Medical Science. MRI Analogue Signs in the Imaging of the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis...
|
|
|
- Barnaby Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
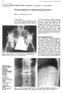
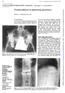
1 Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No IF : IC Value : MRI Analogue Signs in the Imaging of the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis...the Many Faces Medical Science KEYWORDS : Ankylosing spondylitis, MRI, spine, sacroiliac joints, early detection, sensitive Divyashree Rashmi Rekha Rajesh Kumar Saket Arjun Raju P Surahi Mehrotra Associate Prof, Department of Radiology, Government Medical College, Haldwani, Assist Prof, Department of Radiology, Government Medical College, Haldwani, ABSTRACT Ankylosing spondylitis is an archetype of seronegative spondyloarthropathies (SpA).The spine and the sacroiliac joints are the primary targets of this chronic idiopathic inflammatory arthritis. MRI is the most sensitive technique in the detection of axial skeletal involvement, permitting earlier diagnosis. Assessment of structural changes in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is essential for diagnosis, management (disease activity) and outcome. MRI of the sacroiliac joints has een shown to e much sensitive and superior compared to plain radiography in depicting sacroiliitis and shown to e of paramount importance in the earliest detection of active sacroiliitis. INTRODUCTION Ankylosing spondylitis is an archetype of the seronegative spondyloarthropathies (SpA) [1], and is a chronic, idiopathic, inflammatory arthritis with a propensity for affection of the axial skeleton. This group of arthritides is characterised y specific skeletal imaging findings, the presence of the HLA-B27 gene and y the asence of rheumatoid factor or nodules. These spondylo-arthropathies can e divided into 5 major groups: (i) ankylosing spondylitis, (ii) reactive arthritis/reiter s syndrome, (iii) arthritis associated with inflammatory owel disease, (iv) psoriatic arthritis and (v) undifferentiated spondylo-arthropathy [1,2]. The clinical presentation of SpA is heterogeneous, and no single shared distinguishing feature exists for the conditions comprising SpA; in daily practice, diagnosis is usually made on the asis of a comination of symptoms, the findings of physical examination, imaging and laoratory investigations. Individuals with the HLA-B27 antigen have a 20 fold greater risk of developing spondyloarthritis [3]. AS affects oth men and women ut is most frequently seen in men. The male to female ratio of ankylosing spondylitis is 3:1 [4]. The disease usually starts etween the second and the fourth decades of life and is rarely found after the age of 40 years. The most important locations in AS are the sacroiliac joints and the spine. Involvement of the sacroiliac joints is a hallmark of ankylosing spondylitis [5-7]. The definite diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis requires imaging evidence of sacroiliitis, which is defined as erosions, suchondral sclerosis, and irregular joint spaces and clinical features, including inflammatory ack pain [5]. Conventional radiographs remain the most widely accepted and availale screening method for ankylosing spondylitis; however, radiographs often show normal findings during the early stages of the disease, and several years may e required for sacroiliitis to ecome apparent on radiography [7-9]. The sacroiliitis grading system associated with the modified New York criteria is as follows: -Grade 0: normal findings. -Grade 1: suspicious changes. -Grade 2: minimum anormality, defined as small localized areas with erosion or sclerosis without alteration in the joint width. -Grade 3: unequivocal anormality (severe erosions, pseudo-widening of the joint space and partial ankylosis). -Grade 4: complete ankylosis. Modified New York Criteria for AS Clinical Criteria Low ack pain 3 months, improved y exercise and not relieved y rest Limitation of movement of lumar spine in sagittal and frontal planes Limitation of chest expansion (relative to normal values corrected for age and sex) Radiological criteria Bilateral grade 2-4 sacroiliitis OR Unilateral 3-4 sacroiliitis Requirements for definite diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis: ilateral grade 2-4 or unilateral grade 3-4 sacroiliitis radiologically AND at least one of the clinical criteria. MRI is the most sensitive techniques in the detection of axial skeletal