Bone pathology. László Kereskai MD
|
|
|
- Augusta Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bone pathology László Kereskai MD
2 Anatomy and function Organic osteoid matrix and mineral calcium hydroxyapatite Dynamic tissue: resorption, renewal, remodeling Osteoprogenitor cells: pluripotent mesenchymal cells, vicinity of all bony surfaces, GF-s stimulationdifferentiation into osteoblasts Osteoblasts and lining cells: matrix formation and initialization of mineralization. Receptors for hormones and other factors, express factors that regulate osteoclasts. Surrounded by matrix- transformation to osteocytes. Flattened quiscent cells: lining cells
3 Anatomy and function Osteocytes: communication with each other and surface cells through canaliculi. Help to control calcium and phosphate levels in the microenvironment, and detect mechanical forces and translate them into biologic activity a process called mechanotransduction Osteoclasts: haematopoietic cell derivation (like macrophages), limited lifespan (about 2 weeks), binding to bone surfaces through integrins- formation of resorption pit (analogous to secondary lysosomes)- removal of mineral by generating acidic environment (proton pump system) and digestion of organic substances by proteases
4 Cellular elements
5 Osteocytes- AgNOR
6 Anatomy and function As osteoclasts disassemble matrix proteins deposited by osteoblasts, growth factors, cytokines, and enzymes (such as collagenase) bound to the matrix are liberated and activated, including some that stimulate osteoblasts. Thus, as bone is broken down to its elemental units, substances are released into the microenvironment that initiate its renewal The proteins of bone include type 1 collagen and many noncollagenous proteins derived mainly from osteoblasts. Osteoblasts deposit collagen either in a random weave known as woven bone or in an orderly layered manner designated lamellar bone Normally, woven bone is seen in sites of rapid bone formation such as the fetal skeleton and the base of growth plates. The presence of woven bone in the adult is always abnormal; however, it is not diagnostic of a particular disease. Lamellar bone, which gradually replaces woven bone during growth, is deposited much more slowly and is stronger than woven bone.
7 Woven and trabecular bone
8 DEFECTS IN HORMONES AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION MECHANISMS Achondroplasia: the most common disease of the growth plate, mutation in the FGF receptor 3 (FGFR3). Normally, FGFmediated activation of FGFR3 inhibits cartilage proliferation; in achondroplasia, the mutations cause constitutive activation of FGFR3 and thereby suppress growth. AD, but mainly with new mutations in paternal allele. Shortened proximal extremities, a trunk of relative normal length, and an enlarged head with bulging forehead and conspicuous depression of the root of the nose. No changes in longevity, intelligence, or reproductive status.
9 Achondroplasia
10 DEFECTS IN HORMONES AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION MECHANISMS Thanatophoric dwarfism: most common lethal form of dwarfism, caused by gain-of-function mutations in FGFR3 that differ from those in achondroplasia. 1:20000 live births. Micromelic shortening of the limbs, frontal bossing, relative macrocephaly, a small chest cavity, and a bellshaped abdomen. The underdeveloped thoracic cavity leads to respiratory insufficiency, and these individuals frequently die at birth or soon after. In the growth plate show diminished proliferation of chondrocytes and poor columnization in the zone of proliferation.
11 Thanatophoric dysplasia
12 DEFECTS IN EXTRACELLULAR STRUCTURAL PROTEINS Osteogenesis imperfecta: brittle bone disease. Various disorders caused by deficiencies in the synthesis of type 1 collagen. It principally affects bone, but also impacts other tissues rich in type 1 collagen (joints, eyes, ears, skin, and teeth). Usually AD. The genotypephenotype relationship underlying osteogenesis imperfecta is based on the location of the mutation within the protein (decreased synthesis of qualitatively normal collagen are associated with mild skeletal abnormalities, more severe or lethal phenotypes have abnormal polypeptide chains that cannot be arranged in the triple helix).
13 DEFECTS IN EXTRACELLULAR Four major subtypes STRUCTURAL PROTEINS The type II variant is at one end of the spectrum and is uniformly fatal in utero or during the perinatal period. It is characterized by extraordinary bone fragility with multiple intrauterine fractures Type I form have a normal life span but experience childhood fractures that decrease in frequency following puberty. Blue sclerae caused by decreased collagen content, making the sclera translucent and allowing partial visualization of the underlying choroid; hearing loss related to both a sensorineural deficit and impeded conduction due to abnormalities in the bones of the middle and inner ear; and dental imperfections (small, misshapen, and blue-yellow teeth) secondary to a deficiency in dentin. The basic abnormality in all forms is too little bone, thus constituting a type of osteoporosis with marked cortical thinning and attenuation of trabeculae.
14 Osteogenesis imperfecta
15 DEFECTS IN METABOLIC PATHWAYS (ENZYMES, ION CHANNELS, AND TRANSPORTERS) Osteopetrosis: or marble bone disease. Bone remodeling deficiency because of the defective lysosomal function of osteoclasts The pathologic tissue consists of lamellar bone and calcified cartilage tissue. The bones easily break (brittle). The nerves are compressed (cranial nerves). The process compromises the normal haematopoeitic development (anaemia). AR (early, frequently fatal) and AD forms (later appearance, fractures, anaemia, nerve compression). Therapy: bone marrow transplantation (the first genetical disease treated with this mood), or recombinant human IFN-.
