Chapter 11: Respiratory Emergencies
|
|
|
- Aron Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 29698_CH11_ANS_p001_005 4/12/05 2:02 PM Page 1 Answer Key Chapter 11 1 Chapter 11: Respiratory Emergencies Matching 1. B (page 373) 8. E (page 370) 2. D (page 369) 9. M(page 389) 3. H (page 370) 10. A (page 370) 4. J (page 372) 11. K (page 376) 5. L (page 374) 12. F (page 373) 6. C (page 373) 13. I (page 375) 7. G (page 368) Multiple Choice 1. D (page 384) 2. C (page 366) 3. D (page 368) 4. C (page 366) 5. B (page 367) 6. D (page 368) 7. B (page 368) 8. A (page 389) 9. B (page 370) 10. A (page 369) 11. D (page 371) 12. A (page 372) 13. D (page ) 14. B (page ) 15. C (page 374) 16. C (page 373) 17. B (page 373) 18. D (page ) 19. C (page 374) 20. A (page 375) 21. B (page 376) 22. B (page 368) 23. D (page 377) 24. A (page 366) 25. D (page 384) 26. B (page 379) 27. D (page 392) 28. D (page 380) 29. C (page 385) 30. D (page 385) 31. D (page 385) 32. C (page 390)
2 29698_CH11_ANS_p001_ /12/05 2:02 PM Page 2 Answer Key Labeling Obstruction, scarring, and dilation of the alveolar sac. (Fig. 11-7, page 372) Fill-in 1. carbon dioxide (page 366) 2. oxygen (page 367) 3. Carbon dioxide, oxygen (page 368) 4. alveoli (page 366) 5. trachea (page 366) 6. 12, 20 (page 367) 7. carbon dioxide (page 366) 8. breathing status (page 379) 9. transport decision (page 379) 10. SAMPLE, OPQRST (page 380) True/False 1. F (page 370) 7. F (page 376) 2. T (page 373) 8. T (page 389) 3. F (page 373) 9. F (page 373 & 379) 4. F (page 373) 10. T (page 370) 5. T (page 375) 11. T (page 378) 6. T (page 376) 12. T (page 382)
3 29698_CH11_ANS_p001_005 4/12/05 2:02 PM Page 3 Answer Key Chapter 11 3 Short Answer Normal rate and depth 2. Regular pattern of inhalation and exhalation 3. Good audible breath sounds on both sides of the chest 4. Regular rise and fall on both sides of the chest 5. Pink, warm, dry skin (page 367) Pulmonary vessels are obstructed from absorbing oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide by fluid, infection, or collapsed air spaces. 2. Damaged alveoli 3. Air passages obstructed by muscle spasm, mucus, weakened airway walls 4. Blood flow to the lungs obstructed 5. Pleural space is filled with air or excess fluid (page 368) Patient is unable to coordinate administration and inhalation 2. Inhaler is not prescribed for patient. 3. You did not obtain permission from medical control or local protocol. 4. Patient has already met maximum prescribed dose before your arrival. (page 385) 4. An ongoing irritation of the respiratory tract; excess mucus production obstructs small airways and alveoli. Protective mechanisms are impaired. Repeated episodes of irritation and pneumonia can cause scarring and alveolar damage, leading to COPD. (page 370) Respiratory rate of slower than 8 breaths/min or faster than 24 breaths/min 2. Muscle retractions above the clavicles between ribs, below rib cage, especially in children 3. Pale or cyanotic skin 4. Cool, damp (clammy) skin 5. Shallow or irregular respirations 6. Pursed lips 7. Nasal flaring (pages 379) 6. A condition characterized by a chronically high blood level of carbon dioxide in which the respiratory center no longer responds to high blood levels of carbon dioxide. In these patients, low blood oxygen causes the respiratory center to respond and stimulate respiration. If the arterial level of oxygen is then raised, as happens when the patient is given additional oxygen, there is no longer any stimulus to breathe; both the high carbon dioxide and low oxygen drives are lost. (page 368) Is the air going in? 2. Does the chest expand with each breath? 3. Does the chest fall with each breath? 4. Is the rate adequate for the age of your victim? (page 378)
4 29698_CH11_ANS_p001_005 4/12/05 2:02 PM Page 4 4 Answer Key Word Fun 1 2 W H E E Z E 3 S T M B O 4 5 R A L E S B I U R D Y S P N E A P O R C O L H N N H O R L Y E C R O U P E P U H N D R O M I C G X O T H E P I G L O T T I T I S N A H S O R 14 A S T H M A X 12 Ambulance Calls 1. This child has all the classics signs of epiglottitis. You should do nothing to excite or frighten the child as doing so will likely cause his airway to spasm and close. Remember to use non-threatening body language (place yourself below his or her eye level), give the child distance (until you establish trust) and perform any exam using the toe-to-head method. This is a true emergency that requires immediate transport to the hospital, but you must do so tactfully. Use parents to assist with patient care efforts such as applying humidified oxygen (blow-by or mask). 2. This patient s chief complaint, age, weight, smoking and birth control use all place her at risk of pulmonary embolism. PE patients most often experience a sudden onset of shortness of breath that they describe as sharp and worsening with inspiration. You should provide high flow oxygen, obtain vital signs, perform a secondary exam en route to the hospital (including auscultation of lung sounds) and prompt transport to the nearest appropriate facility. 3. Place patient in position of comfort. -High-flow oxygen via nonrebreathing mask -Monitor vital signs -Rapid transport Skill Drills Skill Drill 11-1: Assisting a Patient With a Metered-Dose Inhaler (page 388) 1. Ensure inhaler is at room temperature or warmer. 2. Remove oxygen mask. Hand inhaler to patient. Instruct about breathing and lip seal. 3. Instruct patient to press inhaler and inhale. Instruct about breath holding. 4. Reapply oxygen. After a few breaths, have patient repeat dose if order/protocol allows.
