Demonstration of the Muscle Type of Intermediate Filament Protein, Desmin, as a Diagnostic Aid
|
|
|
- Cory Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Demonstration of the Muscle Type of Intermediate Filament Protein, Desmin, as a Diagnostic Aid M. MIETTINEN, MD, V.-P. LEHTO, MD, R. A. BADLEY, PhD, and I. VIRTANEN, MD From the Department of Pathology, University of Helsinki, Haartmaninkatu 3, SF Helsinki 29, Finland and Unilever Research, Colworth Laboratory, Shambrook, Bedford, United Kingdom Three cases of soft-tissue sarcomas with the characteristic histologic features of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, but lacking cytoplasmic cross-striations, were studied ultrastructurally and immunohistochemically to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the histogenesis. The results showed that it was not possible to judge the skeletal muscle derivation of the cells at the ultrastruc- tural level. However, immunohistochemically, the results ofevery case were positive for desmin-the muscle type of the intermediate filament protein. The results suggest that demonstration of desmin may be a helpful adjunct tool in the diagnosis of poorly differentiated alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas. (Am J Pathol 1982, 108: ) ALVEOLAR RHABDOMYOSARCOMA was introduced by Riopelle and Thieriault' and by Enterline and Horn2 as a round cell sarcoma with peculiar alveolar-like arrangement of the tumor cells between the fibrous septa. Larger series have since shown that only a minority of neoplasms with such histologic features show cross-striations in the cells, and thus the ascertainment of the skeletal muscle nature of these tumors has remained difficult.3 In the majority of the cases,46 the same problem also is obvious at the ultrastructural level. Therefore, it may be asked whether all these neoplasms are truly of skeletal muscle cell origin. In this report we demonstrate the presence of the desmin type of cytoskeletal intermediate filaments in 3 cases of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. The presence of these filaments reflects the muscle cell derivation of these tumors and demonstrates the usefulness of anti-desmin antibodies as a tool in the diagnosis of poorly differentiated sarcomas. Materials and Methods Three cases of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma were studied immunohistochemically and by means of light and electron microscopy. The following are short case reports. Case 1: An 11-year-old girl had a swelling at the base of the nose, and a subcutaneous tumor 2 cm in diameter was extirpated. Two local recurrences developed within a year. One of the recurrences was available for this study. Case 2: A 23-year-old woman had noticed a tumor 3 cm in diameter on her left foot. Simultaneously, she found an inguinal tumor, which was interpreted histologically as a metastasis. The tumor from the foot was extirpated and studied in detail. Case 3: A 17-year-old girl had noticed a tumor that had grown rapidly in the vulva. The tumor, which was 6 cm in diameter, was removed. The patient died 8 months later because of widespread metastases. Paraffin blocks were available for all of the tumors. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin (PTAH), and periodic acid-schiff (PAS) staining with and without prior diastase treatment was used in all cases. Supported by grants from the Finnish Medical Research Council and the Association of Finnish Life Insurance Companies. Accepted for publication April 2, Address reprint requests to M. Miettinen, MD, University of Helsinki, Haartmaninkatu 3, SF Helsinki 29, Finland /82/ $01.10 i American Association of Pathologists 246
2 Vol. 108 * No. 2 Specimens for electron-microscopic examination were taken from formalin-fixed tissue in 2 cases and from a dewaxed piece of a paraffin block in 1 case. Small tissue pieces were postfixed in 0.507o osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, at ph 7.2; dehydrated in acetone, and embedded in Epon 812. Five to 10 blocks were made in each case, and a cellular area was chosen for thin sections with the use of semithin sections of 11 1 stained with toluidine blue. Thin sections were poststained with lead citrate and uranyl acetate and examined in a Hitachi HS-7S electron microscope at an acceleration voltage of 50 kv. One block and 3-5 grids of each case were examined. Desmin was purified from chicken gizzards according to Small and Sobieszek.' Antiserum was raised in rabbits and purified on a desmin-sepharose CL4B column.8 The purified antiserum stained typically frozen sections of skeletal muscle and cultured rhabdomyosarcoma cells, but not fibroblasts or fibrosarcoma cells,10 fibrosarcoma, or adipose tissue sections ALVEOLAR RHABDOMYOSARCOMA 247 viewed by immunofluorescence microscopy. On the other hand, tumors consisting of