Synovial giant cells in rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Shawn Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aniii. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 94 Synovial giant cells in rheumatoid arthritis and other joint diseases A. K. BHAN AND S. ROY Department of Pathology, All-India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Dellhi- 16, India The presence of a distinctive multinucleated giant cell has recently been described in the s,,a vial membrane in rheumatoid arthlitis and its diagnostic significance has been stressed (Grimley and Sokoloff, 1966; Donald and Kerr, 1968). Although passing reference to the presence of multinucleated synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis was made by Hirohata and Kobay.-.s'i (1964), thle occurrence of any such cell has not been mentioned in textbooks describing the pathological features of joint diseases (Allison and Gholrmley, 1931; Collins, 1949; Copeman, 1964; Gardner, 1965). Similar giant cells have not so far been observed in any other arthritic condition in man. We have studied the synovial membrane from cases of rheumatoid arthritis and various other arthritic conditions, including tuberculous arthritis, to find out the presence of giant cells and the results are reported here. Material and methods Synovial biopsies from 6 cases of 'definite' or 'classical' rheumatoid arthritis (Ropes, Bennett, Cobb, Jacox, and Jessar, 1959), twenty cases of tuberculous synovitis, three cases of villonodular synovitis, and eight cases of traumatic arthritis were examined. Synovial membranes collected post mortem from ten normal individuals without any joint disease and from ten cases of osteoarthritis were also included in this study. The cases of rheumatoid arthritis wvere of both sexes and tlheir ages varied from 19 to 65 years. The duration of disease ranred from 9 months to 1 years. Patients with tuberculous arthritis were also of both sexes (age range 8 to 4 yrs; duration of dismase 3 mths to 4 yrs). Tile duration of the traumatic arthritis ranged from 3 mths to yrs. In the 6 cases of rheulmatoid arthritis, serological tests (sensitized sheep cell agglutination) for rheumatoid factor wer positive in eleven cases and negative in eleve i; in the remaining four patients the test was not carried out. Serological tests for rheumatoid factor were negative in the six cases of tuberculous arthritis in which they were performed. The specimens were fixed in 1 per cont. neutral formalin processed for li-ht microscopy and 6,u raraffin sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin. The representative sections were also stained with periodic acid-schiff, with and without diastase digestion, Alcian blue (ph 6), and colloidal iron stain (McManus and Accepted for publication November 3, 197 Mowry, 196) to study the cytoplasmic charactersiscs of the giant cells. Two or three blocks were examined from most of the cases. Results Mor-phology anid locationi oj synovial giant cell The synovial giant cells obse;ved in all the conditions described below have similar mor-phological features. They are round or ovoid containing slightly sasophilic c.y toplasm and four to ten round or oval vesicular or densely staining nuclei, situated at the periphery of the cells (Figs 1,, 3, and 4). The giant cells are usually located in the superficial sub-synovial tissue just deep to the deeper layer of the synovial lining cells but are present at times within the synovial layer (Fig. 5, overleaf). They are rarely seen very deep in the sub-synovial tissue. Not infrequently, binucleated cells, which appear to be the transitional forms from the synovial lining cells to the fully developed giant cells, are seen (Figs 1 and 5). These giant cells can be easily distinguished frorr the Langhans's giant cells of tuberculosis which are often much larger than the synovial giant cells, have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, and are usually present much deeper in the sub-synovial tissue in i-elation to the granulomas. ; % -> I.' vk 1 CW,, A 4 P %:.^ ). x 4:.44 O n. E *', FIG. l Synovial membrane from a case of rheumlatoid arthritis, showing many giant cells in an area of' wellmarked hyperplasia of the synovial intimal cells. Haematoxylin and eosin. x 16. Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 May Downloaded from on 1 November 18 by guest. Protected by
