Developmental Milestones
|
|
|
- Dylan Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Developmental Milestones AGE GROSS MOTOR FINE MOTOR LANGUAGE SOCIAL/COGNITIVE 2 months Lifts head/chest when Tracks past midline. Alerts to sound; Recognizes parent; prone. coos. social smile. 4 5 months Rolls front to back, Grasps rattle. Orients to voice; Enjoys looking back to front. begins to make around; laughs. consonant sounds, razzes 6 months Sits unassisted. Transfers objects; raking grasp months Crawls; pulls to stand. Uses three-finger (immature) pincer grasp Babbles. Says mama/dada (nonspecific). Stranger anxiety. Waves bye-bye; plays pat-a-cake. 12 months Cruises (11 months); Uses two-finger Says mama/dada Imitates actions. walks alone. (mature) pincer (specific). grasp. 15 months Walks backward. Uses cup. Uses 4 6 words. Temper tantrums. 18 months Runs; kicks a ball. Builds tower of 2 4 cubes. Names common objects. Copies parent in tasks (e.g., sweeping). 2 years Walks up/down steps Builds tower of six Uses two-word Follows two-step with help; jumps. cubes. phrases. commands; removes clothes. 3 years Rides tricycle; climbs Copies a circle; uses Uses three-word Brushes teeth with stairs with alternating utensils. sentences help; washes/dries feet (3 4 years). hands. 4 years Hops. Copies a square. Knows colors and some numbers. Cooperative play; plays board games. 5 years Skips; walks backward Ties shoelaces; Uses five-word Domestic role for long distances. knows left and sentences. playing; plays dress- right; prints letters. up.
2 Delayed Milestones Predominant Speech Delay: A. Autism spectrum disorders B. Hearing impairment C. Congenital bilateral perisylvian syndrome CBPS Predominantantly Motor Delay: A. Brain: Cerebral Palsy (spastic, ataxic, athetoid, dystonic) B. Spinal cord: 1. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: SPG (spastic gait genes) mutations, 70 different loci identified. SPG4 (spastin) is the most common. 2 peaks at 2 and 40 years Diagnosed by family history and exclusion of other conditions 2. Primary lateral sclerosis, juvenile variant: ALS2 gene mutation, inheritance Begins in early childhood and progress over years C. Anterior horn cells: 1. Spinal muscle atrophy: 5q13 deletion Autosomal recessive Proximal weakness & respiratory involvement Type I (Werdnig Hoffmann, at birth), Type II (Dubowitz, after 6 months), Type III (Kugelberg Welander, after 1 year) Normally there is two genes at 5q13, one is SMN1 which encodes most of the SMN protein and the other is SMN2 which encodes only 10-20% of SMN protein (has different nucleotide which makes its protein undergoes variable degree of splicing and degradation. SMA patients have mutated SMN1 so the variation of protein produced by SMN2 gives the variable age of presentation. 2. X-linked spinal muscle atrophy type II SMAX2 Similar to SMA type I but different gene mutation. NB SMAX1 is Kennedy disease, adult onset. D. Peripheral nerves: 1. Dejerine Sottas Syndrome (HSMN 3 CMT 3) PMP22 or MPZ mutation, onset in infancy, demyelinating E. Muscle disease: 1. Muscle Dystrophy: Duchenne Baker Congenital myopathies (Fukuyama Merosin deficient) 2. Muscle Channelopathy: Myotonia congenita (ClCN,, less severe, at 4-6 years) Thompson disease (SCN4A, AD, severe, at birth) Paramyotonia congenita (worse with exercise, SCN4A, AD) 3. Mitochondrial disease: (MELAS MERRF) Global Delay: A. Cerebral malformations B. Chromosomal abnormalities C. Intrauterine infection D. Perinatal disorders E. Metabolic progressive encephalopathies Amino acid: Lysosomal enzymes: Glycogen storage: Mitochondrial disorders: Leukodystrophies
3 A. Congenital cerebral malformations: Malformation Description Lissencephaly Absence of sulci, smooth brain Pachygyri Polymicrogyri Schizencephaly Porencephaly Hydranencephaly Few gyri that are broad and thick. Incomplete lissencephaly. (pachy means thick). Numerous small gyri Cleft lined with grey matter connecting the ventricle to the pial surface of the brain. Either open lip or closed lip. Cleft or cyst in the cerebral hemisphere, not lined with grey matter; encephalomalacia. Cerebral hemispheres are absent and replaced by CSF Holoprosencephaly Anencephaly Alobar Semilobar Lobar Encephalocele Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD) (De Morsier synd) Dandy Walker Syndrome: Forebrain fails to divide