 999 Collip Circle, London, Ontario, Canada N6G 0J3. M. G. Teeter, BSc, PhD Candidate Medical Biophysics D. W. Holdsworth, PhD, Professor Department of Surgery, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry University of Western Ontario, Robarts Research Institute, 100 Perth Drive, London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5K8. Correspondence should be sent to Professor R. W. McCalden; Richard.McCalden@lhsc.on.ca 2011 British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery doi: / x.93b $2.00 J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2011;93-B: Received 7 June 2010; Accepted after revision 25 October 2010 Survivorship after total hip replacement (THR) in the long term has been limited by aseptic loosening and osteolysis secondary to wear and particulate polyethylene debris. 1-3 In response, many bearing options and materials are now available in the hope that implants will last longer. Recently, a material known as oxidised zirconium, or Oxinium (Smith & Nephew, Memphis, Tennessee), has been used to manufacture femoral head components for THR, as it demonstrates excellent wear characteristics against polyethylene in vitro. 4,5 We report the case of the early retrieval of an Oxinium femoral head and corresponding polyethylene liner which demonstrated significant surface damage to the head and adjacent polyethylene. The implants were retrieved at the time of revision surgery for leg-length discrepancy after only 48 hours in situ. The patient whose specimen was retrieved gave informed consent to her case being written-up. Case report A 62-year-old semi-retired physiotherapist presented with osteoarthritis of the left hip and underwent THR through a direct lateral approach. The surgery was performed by an orthopaedic resident under the direct supervision of an experienced arthroplasty surgeon in a university teaching hospital. The surgery was uneventful. Approximately 5 mm of leg lengthening and restoration of femoral offset was achieved, based on intra-operative assessment using a leg-length/offset guide. The components consisted of an R3 no-hole shell (with a diameter of 52 mm) (Smith & Nephew), an R3 zero degree cross-linked polyethylene liner with a 32 mm inner diameter (Smith & Nephew) a Synergy high-offset femoral component (size 11) (Smith & Nephew) and a Oxinium femoral head (Smith & Nephew). The immediate post-operative radiographs were satisfactory. On the first post-operative morning, she complained of excessive lengthening of the left leg when mobilised for the first time. Clinical examination and repeat radiographs suggested a true leg-length discrepancy of approximately 1.0 cm to 1.3 cm. She was unhappy with this situation and was offered an immediate revision which was undertaken on the second morning. After removing the staples and the fascial sutures the hip was dislocated. The femoral head was carefully disassociated from the trunnion. On inspection, there was clear evidence of metal transfer, consisting of a metallic line on the inferior aspect of the black femoral articulating surface. There were also corresponding deep scratches in the adjacent polyethylene. It was clear that there had been contact between the Oxinium head and the exposed metal rim of the acetabular component at the time of the initial reduction. VOL. 93-B, No. 3, MARCH
2 410 R. W. MCCALDEN, K. D. CHARRON, R. D. DAVIDSON, M. G. TEETER, D. W. HOLDSWORTH Fig. 1 Micro-CT scanned image showing the polyethylene liner at retrieval. Damage to the articular surface is broad in the medial/anterior area of articulation. Fig. 2 Surface deviation map showing the polyethylene liner (constructed from micro-ct image with Geomagic software). Gradient scale depicts depth of damage to articular surface. Accordingly, the liner was replaced. Although it was found to be stable, the femoral component was removed and the femur was re-prepared such that the final broach was advanced approximately 8 mm or 9 mm further than the primary component. The final component, a size 12 high-offset Synergy stem (Smith & Nephew) was then inserted and was deemed to be axially and rotationally stable. A mm Oxinium femoral head component (Smith & Nephew) was used. The hip was reduced with care, ensuring that there was no contact between the head and the exposed metal rim of the acetabular component. Post-operatively there were no complications and she made an uneventful recovery. At one year she has a Harris hip score 6 of 93 with a satisfactory radiological appearance. Implant analysis Materials and methods. A thorough investigation of the retrieved head and liner was undertaken. After removal, the liner and head were