Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
|
|
|
- Maximilian Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6
2 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement.
3 ANSWER Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement.
4 The humerus is an example of a bone. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
5 ANSWER The humerus is an example of a bone. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
6 Endochondral ossification begins with the formation of A. a fibrous connective-tissue model. B. a cartilage model. C. a membranous model. D. a calcified model. E. no model at all, just the presence of osteoblasts.
7 ANSWER Endochondral ossification begins with the formation of A. a fibrous connective-tissue model. B. a cartilage model. C. a membranous model. D. a calcified model. E. no model at all, just the presence of osteoblasts.
8 When cartilage is produced at the epiphyseal side of the metaphysis at the same rate as bone is deposited on the opposite side, bones A. grow longer. B. grow wider. C. become shorter. D. become more porous and weaker. E. become thicker.
9 ANSWER When cartilage is produced at the epiphyseal side of the metaphysis at the same rate as bone is deposited on the opposite side, bones A. grow longer. B. grow wider. C. become shorter. D. become more porous and weaker. E. become thicker.
10 A child with rickets would have A. oversized facial bones. B. long limbs. C. weak, brittle bones. D. bowed legs. E. inadequate muscle development.
11 ANSWER A child with rickets would have A. oversized facial bones. B. long limbs. C. weak, brittle bones. D. bowed legs. E. inadequate muscle development.
12 Premature closure of the epiphyseal plates could be caused by A. high levels of vitamin D. B. too much calcium in the diet. C. elevated levels of sex hormones. D. too little thyroxine. E. an excess of growth hormone.
13 ANSWER Premature closure of the epiphyseal plates could be caused by A. high levels of vitamin D. B. too much calcium in the diet. C. elevated levels of sex hormones. D. too little thyroxine. E. an excess of growth hormone.
14 In normal adult bones, A. there is no turnover of minerals. B. a portion of the protein and mineral content is replaced each year. C. osteoblast activity exceeds osteoclast activity, once bone has been formed. D. osteoclasts continue to be active long after osteoblast activity ceases. E. stresses will have no effect on the thickness of bone.
15 ANSWER In normal adult bones, A. there is no turnover of minerals. B. a portion of the protein and mineral content is replaced each year. C. osteoblast activity exceeds osteoclast activity, once bone has been formed. D. osteoclasts continue to be active long after osteoblast activity ceases. E. stresses will have no effect on the thickness of bone.
16 The following are major steps in the process of endochondral ossification. 1. Blood vessels invade the perichondrium. 2. Osteoclasts create a marrow cavity. 3. Chondrocytes enlarge and calcify. 4. Osteoblasts replace calcified cartilage with spongy bone. 5. The perichondrium is converted into a periosteum and the inner layer produces bone. The correct order for these events is A. 3, 1, 5, 4, 2. B. 1, 3, 5, 4, 2. C. 1, 5, 3, 4, 2. D. 2, 3, 1, 5, 4. E. 3, 1, 4, 5, 2.
17 ANSWER The following are major steps in the process of endochondral ossification. 1. Blood vessels invade the perichondrium. 2. Osteoclasts create a marrow cavity. 3. Chondrocytes enlarge and calcify. 4. Osteoblasts replace calcified cartilage with spongy bone. 5. The perichondrium is converted into a periosteum and the inner layer produces bone. The correct order for these events is A. 3, 1, 5, 4, 2. B. 1, 3, 5, 4, 2. C. 1, 5, 3, 4, 2. D. 2, 3, 1, 5, 4. E. 3, 1, 4, 5, 2.
18 The ankle bones are examples of bones. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
19 ANSWER The ankle bones are examples of bones. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
20 The patella is an example of a bone. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
21 ANSWER The patella is an example of a bone. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
22 Secondary ossification centers occur A. in the medullary cavity of the diaphysis. B. at the outer surface of the diaphysis. C. in the center of the epiphyses. D. at the surface of the epiphyses. E. in the dermis of the skin.
23 ANSWER Secondary ossification centers occur A. in the medullary cavity of the diaphysis. B. at the outer surface of the diaphysis. C. in the center of the epiphyses. D. at the surface of the epiphyses. E. in the dermis of the skin.
