Blood Purification for Sepsis - Which Molecules Should We Remove Endotoxin or Cytokines?
|
|
|
- Kevin Robinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Plenary 5 MINI SYMPOSIA Challenges and Controversies in Renal Support and CRRT Blood Purification for Sepsis - Which Molecules Should We Remove Endotoxin or Cytokines? Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba, Japan Professor, Graduate School of Medicine International University of Health and Welfare, Chiba, Japan (March 8, Thursday, 2018)
2 Keywords in a New Pathophysiology of Sepsis PRRs (pattern-recognition receptors): A primitive part of the immune system. They are proteins expressed by cells of the innate immune system to identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), and/or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) or alarmins. PAMPS (pathogen-associated molecular patterns): Molecules associated with groups of pathogens, that are recognized by cells of the innate immune system. DAMPs (damage-associated molecular patters), Alarmins: An array of structurally diverse multifunctional host proteins that are rapidly released during infection or tissue damage, and that have mobilizing and activating effects on receptor-expressing cells engaged in host defense and tissue repair. 2
3 Exogenous Ligands (PAMPS) Endogenous Ligands (DAMPs Alarmin) Immuno-inflammatory Response Triggered by PAMPs and DAMPs / Alarmins through Toll-like Receptors Triacyl lipopeptide Peptideglycan Lipoprotein Necrotic cells HSPs Biglycan Diacyl lipopeptide dsrna LPS receptors Fibrinogen HSPs NE Biglycan HMGB1 β-defensin2 Heparan sulfate Hyaluronic acid Imidazoquinolines ssrna CpG DNA Hemozoin Chromatin Ig-G complex Flagellin Profilin-like protein Uropathogenic Bacteria (E.coli) Endogenous Ligands (Alarmin) Self mrna (Adapted from Kawai T, Akira S: Cell Death Differ 2006;13:816-25)
4 A List of PAMPS and DAMPs / Alarmins PAMPS (Exogenous) Triacyl lipopeptide Peptideglycan Lipoprotein Double-stranded RNA endotoxin Flagellin Diacyl lipopeptide Single-stranded RNA Unmethylated CpG DNA Uropathogenic Echerichia coli Lipoteicoic acid DAMPs / Alarmins (Endogenous) Necrotic tissue HSPs (HSP-60, HSP-70, Gp-96) Biglycan Self-messenger RNA Extra domain A-containing fibronectin Fibrinogen Polysaccharide fragments of heparin sulfate Oligosaccharides of hyaluronic acid Oxidized low-density lipoprotein Surfactant protein A in the lung epithelium 1 Neutrophil elastase Chromatin-IgG complex β-defensin 2 HMGB1 S100s HDGF IL-1a Uric acid Cathelicidins Defensins EDN Galectins Thymosins Nucleolin Annexins
5 PAMPs Pattern Recognition Receptors Hypercytokinemia Infection DAMPs or Alarmins (Lancet 2013;381:774-5)
6 Comparison of Severity and Survival between Endotoxin Positive and Negative Septic Patients (mean ±SD, Unpaired t-test) Endotoxin (+) Endotoxin (-) (32 cases) (83 cases) p-value APACHE Ⅱ score 25.1± ±9.6 N.S. SOFA score 10.8± ±4.2 N.S. Survival 69.1% 59.8% N.S.
7 Correlation between Blood Endotoxin Level and Severity Endotoxin Endotoxin (pg/ml) (pg/ml) n= N.S. 50 N.S APACHEⅡscore SOFA score
8 (Opal SM, et al: JAMA 2013;309: ) Antagonist of MD2-TLR4 to block cytokine release by LPS is not effective on the patients with severe sepsis. This is the another evidence that LPS is not a central player in the pathophysiology of sepsis
9 Therapeutic Approach to PAMPs and DAMPs / Alarmins Pathway PAMPs Blockade PRRs Blockade Cytokine Blockade PAMPS Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) Hypercytokinemia Infection Alarmins Damps or Alarmins Blockade
10 EUPHAS Study (PMX-DHP on Abdominal Sepsis) (Log-rank p=0.03) 68% 47% CHDF Chiba Series:82% SSCG Phase Ⅲ:70% E5564 Study Control:67% Problems 1) Too low survival in control group 2) Questionable statistical analysis (Cruz DN, et al: JAMA 2009;301: )
11 (Iwagami M, et al: Crit Care Med: 2014;42: ) In this retrospective study, postoperative polymyxin B hemoperfusion did not show any survival benefit for the overall study population or any of the studied subgroups of patients with abdominal septic shock. A large multicentered prospective randomized trial is warranted to identify the true role of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in sepsis caused by Gram-negative bacteria.
12 (Payen DM for ABDOMIX group: Intensive Care Med:2015;41: ) This multicenter randomized controlled study demonstrated a non-significant increase in mortality and no improvement in organ failure with direct hemoperfusion with polymyxin-immobilized endotoxin adsorbing column compared to conventional treatment of peritonitis-induced septic shock.
13 (Nakamura Y for JSEPTIC DIC study group: Crit Care 2017;21:134) This was a retrospective, multicenter study. We Performed propensity-score matching analyses of the Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (JSEPTIC DIC) Study database. Our results strongly suggest that PMX-HP reduced hospital mortality and length of ICU stay in patients with septic shock.
14 (Saito N, et al: PLoS ONE e , March 30, 2017) We conclude that PMX-based endotoxin adsorption within 24 hours from ICU admission was not associated with mortality among patients with septic shock due to Gram-negative bacillus. (28 day survival: PMXHP 29.1% vs Conventional treatment 29.0%, p=0.98)
15 (Intensive Care Med, 2018) Conclusion: There is currently insufficient evidence to support the routine use of PMX-HP to treat patients with sepsis or septic shock.
