, DISEASES oftl Nervous System
|
|
|
- Iris Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol. XXXI DECEMBER 1970 Number 12, DISEASES oftl Nervous System i A P R A C T IC A L J O U R N A L ON P S Y C H IA T R Y A N D N E U R O L O G Y! a.-'v The Mathematical Relationship of Drinking Water Lithium and Rainfall to Mental Hospital Admission \. E. B. D a w s o n, Ph.D., T. D. M o o r e, B.S., and W. J. M c G a n i t y, M.D. e: lung. Both, ironica'-y,.an 75% of lung cancers is excessive exposure to asily cured in their early i too often accompany it, new films, both available loking'. SEN SE IN T H E /films; their object is to e facts about cancer with erican cancer society Introduction ) Since 1949, lithium, in the form of lithium J carbonate, has been used with increasing fre-. quency as an effective sedative in the treat- ' rnent of both acute and chronic manic-depres- sive psychosis.1"3 The results of the clinical studies reported by Cade in 1949 led him to I suggest a specific role for lithium in the manj agement and prevention of psychogenic exi citement. He felt that this was consistent with the concept that lithium is an essential element for man. Along with others, however, he i celt that the nature and limited frequency of such illnesses precluded well controlled ) human studies. Even in a large mental hospi- \ tal, many years would be required to accumu- late sufficient data to prove statistically signi- ) ficant.1'4 j In 1968, Gershon reviewed the scattered 1 reports in the literature and added his own } studies which indicated beneficial effects of I lithium in schizophrenia, other associated behavior disorders and epilepsy as well as in 3 women with premenstrual tension and depres- \ sion syndrome.4 Kerry and Owen reported / lithium s effectiveness in stabilizing the fluctu- } e Ling volumes of total body water associated '' with the mood changes of the manic-depres- ( sive.3 Baer et al. demonstrated with isotope tracers that this is accomplished within the j Lssue cell by the displacement of sodium and. potassium which results in saluresis, kaluresis, i ~ x From the Department of Obstetrics and Gyne- cology and The Texas Nutrition Survey Team,! The University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston Texas. J Supported by Public Health Service Grant PH! and increase in urine volume.5 Foulks reported that ingested lithium is evenly distributed throughout the body and slowly accumulated intracellularly against a concentration gradient of sodium and potassium.6 Lithium has been found widely distributed in the drinking water of major cities in the United States.7 The metal is present in small, but measureable quantities. Blachly reported that inhabitants of cities with high drinking water lithium levels have a statistically significantly (P <.001) lower mortality from arteriosclerotic heart disease.8 However, the correlation between drinking water lithium levels and mental illness has not been reported previously. This study reports the levels of lithium in the drinking water of numerous Texas communities and the relationship between these levels and both the incidence and frequency of mental illness admissions. The data were gathered as a part of the 1968 National Nutritional Survey in Texas. W e have considered the possibility that other environmental features such as altitude, temperature, and/or rainfall may have an effect on the frequency of mental hospital admission and drinking water lithium concentration. These environmental factors have also been examined. M ethods and M aterials During the summer and fall of 1968, the Texas Nutrition Survey was undertaken in municipalities within 26 randomly selected counties in the State of Texas. As a part of the survey procedure, and for the purposes of this paper, multiple samplings (between 2 and'5) of the local tap water were measured for lithium content. Water samplings from
2 812 DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM DECEMBER Galveston were also included because of their availability, even though the city of Galveston was not in the survey protocol. Total lithium content was measured in each sample of tap water using a Perkin-Elmer Spectrophotometer, Model 303, equipped with a Perkin- Elmer Recorder Readout. The concentrations were expressed as fig/liter. State mental hospital admission data were obtained from the Texas Department of Mental Health and Mental Retardation. The data were in the form of annual reports summarizing the annual admission records to the State Mental Hospitals located at Houston, Harlingen, Austin, Big Spring, Kerrville, Rusk, San Antonio, Terrell, and Wichita Falls. To compare admission data over the same period of time that the municipal water samples were obtained during the nutrition survey, two years of mental health annual reports were used September 1, 1967 to August 31, These reports itemized all patients admitted to the nine mental hospitals according to their county of residence as well as by type of admission first, readmissions, and all admission levels. The all admission category was further sub-divided into major diagnostic categories: psychotic, neurotic, personality, alcoholic and drug abuse, mentally deficient, transient, etc. Only the diagnostic groups: psychotic (acute, chronic, unspecified), neurotic, and personality (specific symptoms, transferral behavior, etc.) occurred in sufficient numbers to warrant inclusion in this study. The absolute number of admissions and the three diagnostic categories were converted into rates of admission and diagnosis. Each absolute value was divided by the county population as calculated for the appropriate time period based on the I96011 and 1970 census.12 All rates were converted to a common population base rate per 100,000 of population. The lithium levels were clustered into four groups which would provide about equal distribution of the population of measured values at consistent increments. The four lithium groups were: <1L0, , , and >70.0 /^g/liter. The admission and diagnosis rates, elevation, median temperature, and average annual rainfall of the respective counties were examined within these four levels of lithium water content. Comparison of the group means did not reveal any mathematical relationship between either county elevation or median annual temperature and any of the other parameters. However, variations in mean rainfall fluctuated with changes in lithium water content, the admission rates, and diagnostic categories by county of residence. Consequently, all of these parameters were then regrouped on the basis of the county s mean annual rainfall at 5 inch intervals from <20 to >35 inches of annual rainfall. This grouping provided five distinct groups of lithium water content to be compared to three types of admissions and the three diagnostic categories. The Students t test was used to determine the statistical significance of the difference in mean values: (1) types of admission and diagnostic categories versus the low (11.0 ^g/liter) and high (>70.0 /xg/liter) lithium level and, (2) level of lithium water content, rates of admission, and diagnostic categories versus the lower ( <25 inches) and high (> inches) annual rainfall communities. The data from Lampasas county have been excluded from some of the computations and analyses for several reasons. Their municipal water supply was not the exclusive source of drinking water as many inhabitants obtained their water from private wells. The municipal water treatment facilities of Lampases were being enlarged and the water source altered during (The period covered in this study.) Results The concentration of lithium in 27 municipal drinking waters of Texas ranged from zero to 160 /xg/liter. Negligible variation was observed in the multiple measurements of any of the individual water samples. In Table 1 the 27 counties are listed that were involved in the study with the following identification characteristics: (1 ) principle municipalities contributing the water samples, (2) the river basin that provided the surface water for each of the communities5 water supply, (3) the elevation of each municipality, (4) the median annual temperature, as well as (5 ) the average annual rainfall, of each county. Thess
3 1070 DRINKING WATER LITHIUM 813 factors have been grouped according to their representative lithium levels. Since most of their drinking waters contained lower concentrations of lithium, the inclusive ranges of higher lithium level groups were expanded progressively to develop adequate groups of naar equal size. In this manner, there resulted [our major groups which provide interesting differences for comparative and correlative analyses. Water supply from the Trinity River Basin appeared only in the cluster of communities whose drinking waters contained less than 11.0 fig /liter of lithium. In contrast, the Rio Grande River Basin provided the drinking water source for four of the six communi TA8LE I: MUNICIPAL WATER LITHIUM LEVELS IN 27 TEXAS COMMUNITIES, RIVER BASINS/AND RESPECTIVE COUNTY ELEVATIONS, AVERAGE ANNUAL RAINFALL, AND MEDIAN TEMPERATURE,, River Annual Median County Municipality Basin Elevation* Rainfall* Temperature* Lithium Lithium: <11. 0 uq/llter D allas D allas Trinity 512 ' Tarrant Fort Worth Trinity *5 0 Wichita W ichita Falls Red ,0 0 Limestone Groesbeck Brazos McLennan W aco Brazos Travis Austin Colorado Anderson Palestine Trinity Hardin Silsbee Neches Newton Newton Sabine G alveston Galveston Coastal Guadalupe Seguin Guadalupe Uvalde Uvalde N ueces ' means: Lithium: uq/liter Ector Odessa Colorado Washington Brenham Brazos Harris Houston San Jacinto Bexar San Antonio Guadalupe Frio Pearsal Nueces means: Lithium: uq/liter H askell H askell Brazos Jones Anson Brazos N ueces Corpus Christi Nueces San Patricio Aransas Pass Nueces means: Lithium: < 70.0 uq/liter El Paso El Paso Rio Grande ' Lampa sas Lampasas Brazos Dimmit Carrlzo Springs N ueces Cameron Harlingen Rio Grande Duval San Diego Rio Grande ' Hidalgo W esla co Rio Grande means: * From the Texas Almanac, D allas, Texas, 1970 Ed0