submerged in a 10% formalin solution for 48 hours. The implants were then removed and placed in an ultrasonic bath for 20 minutes. After drying, the Oxinium head was digitally photographed (Canon EOS (Canon Virginia Inc., Newport News, Virginia), Olympus C5050 digital camera with Olympus Z4045 stereomicroscope (Olympus Imaging America Inc., Center Valley, Pennsylvania)) while the polyethylene liner was imaged with the use of micro-ct, from which surface deviation maps were created. The Oxinium head was examined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (LEO 440 SEM (Carl Zeiss SMT Inc., Peabody, Massacheusetts) equipped with Quartz Xone EDX system (Quartz Imaging Corporation, Vancouver, British Columbia)). Both secondary electron and back-scattered electron imaging techniques were used. The former provides information on surface topography and the latter is sensitive to differences in atomic number. Elemental analysis was carried out using energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry. This can detect all elements above the atomic number 5 (carbon through to uranium) and has a minimum detection limit of ~0.5wt% for most elements. An electron beam of 10 kv was used to obtain both SEM images and energy-dispersive X-ray intensity element maps. Lastly, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis was conducted to identify whether carbon-based deposits represented organic matter or polyethylene debris. Results. Surface damage, in the form of deep scratches and gouges, was readily apparent to the naked eye on the polyethylene liner. Using a micro-ct imaging technique 7 the liner was imaged (Fig. 1). A map of the surface deviation was created with specialised software (Geomagic Qualify (Geomagic Inc., Durham, North Carolina)) (Fig. 2). Analysis demonstrated surface deviations in the cross-linked polyethylene surface ranging from 14 μm to 38 μm in depth. The Oxinium femoral head was inspected and demonstrated an intersection of two material transfers/scratches on the articulating surface (Fig. 3a). Attention was focused at the intersection and was photographed with a stereomicroscope at 20 magnification (Fig. 3b). The area of interest underwent SEM imaging at various magnifications (Fig. 4). This revealed damage to the surface consisting of a raised area (possible titanium transfer from the acetabular shell), deep scratches in the oxidised zirconium surface with possible exposure of the underlying zirconium substrate, THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
3 DAMAGE OF AN OXINIUM FEMORAL HEAD AND POLYETHYLENE LINER FOLLOWING ROUTINE TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 411 Fig. 3a Fig. 3b Digital photographs of the retrieved Oxinium femoral head, showing a) two obvious damage features, potentially material transfer from the acetabular shell or scratches through the Oxinium surface, and b) a stereo-microscope image (20 magnification) of the intersection of the two damage features, which appear to be scratches with suspected titanium transfer from the acetabular shell. Fig. 4a Fig. 4b Fig. 4c Secondary electron images showing macro and micro damage to the Oxinium coating at different levels of magnification. Figure 4a (magnification 30) there appears to be a tangential pattern of surface fatigue bordering scratch 1 (A). Darker borders of the scratches (B) may represent the transfer of titanium from the acetabular shell. The darker debris (C) is carbon rich, possibly polyethylene debris or organic material. Figure 4b (magnification 100) the tangential pattern of fatigue (A) suggests that Oxinium has flaked off the surface of the femoral head along the outer edges of scratch 1 and in part on scratch 2. Hairline cracking is visible (B) along scratch 2. Figure 4c (magnification 250) surface fatigue has resulted in the loss of the Oxinium surface, exposing the zirconium substrate (A). Granules of oxidised zirconium that are about to flake off are identifiable (B). Extensive surface cracking has occurred. and tangential cracking along the edges of the scratch damage. Examination at higher magnification (Fig. 4c) clearly showed the presence of smaller cracks in the Oxinium coating. These cracks indicated that the coating had been damaged and could delaminate or flake off at any time. Back-scattered electron imaging revealed the difference in composition of the materials based on atomic number differences (Fig. 5). Elements with higher atomic numbers back-scatter electrons more strongly than those with a lower atomic number, thus appearing brighter in the image. Energy-dispersive x-ray intensity element maps were obtained for the area shown in Figure 6. These