Women s Imaging Original Research
|
|
|
- Walter Short
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mammography of Recurrent Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Renee W. Pinsky 1 Murray Rebner 2 Lori J. Pierce 3 Merav A. Ben-David 3,4 Frank Vicini 5 Karen A. Hunt 1,6 Mark A. Helvie 1 Pinsky RW, Rebner M, Pierce LJ, et al. Keywords: breast, breast cancer, cancer recurrence, DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ, mammography, women s imaging DOI: /AJR Received September 27, 2006; accepted after revision January 26, Department of Radiology, University of Michigan Health System, 1500 E Medical Center Dr., Ann Arbor, MI Address correspondence to R. W. Pinsky (rpinsky@umich.edu). 2 Department of Radiology, William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, MI. 3 Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor, MI. 4 Present address: Oncology Department, Radiation Oncology Unit, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel. 5 Department of Radiation Oncology, William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, MI. 6 Present address: Department of Radiology, Henry Ford Hospital, West Bloomfield, MI. AJR 2007; 189: X/07/ American Roentgen Ray Society Recurrent Cancer After Breast-Conserving Surgery with Radiation Therapy for Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: Mammographic Features, Method of Detection, and Stage of Recurrence OBJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to determine the mammographic appearance, detection method, and stage of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence in women treated with breastconserving surgery and whole-breast radiation therapy for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). MATERIALS AND METHODS. Following institutional review board approval, records of women treated with breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for DCIS who developed an ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence from 1981 to 2003 were reviewed retrospectively. Multiinstitutional database records showed 513 women were treated, of whom 42 (8.2%) developed local recurrence. Study criteria were fulfilled and complete records were available for 32 women. Mean age at initial diagnosis was 49 years (range, years). RESULTS. Of the 32 patients included in our study, 31 (97%) recurrences were mammographically apparent. Twenty-nine (91%) of 32 were diagnosed exclusively by mammography. Mammographic findings at recurrence were calcifications in 24 (75%) of 32, mass in six (19%) of 32, and distortion in one (3%) of 32. The mean time to recurrence was 4.5 years. Twelve (40%) of 30 had the recurrence in a remote quadrant from the original cancer. Recurrences were DCIS in 17 (53%) of 32, DCIS with microinvasion in six (19%) of 32, invasive ductal cancer in three (9%) of 32, invasive lobular cancer in two (6%) of 32, and mixed DCIS and invasive cancer in four (13%) of 32. Six (67%) of nine patients with invasive cancer (excluding microinvasion) had tumors smaller than 1 cm. Ninety-one percent of recurrences were minimal cancers. All recurrences were stage 0 or 1. CONCLUSION. Mammography successfully detected ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence, predominantly as calcifications or masses, after breast-conserving surgery with radiation therapy for DCIS in 97% of cases. The recurrences were located at variable distances from the lumpectomy site. Ninety-one percent of recurrences were minimal cancers and all were early stage, connoting excellent prognosis. omen newly diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of W the breast face a perplexing array of treatment options ranging from mastectomy with hormonal therapy to lumpectomy alone. Although multiple randomized controlled trials have documented the equivalency of lumpectomy and radiation therapy to that of mastectomy in terms of survival for invasive breast cancer, DCIS is less well studied. Hence, clinical decisions regarding best treatment are based on nonuniform and nonrandomized trials. Mastectomy for DCIS has been associated with a long-term local regional disease-free survival of 95% or greater [1 5]. Although breast conservation surgery with whole-breast radiation therapy has proven to be effective, women electing this treatment are faced with the prospect of a local regional recurrence rate of approximately 1% per year [6]. This decreases with the addition of tamoxifen in selected women [7, 8]. Although many consider mastectomy to be curative, a small percentage of patients (1 4%) will eventually develop chest wall recurrence [1 5]. These recurrences are usually invasive carcinomas that are detected once they are palpable. Because the rate of local recurrence with lumpectomy and breast radiation is higher than with mastectomy, it is important for a woman electing this treatment path to understand not only the risk of recurrence but also the implications of a recurrence. We therefore reviewed our data of women experiencing a local recurrence after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy. We were particularly interested to observe the radiographic appearance, method of detection, location of recurrence, and, most important, the size and stage of recurrence that would provide in- 140 AJR:189, July 2007
2 Mammography of Recurrent Breast Cancer formation regarding prognosis after recurrence. This information should be helpful in guiding radiologists, oncologists, and patients facing treatment decisions and planning surveillance methods when breast conservation is chosen. Materials and Methods Institutional review board approval was obtained from both study institutions. Written informed consent was not required for this retrospective study. Study Population We performed a retrospective review of women treated for DCIS with breast-conserving surgery and whole-breast radiation therapy who subsequently developed an ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence. Breast imaging studies and medical records, including demographic and pathology records, were analyzed. Local recurrence was defined as the presence of cancer anywhere in the treated breast. The study population was gathered from the radiation oncology databases from two hospitals, one a large, academic, National Cancer Institute designated comprehensive cancer center and the other a large private teaching hospital. The databases were searched for cases in which the initial cancer and recurrence occurred between January 1986 and December 2003 at one institution and between January 1981 and December 2003 at the other. All initial cancers were primary unifocal DCIS, stage 0 according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system, version 5 [9]. No microinvasion was present on histopathology. A total of 513 women were treated with breastconserving surgery and radiation therapy for DCIS at the two institutions during the study period. Of these women, 42 developed local recurrence (crude recurrence rate, 8.2%). Complete records, including mammograms (or detailed mammographic reports) and medical records, were available for the 32 patients who constitute our study population. Seven patients were excluded