involvement, permitting earlier diagnosis. Assessment of structural changes in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is essential for diagnosis, management (disease activity) and outcome. MRI of the sacroiliac joints has een shown to e much superior and sensitive as compared to plain radiography in depicting sacroiliitis and shown to e useful in the early detection of active sacroiliitis. Spinal changes associated with spondyloarthritis are florid anterior spondylitis (Romanus lesion), florid discitis (Andersson lesion), ankylosis, insufficiency fractures of the ankylosed spine, syndesmophytes, arthritis of the apophyseal and costoverteral joints and enthesitis of the interspinal ligaments. Aims and ojectives :The purposes of our study were to evaluate MRI of the spine and sacroiliac joints in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and to determine IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH 27
2 Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No IF : IC Value : whether MRI findings of edema, erosion, sclerosis and fatty marrow changes were correlated with clinical features and measures of disease activity. To provide an educational and pictorial review of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) ased on MRI features. MATERIALS AND METHODS: This is a cross sectional prospective case series study. From the period of January 2014 to Decemer 2015, a total of 40 patients (32 males and 8 females) with low ack pain with clinical signs and suspicion /radiographic suspicion of sacroilitis were recruited for dedicated MRI evaluation of lumosacral spine at Deptt of Radiodiagnosis GMC and associated Dr. STH Haldwani, Nainital (U.K.) India. Inclusion criteria: All patients who conformed to the modified New York criteria /all patients with HLA B27 positivity and low ack pain were included in the study. All patients with seropositivity for RA factor and other estalished causes of sacroilitis or infective etiology like septic arthritis were excluded from the study. MR imaging protocol useful for evaluating the spinal column comprises of a sagittal T1 and T2 -weighted turo spinecho sequence and a coronal short inversion time and recovery (STIR) sequence. Coronal sections short inversion time and recovery (STIR) sequence of the lumar spine including the sacroiliac joints were particularly useful for early detection and screening of sacroilitis. Additional detailed axial evaluation of the sacroiliac joints oth T1w and T2w spin echo sequences were undertaken when the coronal sections showed anormality of the sacroiliac joints. OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS: In our study total 40 patients with confirmed ankylosing spondylitis (On the asis of modified New York criteria) are included. Out of these 34 were males and 6 were females. The male to female radio was 5.6:1. The youngest patient was 16 years old and oldest patient was 64 with mean age was 32 years. Most of the patients were young adult males etween 20-30years. Out of 40 patients 32 patients (80%) had the HLA-B*27 positive. Of these, 28 were male (87.5%) and 4 were female (12.5%), the male-to-female ratio eing 7:1, while in those patients who did not have the HLA-B*27 allele the ratio was 3: 1. The main presenting symptom in most patients was chronic ack pain which was not relieved y rest and improved y non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, that is inflammatory ack pain which was present in 37 patients (92.5%). Sacroiliac joint involvement Out of 40 patients, 36(90%) patients had anormality in sacroiliac (SI) joints. Of these 34 patients had ilateral symmetrical involvement and 2 patients had unilateral sacroilitis. Out of 36 patients ;18 patients had active disease with early stage changes, 10 patients had comination of chronic changes mixed with signs of disease activity and 8 patients had advanced chronic changes. The sacroiliac joints were predominantly involved in the inferior ileal aspects followed y inferior ileal + inferior sacral regions of the sacroiliac joint. The changes on MRI were deemed to e early and acute if marrow edema,erosions / joint widening were present. Changes were surmised to e chronic if suchondral sclerosis and fatty marrow replacement of the suarticular regions were present on either side of the sacroiliac joint. TABLE-1 (sacroiliac joint involvement) Sacroilitis 36 (ilateral-34, unilateral-2) 90% Active disease with early changes 18 50% Original Research Paper Comination of chronic changes with