IN VIVO EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION IN LETHALLY IRRADIATED MICE
|
|
|
- Blake Virgil May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluoride Vol. 35 No Research Report 81 IN VIVO EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION IN LETHALLY IRRADIATED MICE Anna Machalinska, a Jaroslaw Nowak, b Alina Jarema, c Barbara Wiszniewska, d Boguslaw Machaliński a Szczecin, Poland SUMMARY: In our previous studies we found that sodium fluoride (NaF) might be toxic to early human hematopoietic cells. One of the mechanisms for such an effect was the induction of apoptotosis in affected cells. Our new experiments were designed to evaluate whether hematopoietic cells exposed to sodium fluoride in ex vivo conditions are able to engraft into lethally irradiated mice and successfully reconstitute hematopoiesis. Untreated cells as well as cells exposed to a moderate (10 mg/l) dose of NaF were able to establish a significant number of new hematopoietic islets on the spleen surface. In contrast, fewer hematopoietic islets were found when the cells were exposed to a higher dose of sodium fluoride (50 mg/l). Morphological parameter values of peripheral blood derived from the mice confirmed these effects. From the results we conclude that a relatively high dose of fluoride may significantly influence hematopoiesis. Keywords: Bone marrow cells, Hematopoietic cell transplantation, Mice irradiation, Sodium fluoride (NaF), Spleen surface. INTRODUCTION Blood cell production is a continuous process, which results from the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs). Biologically, HSCs are characterized by their ability to self-renew and to differentiate into HPCs of all lineages both myeloid and lymphoid. 1,2 Each time an HSC divides, two functionally distinct daughter cells are produced. One remains stem-like and replenishes the HSC pool. The other enters a differentiation pathway that gives rise to an HPC and undergoes further divisions. Thanks to them the hematopoietic system is constantly renewed. Because HSCs and HPCs exist as a developmental continuum, it is technically extremely difficult to isolate a pure fraction of HSCs. 1 The functional proof that HSCs exist in a cell suspension is the full reconstitution of hematopoiesis in patients undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. HSCs are influenced by a wide range of stimulatory and inhibitory signals delivered in the form of cytokines and growth factors. Certain biological microelements can influence or disturb normal hematopoiesis. 1,3 Among them fluorine is one of the most reactive. 4 a For Correspondence: Boguslaw Machaliński MD PhD, Dept. of General Pathology, Pomeranian Academy of Medicine (PAM), Al. Powstancow Wlkp. 72, Szczecin, Poland; b Provincial Blood Bank, ul. Wojska Polskiego 80/82, Szczecin, Poland; c Clinic of Radiotherapy, PAM, ul. Strzalowska 22, Szczecin, Poland; d Dept. of Histology and Embryology, PAM, Al. Powstancow Wlkp. 72, Szczecin, Poland. machalin@sci.pam.szczecin.pl
2 82 Machalinska, Nowak, Jarema, Wiszniewska, Machaliński Previously, we found that fluorides could influence clonogenic growth and also induce apoptosis in human hematopoietic progenitor cells. 5,6,7 Extending that research, we have now performed additional experiments designed to evaluate the influence of sodium fluoride (NaF) on hematopoietic stem cells using an animal model. In this study, we investigated the hematopoiesis reconstituting ability of such cells exposed to different doses of NaF and subsequently engrafted to lethally irradiated Balb C mice. MATERIALS AND METHODS Cells: Bone marrow cells were obtained from 12 freshly decapitated 6-week old mature, healthy, female inbred Balb C mice (Polish Academy of Sciences, Wrocław, Poland). A fraction of bone marrow mononuclear cells (BM MNCs) was isolated after centrifugation over Gradisol L (Polfa Kutno, Poland) gradient and depleted of adherent cells after overnight incubation in plastic Petri dishes as described. 8,9 Cell viability was assessed by the 0.5% trypan blue exclusion test. Sodium fluoride (Sigma, USA) was diluted in a phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at a concentration of 1 g/kg and was stored at 4 o C. BM MNCs (5x10 7 ) were resuspended in 1 ml of PBS + 5% BCS (bovine calf serum) and then exposed to NaF at different concentrations: 0 mg/l (group 1), 10 mg/l (0.24 mm; group 2), and 50 mg/l (1.19 mm; group 3) for 12 hr at 37 o C. After incubation the cells were washed twice in IMDM (Iscove s Modified Dulbecco s Medium) and subsequently used for transplantation studies. Mice: The transplantation experiment was performed on pathogen-free, 6- week old mature female inbred Balb C mice (Polish Academy of Sciences, Wrocław, Poland). The animals were randomly divided into three experimental groups (group 1 irradiated mice injected with cells unexposed to NaF; group 2 irradiated mice injected with cells exposed to NaF at a concentration of 10 mg/l; group 3 irradiated mice injected with cells exposed to NaF at a concentration 50 mg/l), 1 control group (mice not