The association between gout and radiographic hand, knee and foot osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study
|
|
|
- Nickolas Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The association between gout and radiographic hand, knee and foot osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study Megan Bevis *, Michelle Marshall, Trishna Rathod and Edward Roddy Abstract Background: Gout is the most common type of inflammatory arthritis and is largely managed in primary care. It classically affects the first metatarsophalangeal joint and distal peripheral joints, whereas the axial joints are typically spared. The reason for this particular distribution is not well understood, however, it has been suggested that osteoarthritis (OA) may be the key factor. One hypothesis is that there is an association between the disease states of gout and OA as the conditions share common risk factors. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is an association between gout and radiographic osteoarthritis (OA). Methods: A cross-sectional study was nested within three observational cohorts of people aged 50 years with hand, knee and foot pain. Participants with gout were identified through primary care medical records and each matched by age and gender to four individuals without gout. The presence and severity of radiographic OA were scored using validated atlases. Conditional logistic regression models were used to examine associations between gout and the presence, frequency and severity of radiographic OA at the hand, knee and foot and adjusted for BMI, diuretic use and site of joint pain. Results: Fifty-three people with gout were compared to 211 matched subjects without gout. No statistically significant associations were observed between gout and radiographic hand, knee or foot OA. However, individuals with gout had increased odds of having nodal hand OA (aor 1.46; 95 % CI 0.61, 3.50), 8 hand joints with moderate to severe OA (aor 3.57; 95 %CI 0.62, 20.45), foot OA (aor 2.16; 95 % CI 0.66, 7.06), 3 foot joints affected (aor 4.00; 95 % CI 0.99, 16.10) and 1 foot joints with severe OA (aor 1.46; 95 % CI 0.54, 3.94) but decreased odds of tibiofemoral (aor 0.44; 95 % CI 0.15, 1.29) or patellofemoral (aor 0.70; 95 % CI 0.22, 2.22) OA in either knee. Conclusion: There was no association between gout and radiographic OA, however, people with gout appeared to be more likely to have small joint OA and less likely to have large joint OA. Keywords: Crystal arthropathies, Osteoarthritis, Epidemiology, Radiology, Primary care rheumatology Background A link has been established between gout and OA, which could explain the distribution of joints affected by gout, particularly the tendency for the first metatarsophalangeal joint (1 st MTPJ) to be affected [1]. Previous studies have shown that joints affected by acute attacks of gout are more likely to display clinical or radiographic features of OA [2, 3]. This is particularly true for the 1 st * Correspondence: meganbevis@hotmail.com Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre, Research Institute for Primary Care and Health Sciences, Keele University, Keele, Staffordshire ST5 5BG, UK MTPJ, mid-foot, knees and the distal interphalangeal finger joints [2]. Furthermore, monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposits at the tibio-talar joints have been shown to occur at sites of degenerative cartilage lesions [4]. A recent primary-care based case control study however, did not find evidence between gout and clinicallyassessed nodal OA, although people with gout were more likely to have hallux valgus and chronic pain in the knee and big toe, compared to age- and gender-matched controls without gout [5] Bevis et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 Page 2 of 7 The aim of this study was to investigate the association between gout and radiographic OA by comparing the presence and severity of radiographic hand, knee and foot OA in adults with and without gout. Methods Study population The study used baseline data from three prospective population-based cohorts of people aged 50 years with pain in the hand, knee and foot: Clinical Assessment Study of the Hand (CASHA) [6], Clinical Assessment Study of the Knee (CASK) [7], Clinical Assessment Study of the Foot (CASF) [8] respectively. Each cohort invited participants to complete a selfreported postal questionnaire. In CASHA, CASK, and CASF, those reporting hand, knee, and foot pain respectively in the last year were invited to attend a research clinic. Radiographs of the hand and knees were taken in CASHA and CASK; radiographs of the hands and feet were taken in CASF [6 8]. Participants with gout Participants with gout were identified through primary care medical records using specific Read codes for gout in the period from 18-months before to 18-months after clinic attendance. Individuals without a Read code for gout but who had gout mentioned in their consultation free-text were also identified and included if there was mention of a gout flare/attack or clinical features suggestive of gout. Participants without gout Each participant with gout was individually matched based on age (±2 years), gender and cohort (CASHA, CASK, CASF) to four participants who had not consulted with gout in the same period. Radiographic assessment and scoring Posterior-anterior (PA) plain radiographs of each hand were obtained from all clinic attenders in all three cohorts. Weight-bearing PA semi-flexed metatarsophalangeal, skyline and lateral knee views were obtained from CASK and CASHA participants and weight-bearing dorso-plantar and lateral views of each foot were obtained from CASF participants. Identical standardised radiographic protocols were used across the cohorts [6 8]. The Kellgren and Lawrence (K&L) system (0 4) was used to grade OA in 16 joints in each hand (interphalangeal joints (IPJs), metacarpophalangeal (MCPs), first carpometacarpal (CMC), trapezioscaphoid (TS)) [9]. K&L and Burnett atlases [10] were used to grade tibiofemoral (TF) and patellofemoral (PF) OA. The Menz atlas was used to grade osteophytes and joint space narrowing (JSN) (0 3) at five joints in each foot: the 1st MTPJ, the 1st and 2nd cuneometatarsal joints (CMJ), the navicular first cuneiform joint (N1stCJ) and the talonavicular joint (TNJ) [11]. Intrarater and inter-rater reproducibility of OA at each joint site has been reported previously [12 14] and were found to be satisfactory. OA definitions Hand OA and moderate-severe hand OA was defined respectively as the presence of radiographic OA K&L grade 2 and grade 3 affecting IPJs on at least two rays on each hand [5]. Radiographic PF joint OA was defined as K&L grade 2 on the skyline view and/or the presence of a definite superior or inferior patellar osteophyte (Burnett grade 1) on the lateral view [10] in either knee. Radiographic TF joint OA was defined as K&L grade 2 on the PA view and/or the presence of definite osteophyte (Burnett grade 1) on the posterior tibial surface on the lateral view [10] in either knee. Moderate to severe radiographic (K&L grade 3 and Burnett grade 3) TF and PF joint OA were also assessed. Radiographic OA at each of the five foot joints was defined as a Menz grade 2 for osteophytes or JSN on either the dorso-plantar or lateral view in either foot, with severe OA categorised using a cut-off of Menz grade 3 [11]. Radiographic foot OA and moderate-severe OA were defined respectively as Menz grade 2 and grade 3 for osteophytes or JSN affecting one or more of the five joints in either foot [11]. Chondrocalcinosis Radiographic chondrocalcinosis (CC) is a common feature of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition; therefore, radiology reports were screened for report of CC in order to assess possible misclassification bias. Statistical analysis Crude odds ratio (OR) and 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were calculated between gout and the presence and severity of radiographic OA in the hand, knee and foot using conditional logistic regression models. ORs (95 % CI) were then adjusted for BMI and diuretic use in all three analyses and further adjustment made for hand pain in the hand analysis and knee pain in the knee analysis. Foot pain was not adjusted for in the foot analysis as all participants originated from CASF and had foot pain. Analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics version 20 and STATA version 12. All analyses were two tailed and a p value of 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Logistic regression models were tested and the assumptions for linearity and multi-collinearity were met.