into two hemispheres. : Severe form, hemispheres fail to separate resulting in cyclopia. : hemispheres are partially separated : Incomplete separation, may lead normal life. : inter-hemispheric fissure is complete, thalami separated but fornices are fused, frontal horns of lateral ventricle are fused, septum pellucidum absent Absence of the brain, skull and scalp A sac like protrusion of the brain and meninges 2 of the following: absence of septum pellucidum, pituitary gland and optic nerves. Can be caused by in utero Valproate exposure. A. DW malformation Most severe form, consists of: -Absence of cerebellar vermis -Large posterior fossa and highly tentorium -Cystic dilatation of 4 th ventricle B. DW Variant: Mild form with hypoplastic vermis, mildly enlarged 4 th ventricle Chiari Syndrome: A. Chiari I: Displacement of Peg tail like cerebellar tonsils through foramen magnum > 5mm B. Chiari II: (Arnold Chiari) Displacement of medulla, 4 th ventricle and vermis through foramen magnum. Usually associated with peaked tectum and lumbar myelomeningocele C. Chiari III: Similar to Chiari II with occipital encephalocele D. Chiari IV (Obsolete): Cerebellar hypoplasia (now called primary cerebellar agenesis).
4 Leukodystrophies: Disease Inheritance Enzyme Clinical Picture MRI XL-R ABCD gene Adrenoleukodystrophy Peroxisomal Zellwiger (cerebrohepatorenal syndrome) Peroxisomal Metachromatic Krabbe (Globoid cell) PEX1 gene SA gene GALC gene Failure of peroxisomal oxidation of VLCFA Absence of peroxisomes Arylsulfatase Galactocerebrosidase 3 Phenotypes: - Childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy - Adrenomyeloneuropathy - Addison s disease - Facies: high forehead, midface hypoplasia - Hepatomegally Renal cysts - Late infantile: gait abnormality, muscle rigidity, loss of vision, developmental delay - Juvenile: slower course - Adult: dementia psychiatric features Peripheral neuropathy, developmental delay, optic atrophy, globoid cells - Posterior - Spares U fibers - 3 zones of different intensities in T2 (inner hyper, middle Iso and outer hypo) - Diffuse hypomyelination involving U fibers - Gyral abnormalities (frontal microgyria, occipital pachygyriia) - Periventricular - Spares U fibers leading to a "butterfly pattern" CT: Hyperdense thalami MRI: Periventricular Fabry Canavan (spongiform degeneration of white matter) Amino-acid Alexander Fibrinoid XL-R Galactosidase Posterior circulation strokes - Peripheral neuropathy of hands/feet, angiokeratomas, cardiovascular disease Aspartocyclase Macrocephaly, severe mental deficits and blindness. GFAP gene Macrocephaly, severe mental deficits Rosenthal fibers in pathology Pulvinar hyperintensity Macrocephaly Diffuse hypomyelination involving U fibers Increased NAA in MRS Macrocephaly Frontal predominance
5 Glycogen storage disease: Disease Enzyme deficiency Hypoglycemia Hepatomegaly Hyperlipidemia von Gierke's glucose-6-phosphatase Yes Yes Yes None Pompe's acid maltase (Lys 1-4 glucosidase) Cori's glycogen debrancher Muscle symptoms mnemonics No Yes No Muscle weakness P for Pump (develop HF) Yes Yes Yes Myopathy Andersen glycogen branching No Yes No None enzyme McArdle muscle glycogen No No No Exercise-induced M for muscles phosphorylase cramps (glycogen phos) Hers' liver glycogen phosph. Yes Yes No None H for Hepatic (glycogen phos) Lysosomal storage disease: Disease Finding Deficient Enzyme Accumulated substrate Inheritance Gaucher s Niemann-pick Tay-Sachs Metachromatic leukodystrophy Hepatosplenomegaly, aseptic necrosis of femur, bone crises, Gaucher s cells (macrophages look like crumpled paper) Progressive neurodegeneration, hepatosplenomegaly, cherry-red spot (on macula),foam cells Progressive neurodegeneration, developmental delay, Cherry red spot, lysosomes with onion skin Central and peripheral demyelination with ataxia, dementia Glucocerebrosidase Glucocerebroside Sphingomyelinase Sphingomyelin Hexosaminidase A GM2 ganglioside Arylsulfatase A Cerebroside sulfate Fabry s Peripheral neuropathy of hands/feet, angiokeratomas, cardiovascular disease Galactosidase A Ceramide trihexoside XR Krabbe s Peripheral neuropathy, developmental delay, optic atrophy, globoid cells Galactocerebrosidase Galactocerebroside Hurler s Hunter s Developmental delay, Gargoylism, airway obstruction, corneal clouding, hepatosplenomegaly Mild Hurler + aggressive behavior, no corneal clouding Iduronidase Heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate Iduronate sulfatase Heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate XR - Gaucher s: no neurological symptoms - Niemann-Pick and Tay Sachs: both associated with cherry red spot, Niemann-Pick also has HSM - Fabry s and Krabbe s: both have peripheral neuropathy. Fabry s has normal development and angiokeratomas, Krabbe s has developmental delay and optic atrophy - Hurler s and Hunter s: Hunter s is a milder form of Hurler s (remember, hunters need good vision, no corneal clouding)
