Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome
|
|
|
- Erin O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome scanning, bone scanning, and radiography M M O'SULLIVAN,' N POWELL,- A P FRENCH, K E WILLIAMS,4 J R MORGAN,4 AND B D WILLIAMS' From the Departments of 'Rheumatology, 2Radiology, 3Medical Physics, and 4Medical Microbiology, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff SUMMARY Patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and osteoarthritis were assessed by clinical evaluation, radiography, and joint scintigraphy using technetium labelled methylene diphosphonate (MDP) and technetium labelled liposomes. Although both scanning techniques were more sensitive than radiographs in detecting joint disease, the liposomes scans were positive only in clinically active inflammatory disease. In patients with rheumatoid arthritis liposome scintigraphy was also able to discriminate between different grades of joint tenderness. In inactive inflammatory polyarthropathies, although the MDP bone scans continued to show increased activity, the liposome scans did not and were therefore a more accurate reflection of the clinical state. The increased uptake in the liposome scans may be due to incorporation of the liposomes into the phagocytic cells of the synovium. This scan may, therefore, by reflecting the activity of cells involved in the disease process, provide a useful way of assessing disease activity and progression. Key words: rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, radionuclide scintigraphy, liposomes. Liposomes are microscopic vesicles containing aqueous compartments separated by phospholipid bilayers.' These particles are taken up by the phagocytic cells of the reticuloendothelial system, and their uptake can be demonstrated in vivo using liposomes radiolabelled with gamma emitting radionuclides such as technetium (Tc).2 Tc labelled liposomes have been used in attempts to identify macrophages surrounding tumour tissue3 and deep seated infection.4 More recently we have shown that radiolabelled liposomes can be used to identify the inflammatory tissue associated with rheumatoid arthritis.? Gammacamera joint scintigraphy with bone seeking radioactive isotopes has also been used to identify early inflammatory changes in a variety of arthropathies and shows abnormalities before the appearance of radiographic changes.6 7 The precise mechanisms which lead to positive scintigraphs in the liposome and bone scans are unclear, and in our previous studies we suggested that the mechanisms are different.8 Accepted for publication 31 October Correspondence to Dr M M O'Sullivan. Rheumatology Department. University Hospital of Wales. Cardiff CF4 4XW. In this paper we extend our preliminary observations on patients with rheumatoid arthritis to include other inflammatory polyarthropathies, and we compare the appearance obtained using technetium radiolabelled methylene diphosphonate and liposome scintigraphy with radiography. We also compare each investigation with respect to sensitivity in detecting clinically active disease. Patients and methods PATIENTS Thirteen patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), fufilling the American Rheumatism Association criteria for either definite or classical RA,9 were randomly selected at entry to a second line therapy trial and were studied by macroradiography of hands and wrists, 9mTc methylene diphosphonate (MDP) bone scintigraphy (99mTc MDP), and 99mTc liposome scans. A further six patients had a clinical evaluation and liposome scan, of whom three also had an MDP bone scan. Four patients with psoriatic arthritis were evaluated by clinical assessment, macroradiographs, and both liposome and MDP bone scan, while a further 485
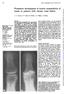
2 486 O'Sullivan, Powell, French, Williams, Morgan, Williams two patients had a clinical evaluation and liposome scan. One of these patients also had an MDP bone scan. Four patients with osteoarthritis had clinical assessment, macroradiographs, and both bone scans and liposome scans. CLINICAL ASSESSMENT A modification of the Ritchie articular index"' was used to assess the degree of tenderness in the wrists (0=non-tender, 1=tender, 2=tender and winced, 3=tender, winced, and withdrew). JOINT IMAGING Anteroposterior films of the hands and wrists were taken on non-screen film and separate macroradiographs of each hand produced. The radiographs were graded using a modification of the Larsen giading index as follows: grade 0=normal; grade v.i w* i"1%1111.p. hiss * 1=one or more of periarticular swelling, periarticular osteoporosis, joint space narrowing; grade 2=erosion and joint space narrowing; grade 3=destructive changes where the original articular surfaces are lost. Liposomes were prepared and radiolabelled with technetium-99 as previously described.8 The patients' hands and wrists were imaged 20 hours after intravenous injection of 350 MBq of 99mTc labelled liposomes. An image of both hands with palms towards the camera and containing counts was acquired on an IGE 400A gammacamera and the information stored on a link Dyanne data processor. A low energy parallel hole collimator was used for all imaging of liposome distribution. WmnTc MDP was obtained from Amersham International. The patients' hands and wrists were similarly imaged approximately two hours after the intravenous injection. In this case, however, i Do, 400 Fig. 1 Radiographs, liposome scan (bottom left), and bonie scan (bottom right) of a patient withi active seropositive RA. Note erosive changes at the metacarpophalangeal joinits and increased activity, in both scans. Note also the increased activity at the ulnar side of the left wrist Onl liposome scan but not on bonie scan. Increased activity at the middle finger seen on bone scan is tiot evident on the liposome scan.
