Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling
|
|
|
- Percival Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling
2
3
4
5 Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1. Intramembranous Bone develops from fibrous membrane Forms bones of skull and clavicle (most flat bones) Contributes to the growth of short bones and thickening of long bones Begins at 8 weeks of development 2. Endochondral Bone develops from hyaline cartilage Responsible for the formation of short and long bones Begins 2 nd month of dvlpmt
6 Intramembranous Ossification (prenatal)
7 Intramembranous Ossification (prenatal)
8 Intramembranous Ossification (prenatal) Mesenchymal cells create fibrous CT framework for ossification Some mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts in an ossification center Osteoblasts secrete bone matrix, osteoid
9 Intramembranous Ossification (prenatal) Mineralization and calcification of osteoid Trapped osteoblasts become osteocytes
10 Intramembranous Ossification (prenatal) Several points of ossification occur and fuse forming spongy bone around embryonic blood vessels Mesenchyme on bone face condense and differentiate into periosteum
11 Intramembranous Ossification (prenatal) The woven bone at the outer edge is remodeled and replaced by compact bone Spongy bone (diploë) remains Note :Osteoblasts remain on bone surface to grow/remodel when needed cavities made up of trabeculae fill with red marrow created from vessels (vascular tissue)
12
13
14
15
16 An anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising any of the soft membranous gaps (sutures) between the cranial bones of a an infant Fontanelles: 1. allow room for the baby s brain to grow 2. enable the head to be compressed during delivery.
17 Endochondral Ossification
18 Endochondral Ossification Bone collar formed around diaphysis by osteoblasts located on inner side of perichondrium The collar impedes diffusion of oxygen and nutrients and the underlying cartilage, promoting degenerative changes there
19 Endochondral Ossification primary ossification center Cartilage calcifies, then the cells die and cavities form (cavitates) Death of chondrocytes creates a porous structure consisting of Calcified cartilage remnants which become covered by a layer of osteoblast Bone collar provides stability during cavitation Cartilage elsewhere continues to elongate
20 Endochondral Ossification Blood vessels from perichondrium (now the periosteum) penetrate through the bone collar, bringing osteoproginator cells to the porous central region Periosteal bud (lymph, blood vessels, nerves, red marrow, osteoblasts and osteoclasts) enters cavity and builds spongy bone
21 Endochondral Ossification Secondary Ossification Center forms in epiphysis Osteoclasts dissolve spongy bone to create medullary cavity
22 Endochondral Ossification Hyaline only remains on epiphyseal surface (articular cartilage) and at diaphysis and epiphysis junction, to form the epiphyseal plates. Secondary Ossification Center
23 Growing taller throughout childhood!
24 Lots of activity! Growing Taller! (A closer look at the epiphyseal plate)
25 Growing Taller! (A closer look at the epiphyseal plate) typical hyaline cartilage (resting) 1- Resting zone rapidly mitotic cartilage, lengthening bone; chondrocytes form columns 2- Growth zone enlarging size of chondrocytes (hypertrophy), this hypertrophy compresses the matrix into thin septa between chondrocytes 3- Hypertrophy zone matrix of cartilage calcifies and cells die forming small cavities 4- Calcification zone Osteoblasts adhere to the remnants of calcified cartilage matrix and produce woven bone. Later this bone reshapes into spongy bone converted into medullary cavity or compact bone later as bone grows. 5- Ossification zone
26 Longitudinal Bone Growth Longitudinal Growth (interstitial) cartilage continually grows and is replaced by bone Bones lengthen entirely by growth of the epiphyseal plates Cartilage is replaced with bone as quickly as it grows Epiphyseal plate maintains constant thickness
27 Bone collar
28 When does lengthening stop? End of adolescence - lengthening stops Chondrocytes stop mitosis. Plate thins out and replaced by bone Diaphysis and epiphysis fuse to be one bone Epiphyseal plate closure (18 yr old females, 21 yr old males) Thickening of bone continuous throughout life
29 Appositional Bone Growth Growing bones widen as they lengthen Appositional growth growth of a bone by addition of bone tissue to its surface Bone is resorbed at endosteal surface and added at periosteal surface Osteoblasts add bone tissue to the external surface of the diaphysis Osteoclasts remove bone from the internal surface of the diaphysis
30 h.swf Recommended el2a/frameset.htm
31 Bone Remodeling Reshaping of the skeleton during growth Maintain calcium levels Repair of microfractures caused by everyday stresses Involves: Dissolving/destroying bone New bone growth
32 Dissolved material passed through osteoclasts and into bloodstream for reuse by the body (endocytosis and transcytosis)
33 Bone Remodeling Bone Depostition Occurs when bone is injured or extra strength is needed Requires a healthy diet - protein, vitamins C, D, and A, and minerals (calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, etc.) Bone Resorption Accomplished by Osteoclasts (multinucleate phagocytic cells) Resorption involves osteoclast secretion of: Lysosomal enzymes that digest organic matrix HCl that converts calcium salts into soluble forms Dissolved matrix is endocytosed and transcytosed into the interstitial fluid the blood
34 Bone is Dynamic! Bone is constantly remodeling and recycling Coupled process between: Bone deposition (by osteoblasts) Bone destruction/resorption (by osteoclasts) 5-7% of bone mass recycled weekly All spongy bone replaced every 3-4 years. All compact bone replaced every 10 years. Prevents mineral salts from crystallizing; protecting against brittle bones and fractures
35 Bone growth regulated by hormones Human Growth Hormone (HGH): from pituitary gland in brain promotes epiphyseal plate activity Thyroid hormones: regulate HGH for proper bone proportions Puberty: Testosterone or Estrogen cause adolescent growth spurt and skeletal differences between the sexes: Wider shoulders, larger bones, narrow pelvis in men Wider hips, smaller upper body in women Excesses in any hormones can cause abnormal skeletal growth Ex. gigantism or dwarfism
36 Robert Wadlow, world s tallest man 8 ft 11 inches Yao Defen, gigantess currently in treatment for pituitary tumor in China. 7 ft 7 inches 396 lbs
37
38 Response to Mechanical/Gravitational Forces Bones respond to muscles pulling on them (mechanical stress) and to gravity by keeping the bones strong where they are being stressed. weight bearing activities stronger projections where muscles/ligaments attach High rate of bone deposition in specific areas.
