PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF ARACHNOID CYSTS
|
|
|
- Kerry Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW ARTICLE PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF ARACHNOID CYSTS Chih-Ping Chen* Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Mackay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, and Department of Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan. SUMMARY Arachnoid cysts are a rare central nervous system malformation, representing only 1% of all intracranial masses in newborns. Primary (congenital) arachnoid cysts are benign accumulation of clear fluid between the dura and the brain substance throughout the cerebrospinal axis in relation to the arachnoid membrane and do not communicate with the subarachnoid space. Secondary (acquired) arachnoid cysts result from hemorrhage, trauma, and infection and usually communicate with the subarachnoid space. The common locations of arachnoid cysts are the surface of the brain at the level of main brain fissures, such as sylvian, rolandic and interhemispheric fissures, sella turcica, the anterior cranial fossa, and the middle cranial fossa. Arachnoid cysts may be associated with ventriculomegaly and dysgenesis of corpus callosum. Prenatal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging have led to the increased diagnosis of fetal arachnoid cysts. This article provides a thorough review of fetal arachnoid cysts, including prenatal diagnosis, differential diagnosis and associated chromosomal abnormalities, as well as comprehensive illustrations of perinatal imaging findings of fetal arachnoid cysts. Prenatal diagnosis of intracranial hypoechoic lesions should include a differential diagnosis of arachnoid cysts and prompt genetic investigations. [Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2007;46(3): ] Key Words: arachnoid cysts, MRI, prenatal diagnosis, ultrasound Introduction Arachnoid cysts are a rare central nervous system malformation, representing only 1% of all intracranial masses in newborns [1]. Primary (congenital) arachnoid cysts are benign accumulation of clear fluid between the dura and the brain substance throughout the cerebrospinal axis in relation to the arachnoid membrane and do not communicate with the subarachnoid space [2]. Secondary (acquired) arachnoid cysts result from hemorrhage, trauma, and infection and usually communicate with the subarachnoid space [1,3]. The common locations of arachnoid cysts are the surface of the brain at the level of main brain fissures, such as sylvian, rolandic and interhemispheric fissures, sella turcica, the anterior cranial fossa, and the middle cranial fossa [4]. Arachnoid cysts *Correspondence to: Dr Chih-Ping Chen, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Mackay Memorial Hospital, 92, Section 2, Chung-Shan North Road, Taipei 104, Taiwan. cpc_mmh@yahoo.com Accepted: June 28, 2007 may be associated with ventriculomegaly and dysgenesis of corpus callosum [5]. Prenatal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have led to the increased diagnosis of central nervous system abnormalities of the fetuses (Figures 1 8: page , cases 1 3). Prenatal Diagnosis Fetal arachnoid cysts can be evaluated prenatally by ultrasound and/or MRI [5 21]. To date, at least 27 cases of fetal arachnoid cysts have been reported (Table). Among these, 9 cases had prenatal MRI evaluation in addition to ultrasound. The arachnoid cyst can appear as a hypoechoic lesion on prenatal ultrasound. Most of fetal arachnoid cysts were first diagnosed in the third trimester. In a few cases, the diagnosis was made in the second trimester. Bretelle et al [18] reported the first-trimester diagnosis of a posterior fossa arachnoid cyst at 13 gestational weeks by transvaginal sonographic examination. The majority of arachnoid cysts are supratentorial with sylvian fissure cysts being Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3 187
