CYTOKINESIS-BLOCK MICRONUCLEUS ASSAY IN HUMAN GLIOMA CELLS EXPOSED TO RADIATION
|
|
|
- Dortha Cooper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Paper CYTOKINESIS-BLOCK MICRONUCLEUS ASSAY IN HUMAN GLIOMA CELLS EXPOSED TO RADIATION JERZY SLOWINSKI 1, GRAZYNA BIERZYNSKA-MACYSZYN 2, URSZULA MAZUREK 3, MARIA WIDEL 4, MALGORZATA LATOCHA 3, MONIKA STOMAL 1, MIROSLAW SNIETURA 4 AND RYSZARD MROWKA 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery and Neurotraumatology, Medical University of Silesia, Al. Legionow 10, Bytom, Poland, 2 Department of Pathology, Medical University of Silesia, Medykow 18, Katowice, Poland, 3 Department of Molecular Biology, Biochemistry and Biopharmacy, Medical University of Silesia, Narcyzow 1, , Sosnowiec, Poland, 4 Department of Radiobiology, Center of Oncology, Wybrzeze Armii Krajowej 15, Gliwice, Poland slowian@mp.pl, rmrowka@mp.pl, macyszyn@wp.pl, umazurek@slam.katowice.pl, mlatocha@slam.katowice.pl, widel@io.gliwice.pl (Accepted April 26, 2004) ABSTRACT Biological tests are efficient in reflecting the biological influences of several types of generally harmful exposures. The micronucleus assay is widely used in genotoxicity studies or studies on genomic damage in general. We present methodological aspects of cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay performed in human gliomas irradiated in vitro. Eight human glioblastoma cell lines obtained from DSMZ (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH, Germany) were gamma-irradiated ( 60 Co) over a dose range of 0-10 Gy. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay was performed to quantitate cytogenetic damage. The cells were fixed directly on dishes, stained with fluorochrome DAPI and evaluated under fluorescent and phase contrast microscope. The micronucleus frequency was expressed as a micronuclei (MN) per binucleated cell (BNC) ratio, calculated after scoring at least 100 BNC per dish. The frequency of spontaneous MN ranged from 0.17 to (mean: 0.29 ± 0.14). After irradiation increase of MN frequency in the range of (mean: 0.98 ± 0.68) was found at 10 Gy. Gliomas are extremely heterogenous in regard to cytogenetic effects of irradiation, as shown in this study by cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay. This test is easily performed on irradiated glioma cell lines and can assist in determining their radiosensitivity. However, in order to obtain reliable and reproducible results, precise criteria for MN scoring must be strictly followed. Simultaneous use of fluorescent and phase contrast equipment improves imaging of morphological details and can further optimize MN scoring. Keywords: glioma, micronucleus assay, radiosensitivity. INTRODUCTION The cytogenetic assay of micronuclei was established almost thirty years ago (Schmid, 1975). Cytokinesis-block was introduced to micronucleus assay by Fenech and Morley (1985, 1986). Micronuclei (MN) are structures that arise from acentric chromosome fragments or complete chromosomes that failed to attach to mitotic spindle during cytokinesis and are excluded from the daughter nuclei into the cytoplasm (Weissenborn and Streffer, 1992; Fuhrmann et al., 1992). MN represent structural chromosomal aberrations (chromosome loss or breakage) induced by ionizing radiation or chemical mutagens (Fenech, 2000). Micronuclei can be measured after DNA staining by the Feulgen reaction, Giemsa or fluorescence dyes. Evaluation of micronucleus frequency is widely used for determination of cellular radiosensitivity (Wandl et al., 1989; Shibamoto et al., 1991, Widel et al., 2001; 2003). Generally, radiosensitive cells are more susceptible to radiation-induced micronucleus formation. In the previous study, performed by one of the authors (MW), usefulness of cytokinesisblock micronucleus (CBMN) assay in evaluating radiosensitivity of malignant melanoma was proved (Widel et al., 1997). Human gliomas, like melanomas, are very heterogeneous tumours in regard to their response to radiotherapy. This prompted us to validate applicability of CBMN assay in irradiated human glioma cell lines and to discuss some methodological aspects related to scoring MN in vitro. The test may allow the grouping of gliomas in terms of sensitivity to 159
2 SLOWINSKI J ET AL: Cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay radiation and to identify tumours with favourable response after radiation treatment. MATERIALS AND METHODS CELL CULTURE AND IRRADIATION Eight human glioma cell lines (42-MG-BA, DBTRG-05-MG, DK-MG, GAMG, GOS-3, LN-405, 8-MG-BA and U-138-MG) were purchased from DSMZ (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH, Braunschweig, Germany) (Drexler et al., 2001). Cells were cultured as monolayers in Easy Y Flasks (Nunc) in DMEM or RPMI medium (according to the manufacturer s recommendations), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 100 units/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin at 37 C, in a humid atmosphere of 5% CO 2 /95% air. The cultures were trypsinized and plated ( cells per plate) into 50 mm plastic culture dishes (Nunc) in 5 ml of growth medium. After 24 hrs (time required for cell attachment) the cells were irradiated in culture dishes using Philips 60 Co γ-ray unit at a dose rate 0.8 Gy/min, at room temperature to a total dose of 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 Gy. The control (non-irradiated) cells were sham exposed for the same period. For subsequent irradiation at a given dose each culture was plated into three dishes, so the data of individual cell lines were pooled as triplicates. MICRONUCLEUS ASSAY CBMN assay with cytokinesis-block induced by cytochalasin B was performed according to the method described by Shibamoto et al. (1991) and Fuhrmann et al. (1992), with minor