13 PATHOLOGY OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Norah Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 PATHOLOGY OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Pathology of muscles Equine rhabdomyolysis White muscle disease Acute myositis Chronic myositis Haemorrhagic myositis Pathology of Bones Fibrous Osteodystrophy Rickets Osteomalacia Osteoporosis Osteopetrosis Osteomyelitis Bone fracture and repair Pulmonary osteoarthropathy Spondylitis Pathology of joints Arthritis Model Questions
2 PATHOLOGY OF MUSCLES EQUINE RHABDOMYOLYSIS It is also known as Azoturia or Monday Morning Disease. The disease occurs in well fed horse after a gap of holiday. Suddenly after walking few steps, the horse is unable to move further and feels pain with intense sweating and hardening of muscles. Accumulation of lactic acid in muscles High glycogen storage Lack of oxygen supply Hardening of muscle just like wood Urine is dark brown with myoglobinmyoglobinuria Tonic spasms in muscles Atrophy of affected muscles in chronic cases Necrosis of muscle fibers Oedema Hyaline degeneration (Fig. 13.1). Invasion of sarcolemma by macrophages and lymphocytes Degeneration and necrosis of tubular epithelium in kidneys. WHITE MUSCLE DISEASE Extensive coagulative necrosis of muscles is observed in calves possibly due to deficiency of vitamin E during 6 month of age (Fig. 13.2). Vitamin E deficiency Selenium deficiency Stress Colour of muscle becomes pale pink, yellowish red, grey or white (Fig. 13.3). Muscle becomes dry, inelastic and firm. Urine is brown/red or chocolate brown in colour because of myoglobin. Coagulative necrosis of muscles. In some muscle cells, cloudy swelling can be observed. Neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes and eosinophils may present. Calcium may be deposited in necrosed areas. ACUTE MYOSITIS Acute myositis is the acute inflammation of skeletal muscles characterized by the presence of serous, fibrinous or haemorrhagic exudate (Fig & 13.5). Trauma Vitamin E/Selenium deficiency Clostridium chauvoei, the cause of black leg in cattle Muscles become extremely moist. Colour becomes red, consistency is firm and tense. Swelling and accumulation of gas in muscles, crepitating sound on palpation. Muscle dark red/ black with gas mixed exudate (Fig & 13.7). Presence of serous, fibrinous and/or haemorrhagic exudate. Infilteration of neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, etc. Degenerative and necrotic changes in muscles. Presence of Gram positive rods in exudate. HAEMORRHAGIC MYOSITIS Haemorrhagic myositis is characterized by the presence of large amount of blood and inflammation in muscles. It may occur due to trauma and muscle rupture (Fig. 13.8). Trauma Clostridial infections 138
3 Fig Photomicrograph showing hyaline degeneration in muscle Fig Photomicrograph showing acute myositis due to clostridia Fig Photograph of white muscle disease (ARS/USDA) Fig Photograph showing gangrenous myositis in poultry Fig Photograph showing muscular distrophy Fig Photograph showing gangrenous myositis in heifer Fig Photograph showing acute myositis Fig Photograph showing haemorragic myositis 139
4 Area becomes red/cyanotic. On cut, large amount of blood comes out from muscles. On touch, the affected area is hard and painful to touch. Regional lymphnodes may become enlarged and swollen. Extravasation of blood in between the myofibrils. Infilteration of neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes in connective tissue between the muscle cells. CHRONIC MYOSITIS Chronic inflammation of muscle is characterized by necrosis, calcification and proliferation of fibrous connective tissue. In case of tuberculosis and pseudotuberculosis, there are multiple, focal nodules containing caseation and fibrous capsule. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Trichinella spp. infection Sarcosporidia spp. infection Muscles become hard to touch Nodules can be seen (Fig. 13.9). On cut the lesions of caseation and calcification observed. Caseative necrosis, infilteration of macrophages, lymphocytes and proliferation of fibrous tissue. Calcification can also be observed. In cases of pseudotuberculosis infilteration of neutrophils is seen. Extensive infilteration of eosinophils in sarcoporidia infection. PATHOLOGY OF BONES FIBROUS OSTERODYSTROPHY Fibrous osteodystrophy occurs as excessive action of parathyroid hormone on bones and characterized by bone resorption with replacement by fibrous tissue, increased osteoid formation which does not get sufficient minerals for deposition and formation of cysts. Hyperparathyroidism Dietary deficiency of calcium or excess of phosphorus Vitamin-D deficiency Excessive bran feeding (Disease in horses of flour millers). Lack of calcification in bone Resorption of calcium from bone, fibrosis Bone becomes shoft, flexible and deformed Rubbery jaw due to involvement of facial bones Fibrous tissue hyperplasia in bones. Enlargement of Haversian canals. Boney tissue is replaced by fibroblasts, with osteoclastic giant cells lining the remaining bone tissue. RICKETS Rickets is failure of adequate deposition of calcium in bones of growing animals caused by deficiency of calcium and vitamin-d and characterized by bending of limbs, enlargement of ends of long bones and skeletal deformities (Fig ). Vitamin D deficiency Calcium deficiency Deficiency of phosphorus Bending of legs, bow legs Pot belly 140
5 Fig Photograph showing chronic myositica (ARS/USDA) Fig Photomicrograph of fracture healing Fig Photograph showing spondylitis(ars/usda) Fig Photograph of calf showing rickets Fig Photomicrograph showing spondylitis (ARS/USDA) Fig Photograph showing osteomyelitis in mandible (Actinomycosis) (ARS/USDA) Fig Photograph showing fracture A B Fig A. Photograph showing arthritis B. Diagram showing immune complex deposition in joint 141
6 Enlarged costochondral articulation Softening of bones Bone becomes brittle and porous Increased fragility of bones Increase in proliferating cartilage adjacent to the area of ossification and its disorderly arrangement. Disorderly penetration of cartilage by blood vessels Increased area of uncalcified osteoid tissue Fibrosis of marrow OSTEOMALACIA Osteomalacia is also known as adult rickets. It occurs in bone of adults caused by deficiency of vitamin D and calcium and characterized by softening of bones. Vitamin-D deficiency Calcium-phosphorus ratio disturbance Softening of bones Irregular diffuse thickening of bones Bone deformities Increase in osteoid tissue with failure of calcification Increase in osteoclastic activity OSTEOPOROSIS Osteoporosis is atrophy of bones caused by possibly hormonal imbalance and characterized by inadequate deposition of calcium, brittleness of bones due to its increased porosity. Hormonal imbalance Vitamin C deficiency Copper deficiency Inadequate calcium deposition Widening of Haversian canals Increased activity of osteoclasts Decrease in zona compacta and thickness of bone trabeculae OSTEOPETROSIS Osteopetrosis is enlargement of bone caused by fluorosis or avian leukosis virus and characterized by increase in bony tissue. It is also known as marble bone disease. Avian leukosis virus of retroviridae family Fluorosis Macroscopic Features Enlargement of bone towards outside and inside. Reduced marrow cavity Bone becomes brittle, marbelling of bones. Cartilage is also calcified, surrounded by osteoid tissue. OSTEOMYELITIS Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone with bone marrow caused by trauma and pyogenic bacteria and characterized by destruction, replacement and excessive growth of new bone adjacent to the infected part (Fig ). Hematogenous infection Direct infection through trauma/fracture Actinomyces pyogenes, A. bovis Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Metastatic abscess in bone marrow 142
7 Excessive growth of bone in adjacent area. Exostosis or endostosis. Infilteration of neutrophils Proliferation of osteoid tissue Demonstration of bacteria in pus BONE FRACTURE AND REPAIR Fracture is the break in the continuity of bone due to trauma. A fracture may be simple or compound depending on the severity of trauma. Healing of fracture occurs by reunion of the broken ends of bone through development and proliferation of fibroblasts, angioblasts, osteoid tissue and infilteration of calcium salts (Fig & 13.13). Trauma Accidents-automobile accidents. Fracture can be identified by break in bones. Healing of fracture is characterized by development of callus at the site of reunion of break ends