2 C.P. Chen Table. Reported cases of fetal arachnoid cysts diagnosed by ultrasound and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) GW at Authors prenatal Sonographic Location [Reference] sonographic findings diagnosis GW at Prenatal MRI prenatal MRI findings in Perinatal outcome diagnosis addition to cyst Diakoumakis et al [6] Suprasellar 32 A 3.5 cm suprasellar cystic Vaginal delivery at 37 weeks, 2,654 g, mass a 4.3 cm suprasellar arachnoid cyst 35 A 4 cm suprasellar arachnoid with hydrocephalus, a solitary seizure cyst with hydrocephalus at age 3 days, a cystoperitoneal shunt at age 19 days Meizner et al [7] Parieto-occipital 22 A cm cystic mass in Vaginal delivery at 39 weeks, 3,400 g, the right parieto-occipital lobe a 6 7 cm arachnoid cyst, no of the brain, no hydrocephalus hydrocephalus, no deficit or seizures, 38 Enlargement of the cyst up to lost to follow-up 5 4cm Raman et al [8] Posterior fossa 24 A cm posterior cranial Cesarean section at 38 weeks, 3,500 g, fossa cyst, dilation of the third a posterior fossa arachnoid cyst, ventricle ventriculomegaly, cystoperitoneal and ventriculoperitoneal shunts, recurrent seizures, death at age 2.5 months Langer et al [9] Case 1 Supratentorial, 25 A cm anechoic Vaginal delivery at 40 weeks, 3,620 g, middle cranial supratentorial mass within the an arachnoid cyst in the middle cranial fossa right parieto-occipital lobe fossa and right parieto-occipital lobe, 28 A slight increase in the diameter hydrocephalus, a cystoperitoneal of the cyst (4 cm), shunt at age 2 months, normal no ventriculomegaly development at age 18 months Case 2 Supratentorial, 32 A 6 cm supratentorial arachnoid Cesarean section at 40 weeks, 3,080 g, midline cyst in the midline, a suprasellar arachnoid cyst, mild ventricular dilation ventricular dilation, cystoperitoneal and ventriculoperitoneal shunts at age 8 days, normal development at age 20 days 188 Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3
3 Arachnoid Cysts Hogge et al [10] Posterior fossa A 1 1 cm cystic structure in Termination of pregnancy, the left posterior fossa, a prominent nose, micrognathia, compressing the right overlapping of the fingers, a thincerebellar hemisphere walled cyst compressing the right cerebellar hemisphere, a karyotype of 46,X, der(x)t(x;9)(q22;q22)mat with partial trisomy 9q and partial monosomy Xq at amniocentesis Hassan et al [11] Case 2 Midline 17 Bilateral ventriculomegaly, Termination of pregnancy at 24 weeks, a midline cystic structure in 886 g, a midline arachnoid cyst, the anterior half of the brain ventriculomegaly, no associated measuring cm malformations, a karyotype of 24 Progressive increase of the 46,XY at amniocentesis cystic size and worsening ventriculomegaly Pilu et al [12] Case 1 Midline and the 23 A large midline cyst in the Cases 1 3: One termination of anterior-middle anterior-middle third of brain, pregnancy, two delivered at term: third of brain agenesis of corpus callosum a cystoperitoneal shunt in both, Case 2 As in Case 1 32 As in Case 1 normal development at ages 6 and Case 3 As in Case 1 22 As in Case 1 9 years Case 4 Midline and the 28 A large midline cyst in posterior Cases 4 5: Delivery at term, posterior third third of brain a cystoperitoneal shunt in one case, of brain normal development at ages 2 and Case 5 As in Case 4 28 As in Case 4 7 years Case 6 Ambient cistern 22 A small cyst in ambient cistern, Termination of pregnancy, trisomy double-outlet right ventricle, 18 at prenatal diagnosis clenched hands Case 7 Ambient cistern 34 A small cyst in ambient cistern, Delivery at term, seizures, developmental agenesis of corpus callosum delay at age 4 years (continued on next page) Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3 189
4 C.P. Chen Table. (continued) GW at Authors prenatal Sonographic Location [Reference] sonographic findings diagnosis GW at Prenatal MRI prenatal MRI findings in Perinatal outcome diagnosis addition to cyst Rafferty et al [13] Middle cranial 33 Macrocephaly, right Cesarean section at 39 weeks, fossa ventriculomegaly, a 5 cm an endoscopic fenestration of the middle cranial fossa cyst on day 1, normal development arachnoid cyst at age 6 months Levine et al [14] Case 1 22 An arachnoid cyst Partial agenesis 31 of corpus callosum with absent body and splenium Case 2 Midline 20 A midline arachnoid cyst Normal corpus callosum that was not visualized by sonography Case 3 26 A large arachnoid cyst Extent of mass 27 effect on 33 surrounding 36 structures Elbers and Furness [15] Supratentorial 18.5 A large midline arachnoid cyst Cesarean section at 38 weeks, normal 30 Decrease of the cyst size development at age 2 years 32 Complete resolution of the cyst Blaicher et al [5] Case 1 Left-temporal, 39 A cm hypoechoic 39 A perisylvian Elective cesarean section, 3,495 g, perisylvian homogeneous lesion in the arachnoid cyst no neurological abnormality, normal left parietal hemisphere with no development at age 6 months compression of surrounding structures Case 2 Third ventricle cm asymmetric 34 Callosal Cesarean section at 39 weeks, 3,300 g, 190 Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3