vimentin-positive cells, like epithelioid sarcoma, were negative for desmin.9 Similarly, no cross-reactivity of the desmin antibodies with keratin, neurofilament proteins, or glial fibrillary acidic protein could be found.10 Immunohistochemical staining for desmin was performed as follows. The 3-5 ua-thick paraffin sections were deparaffinized and treated with 0.4% pepsin in 0.01 N HCl for 2 hours. Endogenous peroxidase was blocked by incubation of the slides for 30 minutes in methanol containing 0.20% H2O2. After being washed, the slides were incubated with rabbit antidesmin antibodies (25 ig/ml). The slides then were exposed to a biotinylated antirabbit immunoglobulin antiserum, (dilution 1: 500), avidin (dilution 1: 1000), and biotinylated horseradish peroxidase complex.11 The reagents were purchased from Vector Laboratories (Vectastain, Burlingame, Calif). We developed the peroxidase reaction by in- Figure 1-Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma shows round, medium-sized, relatively uniform cells with formation of alveolar or glandlike structures between the connective tissue septa. No rhabdomyoblastic features are evident light-microscopically. (H&E, x 400) (With a photographic reduction of 2%)
3 248 MIETTINEN ET AL cubating the slides in 0.01% H202 and '3- diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (Fluka AG, Buchs, Switzerland) for 10 minutes in the dark. The slides were counterstained for nuclei with Meyer's hematoxylin for 1 minute, rinsed, and mounted in Aquamount. The results of control stainings, made with preimmune serum or serum run through the desmin-sepharose 4B column, were negative. Light Microscopy Results The tumors were closely similar at the light microscopic level, showing rounded, medium-sized uniform cells with diffusely hyperchromatic nuclei, usually containing inconspicuous nucleoli and having sparse, but occasionally more copious, eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cell cohesion often was poor, and the clefts had an alveolar or glandlike appearance (Figure 1). At some areas, the tumors had a solid pattern (Figure 2). Thick fibrous septa containing blood vessels irregularly lobulated the tumor tissue. Mitoses were numerous; there were three to four in the highpower field in the cellular areas. In 2 cases, the tumor infiltrated and destroyed adjacent striated muscle tissue. Many cells showed cytoplasmic diastase-labile PAS-positivity (ie, glycogen). Cytoplasmic cross-striations after PTAH staining were not found in any of the cases. Electron Microscopy (EM) The tumor cells were uniform in appearance, having rounded nuclei and evenly distributed chromatin. The cytoplasm was sparse and contained only few organelles, such as short strands of rough endoplasmic reticulum, and few mitochondria. Clusters of polyribosomes were often numerous. In 1 case, some neoplastic cells facing the collagenous stroma were endowed with a well-defined basal lamina (external lamina) (Figure 3). No specific signs suggesting rhabdomyosarcoma, such as myofilament bundles or sarcomeres, were seen in the cells of any of the tumors. Immunohistochemical Findings AJP * August 1982 All 3 cases showed cytoplasmic desmin positivity, especially in the cells lining the alveolar clefts. Some neoplastic giant cells with abundant cytoplasmic desmin staining were seen in 1 case (Figure 4). In solid 1w -to wir "I I.4 0-0? 0 -t.4p, 4 0 Is "N. Figure 2-Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma may show a solid pattern of growth at places. (H&E, x 400)
4 Vol. 108 * No. 2 areas, the tumor cells stained positively for desmin only occasionally. The entrapped striated muscle cells were also positive for desmin (Figure 5). The results in fibrous septa were completely negative, and the background staining was minimal. Discussion The results and previous reports6 show that muscle derivation of poorly differentiated alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas is difficult to demonstrate by light and even by electron microscopy. However, the EM sampling was limited and no large cells (Figure 4) were found in the EM sections. In this study we show that desmin, the major subunit protein of the muscle type of intermediate filaments can be demonstrated immunohistochemically in paraffin-embedded tissues and used as a marker of muscle differentiation. However, desmin is not specific for skeletal muscle; it is also seen in some smooth muscle cells,"2 although not in all.'3'14 None of the histologic features of our cases, however, suggested leiomyosarcoma. ALVEOLAR RHABDOMYOSARCOMA 249 In this study, all 3 cases of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma showed positive results for desmin. Because only a portion of the cells showed positive staining, it is understandable that ultrastructural methods showed no specific features. It seems likely that