STUDIES ON THE NEOPLASTIC GROWTH IN FISH JOHNIUS DUSSUMIERI (VALENCIENNES, 18883) DUE TO UNKNOWN ETIOLOGY
|
|
|
- Diana Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. Biol. Res., 2(1): 33-37, STUDIES ON THE NEOPLASTIC GROWTH IN FISH JOHNIUS DUSSUMIERI (VALENCIENNES, 18883) DUE TO UNKNOWN ETIOLOGY Rakhshinda Khurram Khan 1, Nasira Khatoon 1*, Rizwana, A. G. 1 and Aly Khan 2 1 Department of Zoology, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. 2 CDRI, PARC, University of Karachi , Pakistan. * Corresponding author nasira_parvez@yahoo.com ABSTRACT The word tumor has often been used generally to signify any hump or swelling. But, scientifically the tumor is defined as new growth of cells which deviate from normal surrounding cells in shape, size, structure and organization. Fishes may also be susceptible to such tumourous growth like many other vertebrates especially the mammals, as observed in the present studies. The fishes were collected from different fish markets in Karachi. A total of 538 fishes specimens Johnius dussumieri (Valenciennes, 1833) were examined for neoplastic growth. Out of 538 fishes 50 were found with tumourous growth, in the epithelial and mesenchymal layers. The etiology and factors which could be responsible for tumour or neoplastic growth are, however, unknown. In gross pathology tumourous region is rich in connective tissue and the tumour considerably deforms and compresses the viscera due to its extensive growth. Here, the tumour was well demonstrated, separated from the surrounding organs but showed no sign of proliferation. No haemorrhage was observed on the tumour or in the organs. The macroscopic appearance of their surface was smooth. Histopathologically, the tumour showed malpighian cells, atrophied cells, hyperplasia and fibrosis with eosinophilia and inflammatory cells infiltration. KEY WORDS: Histology, Neoplastic growth, Fish, Unknown etiology, Malpighian cells, Hyperplasia. INTRODUCTION Fishes have economic value all over the world. Marine fishes are important source of protein and organic products without deposition of cholesterol. Fishes are highly valueable because of their delicious taste. Doctors suggest fish meat to the patients suffering from hypertension and heart disease. Fish meat may become affected by various pathogens like viruses, bacteria, parasites and also by neoplastic growth. In recent medical terminology, a tumour is defined as neoplasm and cancer and is often used in an alternative way. Generally, the term cancer refers as a malignant disease in which the cancer, unless safe by medical treatment, has the capacity to infiltrate and disseminate throughout the body (metastasize), finally killing the host. The neoplasia defined (the disease process) and neoplasm (a tumour), include both the malignant and non-malignant (benign) forms of the disease. The term neoplasia are defined by their "an abnormal growth of cells, which by proliferation, press upon, infiltrate, healthy tissues, thereby damaging of cells and organs and affecting the physiological functions, resulting ultimately in the death of an animal". In fish, as in mammals, neoplasm is recognized as a particular range of growth potentials from those that seems to be very-slow growing and localized, to that part and those are obviously infiltrate the host's tissues and are eventually recognized to be a cancerous (Black, 1984). According to Robert (1978) known and suspected factors studied to tumour formation in fish include viruses, chemical or biological toxins, physical agents and immunological competence of the host. Various fishes of Karachi coast have tumorous growth. Most of the general disease conditions that are reported in mammals, e.g. inflammation, wound repair, hemorrhage, necrosis, septicemia, atrophy, metaplasia, hyperplasia, and neoplasia, (Pathologically neoplasia is called tumour) are also present in fishes. MATERIALS AND METHODS Live as well as freshly killed specimens of Johnius. dussumieri were collected from various markets like Fisheries, West Wharf, Empress Market and other local Markets. Selection criterion of a specimen was to select older fish to optimize the possibility of finding neoplasms. A total of 538 fishes were dissected out of which 50were found to be suffering from neoplastic growth. The selected tissues with neoplastic growth were fixed in 10% formalin for 24 hours, and then washed with graded series of alcohols. Tissues were then cleared by cedar wood oil by placing them for 6-12 hours, and then bath in xylene followed to remove excess oil. After the removal of excess oil the tissue were embedded in paraffin wax (melting point 60% ) for 24 hours, wax block were made and the sections were cut (6 8 microns thick ) were stained to bring difference among the tissue components by staining later counter staining using haemotoxylin and eosin and mounting permanently in Canada balsam. Photographs were taken with Nikon (Optiphot 2) photomicroscope and Fuji colour film was used. Selected photographs are presented here in support of observations.
