Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia, a Rare Differential Diagnosis
|
|
|
- Edmund Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Journals Case Report June 2018 Vol.:9, Issue: 4 All rights are reserved by Vladimir Macavei et al. Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia, a Rare Differential Diagnosis Keywords: Airway diseases; eosinophilic pneumonia; chronic idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonia; Charcot-Leyden crystals; interstitial lung disease. Serena Yi Ling Tan 1, Dalila ABD Rahman 2, Terry O Shaughnessy 3, Vladimir Macavei* 4 1 Respiratory Department Newham University Hospital, London, E13 8SL 2 Respiratory Department Newham University Hospital, London, E13 8SL 3 Respiratory Department Newham University Hospital, London, E13 8SL 4 Respiratory Department Newham University Hospital, London, E13 8SL Submission: 29 May 2018 Accepted: 5 June 2018 Published: 30 June ABSTRACT Eosinophilic pneumonia remains a rare clinical diagnosis, and one not often seen in clinical practice. Eosinophilic pneumonia can present with acute presentations, such as in Löeffler s syndrome in which patient develops low-grade fever, and respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea, nonproductive cough or haemoptysis. These respiratory manifestations of Löeffler s syndrome are typically selflimiting and only last for about 1 to 2 weeks. On the other hand, eosinophilic pneumonia can also present with subacute or chronic presentations, such as in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP), where symptoms are usually present for several months before a clear diagnosis is made. Patients with CEP commonly present with weight loss, low-grade fever, drenching night sweats and an initial dry cough which later turns productive of mucoid sputum. However, in some cases, severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and severe hypoxaemia have also been reported. Although rare, eosinophilic pneumonia should be considered in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary and peripheral blood eosinophilia.[1] Long-term corticosteroids therapy remains the treatment of choice, resulting in prompt treatment response and resolution of symptoms. In this case, we would like to present the case of a 51-year-old patient who presented with characteristic clinical and radiological features of CEP, as well as the presence of abundant eosinophils and Charcot- Leyden crystals in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL).
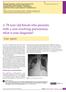
2 CASE REPORT A 51-year old carpenter initially presented with one-week history of shortness of breath on exertion and an initial dry cough that later turned productive of green sputum. He is a nonsmoker with no previous underlying lung disease. On arrival at the Emergency Department, he was saturating at 93% on air and his physical examination revealed few crepitations at both lung bases. His initial arterial blood gas (ABG) on admission showed type 1 respiratory - failure with ph 7.43, pco , po , HCO and base excess of 3.0. His admission blood showed not only a mildly raised white cell count (WCC) of 11.7x10 9 /L with neutrophil count of 8.0x10 9 /L but also an eosinophilia of 1.2x10 9. Over the course of an hour he then gradually desaturated and had increasing oxygen requirements of up to 4L/min. His chest radiograph showed clear lung fields. In view of his ongoing hypoxaemia and increasing oxygen requirements, a d-dimer test was performed and returned negative, ruling out pulmonary embolism (PE). Other than that, various tests such as sputum acid-fast bacilli (AFB), HIV serology, atypical pneumonia screen and flu swabs have all returned negative. A HRCT of the chest was later performed and reported to be evidence of focal ground glass opacities in apical segments of both lungs (figure 1). He was then treated with 7-day course of antibiotics according to trust policy for community acquired pneumonia (CAP). FIGURE 1. HRCT performed on first admission showing focal area of ground glass opacities noted in apical segments of both lungs. There was also a couple of small volume pre-tracheal lymph nodes present, with no evidence of mass lesions or nodules. The rest of the lung parenchymal attenuation is normal. A week after discharge the patient was readmitted, presenting with non-resolving symptoms and a widespread bilateral expiratory wheeze. He denied having any weight loss, night 169
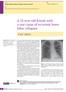