of bone. Callus may be soft or hard. Proliferation of fibroblasts, angioblasts and metaplasia of connective tissue to osteoid tissue. Areas of calcification in osteoid tissue PULMONARY OSTEOARTHROPATHY Pulmonary osteoarthropathy is a rare disease of dog, sheep, cat, horse, and lion caused by prolonged anoxia and characterized by cough, dyspnea, respiratory disturbances and formation of new bone leading to thickening and deformity of limbs. Prolonged anoxia Toxaemia Pneumonia New bone formation just beneath the periosteum in long bones. The proliferation of bone is irregular leading to rough surface. Bone becomes enlarged twice to its normal size. Heart worms in case of dogs. Bronchogenic carcinoma Granulomatous lesions of tuberculosis Chronic bronchiectasis Hyperplasia of osteoid tissue with no indication of any kind of neoplastic growth in bones. SPONDYLITIS Spondylitis is the inflammation of vertebrae caused by bacteria/fungi and characterized by caseation, intraosseous abscess formation granulomatous lesions and fibrosis (Fig & 13.15). Brucella abortus, Br. ovis, Br. meletensis Actinomyces bovis Coccidioidomyces sp. Intraosseous abscess Granuloma encapsulated by fibrous tissue involving one or two adjacent vertebrae. Local enlargement of bone. Granulomatous lesions with caseation Proliferation of osteoid tissue Infiteration of neutrophils in intraoseous abscess. PATHOLOGY OF JOINTS ARTHRITIS Arthritis is the inflammation of joint caused by bacteria, virus, chlamydia, mycoplasma and 143
8 immune complexes and characterized by serus, fibrinous, purulent or ankylosing lesions in joints. Bacteria- E. coli, Erysipelas rhusiopathae, Streptococus sp., Shigella sp. Corynebacterium ovis, Brucella sp. Mycoplasma- Mycoplasma mycoides, Mycoplasma sinoviae Virus- Reovirus (Tenosynovitis in birds) Antigen antibody complexes Trauma Swelling of joints with increase in synovial fluid (Fig ). Difficulty in movement In chronic cases fusion of two bony processes leaving no joint (ankylosing) Synovial fluid diminishes, becomes dirty, thick in chronic illness Presence of increased number of leucocytes in synovial fluid. Serus, fibrinous or purulent exudate in joints. Thickening of synovial membrane Presence of plasma cells and immune complexes in synovial fluid. MODEL QUESTIONS Q. 1. Fill in the blanks with suitable word(s). 1. Gas gangrene is produced by... in thigh muscles of heifer which is manifested by...sound on palpation due to accumulation of... and Equine rhabdomyolysis occurs in horses on... after a day rest and is characterized by...,...,... and... of muscles. 3. Osteomalacia is also known as... which is caused by deficiency of... and disturbances in ratio of... and... characterized by ,... and... may led to osteoporosis in animals characterized by... of bones. 5. Avian leucosis virus may cause... in birds characterized by... of bone. 6. Osteomyelitis is inflammation of... and... caused by... and... and characterized by...,... and... of new bone adjacent to the infected part. 7. Healing fracture is characterized by the development of... at the site of reunion of break ends of bone. 8. Arthritis is inflammation of... characterized by... of joints. Q. 2. Write true and false and correct the false statement In white muscle disease the colour of urine becomes redish brown due to presence of haemoglobin Sarcosporidia causes eosinophilic myositis In rickets, the deficiency of calcium may lead to softening of bones 4....Osteopetrosis is enlargement of bones Osteoporosis is atrophy of bones Metastatic abscess are formed in bone marrow due to osteomyelitis Fracture is break in continuity of bones due to trauma. 144
