Cell Cycle Regulation. Adrian R. Black
|
|
|
- Howard Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell Cycle Regulation Adrian R. Black
2 Loss of Growth Control Block of Apoptosis Evasion of Senescence Angiogenesis Invasion
3 hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome Segregation and Cytokenesis M
4 hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome Segregation and Cytokenesis M Gap 2: reparation for Cell Division G 2 G 1 Gap 1: reparation for DNA Replication S Synthesis: DNA Replication
5 Cyclins regulate the cell cycle Expression Oscillates During the Cell Cycle Main Cell Cycle Regulatory Cyclins: cyclin D1-3, cyclin E, cyclin A and cyclin B
6 "Mammalian cell-cycle regulation: several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms." Satyanarayana, A. and. Kaldis (2009). Oncogene 28(33): After a decade of extensive work on gene knockout mouse models of cell-cycle regulators, the classical model of cell-cycle regulation was seriously challenged. Several unexpected compensatory mechanisms were uncovered among cyclins and Cdks in these studies. The most astonishing observation is that Cdk2 is dispensable for the regulation of the mitotic cell cycle with both Cdk4 and Cdk1 covering for Cdk2's functions. Similar to yeast, it was recently discovered that Cdk1 alone can drive the mammalian cell cycle, indicating that the regulation of the mammalian cell cycle is highly conserved. Nevertheless, cellcycle-independent functions of Cdks and cyclins such as in DNA damage repair are still under investigation. Here we review the compensatory mechanisms among major cyclins and Cdks in mammalian cell-cycle regulation.
7 Cyclin Expression During Cell Cycle Cyclin E Cyclin A Cyclin B Cyclin D G 1 S G 2 M
8 hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome Segregation and Cytokenesis Growth Factor Withdrawal M G 0 Growth Factor Addition G 2 G 1 eriod during which growth factors are required S Synthesis: DNA Replication Restriction oint oint at which growth factors no longer required
9 Cell cycle checkpoints Growth Factor Withdrawal G 0 Check of DNA integrity Spindle checkpoint M Growth Factor Addition G 2 G 1 S Check of DNA integrity and readiness for replication Check of DNA integrity
10 hases of the cell cycle Growth Factor Withdrawal Mitosis: Chromosome Segregation and Cytokenesis M G 0 Growth Factor Addition Gap 2: reparation for Cell Division G 2 G 1 eriod during which growth factors are required S Synthesis: DNA Replication Restriction oint oint at which growth factors no longer required
11 Cyclin Expression During Cell Cycle Cyclin E Cyclin A Cyclin B Cyclin D Growth Factors G 1 S G 2 M R
12 Cyclin D1 acts as a sensor of the growth environment for the cell cycle Ral RTK Ras Raf Mek Erk AK I3K Rac Akt 4EB1 mrna nuclear export ILK Integrins GSK3β mtor S6K β-catenin Wnt/ Frizzled AC Nuclear Export and roteasoma degradation Ub Ub Ub Translation cyclin D1 gene Transcription Ras KC
13 Cyclins Regulate Cyclin-Dependent Kinases Cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) Multigene Family [cdk4, cdk6, cdk2, cdk1 (cdc2)] Serine/Threonine Kinases Require Cyclin Binding for Activity Regulated by hosphorylation Regulated by Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors (ckis) Cyclins Regulatory Subunits of Cyclin/cdk Complexes Main Cell Cycle Regulatory Cyclins: cyclin D1-3, cyclin E, cyclin A and cyclin B Cyclin/cdk Associations: cyclin D/cdk4, cyclin D/cdk6, cyclin E/cdk2, cyclin A/cdk2, cyclin A/cdk1 and cyclin B/cdk1 Expression Oscillates During the Cell Cycle
14 Interaction of cyclins and cdks during the cell cycle Figure 8.8 The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
15 Cyclin Dependent-Kinase Inhibitors (ckis) INK Family p15 b, p16 a, p18 c, p19 d Bind cyclin D-associating cdks (cdk4 and cdk6) Block interaction of cdks with cyclins CI/KI Family p21 WAF1/CI1, p27 KI1, p57 KI2 Inhibit Cyclin A/cdk2 and Cyclin E/cdk2 Required for assembly of Cyclin D/cdk complexes Do not inhibit cyclin D/cdk complexes at physiological levels p21 binds CNA