3 sweats, or haemoptysis and his sputum cultures have all returned negative for AFB. However, his full blood count (FBC) on second admission showed a worsening eosinophilia of 3.2x10 9 /L and a raised white cell count of 13x10 9 /L. His chest radiograph revealed a new rounded opacity in the right upper lobe apex with no cavitary changes despite completing 7- day course of antibiotics (figure 2). FIGURE 2. Chest radiograph performed after 7 days of antibiotics treatment, showing a new rounded opacity in the right upper lobe apex with no cavitary changes. The rest of the lungs and pleura are clear. Due to recent hospitalization, he was then started on intravenous (IV) tazocin to cover for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP). Despite IV tazocin treatment, his eosinophil count continued to rise and peaked at 6.2x10 9 /L. A CT chest, abdomen and pelvis was also performed, which showed multifocal areas of patchy consolidation and ground glass changes in the lung apices, worse compared to that on first admission (figure 3). FIGURE 3. CT chest performed on second admission showing multifocal areas of patchy consolidation and ground glass change involving upper lobes bilaterally but more on the right 170
4 side. There is also mild bronchial wall thickening with early bronchiectatic changes mainly in the upper lobes. Other than that, he was also found to be weakly positive for perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (panca) IgG, which however seroconverted to a negative result on subsequent measurements. He was also tested negative for PR3/MPO ELISA and galactomannan. His serum IgE was found to peak at 2,078 kunits/l. A BAL was performed on the second admission, and approximately 7mls of cloudy colourless fluid was obtained. Microscopic examination of the bronchial washing later revealed a marked excess of eosinophils, greater than 10% of the total cells present with the presence of Charcot Leyden crystals (figure 4 and 5). Charcot Leyden crystals are produced from the breakdown of eosinophils. They stain purplish-red on trichome stain and appear as paired hexagonal pyramids joined at the bases. They consist of lysophospholipase, an enzyme synthesized by eosinophils.[2] The presence of Charcot Leyden crystals gave us a broad differential diagnosis including fungal infections such as Aspergillus fumigatus, parasitic infections such as schistosomiasis, Ascaris and Strongyloides, drugs and toxins related, and autoimmune conditions such as Churg Strauss syndrome.[1] However, the specimen from bronchial washing was not only tested negative for microscopy, culture and sensitivity (MC&S) but was also negative for all other pathogens such as Strongyloides, Schistosoma, toxoplasma, filarial and fungal infections. Although these findings were in keeping with Churg Strauss Syndrome, it was deemed unlikely that the patient indeed suffers from eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) as he did not have symptoms suggestive of sinusitis or asthma. Hence, a differential diagnosis of eosinophilic pneumonia was considered. FIGURE 4. Bronchial washing Charcot-Leyden crystals. 171
5 FIGURE 5. Charcot-Leyden crystals. TREATMENT AND FOLLOW-UP After excluding all the possible infectious causes to his symptoms, he was then started on both prednisolone 40mg once daily and inhaled beclomethasone and formoterol (Fostair ). 1-month post discharge the patient was reviewed in outpatient clinic. He appeared well with no respiratory symptoms, and his chest was clear on auscultation. A respiratory function test showed normal values of FEV (83% predicted); FVC 3.49 (79% predicted) and ratio of 85%. However, 10 days after discontinuing his prednisolone, he then re-attended Emergency Department presenting with another episode of symptoms relapse and hypoxia, with po 2 of He was then again restarted on prednisolone 60mg and was advised to continue with corticosteroid treatment for at least 6 months. When reviewed in outpatient clinic again, his repeat chest radiograph showed a resolution of the previous consolidation with clear lung fields (figure 6). The patient also reported a full resolution of his respiratory symptoms, and his eosinophilia has also improved, with eosinophil count of 0.3x10 9 /L. 172
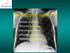
6 FIGURE 6. A repeat chest radiograph following commencement of corticosteroid treatments, showing clear lung fields and costophrenic recesses. DISCUSSION - INVESTIGATION FOR CEP The association between eosinophilia and pulmonary infiltrates was initially identified by Löffler in Later in 1969, Liebow and Carrington subsequently described the term eosinophilic pneumonia as an umbrella term to include all disorders characterised by eosinophilic infiltration of the lungs, with or without blood eosinophilia.[1] The exact role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of various eosinophilic pneumonia remains unclear. In parasitic infections such as strongyloidiasis, eosinophils play a vital role in eradicating the infectious offending pathogen; however, in conditions like allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and asthma, eosinophils accumulate in the lungs due to immune hypersensitivity and act as the prominent driver for further tissue injury. There are a number of aetiology that are known to trigger pulmonary eosinophilic syndromes, such as parasitic infestations in tropical pulmonary eosinophilia, as well as some commonly used drugs including clarithromycin, ibuprofen, and diclofenac in drug-or toxin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia. However, in some cases such as idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonia, the culprits causing such syndromes are poorly recognized.