Layered-IHC (L-IHC): A novel and robust approach to multiplexed immunohistochemistry So many markers and so little tissue
|
|
|
- Jonas Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to understanding the activation status of particular pathways in specific cell types and can be indicative of disease diagnosis, prognosis, prediction of therapeutic efficacy and monitoring of treatment outcomes. This information is of further importance in identifying and validating novel drug targets. While in certain instances detection of single biomarkers is sufficient, it is rapidly becoming clear that both panels of multiple markers and variations in biomarker levels relative to each other is more informative and more diagnostic of cell and disease status. What is L-IHC? The ideal biomarker tests conserve precious tissue by multiplexing marker measurements, retain information regarding tissue morphology and cell type localization, and normalize marker levels to objective standards. 20/20 s Layered-Immunohistochmistry (L-IHC) platform meets all of these requirements. The L-IHC technology platform also known as Multiplex Tissue Immunoblotting (MTI) was developed by 20/20 together with the NCI s Laboratory of Pathology under a Cooperative Research & Development Agreement (CRADA). In L-IHC the proteins of the tissue are released from a standard tissue section and captured on series of stacked membranes (Figure 1). The heart of the platform is the stacked membrane substrates. Tissue proteins are channeled upward through the membrane stack with each layer capturing a certain percentage of total protein. Thus each membrane represents a carbon copy of the tissue and can be probed for a different biomarker using standard immunoblotting techniques. Specific marker staining is detected using fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies and is always normalized to total protein to account for differences in tissue transfer. The advantages of L-IHC are listed in Box 1. L-IHC can detect 5 10 Biomarkers per tissue section. L- IHC has been demonstrated to detect multiple biomarkers in a single tissue section (Figure 2). More than 25 biomarkers have been validated for use in L-IHC on a diverse set of tissue types (Table 1). Over 500 tissue specimens have been successfully analyzed by L-IHC. An important advantage of L-IHC over standard IHC is that because the antibodies are used to bind blotted tissue protein instead of binding directly to the tissue itself, many antibodies that do not function in IHC but work in western Figure 1: In L-IHC proteins are released from a standard tissue section and captured on a stack of 5-10 membranes. Each membrane is then probed with marker specific antibodies using standard immunoblotting techniques. Detection utilizes fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies and is normalized to total protein. Box 1: Advantages of L-IHC: Multiplexing of 5-10 markers per tissue section Retains morphological information and cell/tissue type localization One layer can be reserved for an objective protein standard for normalization Quantitative fluorescence data allows for continuousscale biomarker measurement Determines both protein expression level & extent of many protein modifications Advanced multifactor analysis enumerates & correlates complex relationships in cell signaling pathways L-IHC antibody panels may include antibodies often not useable in standard IHC allowing for measure of certain markers undetectable with standard IHC Compatible with routinely prepared specimens & TMAs including both FFPE and frozen tissues Figure 2: Example of simultaneous detection of 7 biomarkers by L-IHC. Breast tumor tissue (DCIS-yellow circle) was used to detect the indicated biomarkers in a single tissue section.
