Schizophrenia is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder
|
|
|
- Geraldine Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 n REPORTS n Balancing Therapeutic Safety and Efficacy to Improve Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Schizophrenia: A Clinical Overview Daniel C. Javitt, MD, PhD Abstract Affecting up to 1% of the global population, schizophrenia is a chronic, disabling psychiatric disorder that has profound effects on patients, families, and caretakers due to its tremendous personal, social, and economic burdens. Schizophrenia commonly presents during late adolescence and early adulthood, and although its onset may be abrupt, the majority of patients experience a slow and gradual development of various clinical signs and symptoms. In addition to psychotic symptoms that may alter one s perception, thoughts, affect, and behavior, schizophrenia is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, reduced life expectancy, and higher risks of homelessness and unemployment. Although much research has been conducted on schizophrenia, the exact etiology of the disease remains unclear and is likely multifactorial, and evidence has suggested that neuroanatomical alterations and neurotransmitter abnormalities contribute to the disease s pathophysiology. It is essential to remember that schizophrenia is a chronic disease that requires long-term treatment. While there are currently no definitive diagnostic tests for schizophrenia, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition criteria should be used to guide proper diagnosis and identification. Further research and an improved understanding of the pathophysiological basis of schizophrenia may drive more effective treatment options and improved patient outcomes for this complex and challenging disease. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20:S160-S165 For author information and disclosures, see end of text. Schizophrenia is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder that commonly presents during late adolescence and early adulthood. 1 Although its prevalence is estimated to be up to 1% of the population worldwide, schizophrenia has profound effects on patients and their families due to the tremendous personal, social, and economic burdens it imposes on these individuals. 2,3 Patients with schizophrenia have a greater likelihood of unemployment and homelessness, and the total economic burden of schizophrenia in the United States is estimated to be approximately $65 billion. 1,3 Much research has been done on schizophrenia, but its exact etiology has yet to be determined and is likely multifactorial. Epidemiology The onset of schizophrenia Managed Care symptoms & typically occurs between Healthcare the late teens Communications, and the mid-30s. Patients LLCwith disease onset before age 17 years are considered to have early-onset schizophrenia (EOS), and those with onset before age 13 years are considered to have very early onset schizophrenia (VEOS). 4 The estimated prevalence of VEOS is 1 per 10,000 individuals, and the lifetime prevalence of developing schizophrenia is approximately 0.3% to 0.7%. 4,5 Male patients tend to have an earlier onset of symptoms, between the ages of 15 and 25 years, whereas female patients have later onset, around age 19 to age 35 years. Further, male patients exhibit a higher lifetime risk of developing schizophrenia, with a male-to-female relative risk of about 1.4, and male patients often experience a more severe disease course. 4,6 Etiology The exact cause of schizophrenia has yet to be determined, but it is likely heterogeneous and multifactorial. 7 Although most patients with schizophrenia have no family history of psychoses, research in families of patients with schizophrenia has shown that there is likely a genetic component, and the risk of schizophrenia increases as the degree of genetic affinity with S160 n n JUNE 2014
2 Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Schizophrenia: A Clinical Overview the patient increases. For example, if 1 individual in a pair of twins has schizophrenia, the risk of schizophrenia developing in the other twin is 10% to 15% for dizygotic twins, and increases to 40% to 50% in monozygotic twins. 7 Despite the significant familial risk, however, no genes of large effect have been identified. This pattern could reflect either the epistatic interaction among multiple genes or the contribution of de novo mutations that arise and persist for only 1 or a few generations. 8,9 Rare copy number variants converge, particularly on genes that affect glutamatergic synaptic networks and N-methyl-Daspartate (NMDA) receptors. Specific genes of interest include NRG1 (neuroregulin 1), DTNBP1 (dysbindin), DRD1-4 (dopamine receptors D1-D4), DISC (disrupted in schizophrenia 1), COMT (catechol-0-methyl-transferase), D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO), D-amino acid oxidase activator (DAOA), and GRM3 (metabotropic glutamate receptor). Despite advances in genetic studies, no particular gene variant has been shown to be sufficient to cause schizophrenia. 7,10 In epidemiological studies, environmental factors such as urban settings, areas with high rates of migrants, exposure to cannabis during adolescence, and lower socioeconomic class have been linked to the development of schizophrenia. Maternal stress and/or infection (eg, influenza) during pregnancy, nutritional deficiency during the prenatal period, obstetric and perinatal complications (eg, fetal hypoxia), birth during late winter or early spring, and childhood trauma(s) can also increase the risk of development of schizophrenia. 4,7,11 Older paternal age (>45 years) at the time of conception has also been associated with a more than 2-fold increased risk of the offspring developing schizophrenia. 12,13 Pathophysiology Neuroanatomical Alterations Magnetic resonance imaging studies of the brains of patients with schizophrenia have shown reductions in whole brain volume and grey matter volume, and the enlargement of ventricles. Reductions are also seen in temporal lobe areas, such as the hippocampus, amygdala, superior temporal gyri, prefrontal cortex, thalamus, anterior cingulate, and corpus callosum. It has been suggested that disturbances in the development of cerebral asymmetry can contribute to the etiopathogenesis of schizophrenia. 14 Leftward asymmetry of the brain structure may also be reduced in patients with schizophrenia due to a larger right planum temporale compared with normal controls. 14,15 Compared with adults with schizophrenia, patients with EOS appear to have similar brain structural changes, but more severe neuroanatomical alterations. 14,16 The integrity of white matter connections between regions of the brain may also be compromised and lead to impairments, as revealed by diffusion tensor imaging, in such processes as behavioral regulation. 17 Neurotransmitter Abnormalities Dopaminergic dysfunction has long been cited as the main cause of schizophrenia symptoms. It has been proposed that patients with schizophrenia have hypoactive mesocortical dopaminergic systems, which are responsible for negative and cognitive symptoms, and hyperactive mesolimbic dopamine systems, which are responsible for the positive symptoms. 