5 29698_CH11_ANS_p001_005 4/12/05 2:02 PM Page 5 Answer Key Chapter 11 5 Assessment Review 1. D (page 392) 2. B (page 393) 3. A (page 392) 4. B (page 393) 5. D (page 393) Emergency Care Summary Respiratory Distress nonrebreathing 10 to 15 oropharyngeal nasopharyngeal Asthma metered-dose expiration date exhale Infection of Upper of Lower Airway humidified Acute Pulmonary Edema ventilatory support Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease full-flow 15 L Sponatneous Pneumothorax supplemental Pleural Effusions high-flow Obstruction of the Upper Airway BLS Pulmonary Embolism cardiac arrest Hyperventilation respirations
Respiratory Emergencies. Chapter 11
 Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be
 1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in hospital
1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in hospital
Respiratory Emergencies
 29698_CH11_Q_p001_012 4/12/05 2:03 PM Page 1 MEDICAL EMERGENCIES S E C T I O N 4 C H A P T E R Respiratory Emergencies 11 Workbook Activities The following activities have been designed to help you. Your
29698_CH11_Q_p001_012 4/12/05 2:03 PM Page 1 MEDICAL EMERGENCIES S E C T I O N 4 C H A P T E R Respiratory Emergencies 11 Workbook Activities The following activities have been designed to help you. Your
Respiratory System Anatomy Respiratory system: all the structures that contribute to
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 15 Respiratory Emergencies Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 15 Respiratory Emergencies Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine.
Chapter 13. Respiratory Emergencies
 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Firefighter Pre-Hospital Care Program Recruit Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Firefighter Pre-Hospital Care Program Recruit Presentation Respiratory Emergencies The Respiratory System Anatomy Pharynx Nasopharynx Oropharynx Epiglottis Larynx Trachea Right main bronchus Left main
Firefighter Pre-Hospital Care Program Recruit Presentation Respiratory Emergencies The Respiratory System Anatomy Pharynx Nasopharynx Oropharynx Epiglottis Larynx Trachea Right main bronchus Left main
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Respiratory Emergencies
 CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons for
CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons for
Anatomy Review. Anatomy Review. Respiratory Emergencies CHAPTER 16
 CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review 1 Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons
CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review 1 Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons
This activity should be used to motivate students to learn about the significance and concerns associated with patients in respiratory emergencies.