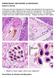
2 34 Rakhshinda Khurram Khan et al., OBSERVATIONS Fish like other vertebrates are frequently affected by neoplastic proliferations. These are classified according to mammalian tumour classifications. Most commonly the skin neoplasia as papillomas, fibromas and fibrosarcomas are diagnosed. Few published cases of neoplasm include papillomas, squamous cells carcinomas, fibromas, chondromas and branchiocarcinomas. (Martineau and Ferguson, 2006, Thatcher and Varella 1980, Wildgoose, 1992, Wildgoose and Bucke, 1995). Specimen of J. dussumieri (Valenciennes, 1833) brought to the Parasitology Laboratory, Department of Zoology University of Karachi with obvious enlarged abdomen (Fig. 1). Autopsy revealed a large rounded and greyish tumour growing from visceral mesentries (Figs. 2-3). They occur in the lower edge of the operculum and the ventral edge of the body near the anus, this kind of tumour has not been observed in any other part of the body. Tumour region is rich in connective tissue and the tumour considerably deformed and compressed the viscera due to the extensive growth of tumour. The tumour was well demonstrated, separated from the surrounding organs and showed no sign of proliferation. No haemorrhage was observed on the tumour or on the organs. There were two basic component of the tumour structure: epithelial and mesenchymal. The prevailing epithelial components were at different stages of development. Besides the comparatively well developed and regular structure of tubules, glandular formations at a lower degree of differentiation were seen with the development of small cyst and adenopapillary formations passing into mesenchymal formations. The macroscopic appearances of their surface were smooth. The larger tumours were folded at the surface which corresponded, to their papillomatous characteristics a lobed branching stroma supported by collagen covered by hyperplastic epidermal tissue (Fig. 3). In the epidermal parts high prismatic basal cells prevailed (Fig. 4). All the three layers were packed close together with the intermediate layer showing significant loss of intarcellular contact (Fig. 5). In the later situation the formation of numerous intercellular spaces gives the tissue a spongy appearance (Figs. 6-7). While the tumour cells in close contact with each other resemble the malpighian cells of normal epidermis (Fig. 8). The cells of spongy regions are greatly altered (Figs. 9-10). As tumour development progresses some of the surrounding cells show absolutely no division activity from the greatest part of the epidermal tumour tissue, but they remain separated from each other from the basal lamina and from the external tumour surface by filament containing the tumour cells of malpighian character (envelope cells) (Fig. 11). As tumour increases in size, increasing numbers of the epidermal tumour cells of malpighian character change into rounded to oval voluminous cells as observed earlier. (Brook et al., 1969) (Fig. 12). Numerous strongly contrasting particles of various shapes and sizes are conspicuous. Inflammatory cells also appeared in the connective tissue of nodules along with undifferentiated mesenchymal cells and fibrosis other than fibroblasts (Fig. 13) are prevalent similar to the finding of (Peters et al., 1978) cells containing eosinophilic granules were also a component tumours (Vicha and Schmale, 1994) (Fig. 14) DISCUSSION To date three kinds of skin papillomatic growth have been observed. These can clearly be distinguished structurally as: 1. Flat (Fish pox) like growth with low connective tissue content. 