3 counts were acquired and a low energy high resolution parallel hole collimator was used. Regions of interest were created using the Dyanne system for the whole hand, the carpus, the five metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints as one region, and for the five hand digits. A background region was drawn between the carpus and the MCP joints. The counts in each region of interest were then randomised to unit area and the ratio for each normalised count to the background normalised count determined. STATISTICS Wilcoxon's sum of rank rests for unpaired data was used to compare scores between different groups. Results All clinical assessments, radiographic and scinti- I.., SS A Inflammatory joint disease 487 graphic grading were done indepenidently, and the observers were blind to the results of the other assessments. Fig. 1 shows the results of the three investigations in a patient with active seropositive erosive rheumatoid arthritis. The radiograph showed erosions in the wrists, MCP, and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints, which are the areas of increased uptake in both the liposome scans and the bone scan. The bone scan, however, showed diffuse uptake in the wrists, whereas the liposome scan showed more focal intake around the synovial proliferation over the ulnar head, particularly on the left side. The bone scan showed increased activity over the right third PIP and left first MCP, which was not evident on the liposome scan. In most patients with active disease, however, very similar patterns of activity were seen with both the bone scan and the liposome scans. In patients with inactive RA the liposome scans were normal even 6 0 0, 0 Fig. 2 Radiographs, liposome scan (bottom left), and bone scan (bottom right) of a patient with active psoriatic arthritis. Note loss ofcartilage at wrists and erosions at metacarpophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal, and distal interphalangeal joints. Note also increased activity at these joints, especially the righl hand on the bone scan. The liposome scan also shows increased activity, but there is more diffuse activity over the left index finger where clinically there was active tenosynovitis.
4 488 O'Sullivan, Powell, French, Williams, Morgan, Willianms though the bone scan showed increased uptake at the wrists and some MCP and PIP joints. In psoriatic arthritis the radiographic changes were similar to those in RA, with periarticular osteoporosis and erosions in the small joints, including the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints (Fig. 2). The bone scan again mirrored the radiological changes, and even though the liposome scan was positive, there were interesting differences between the scans. The liposome scan showed the tenosynovitis of the left index finger, which clinically had a sausage digit appearance. The diffuse uptake did not correspond with the more localised area of uptake over the DIP joint visible on the bone scan. In a patient with arthritis mutilans, however, the extensive osteolysis was evident on the radiographs and bone scan (Fig. 3), but in the absence of synovitis there was no uptake evident on the liposome scan of the small joints. The liposome scan failed to identify 43 *_e' * areas of inactive disease even though there was extensive joint destruction. Fig. 4 shows the three investigations in a patient with osteoarthritis, who as well as having cystic changes in the wrists had an acutely tender Bouchard's node over the PIP joint of the third finger on the right hand. A Heberden node over the DIP joint of the same finger was also tender. These clinically painful and tender joints were identified on bone scan and also by the liposome scan, though the degree of uptake appeared less than that observed in patients with RA or psoriatic arthritis. In non-inflammatory osteoarthritis Heberden's nodes were present over the DIP joints, but these joints were non-tender and associated with increased activity only on the bone scan. We also compared the scintigraphic and radiographic findings with the clinical assessment of joint inflammation. The patients with RA and high S Fig. 3 Radiographs, liposome scan (bottom left), and bone scan (bottom right) of a patient with arthritis mutilans (PA). Extensive destructive changes of both wrists and fingers are seen. The bone scan shows increased activity, but very little activity is evident on the liposome scan, except over the wrists.
