FXTAS: a bad RNA and a hope for a cure
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Future Perspective ene Therapy FXTAS: a bad RNA and a hope for a cure 1. Introduction 2. Perspective 3. Expert opinion e Shan, Shunliang Xu & Peng Jin Emory University School of Medicine, Department of Human enetics, Atlanta, A 30322, USA Background : Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) is a newly identified neurodegenerative disorder due to intermediate expansion of trinucleotide repeats ( repeats) in the 5 untranslated region (UTR) of the Fragile X mental retardation 1 ( FMR1 ) gene. FXTAS is now considered to be one of the most common inherited neurodegenerative disorders in males. Objective : To examine the future of potential therapies for this late-onset disease. Methods : Examination of relevent literature. Results/conclusions : Accumulating evidence indicates that overproduced ribo repeats in the 5 UTR of FMR1 mrna are toxic. Recently, proteins that bind specifically to r repeats were identified. Progress in understanding the molecular pathogenesis of FXTAS, plus the availability of different animal models are discussed. Keywords: animal models, UBP1, FXTAS, hnrnp A2/B1, non-coding RNA, Pur α, r repeats, RNA toxicity, trinucleotide repeats Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2008) 8(3): Introduction Expansion of trinucleotide repeats is the cause of many heritable human diseases such as Fragile X syndrome and Huntington s disease [1-3]. Expansion of trinucleotide repeats could occur in the exon region of a gene (for example Huntington s disease). This kind of expansion results in the generation of polypeptides with a poly-glutamine or poly-alanine stretch, which has been shown to be toxic [2-5]. In Fragile X syndrome, the trinucleotide expansion occurs in the 5 untranslated region (UTR), resulting in hypermethylation of the promoter region, and eventually, shutting down the transcription of the Fragile X mental retardation 1 ( FMR1 ) gene [6]. In the normal population, the repeat number in the 5 UTR of FMR1 gene is between 5 and 54, and an expansion to 200 or higher (full mutation) leads to Fragile X syndrome. Repeat numbers between 55 and 200 are called premutation. Premutation was previously considered not to directly cause any human disorder, and only to pose an increased risk of expanding into a full mutation when passed to the next generation. Recently neurologists have started recognizing unique neurological symptoms that are associated with Fragile X premutation carriers, which are distinguished from Fragile X syndrome [7-11]. This newly identified disorder is named Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS). Major symptoms of this disorder include intention or postural (action) tremor, cerebellar gait and limb ataxia and Parkinsonism [7-11]. Neurodegenerative features, such as intracellular inclusion bodies, have been identified from neuroimaging and postmortem brain tissue [12-14]. It has been known that FMR1 mrna level is elevated 5 10 times in premutation carriers, while the FMR protein (FMRP) level is about normal [15]. This phenomenon leads us and others to argue that the excess of FMR1 mrna with expanded repeats in its 5 UTR is toxic. Indeed ribo (r) repeats / Informa UK Ltd ISSN
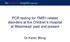
2 FXTAS: a bad RNA and a hope for a cure AO2 Dicer UBP1 hnrnp A2/B1 Pur α FMRP FMRP FMR1 mrna UTR AU/FMR1 coding region AAAAAA 54<()n<200, promoter hyper-activated ()n>200, promoter hypermethylated FXTAS Fragile X syndrome Figure 1. The normal human FMR1 gene has a repeat size of between 5 and 54. A repeat size > 200 triggers hypermethylation of the FMR1 promoter and leads to the shutdown of transcription, which results in FRAXA in males. When repeat size is between 55 and 200, the promoter is hyper-activated, leading to overproduction of FMR1 mrna with an expanded 5 UTR with toxic ribo repeats, while the FMRP level remains about normal. The r repeats can form a hairpin structure, and can be processed by Dicer and the RNAi machinery, including AO2. Recently, Pur α, UBP1, and hnrnp A2/B1 were shown to bind specifically to r repeats. Sequestrations of these proteins by r repeats has been shown to underlie the molecular pathology of FXTAS. AO2: Argonaute 2; UBP1: U-binding protein 1; FMR1: Fragile X mental retardation 1; FRAXA: Fragile X syndrome; FRMP: FMR protein; FXTAS: Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome; hnrnp: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein; Pur α: Purine-rich element containing-protein alpha; RNAi: RNA interference; UTR: Untranslated region. have been shown to be toxic in human neural cell culture as well as in transgenic flies [16,17]. In fly model of FXTAS, non-coding r repeats have been further shown to cause the formation of inclusion bodies and lead to neurodegeneration, cellular hallmarks of FXTAS in patients [17]. Emerging evidence suggests that the RNA-mediated gain-of-function mechanism could underlie several additional inherited diseases, including myotonic dystrophy type 1 and 2 (DM1 and DM2), spinocerebellar ataxia type 8 (SA8), and Huntington s disease-like syndrome 2 (HDL2) [18]. As a new and possibly currently under-diagnosed disease, FXTAS is considered to be one of the most common heritable neurodegenerative disorders in males: 1 in 813 males in the general population are carriers of an FMR1 premutation with about 40% penetrance for males aged > 50 years [19]. Therefore, there is a great need to develop therapies to alleviate and cure this disease. 2. Perspective urrently, there is no specific treatment for FXTAS to target the underlying pathological mechanism. Treatments to relieve specific symptoms are the main medical practice at present [19,20]. 250 Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2008) 8(3)