2. Prominent growths with distinct collagen rich stroma and 3. Complex papillomas, the epidermal portion of which is composed of a characteristic arrangement of a rounded cells and smaller cells of malpighian character (envelope cells) in between. The first two types correspond to the widely distributed kinds of simple fish papilloma are composed purely of cells of Malpighian character. Substantial evidence indicates that the structural differences of the three types depend much less on the difference in the reaction patterns of the species involved than on the kind and method in which the tumours causing stimuli operates. The first type of tumour is found both in the dab and in the plaice. The second type appears in various Atlantic and pacific species, forming in the same manner. The complex type-3 seems to be limited to pacific specices although a series of genera with closely related species occurs in the both oceans (Peters and Watermann, 1979). Type-1 and type-2 tumours are most of the time observed in flat fishes of both Atlantic and Pacific oceans. But in Arabian ocean type-3 tumour was observed in J. dussumeri. It is of concerns regarding the reason for the cause of the tumour in this fish, and one of the reasons could be tumour in the prevalence of trematode infection which leads to the biochemical change which in turn originate the tumour or the other possibility could be the pollutants in water responsible for such type of growth in water as reported earlier by Dethlefsen (1978) for fish pox growth in most of fishes. In Arabian Sea this type of growth have been observed in J. dussumeri while this type of growth was also observed in fishes of Japanese coastal water, in Pacific and Atlantic coast. It can thus be concluded that the trematodes along with the pollutants in the water were responsible for promoting tumours. It is difficult to suggest that either of the two were solely responsible for promoting tumour development in J. dussumieri.
3 Studies on the neoplastic growth in fish 35 Fig. 1. Specimen of Johnius dussumieri (Valenciennes, 1833) with enlarged abdominal region, inflammated fins and one of the specimens with prominent tumourous growth. Fig. 4. Photomicrograph of tumour section showing stroma on outer surface and under layers showing neoplastic cells along with inflammatory cells; X20. Fig. 2. Autopsied specimen showing rounded, enlarged and greyish tumour. Fig. 5. Photomicrograph shows atrophied under layers of a portion of tumour; X50. Fig. 3. One of the specimens with tumour growing near pelvic region. Fig. 6. Photomicrographs shows the under layers with spongy appearance; X100.
4 36 Rakhshinda Khurram Khan et al., Fig. 7. The under layers of tumour collar region shows inter spaces between the cells; X100. Fig. 10. Photomicrograph shows the portion of tumour section with cell converted into unidentifiable cells; X200. Fig. 8. Photomicrograph shows malpighian cells; X200. Fig. 11. Portion of tumour section showing malpighian cell and inflammatory cells; X200. Fig. 9. Photomicrographs shows cells deviated in shape, size, structure and organization from the normal epithelial and mesenchymal cells; X200. Fig. 12. Photomicrographs shows malpighian cells converted into rounded oval enlarged cells (arrow); X200.