3 Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 Page 3 of 7 Results Following exclusions for non-consent for medical record review (n = 109), inflammatory arthritis (n = 67) and no radiographs (n = 29), 1797 participants were eligible for sampling (Fig. 1). Fifty-three participants with gout were identified (CASHA n = 11, CASK n = 17, CASF n = 25). Each was matched for age (±2 years) and gender to four individuals without gout from the same study cohort, with the exception of one gout individual from CASF for whom only three matched controls could be identified. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of the two groups are shown in Table 1. Mean BMI, diuretic use, ischaemic heart disease and hyperlipidaemia were higher in those with gout compared to those without gout. Knee and foot pain were more frequent and CC less frequent in those with gout than in those without. Hand analysis Fifty-three participants with gout were compared with 108 matched participants without gout. No statistically significant association was observed between gout and radiographic hand OA on univariable analyses or after adjustment for BMI, diuretic use and hand pain. Although non-significant, participants with gout were more likely to have nodal hand OA and eight hand joints affected with moderate to severe radiographic hand OA compared to those without gout (Table 2). Knee analysis Twenty-seven participants with gout were compared to 108 matched participants without gout. One participant with gout had missing x-ray data for the right knee and so this individual and their four matched controls were excluded from this analysis. No statistically significant associations were observed between gout and radiographic knee OA on univariable analyses, or after adjustment but the magnitude of adjusted ORs suggested that participants with gout were less likely to have TF and PF OA than those without gout (Table 2). Foot analysis Twenty-five participants with gout from CASF were compared to 99 matched participants without gout. No statistically significant associations were observed between gout and radiographic foot OA on univariable analyses or after adjustment but individuals with gout had 4 times the odds of having three foot joints affected with radiographic OA (Table 2). Although statistically non-significant, participants with gout were also more likely to have radiographic foot OA affecting at Fig. 1 A flowchart showing participants eligible for sampling and analysis including exclusions
4 Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 Page 4 of 7 Table 1 Baseline characteristics of participants with gout and participants without gout Gout No gout (n = 53) (n = 211) Age: years, mean (SD) 66.4 (9.5) 66.6 (9.4) Gender: Male % % BMI: kg/m 2, mean (SD) 31.3 (5.4) 29.2 (5.1) BMI categories: <18.5 kg/m % 1 <1 % kg/m % % kg/m % % 30 kg/m % % Occupational class: managerial & professional % % intermediate % % routine & manual % % Diuretic use % % Co-morbidities: Hypertension % % Ischaemic heart disease % % Hyperlipidaemia % % Diabetes mellitus 5 9 % % Chronic renal failure 2 4 % 1 <1 % Knee pain % % Hand pain % % Foot pain % % Chondrocalcinosis 2 4 % % BMI body mass index, SD standard deviation least one joint or a specific joint (1 st MTP, N1 st CJ and TNJ) compared to those without gout (Table 2). Discussion The rationale for investigating the association between gout and nodal OA was as an exemplar of generalised OA. However, no significant association was found between gout and radiographic hand OA. These findings are consistent with the only previous study examining the association between gout and hand OA, where nodal OA was found to be no more common in those with gout than those without gout [5]. There were several differences between that study and our current study. Although both studies used participants recruited from primary care, the previous study included younger adults (aged 30 years), based the diagnosis of gout on specialist clinical opinion, and used self-report instruments to assess clinical OA [5]. In contrast, in our study, OA was radiographically assessed; nevertheless, the definition of radiographic hand OA affecting at least two rays on each hand was comparable. Although not statistically significant, there were findings in this study suggesting that participants with gout were more likely to have widespread or severe OA involvement of small joints in the hand and foot compared to those without gout but less likely to have TF or PF OA. At the foot, individuals with gout were more likely to have foot OA, severe foot OA, and specific involvement of the 1st MTP, N1stCJ, TNJ and multiple joints compared to those without gout. 1st MTPJ involvement is not surprising as it is a common site for both OA and gout, and an association with OA has been suggested as a possible explanation for the striking predilection of gout for this joint [1, 15]. Previous research has also shown that the mid-foot region can be commonly affected by gout when clinical OA is evident [2], which is consistent with our observation that people with gout had a higher likelihood of mid-foot OA. The frequency of OA at individual foot joints may reflect the association of gout with generalised OA or that the pain associated with gout could alter biomechanics of the foot potentially predisposing to subsequent OA [2, 4]. This study, to our knowledge, is the first to examine the relationship between gout and radiographic OA across multiple joint sites. The study was undertaken in a primary care setting so the results are generalizable to most people with gout who are managed entirely in primary care. The major limitation of the study was inadequate statistical power, making it liable to a type II error. The study involved secondary analysis of data from three existing cohorts and therefore the number of available gout cases was limited. The sample population may also have differed from the general population as the frequency of radiographic OA was found to be considerably higher in these participants, who had all reported joint pain at the hand, knee or foot in the last year, than in other adult general populations. Therefore, an association between gout and OA may have been masked. A further caveat is the reliance on primary care records to diagnose gout, and whilst morbidity coding in the participating practices undergoes regular quality review [16, 17] and previous work has suggested that diagnosis of gout by GPs is reasonably accurate [18], there is still a risk of misclassification bias. Synovial fluid MSU crystal identification is the gold standard for the diagnosis of gout [19], however, this is rarely performed in primary care. It is, however, reassuring that only a small minority of participants had radiographic CC. Conclusion In summary, no statistically significant association was observed between gout and hand, knee and foot OA, however there were findings to suggest that people with gout were more likely to have OA affecting the small joints of the hands and feet but less likely to have large joint OA at the knee. Further research is needed to understand the relationship between gout and OA, using