16 Osteopetrosis
17 DECREASED BONE MASS Osteoporosis: Localized (immobilized limb) and diffuse Decreased bone mass Age-related loss normally: 0,7% per year Most common forms: senile and postmenopausal Senile: decreased activity of osteoblasts and other factors: decreased bone formation; decreased physical activity Postmenopausal: decreased estrogen, increased osteoclast activity leading to resorption Main complication: bone fracture (neck of femur, per- and subtrochanter fracture) Important to rule out other causes: metastases, myeloma
18 Osteoporosis
19 OSTEOCLAST DYSFUNCTION Paget disease (osteitis deformans): 90 % of patients is over 55 ys, before 40 is rare. Localisation: lumbosacral spine, pelvic bones, skull are the most frquent locations, other involvement can happen, but the ribs are spared. Usually polyostotic with elevated ALP level. Monoostotic form: in long bones and vertebrae (ALP level can be normal). Etiology is not known: viral origin was suspected because of inclusions in osteoclast nuclei. There is some genetic predisposition (familial clustering)
20 OSTEOCLAST DYSFUNCTION Paget disease, course: lytic, osteoclastic start, secondly abnormal hyperplasia with the formation of primitive, dyscontinuous bone trabeculae, and later thick trabeculae are formed (better visualisation with reticulin stain than polarisation). The formation of lamellar bone is not well organized, there is a formation of so-called cement lines (sudden changes during the formation of trabeculae, degradation and regeneration follow each other). Cement lines are the keys of diagnosis (other diseases: irradiation defects, chronic osteomyelitis, reactive bone growth around metastasis, in polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, but in these cases they are more regular).
21 Paget disease
22 Paget disease
23 OSTEOCLAST DYSFUNCTION Paget disease, symptoms: Pain, deformities, in weight bearing places secondary osteoarthritis. Complications: fractures, secondary sarcoma formation (usually osteosarcoma, but can be chondrosc, fibrosc and giant cell tumor as well) in different locations (femur, humerus, pelvis, tibia, skull).
24 ABNORMAL MINERAL HOMEOSTASIS Rickets and osteomalacia: D-vitamine deficiency or metabolism disorder. Before the closure of epiphysis phuges: ricketts. Increase of non-mineralised matrix, decreased Caincorporation. Microscopically: nonmineralised matrix zone around bony trabeculae. Deformity, fragility.
25 Ricketts and osteomalacia
26 ABNORMAL MINERAL HOMEOSTASIS Hyperparathyroidism: mainly primary caused by adenoma. The increased PTH concentrations are detected by receptors on osteoblasts, which then release factors that stimulate osteoclast activity. The anatomic changes of severe hyperparathyroidism, known as osteitis fibrosa cystica, are now rarely encountered, because hyperparathyroidism is usually diagnosed and treated at an early asymptomatic stage detected on routine blood tests.
27 ABNORMAL MINERAL HOMEOSTASIS The increased osteoclast activity in hyperparathyroidism affects cortical bone (subperiosteal, osteonal, and endosteal surfaces) more severely than cancellous bone. Subperiosteal resorption produces thinned cortices and the loss of the lamina dura around the teeth. In cancellous bone, osteoclasts tunnel into and dissect centrally along the length of the trabeculae, creating the appearance of railroad tracks and producing what is known as dissecting osteitis. The bone loss predisposes to microfractures and secondary hemorrhages that elicit an influx of macrophages and an ingrowth of reparative fibrous tissue, creating a mass of reactive tissue, known as a brown tumor. Result: generalized osteitis fibrosa cystica (von Recklinghausen disease of bone).
28 Hyperparathyreosis
29 ABNORMAL MINERAL HOMEOSTASIS Renal osteodystrophy: (1) increased osteoclastic bone resorption mimicking osteitis fibrosa cystica, (2) delayed matrix mineralization (osteomalacia), (3) osteosclerosis, (4) growth retardation, and (5) osteoporosis. High-turnover osteodystrophy is characterized by increased bone resorption and bone formation, with the former predominating. In contrast, low-turnover or aplastic disease is manifested by adynamic bone (little osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity) and, less commonly, osteomalacia. Many affected individuals have the third type, which is a mixed pattern of disease.
30 Renal osteodystrophy
31 ABNORMAL MINERAL HOMEOSTASIS Chronic renal failure results in phosphate retention and hyperphosphatemia. Hyperphosphatemia induces secondary hyperparathyroidism Hypocalcemia develops as the levels of vitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D 3 ; 1,25-(OH) 2 D 3 ) fall because of decreased conversion from the vitamin D metabolite 25- (OH)D 3 by damaged kidneys Secondary hyperparathyroidism produces increased osteoclast activity Metabolic acidosis associated with renal failure stimulates bone resorption and the release of calcium hydroxyapatite from the matrix.