24 The sternum is an example of a bone. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
25 ANSWER The sternum is an example of a bone. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
26 Mary is 50 years old. During a checkup, a bone scan reveals that portions of her skeleton show greater than normal demineralization. After reviewing the test results, her physician suggests hormone therapy. What hormone will she prescribe for her patient? A. thyroid hormone B. growth hormone C. estrogen D. parathyroid hormone E. calcitonin
27 ANSWER Mary is 50 years old. During a checkup, a bone scan reveals that portions of her skeleton show greater than normal demineralization. After reviewing the test results, her physician suggests hormone therapy. What hormone will she prescribe for her patient? A. thyroid hormone B. growth hormone C. estrogen D. parathyroid hormone E. calcitonin
28 The term diploe refers to A. The shaft of a long bone B. The ends of a long bone C. Bone with no medullary cavity D. Two thin flat plates of compact bone E. The internal layer of spongy bone in a flat bone
29 ANSWER The term diploe refers to A. The shaft of a long bone B. The ends of a long bone C. Bone with no medullary cavity D. Two thin flat plates of compact bone E. The internal layer of spongy bone in a flat bone
30 When production of sex hormones increases, bone growth A. slows down. B. accelerates rapidly. C. increases slowly. D. increases, but only in thickness. E. is not affected.
31 ANSWER When production of sex hormones increases, bone growth A. slows down. B. accelerates rapidly. C. increases slowly. D. increases, but only in thickness. E. is not affected.
32 The vertebrae are examples of bones. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
33 ANSWER The vertebrae are examples of bones. A. long B. short C. flat D. irregular E. sesamoid
34 The innermost part of compact bone is known as the A. medullary cavity. B. metaphysic. C. spongy bone. D. epiphysis. E. diaphysis.
35 ANSWER The innermost part of compact bone is known as the A. medullary cavity. B. metaphysic. C. spongy bone. D. epiphysis. E. diaphysis.
36 The most abundant mineral in the human body is A. sodium. B. potassium. C. phosphorus. D. calcium. E. sulfur.
37 ANSWER The most abundant mineral in the human body is A. sodium. B. potassium. C. phosphorus. D. calcium. E. sulfur.
38 How would increasing the amount of osteoid in the bony matrix affect the physical characteristics of bone? A. The bone would be less flexible B. The bones would be stronger C. The bones would be more brittle D. The bones would be larger E. The bones would be less compressible
39 ANSWER How would increasing the amount of osteoid in the bony matrix affect the physical characteristics of bone? A. The bone would be less flexible B. The bones would be stronger C. The bones would be more brittle D. The bones would be larger E. The bones would be less compressible
40 Our bones are constantly changing to adapt to the demands we place on them. A. True B. False
41 ANSWER Our bones are constantly changing to adapt to the demands we place on them. A. True B. False
42 Mature bone cells are called A. osteocytes. B. osteoblasts. C. osteoclasts. D. chondrocytes. E. osteons.
43 ANSWER Mature bone cells are called A. osteocytes. B. osteoblasts. C. osteoclasts. D. chondrocytes. E. osteons.
44 Bundles of collagen fibers that run in a particular direction around the entire bone are called A. Concentric lamellae B. Circumferential lamellae C. Interstitial lamellae D. Lacunae
45 ANSWER Bundles of collagen fibers that run in a particular direction around the entire bone are called A. Concentric lamellae B. Circumferential lamellae C. Interstitial lamellae D. Lacunae
46 The tissue found in the medullary cavity that is primarily adipose tissue is A. Yellow marrow B. Red marrow C. Cartilage D. Collagen E. Osseous tissue
47 ANSWER The tissue found in the medullary cavity that is primarily adipose tissue is A. Yellow marrow B. Red marrow C. Cartilage D. Collagen E. Osseous tissue
48 Elevated levels of calcium ion in the blood stimulate the secretion of the hormone A. calcitonin. B. thyroid hormone. C. parathyroid hormone. D. growth hormone. E. testosterone.
49 ANSWER Elevated levels of calcium ion in the blood stimulate the secretion of the hormone A. calcitonin. B. thyroid hormone. C. parathyroid hormone. D. growth hormone. E. testosterone.
50 Cells that synthesize the organic components of the bone matrix are called A. osteocytes. B. osteoprogenitor cells. C. osteoblasts. D. osteoclasts. E. chondrocytes.
51 ANSWER Cells that synthesize the organic components of the bone matrix are called A. osteocytes. B. osteoprogenitor cells. C. osteoblasts. D. osteoclasts. E. chondrocytes.