5 m 4. I- cu- 3- Eco 0) 2- E 0 o 1-.Q a 6 41 ~~~~~~~~~9 r1*. * _%. ~~~~*.~~~~~~3 b.~~~~$ m 3~~~~~~ O~~~~ A O Clinical index Inflammatory joint disease 489 r 0 3. t Y laco I L- Fig. 4 Radiographs, liposome scan (bottom left), and bone scan (bottom right) ofa patient with nodal osteoarthritis. Note the loss ofcartilage at both wrists, erosion ofthe right middle finger distal interphalangeal joint and the increased activity on both scans. Bouchard's node at the right middle proximal interphalangeal joint shows little abnormality on the radiograph, but there is activity on both scans..0 C o * S _ o~~~s.., Fig. 5 Comparison of liposome scans, MDP bones scans (target to background (TIB) ratio), and radiographs (grade) the clinical grading ofjoint with tenderness in wrists ofpatients with rheumatoid arth,ritis (@), psoriatic arthritis (A), and osteoarthritis (0).
6 490 O'Sullivan, Powell, French, Williams, Morgan, Williams tenderness scores had higher target to background ratios (Fig. 5). The patients with osteoarthritis and psoriatic arthritis were scanned primarily to look at the DIP joints, and therefore the wrists scans served as controls for the patients with RA. The mean target to background (TIB) ratio for all patients judged clinically to be grade 3 (2 08) was significantly higher than those judged to be grade 0 (1-21) (p<0-0i). The mean T/B ratios for the groups of patients with RA were 2 06, 1-54, and 1-49 for groups 3, 2, and 1 respectively. When the groups of patients with RA were compared a significant difference was again seen between the mean T/B ratios for group 3 compared with group 1 (p<001) and group 2 (p<0.05), but the difference between group 1 and group 2 was not significant at the 5% level. All the patients with osteoarthritis who had liposome scans had non-tender joints and normal scans. Of the patients with psoriatic arthritis, seven joints were non-tender, and the scans were normal. Two wrists were grade 1 and two were grade 2, and these had positive scans, while one wrist which was clinically grade 3 had a high T/B ratio (2.41). The numbers in these groups were not sufficient for adequate statistical comparisons. The bone scans were more sensitive in discriminating between clinically active and inactive joints. The mean T/B ratio for grade 0 was 181 and for grade 1 was This difference was significant at the 1/% level. The mean T/B ratio for grade 3 was In the patients with RA, however, there was a wide scatter of T/B ratios among the different grades of joint tenderness; the mean T/B ratio for grade 3 was 3-2 and for grade 1 was This difference was not significant at the 5% level. There was also no significant difference between the scores obtained for grade 3 and those for grade 2 (2.20). The plain radiographs were the least able to discriminate between clinically tender and non-tender joints, with a wide scatter of radiological abnormality within each clinical grade group. Discussion These studies confirm our earlier findings that radiolabelled liposomes accumulate in inflamed joints.58 Although this was most clearly seen in patients with active rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, it also occurred occasionally in patients with inflammatory osteoarthritis. When comparisons were made, however, with the radiographs and the bone seeking MDP scans it was apparent that the bone scan was the most sensitive method of detecting clinically active disease. Previous studies have alluded to the increased sensitivity of bone scanning over radiography. In the quantitative assessment of joint tenderness in rheumatoid arthritis, however, the liposome scans were best able to discriminate between different degrees of joint tenderness. This finding is a little surprising given that joint tenderness may arise from the subcutaneous tissues, pericapsular, capsular, synovial, and bony structures, with the contribution of each varying with different types of joint disease. In inactive inflammatory polyarthropathies, however, there are clear differences. It appears that once inflammation has initiated joint damage the bone scan continues to reflect bone damage, whereas the liposome scan more accurately reflects the clinical picture of inactive disease. Weissberg et al in their study of bone scanning in RA showed that in three patients with subjective improvement after treatment there was no record of change in nuclear scanning.7 Similarly, Desauliers et al reported that in eight of 16 patients imaged before and during treatment, there was concordant progression of scan and clinical course."' In the other eight the scans continued to show disease despite clinical improvement, or they became worse without any corresponding change of clinical status. The few differences seen in active disease between the two scans do, however, suggest more specific localisation of the liposomes to synovial tissue in inflamed joints and the tendon sheaths. These findings suggest, therefore, that the