14,18 Presynaptic dopamine synthesis and release mechanisms may be most affected; however, dopamine abnormality does not explain all of the symptoms associated with schizophrenia. 11,19 Current antipsychotic medications are effective for many individuals, but nevertheless, a high percentage of patients have no or only partial relief of symptoms, even with the best available agents. Persistent negative and cognitive symptoms are particularly associated with poor outcomes, and do not respond well to existing medications. 11,20 There is increasing evidence that glutamatergic dysfunction is another possible cause of schizophrenia. The observation that NMDA receptor antagonists, such as phencyclidine and ketamine, can cause clinical symptoms similar to those seen in patients with schizophrenia suggests that schizophrenia may be related to a decrease in NMDA receptor function in the brain More recently, NMDA receptor theories have been supported by the observation that antibodies to NMDA receptors may induce a psychotic state that resembles schizophrenia. 24 As opposed to the dopamine system, which projects preferentially to basal ganglia and frontotemporal regions, the glutamate system is widely distributed throughout the brain and affects sensory regions, as well as those involved in such higher-order processes as memory or executive processing. 23 Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), released in May 2013, provides updated criteria for the diagnosis and classification of various mental disorders, including schizophrenia. For a patient to be appropriately diagnosed with VOL. 20, NO. 8 n THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE n S161
3 Reports n Table. Symptoms of Schizophrenia 1,11 Positive Negative Cognitive Hallucination Delusion Disorganized thinking Suspiciousness Apathy Avolition Alogia Anhedonia Memory impairment Decrease in attention Impaired executive functioning schizophrenia, they should exhibit at least 2 Criterion A symptoms for a significant portion of time, defined as a 1-month period or longer, unless successfully treated before this 1-month period has elapsed. Criterion A symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech (eg, frequent derailment or incoherence), grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior, and negative symptoms (ie, diminished emotional expression or avolition). Patients should also show a reduced level of functioning in areas such as self-care, work, and interpersonal relations. Further, some signs of the disturbance, such as mumbling in public, magical thinking, or becoming more withdrawn, must persist for a continuous period of at least 6 months. Differential diagnoses, such as schizoaffective disorder, depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features, and psychosis caused by a substance or medical condition should be ruled out. 25 Compared with DSM-IV, in which only 1 Criterion A symptom is required for diagnosis of schizophrenia if the delusions are bizarre (ie, clearly implausible and inconsistent within the culture or from ordinary life experiences) or if hallucinations consist of a voice keeping up a running commentary on the person s behavior or thoughts or consist of 2 or more voices conversing with each other, DSM-5 requires patients to have 2 or more Criterion A symptoms regardless of the characteristics of the delusions or hallucinations. Other communication disorder of childhood onset was added to Criterion F. Additionally, DSM-5 does not distinguish the subtypes of schizophrenia, such as paranoid, disorganized, catatonic, undifferentiated, and residual, due to the lack of clinical utility and diagnostic value. 26 Patients with schizophrenia can present with a wide variety of signs and symptoms, including positive symptoms, negative symptoms, and cognitive impairment (Table). Positive symptoms are usually the most recognizable by family and healthcare providers, and include delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia. Persecutory delusions and delusions of reference are the most common types of delusions. Of hallucinations, auditory forms are the most common, but patients may experience hallucinations in other sensory modalities as well. Negative symptoms include the impairment of affective expression, such as apathy (lack of interest), avolition (lack of initiative), alogia (poverty of speech), and anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure). Cognitive impairment includes deficits in information and motor processing speed, decline in verbal and visual memory, and attention deficits. 1 Cognitive impairment is strongly associated with functional disability, as it often leads to poor performance at work or school, the development of social relationship problems, or an inability to live independently. 20,27 In addition to the 3 clusters of symptoms discussed above, patients with schizophrenia often experience depressive symptoms and anxiety. Clinical Progression Schizophrenia is a chronic and persistent serious mental illness that requires ongoing treatment. 28 Although disease onset may be abrupt, the majority of patients with schizophrenia have a slow and gradual development of various clinical signs and symptoms. Some patients with schizophrenia may present with a range of developmental, behavioral, emotional, and cognitive impairments during childhood, which is characterized as the premorbid phase (Figure). These patients often have delays in motor and language development, reduced attention span, social isolation, and emotional detachment. 1 The prodromal phase often occurs in mid-adolescence, approximately 2 to 3 years before the onset of the first psychotic episode. During the prodromal phase, patients often exhibit subclinical psychotic symptoms, cognitive deficits, negative and mood symptoms, and functional decline. 1,29 The development of overt psychotic symptoms consistent with Criterion A in the DSM-5 indicates the formal onset of the first episode of schizophrenia (ie, psychotic phase). Patients usually experience an initial increase in negative and mood symptoms followed by an increase in positive symptoms. Although substance use (ie, substance abuse or dependence) and life stressors have been identified as possible triggers that can precipitate the S162 n n JUNE 2014
