EKSPERIMENTINIAI TYRIMAI
|
|
|
- Julie Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EKSPERIMENTINIAI TYRIMAI 47 Effects of cadmium ions on the initial stage of translation and the cell death in mouse liver Leonid Ivanov 1, 2, Vaiva Lesauskaitė 3, Laima Ivanovienė 2, Ilona Sadauskienė 1, 2, Rasa Gailevičiūtė 1, Dovilė Karčiauskaitė 3, Hiliaras Rodovičius 2 1 Institute for Biomedical Research, 2 Department of Biochemistry 3 Institute of Cardiology, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania Key words: cadmium, trna, leucyl-trna synthetase, apoptosis, necrosis. Summary. Objective. To evaluate in vivo and in vitro effects of cadmium ions on the activities of mice liver trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase and on the type of liver cells death. Material and methods. White laboratory mice were intoxicated by intraperitoneal injection of cadmium chloride solution (1.6 mg cadmium ions/1 kg of body weigh). Total trnas were isolated by adding ethanol and isopropanol into the phenol-deproteinized supernatant of mouse liver homogenate. Post-mitochondrial fraction of the liver cells was used as a source of leucyltrna synthetase. Acceptor activity of trna Leu and activity of leucyl-trna synthetase were measured in trna aminoacylation reaction with [ 14 C]-labeled leucine as a substrate. An apoptotic cell death was assessed by the TUNEL assay using in situ cell death detection kit. DNA degradation was verified by electrophoresis. Results. It was determined that 2 24 hours after intoxication with sublethal dose of cadmium ions the acceptor activity of mice liver trna Leu was decreased by 43 73% as compared to control. At the same time intervals, the activity of leucyl-trna synthetase was reduced about 2 3%. Experiments in vitro revealed that 1 2 µm concentrations of cadmium ions suppressed the activities of mice liver trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase by 4 98%. No significant difference was observed between the number of TUNEL positive apoptotic liver cells in the control mice and 24 hours after intoxication with cadmium chloride. Electrophoresis revealed extensive degradation of nuclear DNA. Conclusions. Cadmium ions significantly reduce activities of trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase in vivo and in vitro. There is no significant difference between the number of apoptotic cells in the control liver specimens and in those after 24 hours of intoxication with cadmium chloride. In latter specimens DNA electrophoresis revealed as extensive degradation of DNA, which is characteristic to the cell necrosis. Introduction Heavy metal cadmium (Cd), a well-known environmental hazard, exerts a number of toxic effects in humans and animals. A decade ago, the International Agency for Research of Cancer attributed Cd to category 1 of carcinogens, which are carcinogenic to the humans (1). Tobacco smoke, food and industrial pollution are the main sources of Cd to the humans. It is recognized that an exposure to Cd can result in various pathologies including neoplasia, osteoporosis, irreversible renal tubular injury, anemia, etc. (1). A number of Cd-induced effects including deterioration of cell-cell adhesion, DNA-related processes, cell signaling and energy metabolism can imply that this metal acts on the different molecular targets in human organism. One of the targets for Cd is the system of protein synthesis or translation. There are some evidences that in translation, Cd activates particular initiation and elongation factors (2). The effect, however, is detectable only in transformed cells. Activation of translation can be a consequence of Cd-induced gene transcription, as it was determined for metallothionein Correspondence to I. Sadauskienė, Institute for Biomedical Research, Kaunas University of Medicine, Eivenių 4, 59 Kaunas, Lithuania. ilona_sad@omni.lt
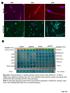
2 48 Leonid Ivanov, Vaiva Lesauskaitė, Laima Ivanovienė et al (3), heat-shock proteins (4) and glutathione (5). It is shown that effect of Cd on the protein synthesis in vivo depends on intoxication duration (6) and, probably, on dose of this metal. According to the data of in vitro study, Cd in low concentrations can activate both the rate and the level of translation but in high concentrations it inhibits those parameters (6). As the system of translation is particularly complicated, its components can differently respond to Cd. There are evidences about inhibitory action of subtoxic amount of Cd on the components of protein synthesis in rat testes (7). However, in the above study, no attention was paid on intoxication time-dependent effects of cadmium. Thus, the effects and mechanisms of Cd action on protein synthesis are controversial and not entirely understood. Acting on the different sites of cellular metabolism Cd can severely diminish cell viability resulting in the cell death (8). Interfering with death signal transduction pathways, Cd can induce two extreme types of the cell death apoptosis and necrosis (9). Mechanisms that are behind Cd-induced cell death strongly depend on the type of the cell. The experiments aimed to elucidate these mechanisms have been done on the distinct types of tissues and cells. Therefore, they can be compared with great precaution. The present study is designed to investigate the relationship between duration of Cd intoxication, protein synthesis and the mode of cell-death induced in mouse liver. We have found almost permanent decrease of activities of the components of priming stage of translation (trna and aminoacyl-trna synthetase) over 2-, 8- and 24-hour periods of Cd intoxication. The effects correlated with a change of the cell-death type from apoptosis to necrosis. Material and methods White laboratory mice (2 25 g) were used for the study (License of State Veterinary Service for Working with Laboratory Animals No. 28). Intoxication with Cd was performed by injection of sublethal dose of CdCl 2 (1.6 mg Cd 2+ per 1 kg of body mass) dissolved in physiological solution into abdominal cavity of mice. Control animals received injection of the same volume of physiological solution. The preparation procedures of both total trnas and post-mitochondrial supernatant (source of leucyl-trna synthetase) from mouse liver were described earlier (1). Acceptor activity of trna Leu was determined in the 1 µl of reaction mixture, consist of 1 mm Tris-HCl (ph 7.5), 1 mm MgCl 2, 1 mm KCl, 4 mm ATP,.2 mm [ 14 C]-leucine, 25 µg protein of postmitochondrial supernatant (source of leucyl-trna synthetase), and 5 µg total trnas. The reaction mixture was incubated at 37 C for 2 min. The reaction was stopped by adding of.2 ml ice-cold 1% trichloroacetic acid. Test tubes with reaction mixture were kept in ice bath for 2 min for formation of precipitate. The precipitate was collected on nitrocellulose filters and washed with 25 3 ml of ice-cold 5% trichloracetic acid. Radioactivity was measured in liquid scintillation counter (Delta 3, Tracor Europe, Netherlands), the efficiency of countering 6%. Acceptor activity of trna Leu was evaluated by the formation of [ 14 C]-leucyl-tRNA Leu. Activity of leucyltrna synthetase was measured in post-mitochondrial supernatant by the initial rate of trna Leu aminoacylation with [ 14 C]-labeled leucine (1). Apoptosis of liver cells was immunohistochemically detected by the TUNEL assay using in situ cell death detection kit, AP (Roche). Sections of formalinfixed and paraffin-embedded liver tissue were dewaxed by washing in xylene and rehydrated through a gradual series of ethanol and distilled water. Proteinase K permeabilized sections were subjected to enzymatic in situ labeling of DNA strand breaks using TUNELtechnique. The DNA strand breaks were revealed by adding alkaline phosphatase (AP)-converter with subsequent staining with NTB/BCIP solution as the chromogenic substrate. DNA-se pretreated tissue sections were used as a positive-control for apoptotic cells detection by TUNEL-assay. After counterstaining with eosin, sections were analyzed by light microscope (objective 2X). The dark-stained (TUNEL+) nuclei of liver cells were counted in randomly selected 1 histological fields per section. Enormously high numbers of TUNEL+ cells were present in DNA-se pretreated sections, whereas their numbers were considerably low (or even absent) in the control and in Cd-affected liver sections (Fig. 1). The nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparison between groups. Results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was set at p<.5. Agarose gel (2% w/v) electrophoresis of DNA preparations extracted from paraffin embedded liver tissue was carried out according to the protocol described in (11). Gels were stained with ethidium bromide (5 microgram/ml) for 1 min and photographed under UV light. DNA extracted from dexamethasone (5 mg/kg from Krka, Slovenia) treated 18-day-old mice thymuses was used for electrophoretic detection of internucleosomal 2 bp fragments typical for apoptotic breakdown of DNA (12).