for lack of mammogram data or incomplete medical records. Three were excluded for initial presentation with multicentric DCIS. In both centers, whole-breast radiation therapy was delivered using two opposed tangential fields. All patients were treated with megavoltage radiation, generally 6 MV, to a dose of Gy in 1.8- to 2.0-Gy fractions over weeks; a supplemental boost to the tumor bed, usually administered using electrons, was delivered in most cases. The median total tumor bed dose was approximately 60 Gy at both institutions. No regional lymphatic radiation was delivered. Specific treatment details for both centers are described elsewhere [10, 11]. Mammography and Imaging Assessment The routine for imaging included physician-monitored diagnostic mammography for all of the initial DCIS studies, including magnification views for calcifications. For women with tumor-associated calcifications on the diagnostic mammogram, a postlumpectomy mammogram was performed to identify residual calcifications. Mammographic evaluation of the affected breast after lumpectomy and radiation therapy at one of the institutions included craniocaudal, mediolateral oblique, and lateral views and a magnification view of the lumpectomy site at 6 months, a bilateral mammogram with a magnification view of the lumpectomy site at 12 and 24 months, and then bilateral mammograms annually. At the second institution, a similar protocol was followed, omitting the lateral view at 6 months and adding a second magnification view of the lumpectomy site at 12 and 24 months. MRI and whole-breast sonography were not routinely performed at the time of diagnosis or as part of an annual surveillance. Digital mammography was not used. Compliance was not analyzed in this study. All cases of recurrence were presented at a multidisciplinary tumor board conference that included breast radiologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, nurses, and other support staff. The mammograms and clinical information were reviewed by two Mammography Quality Standards Act certified radiologists with 14 and 22 years of experience in mammographic interpretation. A recurrence was defined as the second occurrence of cancer in the treated breast. Original mammogram films were used when available. Alternatively, detailed mammography reports were used if they contained information regarding method of detection, location, size, and mammographic appearance of the recurrence. Mammographic findings on the initial and recurrence images were classified as calcifications, mass plus calcifications, mass alone, distortion, asymmetry, edema, and negative examination. Calcifications were categorized as amorphous and indistinct, coarse and heterogeneous, pleomorphic, or linear and branching. When it was available, the BI-RADS final assessment category was recorded [12]. The distance from the site of the primary cancer was measured or estimated from the lumpectomy site when original films were not available for review. The quadrant and distance from the nipple were identified for both the initial and recurrent carcinomas. The method of presentation (mammographic, palpable, nipple discharge, or other) of both the original and the recurrent cancers was recorded. Pathologic Assessment The pathologic results of the recurrent cancers were recorded from the medical record. These diagnoses were categorized as DCIS, DCIS with microinvasion, invasive ductal cancer, invasive lobular cancer, or other invasive cancer. Microinvasion was defined as DCIS with an invasive component of 0.1 cm or less [9]. Lobular carcinoma in situ was not considered malignant. When available, the type and grade of DCIS and the presence or absence of axillary lymph node metastases and angiolymphatic invasion were recorded. The size of the recurrent cancer was based on pathologic size in the medical record. When this was not available, the mammographic size of the abnormality was used as the size of the recurrence. A tumor recurrence was further characterized as minimal cancer if it was noninvasive or, if invasive, as measuring 1 cm or less [13]. The status of the original surgical margins was described as positive, negative, or close. A close margin was defined as DCIS less than 3 mm from the inked margin. Clinical Assessment The time to recurrence was calculated from the date of initial diagnosis to date of recurrence. Time to recurrent DCIS versus invasive recurrence was compared. Time to recurrence in the same quadrant and elsewhere in the breast was analyzed as well. Tamoxifen use was not analyzed. Statistics Two-sample Student s t tests were used to determine the significance between the interval to a noninvasive recurrence versus an invasive recurrence and the interval to recurrence in the same quadrant versus recurrence elsewhere in the breast. A difference with a p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant. Results Five hundred thirteen women were treated with lumpectomy and radiation therapy for DCIS. Of these women, 42 developed local recurrence, a crude recurrence rate of 8.2%. The mean age at the time of the initial DCIS diagnosis was 49 years (range, years). Thirty-two of the 42 patients with recurrence had adequate medical and radiographic records and unifocal DCIS, and they constitute our study population. Thirty-one (97%) of 32 cancer recurrences were mammographically visible. Twenty-nine (91%) were exclusively diagnosed on mammography. Two (6%) were diagnosed by both palpation and mammography, and one (3%) was diagnosed by visual inspection with a normal mammogram (Paget s disease). The two recurrent cases that were palpable were invasive cancer. Original mammogram films were available for review in 28 (88%) of 32 patients. The mammographic appearances of the initial and recurrent cancer are detailed in Table 1. Seventy-five percent of recurrences presented mammographically as microcalcifications, and 18% presented as masses on the mammogram. The calcifications of the primary DCIS were all AJR:189, July
3 TABLE 1: Mammographic Appearance of Initial Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) and Recurrent Tumor Mammographic Appearance Initial a % Recurrence % Calcifications only 27/ /32 75 Mass only 1/30 3 6/32 18 Distortion 0/30 0 1/32 3 Calcifications 1/ mass 0/32 0 Negative 1/30 3 1/32 3 a Two cases had inadequate data from initial DCIS mammogram. pleomorphic or of the linear branching type. Morphologic analysis of the calcifications was possible for 22 (92%) of 24 calcification-containing recurrences. Twenty-one (95%) were either pleomorphic or of the linear branching type. One (5%) was in the amorphous indistinct category. Eighty percent of the patients who presented initially with microcalcifications had a recurrence manifested by microcalcifications. The appearance of the calcifications in both the initial and recurrent tumors was available in 18 patients. In 17 (94%) of 18 patients, the recurrent tumor calcifications had a morphology similar to the initial DCIS (Fig. 1). Recurrences were pure DCIS in 17 (53%) of 32 (including one case of Paget s disease with DCIS), DCIS with microinvasion in six (19%) of 32, invasive ductal carcinoma in three (9%) of 32, invasive