[1] Idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonia can present with either acute or chronic manifestations.[3]chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) occurs predominantly in middleaged women and can occur in conjunction with asthma in more than 50% of the cases.[4,5]there are no clearly established criteria for the diagnosis of CEP but the diagnosis can be based on the presence of classical respiratory symptoms of more than 2 weeks duration, pulmonary infiltrates on chest radiography, alveolar and/or peripheral blood 173
7 eosinophilia and a prompt response to corticosteroids treatment.[4,6]bal of >25% eosinophils is highly suggestive of CEP. The diagnosis of CEP is crucial as less than 10% of cases resolve spontaneously. If untreated, CEP can progress to irreversible pulmonary fibrotic changes.[7] We, therefore, suggest that CEP should be considered in patients with bilateral lung consolidation and peripheral blood eosinophilia, and BAL should be considered as the gold-standard investigation to confirm the diagnosis. DISCUSSION - MANAGEMENT OF CEP A case report published by Fox and Seed described three cases of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, all of which have unknown aetiology. All of these patients were found to have chest radiographs evident of widespread shadowing bilaterally, as well as blood eosinophilia. In two of these three cases the patients present with at least 6-week history of progressive dyspnoea, malaise, and weight loss. Similar to our patient, one of the patients in Fox and Seed s report was initially treated with combined antibiotics for lower respiratory tract infection but continued to deteriorate both clinically and radiologically. All of the patients in Fox and Seed s case report underwent open lung biopsy, all of which revealed both interstitial and intra-alveolar eosinophilic pneumonia with vasculitis and bronchiolitis obliterans. Electron microscopy also revealed eosinophilia and the presence of eosinophilic granules within macrophages. One patient recovered spontaneously, while the two other had drastic improvement of their clinical symptoms and radiological clearance after treatment with oral prednisolone. These patients were given oral prednisolone for at least 6 months. However, similar to our patient, one patient from Fox and Seed s report suffered both symptoms and radiological relapse only five months after steroid withdrawal.[8] An article published by Ono et al. suggested although both acute and chronic eosinophilic pneumonia was shown to have excellent response to corticosteroids treatment, the risk of relapse during steroid weaning is very high.[3,5]a long-term follow-up of 12 CEP patients over an average of 10.2 years showed that only 2 out of 12 patients were able to successfully discontinue their high-dose steroid therapy at 1 and 3 years respectively, without demonstrating a clinical relapse of their symptoms for at least 6 years. For the remaining of the patients, a large proportion relapsed, some on more than one occasions. These relapses were found to have occurred either when corticosteroids therapy was completely discontinued, or even during tapering of steroids doses. Once corticosteroids treatment was recommended in these patients, they again responded with the same dramatic improvement in 174
8 their symptoms. However, this improvement is generally only sustainable until the steroids dose was again decreased, leading to a pattern of remission and recurrence of symptoms.[4] The long-term use of corticosteroid therapy can lead to significant side effects such as development of cushingoid habitus, osteoporosis, growth suppression and hyperlipidaemia.[9,10]in 2012, Shin YS et al explored the option of treating CEP with anti- IgE therapy.[5]anti-ige antibody was one of the most novel and striking discovery in allergy field. It not only is capable of down-regulating the expression of high-affinity IgE receptors (FcεRI) in inflammatory cells but is also able to rapidly reduce the levels of circulating free IgE. Both patients in their case report were diagnosed with CEP and were initially treated with systemic corticosteroids. However, they both suffered recurrent pulmonary and peripheral eosinophilia after reduction of oral steroid doses. Anti-IgE therapy was later started in these two patients and the result was that anti-ige therapy when administered once every two weeks for ten cycles successfully induced remission of respiratory symptoms with no further evidence of both peripheral eosinophilia and eosinophilic infiltration on radiological imaging for at least 15 months.