Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying Radiographic Features of Osteoarthritis
|
|
|
- Kelley Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp DOI /acr , American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying Radiographic Features of Osteoarthritis FRANCES REES, 1 SALLY DOHERTY, 1 MICHELLE HUI, 1 ROSE MACIEWICZ, 2 KENNETH MUIR, 3 WEIYA ZHANG, 1 AND MICHAEL DOHERTY 1 Objective. To determine the distribution of clinically palpable hand interphalangeal (IP) nodes at each finger and thumb joint in a population with nodes, the influence of left or right hand dominance and sex on the development of nodes, and the association between nodes and underlying radiographic features of osteoarthritis (OA). Methods. We performed a cross-sectional analysis of participants in the Genetics of Osteoarthritis and Lifestyle (GOAL) study who had >1 Heberden s nodes or Bouchard s nodes on clinical examination. Frequencies (%) of nodes were described for each IP joint in the hand. Associations between nodes and underlying radiographic OA were shown with odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals. A logistic regression model was used to adjust for the following confounding factors: age, sex, body mass index, left or right hand dominance, hand trauma, occupation with heavy manual activity, and participation in sports. Results. Of the 3,170 GOAL participants, 1,939 had >1 nodes (mean age 68 years, 54% women). The distal IP joints of the index finger were the most frequently affected, followed by the thumb IP joint. Nodes were more common in dominant hands and women. There was a significant association between nodes and underlying radiographic OA (OR range ). This association was stronger for joint space narrowing than for osteophytes. A dose-response relationship was found between clinical severity of Heberden s nodes and underlying radiographic change. Conclusion. Our study supports the positive association between nodes and radiographic OA, especially narrowing, and the influence of sex and left or right hand dominance on development of nodes. In this age group, presence of nodes may be taken as an indication of underlying small joint OA. INTRODUCTION Hand interphalangeal (IP) joint osteoarthritis (OA) is a common condition that can cause pain and functional impairment (1). Hand OA can be diagnosed radiographically by presence of joint space narrowing (JSN), osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, and subchondral cysts, or clinically by symptoms and physical signs (2). Clinically, AstraZeneca, Macclesfield, UK provided financial support to establish the original Genetics of Osteoarthritis and Lifestyle study. 1 Frances Rees, BMBS, Sally Doherty, RGN, Michelle Hui, MBChB, Weiya Zhang, PhD, Michael Doherty, MD: University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK; 2 Rose Maciewicz, PhD: AstraZeneca, Mölndal, Sweden; 3 Kenneth Muir, PhD: University of Warwick, Coventry, UK. Dr. Maciewicz owns stock or stock options in AstraZeneca. Address correspondence to Frances Rees, BMBS, Academic Rheumatology, Clinical Sciences Building, City Hospital, Nottingham NG5 1PB, UK. frees@doctors. org.uk. Submitted for publication August 25, 2011; accepted in revised form December 9, hand OA is often accompanied by the presence of Heberden s nodes and Bouchard s nodes (3). Multiple nodes are regarded widely as a marker for generalized OA (4). Few studies have investigated the association between hand nodes and underlying structure changes (5 8). In the studies that have investigated this, the measures used to assess the association were inconsistent, which led to a different clinical interpretation of the association. For example, Caspi et al (5) used a composite radiographic score (JSN, osteophytes, cysts, sclerosis, and subluxation) and reported a good correlation with clinical score (nodes and lateral deviation). However, Cicuttini et al (6) reported poor agreement between Heberden s nodes and radiographic distal IP (DIP) joint osteophytes, although after examining the statistics there was a small but statistically significant relationship. Thaper et al (7) reported a positive association with both JSN and osteophytes and suggest they can be used as a clinical marker. Hart et al (8) examined Kellgren/Lawrence (K/L) scores and reported a high specificity but low sensitivity association and concluded that they were not able to replace radiographic definition with clinical nodes. 533
2 534 Rees et al Significance & Innovations There was a strong positive association between clinical nodes and radiographic osteoarthritis (OA). Therefore, in this age group, the presence of nodes would appear to be a good surrogate marker for underlying radiographic hand OA, a finding that may be of relevance in epidemiologic and genetic studies of OA where hand radiographs are unavailable. Nodes were more common in the dominant hands and women. A dose-response relationship was found between clinical severity of Heberden s nodes and underlying radiographic change (osteophyte and joint space narrowing). Nodes were most common at the index distal interphalangeal and thumb interphalangeal joints, which are 2 adjacent joints used in fine precision and pincer grip. The overall distribution of nodes suggests that biomechanical factors are important in their development. Hand OA is observed to occur more frequently in women and with increasing age. Other reported risk factors for hand OA include positive family history, obesity, occupation, and prior injury (9). There is conflicting evidence as to whether dominance of the left or right hand affects development of hand OA (5,10,11). The aims of this study were to determine the distribution of palpable nodes at each joint in a population with nodes, the influence of left or right hand dominance and sex on the development of nodes, and whether palpable nodes are associated with underlying radiographic features of OA. The latter issue is of relevance particularly in epidemiologic and genetic studies of OA where hand radiographs are not always available. PATIENTS AND METHODS Participants. Participants were taken from the Nottingham Genetics of Osteoarthritis and Lifestyle (GOAL) study, which has been described previously (12). In summary, the GOAL study was a case control study where the participants were recruited from a hospital-based population in Nottingham, UK from Cases were patients with symptoms and radiographic changes of OA at the hip or knee sufficiently clinically severe enough to warrant hospital referral for consideration of joint replacement (n 2,049). Controls were people who had undergone intravenous urography at the same Nottingham hospitals and who had no symptoms, signs, or radiographic evidence of hip or knee OA (n 1,123). One patient subsequently withdrew her consent and 1 patient had withdrawn because it became apparent that she had secondary rather than primary hip OA. Ethical approval was obtained from the Nottingham Research Ethics Committee. Clinical assessment. Evidence of palpable nodes was determined by 5 specifically trained metrologists. Over the DIP and proximal IP (PIP) joints of all fingers, Heberden s nodes (DIP joints) were graded as the following: no nodes, radial node, ulnar node, both radial and ulnar nodes, or a single dorsal transverse bar. Bouchard s nodes (PIP joints) were graded as either present or absent. The nodes affecting the thumb IP and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints were also documented. This method has been previously validated (7,13). Intraobserver reproducibility was determined by the metrologists reassessment every 2 3 months. Age, sex, left or right