lobular carcinoma in two (6%) of 32, and DCIS with invasive cancer in four (13%) of 32. Seventeen of the recurrences (53%) were stage 0 and 15 (47%) were stage 1. Of the 15 patients with an invasive recurrence, 12 (80%) measured less than 1 cm. Overall, the recurrences were minimal cancers in 29 (91%) of 32 patients. Excluding cases of microinvasion, the median and mean sizes of the invasive cancers were 0.8 and 1.1 cm, respectively (range, cm). None of 15 invasive carcinomas had angiolymphatic invasion. Seven patients with invasive cancer and two with pure DCIS had lymph node sampling at the time of the recurrence, and all were negative for metastasis. The mean distance between the initial and the recurrent cancers was 3.8 cm (median, 3.5 cm; range, 0 9 cm) in 30 patients for whom these data were available. Eighteen (60%) of 30 patients had their recurrence in the same quadrant as the original DCIS (Figs. 1 and 2). Of 26 patients with available margin status before radiation therapy, 16 had negative margins, nine had close margins, and one patient had positive margins. The mean time to recurrence for all patients was 4.5 years. See Figure 3 for distribution of frequency of time to recurrence. No significant difference was seen in time to recurrence between noninvasive and invasive cancers (3.8 and 5.2 years, respectively) A B C Fig year-old woman developed pleomorphic microcalcifications on follow-up mammography 7 years after breastconserving surgery and radiation therapy for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Her recurrence was invasive lobular carcinoma, with lobular carcinoma in situ located 9 cm from original lumpectomy site in same quadrant. A, Mediolateral oblique mammogram at time of recurrence. Surgical clips indicate lumpectomy bed. Circle indicates site of recurrence. B, Spot magnification view of primary DCIS at time of wire localization shows microcalcifications. C, Spot magnification view of recurrence also shows microcalcifications. (p = 0.14). However, a trend was seen toward longer time to an invasive recurrence. No significant difference was seen in the mean time to recurrence in the same quadrant versus mean time to recurrence elsewhere in the breast (4.9 vs 4.1 years) (p = 0.42). 142 AJR:189, July 2007
4 Mammography of Recurrent Breast Cancer Fig year-old woman with recurrence presenting as microcalcifications 3 years after treatment. Magnification of mediolateral oblique view of lumpectomy site shows clips and scar. Note new pleomorphic microcalcifications nearby. These microcalcifications were ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion located 2 cm from lumpectomy site. Discussion Women treated for DCIS with breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy can expect a low rate of recurrent disease. In our study, mammography was effective at detecting recurrence, with 97% of cases detected on mammography. When cancer did recur, 91% were minimal cancers and all were stage 0 or 1. This provides inferential support for excellent prognosis even when recurrence does occur. For the radiologist, the appearance of the recurrence and follow-up imaging strategies are paramount. The crude recurrence rate of 8.2% confirms the low rate of tumor recurrence after breastconserving surgery with radiation therapy. Several studies have addressed the rate of local recurrence after the various treatment options for Fig. 3 Time interval (in years) from initial diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ to recurrence versus percentage of total patients. % of All 32 Patients DCIS [3, 4, 10, 14 17]. In the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) B-17 trial, local recurrence rates after breastconserving surgery and radiation therapy were reported to be 7% at 5 years and 12% at 8 years [14, 17, 18]. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) trials confirmed reduced recurrence rates with radiation therapy, reporting 10-year local recurrence rates of 14.8% for the group treated with radiation and 26% for the group treated with lumpectomy alone (p < ) [19]. The United Kingdom Coordinating Committee on Cancer Research (UKCCCR) study showed 5-year ipsilateral recurrence rates of 6% for the radiation therapy group versus 14% for the group with lumpectomy alone (p < ) [20]. Mastectomy is an alternative treatment option for DCIS; however, it does not completely eliminate the risk of local recurrence. The incidence of locally recurrent cancer after mastectomy for DCIS has been variably reported as 1 4% for follow-up periods of 5 9 years [2 6]. These recurrences occur in the form of chest wall recurrences, and typically are invasive cancers detected by palpation because mammographic evaluation is not performed [1, 4]. As screening mammography has become standard practice, the incidence of DCIS has increased. It is estimated to represent 22% of all breast cancers diagnosed in the United States in 2005 [21]. The American Cancer Society estimates of the annual incidence of DCIS has increased from 30,000 in 1996 to more than 58,000 in Just as the initial diagnosis of DCIS is primarily made mammographically, recurrences are also primarily detected mammographically. Postsurgical and postirradiation changes may diminish mammographic sensitivity [22, 23]. Postoperative seroma, hematoma, scarring, and edema can alter the density and architecture of the breast. < Time Interval to Recurrence (y) Progressively better mammography, regular use of magnification views of the lumpectomy site before radiation therapy, a baseline study after radiation therapy, routine follow-up mammograms, and better surgical and radiation therapy techniques resulting in less deformity [22] may enhance our ability to detect suspicious changes in the breast. Most patients who presented with calcifications in the original DCIS had recurrences with calcifications. The finding of new suspicious calcifications on a follow-up mammogram should prompt a biopsy. Similarity in morphology between the primary and recurrent calcifications was seen in 94% of these patients. We consider this an aid for the radiologist in assessing follow-up studies, which underscores the value of having prior films for comparison. The prognosis of breast cancer is closely tied to its stage at the time of diagnosis. In our study, all recurrences were diagnosed as an AJCC stage 0 or 1. The high percentage of recurrence as DCIS (53%) and as minimal breast cancer (91%) predicts an excellent prognosis [24]. Orel et al. [25] reported a statistically significant association between detection of a tumor recurrence on mammography alone and a lower tumor stage after treatment for earlystage invasive breast cancers. A trend was also noted toward noninvasive histology and longer disease-free survival. In our study, only 60% of the recurrences occurred in the same quadrant and 40% recurred elsewhere in the breast. Tumor recurrence has previously been reported to occur with greatest frequency at or close to the lumpectomy site [2, 26]. Fisher et al. [17] reported early results of the NSABP B-17 trial, in which 84% of recurrences were in the same quadrant of the breast or at the border of the quadrant. In a study by Liberman et al. [26] of breast-conserving surgery for DCIS, 90% of the recurrences occurred in the same quadrant. We found no significant difference between the time to recurrence in the same quadrant and time to recurrence elsewhere in the breast. The former was 4.9 years and the latter was 4.1 years (p =0.42). In our study, all recurrences occurred after 1 year from the date of diagnosis. The mean time between the initial and recurrent cancers was 4.5 years (range, 1 12 years), with a clustering between 1 and 7 years. This time interval is longer than the mean time to recurrence of 2.8 years reported by Weng et al. [3] in a similar treatment group. In a multiinstitutional study reported by Solin et al. [27], mean time to recurrence was 5.7 years. These studies suggest that long-term mammographic surveillance is AJR:189, July
