NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Int J Cancer. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 January 15.
|
|
|
- Andrea Merry Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Cancer December 15; 127(12): doi: /ijc Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microrna markers Lei Yu 1, Nevins W. Todd 2, Lingxiao Xing 1, Ying Xie 1, Howard Zhang 2, Zhenqiu Liu 3, HongBin Fang 3, Jian Zhang 4, Ruth L. Katz 5, and Feng Jiang 1,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 2 Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 3 Division of Biostatistics of The University of Maryland Greenebaum Cancer Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 4 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 5 Department of Pathology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Summary Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. Early detection is the key to improve the survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients. We have previously shown that micrornas were stably present in sputum and could be applied to diagnosis of lung cancer. The aim of this study was to develop a panel of micrornas that can be used as highly sensitive and specific sputum markers for early detection of lung adenocarcinoma. This study contained three phases: (1) marker discovery using microrna profiling on paired normal and tumor lung tissues from 20 patients with lung adenocarcinoma; (2) marker optimization by real-time RT-qPCR on sputum of a case-control cohort consisting of 36 cancer patients and 36 health individuals; and (3) validation on an independent set of 64 lung cancer patients and 58 cancer-free subjects. From the surgical tissues, seven micrornas with significantly altered expression were identified, of which four were overexpressed and three were underexpressed in all 20 tumors. On the sputum samples of the case-control cohort, four (mir-21, mir-486, mir-375, and mir-200b) of the seven micrornas were selected, which in combination produced the best prediction in distinguishing lung adenocarcinoma patients from normal subjects with 80.6% sensitivity and 91.7% specificity. Validation of the marker panel in the independent populations confirmed the sensitivity and specificity that provided a significant improvement over any single one alone. The sputum markers demonstrated the potential of translation to laboratory settings for improving the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma. Keywords MicroRNA; sputum; lung adenocarcinoma; real-time RT-qPCR; diagnosis Introduction Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States. NSCLC is histologically subdivided into four major subtypes with distinct * Correspondence to Feng Jiang, Department of Pathology, The University of Maryland School of Medicine, 10 South Pine Street, MSTF 7th floor, Baltimore, MD , USA. fjiang@som.umaryland.edu.
2 Yu et al. Page 2 pathological characteristics: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma and other (neuroendocrine cancers, carcinoids etc.). The disease is usually diagnosed at advanced stages when the prognosis is poor, resulting in an overall 5-year survival rate of approximately 14% 1. However, the 5-year survival rate in patients with stage I NSCLC that has been resected can be as high as 83% 1. Therefore, finding early stage NSCLC may reduce the mortality 1. In particular, early identification of lung adenocarcinoma is clinically important, because it is now the most common type of lung cancer 1, accounting for 40% of all NSCLCs. Furthermore, the incidence of lung adenocarcinoma is on the rise in many countries, mainly, in women and nonsmokers 2,3. In addition, because adenocarcinoma arises in peripheral lung tissue and originates from the smaller airways, it is more difficult to be detected by bronchoscopy or sputum cytology 3. Moreover, computed tomography (CT) provides excellent anatomic information and can detect lung tumor at small size, however the improved sensitivity is associated with overdiagnosis 1-3. Thus, the major obstacle in management of lung adenocarcinoma is the lack of adequate method for its early detection. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are a new class of small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression and are involved in a variety of biologic and pathologic processes 4. The differential expression of mirnas in human cancers and its potential diagnostic values have been previously investigated 4-7. For instance, by analyzing changes of a large-scale mirnas on 540 human cancer specimens including lung, breast, stomach, prostate, colon, and pancreatic tumors, Volinia et al, identified a solid cancer mirna signature composed by a large portion of overexpressed mirnas that provides potential diagnostic targets for the tumors 4. Our recent proof of principle study 8 showed that endogenous mirnas were present in sputum in a remarkably stable form and could reliably be detected by real-time reverse transcription (RT)-quantitative (q)pcr. Furthermore, detecting elevated expression of a single mirna, mir-21, produced a higher sensitivity in diagnosis of lung cancer compared with sputum cytology. Our data suggested that the measurement of altered mirna expressions in sputum sample could be a useful noninvasive approach for lung cancer diagnosis. However, the sensitivity reached by a single mirna is low for clinical application 8. It has been widely accepted that lung tumor is a heterogeneous disease and develops from complex and multistep processes 2, 9. We therefore hypothesized that simultaneous assessment of a panel of tumor-specific mirnas that, used in combination in sputum, could provide a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic test for early stage lung adenocarcinoma. To verify the hypothesis, we first identified mirna signatures of stage I lung adenocarcinoma using mirna profiling on primary tumor tissues. From these signatures, we then optimized and validated a panel of mirnas that could be detected in sputum for the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma. Materials and Methods Patients and clinical specimens To define mirna signatures for lung adenocarcinoma, surgical specimens were obtained from 20 lung cancer patients who had either a lobectomy or a pneumonectomy. All cases were diagnosed with histologically confirmed stage I lung adenocarcinoma (Table 1). None of the patients had received preoperative adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Tumor tissues were intraoperatively dissected from the surrounding lung parenchyma; paired normal lung tissues were also obtained from the same patients at an area distant from their tumors. Serial cryostat sections from the specimens were stained with hematoxylin and eosin to confirm the diagnosis based on the most recent WHO classification of tumors of the lung 10.