2 Page 2 blotting can be used in L-IHC. This opens up the potential to monitor markers that have heretofore been inaccessible by standard IHC. It also often allows the same antibody that has been qualified in western blotting to be used for IHC. Normalization of L-IHC specific signal. The transfer conditions for L-IHC have been optimized to afford consistent transfer of tissue protein throughout the stack of membranes. However, due to the inherent nature of the technique there is a gradual loss of protein from membrane to membrane through the stack, limiting the total number of membranes that can be used and requiring that there be a normalization of specific biomarker signals (Figure 3). Normalization is achieved by comparing specific signal to that of total protein on each membrane. Agreement with standard IHC. L-IHC data compares favorably with that obtained by standard immunohistochemistry. The experiment displayed in Figure 4 investigated the expression of four biomarkers in a section of breast tissue encompassing a region of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) as well as significant portions of normal breast tissue. One section was transferred to a stack of membranes and each layer was probed with antibodies against a specific antigen; including p-mtor, p-akt, estrogen receptor (ER) and HER2. Four other (non-consecutive) sections of this tissue were analyzed for each of the markers separately by IHC. The results obtained with all four markers by both L-IHC and standard IHC are presented in Figure 4 with a magnification of the primary area identified as DCIS by a pathologist. Note the strong correlation of the results from MTI for each marker with the areas that are stained in standard IHC. Dynamic range of L-IHC. Quantitative image analysis is a vital element of tissue immunohistochemistry. Pathologists commonly grade immunohistochemistry in terms of both the intensity and frequency of staining for a given marker. Like standard IHC, L-IHC is capable of differentiating staining intensity levels, furthermore because quantification of L-IHC is a function of direct measurement of fluorescent intensity and utilizes a continuous scale making it far more objective than standard IHC. Staining for the HER2 biomarker in breast cancer is a primary example where staining intensity A Table 1: Validated Biomarkers Validated Tissue Types Annexin 1 pan-cytokeratin Bile duct c-jun pan mtor Breast Cytokeratin 7 Patched Brain Cytokeratin 14 phospho c-jun (S-63) Colon COX-2 phospho-akt(s473) Esophagus EGFR phospho-mtor Kidney ER PR Liver EZH2 ps6 Ribosomal Protein Lung HER2 PTEN Lymph node INT6 SMA Ovary Ki67 SPARC Prostate p300 TID6 p53 vimentin Pan-actin B C Figure 3: Normalization and reproducibility of L-IHC signal. (A) Relative intensity of total protein among 10 membranes. (B) Fluorescence images of Cy5-labeled total protein and FITC-labeled specific antigens, as stained on different layer numbers. (C) Comparison of p-akt signal determined from membranes 3 & 6. The bars represent the ratio of specific signal to total protein. Reproduced from Chung et al. Proteomics 2006; Figure 4: Comparison of L-IHC and standard immunohistochemistry for four markers in a breast cancer section. A. p-mtor. B. p-akt. C. ER. D. HER2. For each marker the three small panels depict immunohistochemical staining, specific marker signal in L-IHC and total protein signal in L-IHCI, respectively. The larger panels are magnifications of the indicated areas.
3 is of the utmost import. Typically staining is graded as 0 (weak), 1+, 2+ or 3+ where 2+ and 3+ are considered significant and warrant possible treatment with the drug trastuzumab. L-IHC has been demonstrated to successfully make this differentiation (Figure 5). In this experiment a single slide contains breast cancer cores representing 1+, 2+ and 3+ staining as previously graded by a pathologist. One slide was transferred to a stack of membranes and one membrane layer was probed with an anti-her2 antibody. In parallel a separate slide was subjected to standard IHC. The superb correlation between L-IHC and standard IHC displayed in this experiment is indicative of both the comparability of L-IHC to IHC as well as the broad dynamic range for marker detection achievable via L-IHC. L-IHC can be used to easily quantify and correlate multiple biomarker changes in a single tissue section to biologically relevant events. In one study L-IHC was used to quantify the expression of seven biomarkers to investigate the normal to tumor transition of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (Figure 6). Expression profiling of the different biomarkers was quantified using image analysis software. Briefly, five equivalent