hand dominance, previous hand trauma, occupation, and activity history were assessed by the GOAL study questionnaire. Body mass index (BMI) was measured at the interview (12). Radiographic assessment. Hand radiographs were dorsal palmar centered on the middle MCP joint. JSN and osteophytes were graded 0 3 using the Osteoarthritis Research Society International atlas (14) by a single observer blinded to the clinical scores. K/L scores 0 4 were also applied (15). Reproducibility has previously been validated (7). Eligibility for the present study. Patients were eligible to be included in this analysis if they had 1 nodes, irrespective of joint site, in either hand. This was regardless of case or control status. Statistical analysis. Distribution of nodes was measured using frequency of nodes at each finger joint. Unlike the prevalence measure that is the percentage of nodes in the total population (with or without nodes), this is a proportional measure that describes the node distribution in people with nodes. The association analysis was person based and undertaken separately for each joint; therefore, there was no need to adjust for within-participant effect. Associations between nodes and radiographic OA were shown with odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI). A logistic regression model was used to adjust for confounding factors, including age, sex, BMI, left or right hand dominance, previous hand trauma, occupations with heavy manual activity, and regular activities undertaken for 7 hours per week that may predispose to hand injury (e.g., rugby, cricket). Associations between left or right hand dominance and nodes were determined by comparing the OR (95% CI) of any node occurring on the right hand with right hand dominance and the OR (95% CI) of any node occurring on the left hand with left hand dominance. SPSS, version 14 was used for all analyses. Statistical significance was taken at P values less than 0.05 (2-sided). The reference group used to calculate the OR was the participants in the GOAL study who did not have a palpable node at the joint under investigation. RESULTS Population characteristics. From a total of 3,170 participants in the GOAL study database, 1,939 had 1 palpable
3 Finger Nodes in OA 535 Table 1. Population characteristics* Total population (n 1,939) Sex, no. (%) Women 1,047 (54) Men 892 (46) Age, mean SD (range) years (45 86) BMI, mean SD kg/m Dominant hand, no. (%) Right 1,758 (90.7) Left 145 (7.5) Both 36 (1.9) * BMI body mass index. nodes. Of these 1,939 participants, 1,400 participants (72.2%) were from the original case group and 539 participants (27.8%) were from the control group. The population characteristics are shown in Table 1. Clinical findings. The frequency of a node at each joint site in these 1,939 patients is shown in Figure 1. The index finger DIP joint was most commonly affected, followed by the thumb IP joint. On every finger, the DIP joints were more frequently affected than the PIP joints. This was also true for the thumb. The ring finger was least affected by nodes. The most frequently affected PIP joint was the middle finger. The right hand was more frequently affected than the left hand at all sites. When stratified by left or right hand dominance, right-handed people had more nodes on the right hand (OR 2.9, 95% CI ; P 0.001), whereas left-handed people had more nodes on the left hand (OR 3.2, 95% CI ; P 0.001). When stratified by sex, all nodes were more frequent in women than men, apart from the thumb MCP joints (Figure 2). With respect to grading of Heberden s nodes (Table 2), the most frequent finding was both, meaning a palpable node on both the radial and ulnar side of the joint. At the index and little fingers ulnar nodes were more frequent than radial nodes. The opposite was found at the middle and ring fingers. Association with underlying radiographic changes. The association between palpable nodes and underlying radiographic change (K/L grade 2) is shown in Figure 3. ORs and 95% CIs were adjusted for age, sex, BMI, left or right hand dominance, previous hand trauma, occupation with heavy manual activity, and regular activity in sports. At every joint there was a significant association between palpable node and underlying radiographic change (P 0.001). The association remained significant for individual radiographic features of osteophytes and JSN (P 0.001). The ORs were greater for JSN than osteophytes at every finger IP joint, except for the thumb. A dose-response relationship was observed for the association between Heberden s node severity and underlying radiographic OA change. Figure 4 shows that the OR of osteophytes increased gradually with severity of palpable node at the index finger DIP joint of the right hand. The same results were observed for all other DIP joints and for JSN. DISCUSSION This study demonstrates that nodes most frequently affect the index finger DIP joint, with the thumb IP joint the second most affected site. At every finger, DIP joint nodes were more frequent than PIP joint nodes and the ring finger was relatively spared from both nodes. The thumb IP joints were more frequently affected than the thumb MCP joints. Left or right hand dominance and female sex were significantly associated with the presence of nodes. Our findings demonstrate a significant association between palpable node and underlying radiographic OA, the association being stronger for JSN than for osteophytes. A dose-response relationship was found between clinical severity of Heberden s node and underlying radiographic change. Therefore, in this age group the presence of nodes would appear Figure 1. The distribution of nodes in people with any interphalangeal nodes (n 1,939).
4 536 Rees et al Figure 2. The frequency of nodes stratified by sex. to be a good surrogate marker for underlying radiographic hand OA, a finding that may be of relevance in epidemiologic and genetic studies of OA where hand radiographs are unavailable. Although a number of studies have examined the frequency distribution of symptoms (1,16) and radiographic changes (10,17,18) of OA at each joint in the hand, no studies have previously focused on the frequency distribution of nodes. The asymmetry related to left or right hand dominance suggests that differing hand functions and biomechanical stress may contribute to node development. Two adjacent distal joints, the index finger DIP joint and the thumb IP joint, were the 2 most affected sites. Both of these joints are required for fine precision pinch (index finger tip to thumb tip) and pincer grip (side to side opposition of the distal index finger to the distal thumb), 2 gripping actions involved in many daily activities. It may be that frequent repetitive gripping between the ends of the index finger and thumb particularly predisposes these 2 joints to microtrauma and subsequent OA. Such a biomechanical explanation has been suggested to explain the difference in prevalence and distribution of radiographic hand OA between dentists (an occupation with physically demanding hand usage) and teachers (an occupation with less physically demanding hand usage) (10) and the different patterns of hand OA observed in 3 groups of female workers who undertook repetitive but contrasting manual activities in an industrial setting (19). The middle finger is Table 2. Frequencies of grade of palpable node at each distal interphalangeal joint (n 1,854)* Index Middle Ring Little Right Left Right Left Right Left Right Left Radial Ulnar Both Bar * Values are the percentage. At the index and little fingers ulnar nodes were more frequent than radial nodes. The opposite was found at the middle and ring fingers.