[5] Despite studies showing successful treatment of CEP with anti-ige therapy, the data on this still remains very limited.[5,11] In our case, our patient presented with an episode of symptoms relapse and hypoxia only 10 days after discontinuing prednisolone treatment. When restarted on prednisolone 60mg, he again responded with dramatic improvement of his symptoms. The treatment with corticosteroids was maintained for at least 6 months, resulting in both radiological and clinical resolution of his symptoms. Although high-dose corticosteroids still remain as the mainstay treatment for CEP, there are no consensuses on the duration or doses of corticosteroids treatment. Most authors recommend an initial dose of 0.5 to 1mg/kg/day of prednisolone with a gradual tapering of doses over a six to twelve-month period. As previously discussed, relapses occurring during and after weaning of corticosteroid doses are observed in up to 50% of the patients. Relapses in these patients remain responsive to corticosteroid therapy, and up to half of patients affected by CEP will require long-term corticosteroid treatment. Therefore, it is advisable to recommend preventative measures to reduce the risks of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis.[12] 175
9 CONCLUSION The patient in our case report presented with clinical features typical of CEP. Unfortunately, the diagnosis of CEP was overlooked on the first admission despite peripheral eosinophilia and HRCT findings suggestive of CEP, resulting in multiple hospital admissions. Although the correct diagnosis was eventually made, we strongly suggest that CEP should be considered in patients with bilateral lung consolidation and peripheral blood eosinophilia, and BAL should be carried out in order to confirm the diagnosis. Other than that, prompt treatment with corticosteroids is also crucial as untreated CEP can lead to irreversible pulmonary fibrotic changes.[7] ACKNOWLEDGMENT Many thanks to Professor Mike Sheaff (consultant histopathologist) from BARTs Health NHS Trust London for the histology contribution on Charcot-Leyden crystals. FINANCIAL / NON-FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES: The authors have reported that no potential conflicts of interest exist with any authors, companies or organisations. REFERENCES 1. Fishman AP, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Grippi MA, Senior RM, and Pack AI. (2008). The eosinophilic pneumonias. Fishman s Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders. 4 th Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, pp Siddique SM, Gilotra. NA (2014). Crystal clear: A unique clue to diagnosis in a patient with recurrent nausea and vomiting. Gastroenterology, 147:e1-e2. 3. Ono E, Taniguchi M, Mita H, et al. (2008). Increased urinary leukotriene E 4 concentration in patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. European Respiratory Journal, 32(2), pp Naughton M, Fahy J, FitzGerald MX. (1993). Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, a long-term follow-up of 12 patients. Chest Journal, 103(1), pp Shin YS, Jin HJ, Yoo HS, et al. (2012). Successful treatment of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia with anti- IgE therapy. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 27(10), pp Marchand E, Cordier JF. (2006) Idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 27(2), pp Kolb AG, Ives ST, Davies SF et al. (2013) Diagnosis in just over a minute: a case of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 28(7): Fox B and Seed WA. (1980). Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Thorax, Volume 35, pp Buchman AL. (2001). Side effects of corticosteroid therapy. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 33(4), pp Stanbury RM, Graham EM. (1998). Systemic corticosteroid therapy - side effects and their management. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 82(6), pp Kaya H, Gümüs S, Uçar E et al. (2012). Omalizumab as a steroid-sparing agent in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Chest, 142(2), pp
10 12. Marchand E, Cordier JF. (2006). Idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 1:
Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum
 Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Eosinophilic lung diseases
 Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
EOSINOPHLIC LUNG DISEASES
 EOSINOPHLIC LUNG DISEASES A wide spectrum of infiltrative lung diseases characterized by infiltration of lung parenchyma with eosinophils and/or peripheral blood eosinophilia. How is the diagnosis made?
EOSINOPHLIC LUNG DISEASES A wide spectrum of infiltrative lung diseases characterized by infiltration of lung parenchyma with eosinophils and/or peripheral blood eosinophilia. How is the diagnosis made?