4 Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Schizophrenia: A Clinical Overview n Figure. Evolution of Schizophrenia With Phases of Illness 1 Natural history and course of schizophrenia Variable degrees of recovery First psychotic episode Premorbid phase Cognitive, motor, or social deficits Prodromal phase Brief/attenuated positive symptoms and/or functional decline Psychotic phase Florid positive symptoms Stable phase Negative symptoms, cognitive/social deficits, functional decline Childhood Adolescence/young adulthood Timeline Reprinted with permission from Tandon R, Nasrallah HA, Keshavan MS. Schizophr Res. 2009;110(1-3):1-23. episode, most patients do not have an identifiable trigger. After the first psychotic break, patients can experience multiple episodes of exacerbations and remissions. Positive symptoms tend to diminish over time, but negative symptoms and cognitive impairment usually persist throughout the patient s lifetime. Functional level tends to decline significantly after the first-break episode, but a plateau in functional impairment is often seen in later life (ie, stabilization phase). 1 Unfortunately, patients with EOS or VEOS often have worse premorbid function, more severe negative and disorganization symptoms, more cognitive deficits, and poorer overall prognosis compared with patients with later-onset schizophrenia. 4 Additional Clinical Considerations Mortality Compared with the general population, the overall mortality rate is increased in patients with schizophrenia, and their lifespan is shortened by approximately 15 to 20 years. 1,30,31 Despite advances in treatment, the relative mortality risk associated with schizophrenia has been increasing over the last 3 decades. Compared with the general population, patients with schizophrenia have 2.5- fold greater risk of dying due to any cause, 12 times the risk of dying of suicide, and a 2- to 3-fold increased risk of death from cardiovascular diseases. 32,33 Whereas suicide has been found to be the leading cause of death in male patients with schizophrenia, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in female patients, and appears to contribute to the largest number of deaths in patients with schizophrenia. 1,34 Suicide In patients with schizophrenia, the rate of death by suicide is approximately 5%, and the rate of suicidal attempts ranges between 20% and 40%. Most patients attempt suicide at the initiation of their first treatment trial or during the period before treatment begins. 35 The risk of suicide seems to increase in patients who are male, live alone, have comorbid affective disorders or substance abuse, have a history of suicidal thoughts, and/or demonstrate poor adherence to treatment. 36 VOL. 20, NO. 8 n THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE n S163
5 Reports However, patients with protective factors, such as family support and social connectedness, are less likely to attempt suicide. Clozapine is the preferred antipsychotic among patients with suicidality, as it may reduce the risk of suicide. Medical Comorbidities Schizophrenia has been associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease; the overall rate of metabolic syndrome in the schizophrenia population was estimated at 32.5%. Female sex, increasing age, second-generation antipsychotic use, and polypharmacy can increase the risk for metabolic syndrome. 37 Studies have shown that, compared with matched healthy control groups, medication-naïve patients with schizophrenia have impaired fasting glucose tolerance; greater insulin resistance; and elevated levels of plasma glucose, insulin, and cortisol. 38,39 Additional risk factors, such as a higher rate of smoking, drug and alcohol use, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, dyslipidemia, and cardiac and metabolic adverse effects associated with antipsychotic use, can all contribute to the increased risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease seen in patients with schizophrenia. 37,40 Medication Nonadherence Patient nonadherence is a major concern in the treatment of schizophrenia the rate of nonadherence has been estimated at 50%. Treatment nonadherence has been associated with increased hospitalization, higher risk of suicide, longer time to remission, poor prognosis, and psychiatric emergencies. The cause of nonadherence is multifactorial; it may be due to poor understanding of the disease, negative attitude toward treatment, concurrent substance use, a poor relationship with the healthcare provider, and/or adverse effects from the medications. Patients with schizophrenia who are male, young, have limited family or social support, and have low socioeconomic backgrounds are more likely to be nonadherent to treatment. To promote adherence, healthcare providers should identify the cause of nonadherence and improve patients knowledge regarding the disease state. Certain pharmacologic interventions, such as long-acting injectable antipsychotics, can also help to improve treatment adherence and promote constant contact between the patient and the treatment team. 41 Conclusion Schizophrenia is a chronic psychiatric disease with multiple etiologies that requires long-term treatment. Although there is no definitive diagnostic test for schizophrenia, clinicians can utilize the criteria listed in DSM-5 to help guide proper diagnosis and identification. Due to the complex nature of the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and the high level of morbidity and mortality associated with the disease, definitive and effective treatment is urgently needed; however, challenges remain for patients and clinicians alike. Additional research and a better understanding of the pathophysiological basis of schizophrenia will hopefully drive the improvement of treatment options available to patients. Author affiliation: Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, NY, and Division of Experimental Therapeutics, Columbia University, New York, NY. Funding source: This activity is supported by educational grants from Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. Author disclosure: Dr Javitt reports receiving grant/research support from Pfizer Inc and Roche, and serving as a consultant for Bristol- Myers Squibb, EnVivo, Lilly, Omeros, Otsuka, SK Biopharmaceuticals, Sunovion, and Takeda. He reports stock ownership with Glytech. Authorship information: Concept and design; drafting of the manuscript; and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. Address correspondence to: dcj2113@columbia.edu. REFERENCES 1. Tandon R, Nasrallah HA, Keshavan MS. Schizophrenia, just the facts 4: clinical features and conceptualization. Schizophr Res. 2009;110(1-3): Javitt DC. Current and emergent treatments for symptoms and neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Curr Treat Options Psychiatry. 2014;1: Knapp M, Mangalore R, Simon J. The global costs of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2004;30(2): Abidi S. Psychosis in children and youth: focus on early-onset schizophrenia. Pediatr Rev. 2013;34(7): McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J. Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiol Rev. 2008;30: Aleman A, Kahn RS, Selten JP. Sex differences in the risk of schizophrenia: evidence from meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(6): Tandon R, Keshavan MS, Nasrallah HA. Schizophrenia, just the facts : what we know in 2008: 2: epidemiology and etiology. Schizophr Res. 2008;102(1-3): Andreasen NC, Wilcox MA, Ho BC, et al. Statistical epistasis and progressive brain change in schizophrenia: an approach for examining the relationships between multiple genes. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17(11): Xu B, Woodroffe A, Rodriguez-Murillo L, et al. Elucidating the genetic architecture of familial schizophrenia using rare copy number variant and linkage scans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(39): Maier W. Common risk genes for affective and schizophrenic psychoses. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2008;258(suppl 2): van Os J, Kapur S. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2009;374(9690): Malaspina D, Harlap S, Fennig S, et al. Advancing paternal age and the risk of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001; 58(4): S164 n n JUNE 2014