5 Studies on the neoplastic growth in fish 37 Fig. 13. Section of tumour portion showing cells of various shape along with fibrosis; X200. Fig. 14. Section of micrograph shows eosinophills, altered malpighian cells and atrophied cells of connective tissue; X200. References Black, J.J. (1984). Aquatic animal neoplasia as an indicator for carcinogenic hazards to man. In: Hazard assessment of chemicalscurrent developments. (Ed.): J. Saxena. Academic Press Inc. New York. pp Brooks, R.E., G.E. McAm and S.R. Wellings. (1969). Ultra- structural observations on an unidentified cell type found in epidermal tumours of flounders. J. Natn. Cancer Inst., 43: Dethlefsen, V. (1978). Occurrence and abundance of some skeletal deformities, diseases and parasites of major fish species in dumping areas off the German Coast. Coun. Meet. int. Coun. Explor. Sea (= C.M. - I.C.E.S.), E: 8 Martineau, D. and H.W. Ferguson. (2006). Neoplasia. In: Systemic Pathology of Fish, ed. Ferguson, H.W. 2nd ed., pp Scotian Press, London, UK. Peters, N. and B. Watermann. (1979). Three Types of Skin Papillomas of Flatfishes and Their Causes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 1: Peters, N., G. Peters, H.F. Stich, A.B. Acton and G. Bresching. (1978). On differences in skin tumours of Pacific and Atlantic flatfish. J. Fish Diseases, 1: Robert, R.J. (1978). Fish pathology. Balliere Tindall London. Thatcher, V.E. and A.B. Varella. (1980). Fish pathology of the Brazilian Amazon. Acta Amazonica, 10: Valenciennes, A., G.L. in Cuvier and A. Valenciennes. (1833). Histarie Naturelle des poissons. Paris: Levrault. Vol pp. pls Vicha, D.L. and M.C. Schmale. (1994). Morphology and distribution of eoslnophilic granulocytes in damselfish neuroflbromatosis, a model of mast cell distribution in neurofibromatosis type 1. Anticancer Res., 14: 947. Wildgoose, W.H. (1992). Papilloma and squamous cell carcinoma in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). Vet. Rec., 130: Wildgoose, W.H. and D. Buckes. (1995). Spontaneous branchioblastoma in a koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). Vet. Rec., 136: (Received February 2014; Accepted April 2014)
STUDY ON RAINBOW TROUT NODULAR GILL DISEASE DETECTED IN POLAND
 Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 51, 547-551, 2007 STUDY ON RAINBOW TROUT NODULAR GILL DISEASE DETECTED IN POLAND JERZY ANTYCHOWICZ Department of Fish Diseases, National Veterinary Research Institute, 24-100 Pulawy,
Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 51, 547-551, 2007 STUDY ON RAINBOW TROUT NODULAR GILL DISEASE DETECTED IN POLAND JERZY ANTYCHOWICZ Department of Fish Diseases, National Veterinary Research Institute, 24-100 Pulawy,
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma in a platy fish (Xiphophorus maculatus): A case report
 Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences 16(4) 1349-1353 2017 Occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma in a platy fish (Xiphophorus maculatus): A case report Rezaie A. 1 ; Tulaby Dezfuly Z. 2* ; Peyghan R. 2
Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences 16(4) 1349-1353 2017 Occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma in a platy fish (Xiphophorus maculatus): A case report Rezaie A. 1 ; Tulaby Dezfuly Z. 2* ; Peyghan R. 2
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
(Iteceived for publication December 3, 1915)
 TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
Introduction to pathology
 Introduction to pathology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 1 st Lecture Lecture outilne Pathology. Disease. Cell injury. Manifestations of disease. Structural diseases. Functional
Introduction to pathology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 1 st Lecture Lecture outilne Pathology. Disease. Cell injury. Manifestations of disease. Structural diseases. Functional
DUSTURBANCES OF GROWTH. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L8 Uz: Musa
 DUSTURBANCES OF GROWTH MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L8 Uz: Musa Agnesia: means complete absence of an organ (Kidney). Aplasia: s defined in general as "defective development
DUSTURBANCES OF GROWTH MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L8 Uz: Musa Agnesia: means complete absence of an organ (Kidney). Aplasia: s defined in general as "defective development
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER. Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D.
 NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
ONCOLOGY. Csaba Bödör. Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research november 19., ÁOK, III.
 ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types. Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed
 External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
The Gastrointestinal Helminth Infection among Backyard Fowl Population of Selected areas of North 24 Parganas, West Bengal
 Biological Forum An International Journal 8(2): 181-18(216) ISSN (Print): 97-11 ISSN (Online): 2249-29 The Gastrointestinal Helminth Infection among Backyard Fowl Population Selected areas North 24 Parganas,
Biological Forum An International Journal 8(2): 181-18(216) ISSN (Print): 97-11 ISSN (Online): 2249-29 The Gastrointestinal Helminth Infection among Backyard Fowl Population Selected areas North 24 Parganas,
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Title. Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): Issue Date
 Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
NEOPLASIA. 3. Which of the following tumour is benign a. Chondrosarcoma b. Osteochondroma c. Chondroblastoma d. Ewing s tumour e.