modifications. Cytochalasin B is used to inhibit the cell division after mitosis. This leads to cells which contain two nuclei, and micronuclei, if chromosome breaks have occurred or the centromere is damaged. Immediately after irradiation the cells were treated with cytochalasin B (Sigma), dissolved in dimethylosulfoxide to a final concentration of 2 µg/ml. After 72 h incubation the cells were fixed in cold (-20ºC) ethanol 96º for 15 min, washed with distilled water, re-fixed in acetic acid:methanol (1:3 v/v) for 15 min and washed. The fixed cells were stained with a drop of fluorochrome DAPI (4,6 -diamidino-2-phenylindole HCl, Serva), dissolved in Tris-buffer (ph 7.5) at a 2 µg/ml concentration. The control (non-irradiated) cells were also incubated with cytochalasin B. MICROSCOPIC EVALUATION AND MN SCORING The preparations were evaluated under photomicroscope Axiophot (Zeiss, Germany), equipped with fluorescence illuminator (HBO50 lamp) and the filter set for 365 nm excitation and 420 nm emission wave length (specific for fluorochrome DAPI). The phase contrast equipment was also used. Analysis was performed at magnification 400. To facilitate discrimination of MN and differentiation between mononucleated, binucleated (which divided once after irradiation) and polynucleated cells (which divided twice or more), the phase contrast was used together with fluorescent microscopy. Microscopic analysis was performed by one observer (MW), excluding the possibility of determining interobserver variability, where a series of preparations was viewed by a second experienced observer. Scoring was performed blindly. The percentage of binucleated cells (%BNC) per dish was evaluated after scoring 1000 consecutive cells distributed as a monolayer. The BNC were selected according to criteria described by Fenech et al. (2003). The apoptotic and necrotic cells were included in the total cell number, however micronuclei were not scored in these cells. The number of MN in at least 100 BNC was scored according to the criteria of Countryman and Heddle (1976), Fenech and Morley (1985), Falkvoll (1990) and Fenech et al. (2003), and the MN/BNC ratio was calculated. The round or oval, non-refractile bodies detached from the nucleus, smooth-outlined and with a diameter not greater than one-third the large diameter of the main nuclei were considered as MN. Only MN separated from the main nucleus and just touching but not overlapping the main nucleus were scored. The experimental data presented in Table 1 and Fig. 1 are the mean values from 3 independent dishes per experimental point. The MN frequency in control (non-irradiated) cells, representing so-called spontaneous MN was regarded as a baseline level. The percentage of binucleated cells (%BNC) in non-irradiated cells was used for measurement of proliferation fraction in vitro (Widel et al., 2001). 160
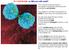
3 Fig. 1. Normalized micronuclei per binucleated cell (MN/BNC) ratio in irradiated human glioma cell lines. A dose dependent increase in micronuclei frequency and relative radioresistance of most cell lines is seen. Table 1. Percentage of binucleated cells and absolute values of micronuclei per binucleated cell ratio in eight human glioma cell lines after gamma-irradiation. Cell line %BNC MN/BNC 0Gy 2Gy 4Gy 6Gy 8Gy 10Gy 0Gy 2Gy 4Gy 6Gy 8Gy 10Gy LN MG-BA GAMG DK-MG DBTRG-05-MG GOS MG-BA U-138-MG %BNC: percentage of binucleated cells; MN/BNC: absolute values of micronuclei per binucleated cell ratio STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The correlation between radiosensitivity of cell lines (expressed as a normalized MN/BNC ratio) and the proliferation fraction (expressed as a %BNC in non-irradiated controls) was evaluated using the nonparametric Spearman s rank correlation coefficient. Variation of the MN/BNC ratio measurements was measured with the coefficient of variation (CV): SD CV = x 100% (1) xxsd: standard deviation; : the mean Inter- and intra-tumour, as well as inter- and intra-observer variations were estimated using oneway ANOVA test and Spearman s rank correlation coefficient. The means were compared with U Mann- Whitney test. The level of significance was set to P < RESULTS The MN/BNC ratio in non-irradiated and irradiated cells is presented in Table 1. For better visualization of percentage increment in MN frequency after irradiation the baseline values were subtracted (normalized MN/BNC) (Fig. 1). The CBMN assay with DAPI staining provided satisfactory preparations, enabling reliable identification and scoring of MN (Fig. 2). 161
4 SLOWINSKI J ET AL: Cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay observers. There was no significant difference between the two series of measurements (P = 0.97, one-way ANOVA) (Fig. 4). The mean MN/BNC in 18 consecutive measurements performed in this culture by the two observers was nearly identical (0.525 vs ). Fig MG-BA cell line after 10 Gy exposure. Numerous binucleated cells (large arrows) containing multiple micronuclei (small arrows). The micronuclei have a similar structure and intensity to the main nuclei. DAPI stain. Fluorescent microscopy. Original magn The examined glioma cell lines showed high heterogeneity in respect to genotoxic effects of ionizing radiation, as quantified with CBMN assay. Generally, a dose-dependent increase of MN frequency was observed. The majority of cell lines, excluding LN-405, 8-MG-BA and GAMG (arbitrarily labeled radiosensitive) proved to be highly radioresistant (Fig. 1). The number of spontaneous MN/BNC ranged from 0.17 to (mean: 0.30 ± 0.15). After irradiation the increment of MN/BNC ratio (i.e., normalized MN/BNC) in the range of (mean: 0.98 ± 0.68) was seen at a dose of 10 Gy. A synchronous dose-dependent decrease in % BNC was