3 Shan, Xu & Jin omprehensive research into the molecular mechanism of FXTAS is needed to aid the development of FXTAS therapies. This review concentrates on current understanding of molecular pathology and construction of animal models of FXTAS. How advances in these areas may aid the development of future therapy will then be discussed. Recently, two studies published by this laboratory and others have advanced our understanding of the pathogenesis of FXTAS one step further by identifying proteins interacting specifically with r repeats [21,22]. Using biochemical and genetic approaches, three proteins, purine-rich element containing-protein α (Pur α ), heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnrnp) A2/B1 (two protein isoforms from one gene), and U vbinding protein 1(UBP1) were found to bind r repeats either directly (Pur α and hnrnp A2/B1) or indirectly (UBP1, through interaction with hnrna A2/B1) ( Figure 1 ) [21,22]. Thus, there are protein complexes physically interacting with r repeats. All these proteins are RNA-binding proteins, and have been shown to function in transcription, mrna trafficking, splicing and translation. Interestingly, Pur α knockout mice appeared normal at birth, but developed severe tremors and spontaneous seizures at 2 weeks of age due to markedly reduced numbers of neurons in regions of the hippocampus and cerebellum [23]. The hypothesis is that over-produced r repeats in FXTAS sequester these proteins from their normal cellular functions, contributing significantly to the pathology of this disorder. This idea is strongly supported by the fact that overexpressing either Pur α or hnrna A2/B1 alleviated neurodegeneration in a fly model of FXTAS [21,22]. These results provide direct insights into the development of future therapies. Presumably, drugs that specifically suppress the interaction between the r repeats and the protein complexes would release these proteins from this requisition. ompounds boosting the expression or function of these proteins may also be found to be useful. Identifying further downstream RNA targets of these proteins is also crucial, and specific therapies based on their affected RNA targets in FXTAS may then be explored. r repeats form, at least in vitro, double-stranded RNA hairpins ( Figure 1 ), which is a structural feature shared by most trinucleotide repeats [24]. This structure resembles the hairpin of microrna precursors, and indeed has been shown to be processed by Dicer, core component of the RNA interference (RNAi) machinery [24]. Interestingly, crossing r and r, two complementary repeats each pathogenic by itself, into transgenic flies rescued phenotypes generated by each individual repeat [25]. This rescue relies on Argonaute 2 (AO2), another core component of the RNAi machinery [25]. RNAi is now under enthusiastic pursuit as a great hope for therapies for many varieties of diseases [26]. Approaches to promote the degradation of r repeats by the RNAi machinery would provide a new direction in exploring therapies of FXTAS. Small-interfering (si) RNA oligonucleotides, constructs or viruses that could generate si in cells may be applied to treat FXTAS. ompounds enhancing the processing of r hairpins by RNAi machinery may be identified and found to be beneficial. It is also crucial to investigate whether the binding of Pur α, hnrnp A2/B1 and UBP1 to r repeats depends on the hairpin structure. If the answer is positive, compounds that disrupt the r hairpins would release the sequestering of these proteins, another possibility for attacking this disease. A caution that must be kept in mind is the possibility of side effects from these kinds of compounds. areful research need to be performed to make sure each drug is r repeats-specific. 3. Expert opinion The concept that non-coding repeats in certain mrnas can be pathogenic is relatively new. The etiology of FXTAS has now been traced to a toxic mrna sequence. An ideal therapy for this disease would be one to neutralize or reduce significantly the presence of the toxic r repeats, while keeping the FMRP level above the minimal requirement. Presently, this is not close to realization. Animal models of FXTAS should give strong support to the development of specific therapies. By using the FXTAS fly model, we have already revealed and will continue to uncover aspects of the pathology of the r repeats. This model can also be used directly in drug discovery. urrently, our laboratory is screening the library of small molecules using the FXTAS fly model (P Jin, unpublished data). hemical compounds identified from these screens can be further investigated, and, there will still be a long wait before one, if any, of them eventually becomes a therapeutic drug. By identifying compounds known to target specific a biochemical pathway, this chemical biology approach could also give us indications regarding the pathology of r repeats. To aid these efforts, we are constructing another invertebrate model of FXTAS, which expresses r repeats in the nematode worm, aenorhabditis elegans ( Shan and P Jin, unpublished). The. elegans genome does encode an obvious FMR1 homologue. In this model, the pathology of r repeats can be investigated independently without considering the role of FMRP. A mouse model of FXTAS is also available, in which both elevated Fmr1 mrna levels and intranuclear inclusions were detected in neurons; both the number and the size of the inclusions were increased during the aging process, which correlates with the progressive character of FXTAS in humans [27]. Although all these models may not be ideal in terms of modeling the human phenotypes, they would complement each other and provide interfaces to work with this disease at the current stage. Many features of FXTAS are still obscure. Like a lot of other neurodegenerative diseases, FXTAS is late onset. The pathology in the context of aging requires more investigation. Better understanding of this feature will provide new angle for therapy development and help to delay and Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2008) 8(3) 251