16 Endotoxin Removal in the Treatment of Septic Shock Endotoxin is only one of PAMPs, not a key player in the pathophysiology of septic shock. There are many septic shock patients without endotoxemia. Therefore, the efficacy of the modality solely aiming at the removal of endotoxin in septic shock treatment is questionable.
17 (J Infect Chemother 2013;19:825-32) Overall, the EAA kit could not measure clinically relevant dose of endotoxin. Because IL-8 induced an increase in EAA level, it is suggested that the EAA level reflects the primed site of polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
18 Sepsis-Related Pathophysiology and Hypercytokinemia Endothelial Hyperpermeability Dysoxia Mediator Network Activation Immunoparalysis Hypercytokinemia Proinflammatory hypercytokinemia Anti-inflammatory hypercytokinemia D I C NETTING Hyperglycemia Hyperpyrexia
19 Cytokine Theory of Disease Shock Organ failure Cytokine level Tissue damage Psoriasis Arthritis Ileus Colitis Disease Depression Fever Anorexia Pain Edema Leukocyte recruitment Antibacterial activity DC maturation Health Physiological manifestation (Tracey KJ. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: )
20 Correlation between IL-6 and Lactate Blood Level in Septic Patients (pg/ml) p<0.01 p<0.01 p<0.01 Log Y= X r=0.57, p<0.01 mean±sd,unpaired t-test IL severe sepsis septic shock p<0.01 p<0.01 p<0.01 sepsis (n=37) severe sepsis (n=39) 10 2 sepsis septic shock (n=39) Lactate (mg/dl)
21 Correlation between Monocytic HLA-DR Expression Rate and IL-10 Blood Level minimum value of monocytic HLA- DR expression during ICU stay (%) 100 y = x r = -0.52, p < 0.01 (%) 100 y = x r = -0.66, p < (%) 100 y = x r = -0.45, p < HLA -DR HLA -DR HLA -DR n= (pg/ml) IL-10 blood level on 2 days before HLA-DR measurement 20 n= (pg/ml) IL-10 blood level on one day before HLA-DR measurement 20 0 n= IL-10 blood level (pg/ml)
22 Pathophysiology of Sepsis and Septic Shock Infection Protease activation Endogenous Activators, Alarmin PAMPS PRRs (TLRs, NLRs, RLRs, CLRs) Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Hypercytokinemia Dysregulation of Host Immune Mechanism Inflammatory Response NETTING Coagulation System Disruption of Tight Junction and Glycocalyx Circulatory Failure Cell Dysfunction / Death necrosis, apoptosis, necroptosis stunning, autophagy Endothelial Hyperpermeability Capillary Leak Syndrome Interstitial Edema Dysoxia Organ Failure (Hirasawa H: Blood Purif 2012;34:164-70)
23 Continuous Hemodiafiltration with AN69ST (a Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilter) for the Patients with Septic Shock
24 Patients and Methods Study design: Prospective multicenter single-arm study involving intensive care units of 6 university hospitals in Japan Inclusion criteria: 1. Sepsis (infection-induced SIRS) 2. Blood lactate concentration 36 mg/dl (4.0 mmol/l) 3. CHDF is applied even when a septic patient has normal renal function Endpoint: 28 day mortality Blood lactate concentration (72 hrs follow-up period) Blood IL-6 concentration (72 hrs follow-up period)
25 Patients Background Basic characteristics of severe sepsis/septic shock patients Age, yrs, mean (SD) 67.1 (12.1) Male, n (%) 19 (55.9%) APACHEⅡ, mean (SD) 32.7 (9.8) Lactate (mg/dl), mean (SD) 69.9 (42.1) IL-6 (pg/ml), mean (SD) 44,797 (77,705) IL-8 (pg/ml), mean (SD) 6,605 (12,389) IL-10 (pg/ml), mean (SD) 664 (1,295) (N=34) Source of infections Intra-abdominal N 15 (%) (44.1) Lung 10 (29.4) Skin and soft tissue 6 (17.6) Others 3 ( 8.8)
26 Changes in Blood Lactate and IL-6 Levels in Septic Shock Patients Treated with AN69ST-CHDF (mg/dl) Blood Lactate AN69ST-CHDF n=28 mean±sd Blood IL-6 (pg/ml) AN69ST-CHDF 10 6 n=28 mean±sd (hr) (hr)
27 Changes in Blood Levels of Cytokines with AN69ST-CHDF(#1) (mean±sd) (pg/ml) 10 4 High (n=13) P<0.01 TNF-α Low (n=15) (pg/ml) 10 2 High (n=11) P<0.01 IL-1β Low (n=17) (pg/ml) 10 6 High (n=26) P<0.01 IL-6 Low (n=2) 10 3 N.S P< (hr) (hr) (hr) (measurement sensitivity:0.6 pg/ml) (measurement sensitivity:10 pg/ml) (measurement sensitivity:4.0 pg/ml)
28 Changes in Blood Levels of Cytokines with AN69ST-CHDF (#2) (mean±sd) (pg/ml) 10 5 High (n=21) P<0.01 IL-8 Low (n=7) (pg/ml) 10 4 High (n=20) P<0.01 IL-10 Low (n=8) (ng/ml) 10 3 High (n=17) P<0.05 HMGB1 Low (n=11) N.S P< N.S (hr) (hr) (hr) (measurement sensitivity:2.0 pg/ml) (measurement sensitivity:2.0 pg/ml) (measurement sensitivity:2.5 ng/ml)
29 Cytokine Clearance with AN69ST-CHDF (Values at 3 hours after the initiation od CHDF)) mean ± SD TNF-α IL-1β IL-6 IL-8 IL-10 HMGB ± 14.2 ml/min (n=15) 18.0 ± 32.7 ml/min (n=19) 11.0 ± 11.3 ml/min (n=32) 57.1 ± 46.0 ml/min (n=23) 19.6 ± 18.5 ml/min (n=32) 6.44 ± 63.6 ml/min (n=18)
30 100 survival (%) Predicted Survival and Observed 28 DAY Survival of Septic Shock Patients Treated with AN69ST CHDF APACHEⅡ score 32.7±9.8 (mean±s.d.) All patients (n =34 ) APACHEⅡ 25 (n = 9 ) APACHEⅡ 30 (n = 6 ) :Predicted survival (predicted with APACHEⅡ score) :Observed 28-day survival (AN69ST-CHDF trial) APACHEⅡ 35 (n = 6 ) APACHEⅡ (n = 13 ) (Hirasawa H, et al: Blood Purif 2012;34:164-70)
