Case Report Cytological diagnosis of patients with extramammary Paget s disease of the vagina
|
|
|
- Rosamond O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7): /ISSN: /IJCEP Case Report Cytological diagnosis of patients with extramammary Paget s disease of the vagina Qijun Chen 1, Yan Qiu 2, Lian Xu 1, Xiao Tang 1, Kaixuan Yang 1, Wei Wang 1 1 Department of Pathology, Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children, Ministry of Education, West China Second Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China; 2 Department of Pathology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China Received May 2, 2018; Accepted May 28, 2018; Epub July 1, 2018; Published July 15, 2018 Abstract: Extramammary Paget s Disease (EMPD), also called extramammary eczematoid carcinoma, is classified as primary and secondary EMPD based on the pathogenic mechanism. The origin of the Paget cells of primary EMPD is still controversial. Apocrine or eccrine gland cells, such as Bartholin s gland, and intraepidermal pluripotent keratinocyte stem cells have been considered possible originating cells of primary EMPD. Secondary EMPD usually originates from the malignancies of rectum, cervix, and urinary bladder. We report a case of a 58-year-old woman suffering from intermittent vaginal bleeding for half a year, who was diagnosed as EMPD by vaginal cytology. Keywords: Vagina, extramammary Paget s disease EMPD is a rare intraepithelial adenocarcinoma, which accounts less than 2% of all vulvar maliganancies [1]. The majority of EMPD are observed in apocrine glands, including scrotum, penis, labia majora, labia minora, and vagina. Rarely, EMPD may also be found in perianal skin, perineum, axilla, etc. Also, Paget cells of perineum EMPD may infiltrate into peripheral organs, such as cervix, rectum, scrotum, or urinary tract [2]. Case report A-58-year-old postmenopausal woman complained of intermittent vaginal bleeding and a foreign body sensation for half a year with a history of progression for 2 months. She underwent lesionectomy 2 year ago for eliminating perianal EMPD. On physical examination, significant scar was observed on the perianal skin. The vaginal opening, lower segment (1/3) of anterior vaginal wall, lower segment (1/2) of posterior vaginal wall, and bilateral vaginal walls had poor elasticity and severe contact bleeding. The cervix was smooth. No abnormalities were found in the uterine body and bilateral adnexa. Vaginal fluid-based cytology (LCT) and the conventional Papanicolaou smears of the vagina and HPV-DNA detection were performed. In this case, tumor cells were detected in the vaginal fluid-based cytology test (LCT) and the conventional papanicolaou smears. The cytologic characteristics of the tumor were as follows: since EMPD is usually susceptible to infections, inflammatory infiltration of neutrophils, or lymphocytes were observed in the smears. Some squamous cells and necrotic debris were also shown in the slides. We also found several Paget tumor cells, which provided direct evidence for diagnosis of this case. Paget tumor cells existed individually or arranged into clusters and nests by microscopy. The tumor cells were usually large, polygonal, or lace-like with one or two round, oval, or irregular medium sized nuclei. Some tumor cells were signet ringshaped since their nuclei were pushed to the edge of the cell. The nuclei were dark stained and often with nuclear vacuoles. Most nuclei had a single nucleolus while multiple nucleoli were observed in one nucleus occasionally. The cytoplasm of most tumor cells was abundant, light stained, and clear with an irregular edge and often contains vacuoles of varying size, while a small subset of Paget cells had no cyto-
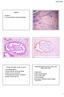