4 FXTAS: a bad RNA and a hope for a cure maybe ease the symptoms. We are still unclear about how the toxic r repeats lead to neural cell death. How r repeats trigger the formation of the inclusion bodies in neurons and astrocytes, and neural cell loss in FXTAS patients requires more investigation. Understanding of these mechanisms would shed new light on future therapy development. Preventing the formation of the inclusion bodies and cell death will certainly offer another tactic for disease treatment. More effort is in need to decode FXTAS, and hopefully excellent treatments and even a cure for this disease will emerge in the near future. Acknowledgement P Jin is supported by NIH grants R01 NS and R01 MH and is the recipient of a Beckman Young Investigator Award and a Basil O onnor Scholar Research Award and is an Alfred P Sloan Research Fellow in Neuroscience. Declaration of interest The authors state no conflict of interest and have received no payment in preparation of this manuscript. Bibliography Papers of special note have been highlighted as of interest ( ) to readers. 1. Mirkin SM. Expandable DNA repeats and human disease. Nature 2007 ;447: Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Ann Rev Neurosci 2007 ;30: Most recent review on trinucleotide repeat disorders. 3. Nithianantharajah J, Hannan AJ. Dynamic mutations as digital genetic modulators of brain development, function and dysfunction. Bioessays 2007 ;29: Riley BE, Orr HT. Polyglutamine neurodegenerative diseases and regulation of transcription: assembling the puzzle. enes Dev 2006 ;20: Albrecht A, Mundlos S. The other trinucleotide repeat: polyalanine expansion disorders. urr Opin enet Dev 2005 ;15: Warren ST. The expanding world of trinucleotide repeats. Science 1996 ;271: Hagerman RJ, Leehey M, Heinrichs W, et al. Intention tremor, parkinsonism, and generalized brain atrophy in male carriers of fragile X. Neurology 2001 ;57: First paper to recognize FXTAS. 8. Jacquemont S, Hagerman RJ, Hagerman PJ, et al. Fragile-X syndrome and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome: two faces of FMR1. Lancet Neurol 2007 ;6: Hagerman RJ, Ono MY, Hagerman PJ. Recent advances in fragile X: a model for autism and neurodegeneration. urr Opin Psychiatry 2005 ;18: Willemsen R, Mientjes E, Oostra BA. FXTAS: a progressive neurologic syndrome associated with Fragile X premutation. urr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2005 ;5: Baba Y, Uitti RJ. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome and movements disorders. urr Opin Neurol 2005 ;18: Jacquemont S, Hagerman RJ, Leehey M, et al. Fragile X premutation tremor/ataxia syndrome: molecular, clinical, and neuroimaging correlates. Am J Hum enet 2003 ;72: First paper to summarize the phenotype and frequency associated FXTAS. 13. ohen S, Masyn K, Adams J, et al. Molecular and imaging correlates of the fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Neurology 2006 ;67: reco M, Hagerman RJ, Tassone F, et al. Neuronal intranuclear inclusions in a new cerebellar tremor/ataxia syndrome among fragile X carriers. Brain 2002 ;125: First paper to report the presence of inclusions in FXTAS brain tissues. 15. Kenneson A, Zhang F, Hagedorn H, Warren ST. Reduced FMRP and increased FMR1 transcription is proportionally associated with repeat number in intermediate-length and premutation carriers. Hum Mol enet 2001 ;10: Arocena D, Iwahashi K, Won N, et al. Induction of inclusion formation and disruption of lamin A/ structure by premutation -repeat RNA in human cultured neural cells. Hum Mol enet 2005 ;14: Jin P, Zarnescu D, Zhang F, et al. RNA-mediated neurodegeneration caused by the fragile X premutation r repeats in Drosophila. Neuron 2003 ;39: First paper to report the fly model of FXTAS and demonstrate that r alone is sufficient to cause neuronal toxicity. 18. Ranum LP, ooper TA. RNA-mediated neuromuscular disorders. Ann Rev Neurosci 2006 ;29: Berry-Kravis E, Abrams L, offey SM, et al. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome: clinical features, genetics, and testing guidelines. Mov Disord 2007 ;22: Hagerman PJ, Hagerman RJ. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome an older face of the fragile X gene. Nat lin Pract Neurol 2007 ;3: Sofola OA, Jin P, Qin Y, et al. RNA-binding proteins hnrnp A2/B1 and UBP1 suppress fragile X premutation repeat-induced neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of FXTAS. Neuron 2007 ;55: This and ref. [22] are the first two papers to report the identification of specific r-binding proteins. 22. Jin P, Duan R, Qurashi A, et al. Pur α binds to r repeats and modulates repeat-mediated neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of fragile X tremor/ ataxia syndrome. Neuron 2007 ;55: This and ref. [21] are the first two papers to report the identification of specific r-binding proteins. 23. Khalili K, Del Valle L, Muralidharan V, et al. Pur α is essential for postnatal brain development and developmentally coupled cellular proliferation as revealed by genetic inactivation in the mouse. Mol ell Biol 2003 ;23: Handa V, Saha T, Usdin K. The fragile X syndrome repeats form RNA hairpins that do not activate the interferon-inducible protein kinase, PKR, but are cut by Dicer. Nucleic Acids Res 2003 ;31: Sofola OA, Jin P, Botas J, Nelson DL. Argonaute-2 dependent rescue of a Drosophila model of FXTAS by FRAXE 252 Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2008) 8(3)
5 Shan, Xu & Jin premutation repeat. Hum Mol enet 2007 ;16: De Fougerolles A, Vornlocher HP, Maraganore J, Lieberman J. Interfering with disease: a progress report on sirna-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007 ;6: Willemsen R, Hoogeveen-Westerveld M, Reis S, et al. The FMR1 repeat mouse displays ubiquitin-positive intranuclear neuronal inclusions; implications for the cerebellar tremor/ ataxia syndrome. Hum Mol enet 2003 ;12: This paper reports the first mouse model for FXTAS. Affiliation e Shan1, Shunliang Xu 2, 3 & Peng Jin 4 Author for correspondence 1Postdoctoral Fellow Emory University School of Medicine, Department of Human enetics, Atlanta, A 30322, USA 2raduate Student Emory University School of Medicine, Department of Human enetics, Atlanta, A 30322, USA 3raduate Student 2nd Hospital of ShanDong University, Department of Neurology, Jinan city, ShanDong Province, , hina 4Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine, Department of Human enetics, Atlanta, A 30322, USA Tel: ; Fax: ; pjin@genetics.emory.edu Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2008) 8(3) 253
6
Are we Close to Solve the Mystery of Fragile X Associated Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (FXPOI) in FMR1 Premutation Carriers?