immunohistologic techniques are superior to ultrastructural methods in recognizing poorly differentiated cells of skeletal muscle derivation that may lack typical ultrastructural organization. Moreover, immunohistologic techniques more easily enable a wide and rapid sampling of specimens. Recently, Gabbiani et all' have shown desmin positivity in rhabdomyosarcoma by the immunofluorescence technique, and Virtanen et al'0 showed desmin positivity in cultured rhabdomyosarcoma cells. A precaution must be taken into account, however, when one is using immunohistochemical methods. One must ascertain that the cells evaluated for the diagnosis truly are neoplastic cells, because, for example, entrapped muscle cells also stain positively for desmin. The counterstain with hematoxylin is a valuable aid in the localization of positive staining in the tumor tissue. Recently, antibodies against different types of cy- Figure 3-At the ultrastructural level, the tumor cells are poorly differentiated with sparse organelles. No structures specific for a skeletal muscle cell can be discerned. This cell, facing a connective tissue septum, is endowed by a well-defined basal lamina (arrow). C = collagen. (x 23,000) (With a photographic reduction of 2%)
5 w..m.. r. N.-`.4..,.. M,' 4 5
6 Vol. 108 * No. 2 ALVEOLAR RHABDOMYOSARCOMA 251 toskeletal intermediate filament (IMF) proteins, have been used successfully in differential diagnosis of epithelial and mesenchymal liver tumors" and in the detection of glial cells in amniotic fluid in cases of anencephaly.17'18 In a recent survey, Gabbiani et all5 even proposed IMF antibodies as a general aid in distinguishing poorly differentiated tumors, because it appeared that tumor cells retained their specific type of IMF proteins.10 Myoglobin also has been shown to be a suitable marker for skeletal muscle differentiation19'20 with the use of immunoenzymatic technique. Corson and Pinkus20 showed myoglobin-positive neoplastic cells in 5 of 7 cases of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Unlike desmin, myoglobin is specific for skeletal muscle and does not occur in smooth muscle cells. 18 It has been suggested recently that methods of immunofluorescence would be superior to methods based on immunoenzymatic techniques. 15 However, our results clearly show the usefulness of the peroxidase method in combination with conventional histologic staining, which enables the use of all histologic criteria, in addition to the immunohistochemical findings. We also found that the peroxidase technique used with untreated sections gave rather poor results, which could be markedly improved by protease treatment of the deparaffinized sections, as has been suggested previously with trypsin2'l22 and with pepsin.23 This method also appears to make it possible for one to carry out retrospective surveys using routine paraffin-embedded material. References 1. Riopelle JL, Theriault JP: Sur une forme Meconnue de sarcome des parties molles: Le rhabdomyosarcome alveolaire. Ann Anat Path 1966, 1: Enterline HT, Horn RC: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: A distinctive tumor type. Am J Clin Pathol 1958, 29: Enzinger FM, Shiraki M: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. An analysis of 110 cases. Cancer 1969, 24: Churg A, Ringus J: Ultrastructural observations on the histogenesis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer 1978, 41: Mierau GW, Favara BE: Rhabdomyosarcoma in children: Ultrastructural study of 31 cases. Cancer 1980, 46: van Haelst UJGM: General considerations on electron microscopy of tumors of soft tissues, Progress in Surgical Pathology. Vol. 2. Edited by CM Fenoglio, M Wolff. New York, Masson Publishing USA, 1980, pp Small, JV, Sobieszek A: Studies on the function and composition of the 10-nm (IOOA) filaments of vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Sci 1977, 23: Badley RA, Woods A, Carruthers L, Rees DA: Cytoskeleton changes in fibroblast adhesion and detachment. J Cell Sci 1978, 43: Miettinen M, Lehto VP, Vartio T, Virtanen I: Epithelioid sarcoma: Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features suggesting a synovial origin. Arch Pathol Lab Med (In press) 10. Virtanen I, Lehto VP, Lehtonen E, Vartio T, Stenman S, Kurki P, Wager 0, Small VJ, Dahl D, Badley RA: Expression of intermediate filaments in cultured cells. J Cell Sci 1981 :50, Guesdon JL, Ternync T, Avrameas S: The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem 1978, 27: Lazarides E: Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature 1980, 283: Frank ED, Warren L: Aortic smooth muscle cells contain vimentin instead of desmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1981:78, Gabbiani G, Schmid E, Winter S, Chaponnier C, de Chastonay C, Vandekerckhove J, Weber K, Franke WW: Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells: Predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific-type actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1981:78, Gabbiani G, Kapanci Y, Barazzone P, Franke WW: Immunohistochemical identification of intermediatesized filaments in human neoplastic cells: A diagnostic aid for the surgical pathologist. Am J Pathol 1981, 104: Bannasch P, Zerban H, Schmid E, Franke WW: Characterization of cytoskeletal components in epithelial and mesenchymal liver tumors by electron and immunofluorescence microscopy. Virchows Arch 1981:36, Aula P, von Koskull H, Teramo K, Karjalainen 0, Virtanen I, Lehto VP, Dahl D: Glial origin of rapidly adhering amniotic fluid cells. Br Med J 1980:281, von Koskull H, Virtanen I, Lehto VP, Vartio T, Dahl D, Aula P: Glial and neuronal cells in amniotic fluid of anencephalic pregnancies. Prenatal Diagnosis 1981:1, Mukai K, Rosai J, Hallaway BE: Localization of myoglobin in normal and neoplastic human skeletal muscle cells using an immunoperoxidase method. Am J Surg Pathol 1979, 3: Corson JM, Pinkus GS: Intracellular myoglobin-a specific marker for skeletal muscle differentiation in soft tissue sarcomas: An immunoperoxidase study. Am J Pathol 1981, 103: Huang SN: Immunohistochemical demonstration of hepatitis B core and surface antigens in paraffin sections. Lab Invest 1975, 33: Denk H, Radazkiewitxz T, Witting CH: Immunofluorescence studies on pathologic routine material: Application to malignant lymphomas. Beitr Pathol 1976, 159: Brozman M: Immunohistochemical analysis of formaldehyde- and trypsin- or pepsin-treated material. Acta Histochem 1978, 63: Acknowledgments The skillful technical assistance of Ms. Raili Taavela and Ms. Pipsa Kaipainen is kindly acknowledged. Figure 4-Immunohistochemical staining for desmin shows cytoplasmic positivity in many cells. A multinucleated neoplastic giant cell with ample cytoplasm shows strong positivity (arrow). (Anti-desmin, counterstain with hematoxylin, x 400) Figure 5-Immunohistochemical staining for desmin. Entrapped striated muscle cells (left) show positive staining. The solid tumor area (right) shows some positively staining cells. (Anti-desmin, counterstained with hematoxylin, x 400)
Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle tumours
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:57-61 Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle tumours DJ EVANS, IA LAMPERT, M JACOBS* From the Department of Histopathology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital,
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:57-61 Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle tumours DJ EVANS, IA LAMPERT, M JACOBS* From the Department of Histopathology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital,
An investigation of,b enolase as a histological marker of rhabdomyosarcoma
 J Clin Pathol 1984;37:905-910 An investigation of,b enolase as a histological marker of rhabdomyosarcoma JANICE A ROYDS,* S VARIEND,t WR TIMPERLEY,t CB TAYLOR* From the Department ofbiochemistry, University
J Clin Pathol 1984;37:905-910 An investigation of,b enolase as a histological marker of rhabdomyosarcoma JANICE A ROYDS,* S VARIEND,t WR TIMPERLEY,t CB TAYLOR* From the Department ofbiochemistry, University
Immunoperoxidase Localization of Keratin in Human
 Immunoperoxidase Localization of Keratin in Human Neoplasms A Preliminary Survey Richard Schlegel, MD, PhD, Susan Banks-Schlegel, PhD, Janet A. McLeod, BA, and Geraldine S. Pinkus, MD The distribution
Immunoperoxidase Localization of Keratin in Human Neoplasms A Preliminary Survey Richard Schlegel, MD, PhD, Susan Banks-Schlegel, PhD, Janet A. McLeod, BA, and Geraldine S. Pinkus, MD The distribution
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors An Immunohistochemical Study of Cellular Differentiation MARKKU MIETTINEN, M.D. Forty-five benign and 11 malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were immunohistochemically
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors An Immunohistochemical Study of Cellular Differentiation MARKKU MIETTINEN, M.D. Forty-five benign and 11 malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were immunohistochemically
R,;habdomyosarcoma, the most common
 Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Special slide seminar
 Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Ulex europaeus / Lectin as a Marker for Tumors Derived from Endothelial Cells
 Ulex europaeus / Lectin as a Marker for Tumors Derived from Endothelial Cells MARKKU MIETTINEN, M.D., HARRY HOLTHOFER, M.D., VELI-PEKKA LEHTO, M.D., AARO MIETTINEN, M.D., AND ISMO VIRTANEN, M.D. Some skin
Ulex europaeus / Lectin as a Marker for Tumors Derived from Endothelial Cells MARKKU MIETTINEN, M.D., HARRY HOLTHOFER, M.D., VELI-PEKKA LEHTO, M.D., AARO MIETTINEN, M.D., AND ISMO VIRTANEN, M.D. Some skin
TitleSarcomatoid carcinoma of the bladde.