3 Effects of cadmium ions on the initial stage of translation and the cell death in mouse liver 49 A B C C Fig. 1. TUNEL reaction in mouse liver specimens A. DNA-se pretreated mouse liver as a positive control. Most cells exhibit dark-stained, TUNEL+ nuclei (original magnification 4). B. Negative control obtained by omitting the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase enzyme from the TUNEL reaction; all cells are TUNEL- (original magnification 2). C. TUNEL+ apoptotic hepatocytes with dark-stained nuclei (arrows) in the liver specimen of a mouse after 2 hours of intoxication by CdCl 2 (original magnification 2). Results The activities of trna one of the key elements of priming stage of translation machinery isolated from normal (control) mice liver and mice liver 2 hours, 8 hours, and 24 hours after intoxication with sublethal dose of Cd (1.6 mg Cd 2+ per 1 kg of body mass) were compared in vivo. The effect of Cd intoxication on the acceptor activity of trna Leu as a representative of all trna families is shown in Fig. 2. After 2 hours, 8 hours, and 24 hours of Cd intoxication, the acceptor activity of trna Leu was reduced by 43%, 73%, and 54%, respectively. Next, we examined influence of Cd 2+ ions on the activity one of the 2 aminoacyl-trna synthetases, namely leucyl-trna synthetase. The results obtained indicate that activity of leucyl-trna synthetase was suppressed down to 81%, 81%, and 7% of the control level 2 hours, 8 hours, and 24 hours after injection of CdCl 2 solution, respectively (Fig. 3). In order to evaluate direct effects of Cd 2+ ions on trna Leu and on leucyl-trna synthetase, the experiments in vitro were performed. CdCl 2 solution was added into the reaction mixture with preparations of trna and aminoacyl-trna synthetases isolated from control mice liver. In reaction mixture, final concentrations of Cd 2+ ions were 5 µm, 1 µm, 15 µm, and 2 µm. Acceptor activity of trna Leu and activity of leucyl-trna synthetase were measured (Fig. 4). These experiments showed that 1 µm concentration of Cd 2+ ions in reaction mixture decreased the acceptor activity of mice liver trna Leu and activity of leucyltrna synthetase by 4%. Higher concentrations of Cd 2+ ions (2 µm) almost fully inactivated the trna Leu, whereas partially reduced activity of leucyl-trna Activity of trna (nmol leu/ mg trna) Control Cd 2h Cd 8h Cd 24h Fig. 2. Acceptor activity of trna Leu, isolated from mouse liver in norm and 2 hours, 8 hours, and 24 hours after injection of CdCl 2 solution (1.6 mg Cd 2+ per 1 kg of body mass) The data represents results of 8 14 separate experiments. Differences between control and experimental groups are statistically significant.
4 5 Leonid Ivanov, Vaiva Lesauskaitė, Laima Ivanovienė et al Activity of leucyl-trna synthetase (pmol leucyl-trna/min/mg protein) Control Cd 2h Cd 8h Cd 24h Fig. 3. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase activity of mice liver post-mitochondrial supernatant in norm and 2 hours, 8 hours, and 24 hours after injection of CdCl 2 solution (1.6 mg Cd 2+ per 1 kg of body mass) Data represent results of 8 1 separate experiments. Differences between control and experimental groups are statistically significant. synthetase was 3% of the control activity (Fig. 4). How Cd-induced partial inactivation of the components of translation in vivo correlates with liver cell viability, we assessed according to the effect of Cd ions on apoptotic cell number in paraffin-embedded liver tissue sections. We have determined that 24 hours after CdCl 2 injection, the number of TUNEL positive cells did not differ from the control range (Fig. 5). Agarose-gel electrophoresis of genomic DNA isolated from Cd-affected mice liver revealed extensively degraded DNA (Fig. 6 A, lane 3). In specimens from the control liver, DNA was concentrated at the top of the lane or displayed large fragments containing more than 2652 bp (Fig. 6, lane 2). Although, there were small numbers of TUNEL positive cells detected in both the control liver and Cd-affected liver, no typical apoptotic ladder of DNA was reveal by electrophoresis (Fig. 6 A, lanes 2 and 3). Extensively degraded DNA trna Leucyl-tRNA synthetase 1 8 Activity (%) Cd concentration (µm) Fig. 4. Activities of mouse liver trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase after treatment with CdCl 2 in vitro Activities were determined in the presence of indicated concentration of Cd 2+. The data represents results of 6 8 separate experiments.