52 Which of the following is a characteristic of bone? A. The matrix of the bone is very dense and contains deposits of calcium salts. B. The matrix of the bone contains osteoclasts. C. Narrow passageways form through the matrix to allow for an exchange of nutrients. D. all of the above E. both A and C
53 ANSWER Which of the following is a characteristic of bone? A. The matrix of the bone is very dense and contains deposits of calcium salts. B. The matrix of the bone contains osteoclasts. C. Narrow passageways form through the matrix to allow for an exchange of nutrients. D. all of the above E. both A and C
54 An inherited collagen disorder, such as osteogenesis imperfecta, might lead to what symptoms A. Brittle bones susceptible to fracture B. Soft bones C. Blister formation D. Increased risk of cancer
55 ANSWER An inherited collagen disorder, such as osteogenesis imperfecta, might lead to what symptoms A. Brittle bones susceptible to fracture B. Soft bones C. Blister formation D. Increased risk of cancer
56 The hormone calcitonin functions to A. stimulate osteoclast activity. B. decrease the rate of calcium excretion. C. decrease the rate of calcium absorption. D. decrease the level of calcium ion in the blood. E. stimulate both osteoblast and osteoclast activity.
57 ANSWER The hormone calcitonin functions to A. stimulate osteoclast activity. B. decrease the rate of calcium excretion. C. decrease the rate of calcium absorption. D. decrease the level of calcium ion in the blood. E. stimulate both osteoblast and osteoclast activity.
58 Large, multinucleated cells that can dissolve the bony matrix are called A. osteocytes. B. osteoprogenitor cells. C. osteoblasts. D. osteoclasts. E. chondrocytes.
59 ANSWER Large, multinucleated cells that can dissolve the bony matrix are called A. osteocytes. B. osteoprogenitor cells. C. osteoblasts. D. osteoclasts. E. chondrocytes.
60 Restoring broken ends of a bone to normal position is called a(n) A. Addition B. Subtraction C. Reduction D. Fracture E. Fusion
61 ANSWER Restoring broken ends of a bone to normal position is called a(n) A. Addition B. Subtraction C. Reduction D. Fracture E. Fusion
62 Jim begins puberty early at age 10. What effect would you predict this will have on his stature? A. Jim will probably be taller than if he had started puberty later B. Jim will probably be shorter than if he had started puberty later C. Jim will be a giant D. The early onset of puberty will have no effect on Jim s stature
63 ANSWER Jim begins puberty early at age 10. What effect would you predict this will have on his stature? A. Jim will probably be taller than if he had started puberty later B. Jim will probably be shorter than if he had started puberty later C. Jim will be a giant D. The early onset of puberty will have no effect on Jim s stature
64 marrow is found between the trabeculae of spongy bone. A. Bone B. Yellow C. White D. Gray E. Red
65 ANSWER marrow is found between the trabeculae of spongy bone. A. Bone B. Yellow C. White D. Gray E. Red
66 Parathyroid hormone functions in all of the following ways, except it A. stimulates osteoclast activity. B. increases the rate of calcium absorption. C. decreases the rate of calcium excretion. D. raises the level of calcium ion in the blood. E. stimulates osteoblast activity.
67 ANSWER Parathyroid hormone functions in all of the following ways, except it A. stimulates osteoclast activity. B. increases the rate of calcium absorption. C. decreases the rate of calcium excretion. D. raises the level of calcium ion in the blood. E. stimulates osteoblast activity.
68 During fracture repair, which of the following is the first step A. Formation of a fracture hematoma B. Soft callus formation C. Bone remodeling D. Hard callus formation
69 ANSWER During fracture repair, which of the following is the first step A. Formation of a fracture hematoma B. Soft callus formation C. Bone remodeling D. Hard callus formation
70 In the process of osteolysis, A. new bone is formed. B. an organic framework is formed. C. the bony matrix is dissolved to release the stored minerals. D. osteoblasts form the osteoid that is later calcified. E. fractured bones repair themselves.
71 ANSWER In the process of osteolysis, A. new bone is formed. B. an organic framework is formed. C. the bony matrix is dissolved to release the stored minerals. D. osteoblasts form the osteoid that is later calcified. E. fractured bones repair themselves.
72 A fracture where a piece of bone is torn away is a fracture A. Stress B. Indirect C. Pathologic D. Avulsion E. Depressed
73 ANSWER A fracture where a piece of bone is torn away is a fracture A. Stress B. Indirect C. Pathologic D. Avulsion E. Depressed
74 A fracture due to weakness from disease such as osteoporosis A. Stress B. Indirect C. Pathologic D. Avulsion E. Depressed
75 ANSWER A fracture due to weakness from disease such as osteoporosis A. Stress B. Indirect C. Pathologic D. Avulsion E. Depressed
76 Vitamin D is necessary for A. collagen formation. B. absorption and transport of calcium and phosphate ions. C. reducing osteoblast activity. D. increasing osteoclast activity. E. the formation of the organic framework of bone.