3 Yu et al. Page 3 To optimize a panel of mirnas that could be detected in sputum, 36 stage I lung adenocarcinoma patients and an equal number of normal subjects were recruited. The case and control were matched in the ratio of 1:1 by age, gender, and smoking history as a nested case-control cohort (Supplement Table 1). Sputum was collected from the participants as described in our recent reports 8, To further validate the identified sputum markers, we collected sputum specimens from a total of 64 NSCLC patients and 58 healthy controls. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the NSCLC patients are summarized in Table 2. Tumors were classified as peripheral or central on the basis of radiographic studies, bronchoscopic or operative findings, and pathologic analysis. The study was approved by Institutional Review Board. RNA isolation Total RNA containing small RNA was extracted from the tissue and sputum specimens as described in our previous study 8 by using a mirvana mirna Isolation Kit (Ambion, Austin, TX). The purity and concentration of RNA were determined from OD260/280 readings using a dual beam UV spectrophotometer (Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany). RNA integrity was determined by capillary electrophoresis using the RNA 6000 Nano Lab-on-a-Chip kit and the Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). Only RNA extracts with RNA integrity number values >6 underwent in further analysis. MiRNA profiling of surgical resected lung adenocarcinoma tissues MiRNA profiling was performed using Taqman human microrna array A (System Biosciences, Mountain View, CA), which is a PCR-based array and contains 377 most commonly found human mature mirnas and 4 small RNA endogenous controls. Briefly, 100 ng of total RNA was polyadenylated by poly(a) polymerase and then reverse transcribed to cdna. RT-qPCR was performed using mirna specific primers provided by the manufacturer in ABI PRISM 7500 Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The cycle threshold (Ct) was defined as the number of cycles required for the fluorescent signal to cross the threshold in PCR. ΔCt was calculated by subtracting the Ct values of the small control RNAs from the Ct values of the mirna of interest. ΔΔCt was then computed by subtracting ΔCt of the normal control tissue from ΔCt of the tumor specimen, and foldchange of mirna gene was determined by the equation 2 ΔΔCt. Analysis of mirna expression in sputum samples Expression of the identified mirna signatures was evaluated in sputum by using real-time RT-qPCR with Taqman mirna assays (Applied Biosystems) as previously described 8. Expression of target mirnas was normalized in relation to expression of small nuclear U6 RNA. U6 RNA was proven as an internal control for mirna quantification in sputum in our previous study 8. All assays were performed in triplicates, and one no-template control and two interplate controls were carried along in each experiment. Expression levels of the mrnas were calculated using comparative Ct method as previously described 8. To determine the sensitivity and dynamic range of mirna quantification in sputum, RNA was extracted from ten sputum specimens and then diluted at different orders of magnitude in diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) water (Sigma Chemical Co.. St. Louis, MO). Expressions of the mirnas were then assessed by using RT-qPCR in the samples as described above. All tests were performed in triplicates. Statistical analysis To find mirna genes that were statistically differentially expressed between lung adenocarcinoma specimens and the corresponding normal tissues, we expected the acceptable number of false positives to be 1.0, fold difference between normal and tumor of samples at 2.0, standard deviation of the gene measurements on the base-two logarithmic
4 Yu et al. Page 4 Results scale at 0.7, and desired power at 0.8. Given 377 mirnas included in the array, at least 15 specimens for each tissue type were required to achieve the statistical criteria 13. To define an optimal mirna marker panel that can be detected in sputum for distinguishing cancer patients from normal controls, a case-control study was designed that consisted of lung cancer cases and cancer-free individuals. We used receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under ROC curve (AUC) to determine sample size in the case-control study. The ROC curve is a plot of diagnostic test's sensitivity, or true positive rate versus 1- specifcity, or the false positive rate at various discrimination cutoffs depicting the trade-offs between the true positives and the false positives in diagnostic accuracy 14. The AUC represents an overall summary of diagnostic accuracy. ROC analysis is considered as a powerful tool to evaluate diagnostic tests and predictive models by assessing accuracy quantitatively or comparing accuracy between tests or predictive models 14,15. Furthermore, ROC analysis can be used to select optimal threshold under a variety of clinical circumstances, balancing the inherent tradeoffs that exist between sensitivity and sensitivity. In addition, ROC analysis is one of the most important approaches that are commonly used to determine sample size 16. In the case-control cohort study, the AUC of H0 (the null hypothesis) was set at 0.5. H1 represented the alternative hypothesis; accordingly, at least 28 subjects were required in each category to show a minimum difference of interest between an AUC of 0.75 versus an AUC of 0.5 with 80% power at the 5% significance level Statistical analysis of RT-qPCR data was done using Statistical Analysis System software version 6.12 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). All P values shown were two sided, and a P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. ROC curve analysis was undertaken using expression level for each mirna in sputum from cancer patients and cancer-free controls by Analyse-it software (Analyse-it Software, Leeds, UK) 8. Briefly, for each mirna, we constructed the ROC curve and computed the AUC value by numerical integration of the ROC curve. Using this approach, the AUC identified maximum sensitivity and specificity levels at which to distinguish cancer patients from healthy subjects, yielding corresponding optimal thresholds defining expression levels of the tested genes. Logistic regression was used to generate prediction model building. Validated biomarkers were fitted into logistic regression models, and the stepwise backward model selection was performed to determine the best discriminating combinations of mirnas. Furthermore, contingency table and logistic regression analysis were applied to determine the associations between the expression levels of the mirnas and both clinicopathologic and demographic characteristics of the cases and controls. Identifying mirna signatures whose aberrant expression levels were associated with lung adenocarcinoma We used a TaqMan-based mirna array to profile mature mirnas in the matched lung adenocarcinoma and normal lung tissues. To determine if expression of these 377 mirnas was readily detectable, wee prepared two RNA pools that contain equal amounts of RNA from 20 tumor tissues and 20 normal lung tissues, respectively. We then performed the mirna array analysis on the pooled RNAs. 346 (92%) of the mirnas had 30 Ct value, however only 32 (8%) of the genes displayed >30 Ct value (Supplement Fig. 1). Furthermore, four replicate sets of raw threshold data obtained by two research staff at two different times on the same specimens are directly compared. The results demonstrated a high degree of correlation (R 2 > 0.992), suggesting that assay format yielded excellent reproducibility on the surgical resected specimens. Therefore, the mirnas could be accurately and reliably measured in the clinical samples by the PCR-based mirna array.