31
32 Comparison of Survival of Patients with Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Treated According to SSCG mean±sd Author Shapiro Shorr Ferrer Castellanos Ortega Levy Chiba PMMA- CHDF Japan AN69ST- CHDF Country US US Spain Spain (SSC database) Japan Japan Year of Publication Number of Cases , , Age (years) 68.0± ± ± ±15.1 unavailable 63.5± ±12.1 APACHE II (predicted survival) 22.6±8.8 (57.6%) 23.3±9.6 (54.0%) 21.3±7.8 (61.1%) 23.2±7.8 (54.0%) unavailable 27.0±7.7 (39.5%) 32.5±10.2 (22.7%) Survival 79.7% 70.0% 68.9% 62.5) 65.2% 82.4% 73.5% Ratio to Predicted Survival
33 (Doi K, et al: Blood Purif 2017;44:184-92) We retrospectively investigated whether AN69ST membrane hemofilter would have salutary effect on survival compared to other membranes using a Japanese Health Insurance data base. Of 2,469 patients, 156 were treated by AN69ST membrane. Adjusted odds ratio of AN69ST membrane use for in-hospital mortality was 0.65 (95% IC 0.45 ~ 0.93). The use of AN69ST membrane was also independently associated with shorter ICU-LOS. Thus, this retrospective observational study suggested that CRRT with AN69ST membrane might be associated with better in-hospital outcomes.
34 Reported Survival with Various Blood Purification Modalities aiming at the Removal of Causative Humoral Mediators in Septic Shock Patients Author HVHF Honore et al Piccinni P et al Cornejo R et al Boussekey N et al Year of publication Number of patients APACHE II 31.5 ± ± ± ±4.1 Predicted survival 26.7% 39.5% 43.1% 29.7% Observed 28d survival 55.0% 55.0% 60.0% 66.7% Observed/ predicted survival ratio PMX-DHP Vincent JL et al Kojika M et al Nakamura T et al Cruz DN et al ± ± ± (19-23) 73.8% 73.8% 57.6% 61.1% 70.6% 87.5% 70.0% 67.7% CAH-CHDF (Chiba Group) PMMA-CHDF 2008 AN69ST-CHDF ± ± % 20.3% 79.1% 73.5% HVHF: high volume hemofiltration, PMX-DHP direct hemoperfusion with an endotoxin-adsorbing column CAH-CHDF: continuous hemodiafiltration using cytokine-adsorbing membrane hemofilter, PMMA: polymethyl-methacrylate
35 Conclusion Thus, causative substances of sepsis which should be removed with blood purification modality seem not to be endotoxin but rather to be pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. We have reported that continuous hemodiafiltration with cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters such as PMMA And AN69ST hemofilter can remove various cytokines from blood stream of patients and that CAH-CHDF is very effective in the treatment of sepsis. In Japan, now CAH-CHDF is approved to be applied on septic patients even when those patients have normal kidney function.
36
37 Comparison of IL-6 Blood Levels among SIRS, SEPSIS, Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock pg/ml p< mean±sd ANOVA p< p< IL Non-infectious SIRS (n=8) sepsis (n=7) severe sepsis (n=11) septic shock (n=14) (Oda S, Hirasawa H, et al: Cytokine 2005; 29: )
38 Comparison of Survival of Severe Sepsis / Septic Shock Patients Treated with PMMA-CHDF or AN69ST-CHDF survival (%) ~ :PMMA-CHDF :AN69ST-CHDF all patients APACHEⅡ APACHEⅡ APACHEⅡ APACHEⅡ n: (107) (35) (21) (9) (19) (6) (19) (6) (48) (13)
39 Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Response in Sepsis (Hotchkiss RS et al: Nat Med 2009;15:496-7)
40 PAMPS Pattern Recognition Receptors Hypercytokinemia Infection Alarmins (Lancet 2013;381:774-5)
41 Endotoxin and Sepsis Endotoxin as a therapeutic target in septic shock (Corriveau CC et al: Infect Agents Dis 1993;2:35-43) The importance of a lipopolysaccaride-initated, cytokinemediated host defense mechanism in mice against extraintestinally invasive Escherichia coli (Cross A et al: J Clin Invest 1995;96:676-86) Mucosal and enterocyte IL-6 production during sepsis and endotoxemia-role of transcription factors and regulation by the stress response (Pritts T et al: Am J Surg 2002;183: )
42 PAMPS Efficacy of PMX-DHP AND CAH-CHDF for Humoral Mediator Network G(-) Bacteria G(+) Bacteria Trauma Pancreatitis ALARMINS Exotoxin Endotoxin Monocyte/Macrophage Burn Others PMX-DHP Production of Anandamide Production of Cytokine CAH-CHDF also can remove metabolic waste products and can maintain body water balance Hypercytokinemia Activation of Humoral Mediator Network CAH- CHDF (Hirasawa H: Contrib Nephrol 2010; 166:21-30) MOF
43 Introduction There has been much advance in the application of various blood purification modality in emergency and critical care medicine. And blood purifications are reported to be especially effective in the treatment of sepsis. Now blood purification is applied not only as artificial support for failing organs but also as remover of causative substances of sepsis. Traditionally endotoxin is thought to play a key role in the pathophysiology of sepsis. Accordingly direct hemoperfusion with polymyxin-b immobilized endotoxin adsorbing column (PMX-DHP) has been widely applied on septic patients to remove causative endotoxin. However, recent elucidation on the pathophysiology of sepsis casts a shadow on the efficacy of PMX-DHP in sepsis.