 NEOPLASIA 1. malignant neoplasms a. are independent of hormonal influence b. are always composed of homogenous cell lines c. arise from differentiated cells by a process of anaplasia d. display abnormal
NEOPLASIA 1. malignant neoplasms a. are independent of hormonal influence b. are always composed of homogenous cell lines c. arise from differentiated cells by a process of anaplasia d. display abnormal
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
XX. Tumours of the nasal cavity *
 XX. Tumours of the nasal cavity * H. STONZI 1 & B. HAUSER2 Tumours of the nasal cavity are rare in domestic animals, most cases occurring in the dog. Epithelial tumours are the most common type in carnivores
XX. Tumours of the nasal cavity * H. STONZI 1 & B. HAUSER2 Tumours of the nasal cavity are rare in domestic animals, most cases occurring in the dog. Epithelial tumours are the most common type in carnivores
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
EXPERIMENTAL PLEURAL EMPYEMA PATHOLOGIC CHANGES
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp 61-65, 2005 Copyright 2005 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution EXPERIMENTAL PLEURAL EMPYEMA PATHOLOGIC
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp 61-65, 2005 Copyright 2005 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution EXPERIMENTAL PLEURAL EMPYEMA PATHOLOGIC
EMBRYONAL NEPHROMA IN THE CHICKEN: REPORT OF TWO CASES
 EMBRYONAL NEPHROMA IN THE CHICKEN: REPORT OF TWO CASES FRANK D. McKENNEY, V.M.D. (Di1!ision of Experimental Surgery and Pathology, The Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota) Few data have been collected
EMBRYONAL NEPHROMA IN THE CHICKEN: REPORT OF TWO CASES FRANK D. McKENNEY, V.M.D. (Di1!ision of Experimental Surgery and Pathology, The Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota) Few data have been collected
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS
 7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia
 Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
In the third part of the present study tumours which previous were described as basal cell tumours but now have been reclassified as trichoblastomas
 170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
-1- Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks).
 -1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
-1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
A neoplasm is defined as "an abnormal tissue proliferation, which exceeds that of adjacent normal tissue. This proliferation continues even after
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Principles of Surgical Oncology. Winnie Achilles Tierklinik Hollabrunn Lastenstrasse Hollabrunn
 Principles of Surgical Oncology Winnie Achilles Tierklinik Hollabrunn Lastenstrasse 2 2020 Hollabrunn boexi@gmx.de The first surgery provides the best chance for a cure in an animal with a tumor Clinical
Principles of Surgical Oncology Winnie Achilles Tierklinik Hollabrunn Lastenstrasse 2 2020 Hollabrunn boexi@gmx.de The first surgery provides the best chance for a cure in an animal with a tumor Clinical
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Upgrade of the Epidermal Papilloma Reported in an Ozark Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis bishopi)
 Proceeding of the Sixth International Symposium on the Pathology of Reptiles and Amphibian Saint Paul, Minnesota, U.S.A. R.G. McKinnell & D.L. Carlson (eds) Q 2002 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Upgrade of the
Proceeding of the Sixth International Symposium on the Pathology of Reptiles and Amphibian Saint Paul, Minnesota, U.S.A. R.G. McKinnell & D.L. Carlson (eds) Q 2002 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Upgrade of the
Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic Bladder Biopsies -A Histopathological Study
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (2 ):1 3 2-1 3 6 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (2 ):1 3 2-1 3 6 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Pathophysiology lab 2. Cellular injury and adaptation
 Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Spinal Cord Compression caused by Metastatic Epithelial Myoepithelial Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland
 Spinal Cord Compression caused by Metastatic Epithelial Myoepithelial Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland Pages with reference to book, From 249 To 250 Irshad N. Soomro,Akber S. Hussainy,Rashida Ahmed,Sheema