5 Table 2 Crude and adjusted OR (95 % CI) for radiographic OA between participants with and without gout Radiographic OA definition Gout No gout Crude OR (95 % CI) Adjusted OR (95 % CI) Hand n =53 n =211 a Radiographic OA (K&L 2) affecting IPJs on 10 (19) 28 (13) 1.57 (0.69, 3.60) 1.46 (0.61, 3.50) at least two rays on each hand (%) Moderate to severe radiographic OA (K&L 3) 3 (6) 12 (6) 1.00 (0.24, 4.11) 1.02 (0.22, 4.70) affecting IPJs on at least two rays on each hand (%) Total number of joints affected by radiographic OA in the hand (K&L 2) [0 32]: 0 (%) 17 (32) 62 (29) (%) 15 (28) 62 (29) 0.91 (0.41, 2.03) 0.85 (0.37, 1.97) 3 7 (%) 13 (25) 65 (31) 0.72 (0.30, 1.75) 0.65 (0.26, 1.67) 8 (%) 8 (15) 22 (10) 1.39 (0.46, 4.15) 1.24 (0.38, 4.06) Total number of joints affected by moderate to severe radiographic OA in the hand (K&L 3) [0 32]: 0 (%) 34 (64) 134 (64) (%) 8 (15) 46 (22) 0.76 (0.33, 1.77) 0.69 (0.29, 1.63) 3 7 (%) 7 (13) 25 (12) 1.17 (0.46, 2.98) 1.16 (0.45, 3.00) 8 (%) 4 (8) 6 (3) 3.48 (0.69, 17.72) 3.57 (0.62, 20.45) Knee n =27 n =108 Radiographic OA (K&L 2 or Burnett grade 1) affecting the TF joint in either knee (%) 11 (41) 49 (45) 0.82 (0.33, 1.99) 0.44 (0.15, 1.29) Radiographic OA (K&L 2 or Burnett grade 1) affecting the PF joint in either knee (%) 20 (74) 76 (70) 1.22 (0.45, 3.29) 0.70 (0.22, 2.22) Radiographic OA (K&L 2 or Burnett grade 1) affecting the TF and PF joints in either knee (%) 11 (41) 41 (38) 1.13 (0.46, 2.78) 0.57 (0.20, 1.65) Radiographic OA (K&L 3 or Burnett grade 3) affecting the TF joint in either knee (%) 4 (15) 27 (25) 0.51 (0.16, 1.63) 0.28 (0.07, 1.09) Radiographic OA (K&L 3 or Burnett grade 3) affecting the PF joint in either knee (%) 7 (26) 26 (24) 1.13 (0.39, 3.25) 0.58 (0.18, 1.86) Radiographic OA (K&L 3 or Burnett grade 3) affecting the TF and PF joints in either knee (%) 3 (11) 10 (9) 1.22 (0.32, 4.71) 0.54 (0.12, 2.40) Foot n =25 n =99 Radiographic OA (Menz 2) affecting at least one of 1 st MTPJ, 20 (80) 67 (68) 2.22 (0.69, 7.15) 2.16 (0.66, 7.06) 1 st CMJ, 2 nd CMJ, N1 st CJ and TNJ in either foot (%) Severe radiographic OA (Menz 3) affecting at least one of 1 st MTPJ, 7 (28) 21 (21) 1.46 (0.54, 3.94) 1.45 (0.53, 3.97) 1 st CMJ, 2 nd CMJ, N1 st CJ and TNJ in either foot (%) Total number of joints affected by radiographic OA (Menz 2) [0 10]: 0 (%) 5 (20) 32 (32) (%) 10 (40) 46 (46) 1.64 (0.47, 5.72) 1.55 (0.44, 5.47) 3 (%) 10 (40) 21 (21) 3.86 (0.97, 15.31) 4.00 (0.99, 16.10) b c Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 Page 5 of 7
6 Table 2 Crude and adjusted OR (95 % CI) for radiographic OA between participants with and without gout (Continued) Total number of joints affected by severe radiographic OA (Menz 3) [0 10]: 0 (%) 18 (72) 78 (79) (%) 7 (28) 21 (21) 1.46 (0.54, 3.94) 1.45 (0.53, 3.97) Radiographic OA (Menz 2) affecting either 1st MTPJ (%) 13 (52) 37 (37) 1.90 (0.75, 4.78) 1.85 (0.73, 4.69) Radiographic OA (Menz 2) affecting either 1st CMJ (%) 2 (8) 13 (13) 0.59 (0.13, 2.75) 0.54 (0.11, 2.56) Radiographic OA (Menz 2) affecting either 2nd CMJ (%) 7 (28) 24 (24) 1.26 (0.45, 3.54) 1.34 (0.46, 3.91) Radiographic OA (Menz 2) affecting either N1 st CJ (%) 6 (24) 12 (12) 2.46 (0.78, 7.73) 2.60 (0.80, 8.46) Radiographic OA (Menz 2) affecting either TNJ (%) 10 (40) 23 (23) 2.18 (0.87, 5.46) 2.24 (0.88, 5.70) a Adjusted for BMI, diuretic use and hand pain. b Adjusted for BMI, diuretic use and knee pain. c Adjusted for BMI and diuretic use. K&L Kellgren and Lawrence, IPJs interphalangeal joints, OR odds ratio, CI confidence interval, TF tibiofemoral, PF patellofemoral, 1st MTPJ first metatarsophalangeal joint, CMJ cuneometatarsal joint, N1stCJ navicular first cuneiform joint, TNJ talonavicular Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 Page 6 of 7
7 Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 Page 7 of 7 robust case definitions based on crystal identification and imaging. Such studies will provide important insights into the aetiology, co-occurrence and clinical presentation of both conditions. Ethics and consent to participate Ethical approval was obtained for all three cohorts (North Staffordshire LREC (1430); Coventry REC (10/H1210/5). All participants provided written informed consent and were also asked for consent to review their medical records. Consent to publish Not applicable as no identifying personal information is being published in this manuscript. Availability of data and materials Requests for further detail on the dataset and queries relating to data sharing arrangements may be submitted to Edward Roddy, e.roddy@keele.ac.uk. Participants were not asked for informed consent for data sharing although the presented data are anonymised and risk of identification is low. Abbreviations BMI: body mass index; CASF: clinical assessment study of the foot; CASHA: clinical assessment study of the hand; CASK: clinical assessment study of the knee; CC: chondrocalcinosis; CI: confidence interval; CMC: carpometacarpal; CMJ: cuneo-metatarsal joint; CPPD: calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate; DIP: distal interphalangeal; GP: general practitioner; IPJ: interphalangeal joint; JSN: joint space narrowing; K&L: kellgren and lawrence; MCP: metacarpophalangeal; MSU: monosodium urate; MTPJ: metatarsophalangeal joint; N1 st CJ: navicular-first cuneiform; OA: osteoarthritis; OR: odds ratio; PA: posteroanterior; PF: patellofemoral; PIP: peripheral interphalangeal; TF: tibiofemoral; TNJ: talo-navicular joint; TS: trapezioscaphoid. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions ER conceived of the study. MB, MM and ER participated in its design and acquisition of data. Statistical analysis was performed by MB and TR. All authors interpreted the data, drafted or revised the manuscript critically for intellectual content and approved the final version of the manuscript. Acknowledgements We would like to thank the administrative, health informatics and research nurse teams at Keele University s Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre, the staff of the participating general practices and the Haywood Hospital, particularly Dr Jackie Saklatvala, Carole Jackson and the radiographers at the Department of Radiography. Funding statement This work is supported by programme grants awarded by the Medical Research Council, UK (Grant code: G ) and Arthritis Research UK (Grant code: 18174), and NHS service support through the West Midlands CLRN. The funders had no role in the study design; data collection, analysis or interpretation; in the writing of the paper; or in the decision to submit the paper for publication. Received: 3 July 2015 Accepted: 14 April 2016 References 1. Simkin PA. The pathogenesis of podagra. Ann Intern Med. 1977;86: Roddy E, Zhang W, Doherty M. Are joints affected by gout also affected by osteoarthritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66: Kawenoki-Minc E, Eyman E, Leo W, Werynska-Przybylska J. Osteoarthrosis and spondylosis in gouty patients. Analysis of 262 cases of gout. Reumatologia. 1974;12: Muehleman C, Li J, Aigner T, et al. Association between crystals and cartilage degeneration in the ankle. J Rheumatol. 2008;35: Roddy E, Zhang W, Doherty M. Gout and nodal osteoarthritis: a case control study. Rheumatology. 2008;47: Myers H, Nicholls E, Handy J, et al. The clinical assessment study of the hand (CAS-HA): a prospective study of musculoskeletal hand problems in the general population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007;8: Peat G, Thomas E, Handy J, et al. The knee clinical assessment study CAS (K). a prospective study of knee pain and knee osteoarthritis in the general population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2004;5:4. 8. Roddy E, Myers H, Thomas M, et al. The clinical assessment study of the foot (CASF): study protocol for a prospective observational study of foot pain and foot osteoarthritis in the general population. J Foot Ankle Res. 2011;4: Lawrence J. Osteo-arthrosis. In: Lawrence J, editor. Rheumatism in populations. London: William Heinemann Medical Books; p Burnett S, Hart D, Cooper C, Spector T. A radiographic atlas of osteoarthritis. London: Springer; p Menz H, Munteanu S, Landorf K, Zammit G, Cicuttini F. Radiographic classification of osteoarthritis in commonly affected joints of the foot. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2007;15: Duncan R, Hay E, Saklatvala J, Croft P. Prevalence of radiographic osteoarthritis it all depends on your point of view. Rheumatology. 2006;45: Marshall M, Nicholls E, Kwok WY et al. Erosive osteoarthritis: a more severe form of radiographic hand osteoarthritis rather than a distinct entity? Ann Rheum Dis published on 4 Oct doi: /annrheumdis Roddy E, Thomas M, Marshall M et al. Population prevalence of symptomatic radiographic foot osteoarthritis in community-dwelling older adults: the Clinical Assessment Study of the Foot (CASF). Ann Rheum Dis Published on 19 November Doi: /annrheumdis Roddy E. Revisiting the pathogenesis of podagra: why does gout target the foot? J Foot Ankle Res. 2011;4: Jordan K, Clarke AM, Symmons DP, et al. Measuring disease prevalence: a comparison of musculoskeletal disease using four general practice consultation databases. Br J Gen Pract. 2007;57: Porcheret M, Hughes R, Evans D, et al. Data quality of general practice electronic health records: the impact of a program of assessments, feedback, and training. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2004;11: Roddy E, Mallen CD, Hider SL, Jordan KP. Prescription and comorbidity screening following consultation for acute gout in primary care. Rheumatology. 2010;49: Zhang W, Doherty M, Pascual E, et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part I: diagnosis. Report of a task force of the standing committee for international clinical studies including therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
Foot problems in people with gout in primary care: baseline findings from a prospective cohort study
 Roddy et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:31 DOI 10.1186/s13047-015-0090-9 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Foot problems in people with gout in primary care: baseline findings
Roddy et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:31 DOI 10.1186/s13047-015-0090-9 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Foot problems in people with gout in primary care: baseline findings
Peter McQueen 1,2, Lucy Gates 1,2,3, Michelle Marshall 4, Michael Doherty 5, Nigel Arden 3,6 and Catherine Bowen 1,2*
 McQueen et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2017) 10:54 DOI 10.1186/s13047-017-0239-9 RESEARCH The effect of variation in interpretation of the La Trobe radiographic foot atlas on the prevalence
McQueen et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2017) 10:54 DOI 10.1186/s13047-017-0239-9 RESEARCH The effect of variation in interpretation of the La Trobe radiographic foot atlas on the prevalence
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2009) 17, 298e303 ª 2008 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2008.07.011 Radiographic evaluation
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2009) 17, 298e303 ª 2008 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2008.07.011 Radiographic evaluation
Chandratre et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2012, 13:219
 Chandratre et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2012, 13:219 STUDY PROTOCOL Open Access Prospective observational cohort study of Health Related Quality of Life (HRQOL), chronic foot problems and their
Chandratre et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2012, 13:219 STUDY PROTOCOL Open Access Prospective observational cohort study of Health Related Quality of Life (HRQOL), chronic foot problems and their
Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying Radiographic Features of Osteoarthritis
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp 533 538 DOI 10.1002/acr.21586 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp 533 538 DOI 10.1002/acr.21586 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
The prevalence and history of knee osteoarthritis in general practice: a case control study
 The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the Framingham Study
 Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA
 Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout. György Nagy
 Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout György Nagy Dec 4, 2017 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic, progressive, autoimmune disorder of the joints with extra-articular
Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout György Nagy Dec 4, 2017 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic, progressive, autoimmune disorder of the joints with extra-articular
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Age related prevalence of hand osteoarthritis diagnosed by photography (HOASCORE)
 Jonsson BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:508 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1870-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Age related prevalence of hand osteoarthritis diagnosed by photography (HOASCORE) Helgi Jonsson
Jonsson BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:508 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1870-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Age related prevalence of hand osteoarthritis diagnosed by photography (HOASCORE) Helgi Jonsson
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review
 Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
Corresponding author: Daniel McWilliams, Arthritis Research UK Pain Centre, Academic
 Erosive and osteoarthritic structural progression in early rheumatoid arthritis Daniel F McWilliams 1,2, Michelle Marshall 3, Keeranur Jayakumar 4, Sally Doherty 2, Michael Doherty 1,2, Weiya Zhang 1,2,
Erosive and osteoarthritic structural progression in early rheumatoid arthritis Daniel F McWilliams 1,2, Michelle Marshall 3, Keeranur Jayakumar 4, Sally Doherty 2, Michael Doherty 1,2, Weiya Zhang 1,2,
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Title: THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RADIOGRAPHIC KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: A FOURTEEN YEAR POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY
 Full Length DOI 10.1002/art.34415 Title: THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RADIOGRAPHIC KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: A FOURTEEN YEAR POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY Running Head: Natural history of radiographic knee OA Authors:
Full Length DOI 10.1002/art.34415 Title: THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RADIOGRAPHIC KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: A FOURTEEN YEAR POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY Running Head: Natural history of radiographic knee OA Authors:
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
F. Birrell 1,3, M. Lunt 1, G. Macfarlane 2 and A. Silman 1
 Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Development of a diagnostic rule for identifying radiographic osteoarthritis in people with first metatarsophalangeal joint pain
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 19 (2011) 939e945 Development of a diagnostic rule for identifying radiographic osteoarthritis in people with first metatarsophalangeal joint pain G.V. Zammit yz, S.E. Munteanu
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 19 (2011) 939e945 Development of a diagnostic rule for identifying radiographic osteoarthritis in people with first metatarsophalangeal joint pain G.V. Zammit yz, S.E. Munteanu
A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout
 A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout Nausheen Khan, MB BS, FCRad (D) Irma van de Werke, MB ChB, FRCR Farzanah Ismail, MB ChB, FCRad (D) Department of Radiology, Kalafong Hospital,
A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout Nausheen Khan, MB BS, FCRad (D) Irma van de Werke, MB ChB, FRCR Farzanah Ismail, MB ChB, FCRad (D) Department of Radiology, Kalafong Hospital,
Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by tumor characteristics: a casecontrol
 Krishnan et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:859 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3871-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by tumor characteristics: a casecontrol study Open Access Kavitha
Krishnan et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:859 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3871-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by tumor characteristics: a casecontrol study Open Access Kavitha
Acute hot swollen joint. Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist
 Acute hot swollen joint Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist Acute monoarthritis: differential diagnosis Septic arthritis Crystal arthritis (gout, pseudogout) Haemarthrosis
Acute hot swollen joint Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist Acute monoarthritis: differential diagnosis Septic arthritis Crystal arthritis (gout, pseudogout) Haemarthrosis
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Hormone replacement therapy and patterns of osteoarthritis: baseline data from the Ulm Osteoarthritis Study
 Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:105 109 105 Department of Epidemiology, University of Ulm, Germany, Helmholtzstr 22, D-89081 Ulm, Germany A Erb H Brenner T Stürmer Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:105 109 105 Department of Epidemiology, University of Ulm, Germany, Helmholtzstr 22, D-89081 Ulm, Germany A Erb H Brenner T Stürmer Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Risk of myocardial infarction with use of selected nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with spondyloarthritis and osteoarthritis
 1/5 We use cookies to improve our service and to tailor our content and advertising to you. More info Home / Archive / Volume 77, Issue 8 Article Text Article menu Clinical and epidemiological research
1/5 We use cookies to improve our service and to tailor our content and advertising to you. More info Home / Archive / Volume 77, Issue 8 Article Text Article menu Clinical and epidemiological research
Hand osteoarthritis and pinch grip strength among middle-aged female dentists and teachers
 84 Scand J Rheumatol 2010;39:8487 Hand osteoarthritis and pinch grip strength among middle-aged female dentists and teachers H Ding, S Solovieva, T Vehmas, E-P Takala, P Leino-Arjas Finnish Institute of
84 Scand J Rheumatol 2010;39:8487 Hand osteoarthritis and pinch grip strength among middle-aged female dentists and teachers H Ding, S Solovieva, T Vehmas, E-P Takala, P Leino-Arjas Finnish Institute of
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2007) 15, 615e623 ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.12.001 Knee osteoarthritis
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2007) 15, 615e623 ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.12.001 Knee osteoarthritis
Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis?