2 Synovial giant cells 95 vn- AbA v - #v The giant cells usually occur in groups and are usually present in areas showing moderate or marked synovial cell proliferation. However, the giant cells can sometimes be seen in areas with no evidence of synovial cell hyperplasia (Fig. ). #'#^-1 g v -i- FIG. 3 Synovial membrane from a case of tuberculous arthritis, showing giant cells located at the superficial sub-synovium in an area of mild synovial cell proliferation. No granuloma was present in the vicinity. Haematoxylin and eosin. x 33.. * a lb II.4 Snva ebaefo llndlrsnvts foa cells in the susnoil tissue.hamtoyi and es 33 fig. 4el n tt u-ynovial ms ueoo ṡam ao y noi eosin. x 33. tis,d FIG. Synovial membrane from a case of tuberculous arthritis, showing giant cells in areas with no synovial intimal cell hyper- 4f* plasia. There was no evidence of granuloma i in the vicinity. Haemotoxylin and eosin..: x53. On periodic acid-schiff staining, the cytoplasm of the giant cells gives a strongly positive reaction which is resistant to diastase digestion. The cytoplasm is either negative or only faintly positive with Alcian blue and colloidal iron stains. Occurrence ofgiant cells in various diseases An analysis of the occurrence of synovial giant cells in the different arthritic conditions examined by us is presented in the Table (overleaf). The giant cells were noted in sixteen out of 6 cases of r.aeumatoid, four out of twenty cases of tuberculous, and two out of eight cases of traumatic arthritis, and in one out of three cases of villonodular synovitis. In rheumatoid arthritis these cells were selen only occasionally in two cases and more frequently in fourteen, five of which showed them in many foci. Their presence was unrelated to the presence or absence of the rheumatoid factor in the p-atient's serum. The age of the patient and the duration of the disease were also unrelated to their occurr%-nce, except that they were not seen in cases of less than 1 year's duration. Although the giant cells usually occurred in the synovium showing mode.:ate- or marked proliferation of the synovial cells (Fig. 1), a few could at times be seen in specimens in which synovial cell proliferation was mild or absent. In one case many giant cells were present in a synovial membrane which showed only mild proliferation of synovial cells In tuberculous arth -itis, four out of sixteen cases showed synovial giant cells, and in two of these the cells w-e:e numerous, with well-marked villous proliferation of the synovial intima. As has been noted already these giant cells could be easily distinguished from those which form part of the granulomatous inflammation of tuberculosis. Occasionally, a larg,-e Langhans's type of giant cell was noted in the synovial intima (Fig. 6, ove.-leaf) adjace-nt to a granuloma situated in the superi-cial sub-synovial tissue. Synovial giant cells in tuber- Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 May Downloaded from on 1 November 18 by guest. Protected by
3 96 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases FIG. 5 Synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis, showing giant cells within the synovial intimal layer andjust below the intima. Haematoxylin and eosin. x 53. Table Occurrence of synovial giant cells in various arthritic conditions Disease No. of Synovial giant cells present cases Occasional Rheumatoid arthritis Total 6 9 Sero-positive 11 4 Sero-negative Serology not tested Tuberculous arthritis Traumatic arthritis 8 1 Villonodular synovitis 3 1 Normal 1 Osteoarthritis 1 FIG. 6 Langhans's giant cell in the intimal layer in a case of tuberculous arthritis. Haematoxylin and eosin. x Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 May Downloaded from culous arthritis were, however, present in areas with None of the ten cases of osteoarthritis or of the ao granulomas. In tuberculous arthritis also, giant ten subjectss with normal synovial membranes showed cells were not seen in cases of less than one year's any synovieal giant cells. duration. Synovial giant cells were seen in two of the eight Diuion cases of non-specific synovitis; in both the cells were few and there was only mild to moderate synovial Diagnostic significance of synovial giant cells cell proliferation. Various tylpes of giant cells are known to occur in A small number of synovial giant cells containing the synovi; al membrane in different arthritic con- most common of these is the foreign haemosiderin pigment were present in one of the ditions. Thle three cases of villonodular synovitis (Fig. 4). body type 4of giant cells seen in traumatic, rheuma- on 1 November 18 by guest. Protected by
4 toid, osteo-, and gouty arthritis. Except in the last condition, the foreign body giant cells in synovial tissue form as a reaction to joint debris, especially fragments of articular cartilage and/or bone. The occurrence oflanghans's giant cells in granulomatous inflammation of the synovial tissue in tuberculosis and of giant cells in pigmented villonodular synovitis is also well known. A distinctive giant cell found in the synovial membrane in cases of rheumatoid arthritis was designated 'synovial giant cell' by Grimley and Sokoloff (1966). These authors failed to find similar giant cells in normal subjects or in other arthritic conditions, and they considered that presence of synovial giant cells, which were seen only in seropositive cases, to be a distinctive feature of rheumatoid arthritis. Similar giant cells were also reported by Donald and Kerr (1968) in severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis, and because they also failed to find these cells in non-rheumatoid conditions they suggested that they might help in establishing the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. In