5 Arachnoid Cysts hypoechoic homogeneous dysgenesis, repeated apneas and generalized lesion in the third ventricle normal falx seizures, anticonvulsive therapy with separating the basal ganglia, cerebri, cortical phenytoin, slightly abnormal mild bilateral dilation of pattern, development at age 5 months with the posterior horns cerebellum, diminished head control and reduced basal ganglia visual fixation and brain stem Golash et al [16] Suprasellar 17 A 2.5 cm midline cystic lesion 28 Slight dilation Elective cesarean section at 38 weeks, 24 Cyst size 3.2 cm of the occipital ventriculomegaly and macrocephaly, 28 Cyst size 3.2 cm horns of the endoscopic cystoventriculostomy lateral and cystocisternostomy, normal ventricles development at age 2 years Nakamura et al [17] Prepontine- 28 Macrocephaly, enlarged 28 A supra and Vaginal delivery at 35 weeks, suprasellar ventricles and a midline infratentorial implementation of a cyst-peritoneal cystic lesion fossae cyst shunt on day 18, endoscopic compressing cystoventriculostomy at age the brain stem 2 months, a 1-month delay of development at age 4 months Bretelle et al [18] Posterior fossa 13 An anechoic mass above the Termination at 15 weeks, 103 g, posterior fossa and between karyotype 46,XY, a posterior median the two occipital lobes arachnoid cyst, no other anomalies Souter et al [19] Case 2 Midline 25 Tetralogy of Fallot Cesarean section at 37 weeks, 1,961 g, 34 IUGR, a cm midline facial dysmorphism, inguinal hernias, intracranial arachnoid cyst, tetralogy of Fallot with a large posterior and superior to overriding aorta, MRI confirmed the thalami a cm midline arachnoid cyst, marked global developmental delay at age 13 months, a postnatal karyotype of 46,XY,der(14)t(14;20) (q32.2;p13) with a subtelomeric deletion of the distal long arm of chromosome 14. (continued on next page) Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3 191
6 C.P. Chen Table. (continued) GW at Authors prenatal Sonographic Location [Reference] sonographic findings diagnosis GW at Prenatal MRI prenatal MRI findings in Perinatal outcome diagnosis addition to cyst Kusaka et al [20] Quadrigeminal 30 An anechoic mass in the 31 No obliteration Normal vaginal delivery, no cistern quadrigeminal cistern of the cerebral hydrocephalus at age 1 year without hydrocephalus aqueduct, no communication between the ventricular system and the cyst Fujimura et al [21] Suprasellar 25 A 3-cm midline cystic lesion, 28 Confirmation of Vaginal delivery at 37 weeks, 2,844 g, no ventriculomegaly a suprasellar endoscopic cystoventriculostomy at arachnoid cyst age 5 months, normal development at age 3 years GW = gestational weeks; = no information; IUGR = intrauterine growth restriction. 192 Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3
7 Arachnoid Cysts the most common. Arachnoid cysts may progressively enlarge in utero, causing ventriculomegaly. Elbers and Furness [15] reported an unusual case of presumed arachnoid cyst diagnosed at 18.5 weeks gestation. The cyst resolved at 32 weeks gestation. Serial prenatal sonographic examinations are able to assess the size of the cyst and the ventricles. Prenatal MRI helps to demonstrate the anatomic details of other central nervous system abnormalities, such as compression of the aqueduct, communication between the cyst and the ventricles, and corpus callosum dysgenesis. Figure 1. Prenatal ultrasound of an arachnoid cyst of case 1. Prenatal ultrasound at 32 weeks gestation revealed a cm midline interhemispheric hypoechoic homogeneous lesion. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 33 gestational weeks showed a left interhemispheric arachnoid cyst, marked dysgenesis of the corpus callosum, and colpocephaly. The karyotype was 46,XY. A 2,788-g male baby was delivered at 37 weeks gestation. Postnatal MRI confirmed the prenatal diagnosis. A cystoperitoneal shunt was performed at age 7 months. The infant was doing well at age 1 year and 2 months. Differential Diagnosis Prenatal diagnosis of intracranial hypoechoic cystic lesions should include a differential diagnosis of arachnoid cysts, porencephalic cysts, glioependymal cysts, choroid plexus cysts, aneurysms of the vein of Galen, schizencephaly, cystic neoplasms, and intracranial hemorrhage [12]. A B C Figure 2. (A) Sagittal, (B) axial and (C) coronal views of magnetic resonance imaging of case 1 at 33 weeks gestation. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3 193