5 Finger Nodes in OA 537 Figure 3. The odds ratio (95% confidence interval) of underlying radiographic changes (Kellgren/Lawrence grade 2) associated with any nodes (adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, dominant hand, hand trauma, occupation with heavy manual activity, and participation in sports). used to a lesser extent in precision grips so it might be less exposed than the index finger to repetitive microtrauma, although being the longest finger, it may be more exposed to external trauma. We hypothesize that the sparing of the ring finger IP joints may be due to its noninvolvement in most precision grips and its position between the middle and little fingers, which might confer protection from external trauma. No previous studies examining this were found. MCP joints, and even IP joints of the thumb, are often not considered to be a site for nodes. Developmentally, the thumb IP joint is a DIP joint, the thumb MCP joint is in fact a PIP joint, and the first carpometacarpal joint is the true MCP joint for the thumb; this whole ray of joints moved proximally in our past evolution in parallel with improved precision gripping and manual dexterity (20). In this study, the thumb MCP joints were affected by firm posterolateral and dorsal swelling with a frequency similar to that of the finger PIP nodes. The thumb MCP joints had the lowest OR when associated with underlying radiographic change, but this was still significant. The lower OR in the thumbs may be related to the fact that the hand radiographs were dorsal palmar centered and consequently the thumb was placed at almost 90 degrees to the other joints, which may have affected the ability to equally assess radiographic OA. This may also explain the stronger association with JSN than osteophytes in the fingers, since JSN in any plane will be captured on an anteroposterior radiograph; however, osteophytes that project posteriorly or anteriorly will not be identified. Female sex has previously been found to be associated Figure 4. The association between grade of node and underlying osteophytes at the right index distal interphalangeal joint. OR odds ratio; 95% CI 95% confidence interval. with hand OA (21). The mechanism for this is unclear, but may be due more to genetic or hormonal influences rather than environmental factors. Few studies have examined the association between radiographic and clinical OA. Our findings are in agreement with Caspi et al (5), who found a positive correlation between composite radiographic and clinical OA scores, and in addition found a correlation with right or left hand dominance. Caspi et al examined an elderly Jewish cohort (mean age 78.8 years) admitted to secondary care for a nonrheumatic reason. Although they found women had higher composite OA scores than men, this was not statistically significant. Cicuttini et al (6) found a small but statistically significant correlation between Heberden s nodes and DIP osteophytes ( correlation coefficient 0.36 [95% CI ]). This was a female twin study in a general (non-nodal) population with a lower mean age (56.4 years) than in our study. Cicuttini et al did not examine JSN. One previous study from our unit by Thaper et al (7) also found a positive relationship between nodes and underlying radiographic change in a nodal OA population. In that study, however, osteophytes had a stronger association than JSN, the opposite finding of that of the present study. However, this previous study differed from the present study in that joints were not analyzed individually due to the limited sample size (n 489), but the ORs for all Heberden s nodes and Bouchard s nodes were pooled and were smaller. This difference in results may have been due in part to our larger study population, with a more equal sex balance (82.6% women in Thaper et al compared with 54% women in our study). Mean age was similar at 65.8 years. The difference may also be because of the sampling variation or different population at risk. Thaper et al examined siblings of people with OA, whereas the present study examined unrelated people with any hand nodes. Whether hand nodes related more to JSN or osteophytes requires further investigation, ideally a prospective study of people at risk of hand OA with a sample randomly selected from the population. There are a number of limitations to this study. First, the GOAL study was established as a case control study to examine genetic and lifestyle differences between patients with large joint OA and controls. We then examined a
6 538 Rees et al subset of this population with clinical evidence of hand OA. The GOAL study population is biased toward individuals with severe OA, so our findings cannot be extrapolated to estimate point prevalence of OA at each joint in the general population. These results would need to be confirmed with a further study. Second, this study only looked at one point in time. A prospective study would be required to examine the temporal relationship between development of clinical nodes and radiographic change. Finally, it is important to emphasize that although the ORs for the association between clinical and radiographic changes were highly significant, the presence of a node does not necessarily guarantee radiographic change will be present. Likewise, the absence of a node does not exclude the presence of radiographic OA. A prospective study using sensitive imaging to assess the development of nodes and radiographic changes over time is required. In conclusion, our study adds further evidence to the strong positive association between nodes and radiographic OA, especially JSN, and that sex and left or right hand dominance are significantly associated with palpable nodes. However, a prospective study is required to confirm the temporal association between nodes and radiographic change. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS All authors were involved in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and all authors approved the final version to be published. Dr. Rees had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study conception and design. Rees, Hui, Muir, Zhang, Michael Doherty. Acquisition of data. Sally Doherty, Zhang, Michael Doherty. Analysis and interpretation of data. Rees, Maciewicz, Muir, Zhang, Michael Doherty. ROLE OF THE STUDY SPONSOR AstraZeneca, Macclesfield, UK provided financial support to establish the original Genetics of Osteoarthritis and Lifestyle study as a collaborative project with the University of Nottingham, but had no involvement in the study design, data analysis, or writing of this manuscript. Publication of this study was not contingent on approval from AstraZeneca. REFERENCES 1. Zhang Y, Niu J, Kelly-Hayes M, Chaisson CE, Aliabadi P, Felson DT. Prevalence of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis and its impact on functional status among the elderly: the Framingham Study. Am J Epidemiol 2002;156: Zhang W, Doherty M, Leeb BF, Alekseeva L, Arden NK, Bijlsma JW, et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of hand osteoarthritis: report of a task force of ESCISIT. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68: Altman R, Alarcon G, Appelrouth D, Bloch D, Borenstein D, Brandt K, et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hand. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33: Kellgren J, Moore R. Generalized osteoarthritis and Heberden s nodes. Br Med J 1952;1: Caspi D, Flusser G, Farber I, Ribak J, Leibovitz A, Habot B, et al. Clinical, radiologic, demographic, and occupational aspects of hand osteoarthritis in the elderly. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2001;30: Cicuttini FM, Baker J, Hart DJ, Spector TD. Relation between Heberden s nodes and distal interphalangeal joint osteophytes and their role as markers of generalised disease. Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57: Thaper A, Zhang W, Wright G, Doherty M. Relationship between Heberden s nodes and underlying radiographic changes of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64: Hart D, Spector T, Egger P, Coggon D, Cooper C. Defining osteoarthritis of the hand for epidemiological studies: the Chingford Study. Ann Rheum Dis 1994;53: Kalichman L, Hernandez-Molina G. Hand osteoarthritis: an epidemiological perspective. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2010;39: Solovieva S, Vehmas T, Riihimaki H, Luoma K, Leino-Arjas P. Hand use and patterns of joint involvement in osteoarthritis: a comparison of female dentists and teachers. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005;44: Acheson RM, Chan YK, Clemett AR. New Haven survey of joint diseases. XII. Distribution and symptoms of osteoarthrosis in the hands with reference to handedness. Ann Rheum Dis 1970;29: Zhang W, Robertson J, Doherty S, Liu JJ, Maciewicz RA, Muir KR, et al. Index to ring finger length ratio and the risk of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58: O Reilly S, Johnson S, Doherty S, Muir K, Doherty M. Screening for hand osteoarthritis (OA) using a postal survey. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1999;7: Altman RD, Hochberg M, Murphy WA Jr, Wolfe F, Lequesne M. Atlas of individual radiographic features in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1995;3 Suppl A: Kellgren J, Lawrence J. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957;16: Niu J, Zhang Y, LaValley M, Chaisson CE, Aliabadi P, Felson DT. Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the Framingham Study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42: Wilder FV, Barrett JP, Farina EJ. Joint-specific prevalence of osteoarthritis of the hand. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2006;14: Buckland-Wright JC, Macfarlane DG, Lynch JA. Osteophytes in the osteoarthritic hand: their incidence, size, distribution, and progression. Ann Rheum Dis 1991;50: Hadler NM, Gillings DB, Imbus HR, Levitin PM, Makuc D, Utsinger PD, et al. Hand structure and function in an industrial setting. Arthritis Rheum 1978;21: Flatt AE. Our thumbs. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2002;15: Srikanth VK, Fryer JL, Zhai G, Winzenberg TM, Hosmer D, Jones G. A meta-analysis of sex differences prevalence, incidence and severity of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2005;13:
Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the Framingham Study
 Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Chopstick Arthropathy
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2004, pp 1495 1500 DOI 10.1002/art.20145 2004, American College of Rheumatology Chopstick Arthropathy The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study David J. Hunter, 1 Yuqing
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2004, pp 1495 1500 DOI 10.1002/art.20145 2004, American College of Rheumatology Chopstick Arthropathy The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study David J. Hunter, 1 Yuqing
Hand osteoarthritis and pinch grip strength among middle-aged female dentists and teachers
 84 Scand J Rheumatol 2010;39:8487 Hand osteoarthritis and pinch grip strength among middle-aged female dentists and teachers H Ding, S Solovieva, T Vehmas, E-P Takala, P Leino-Arjas Finnish Institute of
84 Scand J Rheumatol 2010;39:8487 Hand osteoarthritis and pinch grip strength among middle-aged female dentists and teachers H Ding, S Solovieva, T Vehmas, E-P Takala, P Leino-Arjas Finnish Institute of
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review
 Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
Papers. Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study. Abstract. Participants and methods.
 Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study Peter Lanyon, Kenneth Muir, Sally Doherty, Michael Doherty Abstract Objectives To study the influence of genetics on the
Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study Peter Lanyon, Kenneth Muir, Sally Doherty, Michael Doherty Abstract Objectives To study the influence of genetics on the
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in the community: definitions and normal joint space
 Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs
 Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
F. Birrell 1,3, M. Lunt 1, G. Macfarlane 2 and A. Silman 1
 Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Knuckle Cracking and Hand Osteoarthritis
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Knuckle Cracking and Hand Osteoarthritis Kevin deweber, MD, FAAFP, Mariusz Olszewski, MD, and Rebecca Ortolano, MD Background: Previous studies have not shown a correlation between knuckle
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Knuckle Cracking and Hand Osteoarthritis Kevin deweber, MD, FAAFP, Mariusz Olszewski, MD, and Rebecca Ortolano, MD Background: Previous studies have not shown a correlation between knuckle
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA
 Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Journal of the OsteoArthritis Research Society International
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $33-$37 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi:10.1053/joca.2000.0334, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on It Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $33-$37 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi:10.1053/joca.2000.0334, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on It Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Journal of the OsteoArthritis Research Society International
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $64-$69 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi: 10.1053/joca. 1999.0340, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on D IF --JI~=L
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $64-$69 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi: 10.1053/joca. 1999.0340, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on D IF --JI~=L
NEW RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING SCALES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HAND
 1584 NEW RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING SCALES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HAND Reliability for Determining Prevalence and Progression DOUGLAS A. KALLMAN, FREDRICK M. WIGLEY, WILLIAM W. SCOTT, JR.. MARC C. HOCHBERG,
1584 NEW RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING SCALES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HAND Reliability for Determining Prevalence and Progression DOUGLAS A. KALLMAN, FREDRICK M. WIGLEY, WILLIAM W. SCOTT, JR.. MARC C. HOCHBERG,
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Hormone replacement therapy and patterns of osteoarthritis: baseline data from the Ulm Osteoarthritis Study
 Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:105 109 105 Department of Epidemiology, University of Ulm, Germany, Helmholtzstr 22, D-89081 Ulm, Germany A Erb H Brenner T Stürmer Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:105 109 105 Department of Epidemiology, University of Ulm, Germany, Helmholtzstr 22, D-89081 Ulm, Germany A Erb H Brenner T Stürmer Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
The association between gout and radiographic hand, knee and foot osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study
 Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1032-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The association between gout and radiographic hand, knee and foot osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional
Bevis et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:169 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1032-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The association between gout and radiographic hand, knee and foot osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional
The prevalence and history of knee osteoarthritis in general practice: a case control study
 The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Title: THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RADIOGRAPHIC KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: A FOURTEEN YEAR POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY
 Full Length DOI 10.1002/art.34415 Title: THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RADIOGRAPHIC KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: A FOURTEEN YEAR POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY Running Head: Natural history of radiographic knee OA Authors:
Full Length DOI 10.1002/art.34415 Title: THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RADIOGRAPHIC KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: A FOURTEEN YEAR POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY Running Head: Natural history of radiographic knee OA Authors:
Associations of radiological osteoarthritis of the hip and knee with locomotor disability in the Rotterdam Study
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:203 208 203 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical School, Rotterdam, the Netherlands E Odding H A Valkenburg D Algra A Hofman R
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:203 208 203 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical School, Rotterdam, the Netherlands E Odding H A Valkenburg D Algra A Hofman R
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2005) 13, 953e957 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.06.007 Trapeziometacarpal subluxation
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2005) 13, 953e957 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.06.007 Trapeziometacarpal subluxation
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 849 854 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0840,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 849 854 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0840,
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
O steoarthritis (OA) of the hip is of particular interest as
 1427 EXTENDED REPORT Validity and reliability of three definitions of hip osteoarthritis: cross sectional and longitudinal approach M Reijman, J M W Hazes, H A P Pols, R M D Bernsen, B W Koes, S M A Bierma-Zeinstra...