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri. Outline
 Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri Dr. Kathy Grange Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University Outline Brief overview of clinical
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri Dr. Kathy Grange Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University Outline Brief overview of clinical
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Fatty Acids Synthesis L3
 Fatty Acids Synthesis L3 The pathway for fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas, oxidation occurs in the mitochondria. The other major difference is the use of nucleotide co-factors. Oxidation
Fatty Acids Synthesis L3 The pathway for fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas, oxidation occurs in the mitochondria. The other major difference is the use of nucleotide co-factors. Oxidation
Torey Stories. Compiled using the following resources: First Aid, 2017 Firecracker
 Torey Stories Compiled using the following resources: First Aid, 2017 Firecracker Osteogenesis Imperfecta First Aid (2017) p.47 The Imperfect Bone 1) Osteogenesis imperfecta Imperfect bone 2) COL1A1 /
Torey Stories Compiled using the following resources: First Aid, 2017 Firecracker Osteogenesis Imperfecta First Aid (2017) p.47 The Imperfect Bone 1) Osteogenesis imperfecta Imperfect bone 2) COL1A1 /
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Structure. Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles. Hydrolytic enzymes. Variable in size & shape need
 Lysosomes Structure Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles Hydrolytic enzymes Variable in size & shape need Degrade material taken up from outside and inside the cell Variable in size and shape Lysosomal
Lysosomes Structure Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles Hydrolytic enzymes Variable in size & shape need Degrade material taken up from outside and inside the cell Variable in size and shape Lysosomal
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS. Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry
 METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
Approach to the Child with Developmental Delay
 Approach to the Child with Developmental Delay Arwa Nasir Department of Pediatrics University of Nebraska Medical Center DISCLOSURE DECLARATION Approach to the Child with Developmental Delay Arwa Nasir
Approach to the Child with Developmental Delay Arwa Nasir Department of Pediatrics University of Nebraska Medical Center DISCLOSURE DECLARATION Approach to the Child with Developmental Delay Arwa Nasir
myelin in the CNS Multiple axons are oligodendrocyte
 Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Inborn Error Of Metabolism :
 Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
NYEIS Version 4.3 (ICD) ICD - 10 Codes Available in NYEIS at time of version launch (9/23/2015)
 D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, Dr. Peter Ostrow
 Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Neurodegenerative disorders: an approach to investigation. Robert Robinson Practical Paediatric Neurology Study Days April 2018
 Neurodegenerative disorders: an approach to investigation Robert Robinson Practical Paediatric Neurology Study Days April 2018 Aims An approach to investigating and diagnosing young children with progressive
Neurodegenerative disorders: an approach to investigation Robert Robinson Practical Paediatric Neurology Study Days April 2018 Aims An approach to investigating and diagnosing young children with progressive
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
The Floppy Baby. Clare Betteridge
 The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
Hereditary disorders of peroxisomal metabolism.