8 C.P. Chen A B Figure 3. (A) Sagittal and (B) axial views of postnatal magnetic resonance imaging of case 1 at age 3 days. fibrous walls. Glioependymal cysts may have a mass effect and are often associated with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Choroid plexus cysts Choroid plexus cysts, unilateral or bilateral, are frequently detected in the second trimester. Choroid plexus cysts are sonolucent cysts within the choroids plexus of the lateral ventricle. Large choroid plexus cysts may be associated with trisomy 18. Figure 4. Prenatal ultrasound of an arachnoid cyst of case 2. Prenatal ultrasound of case 2 at 31 weeks gestation revealed a cm left interhemispheric hypoechoic homogeneous lesion. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 32 weeks gestation showed a left interhemispheric arachnoid cyst and colpocephaly. A 2,620-g male baby was delivered at term. Postnatal MRI confirmed the prenatal diagnosis. The size of the arachnoid cyst was measured about cm. There was a left-to-right midline shift. A cystoperitoneal shunt was performed at age 8 months. The child was doing well at age of 3 years and 4 months. Porencephalic cysts Porencephalic cysts are usually unilateral and communicate with the ventricular system with a cavity lined with white matter. Porencephalic cysts result from infarction of the brain secondary to vascular insults, trauma, infection, hemorrhage, or monochorionic monozygotic twin twin transfusion. In contrast, arachnoid cysts are usually asymmetric and smooth-walled; they do not communicate with the ventricular system and have a mass effect. Glioependymal cysts Glioependymal cysts are usually multilocular and located within the brain parenchyma. Glioependymal cysts have an ependymal lining, whereas, arachnoid cysts have Aneurysms of the vein of Galen Aneurysms of the vein of Galen are vascular anomalies of the vein of Galen located in the brain deeply and posteriorly to the thalami and in the subarachnoid space. Color Doppler is helpful for the diagnosis of aneurysms of the vein of Galen. Prenatal sonographic detection of fluid-filled lesions in the posterior third of the brain, which are found in association with hydrops fetalis, ventriculomegaly, porencephaly, single umbilical artery, chorioangioma or limb reduction defects, should raise the suspicion of aneurysms of the vein of Galen. Schizencephaly Schizencephaly or true porencephaly is characterized by unilateral, asymmetric or bilateral congenital fullthickness clefts of the cerebral mantle. Schizencephaly may or may not communicate with the ventricular system and are lined by gray matter. Schizencephaly can be associated with ventriculomegaly, polymicrogyria, heterotopias, agenesis of the corpus callosum, absent septum pellucidum, and optic nerve hypoplasia. Cystic neoplasms Cystic neoplasms, such as cystic teratoma and cystic astrocytoma, consist of solid and irregular cystic components and have a mass effect. 194 Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3
9 Arachnoid Cysts A B C Figure 5. (A) Sagittal, (B) axial and (C) coronal views of magnetic resonance imaging of case 2 at 32 weeks gestation. Intracranial hemorrhage Intracranial hemorrhage usually occurs in the subependymal germinal matrix region and is associated with hypoxia, platelet disorders, coagulopathy, alterations in cerebral blood pressure in the case of twin twin transfusion or demise of a monozygotic co-twin, fetomaternal hemorrhage, and maternal medications. Intracranial hemorrhage may initially present echogenic blood clots in the ventricles and subsequently lead to ventricular dilation. Chromosomal Abnormalities Associated with Congenital Arachnoid Cysts Fetal arachnoid cysts can be associated with chromosomal abnormalities. Therefore, prenatal diagnosis of an arachnoid cyst, especially in association with structural abnormalities, should prompt a cytogenetic investigation. Various associated chromosomal abnormalities have been reported. For instance, Hogge et al [10] reported partial trisomy 9q (9q22 qter) and partial monosomy Xq (Xq22 qter) in a fetus with an infratentorial arachnoid cyst. The fetus postnatally manifested a prominent nose, micrognathia, overlapping of the fingers, and a thin-walled cyst compressing the right cerebellar hemisphere. Souter et al [19] reported a subtelomeric deletion of the distal long arm of chromosome 14, i.e. monosomy 14q (14q32.3 qter), in a fetus with tetralogy of Fallot, intrauterine growth restriction, and a midline intracranial arachnoid cyst. The infant postnatally manifested facial dysmorphism, inguinal hernias, tetralogy of Fallot, a midline arachnoid cyst, and marked global developmental delay. Pilu et al [12] reported trisomy 18 in a fetus with a small arachnoid cyst in the ambient cistern, a double-outlet right ventricle, and clenched hands. Elbers and Furness [15] additionally reported their experience of the association of triploidy with a fetus with an arachnoid cyst. Fetal Outcome The prognosis of fetal arachnoid cysts is dependent on the presence or absence of the corpus callosum, the presence or absence of other congenital malformations, parenchymal hemorrhages, the rate of the growth of the cyst, and progression of ventriculomegaly. Fetal Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3 195