the present study, although the giant cells were frequently present in rheumatoid arthritis both sero-positive and sero-negative, they were also seen in a few cases of tuberculous and non-specific arthritis and in one case of villonodular synovitis (Table). They were not present in normal synovial membrane or in cases of osteoarthritis. It appears, therefore, that although synovial giant cells are more frequent in rheumatoid arthritis, their presence should not be considered as specific for the disease. Muirden and Peace (1969) demonstrated the presence of similar giant cells in arthritis produced experimentally by the intra-articular injection of carragheenin, which again indicates their non-specific nature. It should be noted that in our study the giant cells could be seen in both sero-positive and sero-negative cases of rheumatoid arthritis and that there was no correlation between their occurrence and the duration of the disease. It is interesting that the giant cells are usually seen in synovial membranes that show marked proliferation of the synovial cells, be it in rheumatoid, tuberculous, or non-specific arthritis; only occasionally do giant cells appear in synovium Synovial giant cells 97 showing only mild proliferative activity or none. Origin of synovial giant cells On the basis of their combined light and electron microscopic study, Grimley and Sokoloff (1966) concluded that these giant cells are derived from the type-a synovial cells which are known to be phagocytic in nature. The presence of synovial giant cells in close proximity to the synovial intima (even at times within the synovial intimal layer) and also the frequent presence of transitional forms between synovial and giant cells also point to their origin from synovial lining cells. Type-A cells are also known to contain many lysosomal bodies. The presence of PAS-positive granules in the synovial giant cells appears to represent the lysosomal structures within them. Electron microscopical observation has also shown many lysosomal bodies within the synovial giant cells (Grimley and Sokoloff, 1966). The precise significance of their presence cannot yet be ascertained. It is considered likely that they form as a reaction to some chronic injury directed primarily towards the synovial lining cells, resulting in synovial hyperplasia and giant cell transformation. The offending agent may be a micro-organism in the form of mycoplasma (Bartholomew, 1965) or diphtheroid bacillus (Stewart, Alexander, and Duthie, 1969), the two agents suggested as possible infective organisms in rheumatoid arthritis, tubercle bacillus in tuberculous synovitis, foreign body in non-specific arthritis, and some undetermined agent in villonodular synovitis. Summary The synovial membrane from normal subjects and patients with arthritic conditions were studied for the presence of distinctive synovial giant cells. Although synovial giant cells were most frequently seen in cases of rheumatoid arthritis, they were also present in a small number of cases of tuberculous arthritis, traumatic arthritis, and villonodular synovitis. The presence of synovial giant cells is not therefore considered to be specific for rheumatoid arthritis. References ALLISON, N., AND GHORMLEY, R. K. (1931) 'Diagnosis in joint disease. A clinical and pathological study of arthritis'. Wood, New York; Oxford University Press, London. BARTHOLOMEW, L. E. (1965) Arthr. and Rheum., 8, 376 (Isolation and characterization of mycoplasmas (PPLO) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and Reiter's syndrome). COLLINS, D. H. (1949) 'The Pathology of Articular and Spinal Diseases'. Arnold, London. COPEMAN, W. S. C. (1964) 'Textbook of the Rheumatic Diseases', 3rd ed. Livingstone, Edinburgh. DONALD, K. J., AND KERR, J. F. R. (1968) Med. J. Aust., 1, 761 (Giant cells in the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis). G Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 May Downloaded from on 1 November 18 by guest. Protected by
5 98 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases GARDNER, D. L. (1965) 'Pathology of the Connective Tissue Diseases'. Arnold, London. GRImLEY, P. M., AND SOKOLOFF, L. (1966) Amer. J. Path., 49, 931 (Synovial giant cells in rheumatoid arthritis). HIROHATA, K., AND KOBAYASHI, I. (1964) Kobe J. med. Sci., 1, 195 (Fine structures of the synovial tissues in rheumatoid arthritis). McMANus, J. F. A., AND MowRY, R. W. (196) 'Staining Methods: Histologic and Histochemical', p Hoeber, New York. MURDDEN, K. D., AND PEACE, G. (1969) Ann. rheum. Dis., 8, 39 (Light and electron microscopic studies in carragheenin, adjuvant, and tuberculin-induced arthritis). RopEs, M. W., BENNErr, G. A., COBB, S., JACOX, R., A JEssAR, R. A. (1959) Ibid., 18, 49 (Diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 1958 revision). STEWART, S. M., ALExANDER, W. R. M., AND Dunm, J. J. R. (1969) Ibid., 8, 477 (Isolation of diphtheroid bacilli from synovial membrane and fluid in rheumatoid arthritis). Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 May Downloaded from on 1 November 18 by guest. Protected by