5 Effects of cadmium ions on the initial stage of translation and the cell death in mouse liver 51 n 12 1 A B bp 75 bp 5 bp 2 Cd 24 h Control Fig. 5. The number of TUNEL-positive cells in mouse liver 24 hours after injection of CdCl 2 solution (1.6 mg Cd 2+ per 1 kg of body mass) Cell counting was carried out in 1 histological fields in each of 3 sections taken from experimental and control liver. The data represents results of 3 separate experiments. indicates on non-apoptotic cell death type (presumably necrosis) as a dominant form of the liver cell death after 24h of Cd exposure. It is noteworthy, that manifestation of non-apoptotic cell death coincided with a significant diminution of protein synthesis rate observed in 24 hours of the liver exposure to Cd. Validity of the data of DNA electrophoresis was verified using preparations of DNA extracted from thymuses of dexamethasone treated 18-day-old mice. Small DNA fragments (about 2 bp) revealed by electrophoresis can be considered as an evidence of active apoptosis of thymocytes (Fig. 6 B, lane 2). Thus, these data confirm reliability of the qualitative detection of state of DNA extracted from Cd-intoxicated mice liver by agarose-gel electrophoresis. Discussion Being a ubiquitous toxic metal Cd causes deterioration of a number of cellular processes. Our previous investigations have revealed initial inhibition of translation in mice liver within the first 2 4 hours, which progressed into stimulation, reaching its maximum at 8 th hour, and subsequent decrease at 24 th hour after injection of a single dose of CdCl 2 (1.6 mg per 1 kg of body mass) (6). Notable, that within 24 hour period after a single injection of CdCl 2 solution (1.6 Fig. 6. Agarose-gel electrophoresis of DNA extracted from the mice liver (A) and from dexamethasone-treated mice thymuses (B) In A, the lane 1 DNA molecular weight marker XIII (Roche), the lane 2 DNA extracted from control mice liver, the lane 3 DNA extracted from 24 hour Cdintoxicated mice liver. In B, the lane 1 DNA extracted from dexamethasone-treated mice thymuses, the lane 2 the molecular weight marker GeneRuler 1 bp DNA Ladder plus. mg per kg of body mass), Cd 2+ ions are being accumulated in liver in a concentration as high as µg/g, what corresponds to.134 µmol/g (13). In vitro Cd 2+ at 4 µm concentration exerted stimulatory effect on both parameters of translation the rate and the level, while at 6 µm concentration the ion caused sharp diminution of those parameters (6). In present study, we focused on evaluation of Cd 2+ ion effects on the translation process and on the activity of key components of liver translation machinery as well as on liver cell viability. Bearing in mind the fact that the translation rate in mouse liver was maximum at 8h after Cd intoxication (6), the decreases in activities of both studied translation machinery components (trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase) (Fig. 2 and 3) seem to be paradoxical at this time point of Cd exposure. These seemingly controversial results can be interpreted in terms of Cd-induced synthesis of cytoprotective proteins such as metallothionein (3) and heat-shock proteins known as chaperons (4). Active synthesis of those proteins can contribute to an increase of the translation rate in mouse liver after 8h of Cd intoxi-
6 52 Leonid Ivanov, Vaiva Lesauskaitė, Laima Ivanovienė et al cation reported in our recent study (6). It is known that Cd 2+ ions directly react with nucleic acids (14) and with sulfhydryl groups of proteins (1). In the present in vivo study, the direct effects of Cd 2+ ions might cause inhibition of the activities of trnaleu and leucyltrna synthetase. Absence of the positive correlation between changes in the translation rate and the activities of trna Leu as well as leucyl-trna synthetase observed in our experiments may be explained by peculiarities of the regulation of translation: neither trna nor aminoacyl-trna synthetases do not exert control over the rate of protein synthesis under Cd intoxication. The process is probably controlled by other components of translation machinery. Cd complexation with protein sulfhydryl groups may disrupt cellular redox state (8) and inhibit a number of enzymes, thereby impairing viability of cells. As Cd 2+ ions accumulate in the liver and the kidney, cells of these organs are the primary targets for toxic action of Cd 2+. Irreversible damage of vitally essential cellular processes can lead to cell death. According to our recent investigations, Cd intoxication up to 8 hours results in an increase of apoptotic (TUNEL+) cell number in mouse liver sections (15). Cd seems to induce apoptosis via a mitochondriadependent pathway (16). Pro-apoptotic Cd effect can be potentiated by a mild decrease of reduced glutathione level in the transformed rat liver cells (8). As Cd induces necrosis under conditions of sulfhydrylgroup deficiency, oxidation of glutathione appears to be critical for changing of the cell death phenotype from apoptosis to necrosis. Cd-caused decrease of reduced glutathione level is intoxication time and dose dependent (17). These findings coincide with our results that have revealed the same number of TUNEL+ cells in both the control liver and the liver of mice subjected to 24h of Cd intoxication (Fig. 5). Although, TUNEL+ cells were identified in both the control and the Cd-affected liver, DNA electrophoresis did not reveal DNA-laddering characteristic to apoptosis. This can be caused by relatively low number of apoptotic cells that is insufficient for detection of apoptosis-specific DNA fragments by electrophoresis (18). There was the smear background pattern found by DNA electrophoresis (Fig. 6A, lane 3), which has been suggested to indicate extensive degradation of nuclear DNA. This can be assumed as an evidence of necrosis induced by 24h exposure of the liver to Cd 2+ ions. Other authors also reported about Cd-caused non-apoptotic cell death (9, 18). Manifestation of necrosis might be a consequence of coincidence of several different events including Cd-caused inhibition of mitochondria (2), down-regulation of antioxidant enzymes expression (21), and inhibition of activity of antioxidant enzymes (22). Thus, depletion of ATP, inhibition of protein synthesis, and uncontrolled oxidative stress may be regarded as the main causes of Cd hepatotoxicity. Conclusions 1. Cadmium ions significantly reduce activities of both, trna and aminoacyl-trna synthetase, what does not positively correlatedoes with the changes of total protein synthesis in mice liver. 2. There is no significant difference between the number of apoptotic cells in the control liver specimens and in those after 24 hours of intoxication with cadmium chloride. In latter specimens DNA electrophoresis revealed as extensive degradation of DNA as in the cell necrosis. Kadmio jonų poveikis pelės kepenų baltymų sintezės pradinei stadijai ir ląstelių žūčiai Leonid Ivanov 1, 2, Vaiva Lesauskaitė 3, Laima Ivanovienė 2, Ilona Sadauskienė 1, 2, Rasa Gailevičiūtė 1, Dovilė Karčiauskaitė 3, Hiliaras Rodovičius 2 1 Kauno medicinos universiteto Biomedicininių tyrimų institutas 2 Biochemijos katedra, 3 Kardiologijos institutas Raktažodžiai: kadmis, trnr, leucil-trnr-sintetazė, apoptozė, nekrozė. Santrauka. Darbo tikslas. Įvertinti kadmio jonų poveikį pelių kepenų trnr Leu ir leucil-trnr-sintetazės aktyvumams in vivo ir in vitro bei nustatyti kadmio jonų indukuotą kepenų ląstelių žūties tipą. Tyrimo medžiaga ir metodai. Intoksikacija kadmio jonais sukelta baltoms laboratorinėms pelėms į pilvo ertmę sušvirkštus kadmio chlorido tirpalo (1,6 mg kadmio jonų 1 kg kūno masės). Suminiai trnr preparatai išskirti pridedant etanolio ir izopropanolio į supernatantą, gautą fenoliu deproteinizavus kepenų homogenatą. Leucil-tRNR-sintetazės aktyvumas nustatytas kepenų bemitochondriniame supernatante. trnr Leu ir leuciltrnr-sintetazės aktyvumai įvertinti pagal [ 14 C]-leucino panaudojimą trnr aminoacilinimo reakcijos metu. Ląstelių žūties fenotipas tirtas imunohistochemiškai panaudojant TUNEL in situ fermentinę reakciją.