1427 EXTENDED REPORT Validity and reliability of three definitions of hip osteoarthritis: cross sectional and longitudinal approach M Reijman, J M W Hazes, H A P Pols, R M D Bernsen, B W Koes, S M A Bierma-Zeinstra...
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis?
 International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2014; 17: 299 303 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis? Ozlem CEMEROGLU, 1 Halil
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2014; 17: 299 303 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis? Ozlem CEMEROGLU, 1 Halil
T he goals of medical management of patients with
 1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target?
 JT [2]2 Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target? Professor Jon Tobias Musculoskeletal Research Unit University of Bristol Slide 1 JT [2]2 I'd like to thank the organisers for inviting me to
JT [2]2 Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target? Professor Jon Tobias Musculoskeletal Research Unit University of Bristol Slide 1 JT [2]2 I'd like to thank the organisers for inviting me to
EULAR EVIDENCE BASED RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF HAND OSTEOARTHRITIS - REPORT OF A TASK FORCE OF THE EULAR
 EULAR EVIDENCE BASED RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF HAND OSTEOARTHRITIS - REPORT OF A TASK FORCE OF THE EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR INTERNATIONAL CLINICAL STUDIES INCLUDING THERAPEUTICS (ESCISIT)
EULAR EVIDENCE BASED RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF HAND OSTEOARTHRITIS - REPORT OF A TASK FORCE OF THE EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR INTERNATIONAL CLINICAL STUDIES INCLUDING THERAPEUTICS (ESCISIT)
Nonspherical Femoral Head Shape (Pistol Grip Deformity), Neck Shaft Angle, and Risk of Hip Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 10, October 2008, pp 3172 3182 DOI 10.1002/art.23939 2008, American College of Rheumatology Nonspherical Femoral Head Shape (Pistol Grip Deformity), Neck Shaft Angle,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 10, October 2008, pp 3172 3182 DOI 10.1002/art.23939 2008, American College of Rheumatology Nonspherical Femoral Head Shape (Pistol Grip Deformity), Neck Shaft Angle,
BRIEF REPORT. KENNETH D. BRANDT, ROSE S. FIFE, ETHAN M. BRAUNSTEIN, and BARRY KATZ. From the Department of Medicine, the Department of
 1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report
 Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report 1 First author Pub. Year Reference Country Allen et al 2010 [1] USA Design Time to follow-up Setting Performed
Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report 1 First author Pub. Year Reference Country Allen et al 2010 [1] USA Design Time to follow-up Setting Performed
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
T he hand is a common site of peripheral osteoarthritis
 151 EXTENDED REPORT Osteoarthritis of finger joints in Finns aged 30 or over: prevalence, determinants, and association with mortality M M Haara, P Manninen, H Kröger, J P A Arokoski, A Kärkkäinen, P Knekt,
151 EXTENDED REPORT Osteoarthritis of finger joints in Finns aged 30 or over: prevalence, determinants, and association with mortality M M Haara, P Manninen, H Kröger, J P A Arokoski, A Kärkkäinen, P Knekt,
Predictors of Functional Impairment and Pain in Erosive Osteoarthritis of the Interphalangeal Joints
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 64, No. 5, May 2012, pp 1430 1436 DOI 10.1002/art.33502 2012, American College of Rheumatology Predictors of Functional Impairment and Pain in Erosive Osteoarthritis of the
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 64, No. 5, May 2012, pp 1430 1436 DOI 10.1002/art.33502 2012, American College of Rheumatology Predictors of Functional Impairment and Pain in Erosive Osteoarthritis of the
OCCUPATIONAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 7, July 2000, pp 1443 1449 2000, American College of Rheumatology 1443 OCCUPATIONAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE DAVID COGGON, PETER CROFT, SAMANTHA
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 7, July 2000, pp 1443 1449 2000, American College of Rheumatology 1443 OCCUPATIONAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE DAVID COGGON, PETER CROFT, SAMANTHA
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 542 546 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0809,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 542 546 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0809,
Summary. Introduction
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 69 77 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/020069+09 $35.00/0 doi: 10.1053/joca.1999.0273, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 69 77 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/020069+09 $35.00/0 doi: 10.1053/joca.1999.0273, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1402e1407
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1402e1407 Comparison of BLOKS and WORMS scoring systems part II. Longitudinal assessment of knee MRIs for osteoarthritis and suggested approach based on their performance:
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1402e1407 Comparison of BLOKS and WORMS scoring systems part II. Longitudinal assessment of knee MRIs for osteoarthritis and suggested approach based on their performance:
Project 15 Test-Retest Reliability of Semi-quantitative Readings from Knee Radiographs
 Project 15 Test-Retest Reliability of Semi-quantitative Readings from Knee Radiographs 1. SAS dataset... 1 2. Purpose and methods... 1 2.1 Background... 1 2.2 Reliability at single time points... 1 2.3
Project 15 Test-Retest Reliability of Semi-quantitative Readings from Knee Radiographs 1. SAS dataset... 1 2. Purpose and methods... 1 2.1 Background... 1 2.2 Reliability at single time points... 1 2.3
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional Study
 Arthritis Volume 2012, Article ID 984060, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/984060 Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional
Arthritis Volume 2012, Article ID 984060, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/984060 Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional
Is Osteoarthritis a Systemic Disorder of Bone?