two scans reflect different disease processes. In active inflammatory polyarthropathies both mechanisms operate, but the bone scan is less able to reflect the change in clinical state from active to inactive disease. Much work to date has centred on the mechanism of uptake of the bone seeking agents. Studies have confirmed the role of increased blood flow '2 and binding of the diphosphonate to the hydroxyapatite crystal,' but there is also evidence that binding onto organic components of bone matrix, such as collagen, may be important. i We are currently investigating the mechanisms responsible for producing positive liposome scans in patients with RA. They are not produced by liposome accumulation in synovial fluid as the scans do not change after the aspiration of large volumes of synovial fluid from the joint. Scanning at 20 hours does not provide information on blood pooling within the inflamed synovium because our earlier studies have clearly shown that between four and 20 hours, when blood radioactivity falls, there is a significant increase in the accumulation of technetium within the joint. More direct evidence of the synovial localisation of technetium has been obtained from a patient with RA who received 99mTc labelled liposomes 20 hours before undergoing surgery for a knee replacement. The synovial
7 tissue contained significantly more radioactivity than did muscle or synovial fluid and it remained associated with cells that were released from the synovium after enzymatic digestion. Although more work is required in this area, these observations would certainly be consistent with the idea that a positive scan reflects phagocytosis of radiolabelled liposomes by macrophages present in synovial tissue. The abnormality is not confined only to rheumatoid arthritis but is also seen in psoriatic arthropathy, where an inflammatory synovitis with mononuclear cell infiltration similar to RA is seen. It is interesting to note that positive liposome scans are also seen in the inflammatory subgroup of osteoarthritis. Recent work on bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis has commented on the marked dissimilarity in severity of involvement on x ray compared with MDP scan,'5 suggesting that the scan reflects a different process from the anatomical change seen on radiographs. We suggest that liposome scanning may be able to help in differentiating between these subgroups. In our study only those patients with clinical evidence of inflammation had positive liposome scans, while in the non-inflammatory subgroup of osteoarthritis, even though the bone scan was positive, there was no increased activity on liposome scan. Despite the lack of specificity associated with the use of radiolabelled liposomes in inflammatory joint disease our studies suggest that, even allowing for the limitations of using a single parameter to assess joint inflammation, it may be a sensitive indicator of changes in the clinical state. Determination of the factors contributing to a positive scan or whether this technique offers any advantages in monitoring disease progression must await further studies. References 1 Gregoriadis G. The carrier potential of liposomes in biology and medicine. N Engl J Med 1967; 295: Inflammatory joint disease Richardson V J. Jeysingh K. Jewkes R F. Ryman B E. Tathersall M H N. Properties of 9"'technetium-labellcd liposomes in normal and tumour bearing rats. Biochein Soc Trans 1977: 5: Richardson V J, Ryman B E, Jewkes R F, et al. Tissue distribution and tumour localisation of 99wtechnetium labelled liposomes in cancer patients. Br J Cancer 1979; 40: Morgan J R. Williams L A. Howard C B. Tcchnetium labclled liposome imaging for deep seated infection. Br J Radiol 1985; 58: Williams B D. O'Sullivan M M. Saggu G S. Williams K E. Williams L A. Morgan J R. Imaging in rheumatoid arthritis using liposomes labelled with technetium. Br Med J 1986; 293: Bekerman C, Genant H K. Hoffer P B. Zokin F. Ginsberg M. Radionuclide imaging of the bones and joints of the hand. Radiology 1976; 118: Weissberg D. Resnick D. Taylor A. Becker M. Alazraki N. RA and its variants: analysis of scintiphotographic. radiographic and clinical examination. AJR 1978: 131: Williams B D. O'Sullivan M M. Saggu G S. Williams K E, Williams L A, Morgan J R. Synovial accumulation of technetium labelled liposomes in rheumatoid arthritis. Antn Rheum Dis 1987; 46: Ropes M W, Bennett G A, Cobb S, Jacox R T, Jessar R A revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1959; 2: Ritchie D M. Boyle J A. Mclnnes J M. et al. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessmcnt of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med 1968: 37: Desauliers M. Fuks A. Jawkins Y, Lacourchicre Y. Rosenthall L. Radiotechnetium polyphosphate joint imaging. J Nucl Med 1974; 15: Genant H K, Bautovich G J, Singh M. Bonc seeking radionuclides: an in-vivo study of factors affecting skelctal uptake. Radiology 1974; 113: Jung A. Bisaz S. Flcisch H. The binding of pyrophosphate and two diphosphonates by hydroxyapatitc crystals. Calcified Tissue Research 1973; 11: ). 14 Rosenthall L. Kayc M. vsmtechnetium pyrophosphatc kinctics and imaging in metabolic bone disease. J Nucl Med 1975: 16: Hutton C W. Higgs E R, Jackson P C. Watt 1. Dieppe P A. 9"mTcHMDP bonc scanning in gcncralised nodal ostcoarthritis. 1. Comparison of the standard radiograph and four hour bone scan image of the hand. Anti Rheuin Dis 1986; 45:
predicts radiographic change
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis
 AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis (General) = inflamed joint - NOT a single disease: covers >100 types - Involves disability + decreased quality of life o Can also occur in young people (not just the
AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis (General) = inflamed joint - NOT a single disease: covers >100 types - Involves disability + decreased quality of life o Can also occur in young people (not just the
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
hands in patients with chronic renal failure
 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: -11 SCINTIFIC PAPRS Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands G J Kieft J L Bloem H M Kroon Department of Rheumatology,
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: -11 SCINTIFIC PAPRS Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands G J Kieft J L Bloem H M Kroon Department of Rheumatology,
(For National Authority Use Only) Page:
 2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Name of Study Drug: Volume: HUMIRA 40 mg/0.8 ml for subcutaneous injection Page: (For National Authority Use Only) Name of Active
2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Name of Study Drug: Volume: HUMIRA 40 mg/0.8 ml for subcutaneous injection Page: (For National Authority Use Only) Name of Active
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
Atlas of Bone Scintigraphy in the Developing Paediatric Skeleton. The Normal Skeleton, Variants and Pitfalls
 Atlas of Bone Scintigraphy in the Developing Paediatric Skeleton The Normal Skeleton, Variants and Pitfalls FOREWORD Since the introduction of Technetium 99m polyphosphate in 1972 by Dr. M. Subramanian,
Atlas of Bone Scintigraphy in the Developing Paediatric Skeleton The Normal Skeleton, Variants and Pitfalls FOREWORD Since the introduction of Technetium 99m polyphosphate in 1972 by Dr. M. Subramanian,
Bones? Did someone say bones? 12/31/2012. W.R Reinus, MD MBA FACR
 William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
Wrist cysts and fistulae
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 388 Wrist cysts and fistulae An arthrographic study of the rheumatoid wrist* J. M. I. IVESON, A. G. S. HILL, AND V. WRIGHT From the Department of Rheumatology, General Infirmary
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 388 Wrist cysts and fistulae An arthrographic study of the rheumatoid wrist* J. M. I. IVESON, A. G. S. HILL, AND V. WRIGHT From the Department of Rheumatology, General Infirmary
For patients with musculoskeletal pain, imaging can aid in making or confirming
 Clinical basics Rheumatology: 3. Getting the most out of radiology Review Synthèse Graham Reid, * John M. Esdaile The case A 72-year-old man has been seeing the same physician for 2 decades, and his only
Clinical basics Rheumatology: 3. Getting the most out of radiology Review Synthèse Graham Reid, * John M. Esdaile The case A 72-year-old man has been seeing the same physician for 2 decades, and his only
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS
 INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
Nuclear Medicine: Manuals. Nuclear Medicine. Nuclear imaging. Emission imaging: study types. Bone scintigraphy - technique
 Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Sonographic appearance of chronic inflammatory rheumatism
 Sonographic appearance of chronic inflammatory rheumatism Poster No.: C-2237 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Elfattach, F. Houari, O. Addou, M. Maaroufi, S. Tizniti ; 1 1 1 1 2
Sonographic appearance of chronic inflammatory rheumatism Poster No.: C-2237 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Elfattach, F. Houari, O. Addou, M. Maaroufi, S. Tizniti ; 1 1 1 1 2
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Systemic forms of stiffness
 Systemic forms of stiffness ANNA LITWIC CONSULTANT RHEUMATOLOGIST SALISBURY DISTRICT HOSPITAL CLINICAL RESEARCH FELLOW MRC LIFECOURSE EPIDEMIOLOGY UNIT Overview Rheumatoid arthritis Know it when you see
Systemic forms of stiffness ANNA LITWIC CONSULTANT RHEUMATOLOGIST SALISBURY DISTRICT HOSPITAL CLINICAL RESEARCH FELLOW MRC LIFECOURSE EPIDEMIOLOGY UNIT Overview Rheumatoid arthritis Know it when you see
Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon. sheath
 Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka.
Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka.