irradiated) and 1 blind group (irradiated mice injected with saline instead of cells). Groups 1, 2, and 3 contained 6 animals each; the control and blind groups consisted of 3 animals each. The animals were maintained under standard laboratory conditions in a 12hr/12hr light-dark cycle, at 21 o C. The mice (except for the control group) were exposed to 800 cgy from a gamma irradiation source 24 hr prior to transplantation. Hematopoietic cell transplantation: The day after irradiation, mice from groups 1, 2, and 3 were given a transplant of 5x10 7 BM MNCs/animal via tail vein injection. Mice from the blind group were injected with saline instead of cells. After transplantation, hematological parameters of the animals were monitored by blood sampling from the retroorbital plexus. Ten and 14 days after the transplantation, mice (half of the animals from each group)
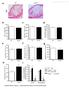
3 In vivo effects of NaF on bone marrow transplantation 83 were sacrificed, and the presence of hematopoietic islets on the surface of spleens was examined under the light microscopy, and the livers and spleens were collected for microscopic analysis. Hematological parameters: Hematological parameters of the peripheral blood samples (n = 5) were evaluated by employing an automatic bloodanalyzer (Cell-DYN 1700, Abbott, USA) according to the manufacturer s protocol. Microscopic analyses: Hematopoietic stem cell recovery was evaluated using the endogenous spleen colony-forming unit (E-CFU) assay. 10 The number of hematopoietic islets on spleen surfaces were evaluated under a stereoscopic microscope immediately after obtaining the organ. For morphological studies the tissues (livers and spleens) were fixed in Carnoy s solution and stained with H-E (Hematoxylin-Eosin) and PAS (Periodic-Acid-Schiff) methods. Microscopic slides from the livers and spleens of the sacrificed mice were evaluated under a light microscope (Olympus, Japan) and subsequently photographed. Statistical analysis. Arithmetic means and standard deviations were calculated on an IBM computer using MS Excel v. 97. Data were analyzed by the Student's t-test for unpaired samples. Statistical significance was defined as p < RESULTS Ability of cells exposed to NaF to engraft in vivo Some of the mice injected with cells exposed to the higher dose of NaF (group 3) as well as all animals from the blind group (injected with saline instead of cells), became sick within 24 hr after the injection. On the 5 th day two animals from group 3, and all from the blind group died. Three mice from the control, and groups 1 and 2, along with two from group 3 were sacrificed on the 10 th day. The rest of the mice were sacrificed on the 14 th day of the experiment. Figure 1 shows the relative numbers of hematopoietic islets on the surface of spleens obtained from the examined mice. A moderate concentration of NaF (10 mg/l) used during preincubation of the injected cells caused little inhibitory effect on the growth of murine early hematopoietic cells 10 days after transplantation, compared to the irradiated mice that were treated with unexposed cells. In contrast, a higher concentration of NaF (50 mg/l) damaged part of the stem and progenitor cells and significantly decreased the number of these islets. Fourteen days after transplantation, renewal of hematopoiesis was not inhibited by sodium fluoride used at a moderate concentration (10 mg/l). At the same time, inhibition of hematopoietic islets formation by the high dose of NaF was similar to that found on the 10 th day of the experiment.
4 84 Machalinska, Nowak, Jarema, Wiszniewska, Machaliński Number of islets as a % of control ,6± days 14 days ,4±7.8 70,8± ±7.1 0 mg/l 10 mg/l 50 mg/l NaF concentration Figure 1. The influence of NaF on hematopoietic islets formed on spleen surface by cells transplanted into mice. The hematopoietic cells before transplantation were exposed to NaF at doses of 10 and 50 mg/l for 12 hr at 37 o C. The numbers of islets are shown as a percent of the islets formed by cells that were not exposed to NaF. In these studies we also evaluated several standard hematological parameters of the peripheral blood (Table). We found that all parameters white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (HGB), hematocrit (HCT), and platelets (PLT) - in the samples collected from mice injected with the cells exposed to 50 mg NaF/L were significantly lower (p < 0.05) compared to those in the samples collected from the other groups of mice. On the other hand, no significant differences in recovery of hematopoiesis were found between peripheral blood samples aspirated from mice injected with cells not exposed to NaF and from mice injected with cells exposed to 10 mg NaF/L (Table). Morphological changes Livers: Cytoplasm of the hepatocytes stained with H-E in all the irradiated groups of mice had regular structure and the chromatin in the nuclei formed nodules located near the nuclear membrane. In every instance, regular distribution of glycogen, which was located mostly around the central vein, was found in the hepatocytes stained with PAS.
