:. Mitosis: Chromosome Replication and Division
|
|
|
- Coleen Sibyl Glenn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 \!- :. Mitosis: Chromosome Replication and Division I. Questions to ponder: 1. How does a human being grow from a single fertilized cell into an individual containing billions of cells? 2. Do all the cells of the body look Iike one another? Do they perform the same jobs? 3. Do all the cells of the body contain the same genetic information? 4. How is the genetic blueprint that makes you who you are transmitted faithfully from one cell to the next? 5. How long does it take for one parent cell to become two daughter cells? 6. Are cells alive? 7. What is a cell, anyway? II. Materials - 2 sets of white and2 sets of red plastic forks, knives and spoons per group for chromosomes 1 large and 2 smaller length ribbons for nuclear membrane Unique color paper per group Scissors String for spindle fibers Rubber bands for centromeres - Pipe cleaners for cell membrane III. Objectives 1. Describe how cells reproduce themselves 2. Explain how chromosomes are copied and distributed to each daughter cell in a precise way 3. Describe the need for, and mechanism for, conservation of hereditary material 4. Be able to define and correctly use the following terms: allele, anaphase, centriole, centromere, chromosome replication, cytokinesis, diploid, DNA synthesis, Gene, homologous chromosomes, interphase, life cycle, metaphase, mitosis, prometaphase, prophase, replicated chromosomes, sister chromatids, spindle fibers, telophase, un replicated chromosomes
2 Background Information Cell Division yo*r body is composed, of more than a billion cells. Cells are continually dying, and new cells are continually being formed. An identical copy of your hereditary material is found in the nucleus of each and"every somatic cell. A somatic cell is any cel1 in the body except for the reprodr-rctive cells in the reproductive system' This geletic blueprint is organized into 46 cirapters or parts known as chrcmosomes. It is esti,rated that, on uu.rug.,-.uch chromosome contains between one and two thousand genes' A gene contains the information for making a single protein or RNA product' Every time a cell divides, each chromosome must be carefully replicated (copi_ed) and tiren distributed to assure that each daughter cell gets a complete and accurate set of information. Thus, nuclear division includes sr-ricessive pio".rr.. of chromosome replication, separation, and distribution (Figure 1). DNA synthesis occurs in the nucleus, producing an exact replica of every chromosome. A cluornoiome can be thought of as a very long DNA double helix. During replication, the dor-rble irelix opeps gp and u rr.*1o*plementary strand is synthesized along each parent strand (Figirre 2). Tirii resulis in two identicai DNA helices, each containing one original parent strand and one newly synthesized strand. :, DNAsynthesisoccursdrrringtheSphaseofinterpha:..li"hcellgoesthrougharegrrlarlife cycle, similar to the cycle of iife in humans' Where we mighi call Jur stages infancy' childhood' adolescence, young adult, aduit, *d 1r;;, titt *u3o""1isiag"' are interphase' mitosis' and cy,tokinesis. Interpnas. is'subdivided t"* ql (gr"* r): s(simthesio, *d ry (growth 2)' and rnitosis is divided into p (prophase), PM b*;;taphase), Ni (mttaprtase)' A (anaphase)' and r iteloohase) This is shown in Figure 3'.,. i a. How many rounds of cluomosome replication occur in the cell prior to mitosis? b. How many times does a cell divide in mitosis?
3 1' You will study-mitosis in the Triffle, a mythicar creature with 6 chromosomes that rook rike forks, t<nivei anj'spoons. you wiil work out each step of the process using pa?ef for cells, ribbons/pip..r...rs_ for membrane!, string for spindte fibers am ptastic tniuesl ro*i anj ;il;; for chromorom.i 2' Go through the entire pro..rt ilverar time+ *iir, uu.h group member taking a turn as the "exprainer.,, Foilow al::.g ;ih inu iro.uoure berow for the first time and perform subsequeniiepetitions rrom-riemory. Answer the questions about EACH stage as you go arong, and answer them each time you go through the process. Expli:n yow unr*ers precisely. 3. Take one paper ror yoriceir; ffi,r. on..llor'i,uoon as rhe nucrear membrane and,use the pipe'ctuun.,. as the cell membrane 4. Begin with a ce, and nrlr.*.*taining o.niororomes represented by two forks (one red u,nd,9n! *r'riiel, i*o tnivei iig.i;, Lo and white) and rwo :f;:.t:rtff.:nd white)' rhislepresenrs u dip"roij'.e, with three pairs of a. What does diploid mean? b. Are most human cells diploid? : liy##liffffi:?'otogo* chromosomes are present in the picture d. 3J:[, circre around each pair of homorogous chromosomes in the picture e' Are the homorogous chromosomes above paired with one another in the cell or are they independentiiom one another? f' what is the best description oi homotogous chromosomes: 1. They are the same ii.. uno shape 2' They contain,the same tp;r of genes in the same order 3' Ilntlrrtnurally contain oi#erent versions iurrui.r; of many of their 4. All of the above 9. h. Define homologous chromosomes uontrast gene and allele