active % disease Chronic disease % Spinal features: Spondylitis was seen in 26 (65%) patients mostly in thoracolumar region ( more commonly involving anterosuperior and anteroinferior verteral end plate, less frequently posterior end plate), followed y upper thoracic and cervical region. Spondylodiscitis was seen in 8 patients (20%). Syndesmophytes and ankylosis was seen in 9 patients (22.5%). TABLE-2(spinal features and extraspinal joint involvement) Spondylitis (Romanus lesions) Present in 26 Thoracolumer-20, upper thoracic-2, 65% cervical % Spondylodiscitis(Anderson lesions) Syndesmophytes & ankylosis % Facet arthopathy 6 15% Costoverteral joint % Insufficiency fracture 3 7.5% Atlanto-occipital joint 1 2.5% Hip joint 1 2.5% Discussion MR Imaging Protocol MRI provides multiplanar imaging with etter soft-tissue contrast and allows assessment of all of the structures involved in musculoskeletal diseases. According to the ASAS classification criteria, active inflammatory lesions are est visualized on fat-suppressed T2-weighted or high-resolution STIR images (512-pixel matrix, 3- to 4-mm slice thickness). T2-weighted fat suppressed (T2wFS) and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) images depict water with a high signal intensity. These are well-suited for detection of oedematous tissue/fluid located in areas e.g. one marrow oedema. Bone marrow anormalities in oth sacroiliac joints and spine are detected almost equally well with the STIR and contrast-enhanced T1w FS sequences in patients with SpA, so contrast injection is generally not needed [Baraliakos et al. 2005; Madsen et al. 2010]. Structural damage and chronic lesions, such as fatty degeneration and erosions, are est visualized on T1-weighted images [10]. For assessment of the sacroiliac joints, coronal and axial olique T1- and T2-weighted sequences with fat suppression or STIR sequences are recommended. An efficient spinal imaging protocol comprises sagittal T1- and fat-suppressed T2-weighted sequences or high-resolution STIR sequences. Axial slices can e useful for assessment of the posterior spinal elements, and coronal slices may e est for assessment of the costoverteral, costotransverse, and facet joints. Sacroiliac Joint Involvement Involvement of the sacroiliac joints is a hallmark of ankylosing spondylitis [5]. Sacroiliitis is usually the first manifestation and is characteristically ilateral and symmetrical in AS [Berens, 1971; Resnick et al. 1977]. Early radiographic findings predominate on the iliac side of the cartilage compartment with erosion of suchondral one causing loss of definition of the articular surfaces usually accompanied y variale degrees of adjacent osteoporosis and surrounding reactive sclerosis. The early inflammatory changes of the joint are est detected with MRI. Bone edema is associated with increased signal in fat-saturated fast spin-echo T2-weighted or STIR sequences. The edema is located periarticularly or on suchondral one surfaces of the sacroiliac joints. Bone marrow edema is typically symmetric and ap- 28 IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
3 pears most commonly in the lower and posterior thirds of the joints [11]. Among the structural lesions that are well visualized on T1w SE sequence, erosion of the SIJ is highly specific for AS. Erosions are identified on T1w SE MRI image y a reak in the cortical one signal together with a change in the signal for adjacent one marrow [12]. New one formation in the SIJ is often easily identified as right areas on T1SE MRI images, representing one marrow fat. The final stage of sacroiliac involvement consists of suchondral sclerosis followed y fusion of the joint with ankylosis. At this stage, MRI may show sclerotic changes, hypointense on T1- and T2-weighted sequences, and fusion of the articulation [13]. However, in cases in which radiographs and MRI are equivocal, CT may e the est imaging technique for depicting suchondral sclerosis and sacroiliac ankylosis [14]. In our study 90% patients had anormalities in the sacroiliac (SI) joints. Of these 85% had ilateral symmetrical involvement and 5% patients had unilateral sacroilitis. There was predominant inferior ileal followed y inferior ileal + inferior sacral regions of the sacroiliac joints. Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No IF : IC Value : a Coronal T1W(a), T2W() and STIR sequences shows features of chronic sacroilitis seen as hypointensitiy in the suchondral regions (suchondral sclerosis) and fatty marrow reparative changes manifested as hyperintensity on T1W and T2W images with suppression on STIR Coronal STIR images showing changes of ilateral acute sacroilitis with suartcular marrow edema (arrows) seen predominantly on the inferior contiguous aspects of the sacro-iliac joints in two different patients of Ankylosing Spondylitis Axial STIR images showing early acute changes of ilateral sacro-ilitis manifested as suarticular one marrow edema with mild joint widening in two different patients. Mixed intermediate changes of sacroilitis with admixture of acute and chronic changes manifested as suarticular marrow edema and fatty changes suppressed on the coronal STIR. Coronal STIR image showing chronic sacroilitis on the left side with pronounced unilateral left sided suchondral sclerosis (a) and advanced ony ankylosis of the ilateral SI joints () in known patient of AS. AXIAL SKELETON The primary site of pathology in the axial skeletal is the enthesis, where the longitudinal ligaments and the annulus firosis collagen merge directly with one. The osteitis caused y the inflammatory process leads to one edema and susequently to ossification of the ligaments. The synovial joints are calso affected y inflammation, with erosions followed y one production and ankylosis. Disease involvement of the spine typically starts at the thoracolumar or lumosacral junctions. As the disease progresses, a the remainder of the thoracic and lumar spine as well as the cervical spine ecome involved. Spondylitis The changes occur exactly at the site of attachment of the anulus firosus to the verteral endplate. Because such a junction of one and ligamentous structure is an enthesis y definition, anterior or posterior spondylitis can e regarded as an enthesitis. These changes consist of irregularities and erosions involving the anterior and/ posterior edges of the verteral endplates and are also known as Romanus lesions. In active disease, these lesions are depicted as reduced signal intensity of the rim of the endplate on T1-weighted MR images and as increased signal intensity on STIR images and represents one marrow edema or osteitis [15]. Later in the disease course, the epiphyseal ring can appear hyperintense on T1-weighted images. Such hyperintense lesions oth on T1W and T2W images represent circumscried areas of postinflammatory fatty one marrow degeneration. IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH 29
4 Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No IF : IC Value : Sagittal T2-weighted images (a & ) and Sagittal T1W image (c) shows florid hyperintense foci at various levels along the anterosuperior and anteroinferior end plates representing fatty marrow changes ( Romanus lesions).similar foci are also noted posteriorly at few levels. Spondylodiscitis Inflammatory involvement of the interverteral disks y spondyloarthritis is known as spondylodiskitis or Andersson lesion. Spondylodiskitis is characterized y high signal intensity at the cortical plates adjacent to interverteral disks on STIR images and fat-suppressed contrastenhanced T1-weighted images. Original Research Paper Spondylitis that is syndesmophyte formation which is characterized y the ossification of the outer fiers of the annulus firosis of the interverteral disk. This causes the corners of one vertera to ridge to another which are delicate and fine in nature. The complete fusion of the verteral odies y syndesmophytes and other related ossified ligaments produces the so-called amoo spine.the syndesmophytes typically associated with AS are seen as ony outgrowths of the anterior verteral edges. MR imaging has its role in depicting florid anterior spondylitis, which is the stage preceding the development of syndesmophytes [19]. Ankylosis involves the verteral edges or centre with ony extension through the disc. Verteral ankylosis is clearly depicted y oth conventional radiography and MRI as it a late manifestation of advanced changes in ankylosing spondyloarthropathy. The zygapophyseal joints (facet joints), costoverteral joints, and costotransverse joints are also involved in ankylosing spondylitis. In facet joint arthritis any facet joint from C2 to S1 can e affected. Any costoverteral joint from T1 to T12 can e affected. Arthritis involving the aove-mentioned joints is characterized y joint effusion, synovitis, erosions, and one marrow edema. Affected joints may undergo ankylosis at late stages and thus impair chest excursion. c Sagittal (a and ) and axial T2W images (c) showing facet joint arthritis and fusion (arrows).additionally Andersons lesions are seen (Image a asterix) and verteral ody fusion () is noted. Sagittal T2W MR images showing advanced changes of florid discitis (Anderson lesion) in known patients of Ankylosing Spondylitis (a.).ti W contrast enhanced images () show high signal intensity along the end plates suggestive of discitis in a known patient of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Enthesopahies: Involvement of ligaments in spondyloarthritis is most extrusively seen when the interspinal ligaments and the supraspinal ligaments are affected. Ligamentous involvement is characterized y increased signal intensity on either STIR or T2W images. Classically, changes are initially noted at the thoraco-lumar and lumo-sacral junctions.spinal extension to the midlumar, as well as the upper thoracic and cervical verterae, occurs with disease progression ut may e arrested at any stage (Resnick 2002c).During the course of AS, the spine may present an admixture of destructive changes as well as features due to one proliferation and ankylosis. Syndesmophytes In the spine, the early stages of spondylitis develop as small erosions at the corners of the verteral odies. This is followed y the much acclaimed hallmark of Ankylosing a Costoverteral arthritis manifested as marrow edema(white arrow) on the STIR sequence with upper loe firosis (asterix ) in a known case of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Insufficiency fractures : The non-inflammatory lesion corresponds to an insufficiency fracture in an ankylosed spine. Insufficiency fracture occurs at the level of the disc (transdiscal) or at the level of the verteral ody (transverteral). Older insufficiency fractures appear hyperintense on T1-weighted images, whereas fresh fractures have a low signal intensity. 30 IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
5 Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No IF : IC Value : c Sagital T1W and T2W MR images showing an insufficiency fracture at C6-C7 level associated with squaring of verterae in a known patient of Ankylosing Spondylitis.Associated compressive changes on the spinal cord noted secondary to retropulsion of the verteral ody. APPENDICULAR SKELETON In the appendicular skeleton the hips, shoulders, and knees are the most common sites of involvement, typically ilateral and symmetric. When the hips are involved, there is axial migration, concentric joint space narrowing, cuff like femoral osteophytes, acetaular protrusion, and eventually ankylosis.at the shoulder, in addition to typical joint space narrowing of the acromioclavicular and glenohumeral joints, a hatchet deformity can form on the humeral head. This defect is a large erosion at the greater tuerosity. At the knee, the radiographic manifestations of involvement are tricompartmental joint space narrowing and erosions. The small joints of the hands and feet as well as the wrists are affected less frequently than large joints. The findings include asymmetric involvement, small erosions, and osseous proliferative changes. Coronal STIR sequence shows left sided hip joint involvement in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis. Marked concentric joint space narrowing with femoral osteophytes and enthesitis manifested as hyperintense foci are noted. Complications The osteoporotic rigid, fused spine of chronic AS is susceptile to fracture from even minimal trauma. Sometimes fractures may occur without known injury [17]. Such fractures are typically horizontal, through the disc or verteral ody, and involve all 3 columns. Spinal stenosis is another potential complication caused y ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum. Dural ectasia with arachnoiditis and cauda equina syndrome have een reported in patients with longstanding disease [18]. CONCLUSION : The early diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis is of unsurmountale importance.we conclude that MRI is the most sensitive imaging modality to detect the earliest changes of this chronic progressively disaling spondyloarthropathy. This is especially important in the light of the fact that early detection of this chronic spondyloarthropathy greatly aids in assessing the disease activity and treatment stategy and may halt the progression of the disease activity y aggressive treatment alternatives. REFERENCES 1. Hermann KGA, Althoff CE, Schneider U, et al. Spinal changes in patients with spondylarthritis: Comparison of MR imaging and radiographic appearances. RadioGraphics 2005;25: Dougados M, Baeten D. Spondyloarthritis. Lancet 2011; 377:2127???2137 [CrossRef] [Medline] 3. Hermann KG, Althoff CE, Schneider U, Zuhlsdorf S, Lemcke A, Hamm B, et al. Spinal changes in patients with spondyloarthritis: comparison of MR imaging and radiographic appearances. Radiographics 2005; 25: Humphreys SC. Ankylosing Spondylitis. (Online) 2008 (Cited 2010 March 30). Availale from URL: article/ overview. 