5 In vivo effects of NaF on bone marrow transplantation 85 Table. Hematological parameters (mean, SD) of peripheral blood obtained from mice after 10 and 14 days since transplantation (n = 5). NI mice not irradiated; group 1 mice injected with unexposed cells; group 2 mice injected with cells exposed to 10 mg NaF/L; group 3 mice injected with cells exposed to 50 mg NaF /L. WBC white blood cells; RBC red blood cells; HCT hematocrit; HGB hemoglobin; PLT platelets. G/L 10 9 /L; T/L /L Group Time WBC G/L RBC T/L HCT % HGB mm PLT G/L NI 10 days 9.2 (1.0) 6.12 (0.9) 0.28 (0.05) 6.8 (0.5) 403 (79) Group 1 10 days 3.3 (0.8) 5.17 (1.0) 0.23 ( (0.3) 243 (51) 14 days 8.1 (1.1) 5.91 (0.8) 0.29 (0.05) 6.9 (0.4) 367 (88) Group 2 10 days 2.5 (0.7) 5.44 (1.7) 0.24 (0.05) 6.0 (0.5) 272 (92) 14 days 8.0 (0.8) 6.0 (1.3) 0.28 (0.03) 6.2 (0.6) 398 (78) Group 3 10 days 2.1 (0.5) 3.7 (1.2) 0.17 (0.02) 4.6 (1.0) 210 (37) 14 days 2.0 (0.4) 4.3 (1.3) 0.20 (0.03) 4.7 (0.9) 322 (45) Spleens: Figure 2 shows spleen morphology of a control, non-irradiated mouse. Ten days after injection of murine cells unexposed to NaF into mice of group 1, large amounts of lymphatic nodules with germinal centers and numerous early cells were found (Figure 3). A small number of megakaryocytes was also visible. After 14 days, expanded white pulp in the spleen sections was noted. Numerous early lymphocytes with normal nuclei as well as megakaryocytes were likewise present. After 10 days, in the case of injection of cells exposed to a moderate dose of NaF (10 mg/l; group 2), large lymphatic nodules were found in which few lymphatic cells with low levels of condensed chromatin were visible (Figure 4). Also few megakaryocytes were present. After 14 days from the injection, many more early forms of lymphatic cells were visible in large lymphatic nodules. The number of megakaryocytes in the spleens was higher. In group 3, 10 days after injection of the cells exposed to the high dose of NaF (50 mg/l), lymphatic nodules containing early forms of lymphocytes were found (Figure 5). Singular megakaryocytes were present. After 14 days the spleen sections were very similar to those in group 2 after 14 days.
6 86 Machalinska, Nowak, Jarema, Wiszniewska, Machaliński Figure 2. Spleen morphology of a control, non-irradiated mouse after 10 days. H-Ex160. Figure 3. Spleen morphology of an irradiated mouse 10 days after injection with bone marrow mononuclear cells not exposed to NaF. Lymphatic nodules with germinal centers and numerous early cells are visible. H-Ex160.
7 In vivo effects of NaF on bone marrow transplantation 87 Figure 4. Spleen morphology of an irradiated mouse 10 days after injection with bone marrow mononuclear cells exposed to 10 mg NaF/L. Large lymphatic nodules in which few lymphatic cells with low levels of condensed chromatin are visible. H-Ex160. Figure 5. Spleen morphology of the mouse 10 days after injection with bone marrow mononuclear cells exposed to 50 mg NaF/L. Lymphatic nodules containing early forms of lymphocytes are visible. H-Ex330.
8 88 Machalinska, Nowak, Jarema, Wiszniewska, Machaliński DISCUSSION Our earlier studies indicated that sodium fluoride affected human hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) and significantly decreased their clonogenic growth. 5,7 This phenomenon occurred at NaF concentrations of 50 mg/l and higher. Moreover, exposure to the same concentration of sodium fluoride induced significant apoptosis in human HPCs. 6 Following these reports, we performed additional experiments designed to evaluate the potential influence of sodium fluoride in increasing doses on hematopoietic stem cell populations. So far, it has not been clear whether murine hematopoietic stem and early progenitor cells, obtained from healthy inbred Balb C mice and subsequently exposed to sodium fluoride in ex vivo conditions, would be able to engraft into lethally irradiated animals (taken from the same breeding) and successfully reconstitute hematopoiesis. Hematopoietic stem and early progenitor cells, which are responsible for hematopoiesis renewal, are very primitive, non-cycling and metabolically quiescent. 1,2 More importantly, they are relatively resistant to different toxic agents. 1 Our present results, which involve numeration of early hematopoietic islets visible on the spleen surface, morphologic examination of spleen and liver and analysis of standard hematological parameters of peripheral blood, suggest that a relatively high concentration of NaF (50 mg/l) disturbed and significantly delayed the reconstitution of hematopoiesis in lethally irradiated mice. Our findings therefore revealed that stem and early progenitor cells can be influenced and damaged by sodium fluoride. Because of the potential toxic effect on the hematopoietic system, we suggest introduction of a professional screening program in regions affected by endemic fluorosis or intensive industrial pollution. Such examination should focus not only on hard tissues but also on hematopoiesis, particularly in children and young adults. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was presented at the XXIIIrd Conference of the International Society for Fluoride Research in Szczecin, Poland, June 11-14, 2000 (Program abstract P-28). REFERENCES 1 Ratajczak MZ, Gewirtz AM. The biology of hematopoietic stem cells. Semin Oncol 1995;22: Spangrude GJ. Biological and clinical aspects of hematopoietic stem cells. Ann Rev Med 1994;45: Ratajczak MZ, Ratajczak J, Kuczynski W, Light B, Lusk EJ, Gewirtz AM. In vitro sensitivity of human hematopoietic progenitor cells to 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide. Exp Hematol 1993;21:
9 In vivo effects of NaF on bone marrow transplantation 89 4 Shivashankara AR, Shivaraja Shankara YM, Hanumanth Rao S, Gopalakrishna Bhat P. A clinical and biochemical study of chronic fluoride toxicity in children of Kheru Thanda of Gulbarga district, Karnataka, India. Fluoride 2000;33: Machaliński B, Zejmo M, Stecewicz I, Machalinska A, Machoy Z, Ratajczak MZ. The influence of sodium fluoride on the clonogenecity of the human hematopoietic progenitor cells. Preliminary report. Fluoride 2000;33: Machalinska A, Machoy-Mokrzynska A, Marlicz W, Stecewicz I, Machaliński B. NaF-induced apoptosis in human bone marrow and cord blood CD34 positive cells. Fluoride 2001;34: Machaliński B, Dziedziejko V, Stecewicz I. [The influence of sodium fluoride on clonogenicity of human bone marrow hematopoietic cells derived from heparinized cadaveric organ donors. Preliminary report]. Metabolism of Fluorine 1999;8: Machaliński B, Honczarenko M, Gontarewicz A, Ratajczak MZ. Isolation of mononuclear cells from bone marrow, peripheral and cord blood employing Ficoll-Paque (Pharmacia) or Gradisol L (Polfa). Comparison of both methods. Pol Arch Med Wewn 1998;99: Ratajczak MZ, Luger SM, De Riel K, Abraham J, Calabretta B, Gewirtz AM. Role of the KIT protooncogene in normal and malignant human hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89: Till JE, McCulloch EA. Early repair processes in marrow cells irradiated and proliferating in vivo. Radiat Res 1963;18: Published by the International Society for Fluoride Research Editorial Office: 727 Brighton Road, Ocean View, Dunedin 9051, New Zealand
THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON THE CLONOGENECITY OF HUMAN HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS: PRELIMINARY REPORT
 168 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 4 168-173 2 Research Report THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON THE CLONOGENECITY OF HUMAN HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS: PRELIMINARY REPORT Boguslaw Machaliński, a Maria Zejmo,
168 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 4 168-173 2 Research Report THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON THE CLONOGENECITY OF HUMAN HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS: PRELIMINARY REPORT Boguslaw Machaliński, a Maria Zejmo,
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration. Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research.
 Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Analysis of the Viability of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells. Sachdeva N
 Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas
 University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
BCR-ABL - LSK BCR-ABL + LKS - (%)
 Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
Hematopoiesis. BHS Liège 27/1/2012. Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne
 Hematopoiesis BHS Liège 27/1/2012 Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne Hematopoiesis: definition = all the phenomenons to produce blood cells Leukocytes = White Blood Cells Polynuclear = Granulocytes Platelet
Hematopoiesis BHS Liège 27/1/2012 Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne Hematopoiesis: definition = all the phenomenons to produce blood cells Leukocytes = White Blood Cells Polynuclear = Granulocytes Platelet
Transfer protocol of human HSC into NOG mice
 Transfer protocol of human HSC into NOG mice Mice: Adult NOG mice are aged 8-12 weeks. Newborn mice are 1 2 days old. 8-12 week old NOG mice irradiated with 2.5 Gy Intravenous transfer of 1-0.5 x 10 5
Transfer protocol of human HSC into NOG mice Mice: Adult NOG mice are aged 8-12 weeks. Newborn mice are 1 2 days old. 8-12 week old NOG mice irradiated with 2.5 Gy Intravenous transfer of 1-0.5 x 10 5
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION GENOTOXICITY. In vitro Genotoxicity Studies
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION GENOTOXICITY In vitro Genotoxicity Studies The in vitro immortalisation (IVIM) assay relies on the induction of a survival advantage by insertional activation of cellular proto-oncogenes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION GENOTOXICITY In vitro Genotoxicity Studies The in vitro immortalisation (IVIM) assay relies on the induction of a survival advantage by insertional activation of cellular proto-oncogenes,
INFLUENCE OF FLUORIDE IONS ON NA + -H + EXCHANGER ACTIVITY IN HUMAN RED BLOOD CELLS
 174 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 3 174-180 2001 Research Report INFLUENCE OF FLUORIDE IONS ON NA + -H + EXCHANGER ACTIVITY IN HUMAN RED BLOOD CELLS J Bober, a,b D Chlubek, a E Kwiatkowska, c K Kędzierska, c E
174 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 3 174-180 2001 Research Report INFLUENCE OF FLUORIDE IONS ON NA + -H + EXCHANGER ACTIVITY IN HUMAN RED BLOOD CELLS J Bober, a,b D Chlubek, a E Kwiatkowska, c K Kędzierska, c E
Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous
 Cancer Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate Bin Zhang,
Cancer Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate Bin Zhang,
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia
 Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Haematopoietic stem cells
 Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Introduction STEM CELLS 1994;12:
 Growth Factor Stimulation of Cryopreserved CD34 Bone Marrow Cells Intended for Transplant: An In Vitro Study to Determine Optimal Timing of Exposure to Early Acting Cytokines Mariusz Z. Ratajczak, Janina
Growth Factor Stimulation of Cryopreserved CD34 Bone Marrow Cells Intended for Transplant: An In Vitro Study to Determine Optimal Timing of Exposure to Early Acting Cytokines Mariusz Z. Ratajczak, Janina
Supplemental Information. Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection. Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Getting to the root of Cancer
 Cancer Stem Cells: Getting to the root of Cancer Dominique Bonnet, Ph.D Senior Group Leader, Haematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute Venice, Sept 2009 Overview
Cancer Stem Cells: Getting to the root of Cancer Dominique Bonnet, Ph.D Senior Group Leader, Haematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute Venice, Sept 2009 Overview
Hemopoietic Precursors in Human Bone Marrow Transplantation
 International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 11-18 Suppl 1 (1986) Hemopoietic Precursors in Human Bone Marrow Transplantation H.A. Messner Ontario Cancer Institute, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 11-18 Suppl 1 (1986) Hemopoietic Precursors in Human Bone Marrow Transplantation H.A. Messner Ontario Cancer Institute, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Long-Term Engraftment of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
 Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Long-Term Engraftment of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells J. M. Heath, A. Chalishazar, C.S. Lee, W. Selleck, C. Cotta-Ramusino, D. Bumcrot, J.L.
Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Long-Term Engraftment of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells J. M. Heath, A. Chalishazar, C.S. Lee, W. Selleck, C. Cotta-Ramusino, D. Bumcrot, J.L.
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Blood & Blood Formation
 Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Hematopoiesis. - Process of generation of mature blood cells. - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human)
 Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
CRISPR-mediated Editing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for the Treatment of β-hemoglobinopathies
 CRISPR-mediated Editing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for the Treatment of β-hemoglobinopathies Jennifer Gori American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy May 11, 2017 editasmedicine.com 1 Highlights Developed
CRISPR-mediated Editing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for the Treatment of β-hemoglobinopathies Jennifer Gori American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy May 11, 2017 editasmedicine.com 1 Highlights Developed
Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia"
 Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia" Hoelzer, D.,l, Harriss, E. B.l, Kurrle, E.l, Schmücker, H.l, Hellriegel,
Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia" Hoelzer, D.,l, Harriss, E. B.l, Kurrle, E.l, Schmücker, H.l, Hellriegel,
Childhood hematopoiesis and hematological features. Yongmin Tang Dept. Hematology-oncology Chidlren s Hospital Zhejiang University School of medicine
 Childhood hematopoiesis and hematological features Yongmin Tang Dept. Hematology-oncology Chidlren s Hospital Zhejiang University School of medicine Questions: How much have you known about our hematopoietic
Childhood hematopoiesis and hematological features Yongmin Tang Dept. Hematology-oncology Chidlren s Hospital Zhejiang University School of medicine Questions: How much have you known about our hematopoietic
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES
 13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
Formation of Blood Cells
 Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
X P. Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Nilotinib LSK LT-HSC. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus
 a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Transplantation
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Automated and Standardized Counting of Mouse Bone Marrow CFU Assays
 Automated and Standardized Counting of Mouse Bone Marrow CFU Assays 2 Automated and Standardized Colony Counting Table of Contents 4 Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Assays for Mouse Bone Marrow 5 Automated Assay
Automated and Standardized Counting of Mouse Bone Marrow CFU Assays 2 Automated and Standardized Colony Counting Table of Contents 4 Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Assays for Mouse Bone Marrow 5 Automated Assay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative. breast cancer patients
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3412
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Investigation of sickle cell disease
 Investigation of sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited disorder which affects people from Africa, India, Middle East and the Mediterranean region The main forms of
Investigation of sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited disorder which affects people from Africa, India, Middle East and the Mediterranean region The main forms of
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Aplastic anemia. Case report. Effect of antithymocyte globulin on erythroid colony formation
 Case report Aplastic anemia Effect of antithymocyte globulin on erythroid colony formation Susan A. Rothmann Hamburger, Ph.D. Department of Laboratory Hematology and Blood Banking James H. Finke, Ph.D.
Case report Aplastic anemia Effect of antithymocyte globulin on erythroid colony formation Susan A. Rothmann Hamburger, Ph.D. Department of Laboratory Hematology and Blood Banking James H. Finke, Ph.D.
Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice
 Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice Jimmy A. Rotolo 1, Branka Stancevic 1, Jianjun Zhang 1, Guoqiang Hua 1, John Fuller 1, Xianglei Yin 1, Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman 2, Kisu
Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice Jimmy A. Rotolo 1, Branka Stancevic 1, Jianjun Zhang 1, Guoqiang Hua 1, John Fuller 1, Xianglei Yin 1, Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman 2, Kisu
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood
 Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228
 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
HEAMATOLOGICAL INDICES AND BONE MARROW BIOPSY
 HEAMATOLOGICAL INDICES AND BONE MARROW BIOPSY HEMATOCRIT Hematocrit is a measure of the percentage of the total blood volume that is made up by the red blood cells The hematocrit can be determined directly
HEAMATOLOGICAL INDICES AND BONE MARROW BIOPSY HEMATOCRIT Hematocrit is a measure of the percentage of the total blood volume that is made up by the red blood cells The hematocrit can be determined directly
Chemotherapeutic Susceptibility of Human Bone Marrow Progenitor Cells and Human Myelogenous Leukemia Cells (HMO) in Co-Culture: Preliminary Report
 International Journal of Cell Cloning 2: 254-262 (1984) Chemotherapeutic Susceptibility of Human Bone Marrow Progenitor Cells and Human Myelogenous Leukemia Cells (HMO) in Co-Culture: Preliminary Report
International Journal of Cell Cloning 2: 254-262 (1984) Chemotherapeutic Susceptibility of Human Bone Marrow Progenitor Cells and Human Myelogenous Leukemia Cells (HMO) in Co-Culture: Preliminary Report
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Interleukin-l Production in Patients with Nonlymphocytic Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes
 Interleukin-l Production in Patients with Nonlymphocytic Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes N. J. Simbirtseva 1 A common feature of all cases of myeloid leukemia is a block in normal maturation of
Interleukin-l Production in Patients with Nonlymphocytic Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes N. J. Simbirtseva 1 A common feature of all cases of myeloid leukemia is a block in normal maturation of
XIV. HLA AND TRANSPLANTATION MEDICINE
 XIV. HLA AND TRANSPLANTATION MEDICINE A. Introduction 1. The HLA system includes a complex array of genes and their molecular products that are involved in immune regulation and cellular differentiation.
XIV. HLA AND TRANSPLANTATION MEDICINE A. Introduction 1. The HLA system includes a complex array of genes and their molecular products that are involved in immune regulation and cellular differentiation.
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
 Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS
 292 Tang, An, Du, Zhang, Zhou 292 IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS Qin-qing Tang, a Xiao-jing An, a Jun Du, a Zheng-xiang Zhang, a Xiao-jun Zhou a
292 Tang, An, Du, Zhang, Zhou 292 IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS Qin-qing Tang, a Xiao-jing An, a Jun Du, a Zheng-xiang Zhang, a Xiao-jun Zhou a
Hematology 101. Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD
 Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
TITLE: Assessing the Mechanisms of MDS and its Transformation to Leukemia in a Novel Humanized Mouse. REPORT DATE: September 2014
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0245 TITLE: Assessing the Mechanisms of MDS and its Transformation to Leukemia in a Novel Humanized Mouse PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Stephanie Halene CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Yale
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0245 TITLE: Assessing the Mechanisms of MDS and its Transformation to Leukemia in a Novel Humanized Mouse PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Stephanie Halene CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Yale
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells
 Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes
 T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Polycthemia Vera (Rubra)
 Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Increased red cells Clonal Myeloid lineages also increased 2-13 cases per million Mean age: 60 years Sites of Involvement Bone marrow Peripheral blood
Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Increased red cells Clonal Myeloid lineages also increased 2-13 cases per million Mean age: 60 years Sites of Involvement Bone marrow Peripheral blood
International Journal of Cell Cloning 6: (1988) Research Laboratory of Blood Physiology, Hunan Medical College, Changsha, Hunan, PRC
 Original Paper International Journal of Cell Cloning 6:290-295 (1988) The Influence of Histamine at Various Concentrations on the Cell Cycle State of Hematopoietic Stem Cells (CF'U-s) I"i Shounan, XU You-Heng
Original Paper International Journal of Cell Cloning 6:290-295 (1988) The Influence of Histamine at Various Concentrations on the Cell Cycle State of Hematopoietic Stem Cells (CF'U-s) I"i Shounan, XU You-Heng
Ordering Physician CLIENT,CLIENT. Collected REVISED REPORT
 HPWET Hematopathology Consultation, MML Embed Client Hematopathology Consult REVISED INAL DIAGNOSIS Interpretation Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and biopsies, bilateral iliac crests: 1. Normocellular
HPWET Hematopathology Consultation, MML Embed Client Hematopathology Consult REVISED INAL DIAGNOSIS Interpretation Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and biopsies, bilateral iliac crests: 1. Normocellular
Selective Enhancement of Donor Hematopoietic Cell Engraftment by the CXCR4 Antagonist AMD3100 in a Mouse Transplantation Model
 Selective Enhancement of Donor Hematopoietic Cell Engraftment by the CXCR4 Antagonist AMD3100 in a Mouse Transplantation Model Yubin Kang 1, Benny J. Chen 2, Divino DeOliveira 2, Jeffrey Mito 2, Nelson