32 OSTEONECROSIS Most frequent cause: corticosterois administration (head of femur), otherwise it is usually idiopathic (others: trauma, infection, radiation therapy, connective tissue disorders, pregnancy, Gaucher disease, sickle cell and other anemias, alcohol abuse, chronic pancreatitis, tumors, epiphyseal disorders) Medullary infarcts: geographical areas. Wedge-shaped subcondral infarcts. Cortical bone and cartilage are spared. Subchondral infarcts cause chronic pain, secondary osteoarthritis, medullary infarcts are usually silent.
33 Osteonecrosis
34 INFECTIONS- OSTEOMYELITIS Pyogenic osteomyelitis: Usually bacterial, % caused by coagulase-positive staphylococcus. Other bacteria: Klebsiella, Aerobacter, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Streptococcus, Pneumococcus, Gonococcus, Meningococcus, Brucella and Salmonella (abnormal hgbsickle-cell anaemia). Cause: fracture (usually mpx), or hematogenous (mainly before 20 ys, in 75% involvement of lower extremities). Acute, subacute and chronic forms, the latter can mimic tumors clinically and radiologically (destructive and regenerative bone changes). Sometimes extensive regeneration can happen: Garré-type or sclerotising osteomyelitis, with other name periostitis ossificans.
35 INFECTIONS- OSTEOMYELITIS Morfology depends: localisation, causative agent, age. Before 1 year: epiphyseal damage and joint infection, metaphysis és diaphysis is involved only in the minority of cases, over 1 year the opposite: extensive corticali metaphyseal involvement, continuous cartilage and joint injury is rare. In case of metaphyseal start cortical spread through Volkmann channels, and progression in the medulla as well, through the periosteum it can break into the neighbourhood. Sequester is fomed with a bony cavity from the periosteum. Around necrotic bone granulation tissue forms, in the necrotic bone mottled appearance.
36 Acute osteomyelitis
37 INFECTIONS- OSTEOMYELITIS Solution: surgical, removal of sequester. In aduts: joint involvement can happen when there is an extensive bone process. Microscopically: mixed inflammation, fibrosis, bone necrosis, new bone formation. Variants: plasma cell-rich, xanthogranulomatous. In chronic processes widespread periosteal bone formation. In soft tissues fistulas covered by epithel, epidermal inclusión cysts.
38 Chronic osteomyelitis
39 Osteomyelitis sclerotisans (Garré)
40 INFECTIONS- OSTEOMYELITIS Tuberculous osteomyelitis: Hematogenous, young adults and children. Most frequently involved bones: vertebrae, pelvic bones, around knees, wrists. In childhood mainly metaphyseal, in adults rather epiphysealis. Joint involvement: synovia and cartilage destruction. Cutaneous sinuses: secundary bact. infection. Healing: joint fusion with total denudation of cartilage ( kissing sequestra ). Here the sequester isn t cortical, like in bacterial infection, but present in cancellous bone.
41 Tuberculous osteomyelitis
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
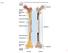 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Awaisheh. Mousa Al-Abbadi. Abdullah Alaraj. 1 Page
 f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
BONE REMODELLING. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Skeletal System Functions
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Section 1. What is osteoporosis? Your bones. Bones and osteoporosis. Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis
 4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Pathophysiology of fracture healing
 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Influence of implants 1 What is the structure of bone? 2 Bone structure Four levels: Chemical
Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Influence of implants 1 What is the structure of bone? 2 Bone structure Four levels: Chemical
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
DISEASE OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS BONES. Determines body size and shape. Mechanical support for movement. Protect vital organs
 https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ca/human_skeleton_front_en.svg/220px-human_skeleton_front_en.svg.png DISEASE OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Thanisa Sanmanee, M.D. FUNCTIONS Determines
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ca/human_skeleton_front_en.svg/220px-human_skeleton_front_en.svg.png DISEASE OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Thanisa Sanmanee, M.D. FUNCTIONS Determines
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
LAB: The Skeletal System System
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name LAB: The Skeletal System System Background: The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are bone with more than 270 bones that
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name LAB: The Skeletal System System Background: The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are bone with more than 270 bones that
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 08a Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 08a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Skeletal System The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are born
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 08a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Skeletal System The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are born
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion. Norbert Wiegand
 Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion Norbert Wiegand 2/3 of traumatology: treatment of fractures We have to understand: Structure of the bone Biology of the bone Bone healing Types of Bone
Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion Norbert Wiegand 2/3 of traumatology: treatment of fractures We have to understand: Structure of the bone Biology of the bone Bone healing Types of Bone
Abdullah Alaraj. Mohammad Alfarra. Mousa al abbadi. Modified by : Saif Yamin. 1 P a g e
 #2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi Modified by : Saif Yamin 1 P a g e introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and
#2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi Modified by : Saif Yamin 1 P a g e introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
Abdullah Alaraj. Mousa al abbadi. Mohammad Alfarra. 1 Page
 f #2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi 1 Page introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and its receptors. However,
f #2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi 1 Page introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and its receptors. However,
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES
 NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling
 Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 ( ) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