2 Figure 1. Pap smear. Paget tumor cells exist individually or arranged into clusters and nests. The tumor cells are usually large, polygonal, or lace-like with one or two round, oval, or irregular medium sized nuclei. The nuclei are dark stained. The cytoplasm of most tumor cells is abundant, light stained, and clear with an irregular edge and often contains vacuoles of varying size. Some tumor cells are signet ringshaped Figure 3. Vaginal fluid-based cytology test (LCT). Paget tumor cells are large, polygonal, or lace-like with one or two round, oval, or irregular medium sized nuclei. Some tumor cells are signet ring-shaped. Nuclei are dark and often have nuclear vacuoles Figure 2. Vaginal fluid-based cytology test (LCT). Inflammatory infiltration of neutrophils and lymphocytes are observed in the smears. Some squamous cells and necrotic debris are also shown in the slides. Paget tumor cells exist individually or arranged into clusters and nests. Some tumor cells are signet ringshaped. The nuclei are dark plasm but a naked nucleus. In addition, mitosis could be observed at high magnification. (Figures 1-3). The result of HPV-DNA test was negative. Based on the above cytological features and clinical history, the patient was diagnosed with perianal EMPD involving the vagina. Figure 4. Vaginal biopsy. Paget cells present singly or occur in packed clusters. Most of these cells are large with abundant pale cytoplasm and distinct borders, which present a balloon-like shape. Large darknuclei with prominent nucleoli can be seen. HE 400. Subsequently, the patient underwent vaginal posterior wall biopsy. During the surgery, it was found that the posterior wall of the vagina, the perineal body, the lower part of labia majora, and the perianal tissue were firm, congested, and had scattered ulcers. The lesion of posterior vaginal wall was removed for further diagnosis. The texture of removed tissue was firm and the incision was difficult to suture. Clinical primary diagnosis was post-operative EMPD with vaginal involvement. Microscopically, Paget cells presented singly or occurred in packed clusters. Most of these cells were large 3766 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):
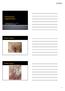
3 Figure 5. Immunohistochemistry showed the Paget cells are positive for CK7. DAB 200. Figure 7. Invasion of Paget tumor cells is observed in the epidermis of perianal EMPD. The tumor cells are large and most of them have large nuclei and prominent nucleoli. The cytoplasm of tumor cells is abundant and light. In some neoplastic cells, the nucleus is peripheral and cells are signet ring-shaped. HE 400. abundant and light staining. In some neoplastic cells, the nucleus was squeezed to the side and presented as signet ring-shaped. The borders between tumor sites and the superficial dermis were ambiguous (Figure 7). Discussion Figure 6. Immunohistochemistry showed the Paget cells are positive for GCDFP-15. DAB 200. with abundant pale-stained cytoplasm and with distinct borders, which present a balloon-like shape. Large dark-stained nuclei with prominent nucleoli can be observed microscopically, similar to the features of Paget cells in the cytologic test (Figure 4). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that Paget tumor cells were focally positive for muc-2, CK7, CEA, GCDFP-15, P16 (Figures 5, 6) and were negative for CK20, P63, CDX2, S-100, ER, PR. The pathological diagnosis of vaginal biopsy was perianal EMPD with vaginal involvement. We reviewed pathological slides from this patient, which were obtained 2 years ago. Invasion of Paget tumor cells were observed in the epidermis. The tumor cells were large and most of them had a large nucleus and prominent nucleoli. The cytoplasm of tumor cells was Clinical features and pathogenesis EMPD most commonly involves regions with distribution of apocrine glands, including scrotum, penis, labia majora, labia minora, and vagina. In a few patients, EMPD may be observed in perianal skin, perineum, axilla, etc. Most EMPD lesions are single while few of them occur multiply. Vulvar EMPD is more common in females than in the corresponding skin in males and almost all female patients are postmenopausal [3] and over 60 years old. Longterm perineal EMPD can invade surrounding organs or tissues of patients, such as vagina, cervix, anus, rectum, or urinary tract. The borders of the lesions usually appear irregular, slightly elevated, and demarcated. EMPD present as a verrucous, nodular, or papillary brown and central flushing plaque with scaling erosion, exudate, superficial scales, or crusts [4]. The most common symptoms are varying degrees of pruritus. The presence of pain and bleeding is reported to be more common in patients with invasive disease Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):