4 1.2 Interphase and Chromosome Replication 1. Throughout interphase, the chromosomes are extended and are not visible in the light microscope. That is, the DNA is uncoiled. We cannot simulate this extended condition with the knives, forks and spoons, so please imagine it. Replicate each of the chromosomes in your Triffle nucleus, pretenoin!'they are extended at the time. Do this by obtaining six more chromosomes thit match the set you already have. Attach a red fork to your red fork, a white fork to your white fork, and so on with a rubber band (represents the centrorn.r.j.-in thi, process, each chromosome has essentially made an identical copy of itself 2. Your nucleus initially contained six unreplicated chromosomes, and now it contains six replicated chromosomes. The two identical copies of each chromosome, sister chromatids, remain attached at a poini called a centromere a. What is the chromatid made of (protein, carbohydrate, lipid and/or DNA)? b. How do sister chromatids differ from chromosomes c. What is a centromere? d. Contrast extended and condensed chromsomes 1.3 Prophase of Mitosis 1. In prophase, the replicated chromosomes condense and become visible. This is the second stage of mitosis a. Are the two sister chromatids that are connected by a centromere identical to one another or do they contain different alleles? Explain b. As noted above, these structures are called replicated chromosomes (or, simply chromosomes). Replicated chromosomes are quite different from the unreplicated chromosomes seen earlier. compare replicated chromosomes to unrepricated ones by filling in the blanks below: a. The amount of DNA in a replicated chromosome is _ times the amount of DNA in an unreplicated chromosome b. The number of copies of each gene in a replicated chromosome is times the number of copies in an unreplicated chlomosome Each replicated chromosome contaifls. (insert number) c. d. d. complete copies of genetic information The copies of genetic information in each chromosome are (identical, homologous or complementary) Do you think that the homologous replicated chromosomes (the two pairs of knives, two pairs of forks, and the two pairs of spoons; witt pair wilh one another during mitosis? Explain How many sister chromatids are in your Triflle nucleus in prophase?
5 e' A diploid human cell contains 46 unreplicated chromosomes in early interphase..how many sister chromatids wilt be present in the human cell during prophase of mitosis? 1.4. Prometaphase of Mitosis 1' In prometaphase, the nuclear membrane literally disappears, which allows the rest of the mitotic events to occur, Remove tnu nr.ii.u;;;;;;re from around the chromosomes in the nucreus of your ceil 2' spindle fibers form, emanating from two stru.irr.r called centrioles that have migrated to opposite poles (ends) of the cell. Spindle fibers are assembled from protein microtubures. eut sfindre fibers in'your ceil using siring ano draw the centriorq: o-n the paper at the appropriate points 3' some of the spindle fibers attach to the rbpticateo chromosomes at their centromeres 1.5 Metaphase of Mitosis 1. In metaphase, replicated chromosomes are lined up along the metaphase plate (across the center of the cell) by spindle noers. Homologous chromosomes are independent of one another. That is, homoiogous replicated chromosomes such as the two sets or repliciteo spoo-ns nnr ruor paired! 2' Arrange your Triffle chromosomes across the center of the cell. The specific order of chromosomes and their orientation (righliid.,p, upside down) is completely random a' How many replicated chromosomes are on the metaphase plate in the Triffle? b' How many replicated chromosomes would be on the metaphase plate in a human cell undergoing mitosis?
6 1.6 Anaphase of Mitosis 1. In anaphase, sister chromatids separate to become daughter chromosomes. Separate your sister chromatids to form daughter chromosomes 2. Daughter chromosomes are moved toward opposite poles by the spindle fibers. Chromatids are flexible. They do not remain rigid, but rather bend on each side of the centromere as they are dragged through the cytoplase a. Are the daughter chromosomes replicated or unreplicated? b. Are the two sets of daughter chromosomes, the one moving toward the left and the other toward the right, identical or non-identical? c. Are the two sets of daughter chromosomes identical to those in the parent cell? d. What is accomplished by this process? 1.7 Telophase of Mitosis 1. Daughter chromosomes reach the poles of the cell and become extended (relaxed). The spindle fibers disappear-actually, the microtubulin subunits are disassembled. You can remove your spindle fibers from your cells and pretend your chromosomes are going into the extended state 2. Two new nuclear membranes form, one around each set of daughter chromosomes. Use the nuclear membrane ribbons to create two new nuclear membranes in your cell. Pinch in the pipe cleaners representing the cell membrane 1.8 Cytokinesis 1. An animal cell pinches in half at the center, from the outside in, until it has produced two separate daughter cells. Divide your cell in half in this manner by replacing the long ribbon representing the parent cell membrane with two shorter pieces of ribbon representing the membranes of the two daughter cells 2. These daughter cells are now entering the early interphase stage. Pretend that your Triffle chromosomes are becoming extended. The cells will grow to full size and, if continuing to divide, will replicate their chromosomes, and repeat the cycle again a. Does the parent cell still exist? b. How are these daughter cells related to one another? c. How are these daughter cells related to the parent cell? d. Overall, what has been accomplished by mitosis? e. You have used materials to model mitosis (nuclear division) and cellular division. Explain some ways in which a model differs from the actual things and processes it represents.