Eosinophilic lung diseases - what the radiologist needs to know
 Eosinophilic lung diseases - what the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-0803 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, F. Japon Sola; Cádiz/ES
Eosinophilic lung diseases - what the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-0803 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, F. Japon Sola; Cádiz/ES
Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging
 July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: An Unusual Complication of Bronchial Asthma
 Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: An Unusual Complication of Bronchial Asthma Pages with reference to book, From 329 To 331 S. Fayyaz Hussain, Javaid A. Khan ( Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: An Unusual Complication of Bronchial Asthma Pages with reference to book, From 329 To 331 S. Fayyaz Hussain, Javaid A. Khan ( Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Disease spectrum. IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
 Aspergillus & ABPA Disease spectrum IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis ABPA ABPA pathophysiology conidia of Aspergillus trapped in mucous and narrowed airways of asthmatics/cf germinate to form hyphae
Aspergillus & ABPA Disease spectrum IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis ABPA ABPA pathophysiology conidia of Aspergillus trapped in mucous and narrowed airways of asthmatics/cf germinate to form hyphae
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected
 Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Imaging Spectrum of Allergic Lung Disease: Hypersensitivity Reactions on the Lung Parenchyma
 Imaging Spectrum of Allergic Lung Disease: Hypersensitivity Reactions on the Lung Parenchyma Moon Sung Kim 1, Ki-Nam Lee 1, Won Jin Choi 1, Bo Ra Kim 1, Eun-Ju Kang 1 1 Department of Radiology, Dong-A
Imaging Spectrum of Allergic Lung Disease: Hypersensitivity Reactions on the Lung Parenchyma Moon Sung Kim 1, Ki-Nam Lee 1, Won Jin Choi 1, Bo Ra Kim 1, Eun-Ju Kang 1 1 Department of Radiology, Dong-A
Interesting cases in fungal asthma
 Interesting cases in fungal asthma Ritesh Agarwal MD, DM Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India Fungal asthma Broadly defined as the
Interesting cases in fungal asthma Ritesh Agarwal MD, DM Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India Fungal asthma Broadly defined as the
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids
 Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA. Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine)
 Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine) Conventional diagnostic criteria for ABPA Primary Episodic bronchial obstruction (asthma) Peripheral blood eosinophilia
Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine) Conventional diagnostic criteria for ABPA Primary Episodic bronchial obstruction (asthma) Peripheral blood eosinophilia
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS
 HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Α 78-year-old female who presents with a non-resolving pneumonia: what is your diagnosis?
 Evangelia Panagiotidou 1, Serafeim-Chrysovalantis Kotoulas 1, Maria Kilmpasani 2, Nikoleta Pastelli 2, Sofia Akritidou 1, Evangelos Chatzopoulos 1, Vasilis Bikos 1, Vasilios Bagalas 1, Katalin Fekete-Passa
Evangelia Panagiotidou 1, Serafeim-Chrysovalantis Kotoulas 1, Maria Kilmpasani 2, Nikoleta Pastelli 2, Sofia Akritidou 1, Evangelos Chatzopoulos 1, Vasilis Bikos 1, Vasilios Bagalas 1, Katalin Fekete-Passa
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
 May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
A 31-year-old female with a rare cause of recurrent lower lobar collapses
 Radhika Banka, Dayle Terrington, Ajay V. Kamath radhika.banka@gmail.com Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK. A 31-year-old female with a rare cause of recurrent
Radhika Banka, Dayle Terrington, Ajay V. Kamath radhika.banka@gmail.com Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK. A 31-year-old female with a rare cause of recurrent
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
A case of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis successfully treated with mepolizumab
 Terashima et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:53 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0617-5 CASE REPORT Open Access A case of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis successfully treated with mepolizumab