44 Infection Pathophysiology of Sepsis Protease activation Endogenous Activators, Alarmin PAMPS PRRs (TLRs, NLRs, RLRs, CLRs) Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Hypercytokinemia Dysregulation of Host Immune Mechanism Inflammatory Response NETTING Coagulation System Disruption of Tight Junction and Glycocalyx Circulatory Failure Cell Dysfunction / Death necrosis, apoptosis, necroptosis stunning, autophagy Endothelial Hyperpermeability Capillary Leak Syndrome Interstitial Edema Dysoxia Organ Failure (Hirasawa H: Blood Purif 2012;34:164-70)
45 Countermeasures against Hypercytokinemia 1) Prevention of Excess Release 2) Immunotherapy 3) Pharmacotherapy 4) Biological Therapy 5) Blood Purification 6) Gene Therapy 7) Immunomodulation 8) Autonomic Nerve Modulation 9) Others
46 Acute Blood Purification Modalities for Removal of Cytokines and Other Humoral Mediators 1) High Filtration Volume Continuous Hemofiltration (CHF) or Continuous Hemodiafiltration (CHDF) 2) Continuous Hemodiafiltration (CHDF) with a Cytokine- Adsorbing Hemofilter 3) On-line Hemodiafiltration 4) Direct Hemoperfusion (DHP) with Endotoxin Adsorbing Polymyxin B Immobilized Column (PMX) 5) Plasma Exchange 6) Coupled Plasma Filtration Adsorption
47 Removal of pro-inflammatory cytokines with renal replacement therapy: Sense or nonsense? (Schetz M, et al: Intensive Care Med 1995;21:169-76)
48 (Legrand M et al: Intensive Care Med 2013;39:101-8) 70%
F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF)
 F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF) Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of
F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF) Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
doi: /ams2.382
 Acute Medicine & Surgery 2019; 6: 60 67 doi: 10.1002/ams2.382 Original Article The 28-day survival rates of two cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters for continuous renal replacement therapy: a single-center
Acute Medicine & Surgery 2019; 6: 60 67 doi: 10.1002/ams2.382 Original Article The 28-day survival rates of two cytokine-adsorbing hemofilters for continuous renal replacement therapy: a single-center
Importance of kinetics of procalcitonin in septic patients. János Fazakas MD, PhD Semmelweis University, Department of Transplantation and Surgery
 Importance of kinetics of procalcitonin in septic patients János Fazakas MD, PhD Semmelweis University, Department of Transplantation and Surgery Host pathogen interactions the innate and the adaptive
Importance of kinetics of procalcitonin in septic patients János Fazakas MD, PhD Semmelweis University, Department of Transplantation and Surgery Host pathogen interactions the innate and the adaptive
Disclosures Paul Walker MD PhD FRCSC
 1 ` Disclosures Paul Walker MD PhD FRCSC CEO Spectral Medical 2001-present Inaugural Critical Care Program Director - University of Toronto Chief of Surgery - University Health Network 1991-1999 COO Toronto
1 ` Disclosures Paul Walker MD PhD FRCSC CEO Spectral Medical 2001-present Inaugural Critical Care Program Director - University of Toronto Chief of Surgery - University Health Network 1991-1999 COO Toronto
Sepsis and Multiple Organ Failure. J.G. van der Hoeven Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre
 Sepsis and Multiple Organ Failure J.G. van der Hoeven Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Sepsis - initiation Microorganism Tissue Damage Pathogen Associated Molecular Pattern (PAMP) Pattern Recognition
Sepsis and Multiple Organ Failure J.G. van der Hoeven Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Sepsis - initiation Microorganism Tissue Damage Pathogen Associated Molecular Pattern (PAMP) Pattern Recognition
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Text-based Document. Implications of the Sepsis-3 Definition on Nursing Research and Practice. Authors Peach, Brian C. Downloaded 5-Jul :03:48
 The Henderson Repository is a free resource of the Honor Society of Nursing, Sigma Theta Tau International. It is dedicated to the dissemination of nursing research, researchrelated, and evidence-based
The Henderson Repository is a free resource of the Honor Society of Nursing, Sigma Theta Tau International. It is dedicated to the dissemination of nursing research, researchrelated, and evidence-based
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS
 Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Towards Precision Medicine in Sepsis Patients: Are We Close?
 Towards Precision Medicine in Sepsis Patients: Are We Close? CRRT San Diego 2018 Peter Pickkers Department of Medicine Radboud university medical centre, Nijmegen No LPS circulating (n=55) P < 0.05 LPS
Towards Precision Medicine in Sepsis Patients: Are We Close? CRRT San Diego 2018 Peter Pickkers Department of Medicine Radboud university medical centre, Nijmegen No LPS circulating (n=55) P < 0.05 LPS
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
HMGB1-TLR4 Interactions: Mediators of Kidney Lung Crosstalk?