7 Effects of cadmium ions on the initial stage of translation and the cell death in mouse liver 53 Rezultatai. Nustatyta, kad, praėjus 2 24 val. po intoksikavimo kadmio jonais, pelių kepenų trnr Leu akceptorinis aktyvumas sumažėjo proc. lyginant su kontrole. Tokios pat trukmės intoksikacijos metu leucil-trnr-sintetazės aktyvumas sumažėjo apie 2 3 proc. Atliekant eksperimentus in vitro, nustatyta, kad reakcijos terpėje, kai kadmio jonų koncentracija 1 2 µm, trnr Leu ir leucil-trnr-sintetazės aktyvumai sumažėja 4 98 proc. Morfologinių tyrimų duomenimis, 24 val. po intoksikavimo kadmio chloridu TUNEL teigiamų, t. y. apoptozinių, kepenų ląstelių skaičius nesiskyrė nuo kontrolės. Atlikus DNR elektroforezę, nustatytas chaotiškas DNR irimas, būdingas nekrozės būdu žuvusioms ląstelėms. Išvados. Kadmio jonai reikšmingai sumažina trnr Leu ir leucil-trnr-sintetazės aktyvumus tiek in vivo, tiek ir in vitro. Praėjus 24 val. po pelių intoksikavimo kadmio jonais, apoptozinių ląstelių skaičius kepenų pavyzdžiuose nesiskyrė nuo kontrolės. Elektroforezės metodu atlikus DNR ekstraktų analizę, nustatytas chaotiškas DNR irimas, būdingas nekrozės būdu žuvusioms ląstelėms. Adresas susirašinėti: I. Sadauskienė, KMU Biomedicininių tyrimų institutas, Eivenių 4, 59 Kaunas El. paštas: ilona_sad@omni.lt References 1. Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B, Beyersmann D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 23;192: Joseph P, Lei YX, Whong WZ, Ong TM. Oncogenic potential of mouse translation elongation factor-1 delta, a novel cadmium-responsive proto-oncogene. J Biol Chem 22;277: McKenna IM, Gordon T, Chen LC, Anver MR, Waalkes MP. Expression of metallothionein protein in the lungs of Wistar rats and C57 and DBA mice exposed to cadmium oxide fumes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1998;153: Goering PL, Fisher BR, Kish C. Stress protein synthesis induced in rat liver by cadmium precedes hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1993;122: Singhal RK, Anderson ME, Meister A. Glutathione, a firts line of defense against cadmium toxicity. FASEB J 1987;1: Ivanov L, Sadauskiene I, Viezeliene D, Stapulionis R. Mice liver protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro after cadmium chloride administration. Trace Elements and Electrolytes 23;2: Nicholls DM, Rakhra GS. Testicular protein synthesis during the response to subtoxic levels of cadmium. Horm Res 1981; 14: Kim SC, Cho MK, Kim SG. Cadmium induced non-apoptotic cell death mediated by oxidative stress under condition of sulfhydryl deficiency. Toxicol Lett 23;144: Habeebu SS, Liu J, Klaassen CD. Cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1998;149: Rodovičius H, Vieželienė D, Stanevičienė I, Sadauskienė I, Kašauskas A, Ivanov L. Švino jonų poveikis pelių kepenų trnr Leu ir leucil-trnr-sintetazės aktyvumui. (The effects of lead ions on activities of trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase from mice liver.) Medicina (Kaunas) 23;39: Lesauskaite V, Epistolato MC, Ivanoviene L, Tanganelli P. Apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in explanted and transplanted hearts. Am J Clin Pathol 23;12: Staley K, Blaschke AJ, Chun J. Apoptotic DNA fragmentation Received 1 February 24, accepted 5 December 24 Straipsnis gautas , priimtas is detected by a semi-quantitative ligation-mediated PCR of blunt DNA ends. Cell Death Differ 1997;4: Naginienė R, Sadauskienė I, Ryselis S, Abdrachmanovas O, Ivanovas L. Kadmio jonų poveikio baltymų biosintezei pelių kepenyse ir inkstuose įvertinimas. (Assessment of the effects of cadmium ions on protein biosynthesis in mice liver and kidney.) Visuomenės sveikata 23;2: Hossain Z, Huq F. Studies on the interaction between Cd(2 + ) ions and nucleobases and nucleotides. J Inorg Biochem 22;9: Ivanov L, Lesauskaitė V, Sadauskienė I, Stapulionis R, Ivanovienė L. Acute cadmium exposure changes protein synthesis in mice liver and activates apoptosis. Biomedicine 22;2: Kondoh M, Araragi S, Sat K, Higashimoto M, Takiguchi M, Sato M. Cadmium induces apoptosis partly via caspases-9 activation in HL-6 cells. Toxicology 22;17: Xu J, Maki D, Stapleton SR. Mediation of cadmium-induced oxidative damage and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression through glutathione depletion. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 23;17: Collins RJ, Harmon BV, Gobe GC, Kerr JF. Internucleosomal DNA cleavage should not be the sole criterion for identifying apoptosis. Int J Radiat Biol 1992;61: Galan A, Troyano A, Vilaboa NE, Fernandez CD, Blas E, Aller P. Modulation of the stress response during apoptosis and necrosis induction in cadmium-treated U-937 human promonocytic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 21;1538: Liu RM, Liun YG. Effects of cadmium on the energy metabolism of isolated hepatocytes: its relationship with the nonviability of isolated hepatocytes caused by cadmium. Biomed Environ Sci 1993;3: Liu J, Kadiiska MB, Corton JC, Qu W, Waalkes MP, Mason RP et al. Acude cadmium exposure induces stress-related gene expression in wild-type and metallothionein-i/ii-nul mice. Free Radic Biol Mrd 22;32: Tatrai E, Kovacikova Z, Hudak A, Adamis Z, Ungvary G. Comparative in vitro toxicity of cadmium and lead on redox cycling in type II pneumocytes. J Appl Toxicol 21;21:
The effects of zinc ions on activities of trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase of mice liver