 TitleSarcomatoid carcinoma of the bladde Author(s) Takashi, Munehisa; Sakata, Takao; N Tatsuya; Miyake, Koji Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(1): 67-70 Issue Date 1992-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/117446
TitleSarcomatoid carcinoma of the bladde Author(s) Takashi, Munehisa; Sakata, Takao; N Tatsuya; Miyake, Koji Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(1): 67-70 Issue Date 1992-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/117446
Part 1. Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013
 Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Title. Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1-2): 1- Issue Date DOI. Doc URL. Type.
 Title MYOID CELLS IN THE CALF'S THYMUS Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1-2): 1- Issue Date 1972-06 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.20.1-2.1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/1986
Title MYOID CELLS IN THE CALF'S THYMUS Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1-2): 1- Issue Date 1972-06 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.20.1-2.1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/1986
Integrated Muscle. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
Coexpression of keratin- and vimentin-type intermediate filaments
 Proc. Nati Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 80, pp. 2618-2622, May 1983 Cell Biology Coexpression of keratin- and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human metastatic carcinoma cells (metastasis/cytoskeleton/immunofluorescence)
Proc. Nati Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 80, pp. 2618-2622, May 1983 Cell Biology Coexpression of keratin- and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human metastatic carcinoma cells (metastasis/cytoskeleton/immunofluorescence)
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Pedunculated Leiomyoma of Breast: A Common Lesion at An Uncommon Location.
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 8 (2015) pp:01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Pedunculated Leiomyoma
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 8 (2015) pp:01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Pedunculated Leiomyoma
Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(3):229 233 Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma CARMEN ARDELEANU 1, 2), MARIA COMĂNESCU 3), VIOLETA COMĂNESCU 4), F. ANDREI 1) 1)
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(3):229 233 Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma CARMEN ARDELEANU 1, 2), MARIA COMĂNESCU 3), VIOLETA COMĂNESCU 4), F. ANDREI 1) 1)
Muscle Tissue. Xie Fenfen. Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Anhui Medical University
 Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
C.L. Davis Foundation Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course
 C.L. Davis Foundation 2015 Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course IHC Resources IHC Identification Targets Antibodies Antibodies 1 Antibodies Specimens Antigen Retrieval Unmasks antigen epitopes Methods
C.L. Davis Foundation 2015 Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course IHC Resources IHC Identification Targets Antibodies Antibodies 1 Antibodies Specimens Antigen Retrieval Unmasks antigen epitopes Methods
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry of Canine Round Cell Tumors
 Vet. Pathol. 24495-499 (1987) Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry of Canine Round Cell Tumors G. E. SANDUSKY, W. W. CAIUTON, AND K. A. WIGHTMAN Lilly Research Laboratories, A Division of Eli Lilly and Company,
Vet. Pathol. 24495-499 (1987) Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry of Canine Round Cell Tumors G. E. SANDUSKY, W. W. CAIUTON, AND K. A. WIGHTMAN Lilly Research Laboratories, A Division of Eli Lilly and Company,
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Division of Pathology
 Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
1/10/2018. Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation. Overview. Desmoplastic/ Spindle Cell Melanoma
 2016 MFMER slide-1 2016 MFMER slide-2 2016 MFMER slide-3 Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
2016 MFMER slide-1 2016 MFMER slide-2 2016 MFMER slide-3 Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
and glycoprotein in human bronchial glands
 Thorax, 1981, 36, 108-115 Ultrastructural localisation of lactoferrin and glycoprotein in human bronchial glands DENISE BOWES, A E CLARK, AND B CORRIN From Midhurst Medical Research Institute, Midhurst,
Thorax, 1981, 36, 108-115 Ultrastructural localisation of lactoferrin and glycoprotein in human bronchial glands DENISE BOWES, A E CLARK, AND B CORRIN From Midhurst Medical Research Institute, Midhurst,
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
HRP cytochemistry. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany
 HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes.
 DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Detection of Hepatitis A Antigen in Human Liver
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1982, p. 320-324 0019-9567/82/040320-05$02.00/0 Vol. 36, No. 1 Detection of Hepatitis A Antigen in Human Liver YOHKO K. SHIMIZU,'* TOSHIO SHIKATA,' PAUL R. BENINGER,2 MICHIO
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1982, p. 320-324 0019-9567/82/040320-05$02.00/0 Vol. 36, No. 1 Detection of Hepatitis A Antigen in Human Liver YOHKO K. SHIMIZU,'* TOSHIO SHIKATA,' PAUL R. BENINGER,2 MICHIO
I n a previous study,
 666 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Expression of smooth muscle markers in so called malignant fibrous histiocytomas T Hasegawa, F Hasegawa, T Hirose, T Sano, Y Matsuno... See end of article for authors affiliations...
666 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Expression of smooth muscle markers in so called malignant fibrous histiocytomas T Hasegawa, F Hasegawa, T Hirose, T Sano, Y Matsuno... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: 2. A. Skeletal muscle tissue ("striated muscle tissue")
 1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
A Histologic, Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study of Fibroma, Myofibroblastoma, Leiomyoma and Hemangiopericytoma in Cattle
 JARQ 38 (3), 191 197 (2004) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp A Histologic, Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study of Fibroma, Myofibroblastoma, Leiomyoma and Hemangiopericytoma in Cattle Hikaru TAKAI
JARQ 38 (3), 191 197 (2004) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp A Histologic, Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study of Fibroma, Myofibroblastoma, Leiomyoma and Hemangiopericytoma in Cattle Hikaru TAKAI
MITOSIS IN DEVELOPING CARDIAC MUSCLE. FRANCIS J. MANASEK. From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115
 Published Online: 1 April, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.37.1.191 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 30, 2018 MITOSIS IN DEVELOPING CARDIAC MUSCLE FRANCIS J. MANASEK. From the Department
Published Online: 1 April, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.37.1.191 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 30, 2018 MITOSIS IN DEVELOPING CARDIAC MUSCLE FRANCIS J. MANASEK. From the Department
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Appendix 1. A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for
 Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS
 FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1637 Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors Sridevi. V*., Susruthan Muralitharan., and Thanka. J Dept of Pathology, SriMuthukumaran Medical
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1637 Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors Sridevi. V*., Susruthan Muralitharan., and Thanka. J Dept of Pathology, SriMuthukumaran Medical
CHOLANGIOFIBROSIS INDUCED BY SHORT-TERM FEEDING OF 3'-METHYL- 4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)AZOBENZENE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVA- TION
 [GANN, 65, 249-260; June, 1974] CHOLANGIOFIBROSIS INDUCED BY SHORT-TERM FEEDING OF 3'-METHYL- 4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)AZOBENZENE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVA- TION Kiyoshi TERAO*1 and Masayuki NAKANO*2 Research
[GANN, 65, 249-260; June, 1974] CHOLANGIOFIBROSIS INDUCED BY SHORT-TERM FEEDING OF 3'-METHYL- 4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)AZOBENZENE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVA- TION Kiyoshi TERAO*1 and Masayuki NAKANO*2 Research
Endometrial Stromal Tumors
 Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
ACCME/Disclosures ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS. Tumor types with ALK rearrangements. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Jason L.
 Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Newer soft tissue entities
 Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Spontaneous Rat Malignant Tumors of Fibrohistiocytic Origin: An Ultrastructural Study
 Vet. Pathol. 19: 497-505 (1982) Spontaneous Rat Malignant Tumors of Fibrohistiocytic Origin: An Ultrastructural Study P. GREAVES, J.-M. MARTIN, and M.-T. MASSON Centre de Recherche, Laboratoires Pfizer,
Vet. Pathol. 19: 497-505 (1982) Spontaneous Rat Malignant Tumors of Fibrohistiocytic Origin: An Ultrastructural Study P. GREAVES, J.-M. MARTIN, and M.-T. MASSON Centre de Recherche, Laboratoires Pfizer,
The distribution pattern of myofibroblasts in the stroma of human bladder carcinoma depends on their invasiveness
 Histol Histopathol (2006) 21: 349-353 DOI: 10.14670/HH-21.349 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology The distribution pattern of myofibroblasts in the stroma of
Histol Histopathol (2006) 21: 349-353 DOI: 10.14670/HH-21.349 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology The distribution pattern of myofibroblasts in the stroma of
Intermediate Filaments in the Human Retina and Retinoblastoma
 Intermediate Filaments in the Human Retina and Retinoblastoma An Immunohisrochemical Study of Vimentin, Glial Fibhllory Acidic Protein, ond Neurofiiomenrs Tero Kivela,* Ahti Tarkkanen,* and Ismo Virranenf
Intermediate Filaments in the Human Retina and Retinoblastoma An Immunohisrochemical Study of Vimentin, Glial Fibhllory Acidic Protein, ond Neurofiiomenrs Tero Kivela,* Ahti Tarkkanen,* and Ismo Virranenf
Prostatic stromal hyperplasia with atypia (PSHA) is a
 Prostatic Stromal Hyperplasia With Atypia Follow-up Study of 18 Cases Deloar Hossain, MD, FRCPC; Isabelle Meiers, MD; Junqi Qian, MD; Gregory T. MacLennan, MD; David G. Bostwick, MD, MBA Context. Prostatic
Prostatic Stromal Hyperplasia With Atypia Follow-up Study of 18 Cases Deloar Hossain, MD, FRCPC; Isabelle Meiers, MD; Junqi Qian, MD; Gregory T. MacLennan, MD; David G. Bostwick, MD, MBA Context. Prostatic
INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY. Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia
 August 1969 Volume 8, Number 4 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia 7?. M. H. Pinkerton and David M. Robertson A case of dysproteinemia with corneal and conjunctival
August 1969 Volume 8, Number 4 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia 7?. M. H. Pinkerton and David M. Robertson A case of dysproteinemia with corneal and conjunctival
Tissue Reaction to Root Canal Filling Material Embedded Subcutaneously in Rats
 11 Chapter 2 Tissue Reaction to Root Canal Filling Material Embedded Subcutaneously in Rats Takanaga Ochiai Keisuke Nakano Hiromasa Hasegawa Toshiyuki Kawakami Abstract The reaction of subcutaneous connective
11 Chapter 2 Tissue Reaction to Root Canal Filling Material Embedded Subcutaneously in Rats Takanaga Ochiai Keisuke Nakano Hiromasa Hasegawa Toshiyuki Kawakami Abstract The reaction of subcutaneous connective
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in a Mare
 Vet Pathol 40:86 91 (2003) Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in a Mare K. HIRAYAMA, Y. HOA, T. SAKO, M. OKAMOTO, N. TSUNODA, M. TAGAMI, A H. TANIYAMA Abstract. A 21-year-old thoroughbred mare
Vet Pathol 40:86 91 (2003) Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in a Mare K. HIRAYAMA, Y. HOA, T. SAKO, M. OKAMOTO, N. TSUNODA, M. TAGAMI, A H. TANIYAMA Abstract. A 21-year-old thoroughbred mare
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
TUMOURS OF THE GLOMUS JUGULARE AND GLOMUS
 449 TUMOURS OF THE GLOMUS JUGULARE AND GLOMUS CAROTICUM. R. SCHADE. From the Department of Pathology, Durham University, ANewcastle-upon-Tyne. Received for publication September 12, 1953. I HAVE had opportunities
449 TUMOURS OF THE GLOMUS JUGULARE AND GLOMUS CAROTICUM. R. SCHADE. From the Department of Pathology, Durham University, ANewcastle-upon-Tyne. Received for publication September 12, 1953. I HAVE had opportunities
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Keratins of Different Molecular Weight in Exfoliated Mesothelial and Adenocarcinoma Cells An Aid to Cell Identification
 Keratins of Different Molecular Weight in Exfoliated Mesothelial and Adenocarcinoma Cells An Aid to Cell Identification ANN E. WALTS, M.D., JONATHAN W. SAID, M.B., CH.B., I. PETER SHINTAKU, PH.D., AARON
Keratins of Different Molecular Weight in Exfoliated Mesothelial and Adenocarcinoma Cells An Aid to Cell Identification ANN E. WALTS, M.D., JONATHAN W. SAID, M.B., CH.B., I. PETER SHINTAKU, PH.D., AARON
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Bilateral Renal Oncocytoma in a Greyhound Dog
 188 Brief Communications and Case Reports Vet Pathol 37:188 192 (2000) Bilateral Renal Oncocytoma in a Greyhound Dog C. D. BUERGELT AND A. ADJIRI-AWERE Abstract. A bilateral, locally invasive renal oncocytoma
188 Brief Communications and Case Reports Vet Pathol 37:188 192 (2000) Bilateral Renal Oncocytoma in a Greyhound Dog C. D. BUERGELT AND A. ADJIRI-AWERE Abstract. A bilateral, locally invasive renal oncocytoma
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Protection, Support, and Movement-Skin, Skeleton, and Muscle Notes
 I. Movement in animals A. Basics: 1. different modes of transportation (running, flying, swimming) have evolved with adaptations for animals to overcome difficulties associated with each type of locomotion
I. Movement in animals A. Basics: 1. different modes of transportation (running, flying, swimming) have evolved with adaptations for animals to overcome difficulties associated with each type of locomotion
Chapter Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function
 Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 35(3). p111-
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Malignant Mesodermal Mixed Tumor of Mwinyimtwana, Ahmed Makata; Toriyam Hideyo; Iwamoto, Masanori Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 35(3). p111- Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Malignant Mesodermal Mixed Tumor of Mwinyimtwana, Ahmed Makata; Toriyam Hideyo; Iwamoto, Masanori Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 35(3). p111- Issue Date
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2.
 Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Preface 1. Fixation and Processing 1
 Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Charles Halsey, DVM, PhD, DACVP Pfizer, Inc. IHC Resources
 Charles Halsey, DVM, PhD, DACVP Pfizer, Inc. IHC Resources 1 IHC Identification Targets Specimens Controls 2 Tissue controls Trouble Spots 3 The Key to Description IHC Description 4 Intermediate Filaments
Charles Halsey, DVM, PhD, DACVP Pfizer, Inc. IHC Resources 1 IHC Identification Targets Specimens Controls 2 Tissue controls Trouble Spots 3 The Key to Description IHC Description 4 Intermediate Filaments
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Muscle Tissue.
 Muscle Tissue Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle cell - myofiber ---extracellular ground substance: CT with BV, LV and nerve Nomenclature in muscular cell Muscular
Muscle Tissue Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle cell - myofiber ---extracellular ground substance: CT with BV, LV and nerve Nomenclature in muscular cell Muscular
Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign
 J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1173-1177 Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign and malignant cutaneous lesions RONA M MacKIE, D B CLELLAND, CHRISTINE J SKERROW From the Department ofdermatology,
J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1173-1177 Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign and malignant cutaneous lesions RONA M MacKIE, D B CLELLAND, CHRISTINE J SKERROW From the Department ofdermatology,
Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in
 J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
J. clin. Path., 1975, 28, 717-721 Immunofluorescent detection of a1-antitrypsin in paraffin embedded liver tissue M. B. RAY AND V. J. DESMET From the Laboratorium voor Histochemie en Cytochemie, Departement
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors
 Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
T to designate a rare tumor of skeletal
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL COMPARISON BETWEEN SKELETAL MUSCLE AND CARDIAC RHABDOMYOMAS JAN F. SILVERMAN, MD,*.$ SAUL KAY, MD,*$ AND C. H. CHANG, MD?-,Il The electron microscope features of three primary cardiac rhabdomyomas
ULTRASTRUCTURAL COMPARISON BETWEEN SKELETAL MUSCLE AND CARDIAC RHABDOMYOMAS JAN F. SILVERMAN, MD,*.$ SAUL KAY, MD,*$ AND C. H. CHANG, MD?-,Il The electron microscope features of three primary cardiac rhabdomyomas
Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test
 753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
Pancreas. Atrophy, acinar cell. Pathogenesis: Diagnostic key features:
 Pancreas Atrophy, acinar cell Pathogenesis: Decrease in number and/or size of acinar cells may be due to spontaneous or experimentally induced degenerative changes, apoptosis, or a sequel of chronic inflammation.
Pancreas Atrophy, acinar cell Pathogenesis: Decrease in number and/or size of acinar cells may be due to spontaneous or experimentally induced degenerative changes, apoptosis, or a sequel of chronic inflammation.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
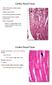 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized, formalin-fixed tissue
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 1228 1232 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl838 Advance Access publication 3 February 2007 Technical Note Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 1228 1232 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl838 Advance Access publication 3 February 2007 Technical Note Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized,
Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report
 Case Report Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report Journal of International Medical Research 2015, Vol. 43(4) 592 596!
Case Report Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report Journal of International Medical Research 2015, Vol. 43(4) 592 596!
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
