Sudden death in asthma
|
|
|
- Alice Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax, 1979, 34, Sudden death in asthma J R M BATEMAN AND S W CLARKE From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, The Royal Free Hospital, London NW3 2QG, UK ABSTRACT Two deaths after sudden severe asthma attacks in young people are reported from a clinic set up to identify and manage "at risk" patients. These deaths occurred despite frequent visits at which recommendations made by previous studies were implemented. The risk factors and management of such episodes have been reviewed. Precautions taken proved inadequate due to the severe, abrupt nature of the attacks, failure of the patients' immediate treatment, and delay in reaching hospital. Consideration should be given to the self-administration of subcutaneous adrenaline or specific beta-agonists, the provision of a detailed medical card, and free access to the nearest hospital in such cases. Until the present century asthma was considered a relatively mild illness with a normal or even long life expectancy. Laennec, Osler (Silverglade, 1971), and Trousseau (Earle, 1953) have all been quoted as holding this belief. The first death from asthma with necropsy findings to be recorded in the English literature was in 1945 (Thomson, 1945). During the 1960s there was concern and controversy over the association of increased asthma mortality with the rise in sales of pressurised aerosol bronchodilators (Inman and Adelstein, 1969). Since then considerable attention has been focused on asthma deaths. These deaths often occur in young people, are unexpected, but even so may be preventable. The fatal attack often develops rapidly, and death ensues before the administration of adequate treatment. Recommendations for the prevention of these episodes include: recognition of "at risk" patients, patient and doctor education, specialised units with a selfadmission service, objective assessment of the severity of the attack, and appropriate drug treatment. During the past 18 months we have attempted to implement the above recommedations but sadly report two cases of sudden death from asthma during this period, which we have been able to examine critically for the factors leading to their deaths. Case histories CASE 1 A 22-year-old female drama student had a long history of asthma and eczema dating from early 40 childhood. Throughout her life she had required continuous bronchodilator treatment and intermittent courses of corticosteroids. She was a tense and determined girl who always delayed seeking advice until her asthma attacks were very severe. She often refused corticosteroids due to the side effects of facial puffiness and weight gain. In January 1977 after an upper respiratory tract infection she was admitted in severe acute asthma requiring intensive treatment (bronchodilators, steroids, antibiotics, oxygen, and physiotherapy). As a result of this admission and a past history of nocturnal and brittle asthma (Turner- Warwick, 1977) she was considered to be an at risk patient and therefore was followed closely as an outpatient with the aid of continuous, twice daily, peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) recordings. Examples of her recordings (fig 1) show the wide diurnal variation in PEFR associated with sputum production and relative stabilisation with appropriate corticosteroids. In July 1977 she was readmitted, unconscious in respiratory failure after a sudden, severe asthma attack. She responded promptly to immediate resuscitation measures (oxygen and intravenous aminophylline) and made a rapid recovery with intensive treatment. She did not require artificial ventilation. After this admission, in an attempt to prevent her arriving in casualty moribund, she was instructed in the self-administration of subcutaneous injections of terbutaline for use during sudden severe asthma attacks that did not respond to pressurised aerosol bronchodilators. In October 1977 she was admitted to a nearby
2 Sudden death in asthma Q O İ -W 0 a R 2'- n.- o0 = U ) c C) 30 20], 10 - O - Salbutamol 4mg tds I eecotide 2 puffs qds Salbutomo[ spandet at night Salbutomol spandet at night *s $ a x 5001~~f. SOO I F ;8mg 16mg 8mg _x MDD MD tm MDD E I I'I I Days Fig 1 Patient 1. Examples of morning (A) and evening ( * ) PEFR recordings. Reversibility of airways obstruetion with an aerosol bronchodilator denoted (--- -). Nocturnal attacks (morning dip: MD) denoted (e). hospital with cardiorespiratory arrest after a final sudden severe asthma attack. Regrettably her terbutaline injection had been left in another handbag at home and consequently was never used. Initial resuscitation was successful, although she remained in coma and required artificial ventilation. Some 18 hours later she died after a second cardiac arrest. At necropsy there was extensive mucus plugging and muscular hypertrophy of the smaller airways, the surfaces of which were denuded of epithelium and their basement membrane thickened. CASE 2 A 25-year-old female hairdresser had a three year history of asthma. Her