6 Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Schizophrenia: A Clinical Overview 13. Weiser M, Reichenberg A, Werbeloff N, et al. Advanced parental age at birth is associated with poorer social functioning in adolescent males: shedding light on a core symptom of schizophrenia and autism. Schizophr Bull. 2008;34(6): Keshavan MS, Tandon R, Boutros NN, Nasrallah HA. Schizophrenia, just the facts : what we know in 2008: part 3: neurobiology. Schizophr Res. 2008;106(2-3): Shapleske J, Rossell SL, Woodruff PW, David AS. The planum temporale: a systematic, quantitative review of its structural, functional and clinical significance. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999;29(1): Kyriakopoulos M, Frangou S. Pathophysiology of early onset schizophrenia. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2007;19(4): Lim KO, Ardekani BA, Nierenberg J, et al. Voxelwise correlational analyses of white matter integrity in multiple cognitive domains in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11): Davis KL, Kahn RS, Ko G, Davidson M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: a review and reconceptualization. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148(11): Howes OD, Kambeitz J, Kim E, et al. The nature of dopamine dysfunction in schizophrenia and what this means for treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(8): Rajji TK, Miranda D, Mulsant BH. Cognition, function, and disability in patients with schizophrenia: a review of longitudinal studies. Can J Psychiatry. 2014;59(1): Javitt DC, Zukin SR. Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148(10): Coyle JT. Glutamate and schizophrenia: beyond the dopamine hypothesis. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006;26(4-6): Kantrowitz JT, Javitt DC. Glutamate: new hope for schizophrenia treatment. Current Psychiatry. 2011;11(4): Dalmau J, Lancaster E, Martinez-Hernandez E, Rosenfeld MR, Balice-Gordon R. Clinical experience and laboratory investigations in patients with anti-nmdar encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(1): American Psychiatric Association. Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders. In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Arlington, VA: Bhati MT. Defining psychosis: the evolution of DSM-5 schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2013;15(11): Rajji TK, Ismail Z, Mulsant BH. Age at onset and cognition in schizophrenia: meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2009;195(4): Lieberman JA. Neurobiology and the natural history of schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(10):e Cornblatt B, Obuchowski M, Roberts S, Pollack S, Erlenmeyer-Kimling L. Cognitive and behavioral precursors of schizophrenia. Dev Psychopathol. 1999;11(3): Auquier P, Lancon C, Rouillon F, Lader M. Mortality in schizophrenia. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2007;16(12): Parks J, Svendsen D, Singer P, Foti M. Morbidity and mortality in people with serious mental illness. National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors Medical Directors Council website. Mortality%20and%20Morbidity%20Final%20Report% pdf. Published Accessed May 21, Saha S, Chant D, McGrath J. A systemic review of mortality in schizophrenia: is the differential mortality gap worsening over time? Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(10): Osborn DP, Levy G, Nazareth I, et al. Relative risk of cardiovascular and cancer mortality in people with severe mental illness from the United Kingdom s General Practice Research Database. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(2): Osby U, Correia N, Brandt L, Ekbom A, Sparén P. Mortality and causes of death in schizophrenia in Stockholm county, Sweden. Schizophr Res. 2000;45(1-2): Melle I, Johannesen JO, Friis S, et al. Early detection of the first episode of schizophrenia and suicidal behavior. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(5): Hawton K, Sutton L, Haw C, Sinclair J, Deeks JJ. Schizophrenia and suicide: systemic review of risk factors. Br J Psychiatry. 2005;187: Papanastasiou E. The prevalence and mechanisms of meta bolic syndrome in schizophrenia: a review. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2013;3(1): Ryan MC, Collins P, Thakore JH. Impaired fasting glucose tolerance in first-episode, drug-naive patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(2): Saddichha S, Manjunatha N, Ameen S, Akhtar S. Diabetes and schizophrenia - effect of disease or drug? results from a randomized, double-blind, controlled prospective study in first-episode schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2008;117(5): Leucht S, Burkard T, Henderson J, Maj M, Sartorius N. Physical illness and schizophrenia: a review of the literature. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2007;116(5): Acosta FJ, Hernández JL, Pereira J, Herrera J, Rodríguez CJ. Medication adherence in schizophrenia. World J Psychiatry. 2012;2(5): VOL. 20, NO. 8 n THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE n S165
Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health
 Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
November 2014 MRC2.CORP.X.00004
 This program is paid for by Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. and Lundbeck, LLC. The speaker is a paid consultant of Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. advice or professional diagnosis. Users seeking
This program is paid for by Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. and Lundbeck, LLC. The speaker is a paid consultant of Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. advice or professional diagnosis. Users seeking
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Roseanna Parkhurst-Gatewood MSN FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder 3 A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive
Roseanna Parkhurst-Gatewood MSN FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder 3 A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive
Update on First Psychotic Episodes in Childhood and Adolescence. Cheryl Corcoran, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Columbia University
 Update on First Psychotic Episodes in Childhood and Adolescence Cheryl Corcoran, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Columbia University Childhood-Onset Psychosis 8% of psychiatrically referred youth
Update on First Psychotic Episodes in Childhood and Adolescence Cheryl Corcoran, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Columbia University Childhood-Onset Psychosis 8% of psychiatrically referred youth
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Accurate Diagnosis of Primary Psychotic Disorders
 Accurate Diagnosis of Primary Psychotic Disorders The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Accurate Diagnosis of Primary Psychotic Disorders The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Program Outline. DSM-5 Schizophrenia Spectrum and Psychotic Disorders: Knowing it Better and Improving Clinical Practice.