 HMGB1-TLR4 Interactions: Mediators of Kidney Lung Crosstalk? Dept of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine The University of Tokyo Kent Doi, MD. PhD Organ crosstalk in AKI Grams ME, Rabb H. Kidney Int.
HMGB1-TLR4 Interactions: Mediators of Kidney Lung Crosstalk? Dept of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine The University of Tokyo Kent Doi, MD. PhD Organ crosstalk in AKI Grams ME, Rabb H. Kidney Int.
oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators
 oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators Heparin-grafted for reduced thrombogenicity Supports renal function POWERED
oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators Heparin-grafted for reduced thrombogenicity Supports renal function POWERED
Immunology in the Trauma Patient
 Immunology in the Trauma Patient Christine S. Cocanour, MD, FACS, FCCM I have no disclosures as it pertains to this presentation 1 Basic Immunology Danger Theory Immune system recognizes not just nonself
Immunology in the Trauma Patient Christine S. Cocanour, MD, FACS, FCCM I have no disclosures as it pertains to this presentation 1 Basic Immunology Danger Theory Immune system recognizes not just nonself
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Sepsis and AKI. Exploring their relationship and therapeutic role of extracorporeal inflammatory mediator removal
 Sepsis and AKI Exploring their relationship and therapeutic role of extracorporeal inflammatory mediator removal 57042F AKI Sepsis Therapy Brochure_v2m.indd 1 02/06/2016 14:36 Overview Sepsis and AKI in
Sepsis and AKI Exploring their relationship and therapeutic role of extracorporeal inflammatory mediator removal 57042F AKI Sepsis Therapy Brochure_v2m.indd 1 02/06/2016 14:36 Overview Sepsis and AKI in
Detecting and Removing Endotoxin in sepsis
 Toronto 2015 Detecting and Removing Endotoxin in sepsis Claudio Ronco, MD Department of Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation International Renal Research Institute San Bortolo Hospital Vicenza Italy
Toronto 2015 Detecting and Removing Endotoxin in sepsis Claudio Ronco, MD Department of Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation International Renal Research Institute San Bortolo Hospital Vicenza Italy
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Relative sizes of infectious agents
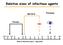 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Pathologic Mechanisms of Septic Shock
 Pathologic Mechanisms of Septic Shock Kenneth J. Goodrum, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline of Topics Definitions: SIRS, sepsis, shock, MODS Morbidity/mortality
Pathologic Mechanisms of Septic Shock Kenneth J. Goodrum, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline of Topics Definitions: SIRS, sepsis, shock, MODS Morbidity/mortality
Intravenous Vitamin C. Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury
 Intravenous Vitamin C Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury Alpha A. (Berry) Fowler, III, MD Professor of Medicine VCU Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine I Have No Disclosures Bacterial Sepsis Approximately
Intravenous Vitamin C Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury Alpha A. (Berry) Fowler, III, MD Professor of Medicine VCU Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine I Have No Disclosures Bacterial Sepsis Approximately
Interessenskonflikt. 1) Cytosorb Register Planung. 2) Studie Seraph Microbind: ExThera Medical. 3) Fan von Arbeitsgruppe PD Dr.
 Interessenskonflikt 1) Cytosorb Register Planung 2) Studie Seraph Microbind: ExThera Medical 3) Fan von Arbeitsgruppe PD Dr. David, MHH Cytokinelimination bei Sepsis JanT Kielstein Braunschweig Cytokinelimination
Interessenskonflikt 1) Cytosorb Register Planung 2) Studie Seraph Microbind: ExThera Medical 3) Fan von Arbeitsgruppe PD Dr. David, MHH Cytokinelimination bei Sepsis JanT Kielstein Braunschweig Cytokinelimination
Disclosure: Member of the advisory board of EUPHAS 2
 Disclosure: Member of the advisory board of EUPHAS 2 SEPSI SEVERA confronto con altre patologie maggiori (USA) MORTALITA Mortality of Severe Sepsis Morti / anno AIDS* CANCRO mammella IMA SEPSI SEVERA
Disclosure: Member of the advisory board of EUPHAS 2 SEPSI SEVERA confronto con altre patologie maggiori (USA) MORTALITA Mortality of Severe Sepsis Morti / anno AIDS* CANCRO mammella IMA SEPSI SEVERA
Supplementary Materials to the Manuscript: Polymorphisms in TNF-α Increase Susceptibility to
 Supplementary Materials to the Manuscript: Polymorphisms in TNF-α Increase Susceptibility to Intra-abdominal Candida Infection in High Risk Surgical ICU Patients A. Wójtowicz, Ph.D. 1, F. Tissot, M.D.
Supplementary Materials to the Manuscript: Polymorphisms in TNF-α Increase Susceptibility to Intra-abdominal Candida Infection in High Risk Surgical ICU Patients A. Wójtowicz, Ph.D. 1, F. Tissot, M.D.