10 C.P. Chen A B C Figure 6. (A) Sagittal, (B) axial and (C) coronal views of postnatal magnetic resonance imaging of case 2. Figure 7. Prenatal ultrasound of an arachnoid cyst of case 3. Prenatal ultrasound of case 3 at 23 weeks gestation revealed a cm midline interhemispheric hypoechoic homogeneous lesion. The karyotype was 46,XY. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 24 weeks gestation showed an interhemispheric arachnoid cyst and dysgenesis of the corpus callosum. Progression of the cyst was noted in late gestation. A 2,350-g male baby was delivered prematurely at 28 weeks gestation. Postnatal MRI confirmed the prenatal diagnosis. A cystoperitoneal shunt was performed at age of 1 week. The child was doing well at age 4 years. arachnoid cysts without associated structural anomalies or chromosomal abnormalities can have a favorable outcome. In some cases with rapid progression of the lesion and ventriculomegaly, appropriate pediatric surgical therapy may be required in early infancy. Currently, postnatal endoscopic cystoventriculostomy and cystocisternostomy have become less invasive surgical alternatives [16,17,21]. The prognosis of fetal intracranial cysts has been shown to rely on the brain integrity rather than the cyst volume or location [22]. Therefore, in order to establish the correct prognosis and intellectual outcome of fetuses with arachnoid cysts, MRI is an important adjunct to ultrasound and helps to optimize neonatal management by accurate determination of the fetal anatomy and objective perinatal counseling. Conclusion This article provides a thorough review of fetal arachnoid cysts, including prenatal diagnosis, differential diagnosis and associated chromosomal abnormalities, as well as 196 Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3
11 Arachnoid Cysts A B C Figure 8. (A) Sagittal, (B) axial, and (C) coronal views of magnetic resonance imaging of case 3 at 24 weeks gestation. comprehensive illustrations of perinatal imaging findings of fetal arachnoid cysts. Prenatal diagnosis of intracranial hypoechoic lesions should include a differential diagnosis of arachnoid cysts and prompt genetic investigations. References 1. Robinson RG. Congenital cysts of the brain: arachnoid malformations. Prog Neurol Surg 1971;4: Pascual-Castroviejo I, Roche MC, Martinez Bermejo A, Arcas J, Garcia Blazquez M. Primary intracranial arachnoidal cysts: a study of 67 childhood cases. Childs Nerv Syst 1991;7: Oliver LC. Primary arachnoid cysts: report of two cases. Br Med J 1958;1: Wester K. Peculiarities of intracranial arachnoid cysts: location, sidedness, and sex distribution in 126 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery 1999;45: Blaicher W, Prayer D, Kuhle S, Deutinger J, Bernaschek G. Combined prenatal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in two fetuses with suspected arachnoid cysts. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18: Diakoumakis EE, Weinberg B, Mollin J. Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of a suprasellar arachnoid cyst. J Ultrasound Med 1986;5: Meizner I, Barki Y, Tadmor R, Katz M. In utero ultrasonic detection of fetal arachnoid cyst. J Clin Ultrasound 1988;16: Raman S, Rachagan SP, Lim CT. Prenatal diagnosis of a posterior fossa cyst. J Clin Ultrasound 1991;19: Langer B, Haddad J, Favre R, Frigue V, Schlaeder G. Fetal arachnoid cyst: report of two cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4: Hogge WA, Schnatterly P, Ferguson JE 2nd. Early prenatal diagnosis of an infratentorial arachnoid cyst: association with an unbalanced translocation. Prenat Diagn 1995;15: Hassan J, Sepulveda W, Teixeira J, Cox PM. Glioependymal and arachnoid cysts: unusual causes of early ventriculomegaly in utero. Prenat Diagn 1996;16: Pilu G, Falco P, Perolo A, Sandri F, Cocchi G, Ancora G, Bovicelli L. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal intracranial hypoechoic lesions: report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9: Rafferty PG, Britton J, Penna L, Ville Y. Prenatal diagnosis of a large fetal arachnoid cyst. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998; 12: Levine D, Barnes PD, Madsen JR, Abbott J, Mehta T, Edelman RR. Central nervous system abnormalities assessed with prenatal magnetic resonance imaging. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94: Elbers SEL, Furness ME. Resolution of presumed arachnoid cyst in utero. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;14: Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3 197