5 necessary after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for women diagnosed with DCIS. However, Doubeni et al. [28] showed that the percentage of breast cancer survivors having regular mammograms declines with time after diagnosis. Our study has several potential limitations. Because all patients had whole-breast radiation therapy, these results may not apply to patients who were treated with lumpectomy alone or with partial breast irradiation. None of the patients had clinical MRI or whole-breast sonography to locate other primary or residual disease. The impact of these tests on detecting future recurrence is unknown. The use of mammography reports when actual films were not available may have introduced a measurement error. It was necessary in some cases to use the mammographic size of a lesion, which is not considered as accurate as a pathologic measurement. Tamoxifen was not in widespread use during a large part of this study period. Studies have shown the expected recurrence rate is lower with the use of tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment after radiation therapy [8]. Postlumpectomy mammography was routinely used in this study to identify residual disease. Institutions that do not perform postlumpectomy mammography may experience different outcomes. Women at both centers were evaluated at comprehensive breast centers using multidisciplinary approaches to diagnosis and treatment, which may influence the course of treatment. In conclusion, ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for DCIS was an infrequent event. Mammography was highly effective at detecting early tumor recurrence, with 97% presenting with an abnormal mammogram. Ninety-one percent of recurrences were minimal cancers at detection, suggesting an excellent prognosis even when tumors recur. References 1. Silverstein MJ, Barth A, Poller DN, et al. Ten-year results comparing mastectomy to excision and radiation therapy for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Eur J Cancer 1995; 31A: Burstein HJ, Polyak K, Wong JS, Lester SC, Kaelin CM. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: Weng EY, Juillard GJ, Parker RG, Chang HR, Gornbein JA. Outcomes and factors impacting local recurrence of ductal carcinoma in situ. Cancer 2000; 88: Vargas C, Kestin L, Go N, et al. Factors associated with local recurrence and cause-specific survival in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast treated with breast-conserving therapy or mastectomy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005; 63: Warneke J, Grossklaus D, Davis J, et al. Influence of local treatment on the recurrence rate of ductal carcinoma in situ. J Am Coll Surg 1995; 180: Harris J, Morrow M, Osborne C, Lippman M. Diseases of the breast, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004: Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, et al. Tamoxifen for the prevention of breast cancer: current status of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005; 97: Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, et al. Tamoxifen in treatment of intraductal breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-24 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999; 353: Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al., eds. AJCC cancer staging handbook. From the AJCC cancer staging manual, 6th ed. New York, NY: Springer- Verlag, 2002: Kestin LL, Goldstein NS, Martinez AA, et al. Mammographically detected ductal carcinoma in situ treated with conservative surgery with or without radiation therapy: patterns of failure and 10-year results. Ann Surg 2000; 231: Ben-David MA, Griffith KA, Hayman JA, Lichter AS, Pierce LJ. Long-term results of conservative surgery and radiotherapy using lung density correction of ductal carcinoma in situ. (abstr) Proceedings of the American Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO), Fairfax, VA: ASTRO, American College of Radiology. Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, 3rd ed. Reston, VA: ACR, Bassett L, Hendrick R, Bassford T. Quality determinants of mammography. In: Clinical practice guideline, number 13. Rockville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Fisher B, Costantino J, Redmond C, et al. Lumpectomy compared with lumpectomy and radiation therapy for the treatment of intraductal breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: Solin LJ, Fourquet A, Vicini FA, et al. Salvage treatment for local recurrence after breast-conserving surgery and radiation as initial treatment for mammographically detected ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer 2001; 91: Jha MK, Avlonitis VS, Griffith CD, et al. Aggressive local treatment for screen-detected DCIS results in very low rates of recurrence. Eur J Surg Oncol 2001; 27: Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, et al. Lumpectomy and radiation therapy for the treatment of intraductal breast cancer: findings from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-17. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: Fisher ER, Dignam J, Tan-Chiu E, et al. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast Project (NSABP) eight-year update of protocol B-17: intraductal carcinoma. Cancer 1999; 86: Bijker N, Meijnen P, Peterse JL, et al. Breast-conserving treatment with or without radiotherapy in ductal carcinoma-in-situ: ten-year results of European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer randomized phase III trial a study by the EORTC Breast Cancer Cooperative Group and EORTC Radiotherapy Group. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: Houghton J, George WD, Cuzick J, Duggan C, Fentiman IS, Spittle M. Radiotherapy and tamoxifen in women with completely excised ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast in the UK, Australia, and New Zealand: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2003; 362: Estimated new cancer cases and deaths by sex for all sites, US, American Cancer Society Website. Available at: content/ downloads/med_1_1x_cff2005_ Estimated_New_Cases_Deaths_by_Sex_US.asp. Accessed June 8, Giess CS, Keating DM, Osborne MP, Rosenblatt R. Local tumor recurrence following breast-conservation therapy: correlation of histopathologic findings with detection method and mammographic findings. Radiology 1999; 212: Dershaw DD. Mammography in patients with breast cancer treated by breast conservation (lumpectomy with or without radiation). AJR 1995; 164: Wirman JA. The clinical significance of minimal breast cancer: a pathologist s viewpoint. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1985; 3: Orel SG, Fowble BL, Solin LJ, Schultz DJ, Conant EF, Troupin RH. Breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation therapy for early-stage disease: prognostic significance of detection method. Radiology 1993; 188: Liberman L, Van Zee KJ, Dershaw DD, Morris EA, Abramson AF, Samli B. Mammographic features of local recurrence in women who have undergone breast-conserving therapy for ductal carcinoma in situ. AJR 1997; 168: Solin LJ, Fourquet A, Vicini FA, et al. Mammographically detected ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast treated with breast-conserving surgery and definitive breast irradiation: long-term outcome and prognostic significance of patient age and margin status. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001; 50: Doubeni CA, Field TS, Ulcickas Yood M, et al. Patterns and predictors of mammography utilization among breast cancer survivors. Cancer 2006; 106: AJR:189, July 2007
Radiation and DCIS. The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging
 Radiation and DCIS The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging Einsley-Marie Janowski, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Oncology
Radiation and DCIS The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging Einsley-Marie Janowski, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Oncology
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast: A Clinical Practice Guideline
 Evidence-based Series #1-10 Version 2.2006: Section 1 Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast: A Clinical Practice Guideline W. Shelley, D. McCready, C. Holloway, M. Trudeau, S. Sinclair,
Evidence-based Series #1-10 Version 2.2006: Section 1 Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast: A Clinical Practice Guideline W. Shelley, D. McCready, C. Holloway, M. Trudeau, S. Sinclair,
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice
 Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Bruno CUTULI Policlinico Courlancy REIMS. WORKSHOP SULL IRRADIAZIONE MAMMARIA IPOFRAZIONATA Il carcinoma duttale in situ
 Bruno CUTULI Policlinico Courlancy REIMS WORKSHOP SULL IRRADIAZIONE MAMMARIA IPOFRAZIONATA Il carcinoma duttale in situ XXI CONGRESSO AIRO GENOVA 22.11.2011 INTRODUCTION Due to wide diffusion of mammography,
Bruno CUTULI Policlinico Courlancy REIMS WORKSHOP SULL IRRADIAZIONE MAMMARIA IPOFRAZIONATA Il carcinoma duttale in situ XXI CONGRESSO AIRO GENOVA 22.11.2011 INTRODUCTION Due to wide diffusion of mammography,
Standards for Diagnosis and Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) of the Breast
 d i a g n o s i s a n d m a n a g e m e n t s t a n d a r d s f o r d c i s Standards for Diagnosis and Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) of the Breast American College of Radiology American
d i a g n o s i s a n d m a n a g e m e n t s t a n d a r d s f o r d c i s Standards for Diagnosis and Management of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) of the Breast American College of Radiology American
Review Article Role of the Radiotherapy Boost on Local Control in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2012, Article ID 748196, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/748196 Review Article Role of the Radiotherapy Boost on Local Control in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Olivier Riou,
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2012, Article ID 748196, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/748196 Review Article Role of the Radiotherapy Boost on Local Control in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Olivier Riou,
Medical Audit of Diagnostic Mammography Examinations: Comparison with Screening Outcomes Obtained Concurrently
 Katherine E. Dee 1,2 Edward A. Sickles 1 Received July 3, 2000; accepted after revision September 12, 2000. Presented in part at the annual meeting of the American Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC,
Katherine E. Dee 1,2 Edward A. Sickles 1 Received July 3, 2000; accepted after revision September 12, 2000. Presented in part at the annual meeting of the American Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC,
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Accuracy of Specimen Radiography in Assessing Complete Local Excision with Breast-Conservation Surgery
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:09/22/2017 Acceptance:01/21/2018 Accuracy of Specimen Radiography in Assessing Complete Local Excision with Breast-Conservation Surgery Saira Naz, Imrana
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:09/22/2017 Acceptance:01/21/2018 Accuracy of Specimen Radiography in Assessing Complete Local Excision with Breast-Conservation Surgery Saira Naz, Imrana
Management of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
 Management of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Stella Hetelekidis, MD Stuart J. Schnitt, MD Monica Morrow, MD Jay R. Harris, MD Introduction Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma,
Management of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Stella Hetelekidis, MD Stuart J. Schnitt, MD Monica Morrow, MD Jay R. Harris, MD Introduction Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma,
Clinical Outcomes of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Treated with Partial Mastectomy without Adjuvant Radiotherapy
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.3.537 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(3):537-542, 2012 Clinical Outcomes of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Treated with
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.3.537 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(3):537-542, 2012 Clinical Outcomes of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Treated with
Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies
 Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation.
 DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation. Poster No.: C-1560 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. B. Ibrahim, P. Morris, S. ANANDAN; Burlington, MA/US Keywords:
DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation. Poster No.: C-1560 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. B. Ibrahim, P. Morris, S. ANANDAN; Burlington, MA/US Keywords:
Effect of tamoxifen and radiotherapy in women with locally excised ductal carcinoma in situ: long-term results from the UK/ANZ DCIS trial
 Effect of and in women with locally excised ductal carcinoma in situ: long-term results from the UK/ANZ trial Jack Cuzick, Ivana Sestak, Sarah E Pinder, Ian O Ellis, Sharon Forsyth, Nigel J Bundred, John
Effect of and in women with locally excised ductal carcinoma in situ: long-term results from the UK/ANZ trial Jack Cuzick, Ivana Sestak, Sarah E Pinder, Ian O Ellis, Sharon Forsyth, Nigel J Bundred, John
Is Lobular Carcinoma In Situ as a Component of Breast Carcinoma a Risk Factor for Local Failure after Breast-Conserving Therapy?
