The Skeletal S 1Jstem
|
|
|
- Blaze York
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 . / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and protecting the body as an internal framework, the skeleton provides a system of levers that the skeletal muscles use to move the body. In addition, the bones provide a storage depot for substances such as lipids and calcium, and blood cell formation goes on within their red marrow cavities. The skeleton consists of bones connected at joints, or articulations, and is subdivided into two divisions. The axial skeleton includes those bones that lie around the body's center of gravity. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs. Topics for student review include structure and function of long bones, location and naming of specific bones in the skeleton, fracture types, and a classification of joint types in the body. BONES-AN OVERVIEW 1. Classify each of the following terms as a projection CP) or a depression or opening CD). Enter the appropriate letter in the answer blanks. 1. Condyle 4. Foramen 7. Ramus 2. Crest 5. Head 8. Spine 3. Fissure 6. Meatus 9. Tuberosity 2. Group each of the following bones into one of the four major bone categories. Use L for long bone, S for short bone, F for flat bone, and I for irregular bone. Enter the appropriate letter in the space provided. 1. Calcaneus 4. Humerus 7. Radius 2. Frontal 5. Mandible 8. Sternum 3. Femur 6. Metacarpal 9. Vertebra 61
2 62 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 3. Using the key choices, characterize the following statements relating to long bones. Enter the appropriate term(s) or letter(s) in the answer blanks. A. Diaphysis B. Epiphyseal plate C. Epiphysis E. Yellow marrow cavity D. Red marrow 1. Site of spongy bone in the adult 2. Site of compact bone in the adult 3. Site of hematopoiesis in the adult 4. Scientific name for bone shaft 5. Site of fat storage in the adult 6. Site of longitudinal growth in a child 4. Complete the following statements concerning bone formation and destruction, using the terms provided in the key. Insert the key letter or corresponding term in the answer blanks. A. Atrophy B. Calcitonin C. Gravity E. Osteoclasts G. Parathyroid hormone D. Osteoblasts F. Osteocytes H. Stress and/or tension 1. When blood calcium levels begin to drop below homeostatic levels, ~ is released, causing calcium to be released from bones. 2. Mature bone cells, called ~ maintain bone in a viable state. 3. Disuse such as that caused by paralysis or severe lack of exercise results in muscle and bone ~. 4. Large tubercles and/or increased deposit of bony matrix occur at sites of ~. 5. Immature, or matrix-depositing, bone cells are referred to as -.J2L. 6. ~ causes blood calcium to be deposited in bones as calcium salts. 7. Bone cells that liquefy bone matrix and release calcium to the blood are called ~. 8. Our astronauts must do isometric exercises when in space because bones atrophy under conditions of weightlessness or lack of ~.
3 5. Five descriptions of bone structure are provided in Column A. First identify the structure by choosing the appropriate term from Column B and placing the corresponding answer in the answer blank. Then consider Figure 5-1A, a diagrammatic view of a cross section of bone, and 5-1B, a higher magnificated view of compact bone tissue. Select different colors for the structures and bone areas in Column B, and use them to color the coding circles and corresponding structures on the figure diagrams. Since the concentric lamellae would be difficult to color without confusing other elements, identify one lamella by using a bracket and label. Chapter 5 The Skeletal System 63 Column A 1. Layers of calcified matrix 2. "Residences" of osteocytes 3. Longitudinal canal, carrying blood vessels and nerves 4. Nonliving, structural part of bone 5. Tiny canals, connecting lacunae Column B A. Central (Haversian) canal 0 B. Concentric lamellae C. Lacunae 0 D. Canaliculi 0 E. Bone matrix 0 F. Osteocyte 0 A Figure 5-1 B 6. Circle the term that does not belong in each of the following groupings. 1. Hematopoiesis Red marrow Yellow marrow Spongy bone 2. Lamellae Canaliculi Circulation Osteoblasts 3. Osteon Marrow cavity Central canal Canaliculi 4. Epiphysis surface Articular cartilage Periosteum Hyaline cartilage
4 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure S-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside surface. Figure S-2B is a drawing of a longitudinal section of the femur. Color the bone tissue gold. Do not color the articular cartilage; leave it white. Select different colors for the bone regions listed at the coding circles below. Color the coding circles and the corresponding regions on the drawing. Complete Figure S-2B by labeling compact bone and spongy bone. o Diaphysis o Epiphyseal plate o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found A '"----- Compact bone B Figure 5-2 AXIAL SKELETON Skull 8. Using key choices, identify the bones indicated by the following descriptions. Enter the appropriate term or letter in the answer blanks. A. Ethmoid E. Mandible I. Palatines L. Temporals B. Frontal F. Maxillae ]. Parietals M. Vomer C. Hyoid G. Nasals K. Sphenoid N. Zygomatic D. Lacrimals H. Occipital