Terashima et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:53 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0617-5 CASE REPORT Open Access A case of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis successfully treated with mepolizumab
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia presenting with ipsilateral pleural effusion: a case report
 Sriratanaviriyakul et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2016) 10:227 DOI 10.1186/s13256-016-1005-5 CASE REPORT Open Access Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia presenting with ipsilateral pleural effusion:
Sriratanaviriyakul et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2016) 10:227 DOI 10.1186/s13256-016-1005-5 CASE REPORT Open Access Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia presenting with ipsilateral pleural effusion:
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
Pneumonia. Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial
 Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
The Pathologic Manifestations of Small Airway Disease. Samuel A. Yousem, MD. Small Airway Disease (SAD) SAD
 The Pathologic Manifestations of Small Airway Disease Samuel A. Yousem, MD Small Airway Disease (SAD) A clinicopathologic syndrome reflecting a CHRONIC inflammatory and cicatricial process primarily affecting
The Pathologic Manifestations of Small Airway Disease Samuel A. Yousem, MD Small Airway Disease (SAD) A clinicopathologic syndrome reflecting a CHRONIC inflammatory and cicatricial process primarily affecting
Prof Neil Barnes. Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital
 Prof Neil Barnes Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital ASTHMA: WHEN EVERYTHING FAILS WHAT DO YOU DO? South GP CME 2013, Dunedin Saturday 17 th August 2013
Prof Neil Barnes Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital ASTHMA: WHEN EVERYTHING FAILS WHAT DO YOU DO? South GP CME 2013, Dunedin Saturday 17 th August 2013
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Radiological syndroms. Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome
 Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach
 Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference
 Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Pulmonary Pearls. Medical Pearls. Case 1: Case 1 (cont.): Case 1: What is the Most Likely Diagnosis? Case 1 (cont.):
 Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
Churg-Strauss syndrome that presented with mediastinal lymphadenopathy and calculous cholecystitis
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:179-183 Churg-Strauss syndrome that presented with mediastinal lymphadenopathy and calculous cholecystitis Jung Yoon Choi 1, Ji Eun Kim 1, In Young Choi
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:179-183 Churg-Strauss syndrome that presented with mediastinal lymphadenopathy and calculous cholecystitis Jung Yoon Choi 1, Ji Eun Kim 1, In Young Choi
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA
 ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
CASE REPORT PHOTOGRAPHIC NEGATIVE OF PULMONARY EDEMA. DIFFERENTIATING CHRONIC EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA FROM CHRONIC HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS.
 CASE REPORT PHOTOGRAPHIC NEGATIVE OF PULMONARY EDEMA. DIFFERENTIATING CHRONIC EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA FROM CHRONIC HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS. Talha Mahmud, Muhammad Omer Naeem, Muhammad Siddique ABSTRACT:
CASE REPORT PHOTOGRAPHIC NEGATIVE OF PULMONARY EDEMA. DIFFERENTIATING CHRONIC EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA FROM CHRONIC HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS. Talha Mahmud, Muhammad Omer Naeem, Muhammad Siddique ABSTRACT:
Immune-mediated lung disease. Ian Sabroe
 Immune-mediated lung disease Ian Sabroe It s all immune? Diseases that doesn t have immune involvement? The processes of response to injury and tissue repair are key homeostatic pathways involved in all
Immune-mediated lung disease Ian Sabroe It s all immune? Diseases that doesn t have immune involvement? The processes of response to injury and tissue repair are key homeostatic pathways involved in all
Index No. All five (05) questions should be answered. All questions carry equal marks.