5 Yu et al. Page 5 When P value <0.01 was used as a cutoff, of the 377 mirna targets, 9 mirnas were downregulated and 11 mirnas were up-regulated with 1.5 fold-change in cancer group (Fig. 1 and Supplement Tables 2-3). Using a predefined criterion of a fold-change 2, we identified seven mirnas that statistically differently expressed between the paired tumor and normal samples. These included three mirnas (mir-486, mir-126, and mir-145) that were underexpressed, and four mirnas (mir-21, mir-182, mir-375, and mir-200b) that were overexpressed in tumor specimens. It should be noted that altered expressions of the seven mirnas existed in all 20 lung adenocarcinoma tissues compared with the paired normal specimens. We therefore assigned the seven mirnas for further analysis. Optimizing a panel of highly specific and sensitive sputum mirna markers for lung adenocarcinoma We have previously demonstrated feasibility of measuring expressions of human endogenous mirnas, mir-21 and mir-155, in sputum by RT-qPCR 8. To determine if the seven newly identified mirnas could be reliably detected in the specimens, we prepared two RNA pools containing equal amounts of RNA from sputum samples of 10 cancer patients and 10 cancer-free individuals, respectively. All tested mirnas had 30 Ct values in both pools, indicating that the mirnas could easily be measured in sputum (data not shown). To further determine the sensitivity of detecting the mirnas by RT-qPCR in sputum, the total RNA was diluted in DEPC water at different concentrations. The serially diluted RNAs served as experimental samples for measuring expression of each mirna. There was an excellent linearity between the RNA input and the Ct values for the mirna tested (Supplement Fig.2). In addition, the assay had a dynamic range of at least six orders of magnitude (R 2 = 0.998), and was capable of detecting as little as 0.86 pg of RNA and 10 copies of the target genes. Altogether, the mirnas identified from the primary tumor tissues were readily detectable in sputum. The seven mirnas were therefore continually tested in all individual sputum samples collected from a case-control of 36 patients diagnosed with stage I lung adenocarcinoma and 36 health subjects. MiR-486, mir-126, and mir-145 showed lower expression levels, whereas mir-21, mir-182, mir-375, and mir-200b displayed higher expression levels in cancer patients' sputum compared with sputum of cancer-free individuals (Table 3) (All p < 0.01). The data was in agreement with the results obtained from the tissue specimens. ROC analyses were performed to evaluate the capability of using the mirnas in sputum to discriminate between cancer patients and cancer-free individuals. As depicted in Table 3, the seven mirnas showed AUC values. When optimum cutoffs were selected, the mirnas yielded % sensitivity and % specificity, respectively, implying that the mirnas held promise as cancer-specific markers in sputum. To optimize a small panel of mirna markers for the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma with high sensitivity and specificity, logistic regression of all seven mirnas using a backward elimination approach was performed. One of the logistic regression models was built based on four mirnas, mir-486, mir-21, mir-200b, and mir-375, which in combination provided the best prediction. Combing the four mirnas produced AUC, being considerably higher than AUC values of each individual gene in distinguishing cancer patients from normal subjects (All P<0.05) (Fig. 2). Accordingly, the ROC curves revealed that the sensitivity and specificity for the combination of the four mirnas were 80.6% and 91.7%, which were significantly higher than % sensitivity and % specificity of the individual mirnas (All p<0.05) (Supplement Fig.3).
6 Yu et al. Page 6 Discussion Validating the sputum mirna markers in an independent set of NSCLC patients To further evaluate the diagnostic performance of the optimal markers, the four mirnas were assessed on sputum samples of 64 patients with different stages and histological types of NSCLC and 58 healthy controls. The mirnas had significantly different expression levels in sputum between NSCLC and cancer-free controls (All p<0.001) (Supplement Table 4). The ROC curve analysis showed that the individual mirnas displayed AUC values in identification of NSCLC patients. When optimal cutoffs were selected, the individual mirnas produced % sensitivity and % specificity (Supplement Table 4). The four mirnas in combination could differentiate the NSCLC patients from healthy controls with AUC, producing 70.3% sensitivity and 80.0% that were statistically higher than those by any single one used alone (all p<0.05) (Supplement Table 4). Furthermore, the panel of markers had different diagnostic efficiency for different histological types of NSCLC (Table 4): the sensitivity and specificity for lung adenocarcinoma were 80.6% and 92.5%, being similar to those (80.6% and 91.7%) in the above case-control cohort that only consisted of the patients diagnosed with stage I adenocarcinoma and healthy controls (All p>0.05). The parameters were statistically higher than those in diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma (64.1 % and 71.3%, all p<0.05), suggesting that the mirna markers had higher diagnostic efficiency for adenocarcinoma compared with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. In addition, the sensitivity and specificity of the four mirnas combined were 78.3% and 93.8% for peripheral cancer, whereas 65.8% and 70.9% for central tumor, respectively (Table 4), indicating that the mirnas had better efficiency in detecting peripherally located cancers than central tumors (All p<0.05). However, no statistically significant difference was found in the sensitivity and specificity of the markers for stage I, II, III, and IV lung adenocarcinomas (p>0.05) (Table 4). Moreover, in a univariate analysis, histological type and location of the tumors were associated with expression levels of the mirnas in sputum samples (Supplement Table 5) (All p > 0.05). There was no association of expressions of the mirnas with the age, gender, ethnic group, tumor stage, or histories of smoking of the lung cancer patients and normal individuals (Supplement Tables 5-6) (All p > 0.05). Taken together, the results confirm that the optimal set of mirnas could be used as specific biomarkers for the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma. The development of highly accurate biomarkers that can be detected in easily accessible body fluids is a major research effort in the field of lung cancer early detection 17. Sputum, particularly, has been considered as potential surrogate material for noninvasive diagnosis of lung cancer, because it is a mirror to lung disease 17. Conventional cytologic analysis of sputum has been used clinically to diagnose lung cancer; however, it was no more effective than chest radiographs in detecting lung cancer in several large prospective randomized trials 18. The molecular genetic alterations could occur before morphological changes that can be found by a cytological test 8, 11,12, Furthermore, the molecular genetic changes seen in sputum may reflect the same abnormalities found in lung tumors 11, 21. Therefore, there is a long history of identifying and developing molecule genetic changes that can be tested in sputum as biomarkers 8, 11, 12, 17, For instance, mutations of oncogene (e.g., K-ras) or tumor suppressor gene (e.g., P53) were detected in sputum of patients with primary adenocarcinoma of the lung 19,20. Hypermethylation of p16 gene was found in sputum collected from patients with lung cancer, 5-35 months before sputum cytological and clinical diagnoses 21. However, to date there is no molecular genetic marker accepted in clinical settings. In our recent proof of principle study 8, we demonstrated that measuring elevated expression level of a single mirna in sputum produced higher sensitivity in identification of lung