77 ANSWER Vitamin D is necessary for A. collagen formation. B. absorption and transport of calcium and phosphate ions. C. reducing osteoblast activity. D. increasing osteoclast activity. E. the formation of the organic framework of bone.
78 Which of the following individuals would have the largest humerus? A. Swimmer B. Ice skater C. Ballerina D. Distance runner E. Weight lifter
79 ANSWER Which of the following individuals would have the largest humerus? A. Swimmer B. Ice skater C. Ballerina D. Distance runner E. Weight lifter
80 Which of the following hormones helps to maintain bone density A. Parathyroid hormone B. Estrogen C. Insulin D. Oxytocin
81 ANSWER Which of the following hormones helps to maintain bone density A. Parathyroid hormone B. Estrogen C. Insulin D. Oxytocin
82 bone reduces the weight of the skeleton and makes it easier for muscles to move the bones. A. Short B. Irregular C. Spongy D. Sesamoid E. Long
83 ANSWER bone reduces the weight of the skeleton and makes it easier for muscles to move the bones. A. Short B. Irregular C. Spongy D. Sesamoid E. Long
84 A lack of exercise would A. cause bones to become thicker. B. cause bones to store more calcium. C. result in thin and brittle bones. D. increase the length of a bone. E. have no effect on a bone.
85 ANSWER A lack of exercise would A. cause bones to become thicker. B. cause bones to store more calcium. C. result in thin and brittle bones. D. increase the length of a bone. E. have no effect on a bone.
86 What is the term for a fracture at the distal radius of the wrist? A. Colle s fracture B. Pott s fracture C. Avulsion fracture D. Comminuted fracture E. Greenstick fracture
87 ANSWER What is the term for a fracture at the distal radius of the wrist? A. Colle s fracture B. Pott s fracture C. Avulsion fracture D. Comminuted fracture E. Greenstick fracture
88 In the epiphyseal plate, chondrocytes swell and die in which layer A. Zone of hypertrophy B. Zone of resting cartilage C. Zone of calcified cartilage D. Zone of proliferating cartilage
89 ANSWER In the epiphyseal plate, chondrocytes swell and die in which layer A. Zone of hypertrophy B. Zone of resting cartilage C. Zone of calcified cartilage D. Zone of proliferating cartilage
90 During fracture repair, which of the following is the second step? A. Formation of a fracture hematoma B. Bone remodeling C. Hard callus formation D. Spongy bone is laid down E. Soft callus formation
91 ANSWER During fracture repair, which of the following is the second step? A. Formation of a fracture hematoma B. Bone remodeling C. Hard callus formation D. Spongy bone is laid down E. Soft callus formation
92 When stress is applied to a bone, A. the minerals in the bone produce a weak electrical field that attracts osteoblasts. B. osteoclast activity increases. C. the bone becomes thin and brittle. D. the bone compensates by becoming thinner in the region of stress. E. trabeculae are formed perpendicular to the zone of stress to increase strength.
93 ANSWER When stress is applied to a bone, A. the minerals in the bone produce a weak electrical field that attracts osteoblasts. B. osteoclast activity increases. C. the bone becomes thin and brittle. D. the bone compensates by becoming thinner in the region of stress. E. trabeculae are formed perpendicular to the zone of stress to increase strength.
94 The narrow passageways that contain cytoplasmic extensions of osteocytes are called A. lamellae. B. lacunae. C. canaliculi. D. marrow cavities. E. matrices.
95 ANSWER The narrow passageways that contain cytoplasmic extensions of osteocytes are called A. lamellae. B. lacunae. C. canaliculi. D. marrow cavities. E. matrices.
96 The outermost layer of compact bone is the endosteum. A. True B. False
97 ANSWER The outermost layer of compact bone is the endosteum. A. True B. False
98 For women, the drop in estrogen as part of aging has what effect on bone tissue? A. a decrease in protein synthesis B. demineralization C. a decreased number of osteoblasts D. a decreased number of osteoclasts E. a decreased number of osteoprogenitor cells
99 ANSWER For women, the drop in estrogen as part of aging has what effect on bone tissue? A. a decrease in protein synthesis B. demineralization C. a decreased number of osteoblasts D. a decreased number of osteoclasts E. a decreased number of osteoprogenitor cells
100 A condition that produces a reduction in bone mass sufficient to compromise normal function is A. osteopenia. B. osteoporosis. C. osteomyelitis. D. osteitis. E. osteomalacia.