4 814 DISEASES OP THE NERVOUS SYSTEM DECEMBER ties whose lithium contents were above 70 ^,g/liter. Variations in altitude and differences in median annual temperature did not vary significantly with the lithium levels. Only a few degrees Fahrenheit separated the highest lithium group s median temperature from that of the lowest group. At the extremes of median temperature the highest (69.9 F.) was associated with the greatest mean lithium level (122 /xg/liter), while the lowest median temperature (66.7 F.) was associated with the least mean lithium level (4 /xg/liter). The mean annual rainfall of the four groups varied inversely with the mean lithium levels (Table I). The grouping of municipal lithium levels according to annual rainfall at 5 inch increments is illustrated in Figure I. Only three of the communities studied had an annual rainfall of less than 20 inches. The mean lithium content of their drinking waters was 98 /xg/liter. With each additional 5 inches of rainfall per year, a progressive decrease in the mean lithium level was observed. Eight of the 27 municipalities had an annual rainfall in excess of 35 inches, with a mean lithium content of their water supply of 6 ^g/liter. Figure 2 shows the geographic zones of average annual rainfall across the state. The sites included in the Texas Nutrition Survey are dotted. Comparison of the measured lithium levels of the water supplies with the rainfall suggests an inverse relationship of lithium level with mean annual rainfall. High levels of rainfall and low water levels of lithium occurred predominately in the eastern section of the state. Progressively lower levels of rainfall and higher levels of lithium were found among the survey sites as one moved westward. The admission rates to state mental hospital by county of residence have been grouped according to water lithium level in Table II. Included are ( I ) rate of total admissions, regardless of diagnosis; (2 ) first admissions, as well as ( 3) readmissions for continuing treatment. The calculated population of each countv is included for reference. From these data, there was an inverse relationship between drinking water lithium level and each of the following: ( 1 ) the total admission rates (Figure 3 ); ( 2 ) mean of overall admission rate which declined from 37.0 to 16.3 per 100,000 (3 ) mean incidence of first admissions which dropped from 18.2 to 10.5 per 100,000 and (4 ) the mean rate of readmission which also dropped from 20.5 to 7.8 per 100,000. These changes were stepwise and proportional to the variations in drinking water levels of lithium. The rates of admission by diagnostic criteria have been examined within the same Fig. 1: Variation of Municipal Drinking Water Levels with Annual Rainfall (from the 1970 Texas Almanac, Dallas, Texas). \ 15 Fig. 2: Geographic distribution of the sites included in the Texas Nutrition Survey and the average annual rainfall. iahh TEXAS, AVERAGE ANNUAL RAINFALL in inches 15 ^ -
5 1970 DRINKING W ATER LITHIUM 815 increments in lithium levels as the overall admission rates, and are itemized in Table III. The means of all three diagnostic categories demonstrated identical progressive decreases as the water lithium levels increased. These increases occurred within individual categories as well as when the means of all categories were combined (Figure 3). The analyses of the t test for the significance of the occurrence of admission and the three diagnostic categories are given in Table IV. All mean differences examined in each of TABLE II: THE CALCULATED STATE MENTAL HOSPITAL ADMISSION RATES PER COUNTY OF RESIDENCE ARBITRARILY GROUPED ACCORDING TO MUNICIPAL WATER LITHIUM LEVELS, FROM SEPT. 1, 1967 TO SEPT. 1, Lithium Level/Countv Populations* Adm issions Per 100, 000 Population 1Thousands A ll First Secondanl <11.0 hg/1.: D allas 1, Tarrant W ichita Limestone McLennan Travis Anderson Hardin Newton G alveston Guadalupe Uvalde means: « u g /1. Ector W ashington Harris 1, Bexar Frio means: u g /1. H askell Jones N ueces San Patricio m eans: ug/l: El Paso Lam pasas* Dimmit Cameron Duval Hidalgo means: Calculated from 1960 and 1970 Census Reports,
6 816 / DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM DECEMBER the categories were statistically significant with a P value of <0.01 except for the difference in the incidence of first admissions versus the lithium water level which was at the <.05 P value. The group mean and range by admission occurrence and diagnostic category within the average annual rainfall appear in Table V and VI. The tendency of these parameters to vary inversely in proportion to the annual rainfall is illustrated by the bar graph in Figure 4. The incremental increase in the rates of admission occurrence and the diagnoses for psychosis, neurosis, and personality disorders is nearly linear and comparable to the alterations observed with increasing lithium levels TABLE III: STATE MENTAL HOSPITAL DIAGNOSTIC RATES PER 100, 000 FOR EACH COUNTY FROM SEPT. 1, 1967 TO SEPT. 1, 1969 ARBITRARILY GROUPED ACCORDING TO MUNICIPAL WATER LITHIUM LEVELS. County Psychosis (A) N eurosis (B) Personality (C) Combined (A+B+C) Lithium: <11.0 uq/liter D allas Tarrant 2, W ichita Limestone McLennan 7, Travis Anderson Hardin Newton G alveston Guadalupe Uvalde ' mean: Lithium: u q /liter Ector W ashington Harris Bexar Frio ' 9.4 mean: Lithium: u q /liter H askell Jones N ueces San Patricio mean: Lithium: 5^70.0 u q /liter El Paso Lampasas * Dimmit Cameron Duval Hidalgo mean: * Not Computed in Group M ean s.
7 1970 DRINKING WATER LITHIUM 817 (12) FROM SEPT. I, 1967 TO SEPT!, 1969 All M ental Adm issions (5) (4) C o u n tie s : (2 6 ) (5) < > J A dm ission > M u n ic ip a l L ith iu m Levels, j i g / L i t e r Fig. 3: Variations in the prevalence of psychotic, neurotic, and personality admission rates and all mental hospital admissions with drinking water lithium levels. Fig. 4: Variations in the prevalence of psychotic, neurotic, and personality admission rates and all mental hospital admissions with average annual rainfall. (Figure 3). The results of the statistical test for significance of the difference between the mean lithium water,levels and both admission and diagnostic rates below 25 inches and above 35 inches of rainfall are given in Table VII. The most significant difference was in the water lithium level (72.7 ± 20.1 versus 6.4 ± 2.1 /xg/liter, P<.Q1). This level of probability tends to confirm the relationship between rainfall and drinking water lithium levels reported above. The prevalence of psychosis, neurosis, and personality disorder diagnoses at higher rainfall levels was statistically significant, but with lower levels of probability. (P <.01 or <.05) The levels o f, probability of rates of all first and secondary admissions compared with the county s annual rainfall were not statistically significant. Discussion Approximately 36 percent of all hospital admissions for mental illness in Texas were to State Mental Hospitals. The remainder were hospitalized in private, municipal, and federal institutions. Each of these other institutions tends to serve different types of patient needs. The private institutions serve patients with sufficient funding to cover their own expenses; the municipal hospitals tend to admit mentally ill patients only briefly for diagnosis and then such patients will be transferred to another mental hospital. The federally operated hospitals usually serve and service committed patients, most of whom are male. In addition, there are numerous ambulatory patients, most of whom are male. In addition, there are numerous ambulatory patient clinics and private practice offices throughout the state which treat patients with mental illness not requiring hospitalization. Thus, it might be concluded that those patients included in this study are those who were sufficiently ill to require hospitalization, are medically indigent, and did not qualify for a federal hospital. We suspect that the proximity of the patient s residence to one of the nine state mental hospitals, as well as the bed availability in each of the state hospitals, also influenced admissions. Be that as it may, the combined capacity of all of the nine state
8 818 DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM DECEMBER mental hospitals is sufficient to insure that their patient load includes a broad cross section of many forms of serious mental illness, in all age groups and ethnic and cultural backgrounds. Of the 23 metropolitan areas in our state, the eleven largest were included in the Texas Nutrition Survey. These eleven plus the other fifteen counties of the study contained 65 percent of the total 1970 population of our state. The results indicate that naturally occurring lithium in drinking water exerts a positive influence on the incidence of initial and readmission rates of State Mental Hospitals, as well as the frequence of admissions in the diagnostic categories psychosis, neurosis, and personality problems. The municipal water lithium levels were very low (0-160 /xg/liter) as compared to the initial daily therapeutic dosage of approximately 5 gm. of TABLE IV: RESULTS OF STUDENTS " t " COMPARISON BETWEEN RATES OF ADMISSIONS AND DIAGNOSIS GROUPED BELOW 11.0 U G /L. AND ABOVE 70.0 U G /L. DRINKING WATER LITHIUM. Rates W ater Lithium P < 1 1 -s 70 N 12 5 Adm ission: All * 3.00 <.0 1 y First <. 05 y Secondary <.01 y D iagn osis: P sychosis <. 01 y N eurosis <.01 y Personality ± <.01 y * Mean + SEM, Rates per 100, 000 County Population, y S tatistically Significant. TABLE V: STATE MENTAL HOSPITAL ADMISSION RATES FROM SEPT. 1, 1967 TO SEPT. 1, 1969 GROUPED ACCORDING TO AVERAGE ANNUAL RAINFALL OF THE PATIENTS COUNTY OF RESIDENCE. Annual Rainfall Counties Adm ission Rates per 100, 000 Population* Inches N A ll! First Secondary < ( ) 9.9 ( ) 9.7 ( ) ( ) 13.9 ( ) 11.0 ( ) ( ) 14.3 ( ) 16.8 ( ) ( ) 14.8 ( ) 17.7 ( ) > ( ) 18.7 ( ) 15.9 ( ) * Mean (range).