7 Yu et al. Page 7 cancer than did conventional sputum cytology. To enhance the diagnostic power of mirnas in sputum for lung adenocarcinoma, here we developed and characterized a sputum-based mirna marker panel with a sensitivity of 80.6% and a specificity of 91.7%. This study further extends our previous research efforts to develop sputum-based diagnostic tool for lung cancer 8, 11,12, 22. Given the expenses associated with quantitative molecular analyses, a marker panel with the smallest number of mirnas and highest diagnostic accuracy would provide a cost-effective diagnostic assay for lung adenocarcinoma. Among the four mirnas identified, up-regulation of mir-21 has been found in many human cancer specimens 23. Therefore, extensive efforts have been taken to identify the downstream genes and gene networks regulated by mir-21 and the upstream factors that can regulate dysfunction of mir For example, elevated mir-21 expression might be associated with apoptosis inhibition and acquisition of invasive properties, likely mediated by its downregulating effects on the expression of target tumor suppressors PTEN, TPM, and PDCD More importantly, mir-21 itself displays oncogenic activity and can be classed as an oncomir, whose overexpression lead to tumor development and progression 24. This current study confirmed our previous finding 8 that the assessment of mir-21 overexpression in sputum had higher sensitivity compared with cytologic examination. Therefore, mir-21 can serve as an important biomarker for the early detection of lung cancer. MiR-200b locates on chromosome 1p36.33, one of the most common regions with genomic amplicons in solid tumors including lung cancer Although biological mechanism of mir-200b dysfunction in lung tumorigenesis is unclear, mir-200b was recently identified as one of a set of mirnas whose aberrant expressions were related to recurrence of stage I NSCLC after surgical resection 31. Consistently, we herein found that mir-200b overexpression existed in lung adenocarcinomas, one of the major histological types of NSCLC. Altogether, the observations suggest that mir-200b could be a potential target of the genomic amplification in 1p36.33, and its activation might be involved in lung carcinogenesis. MiR-375 down-regulation was found in some human malignancies 32,33. However, mir-375 was consistently up-regulated in adenocarcinoma rather than squamous cell carcinoma of lungs 34. Furthermore, when comparing cancerous tissue expression between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma patients with esophagus cancer, Mathé et al. 33 found that mir-375 was elevated in adenocarcinoma patients. In good agreement with the findings, our present data showed that mir-375 was overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma, and Moreover, measuring its expression in sputum displayed higher accuracy in diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma compared with squamous cell lung cancer. On the other hand, mir-486 is located on one of the most frequent genomic rearrangement regions, chromosome 8p11.21 that contain potential tumor suppressor genes in lung tumorigenesis 27,28. Navon et al. recently found that mir-486 was underexpressed in eight types of human tumors, including lung cancer 35. The observation from our present research is consistent with the previous findings, suggesting that mir-486 might be a potential tumor suppressor in carcinogenesis. Although mir-182 was not eventually included in the panel of the four mirnas, its over-expression was found in primary NSCLC tissues and sputum from the patients. MiR-182 is a member of a mirna cluster in a chromosomal locus (7q31-34) frequently amplified in solid tumors 36. Segura, et al recently found that mir-182 was commonly up-regulated in human melanoma cell lines and tissue samples, and this upregulation correlated with gene copy number in a subset of melanoma cell lines 36. Furthermore, the aberrant mir-182 expression could promote tumorigenesis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in several types of human cancers Our primary goal of the current study is marker development. We showed for the first time that measuring altered expressions of a small panel of mirnas in sputum might be a potential noninvasive test for the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma. The biological relevance of the mirna dysfunctions in lung tumorigenesis are currently being investigated at our laboratory.
8 Yu et al. Page 8 The panel of sputum markers could also identify squamous cell lung cancer with 64.1 % sensitivity and 71.3% specificity. However, the markers are more accurate to lung adenocarcinoma with 80.6% sensitivity and 92.5% specificity. The main reason might be that the mirnas are identified from surgically resected primary adenocarcinomas, thus should be more specific for the type of NSCLC. It is also not surprising to find that the abnormal mirnas expression levels are related to the tumors located in peripheral airways, because most peripheral tumors are adenocarcinomas. These observations would be clinically important, because the majority of NSCLCs detected by cytologic analysis and visible by bronchoscopy are squamous cell carcinoma predominantly locating in central areas of the lungs, rather than adenocarcinoma that is the most common type in NSCLC. Once confirmed, the sputum mirna panel might improve the detection rate for lung adenocarcinomas that are more difficult to be found by these conventional techniques. Most of the previously identified lung cancer associated molecular genetic changes were related to the smoking status. Some of the changes can be found in healthy smokers who never develop lung cancer 2,3, 8, 17. The use of such molecular genetic alterations as biomarkers might produce high false positive diagnostic rate or over-diagnosis, thus impeding their application in clinical settings in screening or early detection of lung cancer. The four mirna markers identified from the present research is encouraging, because expression levels of the mirnas appear to be independent of subject age, gender, ethnic subgroup, and tobacco smoking. The identified mirnas could dysregulate in a cancerspecific manner. In addition, no significant differences of the mirna expression levels were observed for the cancerous samples at different stages of the disease, implying that the potential markers were not stage-specific. The results further provide evidence that this mirna marker panel might be useful in the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma, although whether the expression levels of the four mirnas