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Cell Division. Introduction. Chromatin, Chromosomes, and Chromatids, Oh My! The Cell Cycle
 Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle
 Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
The Cell Cycle Guided Reading
 Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase
 Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities
 Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis. Cell Cycle. interphase. Five Phases. prophase. metaphase
 Mitosis Have you ever wondered how living things grow? Living things are made of cells. To grow bigger, they need more cells. Where do the new cells come from? Each cell divides, turning into two cells.
Mitosis Have you ever wondered how living things grow? Living things are made of cells. To grow bigger, they need more cells. Where do the new cells come from? Each cell divides, turning into two cells.
Chromosomes & Cell Division
 Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Learning Objectives: Model the steps of mitosis in order to gain a better understanding of the process
 Mitosis On Goodness as a Final Cause: Since goodness is that which all things desire, it is clear that that goodness implies the aspect of an end....for a thing is perfect when it can reproduce its like,
Mitosis On Goodness as a Final Cause: Since goodness is that which all things desire, it is clear that that goodness implies the aspect of an end....for a thing is perfect when it can reproduce its like,
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET
 Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET This packet is designed to help you understand several concepts about Cell Division. As you practice the exercises on each handout, you will be able to: Use a model to illustrate
Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET This packet is designed to help you understand several concepts about Cell Division. As you practice the exercises on each handout, you will be able to: Use a model to illustrate
Major concepts: Notes: Cell Reproduction: From One Cell to Two. Why do Cells Reproduce?
 Grade 7 Standard: Life Science 1e Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. Major concepts:
Grade 7 Standard: Life Science 1e Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. Major concepts:
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Chromosomes
 & Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
& Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS
 CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Guided Notes: Chromosomes. What type of macromolecule is DNA? DNA stands for: DNA is made up of repeating (the monomer of nucleic acids!
 Guided Notes: Chromosomes The Structure of DNA What type of macromolecule is DNA? DNA stands for: DNA is made up of repeating (the monomer of nucleic acids!) 1) Where is it found (use figures 1 and 2 to
Guided Notes: Chromosomes The Structure of DNA What type of macromolecule is DNA? DNA stands for: DNA is made up of repeating (the monomer of nucleic acids!) 1) Where is it found (use figures 1 and 2 to
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells.
 MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION
 NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Section Cell Growth. A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. DNA Overload 2. Exchanging Materials 3. Ratio of Surface Area to Volume 4.
 Getting Through Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all
Getting Through Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division The Links in Life s Chain: Genetics and Cell Division 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics 9.2 An Introduction to Cell Division 9.3
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division The Links in Life s Chain: Genetics and Cell Division 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics 9.2 An Introduction to Cell Division 9.3
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Mitosis. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Cell Division
 Mitosis An Introduction to Genetics An Introduction to Cell Division DNA is Packaged in Chromosomes Cell Cycle Mitosis and Cytokinesis Variations in Cell Division Cell Division and Cancer An Introduction
Mitosis An Introduction to Genetics An Introduction to Cell Division DNA is Packaged in Chromosomes Cell Cycle Mitosis and Cytokinesis Variations in Cell Division Cell Division and Cancer An Introduction
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide)
 Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division 1 The cell cycle Living cells go through a series of stages known as the cell cycle. They undergo a continuous alternation
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division 1 The cell cycle Living cells go through a series of stages known as the cell cycle. They undergo a continuous alternation
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Pre-Test. 4. Inside of cells, nearly all the genes are located on special structures known as microtubules.
 1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each question TRUE OR FALSE. 1. Cells in the bodies of multicelled creatures, such as humans, are reproduced in a way that is very similar to the method used by most protozoa.
1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each question TRUE OR FALSE. 1. Cells in the bodies of multicelled creatures, such as humans, are reproduced in a way that is very similar to the method used by most protozoa.
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
3/19/17. Chromosomes. Chromosome Structure. Chromosome Structure. Chromosome Structure. Chapter 10: Cell Growth & Division
 Chapter 10: Cell Growth & Division Section 2: The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) a molecule that stores genetic information, which controls the development and functioning
Chapter 10: Cell Growth & Division Section 2: The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) a molecule that stores genetic information, which controls the development and functioning
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2)
 Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Growth and Reproduction. Page 201
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Page 201 Describe cells that make up a multicellular organisms Comes in wide variety of shapes and sizes Name the cell with the largest diameter. Yolk of an ostrich egg Name
Cell Growth and Reproduction Page 201 Describe cells that make up a multicellular organisms Comes in wide variety of shapes and sizes Name the cell with the largest diameter. Yolk of an ostrich egg Name
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
DR. RAMESH U2 L3. MITOSIS and Cell Cycle
 DR. RAMESH U2 L3 MITOSIS and Cell Cycle Do Now! Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Describe how bacteria reproduce. Describe how cats reproduce.are there any similarities
DR. RAMESH U2 L3 MITOSIS and Cell Cycle Do Now! Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Describe how bacteria reproduce. Describe how cats reproduce.are there any similarities
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis
 Cell Division Answer Key Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Cell Division Answer Key Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Essential Questions. Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase?
 Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
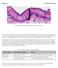 Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