 Are we Close to Solve the Mystery of Fragile X Associated Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (FXPOI) in FMR1 Premutation Carriers? Yoram Cohen M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, IVF Unit, Sheba
Are we Close to Solve the Mystery of Fragile X Associated Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (FXPOI) in FMR1 Premutation Carriers? Yoram Cohen M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, IVF Unit, Sheba
The Fragile X-Associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) READ ONLINE
 The Fragile X-Associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) READ ONLINE If you are searching for a ebook The Fragile X-Associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) in pdf form, then you have come on to correct
The Fragile X-Associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) READ ONLINE If you are searching for a ebook The Fragile X-Associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) in pdf form, then you have come on to correct
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1. BACKGROUND Fragile X mental retardation 1 gene (FMR1) is located on the X chromosome and is responsible for producing the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) which
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1. BACKGROUND Fragile X mental retardation 1 gene (FMR1) is located on the X chromosome and is responsible for producing the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) which
Argonaute-2-dependent rescue of a Drosophila model of FXTAS by FRAXE premutation repeat
 Argonaute-2-dependent rescue of a Drosophila model of FXTAS by FRAXE premutation repeat Oyinkan A. Sofola 1, Peng Jin 2, Juan Botas 1,{ and David L. Nelson 1, *,{ 1 Department of Molecular and Human Genetics,
Argonaute-2-dependent rescue of a Drosophila model of FXTAS by FRAXE premutation repeat Oyinkan A. Sofola 1, Peng Jin 2, Juan Botas 1,{ and David L. Nelson 1, *,{ 1 Department of Molecular and Human Genetics,
Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) an older face of the fragile X gene
 Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) an older face of the fragile X gene Fragile X Association of Australia August, 2015 Paul J Hagerman MD. PhD Professor, Department of Biochemistry and
Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) an older face of the fragile X gene Fragile X Association of Australia August, 2015 Paul J Hagerman MD. PhD Professor, Department of Biochemistry and
Kim M. Cornish, PhD* Darren R. Hocking, PhD* Simon A. Moss, PhD Cary S. Kogan, PhD
 ARTICLES Selective executive markers of at-risk profiles associated with the fragile X premutation Kim M. Cornish, PhD* Darren R. Hocking, PhD* Simon A. Moss, PhD Cary S. Kogan, PhD Address correspondence
ARTICLES Selective executive markers of at-risk profiles associated with the fragile X premutation Kim M. Cornish, PhD* Darren R. Hocking, PhD* Simon A. Moss, PhD Cary S. Kogan, PhD Address correspondence
FRAGILE X-ASSOCIATED TREMOR/ATAXIA SYNDROME (FXTAS)
 FRAGILE X CLINICAL & RESEARCH CONSORTIUM Consensus of the FXTAS Task Force and the Fragile X Clinical & Research Consortium FRAGILE X-ASSOCIATED TREMOR/ATAXIA SYNDROME (FXTAS) First Published: June 2011
FRAGILE X CLINICAL & RESEARCH CONSORTIUM Consensus of the FXTAS Task Force and the Fragile X Clinical & Research Consortium FRAGILE X-ASSOCIATED TREMOR/ATAXIA SYNDROME (FXTAS) First Published: June 2011
Repeat Associated Non-AUG initiated Translation mediates. neurodegeneration in a Drosophila models of Fragile X-associated. Tremor Ataxia Syndrome.
 Repeat Associated Non-AUG initiated Translation mediates neurodegeneration in a Drosophila models of Fragile X-associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome. Michelle Frazer Todd Lab University of Michigan Honors
Repeat Associated Non-AUG initiated Translation mediates neurodegeneration in a Drosophila models of Fragile X-associated Tremor Ataxia Syndrome. Michelle Frazer Todd Lab University of Michigan Honors
Research Advances in Fragile X-X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS)
 Research Advances in Fragile X-X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) Stephen T Nowicki, MD, PhD Clinical Fellow, Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics M.I.N.D. Institute University of California,
Research Advances in Fragile X-X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) Stephen T Nowicki, MD, PhD Clinical Fellow, Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics M.I.N.D. Institute University of California,
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing. Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM
 MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
+ Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS)
 + Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) Le point de vue du neurologue n Gaëtan Garraux n CHU de Liège n www.movere.org + Background FXTAS was first described by Hagerman and coll. (2001) as they collected
+ Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) Le point de vue du neurologue n Gaëtan Garraux n CHU de Liège n www.movere.org + Background FXTAS was first described by Hagerman and coll. (2001) as they collected
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Fragile X One gene, three very different disorders for which Genetic Technology is essential. Significance of Fragile X. Significance of Fragile X
 Fragile X One gene, three very different disorders for which Genetic Technology is essential Martin H. Israel Margaret E. Israel mhi@wustl.edu meisrael@sbcglobal.net uel L. Israel Association of Genetic
Fragile X One gene, three very different disorders for which Genetic Technology is essential Martin H. Israel Margaret E. Israel mhi@wustl.edu meisrael@sbcglobal.net uel L. Israel Association of Genetic
SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]
![SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]](/thumbs/72/67086153.jpg) SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
Histone Deacetylases Suppress CGG Repeat Induced Neurodegeneration Via Transcriptional Silencing in Models of Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome
 Histone Deacetylases Suppress CGG Repeat Induced Neurodegeneration Via Transcriptional Silencing in Models of Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome Peter K. Todd 1 *, Seok Yoon Oh 1, Amy Krans 1, Udai B. Pandey
Histone Deacetylases Suppress CGG Repeat Induced Neurodegeneration Via Transcriptional Silencing in Models of Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome Peter K. Todd 1 *, Seok Yoon Oh 1, Amy Krans 1, Udai B. Pandey
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Molecular genetic testing for fragile X syndrome: laboratory performance on the College of American Pathologists proficiency
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Molecular genetic testing for fragile X syndrome: laboratory performance on the College of American Pathologists proficiency
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for FMR1 Mutations Including Fragile X Syndrome File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review Next CAP Review Last Review genetic_testing_for_fmr1_mutations_including_fragile_x_syndrome
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for FMR1 Mutations Including Fragile X Syndrome File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review Next CAP Review Last Review genetic_testing_for_fmr1_mutations_including_fragile_x_syndrome
Discovery of Schizophrenia Drug Targets from DISC1 Mechanisms Atsushi Kamiya M.D., Ph.D.