101 ANSWER A condition that produces a reduction in bone mass sufficient to compromise normal function is A. osteopenia. B. osteoporosis. C. osteomyelitis. D. osteitis. E. osteomalacia.
102 The type of bone that is adapted to withstand stresses that arrive from a limited range of directions is bone. A. spongy B. trabecular C. compact D. lamellar E. irregular
103 ANSWER The type of bone that is adapted to withstand stresses that arrive from a limited range of directions is bone. A. spongy B. trabecular C. compact D. lamellar E. irregular
104 During endochondral bone formation, the primary center of ossification forms in the A. Proximal epiphysis B. Distal epiphysis C. Epiphyseal plate D. Diaphysis E. Metaphysis
105 ANSWER During endochondral bone formation, the primary center of ossification forms in the A. Proximal epiphysis B. Distal epiphysis C. Epiphyseal plate D. Diaphysis E. Metaphysis
106 The following are steps in the process of bone repair. 1. Cells of the periosteum and endosteum divide rapidly. 2. A fracture hematoma forms. 3. Osteoclasts and osteoblasts remodel the region of the injury. 4. An external callus encircles the bone at the level of the fracture and an internal callus organizes within the marrow cavity. 5. Osteoblasts replace the central cartilages with spongy bone. 6. Cells at the center of the callus differentiate into chondrocytes and cells at the edges of the callus differentiate into osteoblasts. The correct order of these events is: A. 2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 3. B. 1, 2, 4, 6, 5, 3. C. 3, 2, 1, 4, 6, 5. D. 2, 1, 4, 6, 5, 3. E. 1, 4, 2, 5, 6, 3.
107 ANSWER The following are steps in the process of bone repair. 1. Cells of the periosteum and endosteum divide rapidly. 2. A fracture hematoma forms. 3. Osteoclasts and osteoblasts remodel the region of the injury. 4. An external callus encircles the bone at the level of the fracture and an internal callus organizes within the marrow cavity. 5. Osteoblasts replace the central cartilages with spongy bone. 6. Cells at the center of the callus differentiate into chondrocytes and cells at the edges of the callus differentiate into osteoblasts. The correct order of these events is: A. 2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 3. B. 1, 2, 4, 6, 5, 3. C. 3, 2, 1, 4, 6, 5. D. 2, 1, 4, 6, 5, 3. E. 1, 4, 2, 5, 6, 3.
108 The function of the epiphyseal plate is to A. Allow more flexiblity in a long bone B. Allow a means by which the bone can increase in diameter C. Allow a means by which bone can increase in length D. Provide nourishment to isolated osteocytes
109 ANSWER The function of the epiphyseal plate is to A. Allow more flexiblity in a long bone B. Allow a means by which the bone can increase in diameter C. Allow a means by which bone can increase in length D. Provide nourishment to isolated osteocytes
110 The function of osteoblasts is to A. Breakdown bone B. Produce blood cells C. Produce new bone formation D. Add new tissue to the periosteum E. Provide nourishment to the cells of the articular cartilage
111 ANSWER The function of osteoblasts is to A. Breakdown bone B. Produce blood cells C. Produce new bone formation D. Add new tissue to the periosteum E. Provide nourishment to the cells of the articular cartilage
112 Intramembranous ossification begins with the cells. A. osteoclast B. osteoprogenitor C. mesenchymal D. osteoblasts E. osteocytes
113 ANSWER Intramembranous ossification begins with the cells. A. osteoclast B. osteoprogenitor C. mesenchymal D. osteoblasts E. osteocytes
114 The tiny plates of bone material found in spongy bone are called A. osteons. B. trabeculae. C. concentric lamellae. D. interstitial lamellae. E. lacunae.
115 ANSWER The tiny plates of bone material found in spongy bone are called A. osteons. B. trabeculae. C. concentric lamellae. D. interstitial lamellae. E. lacunae.
116 When an osteoblast beomes isolated in a lacuna, it is transformed into a(n) A. Macrophage B. Osteocyte C. Osteoclast D. Fibroblast E. Osteal fiber
117 ANSWER When an osteoblast beomes isolated in a lacuna, it is transformed into a(n) A. Macrophage B. Osteocyte C. Osteoclast D. Fibroblast E. Osteal fiber
118 fractures are completely internal; they do not break through the skin. A. Open B. Closed C. Compound D. Recurrent E. both B and D
119 ANSWER fractures are completely internal; they do not break through the skin. A. Open B. Closed C. Compound D. Recurrent E. both B and D
120 The central canal of an osteon contains A. bone marrow. B. osteocytes. C. concentric lamellae. D. blood vessels. E. lacunae.