are affected in non-cancer associated lung pathologies remains to be investigated. This panel of mirna markers detected by RT-qPCR platform provides a significant improvement over any single one, and hence shows promise as a lung adenocarcinomaspecific test on sputum. In the future, developing and using an independent methodology, e.g., solution hybridization 40, to evaluate the expression levels of the mirnas may continue to improve efficiency of the sputum-based biomarkers. Furthermore, comparing the mirnas on sputum to CT imaging for the early detection of lung adenocarcinoma will lead to more understanding the diagnostic value of the biomarkers. In addition, integration of the sputum-based markers with the current conventional modalities, especially CT, could facilitate noninvasive diagnostic efficiency and accuracy for early lung adenocarcinoma or screening of high-risk patients for the cancer. In conclusion, we have developed a panel of mirnas that can be reliably measured in sputum. Detection of the mirnas could be used as a noninvasive and cost-effective diagnostic tool for early lung adenocarcinoma. Nonetheless, a large multi-center clinical project to further validate the full utility is warranted before it could potentially be adopted in routine clinical settings. Supplementary Material Acknowledgments Refer to Web version on PubMed Central for supplementary material. Grant support: This work was supported in part by National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants CA , CA , and CA , American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant, an clinical innovator award from Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute, a scholar career development award from NIH K12RR University of
9 Yu et al. Page 9 References Maryland Multidisciplinary Research Career Development Program, and an exploratory research grant from Maryland Stem Cell Fund (F. J.). 1. American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts & Figures. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; Minna JD, Roth JA, Gazdar AF. Focus on lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 2002; 1: [PubMed: ] 3. Sun S, Schiller JH, Gazdar AF. Lung cancer in never smokers--a different disease. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7: [PubMed: ] 4. Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, et al. A microrna expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103: [PubMed: ] 5. Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005; 435: [PubMed: ] 6. Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al. Unique microrna molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006; 9: [PubMed: ] 7. Wang QZ, Xu W, Habib N, Xu R. Potential uses of microrna in lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009; 9: [PubMed: ] 8. Xie Y, Todd NW, Liu Z, Zhan M, Fang H, Peng H, Alattar M, Deepak J, Stass SA, Jiang F. Altered mirna expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010; 67: [PubMed: ] 9. Colby TV, Wistuba II, Gazdar A. Precursors to pulmonary neoplasia. Adv Anat Pathol. 1998; 5: [PubMed: ] 10. Colby, TV.; Noguchi, M.; Henschke, C. Adenocarcinoma. In: Travis, WD.; Brambilla, E.; Muller- Hermelink, HK., et al., editors. Pathology and Genetics, Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. Lyon, France: IARC Press; p. 2005p Li R, Todd NW, Qiu Q, Fan T, Zhao RY, Rodgers WH, Fang HB, Katz RL, Stass SA, Jiang F. Genetic deletions in sputum as diagnostic markers for early detection of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13: [PubMed: ] 12. Qiu Q, Todd NW, Li R, Peng H, Liu Z, Yfantis HG, Katz RL, Stass SA, Jiang F. Magnetic enrichment of bronchial epithelial cells from sputum for lung cancer diagnosis. Cancer. 2008; 114: [PubMed: ] 13. Sahai H, Kurshid A. Formulae and tables for the determination of sample sizes and power in clinical trials for testing differences in proportions for the two-sample design: A review. Statistics in Medicine. 1996; 15:1 21. [PubMed: ] 14. Dodd LE, Pepe MS. Partial AUC estimation and regression. Biometrics. 2003; 59: [PubMed: ] 15. Zou KH, O Malley AJ, Mauri L. Receiver-operating characteristic analysis for evaluating diagnostic tests and predictive models. Circulation. 2007; 115: [PubMed: ] 16. Obuchowski NA, McClish DK. Sample size determination for diagnostic accuracy studies involving binormal ROC curve indices. Stat Med. 1997; 16: [PubMed: ] 17. Thunnissen FB. Sputum examination for early detection of lung cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2003; 11: [PubMed: ] 18. Flehinger BJ, Melamed MR, Zaman MB, Heelan RT, Perchick WB, Martini N. Early lung cancer detection: results of the initial (prevalence) radiologic and cytologic screening in the Memorial Sloan-Kettering study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984; 4: [PubMed: ] 19. Yakubovskaya MS, Spiegelman V, Luo FC, Malaev S, Salnev A, Zborovskaya I, Gasparyan A, Polotsky B, Machaladze Z, Trachtenberg AC. High frequency of K-ras mutations in normal appearing lung tissues and sputum of patients with lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995; 63: [PubMed: ]
10 Yu et al. Page Mao L, Hruban RH, Boyle JO, Tockman M, Sidransky D. Detection of oncogene mutations in sputum precedes diagnosis of lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1994; 1: [PubMed: ] 21. Belinsky SA, Liechty KC, Gentry FD, Wolf HJ, Rogers J, Vu K, Haney J, Kennedy TC, Hirsch FR, Miller Y, Franklin WA, Herman JG, Baylin SB, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in sputum precedes lung cancer incidence in a high-risk cohort. Cancer Res. 2006; 66: [PubMed: ] 22. Jiang F, Todd NW, Qiu Q, Liu Z, Katz RL, Stass SA. Combined genetic analysis of sputum and computed tomography for noninvasive diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2009; 66: [PubMed: ] 23. Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem. 3007; 282: [PubMed: ] 24. Pezzolesi MG, Platzer P, Waite KA, Eng C. Differential expression of PTEN-targeting micrornas mir-19a and mir-21 in Cowden syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2008; 82: [PubMed: ] 25. Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem. 3007; 282: [PubMed: ] 26. Allgayer H. Pdcd4, a colon cancer prognostic that is regulated by a microrna. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2010; 73: [PubMed: ] 27. Jiang F, Yin Z, Caraway NP, Li R, Katz RL. Genomic profiles in stage I primary non small cell lung cancer using comparative genomic hybridization analysis of cdna microarrays. Neoplasia. 2004; 6: [PubMed: ] 28. Li R, Wang H, Bekele BN, Yin Z, Caraway NP, Katz RL, Stass SA, Jiang F. Identification of putative oncogenes in lung adenocarcinoma by a comprehensive functional genomic approach. Oncogene. 2006; 18: [PubMed: ] 29. Jeon JP, Shim SM, Nam HY, Baik SY, Kim JW, Han BG. Copy number increase of 1p36.33 and mitochondrial genome amplification in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007; 2: [PubMed: ] 30. Scaruffi P, Parodi S, Mazzocco K, Defferrari R, Fontana V, Bonassi S, Tonini GP. Detection of MYCN amplification and chromosome 1p36 loss in neuroblastoma by cdna microarray comparative genomic hybridization. Mol Diagn. 2004; 8: [PubMed: ] 31. Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Knudsen S, Yendamuri S. Evaluation of microrna expression profiles that may predict recurrence of localized stage I non-small cell lung cancer after surgical resection. Cancer Res. 2010; 70: [PubMed: ] 32. Avissar M, McClean MD, Kelsey KT, Marsit CJ. MicroRNA expression in head and neck cancer associates with alcohol consumption and survival. Carcinogenesis. 2009; 12: [PubMed: ] 33. Mathé EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y, Budhu A, Schetter AJ, Braun R, Reimers M, Kumamoto K, Hughes D, Altorki NK, Casson AG, et al. MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15: [PubMed: ] 34. Lebanony D, Benjamin H, Gilad S, Ezagouri M, Dov A, Ashkenazi K, Gefen N, Izraeli S, Rechavi G, Pass H, Nonaka D, Li J, et al. Diagnostic assay based on hsa-mir-205 expression distinguishes squamous from nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27: [PubMed: ] 35. Navon R, Wang H, Steinfeld I, Tsalenko A, Ben-Dor A, Yakhini Z. Novel rank-based statistical methods reveal micrornas with differential expression in multiple cancer types. PLoS One. 2009; 25:e8003. [PubMed: ] 36. Segura MF, Hanniford D, Menendez S, Reavie L, Zou X, Alvarez-Diaz S, Zakrzewski J, Blochin E, Rose A, Bogunovic D, Polsky D, Wei J, et al. Aberrant mir-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 6: [PubMed: ] 37. Guttilla IK, White BA. Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by mir-27a, mir-96, and mir-182 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2009; 28: [PubMed: ]
11 Yu et al. Page Nagaraja AK, Creighton CJ, Yu Z, Zhu H, Gunaratne PH, Reid JG, Olokpa E, Itamochi H, Ueno NT, Hawkins SM, Anderson ML, Matzuk MM. A link between mir-100 and FRAP1/mTOR in clear cell ovarian cancer. Mol Endocrinol. 2010; 22: [PubMed: ] 39. Myatt SS, Wang J, Monteiro LJ, Christian M, Ho KK, Fusi L, Dina RE, Brosens JJ, Ghaem- Maghami S, Lam EW. Definition of micrornas that repress expression of the tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2010; 1: [PubMed: ] 40. Coutlee F, Rubalcaba EA, Viscidi RP, Gern JE, Murphy PA, Lederman HM. Quantitative detection of messenger RNA by solution hybridization and enzyme immunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265: [PubMed: ] Abbreviations used NSCLC MiRNAs CT ROC AUC RT-qPCR Ct DEPC non-small-cell lung cancer micrornas computed tomography receiver-operator characteristic the area under receiver operating characteristic curve reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction cycle threshold diethylpyrocarbonate
12 Yu et al. Page 12 Brief statements describing the novelty and impact of the paper MicroRNAs (mirnas) are emerging as highly tissue-specific biomarkers with potential for clinical applicability in indentifying and defining cancer type. Here we aimed to develop a panel of mirnas that can be used as highly sensitive and specific sputum markers for early detection of lung adenocarcinoma, the most common type of lung cancer. This study was divided into three phases: (1) marker discovery using reverse transcription (RT) PCR-based mirna profiling on 20 stage I lung adenocarcinoma tissues; (2) marker optimization by real-time RT-quantitative (q)pcr on sputum of 36 cancer patients and 36 health individuals; and (3) validation on an independent set of 64 lung cancer patients and 58 cancer-free subjects. We successfully developed a small panel of sputum markers consisting of four mirnas, which in combination yielded 80.6% sensitivity and 91.7% specificity for the diagnosis of early stage lung adenocarcinoma. This is the first report that measuring a mirna panel in sputum for early detection of lung adenocarcinoma. Future integration of the sputum-based markers with the current conventional modalities, especially computed tomography, could provide a noninvasive and cost-effective diagnostic tool for early stage lung adenocarcinoma or screening of high-risk patients for the disease.
13 Yu et al. Page 13 Fig. 1. MiRNAs differentially express in lung adenocarcinomas versus normal lung tissues. Hierarchical clustering of 20 mirna genes with a significantly different expression (p < 0.01) in tumor tissues. Rows represent individual genes; columns represent individual tissue samples. The scale represents the intensity of gene expression (log2 scale ranges between 3.0 and 3.0).
14 Yu et al. Page 14 Fig. 2. Receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of expression levels of the four mirnas in sputum of 36 patients diagnosed with stage I lung adenocarcinoma and 36 health subjects. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) for each mirna conveys its accuracy for differentiation of lung adenocarcinoma patients and healthy subjects in terms of sensitivity and specificity. The individual genes produce AUC values (A-D), being significantly lower than AUC by the four genes combined as a marker panel (E) (All P<0.05).
15 Yu et al. Page 15 Table 1 Demographics of 20 patients diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma Age * 65 (55-78) Sex Female 8 Male 12 Smoking status 17 smokers Pack-years 35 ± 22 Location of tumor Stage Histology All are peripheral tumors All are stage I * Data are presented as median (range). All are lung adenocarcinoma Peripheral tumors were located at or within 1 cm of the visceral pleura.
16 Yu et al. Page 16 Table 2 Demographic and clinical characteristics of NSCLC patients and healthy subjects in an independent corhot NSCLC (n = 64) Controls (n = 58) P-value Age 67 (SD 11.5) 65 (SD 10.6) >0.05 Sex Race Female >0.05 Male >0.05 White >0.05 African American >0.05 Smoking status Pack-years 30.9 (SD 24.8) 27.7 (SD 28.4) >0.05 Location of tumor * >0.05 Central 30 Peripheral 34 Stage >0.05 Stage I 16 Stage II 15 Stage III 17 Stage IV 16 Histology >0.05 AC of lung 33 SC of lung 31 Abbreviations: NSCLC: non small-cell lung cancer; SD, standard deviation. AC, adenocarcinoma; SC, squamous cell carcinoma. * Peripheral tumors were located at or within 1 cm of the visceral pleura.
17 Yu et al. Page 17 Table 3 Expression levles of the seven mirnas and their diagnostic significace in sputum of 36 lung adenocarcinoma patients and 36 healthy controls MiRNA Mean (SD) in cancer patients Mean (SD) in healthy controls P * AUC * (SE) Cutoffs Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) MiR (0.034) (0.167) < (0.034) MiR (0.087) (0.198) < (0.032) MiR (0.073) (0.297) < (0.031) MiR (5.680) (2.354) < (0.038) MiR (5.822) (1.164) < (0.033) MiR-200b (5.367) (1.285) < (0.036) MiR (6.012) (1.766) < (0.035) Abbreviations: AUC, the area under receiver operating characteristic curve; SD, standard deviation; SE, standard error. * Both the P value and AUC were obtained using the U6-normalized values
18 Yu et al. Page 18 Table 4 Diagnostic efficiency of the mirna marker panel on sputum of 64 NSCLC patients and 58 healthy subjects* Sensitivity Specificity P Histological types All <0.05 AC 80.60% 92.50% SC 64.10% 71.30% Tumor location All <0.05 Peripheral tumor 78.26% 93.80% Central tumor 65.80% 70.92% Stage of NSCLC All >0.05 I 69.22% 81.70% II 69.90% 82.50% III 71.50% 79.10% IV 70.90% 82.70% The results were determined by using ROC curve analysis with optimum cutoffs. Abbreviations: NSCLC, non small-cell lung cancer; AC, adenocarcinoma; SC, squamous cell carcinoma. Peripheral tumors were located at or within 1 cm of the visceral pleura.