9 1970 DRINKING W ATER LITHIUM 819 lithium carbonate (520 mg. lithium). If one assumes a total water intake of two liters per day per person, this would provide not more than 320 /xg of lithium per day. This would appear to be an insignificant quantity; however, any quantity of ingested lithium gradually cumulates in tissues,6 and this could eventually exert a pharmacodynamic effect. This accumulative action is demonstrated in clinical practice as the stabilizating dosage is designed to maintain the plasma level at meq./liter in order to avoid the toxic manifestations of lithium. The relationship between water lithium TABLE VI: STATE MENTAL HOSPITAL DIAGNOSTIC RATES FROM SEPT. 1, 1967 TO SEPT. 1, 1969 GROUPED ACCORDING TO AVERAGE ANNUAL RAINFALL OF THE PATIENTS' COUNTY OF RESIDENCE. Annual Ra in fa 11 Counties D iagnostic Rates per 100, 000 Population* Inches N (A) Psychotic (B) Neurotic (C) Personality (A+B+C) < ( ) 0.8 ( ) 3.1 ( ) 7.8 ( ) ( ) 0.9 ( ) 2.2 ( ) 8.0 ( ) ( ) 1.8 ( ) 5.2 ( ) 12.3 ( ) ( ) 2.3 ( ) 6.8 ( ) 15.6 ( ) /( ) 2.2 ( ) 5.9 ( ) 16,4 ( ) * Mean (range). TABLE VII; RESULTS OF STUDENTS " t " COMPARISON BETWEEN LITHIUM LEVELS AND ADMISSION DIAGNOSTIC RATES OF THE AVERAGE ANNUAL RAIN FALL GROUPS BELOW 25 INCHES AND ABOVE 35 INCHES. Rates Annual Rainfall " t P <25 ^35" N 9 8 Lithium * 3.25 <.o i x A dm issions: All Y <.10 First <.10 Secondary <.20 D iagn osis: P sych osis <.0 2 x N eurosis <.0 5 x Personality < 05 x * Mean + SEM, u g /L. y Mean + SEM, Rates per 100, 000 County Population, x Statistically Significant
10 820 DISEASE^ OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM DECEMBER and rainfall is obviously due to physical factors. Drinking water in the Texas communities originates primarily from rainfall.13 Only five of the drinking water samples from our study municipalities did not have measureable amounts of lithium present..whether the variation in water lithium level is a reflection of the regional soil content, the leaching out phenomena related to rainfall. amounts or some other environmental factor affecting the area can not be answered at this time. We do feel that the apparent relationship of annual rainfall to both the admission and diagnostic rates is not a primary effect. The higher level of statistical probability between lithium water levels and annual rainfall than between annual rainfall and the admission or diagnostic rates supports this hypothesis. While the relationship between therapeutic lithium and some forms of mental illness is well documented, to seriously suggest that falling rain influences the occurrence of mental illness in the populations extends the imagination beyond the stretch point. We have analyzed the drinking water samples for many other elements and have found a mathematical relationship between annual rainfall and the level of calcium, magnesium, sodium, and fluoride identical to the water lithium-rainfall correlation. These data will be reported in the near future. Approximately 95 percent of the ingested lithium used in therapy is excreted in the urine.4 Urinary lithium levels have been measured in the over 3000 subjects sampled in the 26 counties during the Texas Nutrition Survey. These levels are being compared to the incidence and prevalence of mental illness and the drinking water lithium levels and will be reported separately. Conclusion Lithium was found in measureable quantities in the drinking waters of 22 of 27 county seats throughout the state of Texas. The incidence of patient s first admissions and prevalence of readmission as well as the diagnosis of psychosis, neurosis, and personality disorder to state mental hospitals from each of the counties was inversely proportional to the lithium content of their residential drinking water. We suggest that the quantity of lithium in the local drinking water may be dependent upon either the soil content or the amount leached from the soil and then diluted,by the amount of rainfall in the region. There is a trend for lower lithium levels and greater prevalence of mental hospital admissions among residents in the eastern part of the state than in any other section of our state of Texas. This study neither confirms nor refutes Cade s theory that lithium is an essential element. However, supportive evidence is presented that naturally occurring lithium exerts a measureable and statistically significant influence on the incidence of patients admitted to our state s mental hospitals and on the certain diagnostic categories of mental illness. The authors gratefu lly acknow ledge the assistance o f Mr. M atthew A. N ations of the Texas W ater Q uality Control Board, H ouston, 'Texas. REFEREN CES 1. Cade, J. F. J.: Med. J. Aust. 2: , Wolpert, E. A. and Mueller, P.: Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 21:155, Kerry, R. J. and Owen, G.: Arch. Gen. P sychiat. 22: , Gershon, S.: Dis. Nerv. 8yst. 29:51-55, Baer, L. et a l: Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 22: , Foulks, J. et al: Am. J. Physiol. 168:642, DUrfor, C. N. and Becher, E.: U. S. Geological Survey Water Supplies Paper 1812, W ashington, D. C., U. 8. Gov. Printing Office, Blachly, P. H.: New Eng. J o f Med. 281:682, Texas Dept, of Mental Health and Mental Retardation: Patient Movement by County of Residency, Sept. 1, 1967-Aug. 31, 1968, Austin, Texas. 10. Texas Dept, of Mental Health and Mental Retardation: Patient Movement by County of Residency, Sept. 1, 1968-Aug. 31, 1969, Austin, Texas. 11. U. S. Bureau of the Census, U. S. Census of Population: 1960, Vol. 1, Characteristics of < the Population, Part A, Number of Inhabitants, Washington, D. C.: U. 8. Govt. Printing Office, U. S. Bureau of the Census, U. S. Census of Population: 1970, Washington, D. C., (pers onal communi cation ). 13. Lowry, R. D.: Surface Water Resources of Texas, Texas Electrical Service Company, Nov., 1958.
(TITLE 17: U S. Relationship of Lithium Metabolism to MentaBHfe ivl/ul jit' in this s. distribution across the state.
 546 A ugust Relationship of Lithium Metabolism to MentaBHfe ivl/ul jit' Hospital Admission and Homicide E. B. D a w s o n, Ph. D,., T. D. M o o r e, B.S., and W. J. M c G a n it y, M.D. Introduction Clinical
546 A ugust Relationship of Lithium Metabolism to MentaBHfe ivl/ul jit' Hospital Admission and Homicide E. B. D a w s o n, Ph. D,., T. D. M o o r e, B.S., and W. J. M c G a n it y, M.D. Introduction Clinical
Texas Department of Criminal Justice Community Justice Assistance Division FY Biennium Grant Funded Programs
 Community Angelina Mentally Impaired Offender Caseload $49,364 Residential Treatment Services Angelina Program $57,743 Angelina High/Medium Reduction Caseload $86,510 Angelina Regional Treatment Program
Community Angelina Mentally Impaired Offender Caseload $49,364 Residential Treatment Services Angelina Program $57,743 Angelina High/Medium Reduction Caseload $86,510 Angelina Regional Treatment Program
Grant scoring methodology:
 Grant scoring methodology: (6) publish on the division's Internet website for each grant awarded: (A) the amount awarded; (B) the method used in scoring the grant applications and the results of that scoring;
Grant scoring methodology: (6) publish on the division's Internet website for each grant awarded: (A) the amount awarded; (B) the method used in scoring the grant applications and the results of that scoring;
Lithium in Drinking Water and the Incidences of Crimes, Suicides, and Arrests Related to Drug Addictions
 Lithium in Drinking Water and the Incidences of Crimes, Suicides, and Arrests Related to Drug Addictions GERHARD N. SCHRAUZER *'~ AND KRISHNA P. SHRESTHA 2 IDepartment of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University
Lithium in Drinking Water and the Incidences of Crimes, Suicides, and Arrests Related to Drug Addictions GERHARD N. SCHRAUZER *'~ AND KRISHNA P. SHRESTHA 2 IDepartment of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University
8. Hypertension (high blood pressure)
 8. Hypertension (high blood pressure) Blood pressure is the force of blood pumped by the heart through the body s blood vessels. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is generally defined as an arterial
8. Hypertension (high blood pressure) Blood pressure is the force of blood pumped by the heart through the body s blood vessels. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is generally defined as an arterial
UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company PPBP (is the PPO)
 UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company PPBP (is the PPO) Texas County Acute Inpatient Hospital Pharmacies Health Care Providers (includes all other provider types) Anderson Met Met Met Andrews Met Met Not
UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company PPBP (is the PPO) Texas County Acute Inpatient Hospital Pharmacies Health Care Providers (includes all other provider types) Anderson Met Met Met Andrews Met Met Not
The ABC s of Ryan White Legislation
 The ABC s of Ryan White Legislation A Basic Overview Dr. Brent J. Pimentel, MD/MPH Texas Program Manager SCAETC Parkland Health & Hospital System Dallas, TX 1 Objective 1 Review the timeline of federal
The ABC s of Ryan White Legislation A Basic Overview Dr. Brent J. Pimentel, MD/MPH Texas Program Manager SCAETC Parkland Health & Hospital System Dallas, TX 1 Objective 1 Review the timeline of federal
Medicaid Dental Coverage Survey Analysis
 Medicaid Dental Coverage Survey Analysis An evaluation of survey responses whose children are eligible for Medicaid dental coverage Analysis By.. Kevin Robinson Graduate Research Assistant Kennesaw State
Medicaid Dental Coverage Survey Analysis An evaluation of survey responses whose children are eligible for Medicaid dental coverage Analysis By.. Kevin Robinson Graduate Research Assistant Kennesaw State
The Role of Opioid Overdoses in Confirmed Maternal Deaths,
 The Role of Opioid Overdoses in Confirmed Maternal Deaths, 2012-2015 Introduction The Department of State Health Services (DSHS) conducted an analysis of maternal deaths resulting from drug overdoses from
The Role of Opioid Overdoses in Confirmed Maternal Deaths, 2012-2015 Introduction The Department of State Health Services (DSHS) conducted an analysis of maternal deaths resulting from drug overdoses from
TB/HIV/STD Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch
 TB/HIV/STD Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch Texas HIV st Quarter The Texas HIV Quarterly Report is generated by: Texas Department of State Health Services TB/HIV/STD Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch,
TB/HIV/STD Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch Texas HIV st Quarter The Texas HIV Quarterly Report is generated by: Texas Department of State Health Services TB/HIV/STD Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch,
Suicide, a tragic and preventable cause of death, claimed the lives of 3,403 Texans in
 SUICIDE IN TEXAS A population health data brief from The University of Texas System Office of Health Affairs. June 2017. Suicide, a tragic and preventable cause of death, claimed the lives of 3,403 Texans
SUICIDE IN TEXAS A population health data brief from The University of Texas System Office of Health Affairs. June 2017. Suicide, a tragic and preventable cause of death, claimed the lives of 3,403 Texans
The ABC s of Ryan White Healthcare
 The ABC s of Ryan White Healthcare An Overview of the Ryan White CARE Act in Texas July 2016 Dr. Brent J. Pimentel, MD/MPH Texas Program Manager SCAETC 1 Objective 1 Review the history of federal funding
The ABC s of Ryan White Healthcare An Overview of the Ryan White CARE Act in Texas July 2016 Dr. Brent J. Pimentel, MD/MPH Texas Program Manager SCAETC 1 Objective 1 Review the history of federal funding
Outline. AIDS & HIV in the Travis County. Global estimates for adults & children end HIV incidence worldwide
 Outline AIDS & HIV in the Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/ Health & Human Services Department Worldwide HIV/AIDS surveillance National Prevalence Trends Disparities Mortality Modes of exposure Risk factors
Outline AIDS & HIV in the Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/ Health & Human Services Department Worldwide HIV/AIDS surveillance National Prevalence Trends Disparities Mortality Modes of exposure Risk factors
2-1-1 Texas United Way of Tarrant County. Serving: Erath, Hood, Johnson, Palo Pinto, Parker, Somervell, Tarrant and Wise Counties
 2-1-1 Texas United Way of Tarrant County Serving: Erath, Hood, Johnson, Palo Pinto, Parker, Somervell, Tarrant and Wise Counties What is 2-1-1? 2-1-1 is an easy to remember 3-digit telephone number nationally
2-1-1 Texas United Way of Tarrant County Serving: Erath, Hood, Johnson, Palo Pinto, Parker, Somervell, Tarrant and Wise Counties What is 2-1-1? 2-1-1 is an easy to remember 3-digit telephone number nationally
Emergency Department Visits for Behavioral Health Conditions in Harris County, Texas,
 Emergency Department Visits for Behavioral Health Conditions in Harris County, Texas, 2007-2008 Prepared by School of Public Health UT Health Patrick Courtney, MA August 2010 1 Table of Contents Executive
Emergency Department Visits for Behavioral Health Conditions in Harris County, Texas, 2007-2008 Prepared by School of Public Health UT Health Patrick Courtney, MA August 2010 1 Table of Contents Executive
LOCAL OPTION ELECTIONS
 LOCAL OPTION ELECTIONS were thirty-two local option elections held in 1950. Eleven were wide, nineteen were justice precinct elections, and two were city DS. 'oting in 1950. In the following tabulations
LOCAL OPTION ELECTIONS were thirty-two local option elections held in 1950. Eleven were wide, nineteen were justice precinct elections, and two were city DS. 'oting in 1950. In the following tabulations
Comprehensive Tobacco in Texas. Barry Sharp, MSHP, MACM, MCHES Manager Tobacco Prevention & Control Branch
 Comprehensive Tobacco in Texas Barry Sharp, MSHP, MACM, MCHES Manager Tobacco Prevention & Control Branch The Foundation CDC guidelines National goals for comprehensive tobacco programs Prevent initiation
Comprehensive Tobacco in Texas Barry Sharp, MSHP, MACM, MCHES Manager Tobacco Prevention & Control Branch The Foundation CDC guidelines National goals for comprehensive tobacco programs Prevent initiation
Summary. Mental health and urbanization
 Summary Mental health and urbanization An investigation of urban-rural and inner-city differences in psychiatric morbidity Introduction The primary focus of this thesis is the examination of the differences
Summary Mental health and urbanization An investigation of urban-rural and inner-city differences in psychiatric morbidity Introduction The primary focus of this thesis is the examination of the differences
Pediatric and Maternal HIV in Texas Border Counties and Urban Area
 Pediatric and Maternal HIV in Texas Border Counties and Urban Area Author: Jessie Ho, Faculty Mentor: Joseph Oppong, Department of Geography, College of Arts and Sciences; Toulouse School of Graduate Studies
Pediatric and Maternal HIV in Texas Border Counties and Urban Area Author: Jessie Ho, Faculty Mentor: Joseph Oppong, Department of Geography, College of Arts and Sciences; Toulouse School of Graduate Studies
Methamphetamine Use in Texas February 28, 2018 Page 1. Texas Substance Use Disorder Landscape Supplement: Methamphetamine Use
 Methamphetamine Use in Texas February 28, 2018 Page 1 Meadows Mental Health Policy Institute Texas Disorder Landscape Supplement: Methamphetamine Use The Drug Enforcement Administration s (DEA) Field Divisions
Methamphetamine Use in Texas February 28, 2018 Page 1 Meadows Mental Health Policy Institute Texas Disorder Landscape Supplement: Methamphetamine Use The Drug Enforcement Administration s (DEA) Field Divisions
TAHFA-South Texas HFMA Fall Symposium. Tuesday, October 17, from 10:45 AM 11:35 AM.
 1 TAHFA-South Texas HFMA Fall Symposium Tuesday, October 17, from 10:45 AM 11:35 AM. Dr. Anil T. Mangla, MS., PhD., MPH., FRSPH Director of Public Health and Associate Professor of Biomedical Science 2
1 TAHFA-South Texas HFMA Fall Symposium Tuesday, October 17, from 10:45 AM 11:35 AM. Dr. Anil T. Mangla, MS., PhD., MPH., FRSPH Director of Public Health and Associate Professor of Biomedical Science 2
TX CLPPP News. Who Gets Tested and When. Inside! How Are We Doing? Pages 2-5. Cover Story:
 Texas Department of State Health Services Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program TX CLPPP TX CLPPP News vol. 5, issue 1 February 2007 Scheduling Blood Lead Tests and Form Pb-110 Who Gets Tested and
Texas Department of State Health Services Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program TX CLPPP TX CLPPP News vol. 5, issue 1 February 2007 Scheduling Blood Lead Tests and Form Pb-110 Who Gets Tested and