circular areas from each region were defined based on the tissue morphology as determined by H&E staining and the mean value of fluorescence was determined. Specific antibody signals were corrected for differential protein transfer and normalized to expression levels in either normal or stromal tissue. As can be seen in Table 2 changes in marker expression levels either up-regulation in the cases of COX- 2, p53 and SPARC or down-regulation in the cases of CK-4, CK-14 and Annexin 1 correlate to the transition from Figure 6: normal to dysplastic to cancerous tissue. The expression level of the control Pan-CK biomarker remained constant over the three cell types. L-IHC can probe post-translational modifications of proteins indicating pathway activation status. L-IHC has been used to profile important cellular pathways. Figure 7 displays the mapping of the mtor pathway in kidney cancer, specifically probing for p-mtor, p-akt, PTEN, p-s6 and pan-mtor. While measurement of marker expression 2 is highly relevant to following a cellular signaling pathway, expression level alone is often not indicative of a pathway s activation status. L-IHC is capable of monitoring the activation state of biomarkers by monitoring B phosphorylation status. Because multiple markers can be C D measured in the same tissue section ratios of activated to E F total protein are more accessible through L-IHC than G H standard IHC. Furthermore, because marker determinations are performed on separated membranes rather than directly on the tissue, two (or more) antibodies Figure 5: HER2 signal ratios as determined by L-IHC are well-correlated to HER2 grade level as determined by standard IHC. In comparison to standard IHC, L-IHC is more objective and yields continuous range of values. Biomarker expression profiling by multiplex tissue immunoblotting in human esophagus tissue. A. H&Estained human esophagus. N, normal; S, stroma; D, dysplasia; T, tumor. Transferred membranes were incubated with antibodies against pan-ck( B), CK-4 (C), CK- 14 (D), annexin 1 (E), COX-2 (F), p53 (G), and SPARC (H). Reproduced from Chung JY, et al. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2006; Page 3
4 Ratio of p-mtor to mtor against the same target (e.g. p-mtor / total mtor) can be used simultaneously avoiding issues of steric hindrance as might occur in standard immunofluorescence. Thus, Figure 7 further demonstrates the measurement of phosphor-mtor and total mtor and direct determination of the ratios of activated protein. Determination of disease prognosis by L-IHC. Recently, Chung et al. (Clin Cancer Res, (2): p ) performed a highly pertinent example of disease prognosis using quantitative multiplexed analysis of PTEN, p-akt and p-mtor ratios in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer) by L-IHC. Individual assay data were comparable to parallel IHC assays (Figure 8). The technique revealed that decreased PTEN/p-AKT (P = 0.003) and PTEN/p-mTOR (P =0.009) expression ratios were better predictors of patient survival than any single protein alone (Figure 9). PTEN is an inhibitor of the pathway while p-mtor and p-akt are activated forms of the mtor and AKT kinases directly involved in furthering the signal. In this case, Simply measuring the total expression level of a single biomarker is not necessarily Phospho-mTOR pakt PTEN ps6 mtor phospho mtor mtor (signal / (signal / total protein) total protein) Ratio p- mtor / mtor Stage II Kidney Cancer Cores AVG ± SD 0.30 ± ± ± 0.14 Normal Kidney Cancer Cores AVG ± SD 0.37 ± ± ± Stage II Cancer Normal Kidney Figure 7: Measurement of marker ratios by L-IHC. Top: L-IHC data for 5 marker experiment using kidney TMA. Bottom: Calculation of relative marker levels by normalization of specific signal to total protein and comparing p-mtor to total mtor. Figure 8: Phosphorylated AKT (p-akt), phosphorylated mtor (pmtor), and PTEN expression by multiplex tissue immunoblotting and immunohistochemical staining of a tissue microarray. A, layered membrane analysis; ratio of marker to total protein; ratio intensity from maximum to minimum is pseudo-colored as: white-yellow-redgreen-blue-black in order. Cases with higher intensity to p-akt and p- mtor showed lower intensity to total PTEN. B, immunohistochemical stain of p-akt, p-mtor, and PTEN protein and dysplasia and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Reproduced from Chung et al. Clin Cancer Res, (2): p Page 4 Figure 9: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of extra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma according to PTEN/p-AKT expression. Patients with low PTEN/p-AKT expression (median survival, 18 mo; n=42) had a significantly worse patients survival time than those with high PTEN/p-AKT expression (median survival, 45 mo; n = 91; log-rank test, P = 0.003). Reproduced from Chung et al. Clin Cancer Res, (2): p