Selective Enhancement of Donor Hematopoietic Cell Engraftment by the CXCR4 Antagonist AMD3100 in a Mouse Transplantation Model Yubin Kang 1, Benny J. Chen 2, Divino DeOliveira 2, Jeffrey Mito 2, Nelson
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS
 DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit
 INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and
 Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and survival of mice with different genotypes. (a) The proper excision of Pten, p110α, p110α and p110δ was
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and survival of mice with different genotypes. (a) The proper excision of Pten, p110α, p110α and p110δ was
Schumacher et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015) 8:64 DOI /s
 Schumacher et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015) 8:64 DOI 10.1186/s13045-015-0152-2 JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY & ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Angptl4 is upregulated under inflammatory conditions in the bone marrow
Schumacher et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015) 8:64 DOI 10.1186/s13045-015-0152-2 JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY & ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Angptl4 is upregulated under inflammatory conditions in the bone marrow
Stem Cell Transplantation with S-59 Photochemically Treated T-Cell Add-Backs to Establish Allochimerism in Murine Thalassemia
 Stem Cell Transplantation with S-59 Photochemically Treated T-Cell Add-Backs to Establish Allochimerism in Murine Thalassemia FRANS A. KUYPERS, a GORDON WATSON, a EZRA SAGE, a MARK C. WALTERS, a JAMES
Stem Cell Transplantation with S-59 Photochemically Treated T-Cell Add-Backs to Establish Allochimerism in Murine Thalassemia FRANS A. KUYPERS, a GORDON WATSON, a EZRA SAGE, a MARK C. WALTERS, a JAMES
COMPOSITION OF BLOOD AND NORMAL ERYTHROPOIESIS
 Composition of Blood and Normal Erythropoiesis MODULE 1 COMPOSITION OF BLOOD AND NORMAL ERYTHROPOIESIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Blood consists of a fluid component- plasma, and a cellular component comprising
Composition of Blood and Normal Erythropoiesis MODULE 1 COMPOSITION OF BLOOD AND NORMAL ERYTHROPOIESIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Blood consists of a fluid component- plasma, and a cellular component comprising
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
LDR and its potential application in clinics
 LDR and its potential application in clinics Lu Cai Departments of Medicine & Radiation Oncology University it of Louisville School of Medicine LDR effects Hormesis Adaptive response Bystander effects
LDR and its potential application in clinics Lu Cai Departments of Medicine & Radiation Oncology University it of Louisville School of Medicine LDR effects Hormesis Adaptive response Bystander effects
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz
 Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
D Bonnet 1,2, M Bhatia 1,3, JCY Wang 1, U Kapp 1 and JE Dick 1. Summary:
 Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 23, 203209 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 02683369/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt Cytokine treatment or accessory cells are required to initiate
Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 23, 203209 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 02683369/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt Cytokine treatment or accessory cells are required to initiate
URINARY FLUORIDE OF SCHOOLCHILDREN IN GDAŃSK
 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 4 239-243 2002 Research Report 239 URINARY FLUORIDE OF SCHOOLCHILDREN IN GDAŃSK W Czarnowski, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: The aim of this study was to determine the concentration
Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 4 239-243 2002 Research Report 239 URINARY FLUORIDE OF SCHOOLCHILDREN IN GDAŃSK W Czarnowski, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: The aim of this study was to determine the concentration
Generation of monocytederived Dendritic Cells (modcs)
 monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED
 Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS
 Fluoride Vol. 37 No. 1 7 12 2004 Research Report 7 FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS I Inkielewicz, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: Eight-week old male
Fluoride Vol. 37 No. 1 7 12 2004 Research Report 7 FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS I Inkielewicz, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: Eight-week old male
Normal & Leukaemic haematopoiesis. Dr. Liu Te Chih Dept of Haematology / Oncology National University Health Services Singapore
 Normal & Leukaemic haematopoiesis 2010 Dr. Liu Te Chih Dept of Haematology / Oncology National University Health Services Singapore Use of Immunophenotyping today Lineage assignment Differentiation of
Normal & Leukaemic haematopoiesis 2010 Dr. Liu Te Chih Dept of Haematology / Oncology National University Health Services Singapore Use of Immunophenotyping today Lineage assignment Differentiation of
Rapid Decline of Clonogenic Hemopoietic Progenitors in Semisolid Cultures of Bone Marrow Samples Derived from Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Original Manuscript International Journal of Cell Cloning 7314-321 (1989) Rapid Decline of Clonogenic Hemopoietic Progenitors in Semisolid Cultures of Bone Marrow Samples Derived from Patients with Chronic
Original Manuscript International Journal of Cell Cloning 7314-321 (1989) Rapid Decline of Clonogenic Hemopoietic Progenitors in Semisolid Cultures of Bone Marrow Samples Derived from Patients with Chronic
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Medical Physics in the Baltic States 2017 Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose Tadas DIDVALIS 1, 2,, Paulius RUZGYS 1, Saulius ŠATKAUSKAS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Medical Physics in the Baltic States 2017 Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose Tadas DIDVALIS 1, 2,, Paulius RUZGYS 1, Saulius ŠATKAUSKAS