 DSM-5 Spectrum and Disorders: Knowing it Better and Improving Clinical Practice Rajiv Tandon, MD Professor of Psychiatry University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Program Outline Changes
DSM-5 Spectrum and Disorders: Knowing it Better and Improving Clinical Practice Rajiv Tandon, MD Professor of Psychiatry University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Program Outline Changes
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
4. General overview Definition
 4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abuse substance. See Substance abuse Acquired disorders presenting as psychosis in children and young adults, 581 608. See also specific
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abuse substance. See Substance abuse Acquired disorders presenting as psychosis in children and young adults, 581 608. See also specific
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
By Jason H. King DECONSTRUCTING THE DSM-5 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS THE NEW LANDSCAPE
 DECONSTRUCTING THE DSM-5 By Jason H. King ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Happy New Year as you engage in your counseling, research, supervision or educational endeavors. I
DECONSTRUCTING THE DSM-5 By Jason H. King ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Happy New Year as you engage in your counseling, research, supervision or educational endeavors. I
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
D. Exclusion of schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic features.
 65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
EARLY ONSET SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Psychiatry and Addictions Case Conference UW Medicine Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences EARLY ONSET SCHIZOPHRENIA JON MCCLELLAN CHILD STUDY AND TREATMENT CENTER GENERAL DISCLOSURES The University of Washington
Psychiatry and Addictions Case Conference UW Medicine Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences EARLY ONSET SCHIZOPHRENIA JON MCCLELLAN CHILD STUDY AND TREATMENT CENTER GENERAL DISCLOSURES The University of Washington
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders
 PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help
 DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Autism. Childhood Autism and Schizophrenia. Autism, Part 1 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-IV-TR) Behavioral Characteristics of Autism
 Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal
 ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
Clinical Staging and the At-Risk Phase of Psychotic Disorder
 Clinical Staging and the At-Risk Phase of Psychotic Disorder Sabina Abidi MD FRCPC IWK Youth Psychosis Program Capital Health Nova ScoCa Early Psychosis Program Key Findings in Early Psychosis Knowledge
Clinical Staging and the At-Risk Phase of Psychotic Disorder Sabina Abidi MD FRCPC IWK Youth Psychosis Program Capital Health Nova ScoCa Early Psychosis Program Key Findings in Early Psychosis Knowledge
Chapter Sixteen. Psychological Disorders
 Chapter Sixteen Psychological Disorders Prevalence of Psychological Disorders? Approximately 25% of the Adult Population here in the U.S. of A. Higher percentages in areas / countries with high poverty
Chapter Sixteen Psychological Disorders Prevalence of Psychological Disorders? Approximately 25% of the Adult Population here in the U.S. of A. Higher percentages in areas / countries with high poverty
DANIEL MOLLOY, MD MENTOR: JAMES STEPHEN, MD
 Blood Glucose Control in a Schizophrenic Population in an Outpatient Setting DANIEL MOLLOY, MD MENTOR: JAMES STEPHEN, MD Schizophrenia Complex psychiatric disorder with many medical and psychosocial complications.
Blood Glucose Control in a Schizophrenic Population in an Outpatient Setting DANIEL MOLLOY, MD MENTOR: JAMES STEPHEN, MD Schizophrenia Complex psychiatric disorder with many medical and psychosocial complications.