 Discovery of Schizophrenia Drug Targets 1 Assistant Professor Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine akamiya1@jhmi.edu How does neurobiology offer
Discovery of Schizophrenia Drug Targets 1 Assistant Professor Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine akamiya1@jhmi.edu How does neurobiology offer
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Rare Monogenic Disorders. Function. Pathophysiology
 Rare Monogenic Disorders Function Pathophysiology Protein Gene Episodic Nervous System Diseases Migraine Epilepsy Periodic Paralysis LQTS Episodic Ataxia Paroxysmal Dyskinesias Phenotypes Muscle diseases
Rare Monogenic Disorders Function Pathophysiology Protein Gene Episodic Nervous System Diseases Migraine Epilepsy Periodic Paralysis LQTS Episodic Ataxia Paroxysmal Dyskinesias Phenotypes Muscle diseases
The Role of Purα in Neuronal Development, the Progress in the Current Researches
 Review Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000152 JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE The Role of Purα in Neuronal Development, the Progress in the Current Researches
Review Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000152 JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE The Role of Purα in Neuronal Development, the Progress in the Current Researches
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN
 Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
Fragile X Syndrome and Infertility Case Example - Not One, but Three
 Vol. 008 Fragile X Syndrome and Infertility Fragile X Syndrome and Infertility Case Example - Not One, but Three Abstract A case review of a female patient who was treated for infertility of unknown reasons
Vol. 008 Fragile X Syndrome and Infertility Fragile X Syndrome and Infertility Case Example - Not One, but Three Abstract A case review of a female patient who was treated for infertility of unknown reasons
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. FMR1 Premutations Associated With Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in Multiple System Atrophy
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION FMR1 Premutations Associated With Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in Multiple System Atrophy Valérie Biancalana, PhD; Mathias Toft, MD; Isabelle Le Ber, MD; François Tison,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION FMR1 Premutations Associated With Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in Multiple System Atrophy Valérie Biancalana, PhD; Mathias Toft, MD; Isabelle Le Ber, MD; François Tison,
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
RNA interference (RNAi)
 RN interference (RNi) Natasha aplen ene Silencing Section Office of Science and Technology Partnerships Office of the Director enter for ancer Research National ancer Institute ncaplen@mail.nih.gov Plants
RN interference (RNi) Natasha aplen ene Silencing Section Office of Science and Technology Partnerships Office of the Director enter for ancer Research National ancer Institute ncaplen@mail.nih.gov Plants
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
REVIEW ARTICLE The Fragile-X Premutation: A Maturing Perspective
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74:805 816, 2004 REVIEW ARTICLE The Fragile-X Premutation: A Maturing Perspective Paul J. Hagerman 1 and Randi J. Hagerman 2 1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74:805 816, 2004 REVIEW ARTICLE The Fragile-X Premutation: A Maturing Perspective Paul J. Hagerman 1 and Randi J. Hagerman 2 1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University
The multiple molecular facets of fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome
 Sellier et al. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders 2014, 6:23 REVIEW The multiple molecular facets of fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome Chantal Sellier 1, Karen Usdin 2, Chiara Pastori 3,
Sellier et al. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders 2014, 6:23 REVIEW The multiple molecular facets of fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome Chantal Sellier 1, Karen Usdin 2, Chiara Pastori 3,
CGG Repeat-Associated Translation Mediates Neurodegeneration in Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome
 Article CGG Repeat-Associated Translation Mediates Neurodegeneration in Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome Peter K. Todd, 1, Seok Yoon Oh, 1 Amy Krans, 1 Fang He, 1 Chantal Sellier, 5,6 Michelle Frazer,
Article CGG Repeat-Associated Translation Mediates Neurodegeneration in Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome Peter K. Todd, 1, Seok Yoon Oh, 1 Amy Krans, 1 Fang He, 1 Chantal Sellier, 5,6 Michelle Frazer,
ASFMR1 splice variant
 ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS ASFMR1 splice variant A predictor of fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome Padmaja Vittal, MD, MS, Shrikant Pandya, BS, Kevin Sharp, MS, Elizabeth Berry-Kravis, MD, PhD, Lili
ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS ASFMR1 splice variant A predictor of fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome Padmaja Vittal, MD, MS, Shrikant Pandya, BS, Kevin Sharp, MS, Elizabeth Berry-Kravis, MD, PhD, Lili
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Clin Psychiatry. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 July 3.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Clin Psychiatry. 2009 June ; 70(6): 852 862. doi:10.4088/jcp.08m04476. Fragile X Premutation Disorders Expanding the Psychiatric
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Clin Psychiatry. 2009 June ; 70(6): 852 862. doi:10.4088/jcp.08m04476. Fragile X Premutation Disorders Expanding the Psychiatric
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Funding: NIDCF UL1 DE019583, NIA RL1 AG032119, NINDS RL1 NS062412, NIDA TL1 DA
 The Effect of Cognitive Functioning, Age, and Molecular Variables on Brain Structure Among Carriers of the Fragile X Premutation: Deformation Based Morphometry Study Naomi J. Goodrich-Hunsaker*, Ling M.
The Effect of Cognitive Functioning, Age, and Molecular Variables on Brain Structure Among Carriers of the Fragile X Premutation: Deformation Based Morphometry Study Naomi J. Goodrich-Hunsaker*, Ling M.