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
SEPSIS & SEPTIC SHOCK
 SEPSIS & SEPTIC SHOCK DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential bias
SEPSIS & SEPTIC SHOCK DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential bias
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Blood purification in sepsis
 Blood purification in sepsis Joannes-Boyau O Dept of anesthesiology and intensive care, University Hospital of Bordeaux, France 1 Types of Blood Purification hemofilters regular pore size (MW < 40,000D)
Blood purification in sepsis Joannes-Boyau O Dept of anesthesiology and intensive care, University Hospital of Bordeaux, France 1 Types of Blood Purification hemofilters regular pore size (MW < 40,000D)
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
VITAMIN D. Christina Nieuwoudt RD(SA) CCSSA/SASPEN 2018
 VITAMIN D Christina Nieuwoudt RD(SA) CCSSA/SASPEN 2018 1 OBJECTIVES Why is it in the spotlight? Vit D and acute illness If it has a role how much should we give? Future 2 Why is it in the spotlight? FUNCTIONS
VITAMIN D Christina Nieuwoudt RD(SA) CCSSA/SASPEN 2018 1 OBJECTIVES Why is it in the spotlight? Vit D and acute illness If it has a role how much should we give? Future 2 Why is it in the spotlight? FUNCTIONS
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER. Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma
 INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity. Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada
 Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Early Goal-Directed Therapy Rivers E et al. NEJM 345:1368-77,
Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Early Goal-Directed Therapy Rivers E et al. NEJM 345:1368-77,
Innate Immunity. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Sepsi: nuove definizioni, approccio diagnostico e terapia
 GIORNATA MONDIALE DELLA SEPSI DIAGNOSI E GESTIONE CLINICA DELLA SEPSI Giovedì, 13 settembre 2018 Sepsi: nuove definizioni, approccio diagnostico e terapia Nicola Petrosillo Società Italiana Terapia Antiinfettiva
GIORNATA MONDIALE DELLA SEPSI DIAGNOSI E GESTIONE CLINICA DELLA SEPSI Giovedì, 13 settembre 2018 Sepsi: nuove definizioni, approccio diagnostico e terapia Nicola Petrosillo Società Italiana Terapia Antiinfettiva
Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Critical Care. Vasopressors, Steroids, and Insulin Therapy
 Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Critical Care Vasopressors, Steroids, and Insulin Therapy Douglas Fish, Pharm.D. Professor of Pharmacy, University of Colorado Denver Clinical Specialist in Critical
Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Critical Care Vasopressors, Steroids, and Insulin Therapy Douglas Fish, Pharm.D. Professor of Pharmacy, University of Colorado Denver Clinical Specialist in Critical
Commentary Recent evolution of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill patient Claudio Ronco
 Commentary Recent evolution of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill patient Claudio Ronco Department of Nephrology, St Bortolo Hospital, Vicenza, Italy Corresponding author: Claudio Ronco, cronco@goldnet.it
Commentary Recent evolution of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill patient Claudio Ronco Department of Nephrology, St Bortolo Hospital, Vicenza, Italy Corresponding author: Claudio Ronco, cronco@goldnet.it
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Pneumonic Septic Shock Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria
 Korean J Crit Care Med 2015 August 30(3):171-175 / ISSN 2383-4870 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2383-4889 (Online) Case Report Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Pneumonic Septic Shock Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria Jung-Wan
Korean J Crit Care Med 2015 August 30(3):171-175 / ISSN 2383-4870 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2383-4889 (Online) Case Report Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Pneumonic Septic Shock Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria Jung-Wan
Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer?
 Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer? Małgorzata Lipinska-Gediga Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Medical University Wroclaw,
Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer? Małgorzata Lipinska-Gediga Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Medical University Wroclaw,
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? Modalities of Dialysis
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? A common condition in ICU patients Associated with high mortality and morbidity Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) is the cornerstone
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? A common condition in ICU patients Associated with high mortality and morbidity Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) is the cornerstone
Novel Sepsis Therapies
 RSEM-GSA 17 Novel Sepsis Therapies Khaled Ahmed Alghamdi, MD, ABEM, FACEP, FAAEM Consultant Emergency Medicine Deputy program director Medical Director of Emergency Medical Services King Faisal Specialist
RSEM-GSA 17 Novel Sepsis Therapies Khaled Ahmed Alghamdi, MD, ABEM, FACEP, FAAEM Consultant Emergency Medicine Deputy program director Medical Director of Emergency Medical Services King Faisal Specialist
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
MICR2209. Innate Immunity. Dr Allison Imrie
 MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction Rudiger, Alain DOI:
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction Rudiger, Alain DOI:
Septic AKI in ICU patients
 Septic AKI in ICU patients Prof. Achim Jörres, M.D. Dept. of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care Charité University Hospital Campus Virchow Klinikum Berlin, Germany achim.joerres@charite.de Agenda Epidemiology
Septic AKI in ICU patients Prof. Achim Jörres, M.D. Dept. of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care Charité University Hospital Campus Virchow Klinikum Berlin, Germany achim.joerres@charite.de Agenda Epidemiology
Redefining sepsis and sepsis treatment
 Redefining sepsis and sepsis treatment What should we change in the treatment algorithm? Ricard Ferrer Critical Care Department Mutua Terrassa University Hospital Barcelona. SPAIN Time dependency Microorganism
Redefining sepsis and sepsis treatment What should we change in the treatment algorithm? Ricard Ferrer Critical Care Department Mutua Terrassa University Hospital Barcelona. SPAIN Time dependency Microorganism
SHOULD THERAPEUTIC AGENTS FOR SEPSIS TARGET THE GLYCOCALYX?
 SHOULD THERAPEUTIC AGENTS FOR SEPSIS TARGET THE GLYCOCALYX? Sir Ganga Ram Hospital New Delhi, India Dr. Seema Bhargava Senior Consultant & Chairperson Department of Biochemistry & Professor, GRIPMER Sir
SHOULD THERAPEUTIC AGENTS FOR SEPSIS TARGET THE GLYCOCALYX? Sir Ganga Ram Hospital New Delhi, India Dr. Seema Bhargava Senior Consultant & Chairperson Department of Biochemistry & Professor, GRIPMER Sir
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one. of the most common diseases found in the population.