first attack was precipitated by an upper respiratory tract infection and necessitated hospital admission. After this admission her asthma remained relatively mild, requiring only intermittent use of a salbutamol inhaler. She did, however, have a history of nocturnal wheezing. After an upper respiratory tract infection in October 1976 she was admitted under X our care for the first time in severe acute asthma. With intensive therapy (bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, oxygen, and physiotherapy) she made a rapid and complete recovery. On discharge her progress was closely followed with the aid of continuous PEFR recordings (fig 2). For the first two months after discharge her asthma was in remission requiring no treatment. From then on, however, she exhibited a moderately wide diurnal variation in PEFR associated with sputum production. Her early morning wheezing improved after the administration of a slow release bronchodilator (salbutamol spandet). Appropriate oral corticosteroid therapy, however, completely stabilised her asthma and sputum production ceased. Again, this young woman had a tense and determined personality and was most unwilling to take corticosteroids, for similar reasons as the first patient. She was not, however, considered to be at risk from sudden severe asthma attacks. In October 1977, after nine months' follow-up, she suffered a sudden severe asthma attack while at work (about seven miles from our hospital), 41 74
3 r.t. 42~~~~~~~~~~~~~~J Al C) 30-, 201- ~>E c c~ 400- E *~ a x -D 100 Y 0 Terbutaline 5mg tds Salbutamd spandet 8mg atnight Becotide 2 puffs qds Ir-, I I t MD i I t tt t MD MD MD MD Days t tt MDMDMD R M Bateman and S W Clarke Salbutamol spandet at night (mg) t MD Fig 2 Patient 2. Examples of morning (A) and evening ( U) PEFR recordings. Nocturnal attacks (morning dip: MD) denoted (0). First seven days are taken from a period of remission. which did not respond to her salbutamol inhaler. She was rushed here by taxi, but on arrival was in cardiorespiratory arrest. The most striking event during resuscitation was the almost immediate response to parenteral adrenaline, with respect to the relief of airways obstruction and the restoration of effective cardiovascular function. Despite this rapid response she remained comatose and finally died one week later. Serial EEG recordings throughout this period were compatible with brain death. Again the classic pathological features of asthma were present in the lungs at necropsy. Discussion Jo treatment 1. Similar features are present in both cases. Firstly, continuous recording showed a wide diurnal variation in PEFR associated with nocturnal wheezing and sputum production, which resolved with appropriate corticosteroids. Neither patient was taking corticosteroids at the time of the abrupt fatal attack. Secondly, parenteral, but not aerosol, administration of bronchodilators rapidly partially relieved the airways obstruction during the acute episode. Finally, the distances travelled and time taken to seek hospital treatment were such that both patients arrived with cardiorespiratory arrest. A long history of asthma (Macdonald et al, 1976a), under-use of corticosteroids (Cochrane and Clark., 1975), and previous admissions with severe acute attacks (Macdonald et a!, 1976b) are factors associated with death from asthma. Recently it has been shown that F-. a wide diurnal variation in PEER during the early days of recovery from
4 Sudden death in asthma severe acute asthma was associated with an increased risk of sudden severe recurrence (Hetzel et al, 1977). Our patients showed this pattern well before the fatal attack, indicating airway instability and the need for more intensive therapy. In our experience the charting of twice daily PEFR on a diary card at home and subsequent modification of therapy has been a useful "biofeedback" procedure in managing asthmatic patients. In this manner the individual's asthma pattern may be easily determined and possible at risk patients identified. Patients showing a wide diurnal variation in PEFR are probably at risk from abrupt severe asthma attacks both during recovery from an acute episode and, as in these two cases, well before the acute episode. A wide diurnal variation in PEFR may well be a better guide to the recognition of the susceptible patient than the factors previously mentioned. Airway obstruction in asthma comprises smooth muscle contraction, mucosal oedema, and mucus plugging (Dunnill, 1971). The cases described suggest that mucosal oedema and mucus plugging were the key underlying disturbances leading to death and that acute smooth muscle contraction was the final event. Modern treatment of acute asthma centres on the reversal of smooth muscle contraction and often little attention is given to the underlying mechanism and treatment of mucosal oedema and mucus plugging. Corticosteroids reduce both mucosal oedema and lung secretions, and although their use in asthma has increased recent reports indicate that they are still under-prescribed (Cochrane and Clarke, 