121 ANSWER The central canal of an osteon contains A. bone marrow. B. osteocytes. C. concentric lamellae. D. blood vessels. E. lacunae.
122 Collagen is secreted by A. Mesenchyme cells B. Osteoblasts C. Osteoclasts D. Hyroxyapatites E. Both B and C are correct
123 ANSWER Collagen is secreted by A. Mesenchyme cells B. Osteoblasts C. Osteoclasts D. Hyroxyapatites E. Both B and C are correct
124 In which step of endochondral ossification does remodeling of the bone occur? A. step 1, cartilage enlargement B. step 2, blood vessel formation around cartilage edges C. step 3, blood vessel penetration of cartilage and central region D. step 4, growth and marrow cavity creation E. both B and D
125 ANSWER In which step of endochondral ossification does remodeling of the bone occur? A. step 1, cartilage enlargement B. step 2, blood vessel formation around cartilage edges C. step 3, blood vessel penetration of cartilage and central region D. step 4, growth and marrow cavity creation E. both B and D
126 All of the following are normal sites of red blood cell formation EXCEPT A. Clavicle B. Hip bone C. Rib D. Sternum E. Vertebral bodies
127 ANSWER All of the following are normal sites of red blood cell formation EXCEPT A. Clavicle B. Hip bone C. Rib D. Sternum E. Vertebral bodies
128 All of the following bones would be produced via endochondral ossification except the A. Tibia B. Femur C. Frontal bone D. Humerus E. radius
129 ANSWER All of the following bones would be produced via endochondral ossification except the A. Tibia B. Femur C. Frontal bone D. Humerus E. radius
130 A fracture where the shaft of one bone is broken and the adjacent bone is bent is best described as a fracture. A. compression B. Pott s C. displaced D. greenstick E. Colles
131 ANSWER A fracture where the shaft of one bone is broken and the adjacent bone is bent is best described as a fracture. A. compression B. Pott s C. displaced D. greenstick E. Colles
132 The medullary cavity of bones contains A. compact bone. B. osteons. C. cartilage. D. marrow. E. periosteum.
133 ANSWER The medullary cavity of bones contains A. compact bone. B. osteons. C. cartilage. D. marrow. E. periosteum.
134 Growth at the epiphyseal plate is shut down by A. Vitamin A B. Human growth hormone C. Calcitonin D. PTH E. estrogens
135 ANSWER Growth at the epiphyseal plate is shut down by A. Vitamin A B. Human growth hormone C. Calcitonin D. PTH E. estrogens
136 While on a school skiing trip in Colorado, Heidi falls and breaks her femur. What would you expect to see as a part of her nursing assessment several hours after the fall? A. hypertension B. tachycardia C. erythema D. hematoma E. cyanosis
137 ANSWER While on a school skiing trip in Colorado, Heidi falls and breaks her femur. What would you expect to see as a part of her nursing assessment several hours after the fall? A. hypertension B. tachycardia C. erythema D. hematoma E. cyanosis
138 The cells responsible for maintaining the daily cellular activities of bone tissue, such as exchange of nutrients and wastes with blood, are the A. Osteogenic cells B. Osteoblasts C. Osteoclasts D. Osteocytes E. chondroblasts
139 ANSWER The cells responsible for maintaining the daily cellular activities of bone tissue, such as exchange of nutrients and wastes with blood, are the A. Osteogenic cells B. Osteoblasts C. Osteoclasts D. Osteocytes E. chondroblasts
140 Bone constantly remodels and redistributes its matrix along lines of A. Blood flow B. Nervous stimulation C. Canaliculi D. Mechanical stress E. Overlying muscles
141 ANSWER Bone constantly remodels and redistributes its matrix along lines of A. Blood flow B. Nervous stimulation C. Canaliculi D. Mechanical stress E. Overlying muscles
142 The shaft of a long bone is called the A. epiphysis. B. diaphysis. C. epiphyseal plate. D. metaphysis. E. lamella.
143 ANSWER The shaft of a long bone is called the A. epiphysis. B. diaphysis. C. epiphyseal plate. D. metaphysis. E. lamella.