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
What is the Role of Albumin in Sepsis? An Evidenced Based Affair. Justin Belsky MD PGY3 2/6/14
 What is the Role of Albumin in Sepsis? An Evidenced Based Affair Justin Belsky MD PGY3 2/6/14 Microcirculation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xao1gsyur7q Capillary Leak in Sepsis Asking the RIGHT Question
What is the Role of Albumin in Sepsis? An Evidenced Based Affair Justin Belsky MD PGY3 2/6/14 Microcirculation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xao1gsyur7q Capillary Leak in Sepsis Asking the RIGHT Question
R2R: Severe sepsis/septic shock. Surat Tongyoo Critical care medicine Siriraj Hospital
 R2R: Severe sepsis/septic shock Surat Tongyoo Critical care medicine Siriraj Hospital Diagnostic criteria ACCP/SCCM consensus conference 1991 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference
R2R: Severe sepsis/septic shock Surat Tongyoo Critical care medicine Siriraj Hospital Diagnostic criteria ACCP/SCCM consensus conference 1991 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Augmented Renal Clearance: Let s Get the Discussion Flowing
 Augmented Renal Clearance: Let s Get the Discussion Flowing Terry Makhoul, PharmD PGY-2 Emergency Medicine Pharmacy Resident University of Rochester Medical Center Strong Memorial Hospital Disclosures
Augmented Renal Clearance: Let s Get the Discussion Flowing Terry Makhoul, PharmD PGY-2 Emergency Medicine Pharmacy Resident University of Rochester Medical Center Strong Memorial Hospital Disclosures
Steroids in ARDS: if, when, how much? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Dept. of Emergency Medicine Kent Hospital, İzmir, Türkiye
 Steroids in ARDS: if, when, how much? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Dept. of Emergency Medicine Kent Hospital, İzmir, Türkiye Steroids in ARDS: conclusion Give low-dose steroids if indicated for another problem
Steroids in ARDS: if, when, how much? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Dept. of Emergency Medicine Kent Hospital, İzmir, Türkiye Steroids in ARDS: conclusion Give low-dose steroids if indicated for another problem
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
The Usefulness of Sepsis Biomarkers. Dr Vineya Rai Department of Anesthesiology University of Malaya
 The Usefulness of Sepsis Biomarkers Dr Vineya Rai Department of Anesthesiology University of Malaya 1 What is Sepsis? Whole Body Inflammatory State + Infection 2 Incidence and Burden of Sepsis in US In
The Usefulness of Sepsis Biomarkers Dr Vineya Rai Department of Anesthesiology University of Malaya 1 What is Sepsis? Whole Body Inflammatory State + Infection 2 Incidence and Burden of Sepsis in US In
Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis
 Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis 1 Shock Systemic hypoperfusion due to: Reduction in cardiac output Reduction in effective circulating blood volume Hypotension Impaired tissue perfusion Cellular hypoxia
Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis 1 Shock Systemic hypoperfusion due to: Reduction in cardiac output Reduction in effective circulating blood volume Hypotension Impaired tissue perfusion Cellular hypoxia
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Adsorbtion of Cytokines Early in Septic Shock: the ACESS trial
 Adsorbtion of Cytokines Early in Septic Shock: the ACESS trial Prof. Zsolt Molnár zsoltmolna@gmail.com Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care University of Szeged Hungary Pathophysiology Local insult
Adsorbtion of Cytokines Early in Septic Shock: the ACESS trial Prof. Zsolt Molnár zsoltmolna@gmail.com Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care University of Szeged Hungary Pathophysiology Local insult
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection. All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention. Infusates/ drugs. hub/lines Dressing
 Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Immune monitoring in intensive care patients
 28th General annual Meeting of the Belgian Hematological Society Immune monitoring in intensive care patients Guillaume Monneret Head Cellular Immunology Unit Hôp. E. Herriot-Hospices Civilsde Lyon -F
28th General annual Meeting of the Belgian Hematological Society Immune monitoring in intensive care patients Guillaume Monneret Head Cellular Immunology Unit Hôp. E. Herriot-Hospices Civilsde Lyon -F
Endotoxin Elimination in Patients with Septic Shock: An Observation Study
 Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (2015) 63:475 483 DOI 10.1007/s00005-015-0348-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endotoxin Elimination in Patients with Septic Shock: An Observation Study Barbara Adamik 1 Stanislaw Zielinski
Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (2015) 63:475 483 DOI 10.1007/s00005-015-0348-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endotoxin Elimination in Patients with Septic Shock: An Observation Study Barbara Adamik 1 Stanislaw Zielinski
Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis
 Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis John C. Marshall, MD FRCSC St. Michael s Hospital Critical Care Canada Forum 2012 Toronto, Canada October 29, 2012 University of Toronto Thanks to Songhui Jia
Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis John C. Marshall, MD FRCSC St. Michael s Hospital Critical Care Canada Forum 2012 Toronto, Canada October 29, 2012 University of Toronto Thanks to Songhui Jia
CASE SERIES IN POSTOPERATIVE CARDIAC SURGERY PATIENTS
 2 nd International User Meeting October 2, 2015 Berlin Prof. Dr. Karl Träger Cardiosurgical ICU Dept. of Cardiac Anesthesiology University Hospital Ulm Albert-Einstein-Allee 23, 89081 Ulm GERMANY karl.traeger@uniklinik-ulm.de
2 nd International User Meeting October 2, 2015 Berlin Prof. Dr. Karl Träger Cardiosurgical ICU Dept. of Cardiac Anesthesiology University Hospital Ulm Albert-Einstein-Allee 23, 89081 Ulm GERMANY karl.traeger@uniklinik-ulm.de
Back to the Future: Updated Guidelines for Evaluation and Management of Adrenal Insufficiency in the Critically Ill
 Back to the Future: Updated Guidelines for Evaluation and Management of Adrenal Insufficiency in the Critically Ill Joe Palumbo PGY-2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Buffalo General Medical Center Disclosures
Back to the Future: Updated Guidelines for Evaluation and Management of Adrenal Insufficiency in the Critically Ill Joe Palumbo PGY-2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Buffalo General Medical Center Disclosures