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Fragile-X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) in Females
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74:1051 1056, 2004 Report Fragile-X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) in Females with the FMR1 Premutation R. J. Hagerman, 1,2 B. R. Leavitt, 10 F. Farzin, 1 S. Jacquemont, 1
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74:1051 1056, 2004 Report Fragile-X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) in Females with the FMR1 Premutation R. J. Hagerman, 1,2 B. R. Leavitt, 10 F. Farzin, 1 S. Jacquemont, 1
Non-Mendelian inheritance
 Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Genetic Testing for FMR1 Variants (Including Fragile X Syndrome)
 Medical Policy Manual Genetic Testing, Policy No. 43 Genetic Testing for FMR1 Variants (Including Fragile X Syndrome) Next Review: February 2019 Last Review: February 2018 Effective: April 1, 2018 IMPORTANT
Medical Policy Manual Genetic Testing, Policy No. 43 Genetic Testing for FMR1 Variants (Including Fragile X Syndrome) Next Review: February 2019 Last Review: February 2018 Effective: April 1, 2018 IMPORTANT
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
FRAGILE X SYNDROME. A Bibliography and Dictionary for Physicians, Patients, and Genome Researchers. A 3-in-1 Medical Reference TO INTERNET REFERENCES
 FRAGILE X SYNDROME A 3-in-1 Medical Reference A Bibliography and Dictionary for Physicians, Patients, and Genome Researchers TO INTERNET REFERENCES FRAGILE X SYNDROME A BIBLIOGRAPHY AND DICTIONARY FOR
FRAGILE X SYNDROME A 3-in-1 Medical Reference A Bibliography and Dictionary for Physicians, Patients, and Genome Researchers TO INTERNET REFERENCES FRAGILE X SYNDROME A BIBLIOGRAPHY AND DICTIONARY FOR
FRAGILE X 101. A guide for the newly-diagnosed and those already living with Fragile X. fragilex.org
 FRAGILE X 101 A guide for the newly-diagnosed and those already living with Fragile X. fragilex.org Introduction Most people first hear about Fragile X disorders when someone in their family is unexpectedly
FRAGILE X 101 A guide for the newly-diagnosed and those already living with Fragile X. fragilex.org Introduction Most people first hear about Fragile X disorders when someone in their family is unexpectedly
Update on the Genetics of Ataxia. Vicki Wheelock MD UC Davis Department of Neurology GHPP Clinic
 Update on the Genetics of Ataxia Vicki Wheelock MD UC Davis Department of Neurology GHPP Clinic Outline Definitions Review of genetics Autosomal Dominant cerebellar ataxias Autosomal Recessive cerebellar
Update on the Genetics of Ataxia Vicki Wheelock MD UC Davis Department of Neurology GHPP Clinic Outline Definitions Review of genetics Autosomal Dominant cerebellar ataxias Autosomal Recessive cerebellar
Helping Patients and Families Understand Fragile X Syndrome
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/helping-patients-families-understand-fragile-xsyndrome/3474/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/helping-patients-families-understand-fragile-xsyndrome/3474/
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation
 A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation Jun Y. Wang, Randi J. Hagerman, Susan M. Rivera 2012 International Fragile X Conference Center for Mind and Brain Subcortical
A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation Jun Y. Wang, Randi J. Hagerman, Susan M. Rivera 2012 International Fragile X Conference Center for Mind and Brain Subcortical
Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) What our children teach us
 Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) What our children teach us IV Congreso Internacional del Síndrome X Frágil Associació Catalana SXF October 10, 2015 Paul J Hagerman MD. PhD Professor,
Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) What our children teach us IV Congreso Internacional del Síndrome X Frágil Associació Catalana SXF October 10, 2015 Paul J Hagerman MD. PhD Professor,
Penetrance of the Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in a Premutation Carrier Population JAMA. 2004;291:
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Penetrance of the Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in a Premutation Carrier Population Sébastien Jacquemont, MD Randi J. Hagerman, MD Maureen A. Leehey, MD Deborah A. Hall,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Penetrance of the Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome in a Premutation Carrier Population Sébastien Jacquemont, MD Randi J. Hagerman, MD Maureen A. Leehey, MD Deborah A. Hall,
Molecular and imaging correlates of the fragile X associated tremor/ ataxia syndrome
 Molecular and imaging correlates of the fragile X associated tremor/ ataxia syndrome S. Cohen, MS; K. Masyn, PhD; J. Adams, BA; D. Hessl, PhD; S. Rivera, PhD; F. Tassone, PhD; J. Brunberg, MD; C. DeCarli,
Molecular and imaging correlates of the fragile X associated tremor/ ataxia syndrome S. Cohen, MS; K. Masyn, PhD; J. Adams, BA; D. Hessl, PhD; S. Rivera, PhD; F. Tassone, PhD; J. Brunberg, MD; C. DeCarli,
New blood test measures levels of fragile X protein
 NEWS New blood test measures levels of fragile X protein BY KELLY RAE CHI 22 SEPTEMBER 2009 1 / 8 C. Iwahashi A new molecular screen allows researchers to determine for the first time the precise amounts
NEWS New blood test measures levels of fragile X protein BY KELLY RAE CHI 22 SEPTEMBER 2009 1 / 8 C. Iwahashi A new molecular screen allows researchers to determine for the first time the precise amounts
This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing.
 11111 Fact Sheet 54 FRAGILE X SYNDROME This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing. In summary Fragile X is a condition caused
11111 Fact Sheet 54 FRAGILE X SYNDROME This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing. In summary Fragile X is a condition caused
TITLE: Targeted Upregulation of FMRP Expression as an Approach to the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome. Davis, CA 95618
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0150 TITLE: Targeted Upregulation of FMRP Expression as an Approach to the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Paul J. Hagerman, MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0150 TITLE: Targeted Upregulation of FMRP Expression as an Approach to the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Paul J. Hagerman, MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Redistribution of transcription start sites within the FMR1 promoter region with expansion of the downstream CGG-repeat element
 Human Molecular Genetics, 2004, Vol. 13, No. 5 543 549 DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddh053 Advance Access published on January 13, 2004 Redistribution of transcription start sites within the FMR1 promoter region with
Human Molecular Genetics, 2004, Vol. 13, No. 5 543 549 DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddh053 Advance Access published on January 13, 2004 Redistribution of transcription start sites within the FMR1 promoter region with
Jay M. Baraban MD, PhD January 2007 GENES AND BEHAVIOR
 Jay M. Baraban MD, PhD jay.baraban@gmail.com January 2007 GENES AND BEHAVIOR Overview One of the most fascinating topics in neuroscience is the role that inheritance plays in determining one s behavior.
Jay M. Baraban MD, PhD jay.baraban@gmail.com January 2007 GENES AND BEHAVIOR Overview One of the most fascinating topics in neuroscience is the role that inheritance plays in determining one s behavior.
The fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) in Indonesia
 Clin Genet 2012 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01899.x The fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome
Clin Genet 2012 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01899.x The fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome
Completed Postdoctoral Fellowship (He) Role: PI 1/01/13-12/31/13
 TRAINING AND EDUCATION Fang He, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Biological and Health Sciences Texas A&M University-Kingsville 900 University Blvd, MSC158 Kingsville, TX 78363 Phone: 361-593-4533
TRAINING AND EDUCATION Fang He, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Biological and Health Sciences Texas A&M University-Kingsville 900 University Blvd, MSC158 Kingsville, TX 78363 Phone: 361-593-4533
Sequestration of DROSHA and DGCR8 by Expanded CGG RNA Repeats Alters MicroRNA Processing in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome
 Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cell Rep. 2013 March 28; 3(3): 869 880. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.02.004. Sequestration of DROSHA and DGCR8 by Expanded CGG
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cell Rep. 2013 March 28; 3(3): 869 880. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.02.004. Sequestration of DROSHA and DGCR8 by Expanded CGG
Emerging Treatment Strategies for FSHD
 Department of Pharmacology Emerging Treatment Strategies for FSHD Peter L. Jones, Ph.D. and Takako I. Jones, Ph.D. Co-Principal Investigators Department of Pharmacology Disclosures: Peter Jones and Takako
Department of Pharmacology Emerging Treatment Strategies for FSHD Peter L. Jones, Ph.D. and Takako I. Jones, Ph.D. Co-Principal Investigators Department of Pharmacology Disclosures: Peter Jones and Takako
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Influence of the FMR1 Gene on Motor Fiber Tracts in Males With Normal and Premutation Alleles
 Research Original Investigation Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Influence of the FMR1 Gene on Motor Fiber Tracts in Males With Normal and Premutation Alleles Jun Yi Wang, PhD; David Hessl,
Research Original Investigation Fragile X Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Influence of the FMR1 Gene on Motor Fiber Tracts in Males With Normal and Premutation Alleles Jun Yi Wang, PhD; David Hessl,
Sequestration of DROSHA and DGCR8 by Expanded CGG RNA Repeats Alters MicroRNA Processing in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome
 Cell Reports Article Sequestration of DROSHA and by Expanded CGG RNA Repeats Alters MicroRNA Processing in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Chantal Sellier, 1,2 Fernande Freyermuth, 1 Ricardos
Cell Reports Article Sequestration of DROSHA and by Expanded CGG RNA Repeats Alters MicroRNA Processing in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Chantal Sellier, 1,2 Fernande Freyermuth, 1 Ricardos
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Reversing the Effects of Fragile X Syndrome
 CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF BASIC RESEARCH Paul J. Lombroso, M.D., Marilee P. Ogren, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Reversing the Effects of Fragile X Syndrome MARILEE P. OGREN, PH.D., AND PAUL J. LOMBROSO, M.D.
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF BASIC RESEARCH Paul J. Lombroso, M.D., Marilee P. Ogren, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Reversing the Effects of Fragile X Syndrome MARILEE P. OGREN, PH.D., AND PAUL J. LOMBROSO, M.D.
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Screen for Excess FMR1 Premutation Alleles Among Males With Parkinsonism
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Screen for Excess FMR1 Premutation Alleles Among Males With Parkinsonism Jeremy Kraff, MD; Hiu-Tung Tang, BA; Roberto Cilia, MD; Margherita Canesi, MD; Gianni Pezzoli, MD; Stefano
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Screen for Excess FMR1 Premutation Alleles Among Males With Parkinsonism Jeremy Kraff, MD; Hiu-Tung Tang, BA; Roberto Cilia, MD; Margherita Canesi, MD; Gianni Pezzoli, MD; Stefano
Marta Puerto Plasencia. microrna sponges
 Marta Puerto Plasencia microrna sponges Introduction microrna CircularRNA Publications Conclusions The most well-studied regions in the human genome belong to proteincoding genes. Coding exons are 1.5%
Marta Puerto Plasencia microrna sponges Introduction microrna CircularRNA Publications Conclusions The most well-studied regions in the human genome belong to proteincoding genes. Coding exons are 1.5%
Fragile X Syndrome. Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype
 Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Neuroscience 410 Huntington Disease - Clinical. March 18, 2008
 Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
Psych 3102 Lecture 3. Mendelian Genetics
 Psych 3102 Lecture 3 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel 1822 1884, paper read 1865-66 Augustinian monk genotype alleles present at a locus can we identify this? phenotype expressed trait/characteristic can
Psych 3102 Lecture 3 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel 1822 1884, paper read 1865-66 Augustinian monk genotype alleles present at a locus can we identify this? phenotype expressed trait/characteristic can
Fragile X Syndrome & Recent Advances in Behavioural Phenotype Research Jeremy Turk
 Fragile X Syndrome & Recent Advances in Behavioural Phenotype Research Jeremy Turk Institute of Psychiatry Psychology & Neurosciences, King s College, University of London Child & Adolescent Mental Health
Fragile X Syndrome & Recent Advances in Behavioural Phenotype Research Jeremy Turk Institute of Psychiatry Psychology & Neurosciences, King s College, University of London Child & Adolescent Mental Health
Experts call for universal fragile X screening
 NEWS Experts call for universal fragile X screening BY ANDREA ANDERSON 1 APRIL 2008 1 / 5 Clean sweep: Universal screening would detect even asymptomatic carriers of fragile X. Screening for genetic precursors
NEWS Experts call for universal fragile X screening BY ANDREA ANDERSON 1 APRIL 2008 1 / 5 Clean sweep: Universal screening would detect even asymptomatic carriers of fragile X. Screening for genetic precursors
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Male Premutation Carriers of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Gene
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Male Premutation Carriers of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Gene Ryu-ichiro Hashimoto, PhD, 1 Siddharth Srivastava, PhD, 2 Flora Tassone, PhD, 2,3 Randi J.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Male Premutation Carriers of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Gene Ryu-ichiro Hashimoto, PhD, 1 Siddharth Srivastava, PhD, 2 Flora Tassone, PhD, 2,3 Randi J.