 Hereditary disorders of peroxisomal metabolism http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/perox.jpg Peroxisomes single membrane organelles from less than 100 to more than 1000 per eucaryotic cell more than
Hereditary disorders of peroxisomal metabolism http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/perox.jpg Peroxisomes single membrane organelles from less than 100 to more than 1000 per eucaryotic cell more than
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Date of commencement: February Principal Investigator Dr. Jayesh J. Sheth CASE RECORD FORM
 ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA)
 DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects
 Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Hereditary disorders of peroxisomal metabolism.
 Hereditary disorders of peroxisomal metabolism http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/perox.jpg Peroxisomes single membrane organelles from less than 100 to more than 1000 per eukaryotic cell more than
Hereditary disorders of peroxisomal metabolism http://www.cytochemistry.net/cell-biology/perox.jpg Peroxisomes single membrane organelles from less than 100 to more than 1000 per eukaryotic cell more than
Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child
 Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child Basil T. Darras, M.D. Neuromuscular Program Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Classification and General Clinical Evaluation
Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child Basil T. Darras, M.D. Neuromuscular Program Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Classification and General Clinical Evaluation
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History. Tuesday, April 16, 2013
 DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History Tuesday, April 16, 2013 Objectives Recognize the importance & impact of newborn screening Describe the process of newborn screening
DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History Tuesday, April 16, 2013 Objectives Recognize the importance & impact of newborn screening Describe the process of newborn screening
Lipid storage diseases
 Lipid storage diseases What are lipid storage diseases? Lipid storage diseases, or the lipidoses, are a group of inherited metabolic disorders in which harmful amounts of fatty materials called lipids
Lipid storage diseases What are lipid storage diseases? Lipid storage diseases, or the lipidoses, are a group of inherited metabolic disorders in which harmful amounts of fatty materials called lipids
Abdallah Q& Razi. Faisal
 27 & Ahmad Attari م ح م د ي وس ف Abdallah Q& Razi Faisal Sphingophospolipids - The backbone of sphingophospholipids is sphingosine, unlike glycerophospholipids with a glycerol as the backbone. Which contains
27 & Ahmad Attari م ح م د ي وس ف Abdallah Q& Razi Faisal Sphingophospolipids - The backbone of sphingophospholipids is sphingosine, unlike glycerophospholipids with a glycerol as the backbone. Which contains
Developmental Neuropathology
 Developmental Neuropathology Pathology, Radiology, and Clinical Correlations Reid Heffner MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Department of Pathology and Anatomy I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Developmental Neuropathology Pathology, Radiology, and Clinical Correlations Reid Heffner MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Department of Pathology and Anatomy I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Posterior fossa malformations
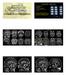 ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
 Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information
 Jame5. L.Jma5, ~reuiry Medical Conditions Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information I Not Listed later Children with medical conditions which
Jame5. L.Jma5, ~reuiry Medical Conditions Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information I Not Listed later Children with medical conditions which
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders
 The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
INTRODUCTION. 1.
 KRABBE DISEASE INTRODUCTION Krabbe disease is a genetic defect that affects the nervous system. It is caused by the shortage (deficiency) of an enzyme called galactosylceramidase. This enzyme deficiency
KRABBE DISEASE INTRODUCTION Krabbe disease is a genetic defect that affects the nervous system. It is caused by the shortage (deficiency) of an enzyme called galactosylceramidase. This enzyme deficiency
Inclusive Education. De-mystifying Intellectual Disabilities and investigating best practice.