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Eosinophilia Associated Lung Diseases
 Eosinophilia Associated Lung Diseases Stephen P. Peters, MD, PhD, FAAAAI, FACP, FCCP, FCPP Thomas H. Davis Chair in Pulmonary Medicine Chief, Section on Pulmonary Critical Care, Allergy & Immunologic Diseases
Eosinophilia Associated Lung Diseases Stephen P. Peters, MD, PhD, FAAAAI, FACP, FCCP, FCPP Thomas H. Davis Chair in Pulmonary Medicine Chief, Section on Pulmonary Critical Care, Allergy & Immunologic Diseases
Chronic lung diseases in children Simple choice 1. Finger clubbing is not characteristic for: a) Diffuse bronchiectasis b) Cystic fibrosis c)
 Chronic lung diseases in children Simple choice 1. Finger clubbing is not characteristic for: a) Diffuse bronchiectasis b) Cystic fibrosis c) Bronchiolitis obliterans d) Complicated acute pneumonia e)
Chronic lung diseases in children Simple choice 1. Finger clubbing is not characteristic for: a) Diffuse bronchiectasis b) Cystic fibrosis c) Bronchiolitis obliterans d) Complicated acute pneumonia e)
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County
 Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions
 Review Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Clinical Radiology and Case Reports Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions D souza M *, Rajiah P, Khan A and Irion K Department
Review Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Clinical Radiology and Case Reports Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions D souza M *, Rajiah P, Khan A and Irion K Department
Efficacy of short-term prednisolone treatment in patients with chronic eosinophilic pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERSTITIAL AND ORPHAN LUNG DISEASE Efficacy of short-term prednisolone treatment in patients with chronic eosinophilic pneumonia Yoshiyuki Oyama 1, Tomoyuki Fujisawa 1, Dai Hashimoto
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERSTITIAL AND ORPHAN LUNG DISEASE Efficacy of short-term prednisolone treatment in patients with chronic eosinophilic pneumonia Yoshiyuki Oyama 1, Tomoyuki Fujisawa 1, Dai Hashimoto
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Lung Injury after HCT
 Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
The Ghost in the Closet. Allergic Sino-Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis Without Bronchial Asthma: A Case Report & Review of the Subject
 Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 24(1): pp. 55-59 2010. The Ghost in the Closet. Allergic Sino-Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis Without Bronchial Asthma: A Case Report & Review of the Subject Department of Pulmonology,
Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 24(1): pp. 55-59 2010. The Ghost in the Closet. Allergic Sino-Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis Without Bronchial Asthma: A Case Report & Review of the Subject Department of Pulmonology,
Dr Conroy Wong. Professor Richard Beasley. Dr Sarah Mooney. Professor Innes Asher
 Professor Richard Beasley University of Otago Director Medical Research Institute of New Zealand Wellington Dr Sarah Mooney Physiotherapy Advanced Clinician Counties Manukau Health NZ Respiratory and Sleep
Professor Richard Beasley University of Otago Director Medical Research Institute of New Zealand Wellington Dr Sarah Mooney Physiotherapy Advanced Clinician Counties Manukau Health NZ Respiratory and Sleep
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
SHO Teaching. Dr. Amir Bhanji Consultant Nephrologist, Q.A hospital, Portsmouth
 SHO Teaching Vasculitis Renal medicine Dr. Amir Bhanji Consultant Nephrologist, Q.A hospital, Portsmouth OUTLINE What is vasculitis Causes Classification Brief look into ANCA Associated Vasculitis (AAV)
SHO Teaching Vasculitis Renal medicine Dr. Amir Bhanji Consultant Nephrologist, Q.A hospital, Portsmouth OUTLINE What is vasculitis Causes Classification Brief look into ANCA Associated Vasculitis (AAV)
Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9338-17 Intern Med 57: 1281-1285, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient Yuki Hosono, Nobuhiko Sawa,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9338-17 Intern Med 57: 1281-1285, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient Yuki Hosono, Nobuhiko Sawa,
Received February 23, Received revised March 15, Accepted for publication March 16, University of California, Davis, CA, USA
 643990HICXXX10.1177/2324709616643990Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case ReportsNguyen et al case-report2016 Case Report Acute Fibrinous and Organizing Pneumonia Associated With Allogenic
643990HICXXX10.1177/2324709616643990Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case ReportsNguyen et al case-report2016 Case Report Acute Fibrinous and Organizing Pneumonia Associated With Allogenic
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Asthma - Chronic. Presentations of asthma Cough Wheeze Breathlessness Chest tightness
 Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION!
 UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
Silicosis in Turkish denim sandblasters
 Occupational Medicine 2006;56:554 558 Published online 4 October 2006 doi:10.1093/occmed/kql094 Silicosis in Turkish denim sandblasters Metin Akgun 1, Arzu Mirici 1, Elif Yilmazel Ucar 1, Mecit Kantarci
Occupational Medicine 2006;56:554 558 Published online 4 October 2006 doi:10.1093/occmed/kql094 Silicosis in Turkish denim sandblasters Metin Akgun 1, Arzu Mirici 1, Elif Yilmazel Ucar 1, Mecit Kantarci
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
ASTHMA. Dr Liz Gamble BRI
 ASTHMA Dr Liz Gamble BRI Diagnosis Clinical: wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness, cough Variable airflow obstruction: peak flow chart, spirometry with reversibility to bronchodilators Airways hyper-responsiveness
ASTHMA Dr Liz Gamble BRI Diagnosis Clinical: wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness, cough Variable airflow obstruction: peak flow chart, spirometry with reversibility to bronchodilators Airways hyper-responsiveness
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Cryptogenic Organising Pneumonia As The Initial Presenting Manifestation of SLE
 BMH Medical Journal 2015;2(3):79-83 Case Report Cryptogenic Organising Pneumonia As The Initial Presenting Manifestation of SLE Neena Mampilly MD, G Manoj MD, Binoy J Paul MD, PhD, DNB, FRCP Baby Memorial
BMH Medical Journal 2015;2(3):79-83 Case Report Cryptogenic Organising Pneumonia As The Initial Presenting Manifestation of SLE Neena Mampilly MD, G Manoj MD, Binoy J Paul MD, PhD, DNB, FRCP Baby Memorial
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Severe fever and dyspnoea in a young girl with Hodgkin lymphoma
 Eleftheria Chaini 1, Dimitra Haini 2, Manos Antonakis 1, Miltos Vassiliou 3 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Corfu, Greece. 2 Radiology Lab, Nikea-Piraeus General Hospital, Athens,
Eleftheria Chaini 1, Dimitra Haini 2, Manos Antonakis 1, Miltos Vassiliou 3 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Corfu, Greece. 2 Radiology Lab, Nikea-Piraeus General Hospital, Athens,
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
Possible eosinophilic pneumonia from Alternaria
 Allergology International (1999) 48: 79 83 Case Report Possible eosinophilic pneumonia from Alternaria Shoichiro Taniuchi, Rika Miyazaki, Satoshi Yoshijima and Yohnosuke Kobayashi Department of Paediatrics,
Allergology International (1999) 48: 79 83 Case Report Possible eosinophilic pneumonia from Alternaria Shoichiro Taniuchi, Rika Miyazaki, Satoshi Yoshijima and Yohnosuke Kobayashi Department of Paediatrics,
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I. December 5, 2012
 SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Professor Rob Miller
 BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2013 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Professor Rob Miller University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Prof Rob Miller
BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2013 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Professor Rob Miller University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Prof Rob Miller
All I Need Is The Air That I Breathe: A Case Study of Immunotherapy and Severe Pneumonitis
 All I Need Is The Air That I Breathe: A Case Study of Immunotherapy and Severe Pneumonitis Presenter Disclosure Faculty/Speaker: Dr. Brett Finney BSc MD CCFP Relationships with financial sponsors: Grants/Research
All I Need Is The Air That I Breathe: A Case Study of Immunotherapy and Severe Pneumonitis Presenter Disclosure Faculty/Speaker: Dr. Brett Finney BSc MD CCFP Relationships with financial sponsors: Grants/Research
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Initial and Follow-up HRCT Features
 Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Initial and Follow-up HRCT Features Poster No.: E-0037 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: Scientific Exhibit M. Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Lung, CT-High Resolution, CT, Computer
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Initial and Follow-up HRCT Features Poster No.: E-0037 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: Scientific Exhibit M. Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Lung, CT-High Resolution, CT, Computer
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas
 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas Rishi Raj MD Director, Interstitial Lung Diseases Program Clinical Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Stanford University
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas Rishi Raj MD Director, Interstitial Lung Diseases Program Clinical Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Stanford University
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Case Report Daptomycin-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia: Late Onset and Quick Recovery
 Hindawi Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2017, Article ID 8525789, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8525789 Case Report Daptomycin-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia: Late Onset and Quick Recovery
Hindawi Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2017, Article ID 8525789, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8525789 Case Report Daptomycin-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia: Late Onset and Quick Recovery
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
 Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