144 Bones that develop within tendons are called bones. A. irregular B. sesamoid C. sutural D. Wormian E. tendon
145 ANSWER Bones that develop within tendons are called bones. A. irregular B. sesamoid C. sutural D. Wormian E. tendon
146 A bedridden person loses bone mass because of A. Decreased calcitonin activity due to immobility B. Lack of sufficient mechanical stress on bones C. Increased conversion of monocytes to osteoclasts D. Pressure on the kidney that leads to reduced calcitriol production E. Insufficient blood flow to bones
147 ANSWER A bedridden person loses bone mass because of A. Decreased calcitonin activity due to immobility B. Lack of sufficient mechanical stress on bones C. Increased conversion of monocytes to osteoclasts D. Pressure on the kidney that leads to reduced calcitriol production E. Insufficient blood flow to bones
148 All of the following are effects of parathyroid hormone except A. Increased protein synthesis B. Increased numbers and activity of osteoclasts C. Reabsorption of calcium ions by the kidney D. Elimination of phosphate ions by the kidney E. Promotion of calcitriol production by the kidney
149 ANSWER All of the following are effects of parathyroid hormone except A. Increased protein synthesis B. Increased numbers and activity of osteoclasts C. Reabsorption of calcium ions by the kidney D. Elimination of phosphate ions by the kidney E. Promotion of calcitriol production by the kidney
150 Bones are more brittle in the elderly because A. Levels of calcitonin are higher in the elderly B. There is less collagen relative to the amount of mineral salts C. Low levels of growth hormone prevent deposition of calcium in bone D. The calcium salts in the bone matrix are of a different type than those in younger people E. Too much collagen takes up space that should be occupied by hydroxyapatites
151 ANSWER Bones are more brittle in the elderly because A. Levels of calcitonin are higher in the elderly B. There is less collagen relative to the amount of mineral salts C. Low levels of growth hormone prevent deposition of calcium in bone D. The calcium salts in the bone matrix are of a different type than those in younger people E. Too much collagen takes up space that should be occupied by hydroxyapatites
152 The lining of the marrow cavity is called the A. endosteum. B. periosteum. C. epimysium. D. perimysium. E. perichondrium.
153 ANSWER The lining of the marrow cavity is called the A. endosteum. B. periosteum. C. epimysium. D. perimysium. E. perichondrium.
154 Small, flat, oddly shaped bones found between some of the large flat bones of the skull are called bones. A. irregular B. sesamoid C. Sutural (wormian) D. sagittal E. tendon
155 ANSWER Small, flat, oddly shaped bones found between some of the large flat bones of the skull are called bones. A. irregular B. sesamoid C. Sutural (wormian) D. sagittal E. tendon
156 The lacunae of bone contain A. blood cells. B. osteocytes. C. chondroblasts. D. bone marrow. E. osteons.
157 ANSWER The lacunae of bone contain A. blood cells. B. osteocytes. C. chondroblasts. D. bone marrow. E. osteons.
158 Which of the following is a condition, usually in children, in which bones fail to calcify resulting in bone defromities? A. Osteogenic sarcoma B. Rickets C. Osteoporosis D. Osteoarthritis E. Paget s disease
159 ANSWER Which of the following is a condition, usually in children, in which bones fail to calcify resulting in bone defromities? A. Osteogenic sarcoma B. Rickets C. Osteoporosis D. Osteoarthritis E. Paget s disease
160 Calcification refers to the A. formation of new bone tissue. B. deposition of calcium salts within a tissue. C. deposition of calcium salts within a bone. D. release of calcium from bone. E. repair of fractured bones.
161 ANSWER Calcification refers to the A. formation of new bone tissue. B. deposition of calcium salts within a tissue. C. deposition of calcium salts within a bone. D. release of calcium from bone. E. repair of fractured bones.
162 If the rate of osteolysis exceeds osteogenesis, bones will A. grow. B. become thicker. C. become demineralized. D. become stronger. E. become calcified.
163 ANSWER If the rate of osteolysis exceeds osteogenesis, bones will A. grow. B. become thicker. C. become demineralized. D. become stronger. E. become calcified.
164 The basic functional units of mature compact bone are called A. lacunae. B. osteocytes. C. osteons. D. canaliculi. E. lamellae.
165 ANSWER The basic functional units of mature compact bone are called A. lacunae. B. osteocytes. C. osteons. D. canaliculi. E. lamellae.
166 During appositional growth A. bones grow longer. B. bones grow wider. C. bone is replaced by cartilage. D. the epiphysis fuses with the diaphysis. E. osteoblasts are inactive.