12 C.P. Chen 16. Golash A, Mitchell G, Mallucci C, May P, Pilling D. Prenatal diagnosis of suprasellar arachnoid cyst and postnatal endoscopic treatment. Childs Nerv Syst 2001;17: Nakamura Y, Mizukawa K, Yamamoto K, Nagashima T. Endoscopic treatment for a huge neonatal prepontinesuprasellar arachnoid cyst: a case report. Pediatr Neurosurg 2001;35: Bretelle F, Senat MV, Bernard JP, Hillion Y, Ville Y. Firsttrimester diagnosis of fetal arachnoid cyst: prenatal implication. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;20: Souter VL, Glass IA, Chapman DB, Raff ML, Parisi MA, Opheim KE, Disteche CM. Multiple fetal anomalies associated with subtle subtelomeric chromosomal rearrangements. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21: Kusaka Y, Luedemann W, Oi S, Shwardfegar R, Samii M. Fetal arachnoid cyst of the quadrigeminal cistern in MRI and ultrasound. Childs Nerv Syst 2005;21: Fujimura J, Shima Y, Arai H, Ogawa R, Fukunaga Y. Management of a suprasellar arachnoid cyst identified using prenatal sonography. J Clin Ultrasound 2006;34: Pierre-Kahn A, Hanlo P, Sonigo P, Parisot D, McConnell RS. The contribution of prenatal diagnosis to the understanding of malformative intracranial cysts: state of the art. Childs Nerv Syst 2000;16: Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol September 2007 Vol 46 No 3
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
GLIOEPENDYMAL AND ARACHNOID CYSTS: UNUSUAL CAUSES OF EARLY VENTRICULOMEGALY IN UTERO
 PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS, VOL. 16: 729-733 (1996) SHORT COMMUNICATION GLIOEPENDYMAL AND ARACHNOID CYSTS: UNUSUAL CAUSES OF EARLY VENTRICULOMEGALY IN UTERO JAMIYAH HASSAN*, WALDO SEPULVEDA*, JERONIMA TEIXEIRA*
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS, VOL. 16: 729-733 (1996) SHORT COMMUNICATION GLIOEPENDYMAL AND ARACHNOID CYSTS: UNUSUAL CAUSES OF EARLY VENTRICULOMEGALY IN UTERO JAMIYAH HASSAN*, WALDO SEPULVEDA*, JERONIMA TEIXEIRA*
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
Prevalence of "Compressed" and Asymmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic
 Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Cavum velum interpositum cyst causing symptomatic trapped ventricle: A case report
 Cavum velum interpositum cyst causing symptomatic trapped ventricle: A case report Poster No: R-0286 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T Singh, S Dupre; NAMBOUR/AU Keywords: CNS, Neuroradiology
Cavum velum interpositum cyst causing symptomatic trapped ventricle: A case report Poster No: R-0286 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T Singh, S Dupre; NAMBOUR/AU Keywords: CNS, Neuroradiology
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Isolated Choroid Plexus Cyst
 Isolated Choroid Plexus Cyst This guideline was updated in April 2015 by Dr Joana De Sousa, with input from members of the New Zealand Maternal Fetal Medicine Network. Background Midtrimester soft markers
Isolated Choroid Plexus Cyst This guideline was updated in April 2015 by Dr Joana De Sousa, with input from members of the New Zealand Maternal Fetal Medicine Network. Background Midtrimester soft markers
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Torch Infections and Prenatal Ultrasound Findings
 Tutorial [1] August 09, 2011 By Eran Casiff, MD [2] TORCH INFECTIONS AND PRENATAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Eran Casiff M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Kaplan Medical Center Rehovot 76100, Israel
Tutorial [1] August 09, 2011 By Eran Casiff, MD [2] TORCH INFECTIONS AND PRENATAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Eran Casiff M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Kaplan Medical Center Rehovot 76100, Israel
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review
 Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects
 Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management?
 Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
KYAMC Journal Vol. 8, No.-1, July Two Cases of Holoprosencephalies
 Case Report Two Cases of Holoprosencephalies Sharif M M 1, Parvin K 2, Rahman M T 3, Ullah N 4, Islam S 5 Abstract Two pregnant women with around 33-34 weeks of gestation were reported to Gynaecology and
Case Report Two Cases of Holoprosencephalies Sharif M M 1, Parvin K 2, Rahman M T 3, Ullah N 4, Islam S 5 Abstract Two pregnant women with around 33-34 weeks of gestation were reported to Gynaecology and
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI)
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGE PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Porencephalic cyst Mugtaba Alghazali, Ikhlas Abdelaziz, Hatim Zain Alabdeen ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images International
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGE PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Porencephalic cyst Mugtaba Alghazali, Ikhlas Abdelaziz, Hatim Zain Alabdeen ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images International
A Rare Aggressive Fetal Intracranial Tumor
 J. Fetal Med. (June 2015) 2:91 95 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0046-y BRIEF COMMUNICATION A Rare Aggressive Fetal Intracranial Tumor Ravi Kapoor 1 Ashutosh Bansal 1 Aakriti Kapoor Aggarwal 2 Abhinav Aggarwal
J. Fetal Med. (June 2015) 2:91 95 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0046-y BRIEF COMMUNICATION A Rare Aggressive Fetal Intracranial Tumor Ravi Kapoor 1 Ashutosh Bansal 1 Aakriti Kapoor Aggarwal 2 Abhinav Aggarwal
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy. Basic Training
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
Nationwide Survey of the Etiology and Associated Conditions of Prenatally and Postnatally Diagnosed Congenital Hydrocephalus in Japan
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 47, 448 452, 2007 Nationwide Survey of the Etiology and Associated Conditions of Prenatally and Postnatally Diagnosed Congenital Hydrocephalus in Japan Kouzo MORITAKE, HidemasaNAGAI,
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 47, 448 452, 2007 Nationwide Survey of the Etiology and Associated Conditions of Prenatally and Postnatally Diagnosed Congenital Hydrocephalus in Japan Kouzo MORITAKE, HidemasaNAGAI,
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
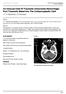 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
Chapter 3. Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance
 Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Diagnosis and Management of a Vein of Galen Malformation in a Neonate
 86 JDMS 26:86-90 March/April 2010 Diagnosis and Management of a Vein of Galen Malformation in a Neonate STACY L. FRENCH, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Vein of Galen arterial malformation (VGAM) is an arteriovenous
86 JDMS 26:86-90 March/April 2010 Diagnosis and Management of a Vein of Galen Malformation in a Neonate STACY L. FRENCH, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Vein of Galen arterial malformation (VGAM) is an arteriovenous
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov Dandy-Walker Malformation
 REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
Suprasellar Arachnoid Cysts. Wan Tew SEOW FRACS Singapore
 Suprasellar Arachnoid Cysts Wan Tew SEOW FRACS Singapore Distribution Intracranial Arachnoid Cysts Sylvian fissure 49% CPA 11% Quadrigeminal 10% Vermian 9% Sellar and suprasellar 9% Interhemispheric 5%
Suprasellar Arachnoid Cysts Wan Tew SEOW FRACS Singapore Distribution Intracranial Arachnoid Cysts Sylvian fissure 49% CPA 11% Quadrigeminal 10% Vermian 9% Sellar and suprasellar 9% Interhemispheric 5%
Sonographic Characteristics of the Cavum Velum Interpositum
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1631 1635, October 1998 Sonographic Characteristics of the Cavum Velum Interpositum Cheng-Yu Chen, Fu-Hwa Chen, Chueng-Chen Lee, Kwo-Whei Lee, and Hai-Sung Hsiao BACKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1631 1635, October 1998 Sonographic Characteristics of the Cavum Velum Interpositum Cheng-Yu Chen, Fu-Hwa Chen, Chueng-Chen Lee, Kwo-Whei Lee, and Hai-Sung Hsiao BACKGROUND AND
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES)
 HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome
 Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 02 Page February 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42 cases
 Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants
 253 Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants Bokyung K. Han 1 Diane S. Babcock Alan E. Oestreich Cranial sonograms of six children with brain tumors (one newborn, four infants, and one 4-year-old child) are
253 Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants Bokyung K. Han 1 Diane S. Babcock Alan E. Oestreich Cranial sonograms of six children with brain tumors (one newborn, four infants, and one 4-year-old child) are
2 Case report. 1 Introduction. Case Report. Snezana Crnogorac, Aleksandra Vuksanovic Bozaric* Galen vein aneurysm challenge for treatment
 Open Med. 2017; 12: 440-445 Case Report Snezana Crnogorac, Aleksandra Vuksanovic Bozaric* Galen vein aneurysm challenge for treatment https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2017-0054 received February 6, 2017; accepted
Open Med. 2017; 12: 440-445 Case Report Snezana Crnogorac, Aleksandra Vuksanovic Bozaric* Galen vein aneurysm challenge for treatment https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2017-0054 received February 6, 2017; accepted
The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease. Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc.