1975; Macdonald et al, 1976a; British Medical Journal, 1978; Seaton, 1978). Regrettably both patients in this report frequently refused to take steroids for cosmetic reasons. Immediate and appropriate treatment is essential to survival during a sudden severe asthma episode. At the time of the final admission both patients immediately responded to parenteral adrenaline. Adrenaline is now little used in treating acute asthma (British Medical Journal, 1978), although it remains an effective first-line drug for the hospital management of the young acute asthmatic (Harris, 1975; Hutchinson, 1975). There is no convincing evidence in published reports that the administration of adrenaline is contraindicated in young otherwise healthy people. Subcutaneous injections of terbutaline have been available since 1971 and of salbutamol since The effectiveness of these more selective betaagonists has not been compared with that of adrenaline, and experience in their use is limited. Patients may easily be instructed in the selfadministration of subcutaneous injections and in this situation such a procedure may be life saving. A self-admission service to a specialised asthma unit is effective in preventing fatal asthma (Crompton and Grant, 1975). Such a service has been in operation at our hospital for the past 18 months. The distances travelled and time taken by the two patients to reach hospital resulted in delay in their receiving appropriate emergency treatment. Their deaths might have been avoided if they had sought advice at the nearest casualty department. In future at risk patients should perhaps be issued with a medical bracelet and identity card displaying basic medical details and instructed to travel to the nearest casualty department in the event of an emergency rather than to try to reach their usual hospital. About 1500 patients die from asthma each year in the UK (British Medical Journal, 1978). Many are young and in most death could have been prevented. We believe that prevention is possible, provided that, firstly, the at risk patient may be identified; secondly, outpatient treatment in such patients is adjusted with the aid of continuous PEFR recording, and thirdly, appropriate treatment is rapidly administered during an acute severe episode, initially by the patients themselves. References British Medical Journal (1978). Management of severe acute asthma. 1, Cochrane, G M, and Clark, T J H (1975). A survey of asthma mortality in patients between ages 35 and 64 in the Greater London hospitals in Thorax, 30, Crompton, G K, and Grant, I W B (1975). Edinburgh emergency asthma admission service. British Medical Journal, 4, Dunnill, M S (1971). The pathology of asthma. In Identification of Asthma, Ciba Foundation Study Group No 38, edited by R Porter and J Birch, pp Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh and London. Earle, B V (1953). Fatal bronchial asthma. A series of fifteen cases with a review of the literature. Thorax, 8, Harris, F (1975). Management of acute asthma. British Medical Journal, 4, 288. Hetzel, M R, Clarke, T J H, and Branthwaite, M A (1977). Asthma: analysis of sudden deaths and ventilatory arrests in hospital. British Medical Journal, 1, Hutchinson, J H (1975). Respiratory diseases. In Practical Paediatric Problems, 4th edn, pp Lloyd-Luke, London. Inman, W H W, and Adelstein, A M (1969). Rise and fall of asthma mortality in England and Wales in relation to use of pressurised aerosols. Lancet, 2,
5 44 Macdonald, J B, Seaton, A, and Williams, D A (1976a). Asthma deaths in Cardiff : 90 deaths outside hospital. British Medical Journal, 1, Macdonald, J B, Macdonald, E T, Seaton, A, and Williams, D A (1976b). Asthma deaths in Cardiff : 53 deaths in hospital. British Medical Journal, 2, Seaton, A (1978). Asthma-contrasts in care. Thorax, 33, 1-2. Silverglade, A (1971). Evaluation of reports of deaths from asthma. Journal of Asthma Research, 8, J R M Bateman and S W Clarke Thomson, J G (1945). Fatal bronchial asthma showing the asthmatic reaction in an ovarian teratoma. Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology, 57, Turner-Warwick, M (1977). On observing patterns of airflow obstruction in chronic asthma. British Journal of Diseases of the Chest, 71, Requests for reprints to: Dr J R M Bateman, Department of Thoracic Medicine, The Royal Free Hospital, London NW3 2QG. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 February Downloaded from on 22 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
An Audit on Hospital Management of Bronchial Asthma
 An Audit on Hospital Management of Bronchial Asthma Pages with reference to book, From 298 To 300 Javaid A. Khan, Shehryar Saghir, Ghazala Tabassum, S. Fayyaz Husain ( Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan
An Audit on Hospital Management of Bronchial Asthma Pages with reference to book, From 298 To 300 Javaid A. Khan, Shehryar Saghir, Ghazala Tabassum, S. Fayyaz Husain ( Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Subcutaneous adrenaline versus terbutaline in the