 Inclusive Education De-mystifying Intellectual Disabilities and investigating best practice. Aims for this session: To understand what the term Intellectual Defiency means To understand the broad spectrum
Inclusive Education De-mystifying Intellectual Disabilities and investigating best practice. Aims for this session: To understand what the term Intellectual Defiency means To understand the broad spectrum
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks
 A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Spinal muscular atrophy
 27-2-8 Orofacial function of persons having Spinal muscular atrophy Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Synonyms: SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander
27-2-8 Orofacial function of persons having Spinal muscular atrophy Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Synonyms: SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]
![SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]](/thumbs/72/67086153.jpg) SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
CONV. TYPE Unspecified pervasive developmental disorder YES NO Approx. F84.9 Pervasive developmental disorder, unspecified YES YES 307.
 to Conversion Table Billing Code: Billable ICD-9/ -CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purpose Eligibility Code: ICD-9/ associated with diagnosed conditions with a high probability
to Conversion Table Billing Code: Billable ICD-9/ -CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purpose Eligibility Code: ICD-9/ associated with diagnosed conditions with a high probability
Letter of Medical Necessity The Use of SPINRAZA (nusinersen) for Spinal Muscular Atrophy
 TEMPLATE Letter of Medical Necessity The Use of SPINRAZA (nusinersen) for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Date: [Insert Name of Medical Director] RE: Patient Name [ ] [Insurance Company] Policy Number [ ] [Address]
TEMPLATE Letter of Medical Necessity The Use of SPINRAZA (nusinersen) for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Date: [Insert Name of Medical Director] RE: Patient Name [ ] [Insurance Company] Policy Number [ ] [Address]
FABRY DISEASE 12/30/2012. Ataxia-Telangiectasia. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease
 Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease ES ROACH,MD. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease Conjunctival lesions Corneal lesions Lesions of iris & lens Retinal vascular lesions
Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease ES ROACH,MD. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease Conjunctival lesions Corneal lesions Lesions of iris & lens Retinal vascular lesions
Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy. Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA
 Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA Neuroimaging in Childhood Neuroimaging issues are distinct from adults Sedation/anesthesia Motion
Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA Neuroimaging in Childhood Neuroimaging issues are distinct from adults Sedation/anesthesia Motion
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Pompe. Lysosomal Disorders. Introduction
 Introduction disease is an inherited, genetic disorder which results in the lack of an enzyme 'acid alpha-glucosidase. disease is also known as acid maltase deficiency or glycogen storage disease type
Introduction disease is an inherited, genetic disorder which results in the lack of an enzyme 'acid alpha-glucosidase. disease is also known as acid maltase deficiency or glycogen storage disease type
Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development
 Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development 201 Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development Why should caregivers know about brain development? The brain is the part of the body that allows us
Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development 201 Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development Why should caregivers know about brain development? The brain is the part of the body that allows us
RED FLAGS IN DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY. DR. Monika Bajaj Royal London Hospital
 RED FLAGS IN DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY DR. Monika Bajaj Royal London Hospital WHAT I HOPE TO COVER Red Flags in developmental milestones when to refer Cases Red flags to suspect ASD IT IS ABNORMAL IF A CHILD
RED FLAGS IN DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY DR. Monika Bajaj Royal London Hospital WHAT I HOPE TO COVER Red Flags in developmental milestones when to refer Cases Red flags to suspect ASD IT IS ABNORMAL IF A CHILD
Spinal Muscular Atrophy in 2017
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy in 2017 Leigh Maria Ramos-Platt, MD Children s Hospital of Los Angeles University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine Disclosures MDA Care Center Grant In this presentation,
Spinal Muscular Atrophy in 2017 Leigh Maria Ramos-Platt, MD Children s Hospital of Los Angeles University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine Disclosures MDA Care Center Grant In this presentation,
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: nusinersen_spinraza 03/2017 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal muscular atrophy
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: nusinersen_spinraza 03/2017 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal muscular atrophy
Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal?
 Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal? Disclosures Research funding from Natera Mary E Norton MD University of California, San Francisco Antepartum and Intrapartum Management June 15, 2017 Burden
Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal? Disclosures Research funding from Natera Mary E Norton MD University of California, San Francisco Antepartum and Intrapartum Management June 15, 2017 Burden
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Part 2: Clinical Problems
 Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Part 2: Clinical Problems Hypopituitarism Deficiencies in: Growth hormone Thyroid hormone ACTH (cortisol) Anti-diuretic hormone (diabetes insipidus) Sex hormones Hypothalamic Dysfunction:
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Part 2: Clinical Problems Hypopituitarism Deficiencies in: Growth hormone Thyroid hormone ACTH (cortisol) Anti-diuretic hormone (diabetes insipidus) Sex hormones Hypothalamic Dysfunction:
Therapy Intake Form Today's Date: General Information: Full name of child: Male/Female: Parents/Guardians Name #1: Parents/Guardians Name #2: Address:
 Inspiring Talkers 10184 E. I25 Frontage Rd. Firestone, CO 80504 720-378-6670 Therapy Intake Form Today's Date: General Information: Full name of child: DOB: Male/Female: Parents/Guardians Name #1: Parents/Guardians
Inspiring Talkers 10184 E. I25 Frontage Rd. Firestone, CO 80504 720-378-6670 Therapy Intake Form Today's Date: General Information: Full name of child: DOB: Male/Female: Parents/Guardians Name #1: Parents/Guardians
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Adrenoleukodystrophy
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Adrenoleukodystrophy 2011 NHLBI Pediatric Workshop Sept. 14, 2011 Paul Orchard, M.D. Division of Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant University of Minnesota
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Adrenoleukodystrophy 2011 NHLBI Pediatric Workshop Sept. 14, 2011 Paul Orchard, M.D. Division of Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant University of Minnesota
panel tests assessing multiple genes at the same time for the diagnosis of one or more related disorders
 NGS tests panel tests assessing multiple genes at the same time for the diagnosis of one or more related disorders UKGTN website lists 13 laboratories offering a total of 56 panel test UKGTN listed panel
NGS tests panel tests assessing multiple genes at the same time for the diagnosis of one or more related disorders UKGTN website lists 13 laboratories offering a total of 56 panel test UKGTN listed panel
Genetics of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Dr. Arianna Tucci
 Genetics of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia 1 Clinical Research Fellow Institute of Neurology University College London Hereditary spastic paraplegia: definition Clinical designation for neurologic syndromes
Genetics of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia 1 Clinical Research Fellow Institute of Neurology University College London Hereditary spastic paraplegia: definition Clinical designation for neurologic syndromes
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Contents 1 Normal Histology and Commonly Used Stains 2 Basic Pathologic Reactions
 Contents 1 Normal Histology and Commonly Used Stains.... 1 1.1 Cells of the Nervous System... 1 1.1.1 Neurons... 1 1.1.2 Astrocytes.... 2 1.1.3 Oligodendrocytes... 5 1.1.4 Schwann Cells... 5 1.1.5 Ependyma....
Contents 1 Normal Histology and Commonly Used Stains.... 1 1.1 Cells of the Nervous System... 1 1.1.1 Neurons... 1 1.1.2 Astrocytes.... 2 1.1.3 Oligodendrocytes... 5 1.1.4 Schwann Cells... 5 1.1.5 Ependyma....
Genetic Testing FOR DISEASES OF INCREASED FREQUENCY IN THE ASHKENAZI JEWISH POPULATION
 Carrier Screening and Diagnostic Testing for the Ashkenazi Jewish Population Genetic Testing FOR DISEASES OF INCREASED FREQUENCY IN THE ASHKENAZI JEWISH POPULATION Our Science. Your Care. An extensive
Carrier Screening and Diagnostic Testing for the Ashkenazi Jewish Population Genetic Testing FOR DISEASES OF INCREASED FREQUENCY IN THE ASHKENAZI JEWISH POPULATION Our Science. Your Care. An extensive
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: nusinersen_spinraza 03/2017 10/2018 10/2019 10/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal muscular atrophy
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: nusinersen_spinraza 03/2017 10/2018 10/2019 10/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal muscular atrophy
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Improving Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi Speech & Language Therapist
 Improving Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi Speech & Language Therapist Communication in ASD We will cover Typical language development Language presentation in ASD Language
Improving Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi Speech & Language Therapist Communication in ASD We will cover Typical language development Language presentation in ASD Language
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST BE FILLED OUT COMPLETELY FOR SAMPLE TO BE PROCESSED. Last First Last First
 #: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
#: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
Increased Density of the Thalamus on CT Scans in Patients with GM2 Gangliosidoses
 125 Increased Density of the Thalamus on CT Scans in Patients with GM2 Gangliosidoses Jan Brismar 1 Gudrun Brismar 2 Robert Coates 1 Generoso Gascon 3 Pinar Ozand 3 In 13 patients, the GM2 gangliosidoses,
125 Increased Density of the Thalamus on CT Scans in Patients with GM2 Gangliosidoses Jan Brismar 1 Gudrun Brismar 2 Robert Coates 1 Generoso Gascon 3 Pinar Ozand 3 In 13 patients, the GM2 gangliosidoses,
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Once a vessel is torn, blood accumulating under arterial pressure can dissect the tightly applied dura away from the inner skull surface producing a
 Once a vessel is torn, blood accumulating under arterial pressure can dissect the tightly applied dura away from the inner skull surface producing a hematoma that compresses the brain surface. - Clinically,
Once a vessel is torn, blood accumulating under arterial pressure can dissect the tightly applied dura away from the inner skull surface producing a hematoma that compresses the brain surface. - Clinically,
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Nusinersen (Spinraza)
 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Nusinersen (Spinraza) Number: 0915 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. Note: REQUIRES PRECERTIFICATION.Footnotes for Precertification of nusinersen
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Nusinersen (Spinraza) Number: 0915 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. Note: REQUIRES PRECERTIFICATION.Footnotes for Precertification of nusinersen
Transcript of learning module Developmental delay: a guide for GPs (Dur: 18' 52") You are listening to an audio module from BMJ Learning.