Outline. Outline. Background Literature and Slides 10/23/2013. The Schizophrenia Research Forum online: Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior
 Background Literature and Slides Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior Roberto Fernández Galán, PhD Assistant Professor of Neurosciences Mt. Sinai Health Care Foundation Scholar Alfred P. Sloan Research
Background Literature and Slides Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior Roberto Fernández Galán, PhD Assistant Professor of Neurosciences Mt. Sinai Health Care Foundation Scholar Alfred P. Sloan Research
Schizophrenia: New Concepts for Therapeutic Discovery
 Schizophrenia: New Concepts for Therapeutic Discovery William T. Carpenter, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry and Pharmacology University of Maryland School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Maryland Psychiatric
Schizophrenia: New Concepts for Therapeutic Discovery William T. Carpenter, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry and Pharmacology University of Maryland School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Maryland Psychiatric
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Severe Mental Disorders. Etheldreda Nakimuli-Mpungu, MMed (Psych), MBChB Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
OF THE ILLNESS. Manote Lotrakul. Aug 2015
 SCHIZOPHRENIA: ALL PHASES OF THE ILLNESS Manote Lotrakul Aug 2015 Outline Diagnostic criteria Clinical features Treatments DSM-5 : Schizophrenia A. Two (or more) of the following, each present for a significant
SCHIZOPHRENIA: ALL PHASES OF THE ILLNESS Manote Lotrakul Aug 2015 Outline Diagnostic criteria Clinical features Treatments DSM-5 : Schizophrenia A. Two (or more) of the following, each present for a significant
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC
 Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Method. NeuRA Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder April 2016
 Introduction Schizophrenia is characterised by positive, negative and disorganised symptoms. Positive symptoms refer to experiences additional to what would be considered normal experience, such as hallucinations
Introduction Schizophrenia is characterised by positive, negative and disorganised symptoms. Positive symptoms refer to experiences additional to what would be considered normal experience, such as hallucinations
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Mental Health: Where Nutrition meets Psychiatry By Nicola Walters, Registered Dietitian
 Mental Health: Where Nutrition meets Psychiatry By Nicola Walters, Registered Dietitian Key Focus Areas Overview of Global & SA Statistics Analysis of the Evidence Sugar & Refined Carbohydrates Fat: dietary
Mental Health: Where Nutrition meets Psychiatry By Nicola Walters, Registered Dietitian Key Focus Areas Overview of Global & SA Statistics Analysis of the Evidence Sugar & Refined Carbohydrates Fat: dietary
CHAPTER 3 SCHIZOPHRENIA. Highlights
 CHAPTER 3 SCHIZOPHRENIA Highlights Schizophrenia affects 1% of the Canadian population. Onset is usually in early adulthood. Schizophrenia can be treated effectively with a combination of medication, education,
CHAPTER 3 SCHIZOPHRENIA Highlights Schizophrenia affects 1% of the Canadian population. Onset is usually in early adulthood. Schizophrenia can be treated effectively with a combination of medication, education,
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Bipolar disorder. Paz García-Portilla
 Bipolar disorder Paz García-Portilla BD I: Epidemiology Life-time prevalence 1% (0.7 1.8%) 30% with diagnosis and without treatment, or with erroneous diagnosis (major unipolar depression, borderline PD)
Bipolar disorder Paz García-Portilla BD I: Epidemiology Life-time prevalence 1% (0.7 1.8%) 30% with diagnosis and without treatment, or with erroneous diagnosis (major unipolar depression, borderline PD)
Brain complexity and disease SM MAAS
 Brain complexity and disease September 9, 2009 Dr. Stefan Maas, BioS Lehigh U. Brain networks lehigh.edu SMAAS Brain Trivia The average number of more than The adult neurons in 100,000 brain weighs the
Brain complexity and disease September 9, 2009 Dr. Stefan Maas, BioS Lehigh U. Brain networks lehigh.edu SMAAS Brain Trivia The average number of more than The adult neurons in 100,000 brain weighs the
Early identification of neurobiological markers of remission. Michael Bodnar, PhD Ashok K. Malla, MD Martin Lepage, PhD
 Early identification of neurobiological markers of remission Michael Bodnar, PhD Ashok K. Malla, MD Martin Lepage, PhD Outline Why study remission? Defining remission Data collection Results neurocognition
Early identification of neurobiological markers of remission Michael Bodnar, PhD Ashok K. Malla, MD Martin Lepage, PhD Outline Why study remission? Defining remission Data collection Results neurocognition
Identifying Youth at Clinical High Risk for Psychosis
 Identifying Youth at Clinical High Risk for Psychosis Jean Addington PhD University of Calgary Department of Psychiatry 1 Identifying Youth at Clinical High Risk for Psychosis Part 1: What do we know about
Identifying Youth at Clinical High Risk for Psychosis Jean Addington PhD University of Calgary Department of Psychiatry 1 Identifying Youth at Clinical High Risk for Psychosis Part 1: What do we know about
The Brain on ADHD. Ms. Komas. Introduction to Healthcare Careers
 The Brain on ADHD Ms. Komas Introduction to Healthcare Careers Ms. Komas Period 9/2/2016 Komas 1 HOOK: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) plagues between 5% and 7% of children and less than
The Brain on ADHD Ms. Komas Introduction to Healthcare Careers Ms. Komas Period 9/2/2016 Komas 1 HOOK: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) plagues between 5% and 7% of children and less than
Week 2: Disorders of Childhood
 Week 2: Disorders of Childhood What are neurodevelopmental disorders? A group of conditions with onset in the developmental period Disorders of the brain The disorders manifest early in development, often
Week 2: Disorders of Childhood What are neurodevelopmental disorders? A group of conditions with onset in the developmental period Disorders of the brain The disorders manifest early in development, often
Diagnosis. Shayna Sokol, LSW, CHC
 Diagnosis Shayna Sokol, LSW, CHC Diagnosis Across the Age Continuum 1 in 5 Children have a diagnosable MH condition I m an adult Service Coordinator, so why do I need to know about child and adolescent
Diagnosis Shayna Sokol, LSW, CHC Diagnosis Across the Age Continuum 1 in 5 Children have a diagnosable MH condition I m an adult Service Coordinator, so why do I need to know about child and adolescent
#CHAIR2016. September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL. Sponsored by
 #CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by Bending the Illness Curve: A New Treatment Model for Early Stage Psychoses Jeffrey A. Lieberman, M.D. Columbia University College
#CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by Bending the Illness Curve: A New Treatment Model for Early Stage Psychoses Jeffrey A. Lieberman, M.D. Columbia University College
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: treatment and management Quality standard title:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: treatment and management Quality standard title:
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Three Minute Review. Test Yourself. and Dissociative Identity Disorder
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
4/29/2016. Psychosis A final common pathway. Early Intervention in Psychotic Disorders: Necessary, Effective, and Overdue
 Early Intervention in Psychotic Disorders: Necessary, Effective, and Overdue Disclosures Financial relationships with commercial interests Douglas R. Robbins, M.D. Maine Medical Center Tufts University
Early Intervention in Psychotic Disorders: Necessary, Effective, and Overdue Disclosures Financial relationships with commercial interests Douglas R. Robbins, M.D. Maine Medical Center Tufts University
Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders
 1 6 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders 16 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders The Toll of Psychiatric Disorders Is Huge Schizophrenia is the major neurobiological
1 6 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders 16 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders The Toll of Psychiatric Disorders Is Huge Schizophrenia is the major neurobiological
Schizophrenia. This factsheet covers -
 Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
2018/05/01 DISCLOSURE EFFECTS OF CANNABIS USE IN ADOLESCENTS
 DISCLOSURE EFFECTS OF CANNABIS USE IN ADOLESCENTS No conflict of interest to declare No pharmaceutical industry support No support from cannabis producers Selene Etches MD, FRCPC Cannabis is the most widely
DISCLOSURE EFFECTS OF CANNABIS USE IN ADOLESCENTS No conflict of interest to declare No pharmaceutical industry support No support from cannabis producers Selene Etches MD, FRCPC Cannabis is the most widely
SCHIZOPHRENIA and PSYCHOSES
 SCHIZOPHRENIA and PSYCHOSES Schizophrenia is a diagnosis which includes psychoses symptoms Greek - Skhizen (to split) Phren (mind) Splitting of the mind or it s function NOT a split personality. Psychoses
SCHIZOPHRENIA and PSYCHOSES Schizophrenia is a diagnosis which includes psychoses symptoms Greek - Skhizen (to split) Phren (mind) Splitting of the mind or it s function NOT a split personality. Psychoses
Review: Psychosocial assessment and theories of development from N141 and Psych 101
 Unit III Theory and Practice of Psychiatric Nursing REQUIRED READINGS AND ACTIVITIES Related Activities Assignments Review: Psychosocial assessment and theories of development from N141 and Psych 101 Anxiety,
Unit III Theory and Practice of Psychiatric Nursing REQUIRED READINGS AND ACTIVITIES Related Activities Assignments Review: Psychosocial assessment and theories of development from N141 and Psych 101 Anxiety,
Linda Carpenter, M.D.
 Stress, Depression and Physical Health Linda Carpenter, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Human Behavior and Medicine Alpert Medical School of Brown University Chief, Butler Hospital Mood Disorders
Stress, Depression and Physical Health Linda Carpenter, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Human Behavior and Medicine Alpert Medical School of Brown University Chief, Butler Hospital Mood Disorders
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia
 Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
The outlook for schizophrenia is better than we think but is being sabotaged by Assembly-line Psychiatry
 The outlook for schizophrenia is better than we think but is being sabotaged by Assembly-line Psychiatry Robin M Murray Department of Psychosis Studies Institute of Psychiatry King s College London robin.murray@kcl.ac.uk
The outlook for schizophrenia is better than we think but is being sabotaged by Assembly-line Psychiatry Robin M Murray Department of Psychosis Studies Institute of Psychiatry King s College London robin.murray@kcl.ac.uk
schizophrenia :The latest news By Dr. Gamal Suliman Elgorashi MB BS,DPM, MRCpsych Consultant psychiatrist Kent & Medway NHS Trust UK
 schizophrenia :The latest news By Dr. Gamal Suliman Elgorashi MB BS,DPM, MRCpsych Consultant psychiatrist Kent & Medway NHS Trust UK The argument Schizophrenia has for too long been known as a single
schizophrenia :The latest news By Dr. Gamal Suliman Elgorashi MB BS,DPM, MRCpsych Consultant psychiatrist Kent & Medway NHS Trust UK The argument Schizophrenia has for too long been known as a single
LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS
 LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS Dolores Malaspina, MD, MS, MSPH Anita & Joseph Steckler Professor of Psychiatry & Child Psychiatry - NYU Langone Medical Center
LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS Dolores Malaspina, MD, MS, MSPH Anita & Joseph Steckler Professor of Psychiatry & Child Psychiatry - NYU Langone Medical Center
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
The Link between Marijuana &
 The Link between Marijuana & mental illness A Survey of Recent Research OFFICE OF NATIONAL DRUG CONTROL POLICY EXECUTIVE OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT July 2007 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview of Marijuana and Mental
The Link between Marijuana & mental illness A Survey of Recent Research OFFICE OF NATIONAL DRUG CONTROL POLICY EXECUTIVE OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENT July 2007 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview of Marijuana and Mental
The Key to Understanding Autism: The Latest in Brain Development and Information Processing
 WORKSHOP G-6 The Key to Understanding Autism: The Latest in Brain Development and Information Processing Daily Behavioral Health and Building Behaviors Autism Center Suggested Audience: Adult Service Provider,
WORKSHOP G-6 The Key to Understanding Autism: The Latest in Brain Development and Information Processing Daily Behavioral Health and Building Behaviors Autism Center Suggested Audience: Adult Service Provider,
Is Lurasidone more safe and effective in the treatment ofschizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia than other commonanti-psychotic medications?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Lurasidone more safe and effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Lurasidone more safe and effective
Are All Older Adults Depressed? Common Mental Health Disorders in Older Adults
 Are All Older Adults Depressed? Common Mental Health Disorders in Older Adults Cherie Simpson, PhD, APRN, CNS-BC Myth vs Fact All old people get depressed. Depression in late life is more enduring and