maps clearly showed the spatial distribution of the major elements of interest (oxygen, titanium, aluminium, zirconium and carbon). The oxygen map confirmed the presence of oxidised zirconium on either side of the damage and scratched regions. The lack of oxygen detected in the scratched region clearly indicated that exposure of the underlying femoral head substrate had occurred. The titanium and aluminium element maps confirmed that metal transfer from the acetabular shell had also occurred. The carbon-rich deposits were further analysed with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy which identified them as organic in nature, most likely fibrinous deposits, rather than polyethylene. Discussion Oxidised zirconium (Oxinium) has been developed by Smith & Nephew as a new material for the counter-face of VOL. 93-B, No. 3, MARCH 2011
4 412 R. W. MCCALDEN, K. D. CHARRON, R. D. DAVIDSON, M. G. TEETER, D. W. HOLDSWORTH Fig. 5 Back-scattered electron image showing the damaged region of interest. Region 1 is the undamaged oxidised zirconium surface. The brighter scratched region (2) is the underlying metal substrate (the Oxinium coating has been removed). Region 3 is titanium transfer from the acetabular shell. Dark regions (4) are carbon-rich material. Fig. 6 Back-scattered electron image and energy dispersive x-ray intensity element maps showing the concentration of major elements at the damaged region of interest. Image intensity is directly proportional to the element concentration. O, oxygen; Ti, titanium; Al, aluminium; Zr, zirconium; C, carbon. The O intensity is much weaker, while the Zr intensity is much higher, confirming the complete loss of the oxidised zirconium coating in this area. The concentration and distribution of material transfer from the acetabular shell is well-represented with the mapping of Ti and Al. the femoral head for articulation against polyethylene in THR. 4,5 Thermally driven oxygen diffusion transforms the surface of the metallic alloy into a low friction oxidised layer approximately 4 μm to 5 μm thick. Hunter and Long 8 demonstrated Oxinium to have 4900 times less abrasive volumetric wear and 640 times less deep scratches than CoCr when articulating against bone cement. Similarly, Good et al, 5 using a roughened-head protocol, demonstrated 61% less polyethylene wear and 45% fewer polyethylene particles with rough Oxinium heads compared to rough CoCr heads. Furthermore, Bourne et al, 4 in reviewing large numbers of retrieved CoCr heads, created an THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 DAMAGE OF AN OXINIUM FEMORAL HEAD AND POLYETHYLENE LINER FOLLOWING ROUTINE TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT 413 experimental dislocation model which demonstrated considerable advantage to the damaged Oxinium heads articulating against both conventional and highly cross-linked polyethylene compared with CoCr heads. In addition, Oxinium heads retrieved from patients with recurrent dislocation demonstrated less deep scratches and less build-up of adjacent material around the scratches compared with those of CoCr. With respect to the clinical results of Oxinium femoral heads for THR, only studies with short follow-up exist. Lewis et al 9 showed no difference in clinical outcome at two years in a randomised controlled trial comparing Oxinium with CoCr heads. Garvin et al 10 reported a low rate of wear (4 μm ± 59 μm per year) at short-term followup with Oxinium heads articulating with highly crosslinked polyethylene. To date, there have been three reports concerning the surface damage observed on retrieved Oxinium heads, all retrieved after many or unsuccessful closed reductions for dislocation Evangelista et al 11 and Kop et al 13 both reported significant surface damage to the Oxinium heads, characterised by gouging and cracking of the oxide layer and metal transfer which was not fully characterised. The latter study further demonstrated greater indentation damage and deeper scratches in the Oxinium heads compared with retrieved CoCr heads, which they associated with the decreased bulk hardness of the underlying Oxinium substrate. More recently, Jaffe et al, 12 through more extensive analysis, demonstrated similar findings on four retrieved Oxinium heads retrieved from patients with recurrent dislocation and confirmed the presence of titanium metal transfer through energy-dispersive x-ray analysis. In addition, they performed in vitro wear analysis on a hip simulator using the retrieved Oxinium heads, artificially damaged Oxinium heads and pristine Oxinium heads, clearly demonstrating an increase in polyethylene wear of up to 50 times associated with increasing