Molecular Pathophysiology of Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome and Perspectives for Drug Development
 DOI 10.1007/s12311-016-0800-2 REVIEW Molecular Pathophysiology of Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome and Perspectives for Drug Development Teresa Botta-Orfila 1,2 & Gian Gaetano Tartaglia 1,2,3
DOI 10.1007/s12311-016-0800-2 REVIEW Molecular Pathophysiology of Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome and Perspectives for Drug Development Teresa Botta-Orfila 1,2 & Gian Gaetano Tartaglia 1,2,3
Population Screening for Fragile X Syndrome
 Population Screening for Fragile X Syndrome FLORA TASSONE PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR MEDICINE AND MIND INSTITUTE UC DAVIS, CALIFORNIA USA Molecular Pathology: Principles in Clinical
Population Screening for Fragile X Syndrome FLORA TASSONE PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR MEDICINE AND MIND INSTITUTE UC DAVIS, CALIFORNIA USA Molecular Pathology: Principles in Clinical
Journal of Psychiatric Research
 Journal of Psychiatric Research 45 (2011) 36e43 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Psychiatric Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/psychires An fmri study of the prefrontal
Journal of Psychiatric Research 45 (2011) 36e43 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Psychiatric Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/psychires An fmri study of the prefrontal
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 13, 2006
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Fragile X-associated disorders: Don t miss them
 CLINICAL Fragile X-associated disorders: Don t miss them Rachael C Birch, Jonathan Cohen, Julian N Trollor Background Fragile X-associated disorders are a family of inherited disorders caused by expansions
CLINICAL Fragile X-associated disorders: Don t miss them Rachael C Birch, Jonathan Cohen, Julian N Trollor Background Fragile X-associated disorders are a family of inherited disorders caused by expansions
A novel fragile X syndrome mutation reveals a conserved role for the carboxy-terminus in FMRP localization and function
 A novel fragile X syndrome mutation reveals a conserved role for the carboxy-terminus in FMRP localization and function Zeynep Okray, Celine E.F. de Esch, Hilde Van Esch, Koen Devriendt, Annelies Claeys,
A novel fragile X syndrome mutation reveals a conserved role for the carboxy-terminus in FMRP localization and function Zeynep Okray, Celine E.F. de Esch, Hilde Van Esch, Koen Devriendt, Annelies Claeys,
CHAPTER 5 RESULTS Previous study: cell culture and organotypical slices
 45 CHAPTER 5 RESULTS 5.1. Previous study: cell culture and organotypical slices Initial experiments have been conducted to ensure that the tet-on system works. A neuronal cell culture from mice expressing
45 CHAPTER 5 RESULTS 5.1. Previous study: cell culture and organotypical slices Initial experiments have been conducted to ensure that the tet-on system works. A neuronal cell culture from mice expressing
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
PCR testing for FMR1-related disorders at the Children s Hospital at Westmead: past and present. Dr Karen Wong
 PCR testing for FMR1-related disorders at the Children s Hospital at Westmead: past and present Dr Karen Wong FMR1-related disorders Fragile X syndrome Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia (FXTAS) Fragile
PCR testing for FMR1-related disorders at the Children s Hospital at Westmead: past and present Dr Karen Wong FMR1-related disorders Fragile X syndrome Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia (FXTAS) Fragile
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California, Davis, Davis, CA 95618
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0150 TITLE: Targeted Upregulation of FMRP Expression as an Approach to the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Paul J. Hagerman, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0150 TITLE: Targeted Upregulation of FMRP Expression as an Approach to the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Paul J. Hagerman, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Journal of Medical Genetics Copyright (C) 1997 by Journal of Medical Genetics.
 Journal of Medical Genetics Copyright (C) 1997 by Journal of Medical Genetics. Volume 34(11) November 1997 pp 924-926 Prenatal diagnosis of the fragile X syndrome: loss of mutation owing to a double recombinant
Journal of Medical Genetics Copyright (C) 1997 by Journal of Medical Genetics. Volume 34(11) November 1997 pp 924-926 Prenatal diagnosis of the fragile X syndrome: loss of mutation owing to a double recombinant
Iron Accumulation and Dysregulation in the Putamen in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Iron Accumulation and Dysregulation in the Putamen in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Jeanelle Ariza, BS, 1 Hailee Rogers, BS, 1 Anna Hartvigsen, BS, 1 Melissa Snell, BS, 1
RESEARCH ARTICLE Iron Accumulation and Dysregulation in the Putamen in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome Jeanelle Ariza, BS, 1 Hailee Rogers, BS, 1 Anna Hartvigsen, BS, 1 Melissa Snell, BS, 1
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
variant led to a premature stop codon p.k316* which resulted in nonsense-mediated mrna decay. Although the exact function of the C19L1 is still
 157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
Spinal Muscular Atrophy as a Focus Indication for Biomarker Development. Meg Winberg, PhD Spinal Muscular Atrophy Foundation February 26, 2007
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy as a Focus Indication for Biomarker Development Meg Winberg, PhD Spinal Muscular Atrophy Foundation February 26, 2007 Why SMA? p Low incidence, but a large orphan indication p Scientifically
Spinal Muscular Atrophy as a Focus Indication for Biomarker Development Meg Winberg, PhD Spinal Muscular Atrophy Foundation February 26, 2007 Why SMA? p Low incidence, but a large orphan indication p Scientifically
Chapter 18 Genetics of Behavior. Chapter 18 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 18 Genetics of Behavior Behavior Most human behaviors are polygenic and have significant environmental influences Methods used to study inheritance include Classical methods of linkage and pedigree
Chapter 18 Genetics of Behavior Behavior Most human behaviors are polygenic and have significant environmental influences Methods used to study inheritance include Classical methods of linkage and pedigree
V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs
 What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models. Yu Wu
 Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 10 (ALS10) and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 6 (ALS6)
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 10 (ALS10) and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 6 (ALS6)