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
inflammation: a six day air pouch model in the mouse
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 873-877 Mast cells in newly formed lining tissue during acute inflammation: a six day air pouch model in the mouse Y M SIN,' A D SEDGWICK,2 E P CHEA,' AND D
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 873-877 Mast cells in newly formed lining tissue during acute inflammation: a six day air pouch model in the mouse Y M SIN,' A D SEDGWICK,2 E P CHEA,' AND D
HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
Microscopic Anatomy of Inferior Medullary Velum Of Cerebellum
 32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Light and electron microscopy study of capillaries in normal and inflammatory human synovial membrane
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 556-562 Light and electron microscopy study of capillaries in normal and inflammatory human synovial membrane ANTOINE DRYLL, JULIETTE LANSAMAN, PAULE CAZALIS, ANDRI_ P. PELTIER,
J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 556-562 Light and electron microscopy study of capillaries in normal and inflammatory human synovial membrane ANTOINE DRYLL, JULIETTE LANSAMAN, PAULE CAZALIS, ANDRI_ P. PELTIER,
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Corneal blood staining after hyphaema
 Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Synovial fluid Waaler-Rose and latex tests
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 67 Synovial fluid Waaler-Rose and latex tests E. C. HUSKISSON, F. DUDLEY HART, AND B. W. LACEY Westminster Hospital, London Positive serum Waaler-Rose and Latex tests provide
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 67 Synovial fluid Waaler-Rose and latex tests E. C. HUSKISSON, F. DUDLEY HART, AND B. W. LACEY Westminster Hospital, London Positive serum Waaler-Rose and Latex tests provide
Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages)
 J. clin. Path. (1966), 19, 368 Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages) in the rectum J. G. AZZOPARDI AND D. J. EVANS' From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Postgraduate Medical School, London
J. clin. Path. (1966), 19, 368 Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages) in the rectum J. G. AZZOPARDI AND D. J. EVANS' From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Postgraduate Medical School, London
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS*
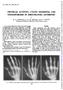 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Malabsorption in rheumatoid disease
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 626 Malabsorption in rheumatoid disease N. H. DYER, M. J. KENDALL, AND C. F. HAWKINS Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham 15 Rheumatoid disease is a systemic disorder involving
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 626 Malabsorption in rheumatoid disease N. H. DYER, M. J. KENDALL, AND C. F. HAWKINS Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham 15 Rheumatoid disease is a systemic disorder involving
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Straingauge plethysmography in the
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 194 Straingauge plethysmography in the assessment of joint inflammation I. VADASZ Department of Physical Medicine and Rheumatology, Guy's Hospital, London The quantitation of
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 194 Straingauge plethysmography in the assessment of joint inflammation I. VADASZ Department of Physical Medicine and Rheumatology, Guy's Hospital, London The quantitation of
A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for
 A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for same. Came to us with recurrence since last one year with
A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for same. Came to us with recurrence since last one year with
Transport of intravenously-injected
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 493 Transport of intravenously-injected ferritin across the guinea-pig synovium M. A. CHAMBERLAIN, V. PETTS, AND E. GOLLINS From the Departments ofrheumatology and Immunology,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 493 Transport of intravenously-injected ferritin across the guinea-pig synovium M. A. CHAMBERLAIN, V. PETTS, AND E. GOLLINS From the Departments ofrheumatology and Immunology,
PREVALENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961),, 11. PREVALENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. S. LAWRENCE From the Empire Rheumatism Council Field Unit, based on the University of Manchester In 1956, a committee of the American
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961),, 11. PREVALENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. S. LAWRENCE From the Empire Rheumatism Council Field Unit, based on the University of Manchester In 1956, a committee of the American
INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE BIOPSY DURING HAND SURGERY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE BIOPSY DURING HAND SURGERY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS By M. RILEY, M.B., M.R.C.P. and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S R.C.S. (Ed.) M.R.C. Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross
INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE BIOPSY DURING HAND SURGERY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS By M. RILEY, M.B., M.R.C.P. and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S R.C.S. (Ed.) M.R.C. Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross
Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in
 J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
aggregated human y-globulin, and examined under the
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 524 Synovial plasma cells in arthritis rheumatoid Electron microscope and immunofluorescence studies G. V. ORLOVSKAYA, P. Y. MULDIYAROV, AND I. S. KAZAKOVA Institute of Rheumatism,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 524 Synovial plasma cells in arthritis rheumatoid Electron microscope and immunofluorescence studies G. V. ORLOVSKAYA, P. Y. MULDIYAROV, AND I. S. KAZAKOVA Institute of Rheumatism,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123
 BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
Virus resistance transferred from human rheumatoid cells to rabbit synovial cells
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1974), 33,173 Virus resistance transferred from human rheumatoid cells to rabbit synovial cells 1. Methods and results of intra-articular injection of human cells into rabbit joints CAROL
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1974), 33,173 Virus resistance transferred from human rheumatoid cells to rabbit synovial cells 1. Methods and results of intra-articular injection of human cells into rabbit joints CAROL
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
different serological and histological manifestations and a high incidence of D-penicillamine side effects. Materials
 Annals of the Rheu)natic Diseases, 1985, 44, 215-219 Anti-Ro(SSA) positive rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a clinicoserological group of patients with high incidence of D-penicillamine side effects HARALAMPOS
Annals of the Rheu)natic Diseases, 1985, 44, 215-219 Anti-Ro(SSA) positive rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a clinicoserological group of patients with high incidence of D-penicillamine side effects HARALAMPOS
Arthritis and Crohn's disease
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma
 Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Cellular Pathology Department University College London Hospital Rockefeller Building University Street London WC1E 6JJ Contact: Gavyn Barrett
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Cellular Pathology Department University College London Hospital Rockefeller Building University Street London WC1E 6JJ Contact: Gavyn Barrett
Comparison of the effects of alclofenac, flurbiprofen, and prednisolone on acute inflammatory response
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 160-165 Comparison of the effects of alclofenac, flurbiprofen, and prednisolone on acute inflammatory response in the rat J. WOODLAND, B. VERNON-ROBERTS, K.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 160-165 Comparison of the effects of alclofenac, flurbiprofen, and prednisolone on acute inflammatory response in the rat J. WOODLAND, B. VERNON-ROBERTS, K.
CHANGES IN BUCCAL CELLS IN THE ANAEMIAS
 J. clin. Path. (1959), 12, 222. CHANGES IN BUCCAL CELLS IN THE ANAEMIAS BY M. M. BODDINGTON From the Department of Pathology, Churchill Hospital, Headington, Oxford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION DECEMBER 19,
J. clin. Path. (1959), 12, 222. CHANGES IN BUCCAL CELLS IN THE ANAEMIAS BY M. M. BODDINGTON From the Department of Pathology, Churchill Hospital, Headington, Oxford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION DECEMBER 19,
IRON IN THE SYNOVIAL MEMBRANE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OTHER JOINT DISEASES*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 38 IRON IN THE SYNOVIAL MEMBRANE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OTHER JOINT DISEASES* BY K. D. MUIRDEN AND G. B. SENATOR From the University of Melbourne Department of Medicine,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 38 IRON IN THE SYNOVIAL MEMBRANE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OTHER JOINT DISEASES* BY K. D. MUIRDEN AND G. B. SENATOR From the University of Melbourne Department of Medicine,
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease
 A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease R. M. CROSS J. clini. Path. (1968), 21, 0-10 From the Royal Air Force Institute ofpathology and Tropical Medicine, Halton, Buckinghamshire
A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease R. M. CROSS J. clini. Path. (1968), 21, 0-10 From the Royal Air Force Institute ofpathology and Tropical Medicine, Halton, Buckinghamshire