 28 Is Lobular Carcinoma In Situ as a Component of Breast Carcinoma a Risk Factor for Local Failure after Breast-Conserving Therapy? Results of a Matched Pair Analysis Merav A. Ben-David, M.D. 1 Celina
28 Is Lobular Carcinoma In Situ as a Component of Breast Carcinoma a Risk Factor for Local Failure after Breast-Conserving Therapy? Results of a Matched Pair Analysis Merav A. Ben-David, M.D. 1 Celina
IORT What We ve Learned So Far
 IORT What We ve Learned So Far The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging Einsley-Marie Janowski, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation
IORT What We ve Learned So Far The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging Einsley-Marie Janowski, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) Ductal Carcinoma in Situ DCIS Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Blohmer / Brunnert / Budach /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) Ductal Carcinoma in Situ DCIS Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Blohmer / Brunnert / Budach /
The Role of a Boost Radiation Dose in Patients with Negative Re-Excision Findings
 24 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 24-28 Open Access The Role of a Boost Radiation Dose in with Negative Re-Excision Melanie C. Smitt and Kathleen C. Horst * Department of Radiation Oncology,
24 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 24-28 Open Access The Role of a Boost Radiation Dose in with Negative Re-Excision Melanie C. Smitt and Kathleen C. Horst * Department of Radiation Oncology,
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
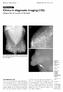 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
J Clin Oncol 27: by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 27 NUMBER 10 APRIL 1 2009 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Effect of Margin Status on Local Recurrence After Breast Conservation and Radiation Therapy for Ductal Carcinoma
VOLUME 27 NUMBER 10 APRIL 1 2009 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Effect of Margin Status on Local Recurrence After Breast Conservation and Radiation Therapy for Ductal Carcinoma
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation
 Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Ductal carcinoma in situ
 Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Ductal carcinoma in situ Management update Kirsty Stuart, BSc (Med), MBBS, FRANZCR, is a radiation oncologist, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, New South
Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Ductal carcinoma in situ Management update Kirsty Stuart, BSc (Med), MBBS, FRANZCR, is a radiation oncologist, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, New South
Articles. For personal use. Only reproduce with permission from The Lancet.
 Articles and tamoxifen in women with completely excised ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast in the UK, Australia, and New Zealand: randomised controlled trial UK Coordinating Committee on Cancer Research
Articles and tamoxifen in women with completely excised ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast in the UK, Australia, and New Zealand: randomised controlled trial UK Coordinating Committee on Cancer Research
Consensus Guideline on Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation
 Consensus Guideline on Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Purpose: To outline the use of accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) for the treatment of breast cancer. Associated ASBS Guidelines
Consensus Guideline on Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Purpose: To outline the use of accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) for the treatment of breast cancer. Associated ASBS Guidelines
Extent of Lumpectomy for Breast Cancer After Diagnosis by Stereotactic Core Versus Wire Localization Biopsy
 Annals of Surgical Oncology, 6(4):330 335 Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 1999 The Society of Surgical Oncology, Inc. Extent of Lumpectomy for Breast Cancer After Diagnosis by Stereotactic Core
Annals of Surgical Oncology, 6(4):330 335 Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 1999 The Society of Surgical Oncology, Inc. Extent of Lumpectomy for Breast Cancer After Diagnosis by Stereotactic Core
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Ahmad Elahi*, Gholamreza Toogeh,Habibollah Mahmoodzadeh, Behnaz Jahanbin, Farhad Shahi,
 Clinical Experience Open Access DOI: 10.1187/abc.20185258-62 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Close to the Inked Margin: A Case Presented in Multidisciplinary Session With Clinical Discussion and Decision Making
Clinical Experience Open Access DOI: 10.1187/abc.20185258-62 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Close to the Inked Margin: A Case Presented in Multidisciplinary Session With Clinical Discussion and Decision Making
doi: /j.ijrobp
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.12.047 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 79, No. 4, pp. 977 984, 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/$ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.12.047 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 79, No. 4, pp. 977 984, 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/$ see front matter
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
259 Patients with DCIS of the breast applying USC/Van Nuys prognostic index: a retrospective review with long term follow up
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2008) 109:405 416 DOI 10.1007/s10549-007-9668-7 REVIEW 259 Patients with DCIS of the breast applying USC/Van Nuys prognostic index: a retrospective review with long term follow
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2008) 109:405 416 DOI 10.1007/s10549-007-9668-7 REVIEW 259 Patients with DCIS of the breast applying USC/Van Nuys prognostic index: a retrospective review with long term follow
SSO-ASTRO Consensus Guidance Margins for Breast-Conserving Surgery with Whole Breast Irradiation in Stage I and II Invasive Breast Cancer
 SSO-ASTRO Consensus Guidance Margins for Breast-Conserving Surgery with Whole Breast Irradiation in Stage I and II Invasive Breast Cancer Dr. Yvonne Tsang St. Paul s Hospital Introductions Breast-conserving
SSO-ASTRO Consensus Guidance Margins for Breast-Conserving Surgery with Whole Breast Irradiation in Stage I and II Invasive Breast Cancer Dr. Yvonne Tsang St. Paul s Hospital Introductions Breast-conserving
Speaker s Bureau. Travel expenses. Advisory Boards. Stock. Genentech Invuity Medtronic Pacira. Faxitron. Dune TransMed7 Genomic Health.