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 2, February 2004, pp 452 457 DOI 10.1002/art.20136 2004, American College of Rheumatology Is Osteoarthritis a Systemic Disorder of Bone? Juliet Rogers, Lee Shepstone,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 2, February 2004, pp 452 457 DOI 10.1002/art.20136 2004, American College of Rheumatology Is Osteoarthritis a Systemic Disorder of Bone? Juliet Rogers, Lee Shepstone,
DRAFT COPY PERSONAL USE ONLY
 Menopausal status, hormone replacement therapy use and risk of self-reported physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis in women attending menopause clinics in Italy Progetto Menopausa Italia Study Group 1, Fabio
Menopausal status, hormone replacement therapy use and risk of self-reported physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis in women attending menopause clinics in Italy Progetto Menopausa Italia Study Group 1, Fabio
hands in patients with chronic renal failure
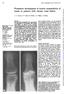 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
THE GENETIC CONTRIBUTION TO RADIOGRAPHIC HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS IN WOMEN
 2410 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 11, November 2000, pp 2410 2416 2000, American College of Rheumatology THE GENETIC CONTRIBUTION TO RADIOGRAPHIC HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS IN WOMEN Results of a Classic
2410 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 11, November 2000, pp 2410 2416 2000, American College of Rheumatology THE GENETIC CONTRIBUTION TO RADIOGRAPHIC HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS IN WOMEN Results of a Classic
The effect of osteoarthritis definition on prevalence and incidence estimates: a systematic review
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 19 (2011) 1270e1285 Review The effect of osteoarthritis definition on prevalence and incidence estimates: a systematic review D. Pereiray a, B. Peleteiroyz a, J. Araújoyz a,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 19 (2011) 1270e1285 Review The effect of osteoarthritis definition on prevalence and incidence estimates: a systematic review D. Pereiray a, B. Peleteiroyz a, J. Araújoyz a,
HERITABILITIES OF RADIOLOGIC OSTEOARTHRITIS IN PERIPHERAL JOINTS AND OF DISC DEGENERATION OF THE SPINE
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 42, No. 8, August 1999, pp 1729 1735 1999, American College of Rheumatology 1729 HERITABILITIES OF RADIOLOGIC OSTEOARTHRITIS IN PERIPHERAL JOINTS AND OF DISC DEGENERATION OF
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 42, No. 8, August 1999, pp 1729 1735 1999, American College of Rheumatology 1729 HERITABILITIES OF RADIOLOGIC OSTEOARTHRITIS IN PERIPHERAL JOINTS AND OF DISC DEGENERATION OF
Lifetime body mass index, other anthropometric measures of obesity and risk of knee or hip osteoarthritis in the GOAL case-control study
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 19 (2011) 37e43 Lifetime body mass index, other anthropometric measures of obesity and risk of knee or hip osteoarthritis in the GOAL case-control study K.L. Holliday y a,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 19 (2011) 37e43 Lifetime body mass index, other anthropometric measures of obesity and risk of knee or hip osteoarthritis in the GOAL case-control study K.L. Holliday y a,
Key Indexing Terms: KNEE ALIGNMENT OSTEOARTHRITIS CARTILAGE VOLUME CHONDRAL DEFECTS
 A Longitudinal Study of the Association Between Knee Alignment and Change in Cartilage Volume and Chondral Defects in a Largely Non-Osteoarthritic Population GUANGJU ZHAI, CHANGHAI DING, FLAVIA CICUTTINI,
A Longitudinal Study of the Association Between Knee Alignment and Change in Cartilage Volume and Chondral Defects in a Largely Non-Osteoarthritic Population GUANGJU ZHAI, CHANGHAI DING, FLAVIA CICUTTINI,
IJDDT. Effects of Quadriceps Dynamic Strengthening and Isometrics Exercise in Non-obese and Obese Osteoarthritis of Knee Joint Patients
 IJDDT International Journal of Drug Discovery and Technology IJDDT 2(1) (2011): 47-53 Research Science Press Effects of Quadriceps Dynamic Strengthening and Isometrics Exercise in Non-obese and Obese Osteoarthritis
IJDDT International Journal of Drug Discovery and Technology IJDDT 2(1) (2011): 47-53 Research Science Press Effects of Quadriceps Dynamic Strengthening and Isometrics Exercise in Non-obese and Obese Osteoarthritis
DISCLOSURES. T. McAlindon: Samumed, grant/research support; Astellas, Flexion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samumed,and Seikugaku, consulting
 Radiographic Outcomes from a Randomized, Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of a Novel, Intra-Articular, Wnt Pathway Inhibitor (SM04690) for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Week
Radiographic Outcomes from a Randomized, Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of a Novel, Intra-Articular, Wnt Pathway Inhibitor (SM04690) for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Week
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma
 Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma Gunnel Sandqvist and Mona Eklund Objective. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) is a hand function test for persons who have systemic sclerosis
Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma Gunnel Sandqvist and Mona Eklund Objective. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) is a hand function test for persons who have systemic sclerosis
Radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis in a Czech cohort
 Radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis in a Czech cohort K. Pavelka, J. Gatterova, R.D. Altman Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic; Department of Medicine, University of Miami School
Radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis in a Czech cohort K. Pavelka, J. Gatterova, R.D. Altman Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic; Department of Medicine, University of Miami School
The association of osteoarthritis risk factors with localized, regional and diffuse knee pain
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1244e1249 The association of osteoarthritis risk factors with localized, regional and diffuse knee pain L.R. Thompson y, R. Boudreau z, A.B. Newman yz, M.J. Hannon
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1244e1249 The association of osteoarthritis risk factors with localized, regional and diffuse knee pain L.R. Thompson y, R. Boudreau z, A.B. Newman yz, M.J. Hannon
Factors for Pain in Patients With Different Grades of Knee Osteoarthritis
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 65, No. 5, May 2013, pp 695 702 DOI 10.1002/acr.21886 2013, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors for ain in atients With Different Grades of Knee Osteoarthritis
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 65, No. 5, May 2013, pp 695 702 DOI 10.1002/acr.21886 2013, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors for ain in atients With Different Grades of Knee Osteoarthritis
Factors Affecting Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis
 IGINAL ARTICLE Factors Affecting Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis Harry Isbagio ABSTRACT Aim: to determine factors affecting radiographic progression of knee OA. Methods: a cross sectional
IGINAL ARTICLE Factors Affecting Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis Harry Isbagio ABSTRACT Aim: to determine factors affecting radiographic progression of knee OA. Methods: a cross sectional
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Diagnostic accuracy of range of motion measurements in early symptomatic hip and/or knee osteoarthritis
 Chapter 1 Diagnostic accuracy of range of motion measurements in early symptomatic hip and/or knee osteoarthritis Jasmijn F.M. Holla, Marike van der Leeden, Leo D. Roorda, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, Jurgen
Chapter 1 Diagnostic accuracy of range of motion measurements in early symptomatic hip and/or knee osteoarthritis Jasmijn F.M. Holla, Marike van der Leeden, Leo D. Roorda, Sita M.A. Bierma-Zeinstra, Jurgen
Table of Contents. Overview Introduction Variables Missing Data Image Type Time Points Reading Methods...