4 Most of the patients with EMPD do not have tumors in deep tissue. The recurrence rate after surgery is about 30%, but no metastasis occurs. About 10% of EMPD may develop to invasive carcinoma, then further progress to metastasis [3]. Pathological diagnosis The cytologic features of this patient were similar to those reported in the previous literature [5-10]. Paget tumor cells existed individually or were arranged into clusters and nests. The tumor cells were usually large, polygonal, or lace-like with one or two round, oval, or irregular medium-sized nuclei. Some tumor cells were signet ring-shaped with nuclei pushed to the edge of the cell. The nuclei are dark-stained and often have nuclear vacuoles. Most nuclei have a single nucleolus while multiple nucleoli are observed occasional cells. The cytoplasm of most tumor cells is abundant, light-stained and clear, with irregular edges and often contains vacuoles of varying size, while small subsets of Paget cells have no cytoplasm but a naked nucleus. In addition, mitosis may be observed at high magnification. Cytologic diagnosis of Paget disease must be combined with a previous history or assistance of immunocytochemistry. On vaginal biopsy Paget cells presented singly or occurred in packed clusters.. Most of these cells were large with abundant pale stained cytoplasm. Large dark stained nuclei with prominent nucleoli can be observed microscopically. Signet-ring like cells and adenoid structure are commonly appeared in EMPD lesions. Paget cells were positive for CK7, CEA, and GCDFP-15 which supports our final diagnosis [11-13] Positive expression of P16 in Paget cells also has been reported in previous literature [14]. In this case, Paget cells were focally positive for P16. The significance of P16 positive expression in Paget cells is still unclear, but we must be wary not to confuse EMPD with squamous epithelial lesions. The differential diagnoses by cytology includes squamous epithelial high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (HSIL), endometrial cancer, and endocervical adenocarcinoma. Squamous intraepithelial tumor cells usually present as small, single, scattered with irregular nucleus, high nucleus/cytoplasm ratio and clumped deep staining chromatin, which can help us differentiate EMPD from HSIL. Adenocarcinoma cells of endometrial cancer may also contain clear cytoplasm as in EMPD. EPMD has no threedimensional balls and eosinophilic cytoplasm. Signet-like cells usually can be observed in endocervical adenocarcinoma but appeared in EMPD commonly [10]. In addition, immunochemistry will be effective for distinguishing EMPD from other disease in clinical practice. Clinical history is also very important for providing an accurate diagnosis. One of main histological differential diagnoses is vaginal VaIN. Immunohistochemistry interpretations for P63, CK7, CEA, and GCDFP-15 are useful to provide a final diagnosis. Additionally, superficial spreading malignant melanoma (SSMM) and immunohistochemistry for S-100, HMB-45, and melan-a will be useful to distinguish EMPD from SSMM [15]. It is also necessary to exclude metastatic poorly differentiated cancer, such as metastatic sites originating from rectal cancer. Treatment The treatment and prognosis of vulvar EMPD depends on the types of lesion. Paget cells that are confined to the epithelium or not are important for evaluating the prognosis of EMPD. Primary intraepithelial Paget disease is usually a kind of indolent, painless, and superficial tumor. For intraepithelial lesions, conservative resection (wide excision) with a gross margin 2-3 cm and resection to the fascia is recommended. For vulvar EMPD patients with invasive lesions, or with different histopathological types of skin adnexal or vulvar adenocarcinomas, ipsilateral inguinal lymph node excision should be performed. If Paget cells are observed in the surgical margins microscopically, EMPD lesions have not been completely removed. On this occasion, an enlarged partial vulvectomy or total vulvectomy should be provided [3, 16, 17]. If the recurrence occurs in the surrounding tissue after EMPD surgical excision, and the recurrence is not associated with adenocarcinoma, only conservative treatment is required. Usually, superficial resection or topical therapy is recommended and imiquimod is most commonly used in clinical practice [18, 19]. Other new therapies including radiation therapy, laser ablation, phototherapy, and topical therapy with 5-fluorouracil are also suggested in clinical work [20]. In this case, the patient with perianal EMPD recurred after surgery, and 3768 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):