 Thorax 1988;43:19-23 Subcutaneous adrenaline versus terbutaline in the treatment of acute severe asthma M A SPITERI, A B MILLAR, D PAVIA, S W CLARKE From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, Royal Free
Thorax 1988;43:19-23 Subcutaneous adrenaline versus terbutaline in the treatment of acute severe asthma M A SPITERI, A B MILLAR, D PAVIA, S W CLARKE From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, Royal Free
Chronic persistent asthma presenting to an accident and emergency department compliance with B.T.S. guidelines
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1993, 10, 347-353 Chronic persistent asthma presenting to an accident and emergency department compliance with B.T.S. guidelines J. R. THOMPSON & M. A. LAMBERT Accident
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1993, 10, 347-353 Chronic persistent asthma presenting to an accident and emergency department compliance with B.T.S. guidelines J. R. THOMPSON & M. A. LAMBERT Accident
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Air or oxygen as driving gas for nebulised salbutamol
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 9-94 Air or oxygen as driving gas for nebulised salbutamol J G A GLEESON, S GREEN, AND J F PRICE Paediatric Respiratory Laboratory, Department of Thoracic Medicine,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 9-94 Air or oxygen as driving gas for nebulised salbutamol J G A GLEESON, S GREEN, AND J F PRICE Paediatric Respiratory Laboratory, Department of Thoracic Medicine,
Nocturnal and morning asthma
 Thorax (1975), 30, 436. Nocturnal and morning asthma Relationship to plasma corticosteroids and response to cortisol infusion C. A. SOUTAR, J. COSTELLO, 0. IJADUOLA, and M. TURNER-WARWICK Cardiothoracic
Thorax (1975), 30, 436. Nocturnal and morning asthma Relationship to plasma corticosteroids and response to cortisol infusion C. A. SOUTAR, J. COSTELLO, 0. IJADUOLA, and M. TURNER-WARWICK Cardiothoracic
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2
 CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2 M1 Objectives To understand how resuscitation techniques should be modified in the special circumstances of: Hypothermia Immersion and submersion Poisoning Pregnancy
CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2 M1 Objectives To understand how resuscitation techniques should be modified in the special circumstances of: Hypothermia Immersion and submersion Poisoning Pregnancy
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
 Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Pathway diagrams Annex F
 Pathway diagrams Annex F Fig 1 Asthma: The patient journey Asthma is diagnosed Making the diagnosis of asthma Confirming the diagnosis may depend on history, response to treatment, measurement of airflow
Pathway diagrams Annex F Fig 1 Asthma: The patient journey Asthma is diagnosed Making the diagnosis of asthma Confirming the diagnosis may depend on history, response to treatment, measurement of airflow
Can Fatal Asthma Be Prevented?
 Can Fatal Asthma Be Prevented? P. Barriot, B. Riou, and P. Duroux Introduction Asthma in France is a common disease which affects approximately 3 to 4 percent of the population and carries considerable
Can Fatal Asthma Be Prevented? P. Barriot, B. Riou, and P. Duroux Introduction Asthma in France is a common disease which affects approximately 3 to 4 percent of the population and carries considerable
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Viral-Induced Asthma:
 Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
Accident and emergency department attendance by
 Thorax 1989;44:700-705 Accident and emergency department attendance by asthmatic children S M O'HALLORAN, D P HEAF From the Respiratory Unit, Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital (Alder Hey), Liverpool
Thorax 1989;44:700-705 Accident and emergency department attendance by asthmatic children S M O'HALLORAN, D P HEAF From the Respiratory Unit, Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital (Alder Hey), Liverpool
Exacerbations. Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 1st WAO Allied Health Session - Asthma: Diagnosi Exacerbations Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark The health professional that care for patients with asthma exacerbation must be able to Identificafy
1st WAO Allied Health Session - Asthma: Diagnosi Exacerbations Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark The health professional that care for patients with asthma exacerbation must be able to Identificafy
beclometasone 100 MDI 2 puffs twice a day (recently changed to non CFC (Clenil Modulite))
 Case 1 Mr Thomson, a 32 year old asthmatic who is well known to you comes into your pharmacy. He is known to have a best peak flow of 640 L/min. He tells you that over the last few weeks he has been wakening
Case 1 Mr Thomson, a 32 year old asthmatic who is well known to you comes into your pharmacy. He is known to have a best peak flow of 640 L/min. He tells you that over the last few weeks he has been wakening
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP?
 THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
Asthma and the competitive swimmer
 Asthma and the competitive swimmer Introduction: One in seven children and one in 25 adults in Great Britain have asthma and the number is growing. Thus every swim squad or club will have a number of asthmatics
Asthma and the competitive swimmer Introduction: One in seven children and one in 25 adults in Great Britain have asthma and the number is growing. Thus every swim squad or club will have a number of asthmatics
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 22-26 Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an acute asthmatic attack D. DaCRUZ & C. HOLBURN Accident and Emergency Department,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 22-26 Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an acute asthmatic attack D. DaCRUZ & C. HOLBURN Accident and Emergency Department,
Frequency of nocturnal symptoms in asthmatic children attending a hospital out-patient clinic
 Eur Respir J, 1995, 8, 2076 2080 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.95.08122076 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1995 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Frequency of nocturnal
Eur Respir J, 1995, 8, 2076 2080 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.95.08122076 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1995 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Frequency of nocturnal
Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma
 Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
COPD/ Asthma. Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer
 COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
Anaphylaxis/Latex Allergy
 Children s Acute Transport Service CATS Clinical Guideline Anaphylaxis/Latex Allergy Document Control Information Author D Lutman Author Position Consultant Document Owner E Polke Document Owner Position
Children s Acute Transport Service CATS Clinical Guideline Anaphylaxis/Latex Allergy Document Control Information Author D Lutman Author Position Consultant Document Owner E Polke Document Owner Position
Recurrent wheezing illnesses 24.9% Similar to Australia Above global averages
 Prof Mike South Department of General Medicine Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Australia www.mikesouth.org.au Asthma is very common in Australia Approx 25% children have recurrent wheezing illnesses
Prof Mike South Department of General Medicine Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Australia www.mikesouth.org.au Asthma is very common in Australia Approx 25% children have recurrent wheezing illnesses
Over the last several years various national and
 Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients
 Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Asthma Management. Photo from
 Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Guideline on the Management of Asthma in adults SHSCT
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Management of Asthma in adults Dr A John, Dr J Lindsay Respiratory Medicine/ MUSC Medicine Date Uploaded: 23/11/15 Review Date
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Management of Asthma in adults Dr A John, Dr J Lindsay Respiratory Medicine/ MUSC Medicine Date Uploaded: 23/11/15 Review Date
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline
 Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
Asthma Action Plan and Education
 Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Asthma in Pregnancy, Labour and Postnatal Guidelines
 Asthma in Pregnancy, Labour and Postnatal Guidelines N.B. Staff should be discouraged from printing this document. This is to avoid the risk of out of date printed versions of the document. The Intranet
Asthma in Pregnancy, Labour and Postnatal Guidelines N.B. Staff should be discouraged from printing this document. This is to avoid the risk of out of date printed versions of the document. The Intranet
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update. Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch
 Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch Acknowledgements BTS/SIGN guidelines GINA guidelines NAEPP guidelines
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch Acknowledgements BTS/SIGN guidelines GINA guidelines NAEPP guidelines
Circadian rhythm of peak expiratory flow in asthmatic and normal children
 Thorax 1;:10-1 Circadian rhythm of peak expiratory flow in asthmatic and normal children A J W HENDERSON, F CARSWELL From the Respiratory Research Group, Institute of Child Health, Royal Hospital for Sick
Thorax 1;:10-1 Circadian rhythm of peak expiratory flow in asthmatic and normal children A J W HENDERSON, F CARSWELL From the Respiratory Research Group, Institute of Child Health, Royal Hospital for Sick
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
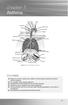 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Running Head: THE PRACTICALITY OF BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY 1. Review of a New Treatment for Severe Asthma: The Practicality of Bronchial Thermoplasty
 Running Head: THE PRACTICALITY OF BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY 1 Review of a New Treatment for Severe Asthma: The Practicality of Bronchial Thermoplasty Jessica Orpen Northeastern University THE PRACTICALITY
Running Head: THE PRACTICALITY OF BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY 1 Review of a New Treatment for Severe Asthma: The Practicality of Bronchial Thermoplasty Jessica Orpen Northeastern University THE PRACTICALITY
Treatment of acute asthmatic exacerbations with an increased dose of inhaled steroid