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
The relationship between soft tissue swelling, joint space narrowing and erosive damage in hand X-rays of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatology 2001;40:297±301 The relationship between soft tissue swelling, joint space narrowing and erosive damage in hand X-rays of patients with rheumatoid arthritis J. Kirwan, M. Byron and I. Watt
Rheumatology 2001;40:297±301 The relationship between soft tissue swelling, joint space narrowing and erosive damage in hand X-rays of patients with rheumatoid arthritis J. Kirwan, M. Byron and I. Watt
Artropathies: what can be seen in hands?
 Artropathies: what can be seen in hands? Poster No.: C-2452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Torres Rodrigues, J. C. Ruivo Rodrigues, C. Albuquerque, D. Silva; Viseu/PT Keywords:
Artropathies: what can be seen in hands? Poster No.: C-2452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Torres Rodrigues, J. C. Ruivo Rodrigues, C. Albuquerque, D. Silva; Viseu/PT Keywords:
Clinical Practice Guideline. Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings. Version
 Clinical Practice Guideline Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings Version 1.1.2017 November 2017 Table of Contents Abbreviations...3 Introduction...4 Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound...6 Definition
Clinical Practice Guideline Ultrasound in Rheumatological Settings Version 1.1.2017 November 2017 Table of Contents Abbreviations...3 Introduction...4 Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound...6 Definition
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Quantitative microfocal radiography accurately
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 379-383 Quantitative microfocal radiography accurately detects joint changes in rheumatoid arthritis J C BUCKLAND-WRGHT, CARMCHAEL, AND S R WALKER From the Macroradiographic
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 379-383 Quantitative microfocal radiography accurately detects joint changes in rheumatoid arthritis J C BUCKLAND-WRGHT, CARMCHAEL, AND S R WALKER From the Macroradiographic
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for
 A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for same. Came to us with recurrence since last one year with
A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for same. Came to us with recurrence since last one year with
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Mr. OA: Case Presentation
 CLINICAL CASES Case 1: Mr. OA OA Mr. OA: Case Presentation 62-year-old lawyer Mild left knee pain for 3 month, but became worse 1 week ago No swelling 1 week earlier: 2-hour walk in the countryside 2 days
CLINICAL CASES Case 1: Mr. OA OA Mr. OA: Case Presentation 62-year-old lawyer Mild left knee pain for 3 month, but became worse 1 week ago No swelling 1 week earlier: 2-hour walk in the countryside 2 days
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Radiolabelled lymphocyte migration in rheumatoid synovitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 995; 54: 9-44 9 Service d'immuno- Rhumatologie, Centre Gui-de- Chauliac, Montpellier, France C Jorgensen C Bologna J Sany Service de Medecine Nucleaire, H6pital Lapeyronie,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 995; 54: 9-44 9 Service d'immuno- Rhumatologie, Centre Gui-de- Chauliac, Montpellier, France C Jorgensen C Bologna J Sany Service de Medecine Nucleaire, H6pital Lapeyronie,
Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the knee in patients referred to hospital
 520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
Management of Chronic Elbow Pain
 Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis
 Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
G. Varjú, C. F. Pieper 1, J. B. Renner 2 and V. B. Kraus
 Rheumatology 2004;43:915 919 Advance Access publication 4 May 2004 Assessment of hand osteoarthritis: correlation between thermographic and radiographic methods G. Varjú, C. F. Pieper 1, J. B. Renner 2
Rheumatology 2004;43:915 919 Advance Access publication 4 May 2004 Assessment of hand osteoarthritis: correlation between thermographic and radiographic methods G. Varjú, C. F. Pieper 1, J. B. Renner 2
Rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 403 Rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow Pattern of joint involvement, and results of synovectomy with excision of the radial head H. STEIN, R. A. DICKSON, AND G. BENTLEY From
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 403 Rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow Pattern of joint involvement, and results of synovectomy with excision of the radial head H. STEIN, R. A. DICKSON, AND G. BENTLEY From
Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis
 Anatomy : MRI Fonction : Nucl Med Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis Functional imaging = distribution of a (radio)- tracer in organs Each tracer is a SPY of a function, usually through a metabolic pathway flow
Anatomy : MRI Fonction : Nucl Med Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis Functional imaging = distribution of a (radio)- tracer in organs Each tracer is a SPY of a function, usually through a metabolic pathway flow
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES
 ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica
 The Open General and Internal Medicine Journal, 29, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia
The Open General and Internal Medicine Journal, 29, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS. Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital
 EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital EIA: Introduction National priority Preventable cause of disability Very common condition High
EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital EIA: Introduction National priority Preventable cause of disability Very common condition High
MR Imaging Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Educational Review
 MR Imaging Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Educational Review Poster No.: C-1598 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. J. Makanji, R. Kedar, S. Anderson, N. Prakash, N. Rao;
MR Imaging Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Educational Review Poster No.: C-1598 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. J. Makanji, R. Kedar, S. Anderson, N. Prakash, N. Rao;
RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1998;37:760 765 RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS P. RAHMAN, D. D. GLADMAN,* R. J. COOK, Y. ZHOU, G. YOUNG and D. SALONEN Department of Medicine and Institute
British Journal of Rheumatology 1998;37:760 765 RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS P. RAHMAN, D. D. GLADMAN,* R. J. COOK, Y. ZHOU, G. YOUNG and D. SALONEN Department of Medicine and Institute
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29578 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Krabben, Annemarie Title: Predictive factors for the development and disease course
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
S tructural joint damage, a major outcome in
 i3 An introduction to the EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas M Østergaard, J Edmonds, F McQueen, C Peterfy, M Lassere, B Ejbjerg, P Bird, P Emery, H Genant, P Conaghan... This
i3 An introduction to the EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas M Østergaard, J Edmonds, F McQueen, C Peterfy, M Lassere, B Ejbjerg, P Bird, P Emery, H Genant, P Conaghan... This
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis
 Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings
 Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings Poster No.: C-0399 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Persechino 1, L. Cristiano 1, A. Bartoloni 1, C. Cantone 2, A. Keywords: DOI:
Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings Poster No.: C-0399 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Persechino 1, L. Cristiano 1, A. Bartoloni 1, C. Cantone 2, A. Keywords: DOI:
Radiological Reasoning: Acutely Painful Swollen Finger. Musculoskeletal Imaging Chew and Richardson Benign-Appearing Bone Mass.
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Chew and Richardson Benign-Appearing Bone Mass AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY This Radiological Reasoning article is available for SAM credit and CME credits
Musculoskeletal Imaging Chew and Richardson Benign-Appearing Bone Mass AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY This Radiological Reasoning article is available for SAM credit and CME credits
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Gastrointestinal tract
 Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
scintigram which failed to detect vertebral metastases
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1989), 65, 22-26 Diagnostic Images Renal metastases shown by 9mTc-methylene diphosphonate scintigram which failed to detect vertebral metastases Presented by L. Kreel, A.
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1989), 65, 22-26 Diagnostic Images Renal metastases shown by 9mTc-methylene diphosphonate scintigram which failed to detect vertebral metastases Presented by L. Kreel, A.
How do polyarthritis, polyarthralgias, and diffuse aches and pains differ?
 Approach to the patient with polyarthritis How do polyarthritis, polyarthralgias, and diffuse aches and pains differ? Polyarthritis is definite inflammation (swelling, tenderness, warmth) of more than
Approach to the patient with polyarthritis How do polyarthritis, polyarthralgias, and diffuse aches and pains differ? Polyarthritis is definite inflammation (swelling, tenderness, warmth) of more than
Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the Framingham Study
 Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Objectives. Joint Pain. Case 1. Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) 12/4/2010
 Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Comparative Analysis of Bone Erosions and -Cysts in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis
 Comparative Analysis of Bone Erosions and -Cysts in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis Stephanie Finzel Department of Internal Medicine 3 Rheumatology & Immunology
Comparative Analysis of Bone Erosions and -Cysts in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis Stephanie Finzel Department of Internal Medicine 3 Rheumatology & Immunology
Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee joint- A Case Report and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
Crystal Deposition Disease and Psoriatic Arthritis
 74 Crystal Deposition Disease and Psoriatic Arthritis Philip J. O Connor, MRCP, FRCR, FFSEM (UK) 1,2 1 Department of Radiology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals, Chapel Allerton Hospital, Leeds, United Kingdom
74 Crystal Deposition Disease and Psoriatic Arthritis Philip J. O Connor, MRCP, FRCR, FFSEM (UK) 1,2 1 Department of Radiology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals, Chapel Allerton Hospital, Leeds, United Kingdom
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Nuclear Medicine and PET. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer
 When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Nancy A. Brown, DO Spring 2015 When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Learning objectives To review the definition and epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Nancy A. Brown, DO Spring 2015 When is it Rheumatoid Arthritis When to Refer Learning objectives To review the definition and epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Magnetic resonance imaging in osteoarthritis of the
 14 Rheumatology Unit, Bristol Royal Infirmary, Bristol BS2 8HW T E M McAlindon I Watt F McCrae Goddard P A Dieppe Correspondence to: Dr McAlindon. Accepted for publication 2 February 1990 Annals of the
14 Rheumatology Unit, Bristol Royal Infirmary, Bristol BS2 8HW T E M McAlindon I Watt F McCrae Goddard P A Dieppe Correspondence to: Dr McAlindon. Accepted for publication 2 February 1990 Annals of the
Straingauge plethysmography in the
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 194 Straingauge plethysmography in the assessment of joint inflammation I. VADASZ Department of Physical Medicine and Rheumatology, Guy's Hospital, London The quantitation of
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 194 Straingauge plethysmography in the assessment of joint inflammation I. VADASZ Department of Physical Medicine and Rheumatology, Guy's Hospital, London The quantitation of
PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENT OF RHEUMATOID FACTOR IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1995;34:1146-1150 PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENT OF RHEUMATOID FACTOR IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS L. PAEVDELA, T. PALOSUO,* M. LEIRISALO-REPO,t T. HELVE
British Journal of Rheumatology 1995;34:1146-1150 PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENT OF RHEUMATOID FACTOR IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS L. PAEVDELA, T. PALOSUO,* M. LEIRISALO-REPO,t T. HELVE
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Figuring out the "fronds"-synovial proliferative disorders of the knee.
 Figuring out the "fronds"-synovial proliferative disorders of the knee. Poster No.: C-1209 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Sivasubramanian; Tamil Nadu/IN Keywords: Imaging sequences,
Figuring out the "fronds"-synovial proliferative disorders of the knee. Poster No.: C-1209 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Sivasubramanian; Tamil Nadu/IN Keywords: Imaging sequences,
Sonographic assessment of adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
 Sonographic assessment of adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Poster No.: C-1485 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. A. S. Ruano, P. L. Pegado, J. M. G. Lourenco, P. Alves, L.
Sonographic assessment of adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Poster No.: C-1485 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. A. S. Ruano, P. L. Pegado, J. M. G. Lourenco, P. Alves, L.
Finger Joint Swelling: Correlation with Age, Gender, and Manual Labor
 Finger Joint Swelling: Correlation with Age, Gender, and Manual Labor PEKKA MAKELA,1 PEKKA VIRTAMA, AND PETER B. DEAN Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 7.44..2 on 01/0/18 from IP address 7.44..2. Copyright
Finger Joint Swelling: Correlation with Age, Gender, and Manual Labor PEKKA MAKELA,1 PEKKA VIRTAMA, AND PETER B. DEAN Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 7.44..2 on 01/0/18 from IP address 7.44..2. Copyright
An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System
 Precision. Insight. Innovation. White Paper: An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System At left: Volume of synovitis in the hand and wrist. Areas of enhancement
Precision. Insight. Innovation. White Paper: An Overview of RAMRIQ: An Automated MRI Rheumatoid Arthritis Quantitative Assessment System At left: Volume of synovitis in the hand and wrist. Areas of enhancement
The Painful Prosthetic Joint: Role of Nuclear Medicine
 The Painful Prosthetic Joint: Role of Nuclear Medicine Christopher J. Palestro, M.D. Professor of Radiology Hofstra North Shore-LIJ of Medicine Chief Division of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging North
The Painful Prosthetic Joint: Role of Nuclear Medicine Christopher J. Palestro, M.D. Professor of Radiology Hofstra North Shore-LIJ of Medicine Chief Division of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging North
Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai
 Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai Case History 9 year old boy presented with a 3 week history of: Swelling of major lower limb joints Progression was additive (right ankle followed
Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai Case History 9 year old boy presented with a 3 week history of: Swelling of major lower limb joints Progression was additive (right ankle followed
Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy
 September 2005 Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy Roxanne Landesman, Harvard Medical School Year III Hypothetical Patient A patient presents with persistent right ankle pain, and no history of trauma. As the
September 2005 Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy Roxanne Landesman, Harvard Medical School Year III Hypothetical Patient A patient presents with persistent right ankle pain, and no history of trauma. As the
Presenter Disclosure Information
 4:15 5:45 pm Diagnostic Challenges of Rheumatologic Disease SPEAKER Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Peng Thim Fan,
4:15 5:45 pm Diagnostic Challenges of Rheumatologic Disease SPEAKER Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Peng Thim Fan,
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