 MULTICENTER OSTEOARTHRITIS STUDY LONGITUDINAL KNEE RADIOGRAPH ASSESSMENTS (BASELINE TO 15-MONTH, 30-MONTH, 60-MONTH AND 84-MONTH FOLLOW-UP) AND MEASUREMENTS FROM BASELINE FULL LIMB RADIOGRAPHS DATASET
MULTICENTER OSTEOARTHRITIS STUDY LONGITUDINAL KNEE RADIOGRAPH ASSESSMENTS (BASELINE TO 15-MONTH, 30-MONTH, 60-MONTH AND 84-MONTH FOLLOW-UP) AND MEASUREMENTS FROM BASELINE FULL LIMB RADIOGRAPHS DATASET
Hip osteoarthritis: influence of work with heavy lifting, climbing stairs or ladders, or combining kneeling/squatting with heavy lifting
 Correspondence to: Dr L K Jensen, Department of Occupational Medicine, Regionshospitalet Skive, Resenvej 25, DK-7800 Skive, Denmark; lilli.kirkeskov.jensen@ sygehusviborg.dk Accepted 18 June 2007 Published
Correspondence to: Dr L K Jensen, Department of Occupational Medicine, Regionshospitalet Skive, Resenvej 25, DK-7800 Skive, Denmark; lilli.kirkeskov.jensen@ sygehusviborg.dk Accepted 18 June 2007 Published
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20431 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Yusuf, Erlangga Title: On how obesity links with osteoarthritis Issue Date: 2013-01-16
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20431 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Yusuf, Erlangga Title: On how obesity links with osteoarthritis Issue Date: 2013-01-16
Summary. Introduction
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, 526 532 1999 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/99/060526+07 $12.00/0 Article No. joca.1999.0256, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, 526 532 1999 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/99/060526+07 $12.00/0 Article No. joca.1999.0256, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Title: Low omega-3 fatty acid levels associate with frequent gout attacks a case
 Title: Low omega-3 fatty acid levels associate with frequent gout attacks a case control study Authors: A Abhishek 1, Ana M Valdes 1, Michael Doherty 1 Affiliation: Academic Rheumatology, University of
Title: Low omega-3 fatty acid levels associate with frequent gout attacks a case control study Authors: A Abhishek 1, Ana M Valdes 1, Michael Doherty 1 Affiliation: Academic Rheumatology, University of
The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea
 J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 293-8 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.293 The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea The purpose of this study was to estimate the
J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 293-8 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.293 The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Community Residents in Korea The purpose of this study was to estimate the
Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: Relation to a Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis
 International Journal of Chinese Medicine 2017; 1(3): 102-107 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcm doi: 10.11648/j.ijcm.20170103.15 Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis
International Journal of Chinese Medicine 2017; 1(3): 102-107 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcm doi: 10.11648/j.ijcm.20170103.15 Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis
Validity and Reliability of Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Measures by Arthroplasty Surgeons
 Validity and Reliability of Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Measures by Arthroplasty Surgeons Daniel L. Riddle, PhD; William A. Jiranek, MD; Jason R. Hull, MD abstract Full article available online at
Validity and Reliability of Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Measures by Arthroplasty Surgeons Daniel L. Riddle, PhD; William A. Jiranek, MD; Jason R. Hull, MD abstract Full article available online at
Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views Hwee-Yee Christian Heng, Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak, Amit Kanta
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views Hwee-Yee Christian Heng, Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak, Amit Kanta
O steoarthritis is a major source of morbidity, disability,
 70 EXTENDED REPORT First line treatment of knee osteoarthritis in outpatients in France: adherence to the EULAR 2000 recommendations and factors influencing adherence L Denoeud, B Mazières, C Payen-Champenois,
70 EXTENDED REPORT First line treatment of knee osteoarthritis in outpatients in France: adherence to the EULAR 2000 recommendations and factors influencing adherence L Denoeud, B Mazières, C Payen-Champenois,
Planning knee OA prevention studies in obese populations Lessons from the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study (MOST) and Osteoathritis Initiative (OAI)
 Planning knee OA prevention studies in obese populations Lessons from the (MOST) and Osteoathritis Initiative (OAI) Michael Nevitt, PhD UCSF Epidemiology and Biostatistics OAI and MOST Coordinating Centers
Planning knee OA prevention studies in obese populations Lessons from the (MOST) and Osteoathritis Initiative (OAI) Michael Nevitt, PhD UCSF Epidemiology and Biostatistics OAI and MOST Coordinating Centers
Association of Squatting With Increased Prevalence of Radiographic Tibiofemoral Knee Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 4, April 2004, pp 1187 1192 DOI 10.1002/art.20127 2004, American College of Rheumatology Association of Squatting With Increased Prevalence of Radiographic Tibiofemoral
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 4, April 2004, pp 1187 1192 DOI 10.1002/art.20127 2004, American College of Rheumatology Association of Squatting With Increased Prevalence of Radiographic Tibiofemoral
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Quadriceps weakness in knee osteoarthritis: the evect on pain and disability
 588 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham NG5 1PB S C O Reilly A Jones M Doherty Department of Public Health Medicine and Epidemiology, Queens Medical Centre, Nottingham K R Muir Correspondence
588 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham NG5 1PB S C O Reilly A Jones M Doherty Department of Public Health Medicine and Epidemiology, Queens Medical Centre, Nottingham K R Muir Correspondence
Physical activity, alignment and knee osteoarthritis: data from MOST and the OAI