surface damage. All authors recommended either replacement of the Oxinium head in the setting of a failed or recurrent closed reduction or, at the very least, close monitoring for excessive wear. The analysis of the retrieved specimens from our case demonstrated clear evidence of surface damage, with loss of the Oxinium layer and exposed underlying substrate, and transfer of titanium material from the acetabular shell at the time of reduction of the THR. The implant was retrieved at the time of early revision for leg-length discrepancy. The amount of polyethylene damage was surprising after only 48 hours in situ, in which the patient had only been mobilised for a period of 24 hours after operation. There is little question that the damage of the articulating surface occurred at the time of the initial reduction as contact was made between the Oxinium head and the exposed titanium shell. It is plausible that lengthening of the leg, by making the reduction of the hip more difficult, contributed to the level of contact between the head and the acetabular shell. To our knowledge, damage occurring at the time of reduction has not been reported previously following a retrieval of an otherwise well-functioning hip replacement. The probability of this head/shell contact has been increased by the design of the R3 shell in which the polyethylene insert is flush with the face of the shell, leaving an exposed rim of metal. The purpose of this report was not to condemn the technology used or the design of this implant system, but rather to highlight the care that needs to be taken when reducing the hip at operation, especially with the hard femoral counter-faces (such as Oxinium or ceramic heads) and in particular where the metal edge of the acetabular shell is prominent. We can only speculate as to the true incidence of this phenomenon or what the long-term effects might be. However, based on the level and speed of polyethylene damage that was observed, it might negate the potential benefits of using a hard counter-face against a highly crosslinked polyethylene liner. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. References 1. Harris WH. The problem is osteolysis. Clin Orthop 1995;311: Sochart DH. Relationship of acetabular wear to osteolysis and loosening in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 1999;363: Willert HG, Bertram H, Buchhorn GH. Osteolysis in alloarthroplasty of the hip: the role of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene wear particles. Clin Orthop 1990;258: Bourne RB, Barrack R, Rorabeck CH, Salehi A, Good V. Arthroplasty options for the young patient: oxinium on cross-linked polyethylene. Clin Orthop 2005;441: Good V, Ries M, Barrack RL, et al. Reduced wear with oxidized zirconium femoral heads. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2003;85-A(Suppl 4): Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthoplasty: an end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1969;51-A: Teeter MG, Naudie DD, Charron KD, Holdsworth DW. Three-dimensional surface deviation maps for analysis of retrieved polyethylene acetabular liners using micro-computed tomography. J Arthroplasty 2010;25: Hunter G, Long M. Abrasive wear of oxidized Zr-2.5Nb, CoCrMo and Ti-6A1-4V against bone cement. Trans 6th World Biomaterials Congress, Society for Biomaterials. 2000: Lewis PM, Moore CA, Olsen M, Schemitsch EH, Waddell JP. Comparison of mid-term clinical outcomes after primary total hip arthroplasty with Oxinium vs cobalt chrome femoral heads. Orthopedics 2008;12(Suppl 2):pii. 10. Garvin KL, Hartman CW, Mangla J, Murdoch N, Martell JM. Wear analysis in THA utilizing oxidized zirconium and crosslinked polyethylene. Clin Orthop 2009;467: Evangelista GT, Fulkerson E, Kummer F, Di Cesare PE. Surface damage to an Oxinium femoral head prosthesis after dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2007;89-B: Jaffe WL, Strauss EJ, Cardinale M, Herrera L, Kummer FJ. Surface oxidized zirconium total hip arthroplasty head damage due to closed reduction effects on polyethylene wear. J Arthroplasty 2009;24: Kop AM, Whitewood C, Johnston DJ. Damage of oxinium femoral heads subsequent to hip arthroplasty dislocation three retrieval case studies. J Arthroplasty 2007;22: VOL. 93-B, No. 3, MARCH 2011
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction. Effects on Polyethylene Wear
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation
 An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
Reaching new heights. Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple.
 Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
R3think your options. For US distribution only.