Are All Older Adults Depressed? Common Mental Health Disorders in Older Adults Cherie Simpson, PhD, APRN, CNS-BC Myth vs Fact All old people get depressed. Depression in late life is more enduring and
Suboptimal Response in Psychotic & Mood Disorders: Causes, Consequences, and Management Strategies
 Suboptimal Response in Psychotic & Mood Disorders: Causes, Consequences, and Management Strategies Henry A. Nasrallah, MD Sydney W. Souers Professor and Chair, Department of Psychiatry, Saint Louis University,
Suboptimal Response in Psychotic & Mood Disorders: Causes, Consequences, and Management Strategies Henry A. Nasrallah, MD Sydney W. Souers Professor and Chair, Department of Psychiatry, Saint Louis University,
Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Early Stages of Psychosis. Learning Objectives
 Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
4/12/2014. Early-Onset Schizophrenia
 Early-Onset Schizophrenia 1 Overview History: Conceptualizations Past and Present DSM Model, Symptoms & Subtypes Epidemiology: Prevalence/Onset/Course/Duration Comorbidity Neurobiology Genetic Underpinnings
Early-Onset Schizophrenia 1 Overview History: Conceptualizations Past and Present DSM Model, Symptoms & Subtypes Epidemiology: Prevalence/Onset/Course/Duration Comorbidity Neurobiology Genetic Underpinnings
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
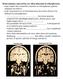 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Estimates of Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions among Children and Adolescents in Texas. March 24, 2016
 Estimates of Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions among Children and Adolescents in Texas March 24, 2016 MMHPI Page 2 Estimates of the Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions among Children and Adolescents
Estimates of Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions among Children and Adolescents in Texas March 24, 2016 MMHPI Page 2 Estimates of the Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions among Children and Adolescents
The relevance of D2-AKT1 signalling for the pathophysiology of cannabis-induced psychosis.
 The relevance of D2-AKT1 signalling for the pathophysiology of cannabis-induced psychosis Edinburgh, 14 April 2016 Dr Marco Colizzi marco.v.colizzi@kcl.ac.uk Developmental cascade towards psychosis Family
The relevance of D2-AKT1 signalling for the pathophysiology of cannabis-induced psychosis Edinburgh, 14 April 2016 Dr Marco Colizzi marco.v.colizzi@kcl.ac.uk Developmental cascade towards psychosis Family
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents
 Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D.
 HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pediatrics University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa The information provided
HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pediatrics University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa The information provided
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders
 The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders
 How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders What are psychological disorders? Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts,
How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders What are psychological disorders? Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts,
When is a Psychological Disorder a Disability? Dr. Leigh Ann Ford, PhD, HSP Licensed Psychologist ABVE 2017 Annual Conference. Goals for presentation
 When is a Psychological Disorder a Disability? Dr. Leigh Ann Ford, PhD, HSP Licensed Psychologist ABVE 2017 Annual Conference Goals for presentation *To review DSM-V criteria for some of the most frequently
When is a Psychological Disorder a Disability? Dr. Leigh Ann Ford, PhD, HSP Licensed Psychologist ABVE 2017 Annual Conference Goals for presentation *To review DSM-V criteria for some of the most frequently
Chapter 14. Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition Abnormal Behavior Historical aspects of mental disorders F 14.1 The medical model What is abnormal behavior? 3 criteria F 14.2 Deviant Maladaptive Causing
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition Abnormal Behavior Historical aspects of mental disorders F 14.1 The medical model What is abnormal behavior? 3 criteria F 14.2 Deviant Maladaptive Causing
Piecing the Puzzle Together: Pharmacologic Approaches to Behavioral Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Piecing the Puzzle Together: Pharmacologic Approaches to Behavioral Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder Hannah Sauer, PharmD PGY1 Pediatric Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives
Piecing the Puzzle Together: Pharmacologic Approaches to Behavioral Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder Hannah Sauer, PharmD PGY1 Pediatric Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives
Clinical Guidelines for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Schizophrenia
 Clinical Guidelines for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Community Behavioral Health (CBH) is committed to working with our provider partners to continuously improve the quality of behavioral healthcare
Clinical Guidelines for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Community Behavioral Health (CBH) is committed to working with our provider partners to continuously improve the quality of behavioral healthcare
ADHD SIV FASCI, MD FAAP DEVELOPMENTAL-BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS DELL CHILDREN S MEDICAL CENTER 9TH ANNUAL PEDIATRIC CONFERENCE - MARCH 24, 2016
 ADHD SIV FASCI, MD FAAP DEVELOPMENTAL-BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS DELL CHILDREN S MEDICAL CENTER 9TH ANNUAL PEDIATRIC CONFERENCE - MARCH 24, 2016 Objectives Epidemiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Co-morbidities
ADHD SIV FASCI, MD FAAP DEVELOPMENTAL-BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS DELL CHILDREN S MEDICAL CENTER 9TH ANNUAL PEDIATRIC CONFERENCE - MARCH 24, 2016 Objectives Epidemiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Co-morbidities
SCHIZOPHRENIA. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders
 Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues. ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland
 Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland Need for a New Treatment Paradigm in Schizophrenia Sixty years after approval for the
Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland Need for a New Treatment Paradigm in Schizophrenia Sixty years after approval for the
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psychosis and schizophrenia in children and young people: recognition and management 1.1 Short title Psychosis and schizophrenia
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psychosis and schizophrenia in children and young people: recognition and management 1.1 Short title Psychosis and schizophrenia