seen due to radiation-induced cell cycle delay (Table 1). However, there was a high correlation between %BNC in non-irradiated controls and MN/BNC ratio in irradiated cells (Spearman s R range: , significant at 6 Gy (P = 0.010) and 8 Gy (P = 0.007)) (Fig. 3). The radiosensitive and radioresistant lines were discriminated by each normalized MN/BNC and %BNC value as well as by absolute MN/BNC values after 6, 8 and 10 Gy doses (p = 0.025). The coefficient of variation of three consecutive MN/BNC values obtained in a single cell culture at a given irradiation dose ranged from 11.32% to 23.91% (mean: 15.48%). For comparison, CV of scorings performed at a given dose in a total of 8 cell lines ranged from 37.8% to 68.6% (mean: 54.95%). The intra-tumour and intertumour mean CV differed significantly (P < , one-way ANOVA). In GOS-3 glioma cell line the MN/BNC ratio was scored independently by two Fig. 3. A scatterplot of normalized micronucleus frequency (MN/BNC) after 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 Gy irradiation vs percentage of binucleated cells (%BNC) in non irradiated controls. Fig. 4. A scatterplot of absolute values of micronucleus frequencies (MN/BNC) scored by two observers (Obs I and Obs II) on three consecutive plates in GOS-3 line. R - Spearman s coefficient of correlation. High inter-observer reproducibility is confirmed. 162
5 DISCUSSION In the present study, the background and radiationinduced DNA damage was measured with the micronucleus assay. Cytokinesis block used in the assay enables accurate evaluation of MN generation after exposure, since cells undergoing mitosis at the time of irradiation (i.e., cells potentially generating micronuclei) are easily identified as binucleated cells (Shibamoto et al., 1991; Fuhrmann et al., 1992; Fenech, 2000). The main advantages of CBMN assay are relative rapidity and simplicity, especially as compared with clonogenic assay, measuring the ability of tumour cells to produce a colony of descendants (Steel, 1993; Widel et al., 1997). The micronucleus assay does not require the clonogenicity of cells. In the analysis of intra-tumour and inter-tumour variability of MN/BNC the estimated CV differed significantly. This finding confirms applicability of CBMN assay for measurement of cellular radiosensitivity in glioma cells in vitro. In our opinion following the strict criteria for scoring of MN guarantees high reproducibility of the results (interobserver variation). Simultaneous use of phase contrast microscopy enables more accurate definition of cell borders, reducing the risk of MN misinterpretation (Fig. 5). automated MN scoring is time-consuming and is thus applicable only to a limited number of slides (Thierens et al., 1997). The studies on automated MN scoring were mostly performed on normal lymphocytes (Castelain et al., 1993; Szirmai et al., 1993, Verhaegen et al., 1994), i.e., cells with relatively uniform morphology as compared to highly pleomorphic cells of human gliomas. Probably, the developing of an appropriate algorithm for automated MN scoring in cultured gliomas would be a very demanding task. Flow cytometric analysis was also used for MN scoring. The main disadvantage of this approach is that apoptotic cells and apoptotic bodies, if present, can influence MN measurement (Nüsse and Marx, 1997). It would probably be a significant obstacle in analysis of irradiated gliomas, as in the studied cell lines the apoptotic index reached over 10% in 4 of 8 lines (data not shown). Analysis of the slides prepared for MN scoring provides additional data regarding cellular kinetics and survival. For example, %BNC and nuclear division index, based on the ratio of mononucleated, bi- and multinucleated cells reflect proliferative activity (Keshava et al., 1996; Widel et al., 1997; Fenech et al., 2003; Palyvoda et al., 2003), (Fig. 6). In our study we found a high correlation between %BNC and normalized MN/BNC ratio that suggests greater radiosensitivity in rapidly proliferating cells. The correlation between %BNC and MN frequency could also be explained by a lower apoptotic rate in rapidly dividing cells. However, the mean apoptotic index in rapidly proliferating lines (LN-405, 8-MG- BA, GAMG) was not significantly lower than in other lines (data not shown). Fig. 5. GOS-3 cell line after 6 Gy exposure. Large micronucleus is seen within binucleated cell (arrow). Binucleation, not clear in fluorescent microscope (A) becomes evident after application of phase contrast equipment (B). DAPI stain. Fluorescent - phase contrast microscopy. Automated scoring of MN by computerized image analysis systems is an interesting alternative to tedious manual scoring. It gives results comparable to those obtained by manual scoring (Castelain et al., 1993, Verhaegen et al., 1994) with even better reproducibility (Thierens et al., 1997). However, Fig. 6. LN-405 cell line after 2 Gy exposure. Numerous multinucleated cells suggest high proliferative activity (nuclear division index). DAPI stain. Fluorescent microscopy. 163