5 the lesion was widely distributed. Topical therapy was adopted to control the progression of this disease and the prognosis was acceptable. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Wei Wang, Department of Pathology, Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children, Ministry of Education, West China Second Hospital, Sichuan University, People s South Road, Chengdu , Sichuan, China. Tel: (86) ; bearwin2000@126.com References [1] Parker LP, Parker JR, Bodurka-Bevers D, Deavers M, Bevers MW, Shen-Gunther J, Gershenson DM. Paget s disease of the vulva: pathology, pattern of involvement, and prognosis. Gynecol Oncol 2000; 77: [2] In: Kurman RJ, Ellenson LH, Ronnett BM, editors. Blaustein s pathology of the female genital tract. 6th edition. New York, NY: Springer; pp. 82Y6. [3] Fanning J, Lambert HC, Hale TM, Morris PC, Schuerch C. Paget s disease of the vulva: prevalence of associated vulvar adenocarcinoma, invasive Paget s disease, andrecurrence after surgical excision. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999; 180: [4] Brainard JA, Hart WR. Proliferative epidermal lesions associated with anogenital Paget s disease. Am J Surg Pathol 2000; 24: [5] Costello TJ, Wang HH, Schnitt SJ, Ritter R, Antonioli DA. Paget s disease with extensive involvement of the female genital tract initially detected by cervical cytosmear. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1988; 112: [6] Gu M, Ghafari S, Lin F. Pap smears of patients with extramammary Paget s disease of the vulva. Diagn Cytopathol 2005; 32: [7] Westacott LS, Cominos D, Williams S, Knight B, Waterfield R. Primary cutaneous vulvar extramammary Paget s disease involving the endocervix and detected by Pap smear. Pathology 2013; 45: [8] Clayton EF, Rubin SC, Dumoff KL. Paget cells in endometrial and endocervical curettings in a patient with recurrent vulvar Paget s disease. Int J Surg Pathol 2014; 22: [9] Gilliland K, Knapik J, Wilkinson EJ. Cytology of vulvar/vaginal paget disease: report of a case and review of the literature. J Low Genit Tract Dis 2013; 17: e [10] Davis G, Anderson L, Pather S. Extramammary paget s disease mimicking localized malignancy on cervical cytology. Diagn Cytopathol 2016; 44: [11] Goldblum JR, Hart WR. Vulvar Paget s disease: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 19 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1997; 21: [12] Crawford D, Nimmo M, Clement PB, Thomson T, Benedet JL, Miller D, Gilks CB. Prognostic factors in Paget s disease of the vulva: a study of 21 cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1999; 18: [13] Liegl B, Leibl S, Gogg-Kamerer M, Tessaro B, Horn LC, Moinfar F. Mammary and extramammary Paget s disease: an immunohistochemical study of 83 cases. Histopathology 2007; 50: [14] Sah SP, McCluggage WG. Florid vulval Paget disease exhibiting p16 immunoreactivity and mimicking classic VIN. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2013; 32: [15] Hill SJ, Berkowitz R, Granter SR, Hirsch MS. Pagetoid lesions of the vulva: a collision between malignant melanoma and extramammary Paget disease. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2008; 27: [16] Baehrendtz H, Einhorn N, Pettersson F, Silfverswärd C. Paget s disease of the vulva: the Radiumhemmet series Int J Gynecol Cancer 1994; 4: 1-6. [17] Crawford D, Nimmo M, Clement PB, Thomson T, Benedet JL, Miller D, Gilks CB. Prognostic factors in Paget s disease of the vulva: a study of 21 cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1999; 18: [18] MacLean AB, Makwana M, Ellis PE, Cunnington F. The management of Paget s disease of the vulva. J Obstet Gynaecol 2004; 24: [19] Hatch KD, Davis JR. Complete resolution of Paget disease of the vulva with imiquimod cream. J Low Genit Tract Dis 2008; 12: [20] Feldmeyer L, Kerl K, Kamarashev J, deviragh P, French L. Treatment of vulvar Paget disease with topical imiquimod: a case report and review of the literature. J Dermatol Case Rep 2011; 5: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Case history: Figure 1. H&E, 5x. Figure 2. H&E, 20x.