 R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
LEGION Total Knee System. Exceptional Durability
 LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals
 Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals Trusted technology. Trusted performance. The POLAR3 Total Hip Solution, powered by Smith & Nephew s proprietary VERILAST Technology,
Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals Trusted technology. Trusted performance. The POLAR3 Total Hip Solution, powered by Smith & Nephew s proprietary VERILAST Technology,
Product Information. *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System
 APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Why precision is powerful
 Why precision is powerful A new answer for isolated patellofemoral OA First generation PFJ implants had sharp, constraining trochlear grooves and were prone to complications such as maltracking and catching
Why precision is powerful A new answer for isolated patellofemoral OA First generation PFJ implants had sharp, constraining trochlear grooves and were prone to complications such as maltracking and catching
We would like to thank the following surgeons for their participation as part of the R3 Acetabular System design team:
 Design Rationale We would like to thank the following surgeons for their participation as part of the R3 Acetabular System design team: Robert Barrack, MD St. Louis, Missouri Robert Bourne, MD London Health
Design Rationale We would like to thank the following surgeons for their participation as part of the R3 Acetabular System design team: Robert Barrack, MD St. Louis, Missouri Robert Bourne, MD London Health
VERILAST Technology. Published articles compendium. Technology Hips Polars Knees Cartilage
 VERILAST Technology Published articles compendium Technology Hips Polars Knees Cartilage OXINIUM published articles compendium This compendium is designed to help Smith & Nephew sales representatives quickly
VERILAST Technology Published articles compendium Technology Hips Polars Knees Cartilage OXINIUM published articles compendium This compendium is designed to help Smith & Nephew sales representatives quickly
Exeter. Designed for Anatomic Restoration. Clinical Evidence Education
 Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Bi-Polar 22.2mm & 28mm System - Operative technique
 Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility
 PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology. porous primary hip series
 The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology porous primary hip series BI-METRIC XR SERIES implant technology The Bi-Metric XR Hip Series
The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology porous primary hip series BI-METRIC XR SERIES implant technology The Bi-Metric XR Hip Series
Designed for life. Implant technology with unmatched wear performance
 Designed for life Implant technology with unmatched wear performance Designed for life Wear performance combined with a multitude of options so you can find the right combination to restore the joints
Designed for life Implant technology with unmatched wear performance Designed for life Wear performance combined with a multitude of options so you can find the right combination to restore the joints
Hip Resurfacing System
 Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
The challenge. Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery
 The challenge Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery THA 52% Post-op TKA 42% Preop 36% Preop 34% Post-op Total
The challenge Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery THA 52% Post-op TKA 42% Preop 36% Preop 34% Post-op Total
Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Enhancing Stability and Increasing Range of Motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique
Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique Enhancing Stability and Increasing Range of Motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head Surgical Technique
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT:
 THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique. *smith&nephew TANDEM. Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System
 Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
Active Articulation E1
 Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
Zimmer TM. Continuum Acetabular System. Bringing together proven technologies.
 Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(4): 216-222, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(4): 216-222, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence.
 RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
OXINIUM Femoral Heads. *smith&nephew
 Femoral Heads *smith&nephew Less wear More options Without the risks Even the best cobalt chrome and ceramic femoral heads come with the risks of wear or breakage. But with femoral heads, those risks are
Femoral Heads *smith&nephew Less wear More options Without the risks Even the best cobalt chrome and ceramic femoral heads come with the risks of wear or breakage. But with femoral heads, those risks are
Peggers Super Summaries: THR and Revision Concepts
 Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval
 Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28. Operative Technique
 Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Orthopedic Surgery (Adult Hip Service) (Seoul National University Hospital)
 Orthopedic Surgery (Adult Hip Service) (Seoul National University Hospital) 1. Introduction Total hip replacement arthroplasty (THRA) using a metal-on-polyethylene articulation has become one of the most
Orthopedic Surgery (Adult Hip Service) (Seoul National University Hospital) 1. Introduction Total hip replacement arthroplasty (THRA) using a metal-on-polyethylene articulation has become one of the most
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician.
 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH Mpact 3D Metal Implants and Augments 3D Metal INSTRUCTION FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can
CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH Mpact 3D Metal Implants and Augments 3D Metal INSTRUCTION FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can
Ceramic Femoral Heads and Acetabular Cup Liners
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists
 : 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
: 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report
 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique
 Trinity Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 6 3. Acetabular
Trinity Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 6 3. Acetabular
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC.