Spinal Cord Compression caused by Metastatic Epithelial Myoepithelial Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland Pages with reference to book, From 249 To 250 Irshad N. Soomro,Akber S. Hussainy,Rashida Ahmed,Sheema
Introduction. Results. Discussion. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Results. conclusions,
 1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2
 Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
polyps of the colon and rectum
 J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 25-31 Pseudo-carcinomatous invasion in adenomatous polyps of the colon and rectum T. MUTO, H. J. R. BUSSEY, AND B. C. MORSON From St Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The histology
J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 25-31 Pseudo-carcinomatous invasion in adenomatous polyps of the colon and rectum T. MUTO, H. J. R. BUSSEY, AND B. C. MORSON From St Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The histology
REPORT TO PENNSYLVANIA FISH AND BOAT COMMISSION ON SKIN LESIONS SUBMITTED FOR HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION
 REPORT TO PENNSYLVANIA FISH AND BOAT COMMISSION ON SKIN LESIONS SUBMITTED FOR HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION Vicki Blazer, PhD National Fish Health Research Laboratory U.S. Geological Survey, Leetown Science
REPORT TO PENNSYLVANIA FISH AND BOAT COMMISSION ON SKIN LESIONS SUBMITTED FOR HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION Vicki Blazer, PhD National Fish Health Research Laboratory U.S. Geological Survey, Leetown Science
Skin Integrity and Wound Care
 Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
IN the kidneys of a wide variety of animals the second convoluted tubule
 Further Observations on the Glomerular Root of the Vertebrate Kidney BY J. F. A. McMANUS (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With five Text-figures INTRODUCTION IN the kidneys
Further Observations on the Glomerular Root of the Vertebrate Kidney BY J. F. A. McMANUS (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With five Text-figures INTRODUCTION IN the kidneys
Adaptation. Skeletal System. Respiratory System 25/06/2013
 Adaptation Written by Elizabeth Hawkins for the Southern Cross University Biology & Conservation of Marine Mammals Unit 2013 Anatomy Muscular system Anatomical system that allows animal to move Specifically
Adaptation Written by Elizabeth Hawkins for the Southern Cross University Biology & Conservation of Marine Mammals Unit 2013 Anatomy Muscular system Anatomical system that allows animal to move Specifically
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland
 Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA
 NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Methodology Prevalence:
 Context of Research Free ranging domestic fowl are very susceptible to parasitic infections owing to their exposure to parasites during their roaming in the backyards in search of food. Heterakis gallinarum
Context of Research Free ranging domestic fowl are very susceptible to parasitic infections owing to their exposure to parasites during their roaming in the backyards in search of food. Heterakis gallinarum
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
SOLITARY BASAL CELL NEVUS STAGE OF BASAL CELL EPITHELIOMA
 SKIN RESEARCH Dec. 1968 Vol.10 No.5 679-686 SOLITARY BASAL CELL NEVUS PREINVASIVE STAGE OF BASAL CELL EPITHELIOMA YOSHIHARU MIKI, M.D. Department of Dermatology, University of Osaka, School of Medicine,
SKIN RESEARCH Dec. 1968 Vol.10 No.5 679-686 SOLITARY BASAL CELL NEVUS PREINVASIVE STAGE OF BASAL CELL EPITHELIOMA YOSHIHARU MIKI, M.D. Department of Dermatology, University of Osaka, School of Medicine,
Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination. Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner
 Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner General Remarks The part II practical examination involved 15 cases which were presented with sufficient clinical data to
Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner General Remarks The part II practical examination involved 15 cases which were presented with sufficient clinical data to