6 SLOWINSKI J ET AL: Cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay The nucleoplasmic bridge frequency in BNC can be used as a biomarker of chromosome rearrangement (Fenech, 2000). Furthermore, apoptotic index can be measured on the same slides as well (Falkvoll, 1990; Abend et al., 2000) (Fig. 7). Fig. 7. DK-MG cell line after 10 Gy exposure. Numerous mononucleated apoptotic cells showing condensed chromatin and early nuclear fragmentation (arrows). DAPI stain. Fluorescent - phase contrast microscopy. It is assumed that frequency of MN is a reliable marker of cellular radiosensitivity (Wandl et al., 1989; Shibamoto et al., 1991; Mariya et al., 1997), although some authors do not agree with this assumption (Bush and McMillan, 1993; Akudugu et al., 2000). Generally, increase in micronucleus frequency after irradiation is indicative of better response to radiotherapy (Zölzer et al., 1995). MN assay is also used for retrospective dosimetry after exposure to ionizing radiation (Streffer et al., 1998), for biological monitoring of populations exposed to mutagenic and carcinogenic agents (Fenech, 2000) and for quantification of DNA damage/repair processes (Palyvoda et al., 2003). There are many potential research applications of the described test. For example, we have used the CBMN assay for evaluating radioprotective properties of histone proteins and the relation between cellular proliferation (evaluated by in situ hybridization for histone mrna) and radioresistance (Slowinski et al., 2003a,b). ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by grant 6P05B from the State Committee of Scientific Research (KBN, Poland). REFERENCES Abend M, Kehe K, Kehe K, Riedel M, Van Beuningen D (2000). Correlation of micronucleus and apoptosis assay with reproductive cell death can be improved by considering other modes of death. Int J Radiat Biol 76: Akudugu JM, Slabbert JP, Serafin A, Bohm L (2000). Frequency of radiation-induced micronuclei in neuronal cells does not correlate with clonogenic survival. Radiat Res 153:62-7. Bush C, McMillan TJ (1993). Micronucleus formation in human tumour cells: Lack of correlation with radiosensitivity. Br J Cancer 67: Castelain P, Van Hummelen P, Deleener A, Kirsch- Volders M (1993). Automated detection of cytochalasin-b blocked binucleated lymphocytes for scoring micronuclei. Mutagenesis 8: Countryman PI, Heddle JA (1976). The production of micronuclei from chromosome aberrations in irradiated cultures of human lymphocytes. Mutat Res 41: Drexler HG, Dirks W, MacLeod RAF, Quentmeier H, Steube KG, Uphoff CC (eds) (2001). DSMZ catalogue of human and animal cell lines. Eighth edition, Braunschweig. Falkvoll KH (1990). The occurrence of apoptosis, abnormal mitoses, cells dying in mitosis and micronuclei in a human melanoma xenograft exposed to single dose irradiation. Strahlenther Onkol 166: Fenech M (2000). The in vitro micronucleus technique. Mutat Res 455: Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003). HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesisblock micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534: Fenech M, Morley AA (1985). Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res 147: Fenech M, Morley AA (1986). Cytokinesis-block micronucleus method in human lymphocytes: effect of in vivo aging and low dose X irradiation. Mutat Res 161: Fuhrmann C, Streffer C, Müller W-U, Becker U (1992). Micronucleus assay prediction and application optimized by cytochalasin B-induced binucleated tumor cells. Strahlenther Onkol 168: Keshava C, Nagalakshmi R, Ong T, Nath J (1996). Inhibitory effect of folinic acid on radiation-induced micronuclei and chromosomal aberrations in V79 cells. Mutat Res 352: Mariya YC, Streffer C, Fuhrmann C, Wojcik A (1997). Correlation of radiation-induced micronucleus frequency with clonogenic survival in cell lines of the same origin. Radiat Res 147: Nüsse M, Marx K (1997). Flow cytometric analysis of micronuclei in cell cultures and human lymphocytes: advantages and disadvantages. Mutat Res 392:
7 Palyvoda O, Polanska J, Wygoda A, Rzeszowska-Wolny (2003). DNA damage and repair in lymphocytes of normal individuals and cancer patients: studies by the comet assay and micronucleus assay. Acta Biochim Pol 50: Schmid W (1975). The micronucleus test. Mutat Res 31:9-15. Shibamoto Y, Streffer C, Fuhrmann C, Budach V (1991). Tumor radiosensitivity prediction by the cytokinesisblock micronucleus assay. Radiat Res 128: Slowinski J, Bierzynska-Macyszyn G, Mazurek U, Glogowska J, Latocha M, Widel M, Mrowka R (2003a). Profile of expression of histone genes differs in radioresistant and radiosensitive human glioma cell lines. Virchows Arch 443:361. Slowinski J, Bierzynska-Macyszyn G, Widel M, Mazurek U, Latocha M, Mrowka R, Snietura M, Lange D (2003b). Cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay in irradiated human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol: S 28. Steel GG (1993). Clonogenic cells and the concept of cell survival. In: Steel GG, ed. Basic clinical radiobiology for radiation oncologists. Ch. 5. London, Edward Arnold, Streffer C, Muller WU, Kryscio A, Bocker W (1998). Micronuclei-biological indicator for retrospective dosimetry after exposure to ionizing radiation. Mutat Res 404: Szirmai S, Bérces J, Köteles GJ (1993). Computerized image analysis for determining micronucleus frequency. Environ Health Perspect 101(Suppl. 3): Thierens H, Vral A, de Scheerder F, dr Ridder L, Tates A (1997). Semi-automated micronucleus scoring in cytokinesis-blocked lymphocytes after irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol 72: Verhaegen F, Vral A, Seuntjens J, Schipper NW, de Ridder L, Thierens H (1994). Scoring of radiation-induced micronuclei in cytokinesis-blocked human lymphocytes by automated image analysis. Cytometry 17: Wandl EO, Ono K, Kain R, Herbsthofer T, Heinert G, Hobarth K (1989). Linear correlation between surviving fraction and the micronucleus frequency. Int J Radiat Biol 56: Weissenborn U, Streffer C (1991). Micronuclei with kinetochores in human melanoma cells and rectal carcinomas. Int J Radiat Biol 59: Widel M, Dobrut M, Maka B, Lubecka B, Pluciennik A (1997). The radiosensitivity of human malignant melanomas evaluated by cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay. Neoplasma 44: Widel M, Jedrus S, Lukaszczyk B, Raczek-Zwierzycka K, Swierniak A (2003). Radiation-induced micronucleus frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes is correlated with normal tissue damage in patients with cervical carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy. Radiat Res 159: Widel M, Kolosza Z, Jedrus S, Lukaszczyk B, Raczek- Zwierzycka K, Swierniak A (2001). Micronucleus assay in vivo provides significant prognostic information in human cervical carcinoma; the updated analysis. Int J Radiat Biol 77: Zölzer F, Alberti W, Pelzer T, Lamberti G, Hülskamp FH, Streffer C (1995). Changes in S-phase fraction and micronucleus frequency as prognostic factors in radiotherapy of cervical carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 36:
Effect of depth on radiation-induced cell damage in a water phantom
 Original Paper Received: 2004.08.06 Accepted: 2004.12.06 Published: 2005.03.16 Effect of depth on radiation-induced cell damage in a water phantom Krzysztof Ślosarek 1, Maria Konopacka 2, Jacek Rogoliński
Original Paper Received: 2004.08.06 Accepted: 2004.12.06 Published: 2005.03.16 Effect of depth on radiation-induced cell damage in a water phantom Krzysztof Ślosarek 1, Maria Konopacka 2, Jacek Rogoliński
Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in vitro
 Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25:195-199 Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in
Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25:195-199 Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in
Biological Dosimetry Method: a Probable way for Measuring Percent Depth Dose
 Biological Dosimetry Method: a Probable way for Measuring Percent Depth Dose Mohammad Mehdi Abtahi (1) Mahmood Reza Aghamiri (2) Masoumeh Yadolahi (3) Aziz Mahmoodzade (4) (1) Physics Department, Imam
Biological Dosimetry Method: a Probable way for Measuring Percent Depth Dose Mohammad Mehdi Abtahi (1) Mahmood Reza Aghamiri (2) Masoumeh Yadolahi (3) Aziz Mahmoodzade (4) (1) Physics Department, Imam
Cytokinesis blocked micronucleus (CB-MN) assay for biodosimetry of high dose accidental exposure
 Volume 12, No 3 International Journal of Radiation Research, July 2014 Cytokinesis blocked micronucleus (CB-MN) assay for biodosimetry of high dose accidental exposure K. Shirsath, N. Bhat, K. Anjaria,
Volume 12, No 3 International Journal of Radiation Research, July 2014 Cytokinesis blocked micronucleus (CB-MN) assay for biodosimetry of high dose accidental exposure K. Shirsath, N. Bhat, K. Anjaria,
APOPTOSIS AND CLONOGENIC SURVIVAL IN THREE TUMOUR CELL LINES EXPOSED TO GAMMA RAYS OR CHEMICAL GENOTOXIC AGENTS
 CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS Volume 8, (23) pp 655 665 http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received 17 January 23 Accepted 21 May 23 APOPTOSIS AND CLONOGENIC SURVIVAL IN THREE TUMOUR CELL LINES EXPOSED TO GAMMA
CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS Volume 8, (23) pp 655 665 http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received 17 January 23 Accepted 21 May 23 APOPTOSIS AND CLONOGENIC SURVIVAL IN THREE TUMOUR CELL LINES EXPOSED TO GAMMA
INFLUENCE OF CELL ENVIRONMENT ON MICRONUCLEATION IN CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY CELLS. A Dissertation NATALIA GENNADIEVNA MEDVEDEVA
 INFLUENCE OF CELL ENVIRONMENT ON MICRONUCLEATION IN CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY CELLS A Dissertation by NATALIA GENNADIEVNA MEDVEDEVA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial
INFLUENCE OF CELL ENVIRONMENT ON MICRONUCLEATION IN CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY CELLS A Dissertation by NATALIA GENNADIEVNA MEDVEDEVA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial
The radiotracer 99m Tc-MIBI is not genotoxic for human peripheral blood lymphocytes at diagnostic radioactive dose
 The radiotracer Tc-MIBI is not genotoxic for human peripheral blood lymphocytes at diagnostic radioactive dose S.J. Hosseinimehr 1, A. Ahmadi 1, D. Beiki 2, A. Mahmoudzadeh 3, M. Babaei 4 and E. Habibi
The radiotracer Tc-MIBI is not genotoxic for human peripheral blood lymphocytes at diagnostic radioactive dose S.J. Hosseinimehr 1, A. Ahmadi 1, D. Beiki 2, A. Mahmoudzadeh 3, M. Babaei 4 and E. Habibi
DNA damage and repair in lymphocytes of normal individuals and cancer patients: studies by the comet assay and micronucleus tests
 Vol. 50 No. 1/2003 181 190 www.actabp.pl DNA damage and repair in lymphocytes of normal individuals and cancer patients: studies by the comet assay and micronucleus tests Olena Palyvoda 1,3, Joanna Polañska
Vol. 50 No. 1/2003 181 190 www.actabp.pl DNA damage and repair in lymphocytes of normal individuals and cancer patients: studies by the comet assay and micronucleus tests Olena Palyvoda 1,3, Joanna Polañska
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Comparison of Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect in QU-DB Cells after Acute and Fractionated Irradiation: An In Vitro Study
 Original Article Comparison of Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect in QU-DB Cells after Acute and Fractionated Irradiation: An In Vitro Study Shokouhozaman Soleymanifard, Ph.D. 1, 2, 3, Mohammad Taghi Bahreyni
Original Article Comparison of Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect in QU-DB Cells after Acute and Fractionated Irradiation: An In Vitro Study Shokouhozaman Soleymanifard, Ph.D. 1, 2, 3, Mohammad Taghi Bahreyni
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
ADVANTAGES OF MICRONUCLEI ANALYSIS THROUGH IMAGES AUTOCAPTURING AND SCREEN SCORING
 ADVANTAGES OF MICRONUCLEI ANALYSIS THROUGH IMAGES AUTOCAPTURING AND SCREEN SCORING González, J.E. 1, *, Martínez-López, W. 2 1 Centro de Protección e Higiene de las Radiaciones (CPHR), La Habana, Cuba.
ADVANTAGES OF MICRONUCLEI ANALYSIS THROUGH IMAGES AUTOCAPTURING AND SCREEN SCORING González, J.E. 1, *, Martínez-López, W. 2 1 Centro de Protección e Higiene de las Radiaciones (CPHR), La Habana, Cuba.
Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Human Lymphocytes using Micronucleus and Microgel Electrophoresis Comet Assays
 Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Human Lymphocytes using Micronucleus and Microgel Electrophoresis Comet Assays Di Giorgio, M.; Sardi, M.; Busto, E.; Vallerga, M.B.; Taja, M.R. and Mairal,
Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Human Lymphocytes using Micronucleus and Microgel Electrophoresis Comet Assays Di Giorgio, M.; Sardi, M.; Busto, E.; Vallerga, M.B.; Taja, M.R. and Mairal,
Radioprotective effects of selenium and vitamin-e against 6MV X-rays in human blood lymphocytes by micronucleus assay
 Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Radioprotective effects of selenium and vitamin-e against 6MV X-rays in human blood lymphocytes
Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Radioprotective effects of selenium and vitamin-e against 6MV X-rays in human blood lymphocytes
The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells
 The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells Piroska Virág The Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. I. Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania Low dose radiation effects on the
The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells Piroska Virág The Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. I. Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania Low dose radiation effects on the
Available online at International Journal of Current Research Vol. 10, Issue, 09, pp , September, 2018
 z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol., Issue, 09, pp.7345-7349, September, 201 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-33X DOI: https://doi.org/.24941/ijcr.32449.09.201
z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol., Issue, 09, pp.7345-7349, September, 201 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-33X DOI: https://doi.org/.24941/ijcr.32449.09.201
CYTOKINESIS-BLOCK MICRONUCLEUS (CBMN) ASSAY/CBMN CYTOME ASSAY IN HUMAN LYMPHOCYTES AFTER IN VITRO IRRADIATION AND ITS USE IN BIODOSIMETRY
 Mil. Med. Sci. Lett. (Voj. Zdrav. Listy) 2011, vol. 80, p. 28-37 ISSN 0372-7025 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CYTOKINESIS-BLOCK MICRONUCLEUS (CBMN) ASSAY/CBMN CYTOME ASSAY IN HUMAN LYMPHOCYTES AFTER IN VITRO IRRADIATION
Mil. Med. Sci. Lett. (Voj. Zdrav. Listy) 2011, vol. 80, p. 28-37 ISSN 0372-7025 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CYTOKINESIS-BLOCK MICRONUCLEUS (CBMN) ASSAY/CBMN CYTOME ASSAY IN HUMAN LYMPHOCYTES AFTER IN VITRO IRRADIATION
Evaluation of genome damage in subjects occupationally exposed to possible carcinogens. D. Želježi, M. Mladini, N. Kopjar, A. Hursidic Radulovic
 Evaluation of genome damage in subjects occupationally exposed to possible carcinogens D. Želježi, M. Mladini, N. Kopjar, A. Hursidic Radulovic WHO Cancer prevention: occupational exposures primary prevention
Evaluation of genome damage in subjects occupationally exposed to possible carcinogens D. Želježi, M. Mladini, N. Kopjar, A. Hursidic Radulovic WHO Cancer prevention: occupational exposures primary prevention
DNA damage in subpopulations of human lymphocytes irradiated with doses in the range of 0 1 Gy of X-radiation
 NUKLEONIKA 2008;53(4):145 149 ORIGINAL PAPER DNA damage in subpopulations of human lymphocytes irradiated with doses in the range of 0 1 Gy of X-radiation Maria Wojewódzka, Eugeniusz K. Machaj, Aneta Goździk,
NUKLEONIKA 2008;53(4):145 149 ORIGINAL PAPER DNA damage in subpopulations of human lymphocytes irradiated with doses in the range of 0 1 Gy of X-radiation Maria Wojewódzka, Eugeniusz K. Machaj, Aneta Goździk,
Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo. Günter Speit
 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo Günter Speit Universität Ulm Institut für Humangenetik D-89069 Ulm (Germany) guenter.speit@uni-ulm.de CEFIC-2012 Günter Speit 1 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde
Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo Günter Speit Universität Ulm Institut für Humangenetik D-89069 Ulm (Germany) guenter.speit@uni-ulm.de CEFIC-2012 Günter Speit 1 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde
Developing Auto-focusing Microscopy For Ultra High- Throughput Biodosimetry
 Developing Auto-focusing Microscopy For Ultra High- Throughput Biodosimetry NINA BAHAR D R. G U Y G A R T Y, M E N T O R R A D I O L O G I C A L R E S E A R C H A C C E L E R A T O R F A C I L I T Y C
Developing Auto-focusing Microscopy For Ultra High- Throughput Biodosimetry NINA BAHAR D R. G U Y G A R T Y, M E N T O R R A D I O L O G I C A L R E S E A R C H A C C E L E R A T O R F A C I L I T Y C
Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain
 Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1527 Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain Original research Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures
Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1527 Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain Original research Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures
Human lymphocytes responses to low and high doses of Iodine-131. Antonina Cebulska-Wasilewska
 Human lymphocytes responses to low and high doses of Iodine-131 Antonina Cebulska-Wasilewska The H. Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Krakow, Poland 13-16.05.2013.
Human lymphocytes responses to low and high doses of Iodine-131 Antonina Cebulska-Wasilewska The H. Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Krakow, Poland 13-16.05.2013.
Online publication date: 28 January 2010 PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [GAMULIN, MARIJA] On: 5 February 2010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 918964596] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales
This article was downloaded by: [GAMULIN, MARIJA] On: 5 February 2010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 918964596] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales
Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Medical Physics in the Baltic States 2017 Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose Tadas DIDVALIS 1, 2,, Paulius RUZGYS 1, Saulius ŠATKAUSKAS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Medical Physics in the Baltic States 2017 Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose Tadas DIDVALIS 1, 2,, Paulius RUZGYS 1, Saulius ŠATKAUSKAS
STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V.
 STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V. Sotnik, T. V. Azizova, and S. V. Osovets Southern Urals Biophysics Institute, Ozyorskoe shosse 19, Ozyorsk, 456780, Russia ABSTRACT The research objective
STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V. Sotnik, T. V. Azizova, and S. V. Osovets Southern Urals Biophysics Institute, Ozyorskoe shosse 19, Ozyorsk, 456780, Russia ABSTRACT The research objective
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Advances in biological dosimetry
 Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Cell Damage. Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence
 Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence Patents: CN 2702421, EP 2208068, TR 201308237, 200880115751 The Platform Motorized, inverse fluorescence microscope
Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence Patents: CN 2702421, EP 2208068, TR 201308237, 200880115751 The Platform Motorized, inverse fluorescence microscope
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to. Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority
 Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to ionizing radiation Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Objectives: Identify clastogenic factors in blood
Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to ionizing radiation Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Objectives: Identify clastogenic factors in blood
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Introduction to biomarkers of exposure what can they tell us
 Introduction to biomarkers of exposure what can they tell us Andrzej Wojcik andrzej.wojcik@su.se acentric fragment dicentric dicentric dicentric acentric fragment What is a biomarker? Any measurement reflecting
Introduction to biomarkers of exposure what can they tell us Andrzej Wojcik andrzej.wojcik@su.se acentric fragment dicentric dicentric dicentric acentric fragment What is a biomarker? Any measurement reflecting
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM
 STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
Lecture -2- Environmental Biotechnology
 Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
OECD/OCDE Adopted: 29 July 2016
 Adopted: 29 July 2016 OECD GUIDELINE FOR THE TESTING OF CHEMICALS In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test INTRODUCTION 1. The OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals are periodically reviewed in
Adopted: 29 July 2016 OECD GUIDELINE FOR THE TESTING OF CHEMICALS In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test INTRODUCTION 1. The OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals are periodically reviewed in
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP
 Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Micronucleus Cartridge
 INSTRUCTIONS Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Micronucleus Cartridge High-Content Imaging Reagents Number R043001MN Description Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Micronucleus Cartridge, sufficient materials for
INSTRUCTIONS Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Micronucleus Cartridge High-Content Imaging Reagents Number R043001MN Description Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Micronucleus Cartridge, sufficient materials for
HER2 FISH pharmdx TM Interpretation Guide - Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 FISH pharmdx TM Interpretation Guide - Breast Cancer For In Vitro Diagnostic Use FDA approved as an aid in the assessment of patients for whom Herceptin TM (trastuzumab) treatment
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 FISH pharmdx TM Interpretation Guide - Breast Cancer For In Vitro Diagnostic Use FDA approved as an aid in the assessment of patients for whom Herceptin TM (trastuzumab) treatment
Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test
 Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Micronucleus test of Californian trout fish after treatment with the herbicide monosan for 48 and 96 hours
 Micronucleus test of Californian trout fish after treatment with the herbicide monosan for 48 and 96 Afrim Zeqiraj 1, Shkelzen Elezaj 2, Zafer Gashi 1, Bujar Gruda 2 Medical laboratory Biolab-Zafi-F Peje,
Micronucleus test of Californian trout fish after treatment with the herbicide monosan for 48 and 96 Afrim Zeqiraj 1, Shkelzen Elezaj 2, Zafer Gashi 1, Bujar Gruda 2 Medical laboratory Biolab-Zafi-F Peje,
Application of chromosomal radiosensitivity assays to temporary nuclear power plant workers
 Application of chromosomal radiosensitivity assays to temporary nuclear power plant workers Research group University Ghent in collaboration with Dr. M. Barbé and the Occupational Medicine Service Nuclear
Application of chromosomal radiosensitivity assays to temporary nuclear power plant workers Research group University Ghent in collaboration with Dr. M. Barbé and the Occupational Medicine Service Nuclear
This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division.