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 21 (2013) 789e795 Physical activity, alignment and knee osteoarthritis: data from MOST and the OAI D.T. Felson yzz *, J. Niu y, T. Yang y, J. Torner #, C.E. Lewis k, P. Aliabadi
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 21 (2013) 789e795 Physical activity, alignment and knee osteoarthritis: data from MOST and the OAI D.T. Felson yzz *, J. Niu y, T. Yang y, J. Torner #, C.E. Lewis k, P. Aliabadi
Knee Pain and Its Severity in Elderly Koreans: Prevalence, Risk Factors and Impact on Quality of Life
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.12.1807 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1807-1813 Knee Pain and Its Severity in Elderly Koreans: Prevalence, Risk Factors and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.12.1807 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1807-1813 Knee Pain and Its Severity in Elderly Koreans: Prevalence, Risk Factors and
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/1699 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Kwok, Wing Yee Title: Clinical aspects of hand osteoarthritis : are erosions of
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/1699 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Kwok, Wing Yee Title: Clinical aspects of hand osteoarthritis : are erosions of
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
Age related prevalence of hand osteoarthritis diagnosed by photography (HOASCORE)
 Jonsson BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:508 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1870-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Age related prevalence of hand osteoarthritis diagnosed by photography (HOASCORE) Helgi Jonsson
Jonsson BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:508 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1870-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Age related prevalence of hand osteoarthritis diagnosed by photography (HOASCORE) Helgi Jonsson
Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Non-commercial use only
 Detection of progression of radiographic joint damage in case of very early osteoarthritis: sensitivity to change of quantitative analysis compared to qualitative grading Margot B. Kinds, 1,2 Anne C.A.
Detection of progression of radiographic joint damage in case of very early osteoarthritis: sensitivity to change of quantitative analysis compared to qualitative grading Margot B. Kinds, 1,2 Anne C.A.
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Disclosures. The Changing Demographics of End-Stage Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. Evidence 11/7/2011. OA: Risk factors
 Disclosures The Changing Demographics of End-Stage Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis Joanne M. Jordan, MD MPH University of North Carolina Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology Johnson & Johnson: contract, consultant
Disclosures The Changing Demographics of End-Stage Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis Joanne M. Jordan, MD MPH University of North Carolina Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology Johnson & Johnson: contract, consultant
Prevention of Incident Knee Osteoarthritis by Moderate Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Females
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 68, No. 10, October 2016, pp 1428 1433 DOI 10.1002/acr.22854 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevention of Incident Knee Osteoarthritis by Moderate
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 68, No. 10, October 2016, pp 1428 1433 DOI 10.1002/acr.22854 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevention of Incident Knee Osteoarthritis by Moderate
Cristal Castellanos 1, Abelardo Camacho 2, Klaus Mieth 3, Gamal Zayed 3, German Carrillo 3, Oscar Rivero 4, Rafael Gómez 4, Sara Jaimes 4
 Inter- And Intra-Observer Concordance Of The Modified Kellgren And Lawrence Scale For Knee Osteoarthritis By Compartments In Patients Of The University Hospital Fundación Santa Fe De Bogotá, Colombia.
Inter- And Intra-Observer Concordance Of The Modified Kellgren And Lawrence Scale For Knee Osteoarthritis By Compartments In Patients Of The University Hospital Fundación Santa Fe De Bogotá, Colombia.
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Radiographic patterns and associations of
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Lack of support for the presence of an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p
 Lack of support for the presence of an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p Meenagh, G. K., McGibbon, D., Nixon, J., Wright, G. D., Doherty, M., & Hughes, A. (2005). Lack of support for
Lack of support for the presence of an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p Meenagh, G. K., McGibbon, D., Nixon, J., Wright, G. D., Doherty, M., & Hughes, A. (2005). Lack of support for
Most Association between lifelong daily. Zanco J. Med. Sci., Vol. 20, No. (1),
 Most Association between lifelong daily activities and knee and hip osteoarthritis in a group of people attending Rizgary Teaching Hospital in Erbil city Received: 3/12/2013 Accepted: 18/3/2015 Avin Mohammed
Most Association between lifelong daily activities and knee and hip osteoarthritis in a group of people attending Rizgary Teaching Hospital in Erbil city Received: 3/12/2013 Accepted: 18/3/2015 Avin Mohammed
The National Arthritis Data Workgroup estimates the
 n report n Early Management of Osteoarthritis Roy Davis Altman, MD The National Arthritis Data Workgroup estimates the prevalence of osteoarthritis (OA) in the United States as 26.9 million in 2005; this
n report n Early Management of Osteoarthritis Roy Davis Altman, MD The National Arthritis Data Workgroup estimates the prevalence of osteoarthritis (OA) in the United States as 26.9 million in 2005; this
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Ann Rheum Dis. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 November 18.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 November ; 67(11): 1570 1573. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.094771. Vitamin K in hand osteoarthritis: results from a randomised
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 November ; 67(11): 1570 1573. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.094771. Vitamin K in hand osteoarthritis: results from a randomised