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Teratoma. Portion of a teratoma composed of neural tissue. The large cells in the central part correspond to ganglion cells.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Teratoma. The tumor is composed predominantly of keratinizing squamous epithelium (Sq), which forms cysts filled with keratin (arrows). The tumor also contains
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Teratoma. The tumor is composed predominantly of keratinizing squamous epithelium (Sq), which forms cysts filled with keratin (arrows). The tumor also contains
Go AKAGI, AKIKO AKAGI, Masuo KIMURA, and Hisashi OTSUKA (2nd Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Tokushima University*2) Synopsis
 [GANN, 64, 331-336; August, 1973] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.62] COMPARISON OF BLADDER TUMORS INDUCED IN RATS AND MICE WITH N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL)- NITROSOAMINE*1 (Plates LIII-LV) Go AKAGI, AKIKO AKAGI,
[GANN, 64, 331-336; August, 1973] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.62] COMPARISON OF BLADDER TUMORS INDUCED IN RATS AND MICE WITH N-BUTYL-N-(4-HYDROXYBUTYL)- NITROSOAMINE*1 (Plates LIII-LV) Go AKAGI, AKIKO AKAGI,
Histogenesis of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
 J. clin. Path., (1966), 19, 114 E. D. WILLIAMS1 From the Institute ofpathology, The London Hospital SYNOPSIS Thirty-one dog thyroid tumours and 28 spontaneous rat thyroid tumours were studied histologically
J. clin. Path., (1966), 19, 114 E. D. WILLIAMS1 From the Institute ofpathology, The London Hospital SYNOPSIS Thirty-one dog thyroid tumours and 28 spontaneous rat thyroid tumours were studied histologically
Microscopic Anatomy of Inferior Medullary Velum Of Cerebellum
 32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body
 Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Pancreas. Atrophy, acinar cell. Pathogenesis: Diagnostic key features:
 Pancreas Atrophy, acinar cell Pathogenesis: Decrease in number and/or size of acinar cells may be due to spontaneous or experimentally induced degenerative changes, apoptosis, or a sequel of chronic inflammation.
Pancreas Atrophy, acinar cell Pathogenesis: Decrease in number and/or size of acinar cells may be due to spontaneous or experimentally induced degenerative changes, apoptosis, or a sequel of chronic inflammation.
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Diploma examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 21 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions ONLY. Time allowed: Three hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
Laboratory Animal & Molecular Pathology
 Laboratory Animal & Molecular Pathology TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY, vol29, no 4, pp 467478,2001 Copyright O 2001 by the Society of Toxicologic Pathology A Retrospective Analysis of Background Lesions and Tissue
Laboratory Animal & Molecular Pathology TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY, vol29, no 4, pp 467478,2001 Copyright O 2001 by the Society of Toxicologic Pathology A Retrospective Analysis of Background Lesions and Tissue
Diploma Examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 20 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions. Time allowed: 3 hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 20 March 2018 Candidates must answer FOUR questions Time allowed: 3 hours 1. Give an account of the genetic aberrations encountered in Spitzoid neoplasms and how these
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 20 March 2018 Candidates must answer FOUR questions Time allowed: 3 hours 1. Give an account of the genetic aberrations encountered in Spitzoid neoplasms and how these
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology. Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016
 Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
A CYSTICERCUS CARCINO-OSTEOCHONDRO- SARCOMA OF THE RAT LIVER WITH MULTIPLE CYSTICERCUS SARCOMATA
 A CYSTICERCUS CARCINO-OSTEOCHONDRO- SARCOMA OF THE RAT LIVER WITH MULTIPLE CYSTICERCUS SARCOMATA 1. D. BUIJIJOCK AND M. 11. CUIlTIs (Proin fhe Ztulitute of Cancor Research, Francis C. Wood, Director) It
A CYSTICERCUS CARCINO-OSTEOCHONDRO- SARCOMA OF THE RAT LIVER WITH MULTIPLE CYSTICERCUS SARCOMATA 1. D. BUIJIJOCK AND M. 11. CUIlTIs (Proin fhe Ztulitute of Cancor Research, Francis C. Wood, Director) It
S1.04 Principal clinician. G1.01 Comments. G2.01 *Specimen dimensions (prostate) S2.02 *Seminal vesicles
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