5 82 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook BONE FRACTURES 29. Using the key choices, identify the fracture (fx) types shown in Figure 5-14 and the fracture types and treatments described below. Enter the appropriate key letter or term in each answer blank. A. Closed reduction B. Compression fracture C. Compound fracture D. Depressed fracture G. Simple fracture E. Greenstick fracture H. Spiral fracture F. Open reduction 1. Bone is broken cleanly; the ends do not penetrate the skin 2. Nonsurgical realignment of broken bone ends and splinting of bone 3. A break common in children; bone splinters, but break is incomplete 4. A fracture in which the bone is crushed; common in the vertebral column 5. A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate through the skin surface 6. Surgical realignment of broken bone ends 7. A result of twisting forces Figure 5-14
6 30. For each of the following statements about bone breakage and the repair process that is true, insert T in the answer blank. For false statements, correct the underlined terms by inserting the correct term in the answer blank. 1. A hematoma usually forms at a fracture site. Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Deprived of nutrition, osteocytes at the fracture site die. 3. Non-bony debris at the fracture site is removed by osteoclasts. 4. Growth of a new capillary supply into the region produces granulation tissue. 5. Osteoblasts from the medullary cavity migrate to the fracture site. 6. The fibrocartilage callus is the first repair mass to splint the broken bone. 7. The bony callus is initially composed of compact bone. JOINTS 31. Figure 5-15 shows the structure of a typical diarthrotic joint. Select different colors to identify each of the following areas and use them to color the coding circles and the corresponding structures on the figure. Then, complete the statements below the figure. o Articular cartilage of bone ends o Fibrous capsule o Synovial membrane o Joint cavity Figure The lubricant that minimizes friction and abrasion of joint surfaces is ~. The resilient substance that keeps bone ends from crushing when compressed is ~. ~ which reinforce the fibrous capsule help to prevent dislocation of the joint.
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Bio 5/6 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide
 Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Why do we need the skeletal system?
 EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Know all the bones of the skull, lateral view and frontal view. From the worksheets, one of the earlier ones in this unit.
 Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System. Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Our Bones - Introduction Identify 2 main functions of our skeletal system. Look for ligaments and tendons. What does each connect? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkvcg
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Our Bones - Introduction Identify 2 main functions of our skeletal system. Look for ligaments and tendons. What does each connect? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkvcg
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
Skeletal system overview. Classification of Bones
 Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes 1/05/13. Skeletal system overview. Bone are identified by:
 Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
The SKELETAL System. The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion.
 The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Skeletal System A&P Week 11
 Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Carpals Tarsals Classification of Bones Flat bones Thin, flattened, and usually curved
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
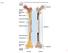 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
The Skeletal System. Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
 5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Webquest The Mystery of Bones
 Skeletal System Webquest The Mystery of Bones Written Response #1: Types of Bone Cells Type of Bone Cell Function of Bone Cell Drawing of Bone Cell Osteocyte Osteoblast Osteogenic Cell Osteoclast Bone
Skeletal System Webquest The Mystery of Bones Written Response #1: Types of Bone Cells Type of Bone Cell Function of Bone Cell Drawing of Bone Cell Osteocyte Osteoblast Osteogenic Cell Osteoclast Bone
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