 12 Paediatrics and Child Health, Dunedin School of Medicine, PO Box 913, University of Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand J Garrett Preventive and Social Medicine, Dunedin School of Medicine S
12 Paediatrics and Child Health, Dunedin School of Medicine, PO Box 913, University of Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand J Garrett Preventive and Social Medicine, Dunedin School of Medicine S
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic
 Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Administration of Short-Acting Beta-agonists for Acute Episodes of Moderate or Severe Asthma by Practice Nurses
 1. Clinical Condition or situation to which this Patient Group Direction applies Definition of clinical condition/situation Adults and children aged 2 years and above presenting with increasing symptoms
1. Clinical Condition or situation to which this Patient Group Direction applies Definition of clinical condition/situation Adults and children aged 2 years and above presenting with increasing symptoms
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Definition and Pathology CHAPTER 1. John Rees
 CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
Management of acute asthma in children in emergency department. Moderate asthma
 152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek
 Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Chronic Disease Management when Resources are Limited
 Chronic Disease Management when Resources are Limited Paul R. Larson MD, MS, DIM&PH Director, Global Health Education UPMC St. Margaret Family Medicine Residency Pittsburgh, PA larsonpr@upmc.edu Disclosures
Chronic Disease Management when Resources are Limited Paul R. Larson MD, MS, DIM&PH Director, Global Health Education UPMC St. Margaret Family Medicine Residency Pittsburgh, PA larsonpr@upmc.edu Disclosures
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Page 1 of 5 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an 'umbrella' term for people with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. With COPD the airflow to the
Page 1 of 5 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an 'umbrella' term for people with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. With COPD the airflow to the
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO
 ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires as measures of the severity and impact of asthma
 Eur Respir J 1999; 1: 591±596 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires
Eur Respir J 1999; 1: 591±596 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Some Facts About Asthma
 Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
ASTHMA ASTHMA DISEASE SUMMARY. Risk Factors
 ASTHMA Risk Factors Family history of asthma or other atopic diseases (eczema, hayfever) Having eczema or hayfever currently or as a child Living in an industrialised area more exposure to airborne pollutants,
ASTHMA Risk Factors Family history of asthma or other atopic diseases (eczema, hayfever) Having eczema or hayfever currently or as a child Living in an industrialised area more exposure to airborne pollutants,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Asthma Assessment & Review
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
COPD in primary care: reminder and update
 COPD in primary care: reminder and update Managing COPD continues to be a major feature of primary care, particularly in practices with a high proportion of M ori and Pacific peoples. COPDX clinical practice
COPD in primary care: reminder and update Managing COPD continues to be a major feature of primary care, particularly in practices with a high proportion of M ori and Pacific peoples. COPDX clinical practice
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
In 2002, it was reported that 72 of 1000
 REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
Asthma. Jill Waldron Respiratory Specialist Nurse
 Asthma Jill Waldron Respiratory Specialist Nurse Asthma morbidity 15 20% of children In a class of c30 children likely to be 4-54 children with asthma In infancy more common in boys but becomes more common
Asthma Jill Waldron Respiratory Specialist Nurse Asthma morbidity 15 20% of children In a class of c30 children likely to be 4-54 children with asthma In infancy more common in boys but becomes more common
Spirometry in primary care
 Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
ASTHMA. Dr Liz Gamble BRI
 ASTHMA Dr Liz Gamble BRI Diagnosis Clinical: wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness, cough Variable airflow obstruction: peak flow chart, spirometry with reversibility to bronchodilators Airways hyper-responsiveness
ASTHMA Dr Liz Gamble BRI Diagnosis Clinical: wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness, cough Variable airflow obstruction: peak flow chart, spirometry with reversibility to bronchodilators Airways hyper-responsiveness
Q. What is a Peak-Flow Meter? A. It is an instrument that measures Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR). PEFR is the amount of air a person can blow out
 1 2 Q. What is a Peak-Flow Meter? A. It is an instrument that measures Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR). PEFR is the amount of air a person can blow out during a forced expiration after taking in as full
1 2 Q. What is a Peak-Flow Meter? A. It is an instrument that measures Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR). PEFR is the amount of air a person can blow out during a forced expiration after taking in as full
C.M. Bosley*, D.T. Parry**, G.M. Cochrane***