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology
 Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology PJL:2011 Bacterial Overview: Morphology, Structure, Jargon General Features Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria Spirochaetes Firmicutes Actinobacteria No nuclear membrane
Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology PJL:2011 Bacterial Overview: Morphology, Structure, Jargon General Features Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria Spirochaetes Firmicutes Actinobacteria No nuclear membrane
Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY)
 Doctoral Thesis Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY) ELSAYED SEDDEK IBRAHEM MOHAMMED Department of Bioresource Science Graduate
Doctoral Thesis Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY) ELSAYED SEDDEK IBRAHEM MOHAMMED Department of Bioresource Science Graduate
Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Robert W. Schrier, MD University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Prevalence of acute renal failure in Intensive
Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Robert W. Schrier, MD University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Prevalence of acute renal failure in Intensive
Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure
 CHAPTER 82 Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure R. Deshpande Introduction Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as an abrupt decrease in renal function sufficient to result in retention of nitrogenous
CHAPTER 82 Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure R. Deshpande Introduction Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as an abrupt decrease in renal function sufficient to result in retention of nitrogenous
Basic immunology. Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
A single-center experience with resin adsorption hemoperfusion combined with continuous veno-venous hemofiltration for septic shock patients
 Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 09; ( ): A single-center experience with resin adsorption hemoperfusion combined
Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 09; ( ): A single-center experience with resin adsorption hemoperfusion combined
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Rationale for renal replacement therapy in ICU: indications, approaches and outcomes. Richard Beale
 Rationale for renal replacement therapy in ICU: indications, approaches and outcomes Richard Beale RIFLE classification (ADQI group) 2004 Outcome AKIN classification Definition: Abrupt (within 48 hrs)
Rationale for renal replacement therapy in ICU: indications, approaches and outcomes Richard Beale RIFLE classification (ADQI group) 2004 Outcome AKIN classification Definition: Abrupt (within 48 hrs)
Sepsis new definitions of sepsis and septic shock and Novelities in sepsis treatment
 Sepsis new definitions of sepsis and septic shock and Novelities in sepsis treatment What is sepsis? Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection A 1991 consensus
Sepsis new definitions of sepsis and septic shock and Novelities in sepsis treatment What is sepsis? Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection A 1991 consensus
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses. Skin Biology Lecture Series
 Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
Objectives. Epidemiology of Sepsis. Review Guidelines for Resuscitation. Tx: EGDT, timing/choice of abx, activated
 Update on Surviving Sepsis 2008 Objectives Epidemiology of Sepsis Definition of Sepsis and Septic Shock Review Guidelines for Resuscitation Dx: Lactate, t cultures, SVO2 Tx: EGDT, timing/choice of abx,
Update on Surviving Sepsis 2008 Objectives Epidemiology of Sepsis Definition of Sepsis and Septic Shock Review Guidelines for Resuscitation Dx: Lactate, t cultures, SVO2 Tx: EGDT, timing/choice of abx,
INFECTION & IMMUNITY. Choi Jung Hyun. Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea
 INFECTION & IMMUNITY Choi Jung Hyun Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Immunity From Latin immunitas - (especially immune to something) having
INFECTION & IMMUNITY Choi Jung Hyun Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Immunity From Latin immunitas - (especially immune to something) having
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
Basics from anatomy and physiology classes Local tissue reactions
 Septicaemia & SIRS Septicaemia is a life-threatening condition that arises when the physical reaction to an infection, causes damage to tissue and organs Basics from anatomy and physiology classes Local
Septicaemia & SIRS Septicaemia is a life-threatening condition that arises when the physical reaction to an infection, causes damage to tissue and organs Basics from anatomy and physiology classes Local
INVESTIGATIONAL TREATMENTS FOR SEPSIS AN OVERVIEW
 INVESTIGATIONAL TREATMENTS FOR SEPSIS AN OVERVIEW THE GLOBAL BURDEN OF SEPSIS Mortality rate estimated to be 30-50% Rates estimated to be as high as 80% in developing nations One third to one half of all
INVESTIGATIONAL TREATMENTS FOR SEPSIS AN OVERVIEW THE GLOBAL BURDEN OF SEPSIS Mortality rate estimated to be 30-50% Rates estimated to be as high as 80% in developing nations One third to one half of all
The Immune System: The Mind Body Connection. Presented by Margaret Kemeny, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco
 The Immune System: The Mind Body Connection Presented by Margaret Kemeny, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco Psychoneuroimmunology Investigation of the bidirectional
The Immune System: The Mind Body Connection Presented by Margaret Kemeny, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco Psychoneuroimmunology Investigation of the bidirectional
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
The Management of Sepsis: What s New in 2013
 The Management of Sepsis: What s New in 2013 Mitchell M. Levy MD, FCCM Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Pulmonary, Sleep, and Critical Care Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Providence,
The Management of Sepsis: What s New in 2013 Mitchell M. Levy MD, FCCM Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Pulmonary, Sleep, and Critical Care Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Providence,