39 What you don t use, you lose. The stresses applied to bones during exercise are essential to maintaining bone strength and bone mass
40 Joints A joint is where two or more bones meet. Also known as an articulation Joints can be classified either by: the tissue that holds the bones together or the degree of movement they provide Synovial joints Permits free movement Fibrous joints Cartilaginous joints Limited or no movement
41 Fibrous joints are connected by dense connective tissue and have no joint cavity. Cartilaginous joints are connected by cartilage and have no joint cavity. Synovial joints have a synovial, fluid-filled cavity that surrounds the articulating bones. Synarthrosis: Joints that do not provide any movement. Amphiarthrosis: Joints that only provide a small degree of movement. Diarthrosis: Joints that allow free movement
42 FIBROUS JOINTS In a fibrous joint, the two bones are connected by dense fibrous connective tissue. These joints can be either synarthrotic or amphiarthrotic. There are three different types of fibrous joints: Suture: between the flat bones of the skull Gomphosis: The roots of a tooth and the alveolar sockets in the maxilla or mandible Syndesmosis: interosseous membrane
43 Sutures Sutural ligament These joints are synarthrotic
44 Gomphoses Gomphoses occur only between the teeth and adjacent bone. In these joints, short collagen tissue fibers in the periodontal ligament run between the root of the tooth and the bony socket.. These joints are synarthrotic
45 Syndesmoses These joints are amphiarthrotic
46 CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS In a cartilaginous joint, the two bones are connected by cartilage. These joints can be either synarthrotic or amphiarthrotic. There are two types of cartilaginous joints: Synchondroses: growth plate Symphyses: intervertebral joints, symphysis pubis
47 Symphysis pubis Intervertebral joints
48 Synovial joints Synovial joints are most commonly found throughout the limbs. In order for the joint to be classified as synovial: Both adjacent bones participating in the joint must be lined with hyaline cartilage (articular cartilage) The joint is encompassed in a capsule that encases the joint cavity. The interior of the capsule is lined with a synovial membrane that is responsible for producing and secreting synovial fluid Synovial fluid lubricates the joint, which aids in reducing the friction between the bones ends as they articulate with each other Further reinforcement of the capsule is provided by ligaments, tendons and skeletal muscle
49 Synovial joints Hinge Joint Example: elbow and knee joints Gliding (plane) Joint Pivot Joint Example: atlantoaxial joint Saddle Joint Ball and Socket Joint Example: shoulder and hip joints
50 Ellipsoid Joint: Example: wrist joint
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Sheets 16&17. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3.
 Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3. How could damage to these areas impact bone growth? WRITE AND
Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3. How could damage to these areas impact bone growth? WRITE AND
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Compact bone; Many parallel Haversian canals contain: small blood vessels. very small nerve. Interconnected by Volkmann s canals.
 Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
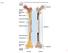 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
The Skeletal System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R. Joints: Part A. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
SKELETAL SYSTEM 1) Components Cartilages Bones Tendons & ligaments joints. Cartilage and Bone Tissues. Cartilage. Hyaline Cartilage 2/1/2013
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 1) Components Cartilages Bones Tendons & ligaments joints 2) FUNCTIONS Structural support Protection of various regions of the body Storage: minerals & bone marrow 3) Movements???? 1 Cartilage
SKELETAL SYSTEM 1) Components Cartilages Bones Tendons & ligaments joints 2) FUNCTIONS Structural support Protection of various regions of the body Storage: minerals & bone marrow 3) Movements???? 1 Cartilage
SKELETAL SYSTEM 1) Components
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 1) Components Cartilages Bones Tendons & ligaments joints 2) FUNCTIONS Structural support Protection of various regions of the body Storage: minerals & bone marrow 3) Movements???? 1 Cartilage
SKELETAL SYSTEM 1) Components Cartilages Bones Tendons & ligaments joints 2) FUNCTIONS Structural support Protection of various regions of the body Storage: minerals & bone marrow 3) Movements???? 1 Cartilage
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 ( ) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Chapter 6. Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Articulations. Articulation. Joint between bones. Does not mean movement! Some joints are immovable; sutures.
 Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Articulations (Joints) Can t We Just All Keep it Together
 Articulations (Joints) Can t We Just All Keep it Together Joints With one exception (the hyoid bone), every bone in the body is connected to or forms a joint with at least one other bone. Functions of
Articulations (Joints) Can t We Just All Keep it Together Joints With one exception (the hyoid bone), every bone in the body is connected to or forms a joint with at least one other bone. Functions of
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