 10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division. This relates to cell theory because this is HOW all cells come
10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division. This relates to cell theory because this is HOW all cells come
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
Dako IT S ABOUT TIME. Interpretation Guide. Agilent Pathology Solutions. ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis)
 INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the
 Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the nuclear export inhibitor, selinexor Joshua M. Marcus 1, Russell T. Burke 1, John A. DeSisto 1, Yosef Landesman
Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the nuclear export inhibitor, selinexor Joshua M. Marcus 1, Russell T. Burke 1, John A. DeSisto 1, Yosef Landesman
An automated scoring procedure for the micronucleus test by image analysis
 Mutagenesis vol. 19 no. 5 pp. 391--397, 2004 doi:10.1093/mutage/geh047 An automated scoring procedure for the micronucleus test by image analysis Dominic Varga, Tilman Johannes 1, Silke Jainta, Sonja Schuster,
Mutagenesis vol. 19 no. 5 pp. 391--397, 2004 doi:10.1093/mutage/geh047 An automated scoring procedure for the micronucleus test by image analysis Dominic Varga, Tilman Johannes 1, Silke Jainta, Sonja Schuster,
FISH and PNA-FISH. FISH and PNA-FISH. Stochastic effect. Radiation and cancer. 1) chromosome 2) FISH 3) PNA-FISH. Chromosome translocations.
 BIODOSIMETRY IN THE 21 st CENTURY Training Meeting HICARE in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency Hiroshima, Japan, June 10-14, 2013. FISH and FISH and Satoshi Tashiro Research Institute
BIODOSIMETRY IN THE 21 st CENTURY Training Meeting HICARE in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency Hiroshima, Japan, June 10-14, 2013. FISH and FISH and Satoshi Tashiro Research Institute
A. Incorrect! All the cells have the same set of genes. (D)Because different types of cells have different types of transcriptional factors.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Micronuclei Assessment of The Radioprotective Effects of Melatonin and Vitamin C in Human Lymphocytes
 Original Article Micronuclei Assessment of The Radioprotective Effects of Melatonin and Vitamin C in Human Lymphocytes Aram Rostami, M.Sc. 1 *, Seyed Akbar Moosavi, Ph.D. 2, Hassan Dianat Moghadam, B.Sc.
Original Article Micronuclei Assessment of The Radioprotective Effects of Melatonin and Vitamin C in Human Lymphocytes Aram Rostami, M.Sc. 1 *, Seyed Akbar Moosavi, Ph.D. 2, Hassan Dianat Moghadam, B.Sc.
Micronucleus Frequencies in Buccal Cells from Patients with Sickle Cell Anaemia
 Iraqi Journal of Cancer and Medical Genetics Micronucleus Frequencies in Buccal Cells from Patients with Sickle Cell Anaemia Esmail K. Shubber*, Jameela Kh. AL-Julandi*, and Safa Kh. AL-Rawahi* *Department
Iraqi Journal of Cancer and Medical Genetics Micronucleus Frequencies in Buccal Cells from Patients with Sickle Cell Anaemia Esmail K. Shubber*, Jameela Kh. AL-Julandi*, and Safa Kh. AL-Rawahi* *Department
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Oncology Genetics: Cytogenetics and FISH 17/09/2014
 Oncology Genetics: Cytogenetics and FISH 17/09/2014 Chris Wragg Head of Oncology Genomics, BGL BGL Bristol Genetics Laboratory (BGL) CPA accredited Genetics laboratory serving a core population of 4-5million
Oncology Genetics: Cytogenetics and FISH 17/09/2014 Chris Wragg Head of Oncology Genomics, BGL BGL Bristol Genetics Laboratory (BGL) CPA accredited Genetics laboratory serving a core population of 4-5million
ab Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells
 ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
IMPACTS OF LOW-DOSE GAMMA-RADIATION ON GENOTOXIC RISK IN AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS
 IMPACTS OF LOW-DOSE GAMMA-RADIATION ON GENOTOXIC RISK IN AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS Cassidy C.L. 1, Lemon J.A. 2 and Boreham, D.R. 2 1 Medical Sciences, McMaster University, 128 Main Street West, Hamilton Ontario,
IMPACTS OF LOW-DOSE GAMMA-RADIATION ON GENOTOXIC RISK IN AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS Cassidy C.L. 1, Lemon J.A. 2 and Boreham, D.R. 2 1 Medical Sciences, McMaster University, 128 Main Street West, Hamilton Ontario,
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa
 Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Fibroadenoma and breast cancer patients lymphocytes sensitivity to gamma rays- An evaluation by micronuclei assay
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2013, 4 (7):148-156 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 76-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Fibroadenoma and
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2013, 4 (7):148-156 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 76-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Fibroadenoma and
Supplementary Information for. Shi and King, Chromosome Nondisjunction Yields Tetraploid Rather than Aneuploid Cells in Human Cell Lines.