Updates to the MODFLOW Groundwater Model of the San Antonio Segment of the Edwards Aquifer
 Updates to the MODFLOW Groundwater Model of the San Antonio Segment of the Edwards Aquifer Presented by Jim Winterle November 14, 2017 EAA Modeling Team: Angang Al Liu Ned Troshanov Andi Zhang Jim Winterle
Updates to the MODFLOW Groundwater Model of the San Antonio Segment of the Edwards Aquifer Presented by Jim Winterle November 14, 2017 EAA Modeling Team: Angang Al Liu Ned Troshanov Andi Zhang Jim Winterle
Lowering the Ozone Standard: Questionable Costs & Benefits. Michael Honeycutt, Ph.D. Toxicology Division Texas Commission on Environmental Quality
 Lowering the Ozone Standard: Questionable Costs & Benefits Michael Honeycutt, Ph.D. Toxicology Division Texas Commission on Environmental Quality 1 Ozone (O 3 ) O 3 is formed when nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Lowering the Ozone Standard: Questionable Costs & Benefits Michael Honeycutt, Ph.D. Toxicology Division Texas Commission on Environmental Quality 1 Ozone (O 3 ) O 3 is formed when nitrogen oxides (NOx)
TEXAS MANAGED CARE DIGEST SERIES TYPE 2 DIABETES REPORT. Texas Business Group on Health TBGH
 2010 Business Group on Health TBGH TEXAS TYPE 2 DIABETES REPORT SPECIAL FEATURE: MSA comparisons Featuring Demographic, Utilization, Pharmacotherapy and Charge Data Business Group on Health MANAGED CARE
2010 Business Group on Health TBGH TEXAS TYPE 2 DIABETES REPORT SPECIAL FEATURE: MSA comparisons Featuring Demographic, Utilization, Pharmacotherapy and Charge Data Business Group on Health MANAGED CARE
Research Article Spatial Analysis of County-Level Breast Cancer Mortality in Texas
 Environmental and Public Health Volume 212, Article ID 959343, 8 pages doi:1.1155/212/959343 Research Article Spatial Analysis of County-Level Breast Cancer Mortality in Texas Arvind B. Bambhroliya, 1
Environmental and Public Health Volume 212, Article ID 959343, 8 pages doi:1.1155/212/959343 Research Article Spatial Analysis of County-Level Breast Cancer Mortality in Texas Arvind B. Bambhroliya, 1
PEDIATRIC SUMMARY REPORT, 2014 EMS & TRAUMA REGISTRIES. Texas Department of State Health Services Injury Epidemiology & Surveillance Branch
 PEDIATRIC SUMMARY REPORT, 2014 EMS & TRAUMA REGISTRIES Texas Department of State Health Services Injury Epidemiology & Surveillance Branch 1 Heidi Bojes, PhD Director, Environmental Epidemiology and Disease
PEDIATRIC SUMMARY REPORT, 2014 EMS & TRAUMA REGISTRIES Texas Department of State Health Services Injury Epidemiology & Surveillance Branch 1 Heidi Bojes, PhD Director, Environmental Epidemiology and Disease
Blood Alcohol Concentration in Texas: Improving Medical Examiner and County Performance
 Blood Alcohol Concentration in Texas: Improving Medical Examiner and County Performance Prepared by Troy Walden. Ph.D Jena Prescott, MPSA Marcelina Perez, MS Paige Ericson-Graber, MIA Sarah Hammond, MS
Blood Alcohol Concentration in Texas: Improving Medical Examiner and County Performance Prepared by Troy Walden. Ph.D Jena Prescott, MPSA Marcelina Perez, MS Paige Ericson-Graber, MIA Sarah Hammond, MS
CERCIT Project 2: Assessing the Quality of Cancer Treatment in Texas. Sharon Giordano
 CERCIT Project 2: Assessing the Quality of Cancer Treatment in Texas Sharon Giordano October 21, 2011 Specific Aims Determine the agreement of the Texas Cancer Registry and claims databases for the rates
CERCIT Project 2: Assessing the Quality of Cancer Treatment in Texas Sharon Giordano October 21, 2011 Specific Aims Determine the agreement of the Texas Cancer Registry and claims databases for the rates
PEDIATRIC SUMMARY REPORT, 2014 EMS & TRAUMA REGISTRIES. Texas Department of State Health Services Injury Epidemiology & Surveillance Branch
 PEDIATRIC SUMMARY REPORT, 2014 EMS & TRAUMA REGISTRIES Texas Department of State Health Services Injury Epidemiology & Surveillance Branch 1 Heidi Bojes, PhD Director, Environmental Epidemiology and Disease
PEDIATRIC SUMMARY REPORT, 2014 EMS & TRAUMA REGISTRIES Texas Department of State Health Services Injury Epidemiology & Surveillance Branch 1 Heidi Bojes, PhD Director, Environmental Epidemiology and Disease
(Asterisk indicates counties wholly wet. all others dry in part)
 WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF DECEMBER 31. 1958 (Asterisk indicates counties wholly wet. all others dry in part) COUNTIES IN WHICH DISTILLED SPiRITS ARE LEGAL: 92 *Aransas *E1 Paso *Kenedy Refugio
WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF DECEMBER 31. 1958 (Asterisk indicates counties wholly wet. all others dry in part) COUNTIES IN WHICH DISTILLED SPiRITS ARE LEGAL: 92 *Aransas *E1 Paso *Kenedy Refugio
Identifying Geographic & Socioeconomic Disparities in Access to Care for Pediatric Cancer Patients in Texas
 Identifying Geographic & Socioeconomic Disparities in Access to Care for Pediatric Cancer Patients in Texas Mary T. Austin, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatric Surgery University of Texas Health Science
Identifying Geographic & Socioeconomic Disparities in Access to Care for Pediatric Cancer Patients in Texas Mary T. Austin, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatric Surgery University of Texas Health Science
SUICIDE IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY:
 SUICIDE IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY: 1998-2007 www.sdchip.org Contents www.sdchip.org SUICIDE IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY: 1998-2007 CHIP's Message Dear Reader, Community Health Improvement Partners (CHIP) is pleased
SUICIDE IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY: 1998-2007 www.sdchip.org Contents www.sdchip.org SUICIDE IN SAN DIEGO COUNTY: 1998-2007 CHIP's Message Dear Reader, Community Health Improvement Partners (CHIP) is pleased
Texas Second-Hand Smoking Municipal Ordinances Database Overview. 12 January 2017
 Texas Second-Hand Smoking Municipal Ordinances Database Overview 12 January 2017 Outline Overview of SHS Ordinances Database Update on website and database upgrade Coverage charts Second-Hand Smoking Ordinances
Texas Second-Hand Smoking Municipal Ordinances Database Overview 12 January 2017 Outline Overview of SHS Ordinances Database Update on website and database upgrade Coverage charts Second-Hand Smoking Ordinances
General Managers of Groundwater Management Area 12
 General Managers of Groundwater Management Area 12 Alan Day, GCD David Van Dresar, GCD Jim Totten, GCD David Bailey, GCD Gary Westbrook, GCD Confirmed Groundwater Conservation Districts * 1. Bandera River
General Managers of Groundwater Management Area 12 Alan Day, GCD David Van Dresar, GCD Jim Totten, GCD David Bailey, GCD Gary Westbrook, GCD Confirmed Groundwater Conservation Districts * 1. Bandera River
WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF AUGUST 31, Indicates sale of mixed beverages is legal in all or part of county (70)
 WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF AUGUST 31, 1975 +Indicates sale of mixed beverages is legal in all or part of county (70) *Indicates counties totally wet for distilled spirits (34); All others dry
WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF AUGUST 31, 1975 +Indicates sale of mixed beverages is legal in all or part of county (70) *Indicates counties totally wet for distilled spirits (34); All others dry
Assessing Vaccination Coverage in Texas. Service Data and Coordination Group November 2007
 Assessing Vaccination Coverage in Texas Service Data and Coordination Group November 2007 Current Population Based Surveys in Texas National Immunization Survey (NIS) Annual Report of Immunization Status
Assessing Vaccination Coverage in Texas Service Data and Coordination Group November 2007 Current Population Based Surveys in Texas National Immunization Survey (NIS) Annual Report of Immunization Status
Liman Summer Fellowship Final Report Vanessa Rodriguez PO Box San Antonio, TX
 Liman Summer Fellowship Final Report Vanessa Rodriguez PO Box 831731 San Antonio, TX 210-710-2781 I was a fellow with Texas Rio Grande Legal Aid (TRLA). I will be spending a year with the organization.
Liman Summer Fellowship Final Report Vanessa Rodriguez PO Box 831731 San Antonio, TX 210-710-2781 I was a fellow with Texas Rio Grande Legal Aid (TRLA). I will be spending a year with the organization.