 982 The effects of zinc ions on activities of trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase of mice liver Hiliaras Rodovičius, Dalė Vieželienė, 2, Ilona Sadauskienė, 2, Sandra Valentukonytė 2, Leonid Ivanov, 2 Department
982 The effects of zinc ions on activities of trna Leu and leucyl-trna synthetase of mice liver Hiliaras Rodovičius, Dalė Vieželienė, 2, Ilona Sadauskienė, 2, Sandra Valentukonytė 2, Leonid Ivanov, 2 Department
Subacute effects of cadmium and zinc ions on protein synthesis and cell death in mouse liver
 131 Subacute effects of cadmium and zinc ions on protein synthesis and cell death in mouse liver Inga Stanevièienë, Ilona Sadauskienë, Vaiva Lesauskaitë 1, Laima Ivanovienë 2, Artûras Kaðauskas 2, Leonid
131 Subacute effects of cadmium and zinc ions on protein synthesis and cell death in mouse liver Inga Stanevièienë, Ilona Sadauskienë, Vaiva Lesauskaitë 1, Laima Ivanovienë 2, Artûras Kaðauskas 2, Leonid
The cytotoxic effects of cadmium chloride on the human lung carcinoma (Calu-6) cell line
 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, October 2008; 3(2): 49-53 Received: Mar 2008 Accepted: Jul 2008 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, October 2008; 3(2): 49-53 Received: Mar 2008 Accepted: Jul 2008 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
Acute toxicity of ibogaine and noribogaine
 984 Asta Kubilienė, Rūta Marksienė, Saulius Kazlauskas, Ilona Sadauskienė 1, Almantas Ražukas 2, Leonid Ivanov 1 Department of Analytical and Toxicological Chemistry, 1 Institute for Biomedical Research,
984 Asta Kubilienė, Rūta Marksienė, Saulius Kazlauskas, Ilona Sadauskienė 1, Almantas Ražukas 2, Leonid Ivanov 1 Department of Analytical and Toxicological Chemistry, 1 Institute for Biomedical Research,
The effects of lead and nickel ions on total proteins and metallothioneins synthesis in mice liver
 BIOLOGIJA. 2014. Vol. 60. No. 1. P. 17 21 Lietuvos mokslų akademija, 2014 The effects of lead and nickel ions on total proteins and metallothioneins synthesis in mice liver Indrė Šveikauskaitė 1 *, Jurgita
BIOLOGIJA. 2014. Vol. 60. No. 1. P. 17 21 Lietuvos mokslų akademija, 2014 The effects of lead and nickel ions on total proteins and metallothioneins synthesis in mice liver Indrė Šveikauskaitė 1 *, Jurgita
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
EVALUATION OF FOLLICULAR ATRESIA AND ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERN OF FOLLICULAR FLUID PROTEINS IN ACYCLIC BUFFALO (Bubalus bubalis)
 Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (December 2013) Vol.32 No.4 EVALUATION OF FOLLICULAR ATRESIA AND ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERN OF FOLLICULAR FLUID PROTEINS IN ACYCLIC BUFFALO (Bubalus bubalis) F.A. Khan 1,*,
Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (December 2013) Vol.32 No.4 EVALUATION OF FOLLICULAR ATRESIA AND ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERN OF FOLLICULAR FLUID PROTEINS IN ACYCLIC BUFFALO (Bubalus bubalis) F.A. Khan 1,*,
Functional changes in rat liver trna following aflatoxin Β 1 administration
 J. Biosci., Vol. 3 Number 3, September 1981, pp. 215-219 Printed in India. Functional changes in rat liver trna following aflatoxin Β 1 administration R. K. BHATTACHARYA and V.S. ABOOBAKER Biochemistry
J. Biosci., Vol. 3 Number 3, September 1981, pp. 215-219 Printed in India. Functional changes in rat liver trna following aflatoxin Β 1 administration R. K. BHATTACHARYA and V.S. ABOOBAKER Biochemistry
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/142604
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/142604
The Comet and TUNEL Assays
 Sperm DNA: organization, protection and vulnerability from basic science to clinical application Methods to assess the status of the sperm DNA: The Comet and TUNEL Assays Lars Björndahl Centre for Andrology
Sperm DNA: organization, protection and vulnerability from basic science to clinical application Methods to assess the status of the sperm DNA: The Comet and TUNEL Assays Lars Björndahl Centre for Andrology
Glutathione Regulation
 The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes
 BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Background Information Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes A. BIOCHEMISTRY The basic pattern of glucose oxidation is outlined in Figure 3-1. Glucose is split
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Background Information Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes A. BIOCHEMISTRY The basic pattern of glucose oxidation is outlined in Figure 3-1. Glucose is split
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit
 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Figure S1. B % of Phosphorylation 32H. 32ss
 Figure S1 8H 32ss 32H 32Hc % of Phosphorylation 3 32H 2 1 32ss 1 2 3 4 Extract (μg) C % of Phosphorylation 18 12 6-32H 32Hc 8H 32ss Dbait Figure S1. List of the Dbait molecules and activation of DN-PK
Figure S1 8H 32ss 32H 32Hc % of Phosphorylation 3 32H 2 1 32ss 1 2 3 4 Extract (μg) C % of Phosphorylation 18 12 6-32H 32Hc 8H 32ss Dbait Figure S1. List of the Dbait molecules and activation of DN-PK
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
HRP cytochemistry. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany
 HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Catalog # Lot # 16875
 MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
Mechanistic Toxicology
 SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II. Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models?