 The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc. Seattle, WA embryology We recognize the VACTERL association and frequency of
The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc. Seattle, WA embryology We recognize the VACTERL association and frequency of
Cribside Neurosonography:
 501 Cribside Neurosonography: Real-Time Sonography for Intracranial Investigation of the Neonate Mary K. Edwards 1 David L. Brown 1 Jans Muller Charles B. Grossman 1 Gonzalo T. Chua 1 prospective study
501 Cribside Neurosonography: Real-Time Sonography for Intracranial Investigation of the Neonate Mary K. Edwards 1 David L. Brown 1 Jans Muller Charles B. Grossman 1 Gonzalo T. Chua 1 prospective study
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal macrocephaly: cerebral PNET or neuroblastoma. cause
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal macrocephaly: cerebral PNET or neuroblastoma as an infrequent cause May 2006 2 Kaczala G, Poskitt K, Steinbok P, Hendson G, Phang M, Solimano A, British Columbia Children
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal macrocephaly: cerebral PNET or neuroblastoma as an infrequent cause May 2006 2 Kaczala G, Poskitt K, Steinbok P, Hendson G, Phang M, Solimano A, British Columbia Children
Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY N.K. Anand A.K. Gupta I.M.S. Lamba ABSTRACT Pattern of neurosonographic (NSG) abnormalities in 150 term
Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY N.K. Anand A.K. Gupta I.M.S. Lamba ABSTRACT Pattern of neurosonographic (NSG) abnormalities in 150 term
RESEARCH ARTICLE RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN RASHT PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
 RESEARCH ARTICLE RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN RASHT PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Elham BIDABADI MD Assistant Professor of Pediatric Neurology, Guilan University of Medical Sciences,Guilan,Iran Corresponding
RESEARCH ARTICLE RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN RASHT PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Elham BIDABADI MD Assistant Professor of Pediatric Neurology, Guilan University of Medical Sciences,Guilan,Iran Corresponding
P rominent Extraaxial CSF Space on Cranial Ultra s o u n d in Infants: C o r relation with Neuro d evelopmental Outc o m e 1
 P rominent Extraaxial CSF Space on Cranial Ultra s o u n d in Infants: C o r relation with Neuro d evelopmental Outc o m e 1 Bokyung Kim Han, M.D., Mu n hyang Lee, M.D. 2, Hye - Kyung Yoon, M.D., Kyung-Jae
P rominent Extraaxial CSF Space on Cranial Ultra s o u n d in Infants: C o r relation with Neuro d evelopmental Outc o m e 1 Bokyung Kim Han, M.D., Mu n hyang Lee, M.D. 2, Hye - Kyung Yoon, M.D., Kyung-Jae
Sectional Anatomy Head Practice Problems
 1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review
 Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
4/19/2018. St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT
 St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
Pathological reaction to disease
 Chapter1 Pathological reaction to disease Normal anatomy Figures 1.1 1.6 2 4 Brain swelling and internal herniation Figures 1.7 1.15 5 9 Epilepsy Figures 1.16 1.18 9 10 Cerebellar atrophy Figures 1.19
Chapter1 Pathological reaction to disease Normal anatomy Figures 1.1 1.6 2 4 Brain swelling and internal herniation Figures 1.7 1.15 5 9 Epilepsy Figures 1.16 1.18 9 10 Cerebellar atrophy Figures 1.19
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Central Nervous System Malformations
 Review rticle Central 10.5005/jp-journals-10009-1472 Nervous System Malformations 1 D ddario Vincenzo, 2 Capuano Pasquale STRCT Ultrasound (US) is a useful tool to evaluate the normal morphology, the developmental
Review rticle Central 10.5005/jp-journals-10009-1472 Nervous System Malformations 1 D ddario Vincenzo, 2 Capuano Pasquale STRCT Ultrasound (US) is a useful tool to evaluate the normal morphology, the developmental
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
The Fetal Cardiology Program
 The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Elliott Sherr, MD University of California, San Francisco
 University of California, San Francisco ACC AND A SSOCIATED F EATURES MRI features associated with ACC Clinical diagnoses found in individuals with ACC Clinical Syndromes in which ACC is a component or
University of California, San Francisco ACC AND A SSOCIATED F EATURES MRI features associated with ACC Clinical diagnoses found in individuals with ACC Clinical Syndromes in which ACC is a component or
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain
 The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems. Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017
 Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017 Not the heart Dextroposition Heart in the right chest with the apex to the left Often caused by left sided chest mass
Bits and Bobs secondary causes of heart problems Dr Angela McBrien 9 th September 2017 Not the heart Dextroposition Heart in the right chest with the apex to the left Often caused by left sided chest mass
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