 Transcript of learning module Developmental delay: a guide for GPs (Dur: 18' 52") Contributors: Dianne Cottle and Mitch Blair Available online at: http://learning.bmj.com/ V/O: You are listening to an
Transcript of learning module Developmental delay: a guide for GPs (Dur: 18' 52") Contributors: Dianne Cottle and Mitch Blair Available online at: http://learning.bmj.com/ V/O: You are listening to an
Brain Imaging. Bearbeitet von Klaus Sartor, Stefan Hähnel, Bodo Kress
 Brain Imaging Bearbeitet von Klaus Sartor, Stefan Hähnel, Bodo Kress 1. Auflage 2007. Taschenbuch. 312 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 143961 1 Format (B x L): 12,5 x 19 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Sonstige
Brain Imaging Bearbeitet von Klaus Sartor, Stefan Hähnel, Bodo Kress 1. Auflage 2007. Taschenbuch. 312 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 143961 1 Format (B x L): 12,5 x 19 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Sonstige
Myelination, Leukodystrophies and Hypomyelinating Disorders. Florian Eichler, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Myelination, Leukodystrophies and Hypomyelinating Disorders Florian Eichler, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Myelin Lipid bilayer enhanced by intrinsic and extrinsic proteins
Myelination, Leukodystrophies and Hypomyelinating Disorders Florian Eichler, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Myelin Lipid bilayer enhanced by intrinsic and extrinsic proteins
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging
 5 Brain: Congenital Disease Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging modality of choice for the study of congenital brain disease. Here, T 1 -weighted scans play a dominant role. T 1 -weighted scans
5 Brain: Congenital Disease Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging modality of choice for the study of congenital brain disease. Here, T 1 -weighted scans play a dominant role. T 1 -weighted scans
9.CEREBELLAR DISEASES
 9.CEREBELLAR DISEASES (By Dr.S.UMA DEVI.MD) Diagnosis: Most important and diagnostic physical signs are: I. Ataxia- ( meaning poor coordination of movements) -gait ataxia -Truncal ataxia -Limb ataxia -
9.CEREBELLAR DISEASES (By Dr.S.UMA DEVI.MD) Diagnosis: Most important and diagnostic physical signs are: I. Ataxia- ( meaning poor coordination of movements) -gait ataxia -Truncal ataxia -Limb ataxia -
1/27/2017. Nursing Care of the Pediatric Neurosurgical Patient. Assessment is the key...
 Nursing Care of the Pediatric Neurosurgical Patient Julie Deibel, APN, NP-C, CNE Pediatric Neurosurgery Illinois Neurological Institute Assessment is the key..... Overview Consideration of development
Nursing Care of the Pediatric Neurosurgical Patient Julie Deibel, APN, NP-C, CNE Pediatric Neurosurgery Illinois Neurological Institute Assessment is the key..... Overview Consideration of development
Chiari Malformations. Google. Objectives Seventh Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/22/13. Kerry R. Crone, M.D.
 Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