 The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
(Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig. 1A). A 5.4-kb EcoRI fragment
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS
 Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS A. STOCK SOLUTIONS FOR DNA ISOLATION 0.5M Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) (ph=8.0) 1M Tris-Cl (ph=8.0) 5M NaCl solution Red cell lysis buffer (10X) White cell
Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS A. STOCK SOLUTIONS FOR DNA ISOLATION 0.5M Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) (ph=8.0) 1M Tris-Cl (ph=8.0) 5M NaCl solution Red cell lysis buffer (10X) White cell
Cadmium Binding Components in the Supernatant Fraction of Liver, Kidney and Intestinal Mucosa Homogenates of Cadmium-Administered Rats
 Cadmium Binding Components in the Supernatant Fraction of Liver, Kidney and Intestinal Mucosa Homogenates of Cadmium-Administered Rats Keiichi Tanaka and Kaori Sueda Department of Public Health, Faculty
Cadmium Binding Components in the Supernatant Fraction of Liver, Kidney and Intestinal Mucosa Homogenates of Cadmium-Administered Rats Keiichi Tanaka and Kaori Sueda Department of Public Health, Faculty
Naoki YAMANAKA, Toshio IMANARI,* Zenzo TAMURA,*
 J. Biochem., 73, 993-998 (1973) Uncoupling of Oxidative Phosphorylation of Rat Liver Mitochondria by Chinoform Naoki YAMANAKA, Toshio IMANARI,* Zenzo TAMURA,* and Kunio YAGI Institute of Biochemistry,
J. Biochem., 73, 993-998 (1973) Uncoupling of Oxidative Phosphorylation of Rat Liver Mitochondria by Chinoform Naoki YAMANAKA, Toshio IMANARI,* Zenzo TAMURA,* and Kunio YAGI Institute of Biochemistry,
Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
CHAPTER 7: REAGENTS AND SOLUTIONS
 7.1. ANALYSIS OF MODULATION OF SOD ENZYME Acetic acid (cat. no. 11007, Glaxo Qualigen, India): Bovine Serum Albumin stock solution (BSA, 1mg/ml): 1 mg of standard bovine serum albumin (cat. no. A2153,
7.1. ANALYSIS OF MODULATION OF SOD ENZYME Acetic acid (cat. no. 11007, Glaxo Qualigen, India): Bovine Serum Albumin stock solution (BSA, 1mg/ml): 1 mg of standard bovine serum albumin (cat. no. A2153,
Available online through ISSN
 Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 PROTECTIVE ROLE OF GLUTATHIONE IN TUNGSTEN-INDUCED TOXICITY IN BLOOD COMPONENTS: A PHARMACOLOGICAL AND TOXICOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Arshad
Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 PROTECTIVE ROLE OF GLUTATHIONE IN TUNGSTEN-INDUCED TOXICITY IN BLOOD COMPONENTS: A PHARMACOLOGICAL AND TOXICOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Arshad
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION. chemistry, polar substances would dissolve in polar solvents while non-polar substances
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Extraction yield of Alpinia scabra Samples of A. scabra were dried in an oven as a method of preservation after which the samples were ground to powder. The latter
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Extraction yield of Alpinia scabra Samples of A. scabra were dried in an oven as a method of preservation after which the samples were ground to powder. The latter
C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein. pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is
 ' ^Summary C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is of greater importance because of its various
' ^Summary C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is of greater importance because of its various
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
Doctor of Philosophy
 Regulation of Gene Expression of the 25-Hydroxyvitamin D la-hydroxylase (CYP27BI) Promoter: Study of A Transgenic Mouse Model Ivanka Hendrix School of Molecular and Biomedical Science The University of
Regulation of Gene Expression of the 25-Hydroxyvitamin D la-hydroxylase (CYP27BI) Promoter: Study of A Transgenic Mouse Model Ivanka Hendrix School of Molecular and Biomedical Science The University of
DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice
 Biology 12 DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice Name: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for a) the sequence of amino acids in a protein b) the sequence of base pairs
Biology 12 DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice Name: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for a) the sequence of amino acids in a protein b) the sequence of base pairs
PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature
 PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. RNAzol BD is a reagent for isolation of total RNA from whole blood, plasma or serum of human
PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. RNAzol BD is a reagent for isolation of total RNA from whole blood, plasma or serum of human
Item Catalog Number Manufacturer 1,4-Dithioerythritol (1 g) D9680 Sigma-Aldrich
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices
 Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices Sittiwat Lertsiri Department of Biotechnology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Phayathai, Bangkok 10400 Thailand Kanchana Dumri Department
Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices Sittiwat Lertsiri Department of Biotechnology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Phayathai, Bangkok 10400 Thailand Kanchana Dumri Department
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit
 HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
Atg5 flox/flox ; CAG-Cre, 19M brain heart lung. spleen stomach colon. Takamura_Fig. S1
 Takamura_Fig. S1 brain heart lung spleen stomach colon kidney SM Supplemental Figure 1 Histological findings of tg5 flox/flox ;CG-Cre mouse tissues. H&E staining of the brain, heart, lung, spleen, stomach,
Takamura_Fig. S1 brain heart lung spleen stomach colon kidney SM Supplemental Figure 1 Histological findings of tg5 flox/flox ;CG-Cre mouse tissues. H&E staining of the brain, heart, lung, spleen, stomach,
Product Manual. Omni-Array Sense Strand mrna Amplification Kit, 2 ng to 100 ng Version Catalog No.: Reactions
 Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
INTERNATIONAL CONCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE Q3D(R1)
 INTERNATIONAL CONCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE GUIDELINE FOR ELEMENTAL IMPURITIES (R1) Draft version Endorsed on 18 May 2018
INTERNATIONAL CONCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE GUIDELINE FOR ELEMENTAL IMPURITIES (R1) Draft version Endorsed on 18 May 2018
SAFETY ASPECTS OF MIDAZOLAM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(12): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(12):30-34 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Alphonsea Sclerocarpa
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(12):30-34 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Alphonsea Sclerocarpa
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit. Catalog Number SIALICQ Storage Temperature 2 8 C
 Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit Catalog Number SIALICQ Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit provides a rapid and accurate determination of total
Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit Catalog Number SIALICQ Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit provides a rapid and accurate determination of total
STUDY ON ANTITUMOR DRUG-INDUCED APOPTOSIS IN HUMAN CANCER CELLS BY TERMINAL DEOXYNU- CLEOTIDYL TRANSFERASE ASSAY
 Chinese JournalofCancer Research 9(3):157-161,199Z Basic Investigations STUDY ON ANTITUMOR DRUG-INDUCED APOPTOSIS IN HUMAN CANCER CELLS BY TERMINAL DEOXYNU- CLEOTIDYL TRANSFERASE ASSAY Tong Tong" ~P~ Sun
Chinese JournalofCancer Research 9(3):157-161,199Z Basic Investigations STUDY ON ANTITUMOR DRUG-INDUCED APOPTOSIS IN HUMAN CANCER CELLS BY TERMINAL DEOXYNU- CLEOTIDYL TRANSFERASE ASSAY Tong Tong" ~P~ Sun
Glutathione Assay Kit
 Glutathione Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1649 250 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Glutathione Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1649 250 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
Activation of Mitochondrial Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase by Cadmium Ions
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1985), 4, 29 34 29 Activation of Mitochondrial Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase by Cadmium Ions H. RAUCHOVÁ, P. P. KAUL* and Z. DRAHOTA Institute of Physiology, Czechoslovak Academy
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1985), 4, 29 34 29 Activation of Mitochondrial Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase by Cadmium Ions H. RAUCHOVÁ, P. P. KAUL* and Z. DRAHOTA Institute of Physiology, Czechoslovak Academy
TRACP & ALP double-stain Kit
 Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
Experiment 1. Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver
 Experiment 1 Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver Figure 35: FIG-2, Liver, PAS, 100x. Note the presence of a few scattered glycogen granules (GG). Objective To illustrate the method for isolating glycogen.