 Management of DCIS Shawna C. Willey, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Georgetown University Director, Medstar Regional Breast Health Program Chief, Department of Surgery Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
Management of DCIS Shawna C. Willey, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Georgetown University Director, Medstar Regional Breast Health Program Chief, Department of Surgery Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients
 236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Breast Cancer? Breast cancer is the most common. What s New in. Janet s Case
 Focus on CME at The University of Calgary What s New in Breast Cancer? Theresa Trotter, MD, FRCPC Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in Canada, accounting for almost a third of
Focus on CME at The University of Calgary What s New in Breast Cancer? Theresa Trotter, MD, FRCPC Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in Canada, accounting for almost a third of
Chief Investigator Adele Francis University of Birmingham UK. Prof MWR Reed (CoI) University of Sheffield
 The LORIS Trial: A multicentre, randomised phase III trial of standard surgery versus active monitoring in women with newly diagnosed low risk ductal carcinoma in situ. Chief Investigator Adele Francis
The LORIS Trial: A multicentre, randomised phase III trial of standard surgery versus active monitoring in women with newly diagnosed low risk ductal carcinoma in situ. Chief Investigator Adele Francis
Promise of a beautiful day
 Promise of a beautiful day Ductal carcinoma in Situ Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Natural History Manosmed Tartous Oct 2009 Gérard ABADJIAN MD Pathology Department Hôtel-Dieu de France. Associate Professor
Promise of a beautiful day Ductal carcinoma in Situ Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Natural History Manosmed Tartous Oct 2009 Gérard ABADJIAN MD Pathology Department Hôtel-Dieu de France. Associate Professor
Watchful Waiting: Well Behaved Breast Cancers Non-Surgical Management of Breast Cancer
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10002 Watchful Waiting: Well Behaved Breast Cancers Non-Surgical Management of Breast Cancer Received:
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10002 Watchful Waiting: Well Behaved Breast Cancers Non-Surgical Management of Breast Cancer Received:
Treatment results and predictors of local recurrences after breast conserving therapy in early breast carcinoma
 Journal of BUON 8: 241-246, 2003 2003 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment results and predictors of local recurrences after breast conserving therapy in early breast
Journal of BUON 8: 241-246, 2003 2003 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment results and predictors of local recurrences after breast conserving therapy in early breast
Balancing Evidence and Clinical Practice in the Treatment of Localized Breast Cancer May 5, 2006
 Balancing Evidence and Clinical Practice in the Treatment of Localized Breast Cancer May 5, 2006 Deborah Hamolsky MS, RN : DCIS Carol Franc Buck Breast Care Center UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Jane
Balancing Evidence and Clinical Practice in the Treatment of Localized Breast Cancer May 5, 2006 Deborah Hamolsky MS, RN : DCIS Carol Franc Buck Breast Care Center UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Jane
Classifying Local Disease Recurrences after Breast Conservation Therapy Based on Location and Histology
 2059 Classifying Local Disease Recurrences after Breast Conservation Therapy Based on Location and Histology New Primary Tumors Have More Favorable Outcomes than True Local Disease Recurrences Eugene Huang,
2059 Classifying Local Disease Recurrences after Breast Conservation Therapy Based on Location and Histology New Primary Tumors Have More Favorable Outcomes than True Local Disease Recurrences Eugene Huang,
Breast Cancer Imaging
 Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Features of Prospectively Overlooked Computer-Aided Detection Marks on Prior Screening Digital Mammograms in Women With Breast Cancer
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Nariya Cho 1 Seung Ja Kim Hye Young Choi Chae Yeon Lyou Woo Kyung Moon Cho N, Kim SJ, Choi HY, Lyou CY, Moon WK Keywords:
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Nariya Cho 1 Seung Ja Kim Hye Young Choi Chae Yeon Lyou Woo Kyung Moon Cho N, Kim SJ, Choi HY, Lyou CY, Moon WK Keywords:
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
J Clin Oncol 26: by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 26 NUMBER 3 JANUARY 20 2008 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Relationship of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Outcome After Breast-Conservation Treatment With Radiation
VOLUME 26 NUMBER 3 JANUARY 20 2008 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Relationship of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Outcome After Breast-Conservation Treatment With Radiation
RADIOTHERAPY IN BREAST CANCER :
 RADIOTHERAPY IN BREAST CANCER : PAST, PRESENT, FUTURE Dr Jyotirup Goswami Consultant Radiation Oncologist Narayana Cancer Institute Narayana Superspecialty Hospital Breast cancer is the classic paradigm
RADIOTHERAPY IN BREAST CANCER : PAST, PRESENT, FUTURE Dr Jyotirup Goswami Consultant Radiation Oncologist Narayana Cancer Institute Narayana Superspecialty Hospital Breast cancer is the classic paradigm
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
When do you need PET/CT or MRI in early breast cancer?
 When do you need PET/CT or MRI in early breast cancer? Elizabeth A. Morris MD FACR Chief, Breast Imaging Service Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center NY, NY Objectives What is the role of MRI in initial
When do you need PET/CT or MRI in early breast cancer? Elizabeth A. Morris MD FACR Chief, Breast Imaging Service Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center NY, NY Objectives What is the role of MRI in initial
Post-operative radiotherapy for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Post-operative radiotherapy for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast(review) GoodwinA,ParkerS,GhersiD,WilckenN GoodwinA,ParkerS,GhersiD,WilckenN. Post-operative
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Post-operative radiotherapy for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast(review) GoodwinA,ParkerS,GhersiD,WilckenN GoodwinA,ParkerS,GhersiD,WilckenN. Post-operative
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy for Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast
 1 Angela Kempen February Case Study February 22, 2012 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy for Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast History of Present Illness: JE is a 45 year-old Caucasian female who underwent
1 Angela Kempen February Case Study February 22, 2012 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy for Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast History of Present Illness: JE is a 45 year-old Caucasian female who underwent
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
ARTICLE IN PRESS. doi: /j.ijrobp METAPLASTIC CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST: A RETROSPECTIVE REVIEW
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
Treatment Results and Prognostic Factors of Early Breast Cancer Treated with a Breast Conserving Operation and Radiotherapy
 Treatment Results and Prognostic Factors of Early Breast Cancer Treated with a Breast Conserving Operation and Radiotherapy Kyoung Ju Kim 1, Seung Jae Huh 1, Jung-Hyun Yang 2, Won Park 1, Seok Jin Nam
Treatment Results and Prognostic Factors of Early Breast Cancer Treated with a Breast Conserving Operation and Radiotherapy Kyoung Ju Kim 1, Seung Jae Huh 1, Jung-Hyun Yang 2, Won Park 1, Seok Jin Nam
Clinical Trials of Proton Therapy for Breast Cancer. Andrew L. Chang, MD 張維安 Study Chair
 Clinical Trials of Proton Therapy for Breast Cancer Andrew L. Chang, MD 張維安 Study Chair AndrewLChangMD@gmail.com Disclosure Proton Center Development Corporation Scripps San Diego Proton Therapy Center
Clinical Trials of Proton Therapy for Breast Cancer Andrew L. Chang, MD 張維安 Study Chair AndrewLChangMD@gmail.com Disclosure Proton Center Development Corporation Scripps San Diego Proton Therapy Center
Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 160:387 391 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 EDITORIAL Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery Monika Brzezinska 1 Linda J.
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 160:387 391 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 EDITORIAL Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery Monika Brzezinska 1 Linda J.