Key Findings. Mortality Rates
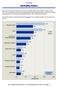 Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from to in nine of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease was in, where the mortality rate decreased
Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from to in nine of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease was in, where the mortality rate decreased
Texas Department of Agriculture Child Care Wellness Grants for Breastfeeding Supportive Child Care Practices
 Texas Department of Agriculture 2012-2013 Child Care Wellness Grants for Breastfeeding Supportive Child Care Practices Early Beginnings Learning Center Early, TX Project title: Developing Super-Heroes
Texas Department of Agriculture 2012-2013 Child Care Wellness Grants for Breastfeeding Supportive Child Care Practices Early Beginnings Learning Center Early, TX Project title: Developing Super-Heroes
suicide Tarrant County
 suicide Tarrant County 2001-2005 Suicide in Tarrant County 2001-2005 Tarrant County Public Health Lou K. Brewer, RN, MPH Director Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Public
suicide Tarrant County 2001-2005 Suicide in Tarrant County 2001-2005 Tarrant County Public Health Lou K. Brewer, RN, MPH Director Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Public
Central New York Care Collaborative, Inc. PPS Community Profile
 Central New York Care Collaborative, Inc. PPS Community Profile Counties served: Cayuga, Lewis, Madison, Oneida, Onondaga, and Oswego DEMOGRAPHICS 1 The total population of the Central New York Care Collaborative
Central New York Care Collaborative, Inc. PPS Community Profile Counties served: Cayuga, Lewis, Madison, Oneida, Onondaga, and Oswego DEMOGRAPHICS 1 The total population of the Central New York Care Collaborative
CHANGES IN TEXAS ORDINANCES IN 2018 AND COMPARISONS OF COVERAGE OF THE TEXAS MUNICIPAL POPULATION BY SMOKE-FREE ORDINANCES AS OF AUGUST 31, 2018
 CHANGES IN TEXAS ORDINANCES IN 2018 AND COMPARISONS OF COVERAGE OF THE TEXAS MUNICIPAL POPULATION BY SMOKE-FREE ORDINANCES AS OF AUGUST 31, 2018 Jessica Mantel, J.D. Leah Fowler, J.D. Phyllis Gingiss,
CHANGES IN TEXAS ORDINANCES IN 2018 AND COMPARISONS OF COVERAGE OF THE TEXAS MUNICIPAL POPULATION BY SMOKE-FREE ORDINANCES AS OF AUGUST 31, 2018 Jessica Mantel, J.D. Leah Fowler, J.D. Phyllis Gingiss,
This document is a key and guide for the interactive maps and tables found at arha.online/pcsaweb
 Policy Paper The status of the Alabama primary care physician workforce, 2018 Produced by the Office for Family Health Education & Research, UAB School of Medicine This document is a key and guide for
Policy Paper The status of the Alabama primary care physician workforce, 2018 Produced by the Office for Family Health Education & Research, UAB School of Medicine This document is a key and guide for
CHANGES IN TEXAS ORDINANCES IN 2016 AND COMPARISONS OF COVERAGE OF THE TEXAS MUNICIPAL POPULATION BY SMOKE-FREE ORDINANCES
 CHANGES IN TEXAS ORDINANCES IN 2016 AND COMPARISONS OF COVERAGE OF THE TEXAS MUNICIPAL POPULATION BY SMOKE-FREE ORDINANCES Allison N. Winnike, J.D. Phyllis Gingiss, Dr.P.H. Melynda Boerm, M.Ed. Submitted
CHANGES IN TEXAS ORDINANCES IN 2016 AND COMPARISONS OF COVERAGE OF THE TEXAS MUNICIPAL POPULATION BY SMOKE-FREE ORDINANCES Allison N. Winnike, J.D. Phyllis Gingiss, Dr.P.H. Melynda Boerm, M.Ed. Submitted
HYDROGEOLOGIC DATA. REPORT FOR 2002
 EDWARDS AQUIFER AUTHORITY HYDROGEOLOGIC DATA. REPORT FOR 2002 EDWARDS AQUIFER AU T HORI T Y REPORT 03-02 EDWARDS AQUIFER AUTHORITY HYDROGEOLOGIC DATA REPORT FOR 2002 Compiled by: J. Mark Hamilton, Senior
EDWARDS AQUIFER AUTHORITY HYDROGEOLOGIC DATA. REPORT FOR 2002 EDWARDS AQUIFER AU T HORI T Y REPORT 03-02 EDWARDS AQUIFER AUTHORITY HYDROGEOLOGIC DATA REPORT FOR 2002 Compiled by: J. Mark Hamilton, Senior
Victims of Assault. National Sexual Assault Hotline (800) 656-HOPE (4673)
 Victims of Assault National Sexual Assault Hotline (800) 656-HOPE (4673) The National Domestic Violence Hotline: 800-799-SAFE (7233) 800-787-3224 (TTY) 800-942-6908 (Spanish) This 24/7 hotline provides
Victims of Assault National Sexual Assault Hotline (800) 656-HOPE (4673) The National Domestic Violence Hotline: 800-799-SAFE (7233) 800-787-3224 (TTY) 800-942-6908 (Spanish) This 24/7 hotline provides
PlaceCodes2015.xls. Effective Date. Place. Zip Code Tdi No. Zone Terr. New X ACKERLY OPA BORDEN
 Effective Date New Place Code Community County Zip Code Tdi No. Zone Terr 20150301 X 03302 ACKERLY OPA BORDEN 79713 6 18 20150301 X 11602 ACKERLY OPA DAWSON 79713 6 18 20150301 X 22703 ACKERLY OPA HOWARD
Effective Date New Place Code Community County Zip Code Tdi No. Zone Terr 20150301 X 03302 ACKERLY OPA BORDEN 79713 6 18 20150301 X 11602 ACKERLY OPA DAWSON 79713 6 18 20150301 X 22703 ACKERLY OPA HOWARD
UPPER MIDWEST MARKETING AREA ANALYSIS OF COMPONENT LEVELS AND SOMATIC CELL COUNT IN INDIVIDUAL HERD MILK AT THE FARM LEVEL 2002
 UPPER MIDWEST MARKETING AREA ANALYSIS OF COMPONENT LEVELS AND SOMATIC CELL COUNT IN INDIVIDUAL HERD MILK AT THE FARM LEVEL 2002 Staff Paper 03-01 Prepared by: Henry H. Schaefer December 2003 Federal Milk
UPPER MIDWEST MARKETING AREA ANALYSIS OF COMPONENT LEVELS AND SOMATIC CELL COUNT IN INDIVIDUAL HERD MILK AT THE FARM LEVEL 2002 Staff Paper 03-01 Prepared by: Henry H. Schaefer December 2003 Federal Milk
Public Health Issues Related to Lead
 Public Health Issues Related to Lead Presentation to the Board of Directors, DC Water and Sewer Authority 6 May 2004 Tee L. Guidotti, MD, MPH Dept. EOH, SPHHS George Washington University Medical Center
Public Health Issues Related to Lead Presentation to the Board of Directors, DC Water and Sewer Authority 6 May 2004 Tee L. Guidotti, MD, MPH Dept. EOH, SPHHS George Washington University Medical Center
TX CLPPP News. Important Survey Inside. Increasing Blood Lead Screening & Testing Rates in Texas Children
 Texas Department of State Heatlh Services Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program TX CLPPP News vol. 6, issue 2 Summer 2008 Increasing Blood Lead Screening & Testing Rates in Texas Children Over the
Texas Department of State Heatlh Services Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program TX CLPPP News vol. 6, issue 2 Summer 2008 Increasing Blood Lead Screening & Testing Rates in Texas Children Over the
SBIRT IOWA. Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION. Iowa Army National Guard
 SBIRT IOWA Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report April 2017 With Funds Provided By: Iowa Department of Public
SBIRT IOWA Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report April 2017 With Funds Provided By: Iowa Department of Public
Dental fluorosis trends in United States oral health surveys:
 Online Supplement, Appendixes for: Dental fluorosis trends in United States oral health surveys: 1986 2012 C. Neurath, H. Limeback, B. Osmunson, M. Connett, V. Kanter, C. Wells Appendix 1. Data tables.
Online Supplement, Appendixes for: Dental fluorosis trends in United States oral health surveys: 1986 2012 C. Neurath, H. Limeback, B. Osmunson, M. Connett, V. Kanter, C. Wells Appendix 1. Data tables.
Local Variations in Arrests of Psychiatric Patients
 Local Variations in Arrests of Psychiatric Patients JOSEPH D. BLOOM, MD* JAM E S H. S H 0 R E, M D ** and BET T Y A R V IDS 0 N, PHD *** The involvement of psychiatric patients in the criminal justice
Local Variations in Arrests of Psychiatric Patients JOSEPH D. BLOOM, MD* JAM E S H. S H 0 R E, M D ** and BET T Y A R V IDS 0 N, PHD *** The involvement of psychiatric patients in the criminal justice
2016 Houston HIV Care Services Needs Assessment: Profile of the Recently Released
 2016 Houston HIV Care Services Needs Assessment: Profile of the Recently Released Page 1 PROFILE OF THE RECENTLY RELEASED The Texas Department of Criminal Justice (TDCJ) estimates that 386 people living
2016 Houston HIV Care Services Needs Assessment: Profile of the Recently Released Page 1 PROFILE OF THE RECENTLY RELEASED The Texas Department of Criminal Justice (TDCJ) estimates that 386 people living
Chapter Two Incidence & prevalence
 Chapter Two Incidence & prevalence Science is the observation of things possible, whether present or past. Prescience is the knowledge of things which may come to pass, though but slowly. LEONARDO da Vinci
Chapter Two Incidence & prevalence Science is the observation of things possible, whether present or past. Prescience is the knowledge of things which may come to pass, though but slowly. LEONARDO da Vinci
2025 Beverage Calories Initiative:
 2025 Beverage Calories Initiative: Report on 2017 Progress toward the Community Calorie Goal PREPARED FOR: American Beverage Association Alliance for a Healthier Generation PREPARED BY: Keybridge November
2025 Beverage Calories Initiative: Report on 2017 Progress toward the Community Calorie Goal PREPARED FOR: American Beverage Association Alliance for a Healthier Generation PREPARED BY: Keybridge November
Texas Council Endorsed Measurement Strategy
 Texas Council Endorsed Measurement Strategy During 2013, the Data Work Group of the Texas Council of Community Centers met to identify a set of clinical quality measures that can be used across the entire
Texas Council Endorsed Measurement Strategy During 2013, the Data Work Group of the Texas Council of Community Centers met to identify a set of clinical quality measures that can be used across the entire
GEOGRAPHY OF HIV INFECTION AMONG ADULTS AGED 50 YEARS AND OLDER IN TEXAS FROM Mara Nicole Hedrich, B.A. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of
 GEOGRAPHY OF HIV INFECTION AMONG ADULTS AGED 50 YEARS AND OLDER IN TEXAS FROM 1999-2009 Mara Nicole Hedrich, B.A. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS August 2012
GEOGRAPHY OF HIV INFECTION AMONG ADULTS AGED 50 YEARS AND OLDER IN TEXAS FROM 1999-2009 Mara Nicole Hedrich, B.A. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS August 2012
John F. DeRosier. District Attorney Calcasieu Parish, Lake Charles Louisiana
 John F. DeRosier District Attorney Calcasieu Parish, Lake Charles Louisiana THE LOUISIANA EXPERIENCE CALCASIEU PARISH Calcasieu Parish Geographical Information ---144 miles east of Houston, Texas ---
John F. DeRosier District Attorney Calcasieu Parish, Lake Charles Louisiana THE LOUISIANA EXPERIENCE CALCASIEU PARISH Calcasieu Parish Geographical Information ---144 miles east of Houston, Texas ---
CHILDHOOD LEAD POISONING
 CHILDHOOD LEAD POISONING Lead is a toxic substance and lead poisoning in children under six years of age is associated with reduced learning ability and poor school performance in later years, and other
CHILDHOOD LEAD POISONING Lead is a toxic substance and lead poisoning in children under six years of age is associated with reduced learning ability and poor school performance in later years, and other
Comparison of Sodium and Potassium Intake with Excretion JOSEPH SCHACHTER, M.D., PH.D., PATRICIA H. HARPER, R.D., MARY E. RADIN, M.A.