 International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2014; 17: 299 303 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis? Ozlem CEMEROGLU, 1 Halil
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2014; 17: 299 303 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis? Ozlem CEMEROGLU, 1 Halil
Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target?
 JT [2]2 Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target? Professor Jon Tobias Musculoskeletal Research Unit University of Bristol Slide 1 JT [2]2 I'd like to thank the organisers for inviting me to
JT [2]2 Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target? Professor Jon Tobias Musculoskeletal Research Unit University of Bristol Slide 1 JT [2]2 I'd like to thank the organisers for inviting me to
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Takashi Yagisawa 1,2*, Makiko Mieno 1,3, Norio Yoshimura 1,4, Kenji Yuzawa 1,5 and Shiro Takahara 1,6
 Yagisawa et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2016) 2:68 DOI 10.1186/s41100-016-0080-9 POSITION STATEMENT Current status of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2015: the data of the Kidney Transplant Registry
Yagisawa et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2016) 2:68 DOI 10.1186/s41100-016-0080-9 POSITION STATEMENT Current status of kidney transplantation in Japan in 2015: the data of the Kidney Transplant Registry
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
 Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Chest pain and subsequent consultation for coronary heart disease:
 Chest pain and subsequent consultation for coronary heart disease: a prospective cohort study Peter R Croft and Elaine Thomas ABSTRACT Background Chest pain may not be reported to general practice but
Chest pain and subsequent consultation for coronary heart disease: a prospective cohort study Peter R Croft and Elaine Thomas ABSTRACT Background Chest pain may not be reported to general practice but
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2464/03
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2464/03 BEFORE: T. Carroll: Vice-Chair G.V. Stewart: Member Representative of Employers D. Gillies: Member Representative of Workers HEARING:
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2464/03 BEFORE: T. Carroll: Vice-Chair G.V. Stewart: Member Representative of Employers D. Gillies: Member Representative of Workers HEARING:
Title: Low omega-3 fatty acid levels associate with frequent gout attacks a case
 Title: Low omega-3 fatty acid levels associate with frequent gout attacks a case control study Authors: A Abhishek 1, Ana M Valdes 1, Michael Doherty 1 Affiliation: Academic Rheumatology, University of
Title: Low omega-3 fatty acid levels associate with frequent gout attacks a case control study Authors: A Abhishek 1, Ana M Valdes 1, Michael Doherty 1 Affiliation: Academic Rheumatology, University of
Clinical features of symptomatic patellofemoral joint osteoarthritis
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical features of symptomatic patellofemoral joint osteoarthritis George Peat *, Rachel C Duncan, Laurence RJ Wood, Elaine Thomas and Sara Muller Abstract Introduction:
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical features of symptomatic patellofemoral joint osteoarthritis George Peat *, Rachel C Duncan, Laurence RJ Wood, Elaine Thomas and Sara Muller Abstract Introduction:
Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in the community: definitions and normal joint space
 Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Summary. Introduction
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2010) 18, 317e322 Crown Copyright ª 2009 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Osteoarthritis Research Society International. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2009.11.010
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2010) 18, 317e322 Crown Copyright ª 2009 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Osteoarthritis Research Society International. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2009.11.010
T he goals of medical management of patients with
 1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Effectiveness of the surgical torque limiter: a model comparing drill- and hand-based screw insertion into locking plates
 Ioannou et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:118 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0458-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Effectiveness of the surgical torque limiter: a model comparing drill- and hand-based
Ioannou et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:118 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0458-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Effectiveness of the surgical torque limiter: a model comparing drill- and hand-based
An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
Radiographic patterns and associations of
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Clinical Practice Guideline. Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings. Version
 Clinical Practice Guideline Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings Version 1.1.2017 November 2017 Table of Contents Abbreviations...3 Introduction...4 Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound...6 Definition
Clinical Practice Guideline Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings Version 1.1.2017 November 2017 Table of Contents Abbreviations...3 Introduction...4 Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound...6 Definition
APLICATION TO EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR CLINICAL AFFAIRS (ESCCA)
 APLICATION TO EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR CLINICAL AFFAIRS (ESCCA) EULAR RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TERMINOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CALCIUM PYROPHOSPHATE CRYSTAL ASSOCIATED ARTHRITIS Convenors: Michael
APLICATION TO EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR CLINICAL AFFAIRS (ESCCA) EULAR RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TERMINOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CALCIUM PYROPHOSPHATE CRYSTAL ASSOCIATED ARTHRITIS Convenors: Michael
Important facts about ORTHOVISC mini
 ORTHOVISC mini A targeted treatment for small joint pain. An increasing number of patients suffer from osteoarthritis (OA), the multisymptomatic joint disease characterized by cartilage degeneration and
ORTHOVISC mini A targeted treatment for small joint pain. An increasing number of patients suffer from osteoarthritis (OA), the multisymptomatic joint disease characterized by cartilage degeneration and
O steoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent form of
 319 EXTENDED REPORT Characterisation of size and direction of in knee osteoarthritis: a radiographic study Y Nagaosa, P Lanyon, M Doherty... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
319 EXTENDED REPORT Characterisation of size and direction of in knee osteoarthritis: a radiographic study Y Nagaosa, P Lanyon, M Doherty... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views Hwee-Yee Christian Heng, Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak, Amit Kanta
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views Hwee-Yee Christian Heng, Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak, Amit Kanta
Gout and Hyperuricemia
 Gout and Hyperuricemia 100 Access publication Sep. 2016 Computed tomography manifestation of gouty arthritis Hu Yabin 1, Yang Qing 1, Cao Qiang 2, Ren Jianan 1, Yang Qing * Objective: Of the most commonly
Gout and Hyperuricemia 100 Access publication Sep. 2016 Computed tomography manifestation of gouty arthritis Hu Yabin 1, Yang Qing 1, Cao Qiang 2, Ren Jianan 1, Yang Qing * Objective: Of the most commonly
Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional Study
 Arthritis Volume 2012, Article ID 984060, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/984060 Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional
Arthritis Volume 2012, Article ID 984060, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/984060 Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Table of Contents. Overview Introduction Variables Missing Data Image Type Time Points Reading Methods...