 Supplementary Information for Shi and King, Chromosome Nondisjunction Yields Tetraploid Rather than Aneuploid Cells in Human Cell Lines Contains Supplementary Methods Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary
Supplementary Information for Shi and King, Chromosome Nondisjunction Yields Tetraploid Rather than Aneuploid Cells in Human Cell Lines Contains Supplementary Methods Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary
Modifications of Bleomycin Induced Cytogenetic Damages by 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose on Normal and Tumor Cells
 Kamla-Raj 2007 Int J Hum Genet, 7(4): 307-314 (2007) Modifications of Bleomycin Induced Cytogenetic Damages by 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose on Normal and Tumor Cells P. Venkatachalam*, V. R. Jayanth and Solomon F.
Kamla-Raj 2007 Int J Hum Genet, 7(4): 307-314 (2007) Modifications of Bleomycin Induced Cytogenetic Damages by 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose on Normal and Tumor Cells P. Venkatachalam*, V. R. Jayanth and Solomon F.
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
NUTRITIONAL PROTECTION OF DNA & TELOMERES
 HDA August 2010 NUTRITIONAL PROTECTION OF DNA & TELOMERES Michael Fenech CSIRO Food and Nutritional Sciences GENOME HEALTH NUTRIGENOMICS LABORATORY michael.fenech@csiro.au DNA DAMAGE BIOMARKERS FOR STUDYING
HDA August 2010 NUTRITIONAL PROTECTION OF DNA & TELOMERES Michael Fenech CSIRO Food and Nutritional Sciences GENOME HEALTH NUTRIGENOMICS LABORATORY michael.fenech@csiro.au DNA DAMAGE BIOMARKERS FOR STUDYING
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE
 COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Evaluation of Micronuclei in Buccal Mucosa Comparing Smokers And Non Smokers
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XIII (September. 2016), PP 08-12 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of Micronuclei in Buccal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XIII (September. 2016), PP 08-12 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of Micronuclei in Buccal
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 9-9 Original Research Article Micronuclei Count in Oral Exfoliated Cells - A Tool for Biomonitoring DNA Damage in Pooja Siwach,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 9-9 Original Research Article Micronuclei Count in Oral Exfoliated Cells - A Tool for Biomonitoring DNA Damage in Pooja Siwach,
OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO FORMALDEHYDE: EFFECTS OF YEARS OF EXPOSURE IN THE FREQUENCY OF MICRONUCLEUS
 The Eighth International Symposium on Biological Monitoring in Occupational and Environmental Health ISBM 2010 OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO FORMALDEHYDE: EFFECTS OF YEARS OF EXPOSURE IN THE FREQUENCY OF MICRONUCLEUS
The Eighth International Symposium on Biological Monitoring in Occupational and Environmental Health ISBM 2010 OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO FORMALDEHYDE: EFFECTS OF YEARS OF EXPOSURE IN THE FREQUENCY OF MICRONUCLEUS
Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy
 Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Why do cells reproduce?
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than. O-Beam
 1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
PCC-ring induction in human lymphocytes exposed to gamma and neutron irradiation.
 PCC-ring induction in human lymphocytes exposed to gamma and neutron irradiation. Ana Ilsa Lamadrid Boada a*, Omar Garcia Lima a, Martine Delbos b, Philipe Voisin b, Laurence Roy b*. a Centro de Protección
PCC-ring induction in human lymphocytes exposed to gamma and neutron irradiation. Ana Ilsa Lamadrid Boada a*, Omar Garcia Lima a, Martine Delbos b, Philipe Voisin b, Laurence Roy b*. a Centro de Protección
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Genotoxic and acute toxic properties of selected synthetic cannabinoids
 Genotoxic and acute toxic properties of selected synthetic cannabinoids Franziska Ferk 1, Verena Koller 1, Halh Al-Serori 1, Volker Auwärter 2, Siegfried Knasmüller 1 1 Medical University of Vienna, Department
Genotoxic and acute toxic properties of selected synthetic cannabinoids Franziska Ferk 1, Verena Koller 1, Halh Al-Serori 1, Volker Auwärter 2, Siegfried Knasmüller 1 1 Medical University of Vienna, Department
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
Monitoring of Individuals following Acute and Chronic Exposures to Ionizing Radiation
 Research Project entitled Monitoring of Individuals following Acute and Chronic Exposures to Ionizing Radiation (IAEA CRP E3.50.08 project: 17085/R0) Chang-Mo Kang, Ph.D. KIRAMS (Korea Institute of Radiological
Research Project entitled Monitoring of Individuals following Acute and Chronic Exposures to Ionizing Radiation (IAEA CRP E3.50.08 project: 17085/R0) Chang-Mo Kang, Ph.D. KIRAMS (Korea Institute of Radiological
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Cellular Stress Response Induced by Low Dose Gamma Radiation
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (2): 139 144 (2014) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Research Article Cellular
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (2): 139 144 (2014) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Research Article Cellular
HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles. Tests were conducted on the separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles added in excess to BEGM (A)
SUPPORTING INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles. Tests were conducted on the separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles added in excess to BEGM (A)
Genotoxicity Biomarkers: Application in Histopathology Laboratories
 Genotoxicity Biomarkers: Application in Histopathology Laboratories Carina Ladeira 1,2, Susana Viegas 1,2, Elisabete Carolino 1, Manuel Carmo Gomes 3 and Miguel Brito 1 1 Escola Superior de Tecnologia
Genotoxicity Biomarkers: Application in Histopathology Laboratories Carina Ladeira 1,2, Susana Viegas 1,2, Elisabete Carolino 1, Manuel Carmo Gomes 3 and Miguel Brito 1 1 Escola Superior de Tecnologia
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