 Comparison of Sodium and Potassium Intake with Excretion JOSEPH SCHACHTER, M.D., PH.D., PATRICIA H. HARPER, R.D., MARY E. RADIN, M.A., ARLENE W. CAGGIULA, PH.D., ROBERT H. MCDONALD, M.D., AND WARREN F.
Comparison of Sodium and Potassium Intake with Excretion JOSEPH SCHACHTER, M.D., PH.D., PATRICIA H. HARPER, R.D., MARY E. RADIN, M.A., ARLENE W. CAGGIULA, PH.D., ROBERT H. MCDONALD, M.D., AND WARREN F.
Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report April 2016
 SBIRT IOWA Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report April 2016 With Funds Provided By: Iowa Department of Public
SBIRT IOWA Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report April 2016 With Funds Provided By: Iowa Department of Public
2016 Results, 2017 Strategy The University of Texas System
 N AT U R A L LY S L I M 2016 Results, 2017 Strategy The University of Texas System 1 / 1 8 / 2 0 1 7 Agenda 2016 Outcomes & Six Month Data 2017 Enhancements & Strategy Q&A Feedback Session 2016 Rollout
N AT U R A L LY S L I M 2016 Results, 2017 Strategy The University of Texas System 1 / 1 8 / 2 0 1 7 Agenda 2016 Outcomes & Six Month Data 2017 Enhancements & Strategy Q&A Feedback Session 2016 Rollout
2017 REPORT ON PROGRAM MERIT AND PROGRESS PURSUANT TO TEXAS HEALTH & SAFETY CODE (C)
 MEMORANDUM To: OVERSIGHT COMMITTEE MEMBERS From: WAYNE ROBERTS, CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER Subject: FY 2017 REPORT ON PROGRAM MERIT AND PROGRESS PURSUANT TO TEXAS HEALTH & SAFETY CODE 102.260(C) Date: FEBRUARY
MEMORANDUM To: OVERSIGHT COMMITTEE MEMBERS From: WAYNE ROBERTS, CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER Subject: FY 2017 REPORT ON PROGRAM MERIT AND PROGRESS PURSUANT TO TEXAS HEALTH & SAFETY CODE 102.260(C) Date: FEBRUARY
MENTAL ILLNESS AND SOCIAL CLASS IN BRISTOL
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1955), 9, 191-195 MENTAL ILLNESS AND SOCIAL CLASS IN BRISTOL During the past 40 years a number of studies have supported the general hypothesis that the incidence of mental illness
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1955), 9, 191-195 MENTAL ILLNESS AND SOCIAL CLASS IN BRISTOL During the past 40 years a number of studies have supported the general hypothesis that the incidence of mental illness
Arizona Behavioral Health Epidemiology Profile
 Arizona Behavioral Health Epidemiology Profile July 2012 Prepared by The Arizona Criminal Justice Commission, on behalf of: The Substance Abuse Epidemiology Work Group The Governor s Office for Children,
Arizona Behavioral Health Epidemiology Profile July 2012 Prepared by The Arizona Criminal Justice Commission, on behalf of: The Substance Abuse Epidemiology Work Group The Governor s Office for Children,
TEXAS REAL ESTATE ECONOMIC DATA 2011
 TEXAS REAL ESTATE ECONOMIC DATA 2011 Jim McAlister Sr. & Hydie H. McAlister 2211 Norfolk St., Suite 803 Houston, TX 77098 (713) 535-2276 or (713) 535-2260 www.mgcfunds.com Why Focus on Single Family Housing
TEXAS REAL ESTATE ECONOMIC DATA 2011 Jim McAlister Sr. & Hydie H. McAlister 2211 Norfolk St., Suite 803 Houston, TX 77098 (713) 535-2276 or (713) 535-2260 www.mgcfunds.com Why Focus on Single Family Housing
Environmental Health Issues
 Environmental Health Issues Broad ranges of different environmental exposures can cause health problems, including air and water pollution, lead and other heavy metals, chemicals and pesticides, and many
Environmental Health Issues Broad ranges of different environmental exposures can cause health problems, including air and water pollution, lead and other heavy metals, chemicals and pesticides, and many
Blood Alcohol Concentration in Texas: Improving Medical Examiner and County Performance
 Blood Alcohol Concentration in Texas: Improving Medical Examiner and County Performance Prepared by Jena Prescott, MPSA Amber Trueblood, DrPH, MPH Marcelina Perez, MS David Hodges, JD Robert Gilbert Troy
Blood Alcohol Concentration in Texas: Improving Medical Examiner and County Performance Prepared by Jena Prescott, MPSA Amber Trueblood, DrPH, MPH Marcelina Perez, MS David Hodges, JD Robert Gilbert Troy
Laws and Incentives for RWH in Texas (and in other states) Dr. Hari J. Krishna Austin, Texas
 Laws and Incentives for RWH in Texas (and in other states) Dr. Hari J. Krishna Austin, Texas Laws, regulations and incentives Laws and regulations need not be restrictive or difficult. Appropriate laws
Laws and Incentives for RWH in Texas (and in other states) Dr. Hari J. Krishna Austin, Texas Laws, regulations and incentives Laws and regulations need not be restrictive or difficult. Appropriate laws
Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report CDC Week 43: Oct 22-28, 2017
 Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 43: Oct 22-28, 2017 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 43: Oct 22-28, 2017 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report CDC Week 51: Dec 17-23, 2017
 Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 51: Dec 17-23, 2017 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 51: Dec 17-23, 2017 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION
 TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION STATEWIDE TRANSPORTATION IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM STIP 2015-2018 STATEWIDE FINANCIALS 2015-2018 TIP HIGHWAY Initial 2015-2018 STIP FY 2015-2018 Statewide Transportation Program
TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION STATEWIDE TRANSPORTATION IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM STIP 2015-2018 STATEWIDE FINANCIALS 2015-2018 TIP HIGHWAY Initial 2015-2018 STIP FY 2015-2018 Statewide Transportation Program
Comprehensive HIV Health Services Plan
 PanWest-West Texas Ryan White Programs Comprehensive HIV Health Services Plan 2010-2013 Executive Summary EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This Comprehensive HIV Services Plan is the first joint plan between the PanWest
PanWest-West Texas Ryan White Programs Comprehensive HIV Health Services Plan 2010-2013 Executive Summary EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This Comprehensive HIV Services Plan is the first joint plan between the PanWest
Office Practice Coding Assistance - Overview
 Office Practice Coding Assistance - Overview Three office coding assistance resources are provided in the STABLE Resource Toolkit. Depression & Bipolar Coding Reference: n Provides ICD9CM and DSM-IV-TR
Office Practice Coding Assistance - Overview Three office coding assistance resources are provided in the STABLE Resource Toolkit. Depression & Bipolar Coding Reference: n Provides ICD9CM and DSM-IV-TR
Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report CDC Week 4: Jan 21-27, 2018
 Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 4: Jan 21-27, 2018 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 4: Jan 21-27, 2018 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report CDC Week 11: Mar 10-16, 2019
 Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 11: Mar 10-16, 2019 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 11: Mar 10-16, 2019 Influenza Activity Code: County and State Levels Tarrant
Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in Texas: A Work in Progress
 Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in Texas: A Work in Progress Elaine Braslow, M.Ed. ESRD Prevention Program Coordinator Texas Department of State Health Services Austin, Texas 2009 Texas ESRD Prevention
Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in Texas: A Work in Progress Elaine Braslow, M.Ed. ESRD Prevention Program Coordinator Texas Department of State Health Services Austin, Texas 2009 Texas ESRD Prevention
Mental Health Statistics, to
 , 1982-83 to 1993-94 Jean Randhawa and Rod Riley* Since the early 1980s, in relation to the size of the population, general and psychiatric hospitals have seen a drop in separations for mental disorders.
, 1982-83 to 1993-94 Jean Randhawa and Rod Riley* Since the early 1980s, in relation to the size of the population, general and psychiatric hospitals have seen a drop in separations for mental disorders.
Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications
 MWSUG 2017 - Paper DG02 Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications ABSTRACT Deanna Naomi Schreiber-Gregory, Henry M Jackson
MWSUG 2017 - Paper DG02 Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications ABSTRACT Deanna Naomi Schreiber-Gregory, Henry M Jackson
HIV as a Risk Factor for TB Henry Pacheco, MD November 13, 2008
 Tuberculosis Updates for Clinicians San Antonio, Texas November 13, 2008 HIV as a Risk Factor for TB Henry Pacheco, MD November 13, 2008 HIV as a Risk Factor for TB Tuberculosis Update for the Clinician
Tuberculosis Updates for Clinicians San Antonio, Texas November 13, 2008 HIV as a Risk Factor for TB Henry Pacheco, MD November 13, 2008 HIV as a Risk Factor for TB Tuberculosis Update for the Clinician
The average potassium content during the last 5. solids. This average decrease of 2.2 meq. per 100. initial potassium content of the arteries.
 THE EFFECT OF NOR-EPINEPHRINE ON THE ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION OF ARTERIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE' By LOUIS TOBIAN 2 AND ADACIE FOX (From the Departments of Pharmacology and Internal Medicine, Southwesters Medical
THE EFFECT OF NOR-EPINEPHRINE ON THE ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION OF ARTERIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE' By LOUIS TOBIAN 2 AND ADACIE FOX (From the Departments of Pharmacology and Internal Medicine, Southwesters Medical
WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF DECEMBER 31, 1965 COUNTIES IN WIDCR DISTILLED SPIRITS ARE LEGAL: 121
 WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF DECEMBER 31, 1965 (Asterisk indicates counties wholly wet, all others dry in part) COUNTIES IN WIDCR DISTILLED SPIRITS ARE LEGAL: 121 Anderson Eastland Jim Wells
WET-DRY STATUS OF TEXAS COUNTIES AS OF DECEMBER 31, 1965 (Asterisk indicates counties wholly wet, all others dry in part) COUNTIES IN WIDCR DISTILLED SPIRITS ARE LEGAL: 121 Anderson Eastland Jim Wells
Mental health as a reason for claiming incapacity benefit a comparison of national and local trends
 Journal of Public Health Vol. 31, No. 1, pp. 74 80 doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdn098 Advance Access Publication 30 October 2008 Mental health as a reason for claiming incapacity benefit a comparison of national
Journal of Public Health Vol. 31, No. 1, pp. 74 80 doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdn098 Advance Access Publication 30 October 2008 Mental health as a reason for claiming incapacity benefit a comparison of national
Michelle L. Gutierrez, PT, DSc CURRICULUM VITAE
 Michelle L. Gutierrez, PT, DSc CURRICULUM VITAE January 2016 BUSINESS ADDRESS: The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) College of Health Sciences Doctor of Physical Therapy Program 1101 N Campbell (physical
Michelle L. Gutierrez, PT, DSc CURRICULUM VITAE January 2016 BUSINESS ADDRESS: The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) College of Health Sciences Doctor of Physical Therapy Program 1101 N Campbell (physical
Pre-Conception & Pregnancy in Ohio
 Pre-Conception & Pregnancy in Ohio Elizabeth Conrey, PhD 1 January 217 1 State Maternal and Child Health Epidemiologist, Ohio Department of Health EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The primary objective of the analyses
Pre-Conception & Pregnancy in Ohio Elizabeth Conrey, PhD 1 January 217 1 State Maternal and Child Health Epidemiologist, Ohio Department of Health EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The primary objective of the analyses
County of San Diego, Health and Human Services Agency IN HOME OUTREACH TEAM PROGRAM REPORT (IHOT)
 County of San Diego, Health and Human Services Agency IN HOME OUTREACH TEAM PROGRAM REPORT (IHOT) Annual Report January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2012 County of San Diego, Health and Human Services Agency
County of San Diego, Health and Human Services Agency IN HOME OUTREACH TEAM PROGRAM REPORT (IHOT) Annual Report January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2012 County of San Diego, Health and Human Services Agency
Going with the Flow Update. An update and comparative analysis of five years of Water Sentinels flow data collection of the Upper Verde River
 Going with the Flow Update An update and comparative analysis of five years of Water Sentinels flow data collection of the Upper Verde River Rachel Shultis Intern for Science-Practice Integration Grand
Going with the Flow Update An update and comparative analysis of five years of Water Sentinels flow data collection of the Upper Verde River Rachel Shultis Intern for Science-Practice Integration Grand
(PERIOD ) STOMACH IN THE NETHERLANDS
 265 THE GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF CANCER OF THE STOMACH IN THE NETHERLANDS (PERIOD 1946-1952) S. W. TROMP From Hofbrouckerlaan 54, Oegstgeest (Leiden), Holland Received for publication February 23,
265 THE GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF CANCER OF THE STOMACH IN THE NETHERLANDS (PERIOD 1946-1952) S. W. TROMP From Hofbrouckerlaan 54, Oegstgeest (Leiden), Holland Received for publication February 23,
Contact Investigation San Antonio, Texas January 14-15, 2013
 Contact Investigation San Antonio, Texas January 14-15, 2013 Detecting and Handling a TB Outbreak Jessica Quintero, BAAS January 15, 2013 Jessica Quintero, BAAS has the following disclosures to make: No
Contact Investigation San Antonio, Texas January 14-15, 2013 Detecting and Handling a TB Outbreak Jessica Quintero, BAAS January 15, 2013 Jessica Quintero, BAAS has the following disclosures to make: No
Cost of Mental Health Care
 Section 4 Cost of Mental Health Care Per capita mental health spending for Americans with a mental health diagnosis has increased among children, peaking in. For adults, the spending has been more stable.
Section 4 Cost of Mental Health Care Per capita mental health spending for Americans with a mental health diagnosis has increased among children, peaking in. For adults, the spending has been more stable.
SBIRT IOWA. Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION. Iowa Army National Guard
 SBIRT IOWA Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report October 2016 With Funds Provided By: Iowa Department of Public
SBIRT IOWA Iowa Army National Guard THE IOWA CONSORTIUM FOR SUBSTANCE ABUSE RESEARCH AND EVALUATION Iowa Army National Guard Biannual Report October 2016 With Funds Provided By: Iowa Department of Public
RURAL VOLUNTEER FIRE DEPARTMENT ASSISTANCE PROGRAM FUNDING SUMMARY-- MEETING 2 November 17, 2011
 RURAL VOLUNTEER FIRE DEPARTMENT ASSISTANCE PROGRAM FUNDING SUMMARY-- MEETING 2 November 17, 2011 The 77 th Texas Legislature passed House Bill 2604 in 2001, establishing the Rural Volunteer Fire Department
RURAL VOLUNTEER FIRE DEPARTMENT ASSISTANCE PROGRAM FUNDING SUMMARY-- MEETING 2 November 17, 2011 The 77 th Texas Legislature passed House Bill 2604 in 2001, establishing the Rural Volunteer Fire Department
Li-based Drugs. Li I : 1) very small (ionic radius 0.60 Å), and mobile (rapid ligand exchange residence time of coordinated water ca.
 Li-based Drugs Li chemistry is perceived as simple and relatively uninteresting except for its organometallic compounds The fascination of Li, however, is that it is the lightest and smallest solid element,,
Li-based Drugs Li chemistry is perceived as simple and relatively uninteresting except for its organometallic compounds The fascination of Li, however, is that it is the lightest and smallest solid element,,
AP Human Geography Kuby: Tracking the AIDS Epidemic. Mapping the Diffusion of AIDS
 AP Human Geography Kuby: Tracking the AIDS Epidemic NAME: HOUR: Mapping the Diffusion of AIDS DIRECTIONS: Click on the website listed below. Under Computerized Chapter Activities please select http://bcs.wiley.com/he-bcs/books?action=resource&bcsid=5267&itemid=0470484799&resourceid=18408
AP Human Geography Kuby: Tracking the AIDS Epidemic NAME: HOUR: Mapping the Diffusion of AIDS DIRECTIONS: Click on the website listed below. Under Computerized Chapter Activities please select http://bcs.wiley.com/he-bcs/books?action=resource&bcsid=5267&itemid=0470484799&resourceid=18408
Health Promotion, Public Education, and Outreach Programs Slate: $1,771,993 March 10, 2010
 Health Promotion, Public Education, and Outreach s Slate: $1,771,993 Mechanism Description: For organizations located in the State of Texas that propose education using culturally competent and evidence-based
Health Promotion, Public Education, and Outreach s Slate: $1,771,993 Mechanism Description: For organizations located in the State of Texas that propose education using culturally competent and evidence-based
Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report CDC Week 35, August 27-September 2, 2017
 Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 35, August 27-September 2, 2017 Influenza Activity Code, County and State
Tarrant County Public Health Division of Epidemiology and Health Information Tarrant County Influenza Surveillance Weekly Report 35, August 27-September 2, 2017 Influenza Activity Code, County and State
Dissolved Lithium Concentrations, Gender, Race, and the Geography of Texas Suicide Mortality Rates : A Correlation Study
 Dissolved Lithium Concentrations and Suicide Rates 1 Dissolved Lithium Concentrations, Gender, Race, and the Geography of Texas Suicide Mortality Rates 1980 1998: A Correlation Study Author: William M.
Dissolved Lithium Concentrations and Suicide Rates 1 Dissolved Lithium Concentrations, Gender, Race, and the Geography of Texas Suicide Mortality Rates 1980 1998: A Correlation Study Author: William M.