Experiment 1 Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver Figure 35: FIG-2, Liver, PAS, 100x. Note the presence of a few scattered glycogen granules (GG). Objective To illustrate the method for isolating glycogen.
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
10 mm KCl in a Ti-15 zonal rotor at 35,000 rpm for 16 hr at
 Proc. Nat. Acad. SCi. USA Vol. 68, No. 11, pp. 2752-2756, November 1971 Translation of Exogenous Messenger RNA for Hemoglobin on Reticulocyte and Liver Ribosomes (initiation factors/9s RNA/liver factors/reticulocyte
Proc. Nat. Acad. SCi. USA Vol. 68, No. 11, pp. 2752-2756, November 1971 Translation of Exogenous Messenger RNA for Hemoglobin on Reticulocyte and Liver Ribosomes (initiation factors/9s RNA/liver factors/reticulocyte
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
Prerequisites Protein purification techniques and protein analytical methods. Basic enzyme kinetics.
 Case 19 Purification of Rat Kidney Sphingosine Kinase Focus concept The purification and kinetic analysis of an enzyme that produces a product important in cell survival is the focus of this study. Prerequisites
Case 19 Purification of Rat Kidney Sphingosine Kinase Focus concept The purification and kinetic analysis of an enzyme that produces a product important in cell survival is the focus of this study. Prerequisites
Superoxide Dismutase Kit
 Superoxide Dismutase Kit Catalog Number: 7500-100-K Reagent kit for the analysis of Superoxide Dismutase in cell extracts. Sufficient reagents for 100 experimental tests, 50 negative controls, and 50 positive
Superoxide Dismutase Kit Catalog Number: 7500-100-K Reagent kit for the analysis of Superoxide Dismutase in cell extracts. Sufficient reagents for 100 experimental tests, 50 negative controls, and 50 positive
Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 8 Number 1 Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives P Igbinaduwa, B Igbinaduwa, I Oforofuo Citation P Igbinaduwa,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 8 Number 1 Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives P Igbinaduwa, B Igbinaduwa, I Oforofuo Citation P Igbinaduwa,
Figure 8.1: Principle reaction behind DPPH assay Unnati Shah Institute of Pharmacy, Nirma University-Ph.D. thesis 136
 8. Antioxidant and DNA fragmentation assay of bioactives of S. racemosa 8.1. Instrument Instruments used in the study were Gel electrophoresis assembly (Genei, India), UV spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan)
8. Antioxidant and DNA fragmentation assay of bioactives of S. racemosa 8.1. Instrument Instruments used in the study were Gel electrophoresis assembly (Genei, India), UV spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan)
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit User Manual (v5)
 Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Audrey van Drogen, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Sidney
AD Award Number: TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Audrey van Drogen, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Sidney
Nitric oxide damages neuronal mitochondria and induces apoptosis in neurons
 Nitric oxide damages neuronal mitochondria and induces apoptosis in neurons WEI Taotao, CHEN Chang, HOU Jingwu, ZHAO Baolu & XIN Wenjuan Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101,
Nitric oxide damages neuronal mitochondria and induces apoptosis in neurons WEI Taotao, CHEN Chang, HOU Jingwu, ZHAO Baolu & XIN Wenjuan Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101,
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Case 19 Purification of Rat Kidney Sphingosine Kinase
 Case 19 Purification of Rat Kidney Sphingosine Kinase Focus concept The purification and kinetic analysis of an enzyme that produces a product important in cell survival is the focus of this study. Prerequisites
Case 19 Purification of Rat Kidney Sphingosine Kinase Focus concept The purification and kinetic analysis of an enzyme that produces a product important in cell survival is the focus of this study. Prerequisites
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
The Biochemistry of apoptosis
 The Biochemistry of apoptosis 1 1 The apoptosis is composed of multiple biochemical events 2 2 Biochemical, cellular, and molecular events in Apoptosis 1. Membrane blebbing; phosphatidyl serine exposure
The Biochemistry of apoptosis 1 1 The apoptosis is composed of multiple biochemical events 2 2 Biochemical, cellular, and molecular events in Apoptosis 1. Membrane blebbing; phosphatidyl serine exposure
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
Kinase Inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 in Apoptosis and Autophagy
 Pivotal Role of the Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 in Apoptosis and Autophagy Keishi Fujiwara, Shigeru Daido, Akitsugu Yamamoto, Ryuji Kobayash, Tomohisa Yokoyama, Hiroshi Aok, Eiji Iwado,
Pivotal Role of the Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 in Apoptosis and Autophagy Keishi Fujiwara, Shigeru Daido, Akitsugu Yamamoto, Ryuji Kobayash, Tomohisa Yokoyama, Hiroshi Aok, Eiji Iwado,
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D.
 Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
BIOENERGETICS. 1. Detection of succinate dehydrogenase activity in liver homogenate using artificial electron acceptors.
 BIOENERGETICS Problems to be prepared: 1. Methods of enzymes activity assessment, the role of artificial electron acceptors and donors. 2. Reactions catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase, succinate dehydrogenase,
BIOENERGETICS Problems to be prepared: 1. Methods of enzymes activity assessment, the role of artificial electron acceptors and donors. 2. Reactions catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase, succinate dehydrogenase,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular
 III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
The University of ~ukurova, Art & Science Faculty, Department of Chemistry, BaIcali, Adana-TURKEY
 BIOCHEMISTRY andmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL pages 227-232 EFFECTS OF SULFHYDRYL COMPOUNDS ON THE INHIBITION OF ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE Na+-K + ATPase BY OZONE Rmnazan Bilgin, Sermin Gill, S. Seyhan Ttikel
BIOCHEMISTRY andmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL pages 227-232 EFFECTS OF SULFHYDRYL COMPOUNDS ON THE INHIBITION OF ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE Na+-K + ATPase BY OZONE Rmnazan Bilgin, Sermin Gill, S. Seyhan Ttikel
Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice
 Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice Jimmy A. Rotolo 1, Branka Stancevic 1, Jianjun Zhang 1, Guoqiang Hua 1, John Fuller 1, Xianglei Yin 1, Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman 2, Kisu
Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice Jimmy A. Rotolo 1, Branka Stancevic 1, Jianjun Zhang 1, Guoqiang Hua 1, John Fuller 1, Xianglei Yin 1, Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman 2, Kisu
IMMP8-1. Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
 IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
XCF TM COMPLETE Exosome and cfdna Isolation Kit (for Serum & Plasma)
 XCF TM COMPLETE Exosome and cfdna Isolation Kit (for Serum & Plasma) Cat# XCF100A-1 User Manual Store kit components at +4ºC and +25ºC Version 1 2/2/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product.
XCF TM COMPLETE Exosome and cfdna Isolation Kit (for Serum & Plasma) Cat# XCF100A-1 User Manual Store kit components at +4ºC and +25ºC Version 1 2/2/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product.
Melatonin and its Role in the Inhibition of Breast Cancer Ciara Nicol Ross Copyright 2014 by Ciara Ross and Koni Stone
 1 Melatonin and its Role in the Inhibition of Breast Cancer Ciara Nicol Ross Copyright 2014 by Ciara Ross and Koni Stone Cancer is a disease caused by out of control division of abnormal cells within a
1 Melatonin and its Role in the Inhibition of Breast Cancer Ciara Nicol Ross Copyright 2014 by Ciara Ross and Koni Stone Cancer is a disease caused by out of control division of abnormal cells within a
Aggregation of Sphingosine-DNA and cell construction using components from egg white
 Integrative Molecular Medicine Research Article ISSN: 2056-6360 Aggregation of Sphingosine-DNA and cell construction using components from egg white Shoshi Inooka* The Institute of Japan Applied Food Materials
Integrative Molecular Medicine Research Article ISSN: 2056-6360 Aggregation of Sphingosine-DNA and cell construction using components from egg white Shoshi Inooka* The Institute of Japan Applied Food Materials
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing hybridization signals for chicken (left) and quail (right) genomic DNA analyzed by Chicken GeneChip (n=3). www.nature.com/nature 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Independent
Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing hybridization signals for chicken (left) and quail (right) genomic DNA analyzed by Chicken GeneChip (n=3). www.nature.com/nature 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Independent
Effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on the activity of hexokinase and lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in regions of the rat brain
 J. Biosci., Vol. 6, Number 3, September 1984, pp. 331-336. Printed in India. Effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on the activity of hexokinase and lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in regions of the rat brain
J. Biosci., Vol. 6, Number 3, September 1984, pp. 331-336. Printed in India. Effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on the activity of hexokinase and lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in regions of the rat brain
Attempts to Create Rickets in Mice Using a Calcium Deficient Diet
 Attempts to Create Rickets in Mice Using a Calcium Deficient Diet Holly Hauser Abstract: Previous research with chickens produced rickets by reducing the calcium content of the diet. When rickets occurred,
Attempts to Create Rickets in Mice Using a Calcium Deficient Diet Holly Hauser Abstract: Previous research with chickens produced rickets by reducing the calcium content of the diet. When rickets occurred,
ALOYSIUS G.M. TIELENS, JOSEPHUS M. VAN DEN HEUVEL and SIMON G. VAN DEN BERGH
 Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 13 (1984) 301-307 Elsevier 301 MBP 00488 THE ENERGY METABOLISM OF FASCIOLA HEPATICA DURING ITS DEVELOPMENT IN THE FINAL HOST ALOYSIUS G.M. TIELENS, JOSEPHUS M. VAN
Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 13 (1984) 301-307 Elsevier 301 MBP 00488 THE ENERGY METABOLISM OF FASCIOLA HEPATICA DURING ITS DEVELOPMENT IN THE FINAL HOST ALOYSIUS G.M. TIELENS, JOSEPHUS M. VAN
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Whole Mount Drosophila Embryo In Situ Hybridization with RNA probes 2/5/2001 Leslie Vosshall
 Whole Mount Drosophila Embryo In Situ Hybridization with RNA probes 2/5/2001 Leslie Vosshall DAY ONE All incubations are done at room temperature unless otherwise noted. All solutions and all containers
Whole Mount Drosophila Embryo In Situ Hybridization with RNA probes 2/5/2001 Leslie Vosshall DAY ONE All incubations are done at room temperature unless otherwise noted. All solutions and all containers
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS LEAF
 42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Pur A Lyzer Midi Dialysis Kit Manual
 Pur A Lyzer Midi Dialysis Kit Manual Pur A Lyzer Midi Dialysis Kit Catalog Numbers PURD10005 PURD35010 PURD60010 PURD35030 PURD60030 PURD35050 PURD60050 PURD35100 PURD60100 Product Description Pur A Lyzer
Pur A Lyzer Midi Dialysis Kit Manual Pur A Lyzer Midi Dialysis Kit Catalog Numbers PURD10005 PURD35010 PURD60010 PURD35030 PURD60030 PURD35050 PURD60050 PURD35100 PURD60100 Product Description Pur A Lyzer
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