 1 Case history: A 49 year-old female presented with a 5 year history of chronic anal fissure. The patient s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On digital rectal examination there was a very
1 Case history: A 49 year-old female presented with a 5 year history of chronic anal fissure. The patient s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On digital rectal examination there was a very
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
Pruritus Ani in an Elderly Man
 Pruritus Ani in an Elderly Man Pedro Redondo, MD; Michel Idoate, MD; Agustín España, MD; Emilio Quintanilla, MD; University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain REPORT OF A CASE A 78-year-old man presented with
Pruritus Ani in an Elderly Man Pedro Redondo, MD; Michel Idoate, MD; Agustín España, MD; Emilio Quintanilla, MD; University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain REPORT OF A CASE A 78-year-old man presented with
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva Malignant melanoma sho
 Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
3/25/2019. J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse
 J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse 1 4 th most common GYN cancer 5% of malignancies of GYN type. 4850 new cases annually 1030 deaths Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (Lichen
J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse 1 4 th most common GYN cancer 5% of malignancies of GYN type. 4850 new cases annually 1030 deaths Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (Lichen
Case Report Scrotal Apocrine Adenocarcinoma with Pagetoid Phenomenon and Inguinal Lymph Node Metastases
 Volume 2016, Article ID 8353745, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8353745 Case Report Scrotal Apocrine Adenocarcinoma with Pagetoid Phenomenon and Inguinal Lymph Node Metastases Aristeidis Hristos
Volume 2016, Article ID 8353745, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8353745 Case Report Scrotal Apocrine Adenocarcinoma with Pagetoid Phenomenon and Inguinal Lymph Node Metastases Aristeidis Hristos
BAP-oma & BEYOND MICHAEL A NOWAK, MD
 BAP-oma & BEYOND MICHAEL A NOWAK, MD CONFLICTS No conflicts with the content of this lecture BAP-oma Wiesner 2011: Families with multiple tan dome-shaped papules of head, neck, trunk, and extremities.
BAP-oma & BEYOND MICHAEL A NOWAK, MD CONFLICTS No conflicts with the content of this lecture BAP-oma Wiesner 2011: Families with multiple tan dome-shaped papules of head, neck, trunk, and extremities.
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo. Case Discussions. 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC
 BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
Cutaneous metastases. Thaddeus Mully. University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology
 Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Case Report Apocrine Adenocarcinoma of the Vulva: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2016, Article ID 1712404, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1712404 Case Report Apocrine Adenocarcinoma of the Vulva: A Case Report and Review of the
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2016, Article ID 1712404, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1712404 Case Report Apocrine Adenocarcinoma of the Vulva: A Case Report and Review of the
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal
 Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions
 Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
2009 USCAP Gyn Pathology Evening Session Case #3. Richard J. Zaino, MD Hershey Medical Center Penn State University Hershey, PA
 2009 USCAP Gyn Pathology Evening Session Case #3 Richard J. Zaino, MD Hershey Medical Center Penn State University Hershey, PA rzaino@psu.edu Clinical history Middle aged woman with an exophytic mass of
2009 USCAP Gyn Pathology Evening Session Case #3 Richard J. Zaino, MD Hershey Medical Center Penn State University Hershey, PA rzaino@psu.edu Clinical history Middle aged woman with an exophytic mass of
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000
 Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients
 236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Case 3 - GYN. History: 66 year old, routine Pap test. Dr. Stelow
 Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Clinical Pathological Conference. Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva
 Clinical Pathological Conference Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva History F/48 Chinese Married Para 1 Presented in September 2004 Vulval mass for 2 months Associated with watery and blood stained discharge
Clinical Pathological Conference Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva History F/48 Chinese Married Para 1 Presented in September 2004 Vulval mass for 2 months Associated with watery and blood stained discharge
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Anal gland adenocarcinoma in situ with pagetoid spread: a case report