9 8....Prolonged anoxia may lead to pulmonary osteoarthropathy in dogs Spondylitis is the inflammation of intervertebral disc Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by reovirus infection. Q. 3. Define the followings. 1. Myoglobinurea 6. Enostosis 2. Millers disease 7. Callous 3. Osteitis 8. Spondylitis 4. Osteomyelitis 9. Tenosynovitis 5. Exostosis 10. Ankylosis Q.4. Write short notes on the followings. 1. Azoturia 6. White muscle disease 2. Osteoporosis 7. Osteopetrosis 3. Gas gangrene 8. Fibrous osteodystrophy 4. Rickets 9. Pulmonary osteoarthropathy 5. Arthritis 10. Fracture healing Q. 5. Select most appropriate word(s) from the four options given against each statement. 1. Equine rhabdomyolysis is also known as. morning disease (a) Sunday (b) Monday (c) Tuesday (d) Wednesday 2. Accumulation of. is responsible for hardening of muscles in azoturia. (a) Lactic acid (b) Myoglobin (d) Haemoglobin (d) Glycogen 3. White muscle disease is caused by. deficiency. (a) Vit-A (b) Vit- D (c) Vit-C (d) Vit-E 4. Rickets is caused by deficiency of vitamin (a) A (b) D (c) C (d) E 5. Osteoporosis is caused by deficiency of. (a) Copper (b) Zinc (c) Iron (d) Calcium 6. Osteopetrosis is also known as disease (a) Brittle bone (b) Marble bone (c) Both a & b (d) None 7. Fibrous osteodystrophy is characterized by.. condition (a) Lock jaw (b) Rubbery jaw (c) Bottle jaw (d) None 8. Osteomyelitis is inflammation of... (a) Bone (b) Bone marrow (c) Both a & b (d) None 9. Brucella sp may cause. in animals and man. (a) Pulmonary osteoarthropathy (b) Spondylitis (c) Rickets (d) Osteopetrosis 10. Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by. (a) Antigen-antibody complex (b) E. coli (c) Reovirus (d) Brucella sp. 145
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
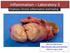 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Bone necrosis. Cross section.
 Bone necrosis. Cross section. Note the large area of necrosis (N) seen as pale discolored bone (beneath physeal cartilage). The texture of the necrotic bone is also changed. Necrotic bone becomes friable
Bone necrosis. Cross section. Note the large area of necrosis (N) seen as pale discolored bone (beneath physeal cartilage). The texture of the necrotic bone is also changed. Necrotic bone becomes friable
Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one
 Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION
 DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
Bone Injury and Inflammatory Diseases of Bone
 Bone Injury and Inflammatory Diseases of Bone Module 3 Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College January 10, 2014 Bone Necrosis / Cross Section Necrotic bone is often difficult to detect grossly but it
Bone Injury and Inflammatory Diseases of Bone Module 3 Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College January 10, 2014 Bone Necrosis / Cross Section Necrotic bone is often difficult to detect grossly but it
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Etiology Bacteria Sand particles Particles of ingesta / intestinal contents Desquamated epithelium
 10 CONCRETIONS Concretions Calculi o Urinary Calculi o Biliary Calculi o Salivary Calculi o Pancreatic Calculi o Enteric Calculi Piliconcretions Phytoconcretions Polyconcretions Model Questions CONCRETIONS
10 CONCRETIONS Concretions Calculi o Urinary Calculi o Biliary Calculi o Salivary Calculi o Pancreatic Calculi o Enteric Calculi Piliconcretions Phytoconcretions Polyconcretions Model Questions CONCRETIONS
20 PATHOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM. Encephalitis Encephalomalacia Spongiform Encephalopathy Meningitis Neuritis Model Questions
 20 PATHOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM Encephalitis Encephalomalacia Spongiform Encephalopathy Meningitis Neuritis Model Questions Nervous system is composed of brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The neuron
20 PATHOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM Encephalitis Encephalomalacia Spongiform Encephalopathy Meningitis Neuritis Model Questions Nervous system is composed of brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The neuron
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Note the large area of necrosis (N) which appears as a pale discolored bone
 Bone Injury and Inflammatory Bone Diseases Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College University i of Pi Prince Edward d Il Island January 7, 2010 Bone Necrosis / Cross Section N The texture of the necrotic
Bone Injury and Inflammatory Bone Diseases Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College University i of Pi Prince Edward d Il Island January 7, 2010 Bone Necrosis / Cross Section N The texture of the necrotic
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS. Ms. Doshi
 CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