5. Van der Linden S, Valkenurg HA, Cats A. Evaluationof diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 1984; 27: Jee WH, McCauley TR, Lee SH, Kim SH, Im SA, Ha KY. Sacroiliitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: association of MR findings with disease activity. Magn Reson Imaging 2004; 22: Braun J, Bollow M, Sieper J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1998; 24: Braun J, Sieper J, Bollow M. Imaging of sacroiliitis. Clin Rheumatol 2000; 19: Braun J, van der Heijde D. Imaging and scoring in ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2002; 16: van den Berg R, van der Heijde DM. How should we diagnose spondyloarthritis according to the ASAS classification criteria: a guide for practicing physicians. Pol Arch Med Wewn 2010; 120:452???457 [Medline] 11. Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, et al. The Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) handook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68(suppl 2):1???44 [Cross- Ref] [Medline] 12. Madsen, K. B. & Jurik, A. G. Magnetic resonance imaging grading system for active and chronic spondylarthritis changes in the sacroiliac joint. Arthritis Care Res. (Hooken) 62, (2010). 13. Bredella MA, Steinach LS, Morgan S, Ward M, Davis JC. MRI of the sacroiliac joints in patients with moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis. AJR 2006; 187: Braun J, Sieper J. Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet 2007; 370: JevticV, Kos-Golja M, Rozman B, McCall I. Marginal erosive discoverteral Romanus lesions in ankylosing spondylitis demonstrated y contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging. Skeletal Radiol2000; 29: CrossRef,Medline 16. Madsen KB, Jurik AG (2009) MRI grading method for active and chronic spinal changes in spondyloarthritis. Clin Radiol 65:6 14PuMedCrossRef 17. Wang Y, Teng M, Chang C, et al. Imaging manifestations of spinal fractures in ankylosing spondylitis. AJNR 2005; 26: Grosman H, Gray R, St. Louis E. CT of long-standing ankylosing spondylitis with cauda equine syndrome. AJNR 1983; 4: Hermann KG, Althoff CE, Schneider U, Zuhlsdorf S, Lemcke A, Hamm B, et al. Spinal changes in patients with spondyloarthritis: comparison of MR imaging and radiographic appearances. Radiographics 2005; 25: IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH 31
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis
 MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Active (acute) inflammation on MRI highly suggestive of sacroiliitis associated with SpA
 MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis
 C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
UPDATE ON MRI OF SPONDYLOARTHRITIS. PART ONE: THE SACRO-ILIAC JOINT
 JR TR, 2014, 97: 222-227. UPDTE ON MRI OF SPONDYLORTHRITIS. PRT ONE: THE SCRO-ILIC JOINT.C. Vande erg, P. Omoumi,. Larbi, F. Lecouvet, J. Malghem 1 In recent years, there has been an increased trend toward
JR TR, 2014, 97: 222-227. UPDTE ON MRI OF SPONDYLORTHRITIS. PRT ONE: THE SCRO-ILIC JOINT.C. Vande erg, P. Omoumi,. Larbi, F. Lecouvet, J. Malghem 1 In recent years, there has been an increased trend toward
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions
 Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Curr Opin Rheumatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 20.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis
 What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis Poster No.: C-2383 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Gutierrez, V. Familiar
What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis Poster No.: C-2383 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Gutierrez, V. Familiar
Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis
 REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany
REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany
Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis
 Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis Poster No.: C-1836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. E. Banegas Illescas, C. López Menéndez, M. L.
Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis Poster No.: C-1836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. E. Banegas Illescas, C. López Menéndez, M. L.
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
MR findings that can be confused with spondyloarthritis lesions
 MR findings that can be confused with spondyloarthritis lesions Poster No.: C-1608 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Zabala Martín-Gil, E. M. Ocón Alonso, N. Gómez León, P. 1 2 2
MR findings that can be confused with spondyloarthritis lesions Poster No.: C-1608 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Zabala Martín-Gil, E. M. Ocón Alonso, N. Gómez León, P. 1 2 2
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
All that glitters is not inflammatory - a review of the differential diagnosis of spondyloarthritis in the spine and sacroiliac joints
 All that glitters is not inflammatory - a review of the differential diagnosis of spondyloarthritis in the spine and sacroiliac joints Poster No.: C-0468 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
All that glitters is not inflammatory - a review of the differential diagnosis of spondyloarthritis in the spine and sacroiliac joints Poster No.: C-0468 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004?
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Elective Student P. H.
 Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review
 Insights Imaging (2011) 2:177 191 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0061-4 PICTORIAL REVIEW Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review Anne Grethe Jurik Received: 3 August 2010 /Revised: 6 November 2010 /Accepted:
Insights Imaging (2011) 2:177 191 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0061-4 PICTORIAL REVIEW Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review Anne Grethe Jurik Received: 3 August 2010 /Revised: 6 November 2010 /Accepted:
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Department of Radiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark; 4. Key words MRI, sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis, axial spondyloarthritis.
 Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
Diagnostic imaging of sacroiliac joints and the spine in the course of spondyloarthropathies
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(2): 43-49 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.889039 REVIEW RTICLE Received: 2013.02.11 ccepted: 2013.04.08 Diagnostic imaging of sacroiliac joints and the spine in the course of spondyloarthropathies
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(2): 43-49 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.889039 REVIEW RTICLE Received: 2013.02.11 ccepted: 2013.04.08 Diagnostic imaging of sacroiliac joints and the spine in the course of spondyloarthropathies
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis
 SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
Unilateral Sacroiliitis: Differential Diagnosis Between Infectious Sacroiliitis and Spondyloarthritis Based on MRI Findings
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kang et al. Use of MRI to Differentiate Infectious Sacroiliitis From Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yusuhn Kang 1 Sung Hwan Hong Ji
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kang et al. Use of MRI to Differentiate Infectious Sacroiliitis From Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yusuhn Kang 1 Sung Hwan Hong Ji
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies
 Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE
 MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in children: frequency of findings and interobserver reliability
 Pediatric Radiology (2018) 48:1621 1628 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4185-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in children: frequency of findings and interobserver reliability
Pediatric Radiology (2018) 48:1621 1628 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4185-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in children: frequency of findings and interobserver reliability
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: Atlantoaxial Ankylosis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
MRI in Seronegative Spondyloarthritis: Imaging Features and Differential Diagnosis in the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Canella et al. MRI in Seronegative Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Clarissa Canella 1,2,3 runo Schau 4 Elisio Ribeiro 5 runa Sbaffi 2,6 Edson Marchiori 1
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Canella et al. MRI in Seronegative Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Clarissa Canella 1,2,3 runo Schau 4 Elisio Ribeiro 5 runa Sbaffi 2,6 Edson Marchiori 1
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging
 Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical
Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical
Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology
 Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Summary. Background. The Role of MRI in the Criteria for Classification of Rheumatic Diseases
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2015; 80: 259-265 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.893670 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2015.01.25 Accepted: 2015.02.08 Published: 2015.05.16 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2015; 80: 259-265 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.893670 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2015.01.25 Accepted: 2015.02.08 Published: 2015.05.16 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
Radiography is typically the first imaging study in evaluation for arthritis. On radiographs, one critical assessment is differentiating inflammatory
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Semiology of arthopathies and its complications
 Semiology of arthopathies and its complications Poster No.: C-1029 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Caba Cuevas, E. M. Ocón Alonso, D. M. Castaño Palacio, I. Zabala Martín-Gil,
Semiology of arthopathies and its complications Poster No.: C-1029 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Caba Cuevas, E. M. Ocón Alonso, D. M. Castaño Palacio, I. Zabala Martín-Gil,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
Oh, My Aching Back! A Review of Spinal Arthropathies
 Oh, My Aching Back! A Review of Spinal Arthropathies Educational Exhibit, 2014 RSNA Annual Meeting, #MKE106 Elana B. Smith, MD Kimberly Gardner, MD Kiran S. Talekar, MD Adam E. Flanders, MD Adam C. Zoga,
Oh, My Aching Back! A Review of Spinal Arthropathies Educational Exhibit, 2014 RSNA Annual Meeting, #MKE106 Elana B. Smith, MD Kimberly Gardner, MD Kiran S. Talekar, MD Adam E. Flanders, MD Adam C. Zoga,
Sacroiliac joint infection
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
3 Sternoclavicular Joints
 3 Sternoclavicular Joints Anne Grethe Jurik and Flemming Brandt Soerensen 29 Contents 3.1 Introduction.......................................................... 29 3.2 Macroscopic Anatomy.................................................
3 Sternoclavicular Joints Anne Grethe Jurik and Flemming Brandt Soerensen 29 Contents 3.1 Introduction.......................................................... 29 3.2 Macroscopic Anatomy.................................................
Small animal Spinal RadiogRaphy SeRieS. Lumbar Spine radiography. 2. Lateral and ventrodorsal projections of the lumbosacral.
 ImagIng EssEnTIals Peer reviewed Small animal Spinal RadiogRaphy SeRieS Lumar Spine radiography Danielle Mauragis, CVT, and Clifford R. Berry, DVM, Diplomate CVR Imaging Essentials provides comprehensive
ImagIng EssEnTIals Peer reviewed Small animal Spinal RadiogRaphy SeRieS Lumar Spine radiography Danielle Mauragis, CVT, and Clifford R. Berry, DVM, Diplomate CVR Imaging Essentials provides comprehensive
Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings
 C A S E R E P O R T Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings Amelia Bargiela*, Esther Rodriguez, Rafaela Soler The present study describes the ultrasound findings of
C A S E R E P O R T Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings Amelia Bargiela*, Esther Rodriguez, Rafaela Soler The present study describes the ultrasound findings of
Spinal infection. Outline ANATOMY 6/2/2017. Anatomy Pathogen
 Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis
 DOI 10.1007/s11926-012-0274-2 SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis Salih Ozgocmen & Muhammad Asim Khan
DOI 10.1007/s11926-012-0274-2 SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis Salih Ozgocmen & Muhammad Asim Khan
IMAGISTICÃ. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of spinal injury
 IMGISTICÃ Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of spinal injury NICOLE OLOG, M.D., IRINEL ONCE, M.D. Radiology & Imaging Department, ucharest Emergency Clinical Hospital uthor for correspondence: NICOLE
IMGISTICÃ Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of spinal injury NICOLE OLOG, M.D., IRINEL ONCE, M.D. Radiology & Imaging Department, ucharest Emergency Clinical Hospital uthor for correspondence: NICOLE
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/02/2010 History Restrained teenager involved in motor vehicle accident. Diagnosis Chance Fracture (Hyperflexion-Distraction Injury) Discussion Chance-type spinal
Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/02/2010 History Restrained teenager involved in motor vehicle accident. Diagnosis Chance Fracture (Hyperflexion-Distraction Injury) Discussion Chance-type spinal
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