Index. endocytosis, 92 fat cells, 99 myelofibrosis, 390 nerves, 99, 100 sinuses, 90 Bone marrow fatty involution, red and yellow marrow,
 A Adherent layer cell types, 256 adipocytes, 261 endothelial cells, 259-261 function, 262, 263 interactions, 261, 262 macrophage and epitheloid cell, 256-259 Association of hematopoiesis and bone formation,209,210
A Adherent layer cell types, 256 adipocytes, 261 endothelial cells, 259-261 function, 262, 263 interactions, 261, 262 macrophage and epitheloid cell, 256-259 Association of hematopoiesis and bone formation,209,210
Leukine. Leukine (sargramostim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CELLULAR ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE CONCENTRATIONS IN ERYTHROCYTES AND SERUM FLUORIDE LEVELS IN TWO BREEDS OF SHEEP
 60 60 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CELLULAR ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE CONCENTRATIONS IN ERYTHROCYTES AND SERUM FLUORIDE LEVELS IN TWO BREEDS OF SHEEP Maria Suska, a Mariola Janiak Szczecin, Poland SUMMARY: The relationship
60 60 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CELLULAR ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE CONCENTRATIONS IN ERYTHROCYTES AND SERUM FLUORIDE LEVELS IN TWO BREEDS OF SHEEP Maria Suska, a Mariola Janiak Szczecin, Poland SUMMARY: The relationship
Insights into the Cell-of-Origin of the Histiocytoses Using Patient-Derived Xenograft Models
 Insights into the Cell-of-Origin of the Histiocytoses Using Patient-Derived Xenograft Models 4 th Annual International Erdheim-Chester Disease Medical Symposium Paris, France September 15, 2016 Benjamin
Insights into the Cell-of-Origin of the Histiocytoses Using Patient-Derived Xenograft Models 4 th Annual International Erdheim-Chester Disease Medical Symposium Paris, France September 15, 2016 Benjamin
Production of the Formed Elements (Chapter 11) *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m62120 1 Production of the Formed Elements (Chapter 11) * Ildar Yakhin Based on Production of the Formed Elements by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under
OpenStax-CNX module: m62120 1 Production of the Formed Elements (Chapter 11) * Ildar Yakhin Based on Production of the Formed Elements by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under
Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO
 Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3150
 Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas
 University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
Erythropoietin In Vitro
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 68, No. 7, pp. 1542-1546, July 1971 Induction of Colonies of Hemoglobin-Synthesizing Cells by Erythropoietin In Vitro (fetal mouse liver/erytbropoietin/erythroid cells/59fe/granulocytes)
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 68, No. 7, pp. 1542-1546, July 1971 Induction of Colonies of Hemoglobin-Synthesizing Cells by Erythropoietin In Vitro (fetal mouse liver/erytbropoietin/erythroid cells/59fe/granulocytes)
Mariusz Z. Ratajczak M.D., Ph.D., d.hc. Stem Cell Institute at the James Graham Brown Cancer Center, University of Louisville.
 Umbilical cord blood-derived CD45 - /SSEA-4 + /OCT-4 + /CD133 + /CXCR4 + /Lin - very small embryonic/epiblast like stem cells (VSELs) Potential Clinical Applications Mariusz Z. Ratajczak M.D., Ph.D., d.hc.
Umbilical cord blood-derived CD45 - /SSEA-4 + /OCT-4 + /CD133 + /CXCR4 + /Lin - very small embryonic/epiblast like stem cells (VSELs) Potential Clinical Applications Mariusz Z. Ratajczak M.D., Ph.D., d.hc.
Canberra, Australia). CD11c-DTR-OVA-GFP (B6.CD11c-OVA), B6.luc + and. Cancer Research Center, Germany). B6 or BALB/c.FoxP3-DTR-GFP mice were
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Mice Female C57BL/6 (B6, I-E null, H-2 b ), BALB/c (H-2 d ) + ), FVB/N (H-2 q, I-E null, CD45.1 + ), and B6D2F1 (H-2 b/d ) mice were purchased from the Animal Resources
Supplemental Materials and Methods Mice Female C57BL/6 (B6, I-E null, H-2 b ), BALB/c (H-2 d ) + ), FVB/N (H-2 q, I-E null, CD45.1 + ), and B6D2F1 (H-2 b/d ) mice were purchased from the Animal Resources
Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1
 RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
Hematopoiesis i starts from. HPC differentiates t to sequentially more mature. HPC circulate in very low
 Upstate Cord Blood Bank Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Hematopoiesis i starts from self renewing HPC HPC differentiates t to sequentially more mature blood cells HPC circulate in very low numbers in adults
Upstate Cord Blood Bank Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Hematopoiesis i starts from self renewing HPC HPC differentiates t to sequentially more mature blood cells HPC circulate in very low numbers in adults
Scientific report: Delineating cellular stages and regulation of human NK cell development to improve NK cell-based therapy for cancer (Dnr )
 Scientific report: Delineating cellular stages and regulation of human NK cell development to improve NK cell-based therapy for cancer (Dnr 130259) The main goal of this project focuses on establishing
Scientific report: Delineating cellular stages and regulation of human NK cell development to improve NK cell-based therapy for cancer (Dnr 130259) The main goal of this project focuses on establishing
Hematopoietic Growth Factors Colony Stimulating Factors. Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa). Granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor (G-CSF).
 Hematopoietic Growth Factors Colony Stimulating Factors. Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor(g-csf). Granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor (G-CSF). Interleukin-11
Hematopoietic Growth Factors Colony Stimulating Factors. Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor(g-csf). Granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor (G-CSF). Interleukin-11