 Ishioka et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:63 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0469-5 CASE REPORT Anal gland adenocarcinoma in situ with pagetoid spread: a case report Open Access Kohei Ishioka 1*,
Ishioka et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:63 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0469-5 CASE REPORT Anal gland adenocarcinoma in situ with pagetoid spread: a case report Open Access Kohei Ishioka 1*,
Cytologic Findings of Cervicovaginal Smears in Women with Uterine Papillary Serous Carcinoma
 J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 93-7 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Cytologic Findings of Cervicovaginal Smears in Women with Uterine Papillary Serous Carcinoma The goal of
J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 93-7 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Cytologic Findings of Cervicovaginal Smears in Women with Uterine Papillary Serous Carcinoma The goal of
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD J M O R G A N
 VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic skin*
 J Cutan Pathol 2005: 32: 50 54 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Denmark Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic
J Cutan Pathol 2005: 32: 50 54 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Denmark Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
Fig Fig
 CASE 23.1 An 85-year-old female from Bangkok Chief complaint Itchy rash at genitalia for 8 months Present illness The patient complainted of longstanding vulvar pruritus. For 8 month her daughter could
CASE 23.1 An 85-year-old female from Bangkok Chief complaint Itchy rash at genitalia for 8 months Present illness The patient complainted of longstanding vulvar pruritus. For 8 month her daughter could
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Histopathology of Melanoma
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Cytyc Corporation - Case Presentation Archive - October 2001
 ThinPrep Pap Test History: 82 Year Old Female Specimen Type: Peritoneal Washings Case provided by Dr. Berle Stratton, Southwest Washington Medical Center, Vancouver, Washington. *The images, analysis and
ThinPrep Pap Test History: 82 Year Old Female Specimen Type: Peritoneal Washings Case provided by Dr. Berle Stratton, Southwest Washington Medical Center, Vancouver, Washington. *The images, analysis and
Article begins on next page
 Metastatic genital tract adenocarcinoma to the vulva: a rare occurrence presenting as painful vulvar enlargement Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access
Metastatic genital tract adenocarcinoma to the vulva: a rare occurrence presenting as painful vulvar enlargement Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access
Extramammary Paget s disease: a report of 2 cases and a review of the literature
 Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(1) : 73 78 EXTRAMAMMARY PAGET S DISEASE CASE REPORT Extramammary Paget s disease: a report of 2 cases and a review of the literature Joon Joon KHOO, MBBS, MPath, and Siew Eng
Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(1) : 73 78 EXTRAMAMMARY PAGET S DISEASE CASE REPORT Extramammary Paget s disease: a report of 2 cases and a review of the literature Joon Joon KHOO, MBBS, MPath, and Siew Eng
Mousa. Lina Al-Lawama. Enas Ajarma. 0 P a g e
 3 Mousa Lina Al-Lawama Enas Ajarma 0 P a g e رب اشرح لي صدري ويسر لي أمري واحلل عقدة من لساني يفقهوا قولي -Last time we were talking about vulvar pathology (non neoplastic epithelial disorder :lichen chronicus
3 Mousa Lina Al-Lawama Enas Ajarma 0 P a g e رب اشرح لي صدري ويسر لي أمري واحلل عقدة من لساني يفقهوا قولي -Last time we were talking about vulvar pathology (non neoplastic epithelial disorder :lichen chronicus
SCAN Gynaecological Group. Clinical Management Protocols vulval cancer
 SE Scotland Cancer Network SCAN Gynaecological Group Clinical Management Protocols vulval cancer 2009 www.scan.scot.nhs.uk August 2001 updated annually, most recently INTRODUCTION The South East Scotland
SE Scotland Cancer Network SCAN Gynaecological Group Clinical Management Protocols vulval cancer 2009 www.scan.scot.nhs.uk August 2001 updated annually, most recently INTRODUCTION The South East Scotland
The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) updated the staging
 Continuing Education Column Revised FIGO Staging System Hee Sug Ryu, MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ajou University School of Medicine E - mail : hsryu@ajou.ac.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2010;
Continuing Education Column Revised FIGO Staging System Hee Sug Ryu, MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ajou University School of Medicine E - mail : hsryu@ajou.ac.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2010;
A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1878 A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre Rachana L Y, S.S. Hiremath*, Prabhu M H, S.S
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1878 A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre Rachana L Y, S.S. Hiremath*, Prabhu M H, S.S
Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Disorders of the vulva
 Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A. Pathological Case Report
 Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
American Journal of. Cancer Case Reports
 American Journals of Cancer Case Reports http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr/index Cancer Case Reports AK H et al. American Journal of Cancer Case Reports 2013, 1:93-97 Vol. 1, Article ID Page 201300216,
American Journals of Cancer Case Reports http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr/index Cancer Case Reports AK H et al. American Journal of Cancer Case Reports 2013, 1:93-97 Vol. 1, Article ID Page 201300216,
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Case Report Management of Adenocarcinoma in the Setting of Recently Operated Perianal Paget s Disease
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 510813, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/510813 Case Report Management of Adenocarcinoma in the Setting of Recently Operated Perianal Paget s Disease
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 510813, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/510813 Case Report Management of Adenocarcinoma in the Setting of Recently Operated Perianal Paget s Disease
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
CPC on Cervical Pathology
 CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
Wendy L Frankel. Chair and Distinguished Professor
 1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Comparison of Cytologic Characteristics between Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Adenoid Basal Carcinoma in the Uterine Cervix
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2015; 49: 396-402 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Cytologic Characteristics between Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Adenoid Basal Carcinoma in the Uterine Cervix
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2015; 49: 396-402 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Cytologic Characteristics between Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Adenoid Basal Carcinoma in the Uterine Cervix
Lessons From Cases of Screened Women Who Developed Cervical Carcinoma
 Lessons From Cases of Screened Women Who Developed Cervical Carcinoma R. Marshall Austin MD,PhD Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center raustin@magee.edu Why Focus Study On Cases
Lessons From Cases of Screened Women Who Developed Cervical Carcinoma R. Marshall Austin MD,PhD Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center raustin@magee.edu Why Focus Study On Cases
Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 386921, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/386921 Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma Deba P. Sarma, 1 Daniel Olson, 1 Jennifer Olivella, 1 Tracey
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 386921, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/386921 Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma Deba P. Sarma, 1 Daniel Olson, 1 Jennifer Olivella, 1 Tracey
Paget. Pigmented Extramammary Paget's Disease. Mei-ju Ko Cheng-Hsiang Hsiao* Chung-Jen Tseng Yi-Hua Liao
 Paget * * Pigmented Extramammary Paget's Disease Mei-ju Ko Cheng-Hsiang Hsiao* Chung-Jen Tseng Yi-Hua Liao Extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) usually presents as an erythematous, scaly patch with crusts,
Paget * * Pigmented Extramammary Paget's Disease Mei-ju Ko Cheng-Hsiang Hsiao* Chung-Jen Tseng Yi-Hua Liao Extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) usually presents as an erythematous, scaly patch with crusts,
BSD 2015 Case 19. Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is:
 BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Bartholin Gland Carcinomas
 Bartholin Gland Carcinomas Hugo Horlings MD PhD The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam, The Netherlands Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee)
Bartholin Gland Carcinomas Hugo Horlings MD PhD The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam, The Netherlands Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee)
Dermatopathology. Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia
 Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia Melanoma and mimics Dr. Martin Mihm Malignant lesions result from the accumulation of mutations Class I lesions (benign) Class II
Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia Melanoma and mimics Dr. Martin Mihm Malignant lesions result from the accumulation of mutations Class I lesions (benign) Class II
Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report
 Case Report Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report Journal of International Medical Research 2015, Vol. 43(4) 592 596!
Case Report Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report Journal of International Medical Research 2015, Vol. 43(4) 592 596!
Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed on cytology
 Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(2) : CERVICAL 139 143 VILLOGLANDULAR ADENOCARCINOMA CYTOLOGY CASE REPORT Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed
Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(2) : CERVICAL 139 143 VILLOGLANDULAR ADENOCARCINOMA CYTOLOGY CASE REPORT Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity
 Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID. Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Article begins on next page
 Vulvar Adenocarcinoma with Neuroendocrine Differentiation: A Case Report Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/51337/story/]
Vulvar Adenocarcinoma with Neuroendocrine Differentiation: A Case Report Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/51337/story/]
Dr. Issraa Ali Hussein
 CLINICAL 09888888;rCYTOLOGY Dr. Issraa Ali Hussein objectives Define diagnostic cytology (clinical cytology). Explain the differences between histopathology and cytopathology. Recognize the methods for
CLINICAL 09888888;rCYTOLOGY Dr. Issraa Ali Hussein objectives Define diagnostic cytology (clinical cytology). Explain the differences between histopathology and cytopathology. Recognize the methods for
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens
 How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals
 PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa
 Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa No financial disclosures No discussion of off-label use of medications or unapproved devices 67 year old male referred to Oculoplastics
Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa No financial disclosures No discussion of off-label use of medications or unapproved devices 67 year old male referred to Oculoplastics
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP)
 Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Vulvar Villoglandular Adenocarcinoma of Colonic Type: A Rare Finding
 Case Report Middle East Journal of Cancer; January 2018; 9(1): 71-75 Vulvar Villoglandular Adenocarcinoma of Colonic Type: A Rare Finding Heidarali Esmaeili*, Mahzad Azimpouran*, Elaheh Olad-Saheb-Madarek**
Case Report Middle East Journal of Cancer; January 2018; 9(1): 71-75 Vulvar Villoglandular Adenocarcinoma of Colonic Type: A Rare Finding Heidarali Esmaeili*, Mahzad Azimpouran*, Elaheh Olad-Saheb-Madarek**
NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS
 NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Abstract: The primary as well as metastatic tumours of the skin can be diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology
NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Abstract: The primary as well as metastatic tumours of the skin can be diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Case Report Paget s Disease of the Vulva in Premenopausal Woman Treated with Only Surgery: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 854827, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/854827 Case Report Paget s Disease of the Vulva in Premenopausal Woman Treated with Only Surgery: A Case Report
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 854827, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/854827 Case Report Paget s Disease of the Vulva in Premenopausal Woman Treated with Only Surgery: A Case Report
Cytoplasmic changes Nuclear changes
 The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors
 An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA. Case Reports Clinical history. Materials and Methods
 DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA A Metastatic Renal Carcinoid Tumor Presenting as Breast Mass: A Diagnostic Dilemma Farnaz Hasteh, M.D., 1 Robert Pu, M.D., Ph.D., 2 and Claire W. Michael, M.D. 2 * We present clinicopathological
DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA A Metastatic Renal Carcinoid Tumor Presenting as Breast Mass: A Diagnostic Dilemma Farnaz Hasteh, M.D., 1 Robert Pu, M.D., Ph.D., 2 and Claire W. Michael, M.D. 2 * We present clinicopathological
Disclosures. I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Vulvar Disease. Precancer and Cancerous Vulvar Disease
 Precancer and Cancerous Vulvar Disease Stefanie M. Ueda, M.D. Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Assistant Clinical Professor Division of Gynecologic Oncology University of California,
Precancer and Cancerous Vulvar Disease Stefanie M. Ueda, M.D. Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Assistant Clinical Professor Division of Gynecologic Oncology University of California,
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. This case was provided by Treant Hospital, Bethesda, Hoogeveen, The Netherlands
 Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma This case was provided by Treant Hospital, Bethesda, Hoogeveen, The Netherlands ADS-01504 Rev. 001 2016 Hologic, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma This case was provided by Treant Hospital, Bethesda, Hoogeveen, The Netherlands ADS-01504 Rev. 001 2016 Hologic, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