 Pre-Lecture I. You Are the Provider Time: 10 Minutes Small Group Activity/Discussion The You are the Provider case study is discussed within the PowerPoint presentation for this chapter. The instructor
Pre-Lecture I. You Are the Provider Time: 10 Minutes Small Group Activity/Discussion The You are the Provider case study is discussed within the PowerPoint presentation for this chapter. The instructor
Chapter 19 - Respiratory_Emergencies
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 19.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 14 15, 41, 54 19.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of respiration. Slides 13 15 19.3 Differentiate
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 19.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 14 15, 41, 54 19.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of respiration. Slides 13 15 19.3 Differentiate
Airway and Ventilation. Emergency Medical Response
 Airway and Ventilation Lesson 14: Airway and Ventilation You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your medical emergency response team has been called to the fitness center by building security on a report
Airway and Ventilation Lesson 14: Airway and Ventilation You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your medical emergency response team has been called to the fitness center by building security on a report
Bronchoconstriction is also treated with medications that inhibit bronchiolar constriction such as: Ipratropium (Atrovent)
 Patients with difficulty breathing (dyspnea) may have problems with: Oxygenation due to alveolar problems Ventilation due to bronchiolar problems Oxygenation due to lung perfusion problems Combinations
Patients with difficulty breathing (dyspnea) may have problems with: Oxygenation due to alveolar problems Ventilation due to bronchiolar problems Oxygenation due to lung perfusion problems Combinations
Chapter 16. Objectives. Objectives. Respiratory Emergencies
 Chapter 16 Respiratory Emergencies Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key
Chapter 16 Respiratory Emergencies Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key
Topics. Seattle/King County EMT-B Class. Pharmacology: Chapter 10. Respiratory Emergencies: Chapter 11. Cardiovascular Emergencies: Chapter 12
 Seattle/King County EMT-B Class Topics 1 Pharmacology: Chapter 10 Respiratory Emergencies: Chapter 11 Cardiovascular Emergencies: Chapter 1 1 Pharmacology 1 General Pharmacology You will be responsible
Seattle/King County EMT-B Class Topics 1 Pharmacology: Chapter 10 Respiratory Emergencies: Chapter 11 Cardiovascular Emergencies: Chapter 1 1 Pharmacology 1 General Pharmacology You will be responsible
Respiratory Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Respiratory Emergencies Lesson Goal Assess and provide timely treatment & transport to patients experiencing respiratory emergencies Lesson Objectives List parts of respiratory system and how they work
Respiratory Emergencies Lesson Goal Assess and provide timely treatment & transport to patients experiencing respiratory emergencies Lesson Objectives List parts of respiratory system and how they work
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress is a broad medical term that applies to any type of breathing difficulty and the associated
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress is a broad medical term that applies to any type of breathing difficulty and the associated
Chapter 15 - Respiratory Emergencies
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
3. Identify the importance in the prehospital setting for the administration of nebulized bronchodilator.
 TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Problem Based Learning Session. Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days.
 Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Copyright, ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved. The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy. Asthma Questionnaire
 Copyright, 1994 - ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire This survey contains a series of statements, written in the first person, concerning your
Copyright, 1994 - ICKE, Inc. All rights reserved The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire This survey contains a series of statements, written in the first person, concerning your
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY
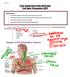 Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Anatomy. The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs.
 Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill
 Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Level of Instruction: 2 Time Required: Three Hours Materials
Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Level of Instruction: 2 Time Required: Three Hours Materials
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Chapter 13. Respiratory Emergencies
 Student Notes Chapter 13: Respiratory Emergencies 1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Unit Summary After students complete this chapter and the related course work, they will understand the significance
Student Notes Chapter 13: Respiratory Emergencies 1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Unit Summary After students complete this chapter and the related course work, they will understand the significance
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Biochemistry of Lungs. Lecture # 35 Lecturer: Alexander Koval
 Biochemistry of Lungs Lecture # 35 Lecturer: Alexander Koval Introduction Biochemistry of lungs Overview of substances produced (surfactant, mucus, collagen), inactivated (ROS, kinins, serotonin, catecholamines)
Biochemistry of Lungs Lecture # 35 Lecturer: Alexander Koval Introduction Biochemistry of lungs Overview of substances produced (surfactant, mucus, collagen), inactivated (ROS, kinins, serotonin, catecholamines)
Respiratory system. Applied Anatomy &Physiology
 Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/18/2012. Respiratory Emergencies
 Chapter 11 Respiratory Learning Objectives List structures & functions of the respiratory system State signs/symptoms of patient with breathing difficulty Describe emergency medical care of patient with
Chapter 11 Respiratory Learning Objectives List structures & functions of the respiratory system State signs/symptoms of patient with breathing difficulty Describe emergency medical care of patient with
1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation.
 Chapter 1: Principles of Mechanical Ventilation TRUE/FALSE 1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation. F
Chapter 1: Principles of Mechanical Ventilation TRUE/FALSE 1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation. F
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
June 2011 Bill Streett-Training Section Chief
 Capnography 102 June 2011 Bill Streett-Training Section Chief Terminology Capnography: the measurement and numerical display of end-tidal CO2 concentration, at the patient s airway, during a respiratory
Capnography 102 June 2011 Bill Streett-Training Section Chief Terminology Capnography: the measurement and numerical display of end-tidal CO2 concentration, at the patient s airway, during a respiratory
GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
 October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History. Chapter 5
 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Respiratory Disorders. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-17. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 5-1. Identify the characteristics,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Respiratory Disorders. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-17. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 5-1. Identify the characteristics,
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
Foundation in Critical Care Nursing. Airway / Respiratory / Workbook
 Foundation in Critical Care Nursing Airway / Respiratory / Workbook Airway Anatomy: Please label the following: Tongue Larynx Epiglottis Pharynx Trachea Vertebrae Oesophagus Where is the ET (endotracheal)
Foundation in Critical Care Nursing Airway / Respiratory / Workbook Airway Anatomy: Please label the following: Tongue Larynx Epiglottis Pharynx Trachea Vertebrae Oesophagus Where is the ET (endotracheal)
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Appendix E Choose the sign or symptom that best indicates severe respiratory distress.
 Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Paramedic Learner Package
 Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Paramedic Learner Package www.lhsc.on.ca/bhp 1 This page left blank intentionally. Table of Contents Introduction & Expectations... 4 Learning Objectives... 4
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Paramedic Learner Package www.lhsc.on.ca/bhp 1 This page left blank intentionally. Table of Contents Introduction & Expectations... 4 Learning Objectives... 4
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
Asthma. If an Ambulance is required - call immediately - do not delay. H & A Training PL RTO No:90871
 Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
Appendix D An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires:
 Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Cardiac Emergencies. Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington
 Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
RESPIRATORY REHABILITATION
 RESPIRATORY REHABILITATION By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak University of kerbala College of nursing CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY Chest physiotherapy (CPT) includes: 1.Postural drainage. 2.Chest percussion and vibration.
RESPIRATORY REHABILITATION By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak University of kerbala College of nursing CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY Chest physiotherapy (CPT) includes: 1.Postural drainage. 2.Chest percussion and vibration.
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Seattle-King County EMS
 Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5 th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4863 January 2011 CBT425-EMT11
Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5 th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4863 January 2011 CBT425-EMT11
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Difficulty Breathing and Respiratory Distress Basics
 Difficulty Breathing and Respiratory Distress Basics OVERVIEW Difficulty breathing (known as dyspnea ) a subjective term that in human medicine means an uncomfortable sensation in breathing or a sensation
Difficulty Breathing and Respiratory Distress Basics OVERVIEW Difficulty breathing (known as dyspnea ) a subjective term that in human medicine means an uncomfortable sensation in breathing or a sensation
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
CPAP. Pre-Hospital Treatment Using The Respironics Whisperflow CPAP Device. Charlottesville Albemarle Rescue Squad - CPAP
 CPAP Pre-Hospital Treatment Using The Respironics Whisperflow CPAP Device CPAP What Is It? C ontinuous P ositive A irway P ressure Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Alveoli Anatomy Review Chest
CPAP Pre-Hospital Treatment Using The Respironics Whisperflow CPAP Device CPAP What Is It? C ontinuous P ositive A irway P ressure Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Alveoli Anatomy Review Chest
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
PEPP Course: PEPP BLS Pretest
 PEPP Course: PEPP BLS Pretest 1. What is the best way to administer oxygen to a child in moderate respiratory distress? Nasal cannula Simple mask Nonrebreathing mask Bag-valve-mask device 2. A 2-year-old
PEPP Course: PEPP BLS Pretest 1. What is the best way to administer oxygen to a child in moderate respiratory distress? Nasal cannula Simple mask Nonrebreathing mask Bag-valve-mask device 2. A 2-year-old
Group B: Directed self-study Group C: Anatomy lab. Lecture: Structure and function of larynx. Lecture: Dead space & compliance of lungs
 Timetable Week 1 (1 st January 2018) Theme: Structure and functions of the lungs Group A: Anatomy lab Group C: Histology lab Upper Group B: Anatomy lab Group C: Anatomy lab Group A: Histology lab Upper
Timetable Week 1 (1 st January 2018) Theme: Structure and functions of the lungs Group A: Anatomy lab Group C: Histology lab Upper Group B: Anatomy lab Group C: Anatomy lab Group A: Histology lab Upper
Appendix (i) The ABCDE approach to the sick patient
 Appendix (i) The ABCDE approach to the sick patient This appendix and the one following provide guidance on the initial approach and management of common medical emergencies which may arise in general
Appendix (i) The ABCDE approach to the sick patient This appendix and the one following provide guidance on the initial approach and management of common medical emergencies which may arise in general
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Lecture Notes. Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns
 Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
COPD and other lung conditions
 COPD and other lung conditions COPD COPD is an umbrella term used to describe a collection of lung diseases including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. C Chronic - long term condition O Obstructive - difficulty
COPD and other lung conditions COPD COPD is an umbrella term used to describe a collection of lung diseases including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. C Chronic - long term condition O Obstructive - difficulty
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 2 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 2 pages 417-419 Hemoglobin has 4 separate protein chains. Each protein chain has a single iron atom (Fe 3+ ). Each iron atom can bind to a single
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 2 pages 417-419 Hemoglobin has 4 separate protein chains. Each protein chain has a single iron atom (Fe 3+ ). Each iron atom can bind to a single
Ch 16 A and P Lecture Notes.notebook May 03, 2017
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN
 Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN The body requires a constant supply of oxygen for survival. AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross
Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN The body requires a constant supply of oxygen for survival. AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 10 Respiratory System Carbon Dioxide Transport Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in three forms Dissolved in plasma 7 to 10%
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 10 Respiratory System Carbon Dioxide Transport Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in three forms Dissolved in plasma 7 to 10%
Respiratory Disease. Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician
 Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