16 Interaction of cdki s with cdks Figure 8.13a The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
17 Cip/Kip cdki s stimulate cyclin D/cdk association and activity Figure 8.17a The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
18 Cyclin D/cdk complexes sequester cip/ kip proteins form cyclin E/cdk2 Figure 8.17b The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
19 Cyclin D1 and TGF-β TGF-β Cyclin E Cdk2 CI/KI Cdk4/6 Cdk4/6 Cdk4/6 Cyclin E Cdk2 CI/KI Cyclin E CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin E CI/KI Cdk2 CI/KI Cdk4/6 Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cyclin D
20 Cyclin D1 and TGF-β TGF-β Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin E Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cyclin D CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin E CI/KI Cdk2 CI/KI Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cyclin D Cyclin D Cyclin D
21 Cyclin D1 and TGF-β TGF-β Cyclin D Cyclin E Cdk2 CI/KI Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cyclin E Cdk2 CI/KI Cyclin E CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin E CI/KI Cdk2 CI/KI Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cyclin D
22 Cyclin D1 and TGF-β TGF-β Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin D Cdk4/6 CI/KI Cyclin D Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin E Cyclin E CI/KI Cdk2 Cyclin D Cyclin D Cyclin D CI/KI Cdk4/6 Cyclin D Cdk4/6 Cyclin D CI/KI
23 How do cyclin/cdk complexes regulate the cell cycle?
24 The E2F-pRB pathway Disrupted in most if not all cancers A major regulator of cell cycle progression Involved in regulation of apoptosis
25 E2F-pRB pathway Major layers: E2F Family of Transcription Factors Retinoblastoma Family of roteins (ocket roteins) Cyclins and Cyclin Dependent Kinases (cdks) Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitors (ckis)
26 E2F-Regulated Genes DNA Synthesis Genes Growth Regulatory Genes dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) DNA polymerase α thymidylate synthase (TS) thymidine kinase (TK) proliferating cell nuclear antigen (CNA) licensing factors (e.g. cdc6, mcm s) c-myc B-myb prb p107 cyclin E cyclin A E2F1 E2F2 cdk1 p21 WAF1/CI1 p27 KI1 p19 ARF
27 The E2F Family of Transcription Factors Cyclin A binding DNA binding Dimerization Marked box ocket protein binding Transactivation Cell cycle regulation E2F- 1 E2F- 2 E2F- 3 rotein expression limited to late G 1 and S-phase. E2F- 4 E2F- 5 Expressed throughout. Nuclear during G 0 /G 1, otherwise cytoplasmic. E2F- 6 Repressor D- 1 D- 2 E2F- 7 Expressed throughout the cell cycle. Repressor
28 ocket roteins Founding member is the Retinoblastoma Gene roduct (prb) mutated in familial retinoblastoma Other members are p107 and p130, named for molecular weight Bind to transactivation domain of E2F s with dual effect a) Blocks transactivation function b) Recruitment of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), causing general repression of promoters Regulated by phosphorylation a) Hypophosphorylated forms bind E2F s and HDAC1 b) Hyperphosphorylated forms do not bind E2F s or HDAC1 c) hosphorylated by cyclin/cdk complexes
29 ocket proteins bind E2F on DNA and actively repress transcription Deacetylation hdac ocket rotein E2F X
30 Cyclin/cdks phosphorylate and inactivate pocket proteins Cyclin Cdk Cyclin Cdk
31 The E2F-Retinoblastoma athway is Targeted by Viral Oncoproteins Adenovirus E1A SV40 large TAg Human apillomavirus E7 E2F prb family E2F S phase Viral Oncoproteins prb family
32 Cyclin D/cdk and cyclin E/cdk sequentially phosphorylate pocket proteins
33 Cyclin D/cdk and cyclin E/cdk sequentially phosphorylate pocket proteins
34 Figure 8.21b The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
35 ocket rotein Interactions with the E2F Family of Transcription Factors Cyclin A binding DNA binding Dimerization Marked box pocket protein binding Transactivation E2F- 1 prb p107 p130 E2F- 2 E2F- 3 E2F- 4 E2F- 5 E2F- 6