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array
 MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA
 Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success
 micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Airway epithelial gene expression in the diagnostic evaluation of smokers with suspect lung cancer
 Airway epithelial gene expression in the diagnostic evaluation of smokers with suspect lung cancer Avrum Spira, Jennifer E Beane, Vishal Shah, Katrina Steiling, Gang Liu, Frank Schembri, Sean Gilman, Yves-Martine
Airway epithelial gene expression in the diagnostic evaluation of smokers with suspect lung cancer Avrum Spira, Jennifer E Beane, Vishal Shah, Katrina Steiling, Gang Liu, Frank Schembri, Sean Gilman, Yves-Martine
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
From reference genes to global mean normalization
 From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
Evaluation of lung flute in sputum samples for molecular analysis of lung cancer
 Anjuman et al. Clinical and Translational Medicine 2013, 2:15 RESEARCH Open Access Evaluation of lung flute in sputum samples for molecular analysis of lung cancer Nigar Anjuman, Ning Li, Maria Guarnera,
Anjuman et al. Clinical and Translational Medicine 2013, 2:15 RESEARCH Open Access Evaluation of lung flute in sputum samples for molecular analysis of lung cancer Nigar Anjuman, Ning Li, Maria Guarnera,
Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell lung Cancer (NSCLC) By CISH Technique
 Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
95% CI: , P=0.037).
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Clinical impact of serum mir-661 in diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5696-5701 Clinical impact of serum mir-661 in diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer G.-H. ZHOU 1, W.-H. YANG 2, B. SUN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5696-5701 Clinical impact of serum mir-661 in diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer G.-H. ZHOU 1, W.-H. YANG 2, B. SUN
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Small nucleolar RNA signatures as biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer
 RESEARCH Small nucleolar RNA signatures as biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer Jipei Liao 1, Lei Yu 1, Yuping Mei 1, Maria Guarnera 1, Jun Shen 1, Ruiyun Li 2, Zhenqiu Liu 3, Feng Jiang 1* Open Access
RESEARCH Small nucleolar RNA signatures as biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer Jipei Liao 1, Lei Yu 1, Yuping Mei 1, Maria Guarnera 1, Jun Shen 1, Ruiyun Li 2, Zhenqiu Liu 3, Feng Jiang 1* Open Access
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Cancer Cell Research 17 (2018)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Prognostic value of MicroRNA-21 in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis Fei Xu, Leina Ma, Lingxin Feng, Yinjie Wu, Xiaoyan Xu, Zhuang
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Prognostic value of MicroRNA-21 in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis Fei Xu, Leina Ma, Lingxin Feng, Yinjie Wu, Xiaoyan Xu, Zhuang
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
Multifocal Lung Cancer
 Multifocal Lung Cancer P. De Leyn, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic Surgery University Hospitals Leuven Belgium LEUVEN LUNG CANCER GROUP Department of Thoracic Surgery Department of Pneumology Department
Multifocal Lung Cancer P. De Leyn, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic Surgery University Hospitals Leuven Belgium LEUVEN LUNG CANCER GROUP Department of Thoracic Surgery Department of Pneumology Department
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Insulinoma-associated protein (INSM1) is a sensitive and specific marker for lung neuroendocrine tumors in cytologic and surgical specimens
 Insulinoma-associated protein (INSM1) is a sensitive and specific marker for lung neuroendocrine tumors in cytologic and surgical specimens Kartik Viswanathan, M.D., Ph.D New York Presbyterian - Weill
Insulinoma-associated protein (INSM1) is a sensitive and specific marker for lung neuroendocrine tumors in cytologic and surgical specimens Kartik Viswanathan, M.D., Ph.D New York Presbyterian - Weill
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers
 Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning
 Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients
 mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
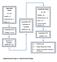 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 (2003) 865 869 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q Jeong-Han Kang, Kil Dong Kim, Kyung
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 (2003) 865 869 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q Jeong-Han Kang, Kil Dong Kim, Kyung
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer Lorena Roa de la Cruz
 Genomics Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer Lorena Roa de la Cruz Gene expression profiling Measurement of the activity of thousands of genes at once Techniques used for gene expression
Genomics Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer Lorena Roa de la Cruz Gene expression profiling Measurement of the activity of thousands of genes at once Techniques used for gene expression
Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction
 www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Value of serum galectin-3 and midkine level determination for assessing tumor severity in patients with thyroid cancer
 148 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2017; 23(3): 148-152 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Value of serum galectin-3 and midkine level determination for assessing tumor
148 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2017; 23(3): 148-152 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Value of serum galectin-3 and midkine level determination for assessing tumor
Evaluation of mir-182/mir-100 Ratio for Diagnosis and Survival Prediction in Bladder Cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of mir-182/mir-100 Ratio for Diagnosis and Survival Prediction in Bladder Cancer Zhanguo Chen MD PhD 1, Lili Wu BA 2, Qi Lin BA 3, Jing Shi MD 4, Xiangyang Lin MD, Liang Shi
Original Article Evaluation of mir-182/mir-100 Ratio for Diagnosis and Survival Prediction in Bladder Cancer Zhanguo Chen MD PhD 1, Lili Wu BA 2, Qi Lin BA 3, Jing Shi MD 4, Xiangyang Lin MD, Liang Shi
Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological staging of the cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 1283-1287 Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 1283-1287 Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Applying Genomics to Cancer 21 st September The Frequency of EGFR mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cardiff Experience
 Applying Genomics to Cancer 21 st September 2015 The Frequency of EGFR mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cardiff Experience Aled Daniels R Butler, R Attanoos, H Davies University Hospital of Wales
Applying Genomics to Cancer 21 st September 2015 The Frequency of EGFR mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cardiff Experience Aled Daniels R Butler, R Attanoos, H Davies University Hospital of Wales
Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients
 Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma
 Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Overregulation of microrna-212 in the poor prognosis of esophageal cancer patients