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging
 Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection
 Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR BREAST CONSERVATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 The American College of Radiology, with more than 30,000 members, is the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States. The College
The American College of Radiology, with more than 30,000 members, is the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States. The College
BREAST CONSERVATION TREATMENT IN EARLY STAGE DISEASE AND DCIS LAWRENCE J. SOLIN, MD, FACR, FASTRO
 BREAST CONSERVATION TREATMENT IN EARLY STAGE DISEASE AND DCIS LAWRENCE J. SOLIN, MD, FACR, FASTRO Chairman Department of Radiation Oncology Albert Einstein Healthcare Network Philadelphia, PA Professor
BREAST CONSERVATION TREATMENT IN EARLY STAGE DISEASE AND DCIS LAWRENCE J. SOLIN, MD, FACR, FASTRO Chairman Department of Radiation Oncology Albert Einstein Healthcare Network Philadelphia, PA Professor
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications. BI-RADS 5 th Edition
 UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 2, p
 Title Conservative surgery for breast cancer Author(s) Poon, RTP; Chow, LWC; Au, GKH Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 2, p. 68-72 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/722/45367 Rights
Title Conservative surgery for breast cancer Author(s) Poon, RTP; Chow, LWC; Au, GKH Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 2, p. 68-72 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/722/45367 Rights
Changes in Surgical Management Resulting From Case Review at a Breast Cancer Multidisciplinary Tumor Board
 2346 Changes in Surgical Management Resulting From Case Review at a Breast Cancer Multidisciplinary Tumor Board Erika A. Newman, MD 1 Amy B. Guest, MD 2 Mark A. Helvie, MD 2 Marilyn A Roubidoux, MD 2 Alfred
2346 Changes in Surgical Management Resulting From Case Review at a Breast Cancer Multidisciplinary Tumor Board Erika A. Newman, MD 1 Amy B. Guest, MD 2 Mark A. Helvie, MD 2 Marilyn A Roubidoux, MD 2 Alfred
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast: Controversial Issues
 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast: Controversial Issues MELVIN J. SILVERSTEIN The Breast Center*, Van Nuys, California, USA Key Words. DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ Noninvasive breast cancer Intraductal
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast: Controversial Issues MELVIN J. SILVERSTEIN The Breast Center*, Van Nuys, California, USA Key Words. DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ Noninvasive breast cancer Intraductal
A DEEPER DIVE INTO DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU: CLINICAL AND PATHOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS IN 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 A DEEPER DIVE INTO DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU: CLINICAL AND PATHOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS IN 2015
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 A DEEPER DIVE INTO DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU: CLINICAL AND PATHOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS IN 2015
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Image guided core biopsies:
 Recommendations on the Surgical, Radiologic and Pathologic Approaches to Breast Disease: Using best practices based on multidisciplinary methodologies developed through the Allina Breast Committee. Image
Recommendations on the Surgical, Radiologic and Pathologic Approaches to Breast Disease: Using best practices based on multidisciplinary methodologies developed through the Allina Breast Committee. Image
Prophylactic Mastectomy
 Prophylactic Mastectomy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.010 01/01/2009 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 08/24/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Prophylactic Mastectomy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.010 01/01/2009 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 08/24/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance
 Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications
 Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Disclosures. Premalignant Lesions of the Breast: What Clinicians Want and Why. NY Times: Prone to Error: Earliest Steps to Find Cancer.
 Disclosures Premalignant Lesions of the Breast: What Clinicians Want and Why I have nothing to disclose Rick Baehner, MD Assistant Professor, UCSF Pathology NY Times: Prone to Error: Earliest Steps to
Disclosures Premalignant Lesions of the Breast: What Clinicians Want and Why I have nothing to disclose Rick Baehner, MD Assistant Professor, UCSF Pathology NY Times: Prone to Error: Earliest Steps to
Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer
 - Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
- Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019. AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division
 BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review
 Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Surgery for Breast Cancer
 Surgery for Breast Cancer 1750 Mastectomy - Petit 1894 Radical mastectomy Halsted Extended, Super radical mastectomy 1948 Modified radical mastectomy Patey 1950-60 WLE & RT Baclesse, Mustakallio 1981-85
Surgery for Breast Cancer 1750 Mastectomy - Petit 1894 Radical mastectomy Halsted Extended, Super radical mastectomy 1948 Modified radical mastectomy Patey 1950-60 WLE & RT Baclesse, Mustakallio 1981-85
Access and take the CME test online and receive 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit at CME.TheOncologist.com
 The Oncologist Breast Cancer Current Treatment and Clinical Trial Developments for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast JUDY C. BOUGHEY, a RICARDO J. GONZALEZ, b EVERETT BONNER, c HENRY M. KUERER b a
The Oncologist Breast Cancer Current Treatment and Clinical Trial Developments for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast JUDY C. BOUGHEY, a RICARDO J. GONZALEZ, b EVERETT BONNER, c HENRY M. KUERER b a
Mammograms, Ultrasounds, MRI: Who gets what and why?
 Mammograms, Ultrasounds, MRI: Who gets what and why? Beast MRI Ultrasound Mammogram Kavita Dhamanaskar, MBBS, DNB, FRCP(C) Associate Professor @ McMaster University Radiologist @ Juravinski Hospital and
Mammograms, Ultrasounds, MRI: Who gets what and why? Beast MRI Ultrasound Mammogram Kavita Dhamanaskar, MBBS, DNB, FRCP(C) Associate Professor @ McMaster University Radiologist @ Juravinski Hospital and
New Palpable Breast Lump With Recent Negative Mammogram: Is Repeat Mammography Necessary?
 Women s Imaging Original Research Leung et al. Repeat Mammogram for Breast Lump Found After Negative Mammogram Women s Imaging Original Research Stephanie E. Leung 1 Ilanit Ben-Nachum Anat Kornecki Leung
Women s Imaging Original Research Leung et al. Repeat Mammogram for Breast Lump Found After Negative Mammogram Women s Imaging Original Research Stephanie E. Leung 1 Ilanit Ben-Nachum Anat Kornecki Leung