36 Components of the E2F-pRB pathway disrupted in cancer RB. mutated or deleted mutated (rare?) yclin D1 overexpressed (amplification/transcriptional) yclin E (rare).. overexpressed dk4 overexpressed mutated to disrupt p16 a binding 16 a... deleted or transcriptionally repressed 27 KI1 downregulated
37 Some levels of regulation that could impinge on the control of E2F activity by p53 roteasome CB/ p300 Mdm2 p19 p53 p21 Cyclin D/E cdk ocket rotein E2F roliferation Cyclin A cdk Apoptosis Black and Azizkhan-Clifford, 1999
38 Cyclin Expression During Cell Cycle Cyclin E Cyclin A Cyclin B Cyclin D Growth Factors G 0 G 1 S G 2 M R
39 hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome Segregation and Cytokinesis M G 0 Check of DNA integrity Gap 2: reparation for Cell Division G 2 G 1 Gap 1: reparation for DNA Replication S Synthesis: DNA Replication Restriction oint: Check of DNA integrity and readiness for replication
40 Ras Regulation of Cyclin D1 Expression Synchronized Cyclin D1 Growth Factors Ras Ras G 0 G 1 S G2 M R Cycling Cyclin D1 Ras G 1 S G2 M
41 M Early G1 Growth Factors G 0 hdac Deacetylation ocket rotein E2F Cyclin D Cdk4/6 X CI/KI Cdk4/6 Cyclin D S G 1 hdac ocket rotein E2F Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 X CI/KI Acetylation and remodeling
42 Early G1 M Growth Factors G 0 Deacetylation hdac ocket rotein E2F Cyclin D Cdk4/6 X CI/KI Cdk4/6 Cyclin D G 1 hdac ocket rotein Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 CI/KI S E2F cyclin E Acetylation and remodeling
43 Mid-Late G1 ocket rotein Cyclin E Cdk2 E2F cyclin E G 1 ocket rotein Cyclin Cdk4/6E Cdk2 Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 Cyclin E Cdk2 CI/KI CI/KI E2F Transcription of S-hase Genes, cyclin E and E2F1-3
44 ositive Feedback Loop for E2F activation Cdk4/6 CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 Cyclin Cdk4/6E ocket rotein hdac p27 cdk2 E2F X Degradation
45 Mid-Late G1 ocket rotein Cyclin E Cdk2 E2F cyclin E G 1 ocket rotein E2F Cyclin Cdk4/6E Cdk2 Other substrates (DNA replication) Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 Cyclin E Cdk2 Transcription of S-hase Genes and E2F1-3 CI/KI CI/KI
46 M E2F 4/5 G 2 G 1 Cyclin AE Cdk2 cytoplasm S E2F 1-3 Transcription of S-hase Genes ocket rotein Cyclin A Cdk2 E2F 4/5 E2F 1-3 S phase
47 M G 2 Cdk1 ocket rotein Cyclin A Cdk2 S Early-mid G 2
48 Mitotic ocket rotein X Cyclin B Cdk1 cdc25 Cyclin A Cdk2 G 2 M S G Late G 2
49 M phase hdac Deacetylation ocket rotein E2F X Transcription of S-phase Genes hdac ocket rotein 1 M E2F cytoplasm G 2 S
50 Early G1 hdac Deacetylation ocket rotein E2F X Transcription of S-phase Genes G 1 S
51 Transition from G 0 p27 kip1 p27 kip1 p21 waf1 p21 waf1 prb E2F 4/5 prb p130 E2F 4/5 p107 p130 p107 cyclin D cyclin D quiescent cells (G 0 ) cycling cells
52 Transition into G 0 p27 kip1 p27 kip1 p21 waf1 p21 waf1 p21 waf1 prb p130 p107 prb E2F 4/5 p130 E2F 4/5 p107 cyclin D cyclin D cycling cells quiescent cells (G 0 )
53 ositive Feedback Loop for E2F activation Cdk4/6 CI/KI CI/KI Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 Cyclin Cdk4/6E ocket rotein hdac p27 cdk2 E2F X Degradation
54 E2F1 and Apoptosis Overexpression of E2F1 induces apoptosis Apoptotic effects of E2F1 blocked by prb Induces p53-dependent and -independent apoptosis p53-dependent a) E2F upregulates p53 levels (through ARF) b) enhances apoptotic function of p53 (e.g. by competition for p300) p53-independent a) enhanced by p300 b) blocks antiapoptotic pathways (e.g. NFkB activity, IA expression) c) inhibition of E2F1 phophorylation in S-phase enhances apoptosis d) May involve p73
55 Negative Feedback Downregulation of E2F activity. Cyclin Cdk4/6D Cdk4/6 Cyclin Cdk4/6E CI/KI ocket rotein Cyclin Cdk4/6A cdk2 hdac cdk2 E2F p27 p21 Antiapoptotic signals p19 ARF Mdm2 p53 Apoptosis X p53 p19 ARF Mdm2 Degradation
56 otential Effects of Overactivation of E2F Activity? Cyclin Cdk4/6D cdk4/6 Cyclin Cdk4/6E CI/KI ocket rotein Cyclin Cdk4/6A cdk2 hdac cdk2 E2F E2F1 p21 p27 Apoptosis Antiapoptotic signals Apoptosis X p53 p19 ARF Mdm2 p19 ARF Mdm2 p53 Degradation