Histology of the lacrimal gland in keratoconjunctivitis sicca
 Brit. _. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 852 Histology of the lacrimal gland in keratoconjunctivitis sicca JOHN WILLIAMSON*, A. A. M. GIBSON**, T. WILSONt, J. V. FORRESTER*, K. WHALEY+, AND W. C. DICK: From the *Eye
Brit. _. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 852 Histology of the lacrimal gland in keratoconjunctivitis sicca JOHN WILLIAMSON*, A. A. M. GIBSON**, T. WILSONt, J. V. FORRESTER*, K. WHALEY+, AND W. C. DICK: From the *Eye
FOREIGN BODY REACTION TO INHALATION OF LENTIL SOUP: GIANT CELL PNEUMONIA *
 J. clin. Path. (1956), 9, 295. FOREIGN BODY REACTION TO INHALATION OF LENTIL SOUP: GIANT CELL PNEUMONIA * BY MARY A. HEAD From the Pathology and Cancer Research Departments, Royal Beatson Memorial Hospital,
J. clin. Path. (1956), 9, 295. FOREIGN BODY REACTION TO INHALATION OF LENTIL SOUP: GIANT CELL PNEUMONIA * BY MARY A. HEAD From the Pathology and Cancer Research Departments, Royal Beatson Memorial Hospital,
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
SYNDROME) BY. these instances they are considered as possibly " rheumatoid " in origin. The inflammation was
 Thorax (1955), 10, 9. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MODIFIED PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN COAL-MINERS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) BY J. GOUGH, D. RIVERS, AND R. M. E. SEAL From the Department of Pathology
Thorax (1955), 10, 9. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MODIFIED PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN COAL-MINERS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) BY J. GOUGH, D. RIVERS, AND R. M. E. SEAL From the Department of Pathology
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
Microscopic Sediment Epithelial Cells
 Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
NON-SILICIOUS, DOUBLY REFRACTILE CRYSTALS IN THE GIANT CELLS OF TUBERCULOSIS
 J. clin. Path. (1958), 11, 23. NON-SILICIOUS, DOUBLY REFRACTILE CRYSTALS IN THE GIANT CELLS OF TUBERCULOSIS BY CHARLES P. FARTHING AND BASIL G. PICKLES From the Departments of Pathology and Gynaecology,
J. clin. Path. (1958), 11, 23. NON-SILICIOUS, DOUBLY REFRACTILE CRYSTALS IN THE GIANT CELLS OF TUBERCULOSIS BY CHARLES P. FARTHING AND BASIL G. PICKLES From the Departments of Pathology and Gynaecology,
Materials and methods SELECTION OF TISSUES. Tissues were obtained from 12 cases of rheumatoid. arthritis, all of whom had received chrysotherapy at
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 477 Selective concentration and localization of gold in macrophages of synovial and other tissues during and after chrysotherapy in rheumatoid patients B. VERNON-ROBERTS*,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 477 Selective concentration and localization of gold in macrophages of synovial and other tissues during and after chrysotherapy in rheumatoid patients B. VERNON-ROBERTS*,
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
peripheral joints in ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 579-586 Histopathology of the synovial membrane of peripheral joints in ankylosing spondylitis P. A. REVELL AND V. MAYSTON From the Bone and Joint Research Unit
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 579-586 Histopathology of the synovial membrane of peripheral joints in ankylosing spondylitis P. A. REVELL AND V. MAYSTON From the Bone and Joint Research Unit
The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes
 Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
glands: a correlation in postmortem subjects
 J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 690-694 Lymphocytic sialadenitis in the major and minor glands: a correlation in postmortem subjects D. M. CHISHOLM, J. P. WATERHOUSE, AND D. K. MASON From the Department of Oral
J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 690-694 Lymphocytic sialadenitis in the major and minor glands: a correlation in postmortem subjects D. M. CHISHOLM, J. P. WATERHOUSE, AND D. K. MASON From the Department of Oral
Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino
 Supplementary Materials Online: Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino synovitis grade and Mankin cartilage pathology scale Hemophilic synovitis was graded 0-10
Supplementary Materials Online: Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino synovitis grade and Mankin cartilage pathology scale Hemophilic synovitis was graded 0-10
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
syndrome and other rheumatic disorders
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 312-316 A study of headaches and migraine in Sjogren's syndrome and other rheumatic disorders B PAL,1 C GIBSON,2 J PASSMORE,' I D GRIFFITHS,' AND W C DICK' From
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 312-316 A study of headaches and migraine in Sjogren's syndrome and other rheumatic disorders B PAL,1 C GIBSON,2 J PASSMORE,' I D GRIFFITHS,' AND W C DICK' From
SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID PROTEINS IN ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 51. SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID PROTEINS IN ARTHRITIS BY MATTHEW WILKINSON AND BRIAN S. JONES From the Clinical Research Department, Charing Cross Hospital, and the Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 51. SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID PROTEINS IN ARTHRITIS BY MATTHEW WILKINSON AND BRIAN S. JONES From the Clinical Research Department, Charing Cross Hospital, and the Department
Ultrastructural characteristics of the synovial membrane in idiopathic haemochromatosis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 465 Ultrastructural characteristics of the synovial membrane in idiopathic haemochromatosis H. RALPH SCHUMACHER, Jr. From the University ofpennsylvania School ofmedicine, Arthritis
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 465 Ultrastructural characteristics of the synovial membrane in idiopathic haemochromatosis H. RALPH SCHUMACHER, Jr. From the University ofpennsylvania School ofmedicine, Arthritis
HYPERTROPHIC OSTEO-ARTHROPATHY IN POLYARTERITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1956), 15, 46. HYPERTROPHIC OSTEO-ARTHROPATHY IN POLYARTERITIS BY R. R. H. LOVELL AND G. B. D. SCOTT From the Medical Unit and Department of Morbid Anatomy, St. Mary's Hospital, Paddington
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1956), 15, 46. HYPERTROPHIC OSTEO-ARTHROPATHY IN POLYARTERITIS BY R. R. H. LOVELL AND G. B. D. SCOTT From the Medical Unit and Department of Morbid Anatomy, St. Mary's Hospital, Paddington
Synovial fluid cells in Reiter's syndrome
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 852-856 Synovial fluid cells in Reiter's syndrome DAN NORDSTROM,' YRJO T KONTTINEN,' VILLE BERGROTH,' AND MARJATTA LEIRISALO-REPO2 From the 'Fourth Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 852-856 Synovial fluid cells in Reiter's syndrome DAN NORDSTROM,' YRJO T KONTTINEN,' VILLE BERGROTH,' AND MARJATTA LEIRISALO-REPO2 From the 'Fourth Department
RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
Lysosomal enzymes in synovial membrane
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (197), 1, 65 Lysosomal enzymes in synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis Relationship to joint damage K. D. MUIRDEN University ofmelbourne Department ofmedicine, The Royal Melbourne
Ann. rheum. Dis. (197), 1, 65 Lysosomal enzymes in synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis Relationship to joint damage K. D. MUIRDEN University ofmelbourne Department ofmedicine, The Royal Melbourne
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Surgical synovectomy and experimental immune synovitis in the rabbit knee joint
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 503 Surgical synovectomy and experimental immune synovitis in the rabbit knee joint H. L. F. CURREY The London Hospital Medical College, London, E. 1 AND C. J. MOORE AND A.
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 503 Surgical synovectomy and experimental immune synovitis in the rabbit knee joint H. L. F. CURREY The London Hospital Medical College, London, E. 1 AND C. J. MOORE AND A.
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
, , 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
PRELIMINARY CRITERIA FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ACUTE ARTHRITIS OF PRIMARY GOUT
 895 PRELIMINARY CRITERIA FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ACUTE ARTHRITIS OF PRIMARY GOUT STANLEY L. WALLACE, HARRY ROBINSON, ALFONSE T. MASI, JOHN L. DECKER, DANIEL J. McCARTY. and T SAI-FAN Yo The American
895 PRELIMINARY CRITERIA FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ACUTE ARTHRITIS OF PRIMARY GOUT STANLEY L. WALLACE, HARRY ROBINSON, ALFONSE T. MASI, JOHN L. DECKER, DANIEL J. McCARTY. and T SAI-FAN Yo The American
HDF Case Whipple s disease
 HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Macrophage-lymphocyte clustering in rheumatoid arthritis
 Antn. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 38 Macrophage-lymphocyte clustering in rheumatoid arthritis F. W. S. WEBB, M. BAKER, R. WEISBART, R. BLUESTONE, AND L. GOLDBERG From the Department of Medicine, Rheumatology
Antn. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 38 Macrophage-lymphocyte clustering in rheumatoid arthritis F. W. S. WEBB, M. BAKER, R. WEISBART, R. BLUESTONE, AND L. GOLDBERG From the Department of Medicine, Rheumatology
Effect of blood on the activity and persistence of antigen induced inflammation in the rat air pouch
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 485-490 Effect of blood on the activity and persistence of antigen induced inflammation in the rat air pouch S YOSHINO, D R BLAKE, S HEWITT, C MORRIS, AND P
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 485-490 Effect of blood on the activity and persistence of antigen induced inflammation in the rat air pouch S YOSHINO, D R BLAKE, S HEWITT, C MORRIS, AND P
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
WSC , Conference 9. Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque.
 Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Three-dimensional structure of the human small intestinal mucosa in health and disease
 Gut, 1969, 10, 6-12 Three-dimensional structure of the human small intestinal mucosa in health and disease C. A. LOEHRY AND B. CREAMER From the Gastrointestinal Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London
Gut, 1969, 10, 6-12 Three-dimensional structure of the human small intestinal mucosa in health and disease C. A. LOEHRY AND B. CREAMER From the Gastrointestinal Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London
Rheumatoid factor tests in the diagnosis and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 684-69 Rheumatoid factor tests in the diagnosis and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis D J WALKER,' J D POUND,2 I D GRIFFITHS,' AND R J POWELL2 From the 'Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 684-69 Rheumatoid factor tests in the diagnosis and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis D J WALKER,' J D POUND,2 I D GRIFFITHS,' AND R J POWELL2 From the 'Department
KNOWLEDGE ACQUISITION STUDY AND ACCURACY RATE EVALUATION FOR CADIAG-2/RHEUMA WITH 308 CLINICAL CASES
 KNOWLEDGE ACQUISITION STUDY AND ACCURACY RATE EVALUATION FOR CADIAG-2/RHEUMA WITH 308 CLINICAL CASES Harald Leitich 1, Klaus-Peter Adlassnig1, Gernot Kolarz2 1 Department of Medical Computer Sciences (Director:
KNOWLEDGE ACQUISITION STUDY AND ACCURACY RATE EVALUATION FOR CADIAG-2/RHEUMA WITH 308 CLINICAL CASES Harald Leitich 1, Klaus-Peter Adlassnig1, Gernot Kolarz2 1 Department of Medical Computer Sciences (Director:
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
rheumatoid synovial tissue
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 552-556 The effect of zinc on alkaline phosphatase activity in rheumatoid synovial tissue J. J. JOHNSTONE, LUCILLE BITENSKY, B. CASHMAN*, AND J. CHAYEN From
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 552-556 The effect of zinc on alkaline phosphatase activity in rheumatoid synovial tissue J. J. JOHNSTONE, LUCILLE BITENSKY, B. CASHMAN*, AND J. CHAYEN From
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms
 J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Corynebacterium acnes in rheumatoid
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972) 31, 28 Corynebacterium acnes in rheumatoid arthritis II. Identification of antigen in synovial fluid leucocytes L. E. BARTHOLOMEW* AND F. R. NELSON From the Rackham Arthritis Research
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972) 31, 28 Corynebacterium acnes in rheumatoid arthritis II. Identification of antigen in synovial fluid leucocytes L. E. BARTHOLOMEW* AND F. R. NELSON From the Rackham Arthritis Research
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase
 Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Immunoglobulin and complement
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 321 Immunoglobulin and complement deposition in skin of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients ARNOLD L. SCHROETER, DOYT L. CONN, AND ROBERT E. JORDON
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 321 Immunoglobulin and complement deposition in skin of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients ARNOLD L. SCHROETER, DOYT L. CONN, AND ROBERT E. JORDON
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
PIGMENTED VILLONODULAR SYNOVITIS OF THE WRIST
 PIGMENTED VILLONODULAR SYNOVITIS OF THE WRIST WITH PENETRATION INTO BONE FRITZ SCHAJOWICZ and ISIDORO BLUMENFELD, BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA From the Latin-American Register of Bone Pathology, Hospital Italiano,
PIGMENTED VILLONODULAR SYNOVITIS OF THE WRIST WITH PENETRATION INTO BONE FRITZ SCHAJOWICZ and ISIDORO BLUMENFELD, BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA From the Latin-American Register of Bone Pathology, Hospital Italiano,
Degenerative arthritis in mice
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 249-253 Degenerative arthritis in mice Study of age and sex frequency in various strains with a genetic study of NZB/B1, NZY/B1, and hybrid mice R. D. WIGLEY,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 249-253 Degenerative arthritis in mice Study of age and sex frequency in various strains with a genetic study of NZB/B1, NZY/B1, and hybrid mice R. D. WIGLEY,
Complement-fixing ability of antinuclear
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 30, 640 Complement-fixing ability of antinuclear factors Studies in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus P. M. COSSIO, R. M. ARANA, 0. GARCIA
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 30, 640 Complement-fixing ability of antinuclear factors Studies in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus P. M. COSSIO, R. M. ARANA, 0. GARCIA
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Complement metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 557 Complement metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis 1. Longitudinal studies J. M. B. VERSEY, J. R. HOBBS, AND P. J. L. HOLT* From the Department of Chemical Pathology, Westminster
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 557 Complement metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis 1. Longitudinal studies J. M. B. VERSEY, J. R. HOBBS, AND P. J. L. HOLT* From the Department of Chemical Pathology, Westminster
Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 46-52 Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis P. C. MAUDGAL AND L. MISSOTTEN From the Eye Research Laboratory of the Department of Ophthalmology.
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 46-52 Histopathology of human superficial herpes simplex keratitis P. C. MAUDGAL AND L. MISSOTTEN From the Eye Research Laboratory of the Department of Ophthalmology.
Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16. Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36. Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73
 Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