167 ANSWER During appositional growth A. bones grow longer. B. bones grow wider. C. bone is replaced by cartilage. D. the epiphysis fuses with the diaphysis. E. osteoblasts are inactive.
168 The following are major steps in the process of intramembranous ossification. 1. Clusters of osteoblasts form osteoid that becomes mineralized. 2. Osteoblasts cluster together to form an ossification center. 3. Small struts of bone called spicules radiate out from the ossification centers to join with neighboring spicules. 4. Osteoblasts differentiate within a connective tissue at the site of arterioles. The correct order for these events is A. 4, 1, 2, 3. B. 2, 1, 3, 4. C. 4, 2, 1, 3. D. 2, 3, 1, 4.
169 ANSWER The following are major steps in the process of intramembranous ossification. 1. Clusters of osteoblasts form osteoid that becomes mineralized. 2. Osteoblasts cluster together to form an ossification center. 3. Small struts of bone called spicules radiate out from the ossification centers to join with neighboring spicules. 4. Osteoblasts differentiate within a connective tissue at the site of arterioles. The correct order for these events is A. 4, 1, 2, 3. B. 2, 1, 3, 4. C. 4, 2, 1, 3. D. 2, 3, 1, 4.
170 To maintain healthy, strong bones the elderly should A. Drink plenty of fruit juice to obtain vitamin C B. Select a diet rich in fats and carbohydrates to obtain energy C. Get plenty of rest indoors and save strength D. Remain physically active as long as possible E. Drink plenty of milk to obtain calcium
171 ANSWER To maintain healthy, strong bones the elderly should A. Drink plenty of fruit juice to obtain vitamin C B. Select a diet rich in fats and carbohydrates to obtain energy C. Get plenty of rest indoors and save strength D. Remain physically active as long as possible E. Drink plenty of milk to obtain calcium
172 The deposition of calcium salts in tissues other than bone is referred to as A. endochondral ossification. B. intramembranous ossification. C. calcification. D. osteogenesis. E. remodeling.
173 ANSWER The deposition of calcium salts in tissues other than bone is referred to as A. endochondral ossification. B. intramembranous ossification. C. calcification. D. osteogenesis. E. remodeling.
174 When the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone, A. puberty begins. B. interstitial bone growth begins. C. appositional bone growth begins. D. long bones have reached their adult length. E. the bone becomes more brittle.
175 ANSWER When the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone, A. puberty begins. B. interstitial bone growth begins. C. appositional bone growth begins. D. long bones have reached their adult length. E. the bone becomes more brittle.
176 The region in the epiphyseal plate where the cartilage cells are rapidly dividing is called the A. Zone of hypertrophic cartilage B. Zone of resting cartilage C. Zone of calcified cartilage D. Zone of proliferating cartilage E. Metaphysis
177 ANSWER The region in the epiphyseal plate where the cartilage cells are rapidly dividing is called the A. Zone of hypertrophic cartilage B. Zone of resting cartilage C. Zone of calcified cartilage D. Zone of proliferating cartilage E. Metaphysis
178 Which of the following is not formed by intramembranous ossification? A. roof of the skull B. lower jaw C. scapulae D. clavicle E. both C and D
179 ANSWER Which of the following is not formed by intramembranous ossification? A. roof of the skull B. lower jaw C. scapulae D. clavicle E. both C and D
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 6. Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
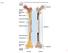 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Bones and Bone Structure
 6 Bones and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Introduction to the Structure and Growth of Bones Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the two main divisions of the skeleton, and list
6 Bones and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Introduction to the Structure and Growth of Bones Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the two main divisions of the skeleton, and list
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Chapter 6. Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Skeletal System. Skeletal System 12/15/15. Bone Classification
 Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the
Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Bone Shapes Long longer than they are wide; have a shaft plus two ends Ex. bones of limbs except wrist and ankle
 SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS 1. Support Bones form the internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. 2. Protection Bones protect soft body organs. 3. Movement Skeletal muscles, which attach
SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS 1. Support Bones form the internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. 2. Protection Bones protect soft body organs. 3. Movement Skeletal muscles, which attach
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Skeletal System Functions
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the erect body. The mandible (jawbone) supports the teeth.
 Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support EXAMPLES: The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight
Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support EXAMPLES: The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Bone. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44789 1 Bone OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m44789 1 Bone OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Trebeculae. Step 4. compact bone. Diploë Pearson Education, Inc.
 Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
The Skeletal S 1Jstem
 . / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
. / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Bone (2) Chapter 8. The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer.
 Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