 Eur Respir J, 1994, 7, 504 509 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.94.07030504 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1994 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Patient compliance with
Eur Respir J, 1994, 7, 504 509 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.94.07030504 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1994 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Patient compliance with
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
 Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Patient Group Direction for SALBUTAMOL INHALER (Version 02) Valid From 1 October September 2019
 Version Control This PGD has been agreed by the following organisations FCMS PDS Medical Doncaster CCG Lancashire CCGs including East Lancashire, Fylde and Wyre and North Lancashire CCGs Change history
Version Control This PGD has been agreed by the following organisations FCMS PDS Medical Doncaster CCG Lancashire CCGs including East Lancashire, Fylde and Wyre and North Lancashire CCGs Change history
Natural history of childhood asthma
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1977, 52, 613-619 Natural history of childhood asthma 20-year follow-up HENRY BLAIR From the Departments ofpaediatrics and Allergy, Prince of Wales's General Hospital,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1977, 52, 613-619 Natural history of childhood asthma 20-year follow-up HENRY BLAIR From the Departments ofpaediatrics and Allergy, Prince of Wales's General Hospital,
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES. Michael Waters MD April 2004
 RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES Michael Waters MD April 2004 ASTHMA Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with variable or reversible airway obstruction Characterized by increased sensitivity
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES Michael Waters MD April 2004 ASTHMA Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with variable or reversible airway obstruction Characterized by increased sensitivity
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Bronchial asthma. E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics. Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013
 Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Assessment of reversibility of airway obstruction. disease. in patients with chronic obstructive airways. FEVy after salbutamol occurred in the
 19 Regional Thoracic Unit, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool M Nisar M Walshaw J E Earis M G Pearson P M A Calverley Address for reprint requests: Dr P M A Calverley, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool, L9 7AL.
19 Regional Thoracic Unit, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool M Nisar M Walshaw J E Earis M G Pearson P M A Calverley Address for reprint requests: Dr P M A Calverley, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool, L9 7AL.
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN BASKET OF CARE SUBCOMMITTEE Report to: Minnesota Department of Health. June 22, 2009
 This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
Type: Clinical Guideline Register No: Status: Public MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN MORE THAN 2 YEARS IN HOSPITAL
 MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN MORE THAN 2 YEARS IN HOSPITAL Type: Clinical Guideline Register No: 09055 Status: Public Developed in Response to: Best practice CQC Fundamental Standard: 9, 12,
MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN MORE THAN 2 YEARS IN HOSPITAL Type: Clinical Guideline Register No: 09055 Status: Public Developed in Response to: Best practice CQC Fundamental Standard: 9, 12,
Paediatric Wheeze and pneumonia. RCH Asthma RCH bronchiolitis RCH pneumonia Dr S Rajapaksa
 Paediatric Wheeze and pneumonia RCH Asthma RCH bronchiolitis RCH pneumonia Dr S Rajapaksa Case Charlotte is a 2 ½ year old who presents to ED with shortness of breath and wheeze. She had been picked up
Paediatric Wheeze and pneumonia RCH Asthma RCH bronchiolitis RCH pneumonia Dr S Rajapaksa Case Charlotte is a 2 ½ year old who presents to ED with shortness of breath and wheeze. She had been picked up
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Measures Document
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Measures Document COPD Version: 3 - covering patients discharged between 01/10/2017 and present. Programme Lead: Jo Higgins Clinical Lead: Dr Paul Albert Number
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Measures Document COPD Version: 3 - covering patients discharged between 01/10/2017 and present. Programme Lead: Jo Higgins Clinical Lead: Dr Paul Albert Number
Clinical guideline for acute wheeze & asthma in children 5 years and over Hospital care
 Clinical guideline for acute wheeze & asthma in children years and over Hospital care Airedale NHS Trust Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS Bradford and Airedale DOB: A&E/Hospital : Weight:
Clinical guideline for acute wheeze & asthma in children years and over Hospital care Airedale NHS Trust Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS Bradford and Airedale DOB: A&E/Hospital : Weight:
1. ASTHMA 1. Eve A. Kerr, MD, MPH and Kenneth A. Clark, MD, MPH
 1. ASTHMA 1 Eve A. Kerr, MD, MPH and Kenneth A. Clark, MD, MPH The general approach to developing quality indicators for asthma diagnosis and treatment was based on Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management
1. ASTHMA 1 Eve A. Kerr, MD, MPH and Kenneth A. Clark, MD, MPH The general approach to developing quality indicators for asthma diagnosis and treatment was based on Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management