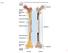 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation
 F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Lecture 9 - Wound Healing
 Lecture 9 - Wound Healing A wound is any disruption to tissue caused by injury The injury is usually traumatic, i.e. physical, mechanical damage to tissue: Wound healing is a special case of acute inflammation
Lecture 9 - Wound Healing A wound is any disruption to tissue caused by injury The injury is usually traumatic, i.e. physical, mechanical damage to tissue: Wound healing is a special case of acute inflammation
The Skeletal S 1Jstem
 . / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
. / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Skin: The Body s Protection
 Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Mohammad Ashraf. - Bahaa Najjar. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 4 - Mohammad Ashraf - Bahaa Najjar - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Fractures (cont d). Healing of fractures: There are a lot of factors determine the proper healing of the fracture. For example: Displaced
- 4 - Mohammad Ashraf - Bahaa Najjar - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Fractures (cont d). Healing of fractures: There are a lot of factors determine the proper healing of the fracture. For example: Displaced
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury. VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016
 Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
6 DISTURBANCES IN CELL METABOLISM
 6 DISTURBANCES IN CELL METABOLISM Cloudy Swelling Hydropic Degeneration Mucinous Degeneration Mucoid Degeneration Psuedomucin Amyloid Infilteration Hyaline Degeneration Fatty Changes Glycogen Infilteration
6 DISTURBANCES IN CELL METABOLISM Cloudy Swelling Hydropic Degeneration Mucinous Degeneration Mucoid Degeneration Psuedomucin Amyloid Infilteration Hyaline Degeneration Fatty Changes Glycogen Infilteration
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Musculoskeletal Disorders. Fractures. Types of Fractures BIO 375. Pathophysiology
 Musculoskeletal Disorders BIO 375 Pathophysiology Fractures A fracture is a break in the rigid structure and continuity of a bone The fracture may be: Complete fracture Incomplete fracture Open fracture
Musculoskeletal Disorders BIO 375 Pathophysiology Fractures A fracture is a break in the rigid structure and continuity of a bone The fracture may be: Complete fracture Incomplete fracture Open fracture
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system
 1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Quiz 6. Cartilage and Bone
 Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Bone myths
 Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 ( ) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Firm Texture. (chronic) Cut surface: purulent exudate in bronchi Sequels: Abscesses,
 2008 Classification of Pneumonias in Domestic Animals There is no universal classification! Based on texture, distribution of lesions and type of exudate, pneumonias in domestic animals are currently classified
2008 Classification of Pneumonias in Domestic Animals There is no universal classification! Based on texture, distribution of lesions and type of exudate, pneumonias in domestic animals are currently classified
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
33.1. Skeletal System. Your skeletal system is made up of the appendicular and axial skeletons.
 33.1 Skeletal System VOCABULARY skeletal system appendicular skeleton axial skeleton vertebrae cartilage joint ligament calcification Key Concept The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are
33.1 Skeletal System VOCABULARY skeletal system appendicular skeleton axial skeleton vertebrae cartilage joint ligament calcification Key Concept The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are
5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION. Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions
 5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions CONGESTION/ HYPEREMIA Hyperemia is increased amount of
5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions CONGESTION/ HYPEREMIA Hyperemia is increased amount of
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