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces
 Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
ESC. Enhanced Stability Liners. Design Rationale & Surgical Technique
 ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem
 Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Understanding Hip Implant Options
 Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Dual Mobility System Surgical technique
 Trinity Dual Mobility System Surgical technique 2 Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 7 3. Acetabular shell implantation
Trinity Dual Mobility System Surgical technique 2 Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 7 3. Acetabular shell implantation
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System
 GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code
 BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
Furlong H-A.C. THR System
 Important Information Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
Radiographic Wear Measurements in a Cementless Metal-Backed Modular Cobalt-Chromium Acetabular Component
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 16 No. 7 2001 Radiographic Wear Measurements in a Cementless Metal-Backed Modular Cobalt-Chromium Acetabular Component Robert L. Barrack, MD,* Carlos Lavernia, MD, Edward
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 16 No. 7 2001 Radiographic Wear Measurements in a Cementless Metal-Backed Modular Cobalt-Chromium Acetabular Component Robert L. Barrack, MD,* Carlos Lavernia, MD, Edward
Session 3: Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR
 : Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the indications and known methods for the use of each of
: Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the indications and known methods for the use of each of
TriboFit Hip System. Issue 3 - August 2013 English
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Technique Guide Hip Resurfacing System
 Technique Guide Hip Resurfacing System Approximately 5%-18% of all hip arthroplasties are completed on patients with a primary diagnosis of osteonecrosis. Patients are generally younger adults age 35 years
Technique Guide Hip Resurfacing System Approximately 5%-18% of all hip arthroplasties are completed on patients with a primary diagnosis of osteonecrosis. Patients are generally younger adults age 35 years
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe
 1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christopher Samujh, MD; Samrath Bhimani, MS; Langan Smith, BS; Arthur L. Malkani, MD abstract A major
Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christopher Samujh, MD; Samrath Bhimani, MS; Langan Smith, BS; Arthur L. Malkani, MD abstract A major
I want that next-generation knee
 I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
TITLE: Metal on Metal Total Hip Replacements or Hip Resurfacing for Adults: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
 TITLE: Metal on Metal Total Hip Replacements or Hip Resurfacing for Adults: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness DATE: 15 November 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Total hip replacement
TITLE: Metal on Metal Total Hip Replacements or Hip Resurfacing for Adults: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness DATE: 15 November 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Total hip replacement
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil
 Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil M.M.Souza 1, R.M. Trommer 2, M.M.Maru 2, C.R.M.Roesler 3, W.S.Barros 1, M.S. Dutra 3 1 Dimensional Metrology Laboratory, Inmetro. Brazil;
Surface evaluation of orthopedic hip implants marketed in Brazil M.M.Souza 1, R.M. Trommer 2, M.M.Maru 2, C.R.M.Roesler 3, W.S.Barros 1, M.S. Dutra 3 1 Dimensional Metrology Laboratory, Inmetro. Brazil;
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
FLH183 04/08. Biomet UK Ltd Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales CF31 3XA, United Kingdom. Tel. +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0)
 FLH183 04/08 Biomet UK Ltd Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales CF31 3XA, United Kingdom Tel. +44 (0)1656 655221 Fax: +44 (0)1656 645454 Exceed ABT Operative Technique The Exceed ABT TM acetabular
FLH183 04/08 Biomet UK Ltd Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales CF31 3XA, United Kingdom Tel. +44 (0)1656 655221 Fax: +44 (0)1656 645454 Exceed ABT Operative Technique The Exceed ABT TM acetabular
JRI Thompson Hemiarthroplasty
 JRI ORTHOPAEDICS LTD 18 Churchill Way, 35A Business Park, Chapeltown, Sheffield, S35 2PY, UK Instructions for Use JRI Thompson Hemiarthroplasty Page 1 of 6 English 3 Page 2 of 6 Important Information Please
JRI ORTHOPAEDICS LTD 18 Churchill Way, 35A Business Park, Chapeltown, Sheffield, S35 2PY, UK Instructions for Use JRI Thompson Hemiarthroplasty Page 1 of 6 English 3 Page 2 of 6 Important Information Please
REFLECTION Constrained Liner Introduction
 Surgical Technique REFLECTION Constrained Liner Introduction Surgical treatment of recurrent dislocation should be directed toward correction of any mechanical abnormalities. If dislocation is caused
Surgical Technique REFLECTION Constrained Liner Introduction Surgical treatment of recurrent dislocation should be directed toward correction of any mechanical abnormalities. If dislocation is caused
Aesculap Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem
 Aesculap Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem Aesculap Orthopaedics Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem CONTENTS 2 Contents Page Trilliance Philosophy 4 Trilliance Design 6 Trilliance Implants
Aesculap Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem Aesculap Orthopaedics Trilliance Triple Tapered Polished Hip Stem CONTENTS 2 Contents Page Trilliance Philosophy 4 Trilliance Design 6 Trilliance Implants
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report
 Syracuse University SURFACE Biomedical and Chemical Engineering College of Engineering and Computer Science 1997 Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report R T. Trousdale
Syracuse University SURFACE Biomedical and Chemical Engineering College of Engineering and Computer Science 1997 Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report R T. Trousdale
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene
 MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY
 FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements.
 Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements. P. Bills*, L. Blunt*, G. Chakrabarty** *University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK **West
Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements. P. Bills*, L. Blunt*, G. Chakrabarty** *University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK **West
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
WHAT IS THE BEST BONE FIXATION TYPE? 2/11/2011
 WHAT IS THE BEST BONE FIXATION TYPE? 2/11/2011 A Comparison of cement vs. bone ingrowth. Thomas P. Gross, M.D. At 2 years of follow-up cemented and uncemented femoral resurfacing is equivalent. Femoral
WHAT IS THE BEST BONE FIXATION TYPE? 2/11/2011 A Comparison of cement vs. bone ingrowth. Thomas P. Gross, M.D. At 2 years of follow-up cemented and uncemented femoral resurfacing is equivalent. Femoral
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement
 The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement Gregory A. Tocks, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Lancaster Ltd. INTRODUCTION Hip replacement is a very common operation, and the number of long-term postoperative
The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement Gregory A. Tocks, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Lancaster Ltd. INTRODUCTION Hip replacement is a very common operation, and the number of long-term postoperative
6.1 Primary Total Knee Replacement with a Zirconia
 New Applications for Ceramics 183 6.1 Primary Total Knee Replacement with a Zirconia Ceramic Femoral Component B. S. Bal, D. D. Greenberg and T. J. Aleto Abstract This report presents the minimum two-year
New Applications for Ceramics 183 6.1 Primary Total Knee Replacement with a Zirconia Ceramic Femoral Component B. S. Bal, D. D. Greenberg and T. J. Aleto Abstract This report presents the minimum two-year
Important Notice to Users in the United States: General Safety Instructions
 SLR-PLUS Revision Stem, SLR-PLUS Revision Stem Lateral Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics AG Oberneuhofstrasse 10d CH-6340 Baar Phone + 41 41 766 22 22 swiss.implants@smith-nephew.com non-sterile cemented non-
SLR-PLUS Revision Stem, SLR-PLUS Revision Stem Lateral Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics AG Oberneuhofstrasse 10d CH-6340 Baar Phone + 41 41 766 22 22 swiss.implants@smith-nephew.com non-sterile cemented non-
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners. Design Rationale Surgical Technique
 Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene. Clinical Value Dossier - APAC
 Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014
![Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014 Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014](/thumbs/89/100531147.jpg) Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
AGGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS IN CEMENTLESS TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 AGGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS IN CEMENTLESS TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY SEPPO SANTAVIRTA, VEIJO HOIKKA, ANTTI ESKOLA, YRJO T. KONTTINEN, TIMO PAAVILAINEN, KAJ TALLROTH From the Orthopaedic Hospitalofthe
AGGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS IN CEMENTLESS TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY SEPPO SANTAVIRTA, VEIJO HOIKKA, ANTTI ESKOLA, YRJO T. KONTTINEN, TIMO PAAVILAINEN, KAJ TALLROTH From the Orthopaedic Hospitalofthe
TaperFit. Cemented Total Hip Replacement Surgical technique
 TaperFit Cemented Total Hip Replacement Surgical technique TaperFit Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative templating 5 Surgical exposure 5 Femoral neck resection 5 Acetabular preparation 5 Cenator
TaperFit Cemented Total Hip Replacement Surgical technique TaperFit Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative templating 5 Surgical exposure 5 Femoral neck resection 5 Acetabular preparation 5 Cenator