57 The E2F-Retinoblastoma athway is Targeted by Viral Oncoproteins Adenovirus E1A SV40 large TAg Human apillomavirus E7 E2F prb family E2F S phase Viral Oncoproteins prb family
58 The p53 athway is Targeted by Viral Oncoproteins p53 Apoptosis
59 The p53 athway is Targeted by Viral Oncoproteins Adenovirus E1A SV40 large TAg Human apillomavirus E6 Viral Oncoproteins p53 p53 Apoptosis
60 Apoptotic Factors Altered in Cancer p53 p19 ARF (p14 ARF in Humans) Others e.g. NFκB survivin (caspase inhibitor)
61 Effect of p19 ARF Mutation on Feedback Downregulation of E2F activity.? Cyclin Cdk4/6D cdk4/6 Cyclin Cdk4/6E CI/KI ocket rotein Cyclin Cdk4/6A cdk2 hdac cdk2 E2F E2F1 p21 p27 Apoptosis Antiapoptotic signals Apoptosis Degradation X X p53 p19 ARF Mdm2 p19 ARF Mdm2 p53 Degradation
62 Effect of p53 Mutation on Feedback Downregulation of E2F activity.? Cyclin Cdk4/6D cdk4/6 Cyclin Cdk4/6E ocket rotein Cyclin Cdk4/6A cdk2 hdac cdk2 E2F E2F1 p21 p27 Apoptosis Antiapoptotic signals Apoptosis X p53 p19 ARF Mdm2 p19 ARF Mdm2 p53 Degradation
63 Components of the E2F-pRB pathway disrupted in cancer RB. mutated or deleted mutated (rare?) yclin D1 overexpressed (amplification/transcriptional) yclin E (rare).. overexpressed dk4 overexpressed mutated to disrupt p16 a binding 16 a... deleted or transcriptionally repressed 27 KI1 downregulated
64 E2F-regulation is cell type-dependent He et al., (2000). E2F is Reqired To revent Inappropriate S-hase Entry of Mammian Cells. Mol Cell Biol 20:
65 hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome Segregation and Cytokenesis Growth Factor Withdrawal M G 0 Growth Factor Addition Gap 2: reparation for Cell Division G 2 G 1 Gap 1: reparation for DNA Replication (2 N DNA Content) (4 N DNA Content) S Synthesis: DNA Replication
66 Flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle S distribution G 1 /G 0 G 2 /M Harvest cells as single cell suspension Number of cells Stain with DNA-intercolating fluorescent dye Laser Detector Fluorescence (DNA Content) Collect and analyze data Run cells through FACScan
67 Flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle S G 1 /G 0 G 2 /M Number of cells DNA Content
68 Effects of MA on Cell Cycle in IEC18 cells MA, 100 nm U 6 h 12 h 16 h 24 h
69 Effects of MA on Cell Cycle in IEC18 cells U 16 6 h12 h h 6 h hh h MA, 100 nm U 6 h 12 h 16 h 24 h
70 Detection of Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry Sub G 1 Apoptotic S G 1 /G 0 G 2 /M Number of cells DNA Content
71 REFERENCES Sherr, C. J. and J. D. Weber (2000). The ARF/p53 pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10(1): Hanahan, D. and R. A. Weinberg (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1): Stacey, D.W. (2003). Cyclin D1 serves as a cell cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 15: Seville, L. L., N. Shah, A. D. Westwell and W. C. Chan (2005). "Modulation of prb/e2f functions in the regulation of cell cycle and in cancer." Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5(3): Musgrove, E. A. (2006). "Cyclins: roles in mitogenic signaling and oncogenic transformation." Growth Factors 24(1): Malumbres, M. and Barbacid, M. (2009). Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nature Reviews: Cancer 9: Gopinathan, L., C. Ratnacaram and. Kaldis (2011). Established and Novel Cdk/Cyclin Complexes Regulating the Cell Cycle and Development. In Cell Cycle in Development. J. Z. Kubiak, Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. 53: Novak, B., O. Kapuy, M. R. Domingo-Sananes and J. J. Tyson (2010). "Regulated protein kinases and phosphatases in cell cycle decisions." Current Opinion in Cell Biology 22(6):
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Cell cycle control (mammalian)
 Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage
 1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Oncogenes and Tumor. supressors
 Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Cancer. Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions.
 Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I. Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017
 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Oncolytic virus strategy
 Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK
 TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
Integration of the prb and p53 cell cycle control pathways
 Journal of Neuro-Oncology 51: 183 204, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Integration of the prb and p53 cell cycle control pathways Craig L. Stewart 1, Alejandro Moro Soria
Journal of Neuro-Oncology 51: 183 204, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Integration of the prb and p53 cell cycle control pathways Craig L. Stewart 1, Alejandro Moro Soria
Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Elm and Carlton Streets, Buffalo, NY 14263
 [Frontiers in Bioscience 5, d406-423, April 1, 2000] PROTEIN KINASE C-MEDIATED REGULATION OF THE CELL CYCLE Jennifer D. Black Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Roswell Park Cancer Institute,
[Frontiers in Bioscience 5, d406-423, April 1, 2000] PROTEIN KINASE C-MEDIATED REGULATION OF THE CELL CYCLE Jennifer D. Black Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Roswell Park Cancer Institute,
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Revisiting post-translational regulation of cell cycle CDKs
 Revisiting post-translational regulation of cell cycle CDKs Cyclin-CDK complexes during cell cycle Cyclin B-CDK1 G0 E2F prb Cyclin A-CDK1 G2 M Cyclin D-CDK4 CDK6 + prb Cyclin A-CDK2 S R G1 Cyclin E-CDK2
Revisiting post-translational regulation of cell cycle CDKs Cyclin-CDK complexes during cell cycle Cyclin B-CDK1 G0 E2F prb Cyclin A-CDK1 G2 M Cyclin D-CDK4 CDK6 + prb Cyclin A-CDK2 S R G1 Cyclin E-CDK2
[Frontiers in Bioscience, 3, d , February 15, 1998] MYC AND THE CELL CYCLE. Bruno Amati, Konstantinos Alevizopoulos and Jaromir Vlach
![[Frontiers in Bioscience, 3, d , February 15, 1998] MYC AND THE CELL CYCLE. Bruno Amati, Konstantinos Alevizopoulos and Jaromir Vlach [Frontiers in Bioscience, 3, d , February 15, 1998] MYC AND THE CELL CYCLE. Bruno Amati, Konstantinos Alevizopoulos and Jaromir Vlach](/thumbs/90/104467726.jpg) [Frontiers in Bioscience, 3, d250-268, February 15, 1998] MYC AND THE CELL CYCLE Bruno Amati, Konstantinos Alevizopoulos and Jaromir Vlach Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research (ISREC), CH-1066
[Frontiers in Bioscience, 3, d250-268, February 15, 1998] MYC AND THE CELL CYCLE Bruno Amati, Konstantinos Alevizopoulos and Jaromir Vlach Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research (ISREC), CH-1066
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Regulation of p16 INK4A
 Regulation of p16 INK4A The Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor & the Tumor Suppressor Gözde Işık Master Thesis Cancer Genomics and Developmental Biology Masters May-2009 Supervised by Dr. Inge The Department
Regulation of p16 INK4A The Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor & the Tumor Suppressor Gözde Işık Master Thesis Cancer Genomics and Developmental Biology Masters May-2009 Supervised by Dr. Inge The Department
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Cell Cycle Checkpoint Genes and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Checkpoint Genes and Cancer Jens Oliver Funk, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Erlangen, Germany and Oncology Research Darmstadt, Global Preclinical R&D, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Several
Cell Cycle Checkpoint Genes and Cancer Jens Oliver Funk, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Erlangen, Germany and Oncology Research Darmstadt, Global Preclinical R&D, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Several
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
 Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition
 Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Cancer: Brief Introduction. First stage: Mutations in genes progressively accumulate so that there is unrestrained cell proliferation
 Cancer: Brief Introduction First stage: Mutations in genes progressively accumulate so that there is unrestrained cell proliferation There has to be mutational amplification Over lifetime about 10 16 divisions
Cancer: Brief Introduction First stage: Mutations in genes progressively accumulate so that there is unrestrained cell proliferation There has to be mutational amplification Over lifetime about 10 16 divisions
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
34 Cancer. Lecture Outline, 11/30/05. Cancer is caused by mutant genes. Changes in growth properties of cancer cells
 34 Cancer Lecture Outline, 11/30/05 Review the Cell cycle Cancer is a genetic disease Oncogenes and roto-oncogenes Normally romote cell growth. Become oncogenic after oint mutations, dulications, deletion
34 Cancer Lecture Outline, 11/30/05 Review the Cell cycle Cancer is a genetic disease Oncogenes and roto-oncogenes Normally romote cell growth. Become oncogenic after oint mutations, dulications, deletion
Cell Cycle and Proliferation
 Cell Signalling Biology Michael J. Berridge Module 9 Cell Cycle and roliferation 9 1 Module 9 Cell Cycle and roliferation Synopsis Cell proliferation is the process whereby cells reproduce themselves by
Cell Signalling Biology Michael J. Berridge Module 9 Cell Cycle and roliferation 9 1 Module 9 Cell Cycle and roliferation Synopsis Cell proliferation is the process whereby cells reproduce themselves by
Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death
 02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer.
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II. Prof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department
 Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Cell Cyc Cell Cy l c e
 Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation 1 Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 2 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation 1 Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 2 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Investigating E2F independent cell cycle control and tumor suppression by prb
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository April 2017 Investigating E2F independent cell cycle control and tumor suppression by prb Michael J. Thwaites The University
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository April 2017 Investigating E2F independent cell cycle control and tumor suppression by prb Michael J. Thwaites The University
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Basic tumor nomenclature
 Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Regulation of Cell Division
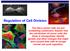 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES. Molecular Oncology Michael Lea
 TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Pancreatic Cancer Research and HMGB1 Signaling Pathway
 Pancreatic Cancer Research and HMGB1 Signaling Pathway Haijun Gong*, Paolo Zuliani*, Anvesh Komuravelli*, James R. Faeder #, Edmund M. Clarke* * # The Hallmarks of Cancer D. Hanahan and R. A. Weinberg
Pancreatic Cancer Research and HMGB1 Signaling Pathway Haijun Gong*, Paolo Zuliani*, Anvesh Komuravelli*, James R. Faeder #, Edmund M. Clarke* * # The Hallmarks of Cancer D. Hanahan and R. A. Weinberg
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Posttranslational Modifications of the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor Protein as Determinants of Function
 619 osttranslational odifications of the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor rotein as Determinants of Function Genes & Cancer 3(11-12) 619 633 The Author(s) 2013 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalsermissions.nav
619 osttranslational odifications of the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor rotein as Determinants of Function Genes & Cancer 3(11-12) 619 633 The Author(s) 2013 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalsermissions.nav
The cell cycle plays a prominent role in development,
 Dynamics of the mammalian cell cycle in physiological and pathological conditions Claude Gérard 1 and Albert Goldbeter 1,2 * A network of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) controls progression along the
Dynamics of the mammalian cell cycle in physiological and pathological conditions Claude Gérard 1 and Albert Goldbeter 1,2 * A network of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) controls progression along the
Analysis of E2F1 target genes involved in cell cycle and apoptosis
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2007 Analysis of E2F1 target genes involved in cell cycle and apoptosis Scott N. Freeman University of South
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2007 Analysis of E2F1 target genes involved in cell cycle and apoptosis Scott N. Freeman University of South
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Molecular Aspects of the Mammalian Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Molecular Aspects of the Mammalian Cell Cycle and Cancer T. SANDAL Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway Key Words. Cell cycle Cancer G 1 /S-transition Retinoblastoma
Molecular Aspects of the Mammalian Cell Cycle and Cancer T. SANDAL Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway Key Words. Cell cycle Cancer G 1 /S-transition Retinoblastoma
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
The central role of CDE/CHR promoter elements in the regulation of cell cycle-dependent gene transcription
 REVIEW ARTICLE The central role of CDE/CHR promoter elements in the regulation of cell cycle-dependent gene transcription Gerd A. Müller and Kurt Engeland Molecular Oncology, Department of Obstetrics and
REVIEW ARTICLE The central role of CDE/CHR promoter elements in the regulation of cell cycle-dependent gene transcription Gerd A. Müller and Kurt Engeland Molecular Oncology, Department of Obstetrics and
Genomic instability. Amin Mahpour
 Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Phospholipase C γ Prof. Graham Carpenter
 Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
mtor e le altre vie di trasduzione del segnale: Implicazioni cliniche Giampaolo Tortora
 mtor e le altre vie di trasduzione del segnale: Implicazioni cliniche Giampaolo Tortora Cattedra di Oncologia Medica UOC Oncologia Medica du Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia e Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria
mtor e le altre vie di trasduzione del segnale: Implicazioni cliniche Giampaolo Tortora Cattedra di Oncologia Medica UOC Oncologia Medica du Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia e Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
BL 424 Test pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points.
 BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer
 BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer Topics we will cover today Introduction to normal and cancer cells Characteristics of cells in culture Cancerous changes in cells Viruses can harbor transforming
BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer Topics we will cover today Introduction to normal and cancer cells Characteristics of cells in culture Cancerous changes in cells Viruses can harbor transforming
MARCH 2001 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 3. Copyright 2001 by the American Chemical Society. p53 Signaling and Cell Cycle Checkpoints
 MARCH 2001 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 3 Copyright 2001 by the American Chemical Society Invited Review p53 Signaling and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Zoe A. Stewart and Jennifer A. Pietenpol* Department of Biochemistry,
MARCH 2001 VOLUME 14, NUMBER 3 Copyright 2001 by the American Chemical Society Invited Review p53 Signaling and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Zoe A. Stewart and Jennifer A. Pietenpol* Department of Biochemistry,
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
UC San Diego UC San Diego Electronic Theses and Dissertations
 UC San Diego UC San Diego Electronic Theses and Dissertations Title Cyclin D:Cdk4/6 Complexes Activate Rb by Mono- Phosphorylation / Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5509h4wq Author Narasimha,
UC San Diego UC San Diego Electronic Theses and Dissertations Title Cyclin D:Cdk4/6 Complexes Activate Rb by Mono- Phosphorylation / Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5509h4wq Author Narasimha,
Toronto, Ontario, Canada M4N 3M5
 »% AD Award Number: DAMD17-00-1-0449 TITLE: The Contribution of P27Kipl Regulation to Tamoxifen Resistance PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jeffrey C. Donovan Doctor Joyce Slingerland CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
»% AD Award Number: DAMD17-00-1-0449 TITLE: The Contribution of P27Kipl Regulation to Tamoxifen Resistance PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jeffrey C. Donovan Doctor Joyce Slingerland CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Review II: Cell Biology
 Review II: Cell Biology Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2006 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2006 Outline Cell Cycle Signal Transduction 1 Cell Cycle Four
Review II: Cell Biology Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2006 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2006 Outline Cell Cycle Signal Transduction 1 Cell Cycle Four
Demystified... Cell cycle. C E Gillett, D M Barnes
 310 Demystified... Hedley Atkins/ICRF Breast Pathology Laboratory, 3rd Floor Thomas Guy House, Guy s Hospital, London SE1 9RT, UK C E Gillett D M Barnes Correspondence to: Dr Gillett. email: gillett@icrf.icnet.uk
310 Demystified... Hedley Atkins/ICRF Breast Pathology Laboratory, 3rd Floor Thomas Guy House, Guy s Hospital, London SE1 9RT, UK C E Gillett D M Barnes Correspondence to: Dr Gillett. email: gillett@icrf.icnet.uk
General introduction: Cell cycle, cancer and transcription.
 General introduction: Cell cycle, cancer and transcription. Cell cycle, cancer and transcription Cell cycle, cancer and transcription. The English naturalist Robert Hooke coined the term cell after viewing
General introduction: Cell cycle, cancer and transcription. Cell cycle, cancer and transcription Cell cycle, cancer and transcription. The English naturalist Robert Hooke coined the term cell after viewing
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer. Dan Fisher. Friday 27th October Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6.
 How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