 MULTICENTER OSTEOARTHRITIS STUDY LONGITUDINAL KNEE RADIOGRAPH ASSESSMENTS (BASELINE TO 15-MONTH, 30-MONTH, 60-MONTH AND 84-MONTH FOLLOW-UP) AND MEASUREMENTS FROM BASELINE FULL LIMB RADIOGRAPHS DATASET
MULTICENTER OSTEOARTHRITIS STUDY LONGITUDINAL KNEE RADIOGRAPH ASSESSMENTS (BASELINE TO 15-MONTH, 30-MONTH, 60-MONTH AND 84-MONTH FOLLOW-UP) AND MEASUREMENTS FROM BASELINE FULL LIMB RADIOGRAPHS DATASET
Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the knee in patients referred to hospital
 520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
Professional organisation statement template
 Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can provide a unique perspective on the technology
Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can provide a unique perspective on the technology
Chopstick Arthropathy
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2004, pp 1495 1500 DOI 10.1002/art.20145 2004, American College of Rheumatology Chopstick Arthropathy The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study David J. Hunter, 1 Yuqing
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2004, pp 1495 1500 DOI 10.1002/art.20145 2004, American College of Rheumatology Chopstick Arthropathy The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study David J. Hunter, 1 Yuqing
To evaluate the role of high resolution ultrasonography in diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
 2018; 4(1): 69-76 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 69-76 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-11-2017 Accepted: 02-12-2017 Ravikant Jain HOD and Prof, Dept of orthopaedics, SAMC & PGI, Indore, Madhya
2018; 4(1): 69-76 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 69-76 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-11-2017 Accepted: 02-12-2017 Ravikant Jain HOD and Prof, Dept of orthopaedics, SAMC & PGI, Indore, Madhya
Comparison of Static and Dynamic Balance in Female Athletes with and without Hallux Valgus
 International Journal of Sport Studies. Vol., 4 (12), 1473-1478, 2014 Available online at http: www.ijssjournal.com ISSN 2251-7502 2014; Science Research Publications Comparison of Static and Dynamic Balance
International Journal of Sport Studies. Vol., 4 (12), 1473-1478, 2014 Available online at http: www.ijssjournal.com ISSN 2251-7502 2014; Science Research Publications Comparison of Static and Dynamic Balance
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Definition and Risk Factors Idiopathic vs. Secondary OA Clinical Features Diagnosis Radiologic Features ACR OA
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Definition and Risk Factors Idiopathic vs. Secondary OA Clinical Features Diagnosis Radiologic Features ACR OA
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
EULAR EVIDENCE BASED RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF HAND OSTEOARTHRITIS - REPORT OF A TASK FORCE OF THE EULAR
 EULAR EVIDENCE BASED RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF HAND OSTEOARTHRITIS - REPORT OF A TASK FORCE OF THE EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR INTERNATIONAL CLINICAL STUDIES INCLUDING THERAPEUTICS (ESCISIT)
EULAR EVIDENCE BASED RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF HAND OSTEOARTHRITIS - REPORT OF A TASK FORCE OF THE EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR INTERNATIONAL CLINICAL STUDIES INCLUDING THERAPEUTICS (ESCISIT)
Rheumatology Advance Access published October 20, Quality of care for OA: the effect of a point-of-care consultation recording template
 Original article Rheumatology Advance Access published October 20, 2014 RHEUMATOLOGY 258 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keu411 Quality of care for OA: the effect of a point-of-care consultation recording template
Original article Rheumatology Advance Access published October 20, 2014 RHEUMATOLOGY 258 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keu411 Quality of care for OA: the effect of a point-of-care consultation recording template
University of Groningen. Forefoot disorders Schrier, Joost
 University of Groningen Forefoot disorders Schrier, Joost IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
University of Groningen Forefoot disorders Schrier, Joost IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 849 854 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0840,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 849 854 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0840,
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS
 RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
RISK FACTORS FOR SUBOPTIMAL OUTCOMES IN HAMMERTOE SURGERY JACOB RANDICH BS RACHEL ALBRIGHT DPM, MOIZ HASSAN MS, ROBERT O KEEFE DPM, ERIN E. KLEIN DPM, MS, LOWELL WEIL JR. DPM, MBA, LOWELL WEIL SR. DPM,
Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Associations of radiological osteoarthritis of the hip and knee with locomotor disability in the Rotterdam Study
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:203 208 203 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical School, Rotterdam, the Netherlands E Odding H A Valkenburg D Algra A Hofman R
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:203 208 203 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical School, Rotterdam, the Netherlands E Odding H A Valkenburg D Algra A Hofman R
Osteoarthritis in the forefoot accompanied with joint pain is potentially associated with bone alterations
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Osteoarthritis in the forefoot accompanied with joint pain is potentially associated with bone alterations Yukio Nakamura 1, Mikio Kamimura 2, Shigeharu Uchiyama 1, Masatoshi Komatsu
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Osteoarthritis in the forefoot accompanied with joint pain is potentially associated with bone alterations Yukio Nakamura 1, Mikio Kamimura 2, Shigeharu Uchiyama 1, Masatoshi Komatsu
Mitsuru Hanada 1, Masaaki Takahashi 2, Hiroki Furuhashi 1, Hiroshi Koyama 1 and Yukihiro Matsuyama 1. Research Article
 Research Article Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 2016, Vol. 53(5) 548 553! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav DOI: 10.1177/0004563215610142 acb.sagepub.com
Research Article Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 2016, Vol. 53(5) 548 553! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav DOI: 10.1177/0004563215610142 acb.sagepub.com
What will happen in the future? How will gout be diagnosed? How is gout treated? prevent
 Rheumatology Day Unit Dr J Hamilton 0191 4458359 0191 4455240 (9-5 Mon-Fri) Dr C Heycock 0191 4452198 Answer phone on 24hours Dr C Kelly 0191 4452193 Dr V Saravanan 0191 4456055 Dr M Rynne 0191 4458359
Rheumatology Day Unit Dr J Hamilton 0191 4458359 0191 4455240 (9-5 Mon-Fri) Dr C Heycock 0191 4452198 Answer phone on 24hours Dr C Kelly 0191 4452193 Dr V Saravanan 0191 4456055 Dr M Rynne 0191 4458359
Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients
 Gout on CT: a symmetric arthropathy. Anthony J Doyle (corresponding author) Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients with gout using computed tomography (CT) and
Gout on CT: a symmetric arthropathy. Anthony J Doyle (corresponding author) Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients with gout using computed tomography (CT) and
Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology
 Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology Poster No.: C-1599 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Pissarra, R. R. Domingues Madaleno,
Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology Poster No.: C-1599 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Pissarra, R. R. Domingues Madaleno,
Disclosures. Ultrasonography. Conventional radiography (XR) Magnetic resonance imaging. Conventional CT 10/27/2013
 What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
hands in patients with chronic renal failure
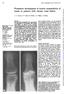 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28958 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Keurentjes, Johan Christiaan Title: Predictors of clinical outcome in total hip
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28958 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Keurentjes, Johan Christiaan Title: Predictors of clinical outcome in total hip
Ultrasonography in gout: a case-control study
 Ultrasonography in gout: a case-control study S. Ottaviani, P. Richette, A. Allard, J. Ora, T. Bardin Université Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, UFR de Médecine, and AP-HP, Service de Rhumatologie,
Ultrasonography in gout: a case-control study S. Ottaviani, P. Richette, A. Allard, J. Ora, T. Bardin Université Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, UFR de Médecine, and AP-HP, Service de Rhumatologie,
Gout. Edward Roddy, 1 Christian D Mallen, 1 Michael Doherty 2 CLINICAL REVIEW
 Gout Edward Roddy, 1 Christian D Mallen, 1 Michael Doherty 2 1 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre, Primary Care Sciences, Keele University, Keele ST5 5BG, UK 2 Academic Rheumatology, University
Gout Edward Roddy, 1 Christian D Mallen, 1 Michael Doherty 2 1 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre, Primary Care Sciences, Keele University, Keele ST5 5BG, UK 2 Academic Rheumatology, University
Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident incident gout: an individual participant data analysis
 This site uses cookies. More info Home / Online First Article Text Article menu Clinical and epidemiological research Concise report Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident
This site uses cookies. More info Home / Online First Article Text Article menu Clinical and epidemiological research Concise report Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident
Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Diagnostic accuracy of range of motion measurements in early symptomatic hip and/or knee osteoarthritis
 Chapter 1 Diagnostic accuracy of range of motion measurements in early symptomatic hip and/or knee osteoarthritis Jasmijn F.M. Holla, Marike van der Leeden, Leo D. Roorda, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, Jurgen
Chapter 1 Diagnostic accuracy of range of motion measurements in early symptomatic hip and/or knee osteoarthritis Jasmijn F.M. Holla, Marike van der Leeden, Leo D. Roorda, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, Jurgen
Daisuke Uritani 1*, Takahiko Fukumoto 1, Daisuke Matsumoto 1 and Masayuki Shima 2
 Uritani et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:18 DOI 10.1186/s13047-015-0076-7 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Associations between toe grip strength and hallux valgus,
Uritani et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (2015) 8:18 DOI 10.1186/s13047-015-0076-7 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Associations between toe grip strength and hallux valgus,
EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS ACTIVITY 1: EARLY COLLABORATION IN THE TREATMENT OF PSA Key Slides COMMON COMORBIDITIES OF PSORIATIC DISEASE
EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS ACTIVITY 1: EARLY COLLABORATION IN THE TREATMENT OF PSA Key Slides COMMON COMORBIDITIES OF PSORIATIC DISEASE
Supplementary Material*
 Supplementary Material* Newberry SJ, FitzGerald JD, Motala A, Booth M, Maglione MA, Han D, Tariq A, O Hanlon CE, Shanman R, Dudley W, Shekelle PG. Diagnosis of gout. A systematic review in support of an
Supplementary Material* Newberry SJ, FitzGerald JD, Motala A, Booth M, Maglione MA, Han D, Tariq A, O Hanlon CE, Shanman R, Dudley W, Shekelle PG. Diagnosis of gout. A systematic review in support of an
Osteoarthritis as a public health problem: the impact of developing knee pain on physical function in adults living in the community: (KNEST 3)
 Rheumatology 2007;46:877 881 Advance Access publication 17 February 2007 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem013 Osteoarthritis as a public health problem: the impact of developing knee pain on physical function
Rheumatology 2007;46:877 881 Advance Access publication 17 February 2007 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem013 Osteoarthritis as a public health problem: the impact of developing knee pain on physical function
Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report
 Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report 1 First author Pub. Year Reference Country Allen et al 2010 [1] USA Design Time to follow-up Setting Performed
Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report 1 First author Pub. Year Reference Country Allen et al 2010 [1] USA Design Time to follow-up Setting Performed
Disclosures. The Changing Demographics of End-Stage Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. Evidence 11/7/2011. OA: Risk factors
 Disclosures The Changing Demographics of End-Stage Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis Joanne M. Jordan, MD MPH University of North Carolina Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology Johnson & Johnson: contract, consultant
Disclosures The Changing Demographics of End-Stage Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis Joanne M. Jordan, MD MPH University of North Carolina Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology Johnson & Johnson: contract, consultant
DISCLOSURES. T. McAlindon: Samumed, grant/research support; Astellas, Flexion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samumed,and Seikugaku, consulting
 Radiographic Outcomes from a Randomized, Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of a Novel, Intra-Articular, Wnt Pathway Inhibitor (SM04690) for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Week
Radiographic Outcomes from a Randomized, Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of a Novel, Intra-Articular, Wnt Pathway Inhibitor (SM04690) for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Week
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Seetha Monrad, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Seetha Monrad, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea
 J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 293-8 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.293 The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea The purpose of this study was to estimate the
J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 293-8 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.293 The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea The purpose of this study was to estimate the
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2005) 13, 953e957 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.06.007 Trapeziometacarpal subluxation
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2005) 13, 953e957 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.06.007 Trapeziometacarpal subluxation
Osteoarthritis. Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow
 Osteoarthritis Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Das S.K. Osteoarthritis In Wagh S. (Ed). Rheumatology
Osteoarthritis Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Das S.K. Osteoarthritis In Wagh S. (Ed). Rheumatology