 Overregulation of microrna-212 in the poor prognosis of esophageal cancer patients B. Qi 1, S.G. Liu 1, X.G. Qin 1, W.J. Yao 1, J.G. Lu 1, L. Guo 1, T.Y. Wang 2, H.C. Li 1 and B.S. Zhao 1 1 Department
Overregulation of microrna-212 in the poor prognosis of esophageal cancer patients B. Qi 1, S.G. Liu 1, X.G. Qin 1, W.J. Yao 1, J.G. Lu 1, L. Guo 1, T.Y. Wang 2, H.C. Li 1 and B.S. Zhao 1 1 Department
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML
 Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11. Dr H Awad FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma
 Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 December 31, 2011 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 December 31, 2011 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control
 microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Negative correlation between mir-375 and its predicted target genes, as demonstrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). 1 The correlation between
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Negative correlation between mir-375 and its predicted target genes, as demonstrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). 1 The correlation between
Gene Expression-Based Approaches in Differentiation of Metastases and Second Primary Tumour
 255 Gene Expression-Based Approaches in Differentiation of Metastases and Second Primary Tumour Tõnu Vooder a, b Kristjan Välk a Raivo Kolde c Retlav Roosipuu e Jaak Vilo c Andres Metspalu a, d a Institute
255 Gene Expression-Based Approaches in Differentiation of Metastases and Second Primary Tumour Tõnu Vooder a, b Kristjan Välk a Raivo Kolde c Retlav Roosipuu e Jaak Vilo c Andres Metspalu a, d a Institute
A circulating serum mirna panel as early detection biomarkers of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4846-4851 A circulating serum mirna panel as early detection biomarkers of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia F. XIN 1, P. LIU 1, C-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4846-4851 A circulating serum mirna panel as early detection biomarkers of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia F. XIN 1, P. LIU 1, C-F.
Cover Letter. Reviewer 1:
 Cover Letter Michael Yang, M.D., Ph.D. Managing Editor of Cancer Research Frontiers 1188 Willis Ave, #109, Albertson, NY 11507, USA Phone: +1-917-426-1571 http://cancer-research-frontiers.org/ Dear Dr.
Cover Letter Michael Yang, M.D., Ph.D. Managing Editor of Cancer Research Frontiers 1188 Willis Ave, #109, Albertson, NY 11507, USA Phone: +1-917-426-1571 http://cancer-research-frontiers.org/ Dear Dr.
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
 Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer
 Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer Eleftherios P. Diamandis, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP(C) EORTC-NCI-ASCO Meeting,November 16, 2007 Yousef GM, Diamandis EP. Endocr.
Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer Eleftherios P. Diamandis, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP(C) EORTC-NCI-ASCO Meeting,November 16, 2007 Yousef GM, Diamandis EP. Endocr.
A complete next-generation sequencing workfl ow for circulating cell-free DNA isolation and analysis
 APPLICATION NOTE Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit A complete next-generation sequencing workfl ow for circulating cell-free DNA isolation and analysis Abstract Circulating cell-free DNA (cfdna) has been shown
APPLICATION NOTE Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit A complete next-generation sequencing workfl ow for circulating cell-free DNA isolation and analysis Abstract Circulating cell-free DNA (cfdna) has been shown
Analysis of the outcome of young age tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data
 Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0046 TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Ittmann, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0046 TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Ittmann, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Diagnosis and Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carlos Eduardo Oliveira Baleeiro, MD. November 18, 2017
 Diagnosis and Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carlos Eduardo Oliveira Baleeiro, MD November 18, 2017 Disclosures I do not have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations
Diagnosis and Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Carlos Eduardo Oliveira Baleeiro, MD November 18, 2017 Disclosures I do not have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations
Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng, Hui Wang, Yinyan Li, Dongsheng Huang, Jian Zheng,
 The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA LEO TUNKLE *
 CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
RECENT ADVANCES IN THE MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF BREAST CANCER
 Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology. 6th Central European Regional Meeting. Cytopathology. Balatonfüred, Hungary, April 7-9, 2011. RECENT ADVANCES IN THE MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF BREAST CANCER Philippe
Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology. 6th Central European Regional Meeting. Cytopathology. Balatonfüred, Hungary, April 7-9, 2011. RECENT ADVANCES IN THE MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF BREAST CANCER Philippe
Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
Long non-coding RNA Loc is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Original Article Serum expression of mirna-103, a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14212-14218 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0024943 Original Article Serum expression of mirna-103, a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14212-14218 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0024943 Original Article Serum expression of mirna-103, a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
Plasma MicroRNA Panel to Diagnose Hepatitis B Virus Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Published Ahead of Print on November 21, 211 as 1.12/JCO.211.38.2697 The latest version is at http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/doi/1.12/jco.211.38.2697 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R
Published Ahead of Print on November 21, 211 as 1.12/JCO.211.38.2697 The latest version is at http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/doi/1.12/jco.211.38.2697 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R
Research Article Plasma HULC as a Promising Novel Biomarker for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 BioMed Research International Volume 213, Article ID 13616, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/13616 Research Article Plasma HULC as a Promising Novel Biomarker for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
BioMed Research International Volume 213, Article ID 13616, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/13616 Research Article Plasma HULC as a Promising Novel Biomarker for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Nanda Horeweg, Carlijn M. van der Aalst, Erik Thunnissen, Kristiaan Nackaerts, Carla Weenink, Harry J.M. Groen, Jan-Willem J.
 Characteristics of lung cancers detected in the randomized NELSON lung cancer screening trial Nanda Horeweg, Carlijn M. van der Aalst, Erik Thunnissen, Kristiaan Nackaerts, Carla Weenink, Harry J.M. Groen,
Characteristics of lung cancers detected in the randomized NELSON lung cancer screening trial Nanda Horeweg, Carlijn M. van der Aalst, Erik Thunnissen, Kristiaan Nackaerts, Carla Weenink, Harry J.M. Groen,