5 indicative of a pathway s activation in a cell. If mtor is highly expressed, but PTEN is also highly expressed the pathway may be inhibited. Thus, measurement of the ratios of two biomarkers such as PTEN to mtor or of the activation state of the biomarker (e.g. p-mtor / total mtor; see above Figure 7) are likely to be more indicative of activation of the pathway. Thus, the utility of L-IHC for determining disease prognosis is clearly demonstrated. Standard IHC cannot provide quantitative ratio data. Thus, clinically useful data can be obtained using L-IHC, which enables simultaneous calculation of ratios among multiple targets that could not have been obtained with standard IHC imagery. This work is a key demonstration of the feasibility and practical application of L-IHC technology. Summary. L-IHC is a powerful technique for multiplexing immunohistochemistry. The method is robust, specific and reproducible and conserves precious clinical specimens. It is highly comparable to standard IHC while affording a broad dynamic range, continuous measurement scale and objective data analysis with internal normalization. Furthermore it allows for intra and inter experimental normalization, ratio-metric measurements and simultaneous determination of activated vs. total biomarker expression. The method is pertinent to pathway profiling, target validation, and clinical diagnosis; including prognosis, prediction of therapeutic efficacy and monitoring of treatment outcomes. Page 5
Immune Cell Phenotyping in Solid Tumors using Quantitative Pathology
 Immune Cell Phenotyping in Solid Tumors using Quantitative Pathology James R. Mansfield Director of Quantitative Pathology Applications 2009 PerkinElmer What is Quantitative Pathology? Quantitative Pathology
Immune Cell Phenotyping in Solid Tumors using Quantitative Pathology James R. Mansfield Director of Quantitative Pathology Applications 2009 PerkinElmer What is Quantitative Pathology? Quantitative Pathology
ANALYTISCHE STRATEGIE Tissue Imaging. Bernd Bodenmiller Institute of Molecular Life Sciences University of Zurich
 ANALYTISCHE STRATEGIE Tissue Imaging Bernd Bodenmiller Institute of Molecular Life Sciences University of Zurich Quantitative Breast single cancer cell analysis Switzerland Brain Breast Lung Colon-rectum
ANALYTISCHE STRATEGIE Tissue Imaging Bernd Bodenmiller Institute of Molecular Life Sciences University of Zurich Quantitative Breast single cancer cell analysis Switzerland Brain Breast Lung Colon-rectum
Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry
 Nat Met, April 2014 Nat Med, April 2014 Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry Journal Club Timo Böge Overview Introduction Conventional Immunohistochemistry
Nat Met, April 2014 Nat Med, April 2014 Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry Journal Club Timo Böge Overview Introduction Conventional Immunohistochemistry
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
SOMAPLEX REVERSE PHASE PROTEIN MICROARRAY HUMAN KIDNEY TUMOR & NORMAL TISSUE
 SOMAPLEX REVERSE PHASE PROTEIN MICROARRAY HUMAN KIDNEY TUMOR & NORMAL TISSUE 45 CLINICAL CASES SERIAL DILUTION MULTIPLE PROTEIN CONCENTRATION QUANTITATIVE ASSAY PRODUCT NUMBER: PM1-001-N SOMAPLEX REVERSE
SOMAPLEX REVERSE PHASE PROTEIN MICROARRAY HUMAN KIDNEY TUMOR & NORMAL TISSUE 45 CLINICAL CASES SERIAL DILUTION MULTIPLE PROTEIN CONCENTRATION QUANTITATIVE ASSAY PRODUCT NUMBER: PM1-001-N SOMAPLEX REVERSE
Quality in Control. ROS1 Analyte Control. Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024
 Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors
 Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
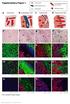
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Vaira et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907676107 0h 24h 48h PTEN pathway Expression 0h 24h 48h Time MAP Kinase Signaling Pathway Expression 0h 24h 48h Time Collagen Expression Fig. S1. Differential
Supporting Information Vaira et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907676107 0h 24h 48h PTEN pathway Expression 0h 24h 48h Time MAP Kinase Signaling Pathway Expression 0h 24h 48h Time Collagen Expression Fig. S1. Differential
Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology
 Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology Cliff Hoyt, CTO Cambridge Research & Instrumentation April 29, 2010 Seeing life in a new light 1 Digital Pathology Today Acquisition, storage, dissemination, remote
Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology Cliff Hoyt, CTO Cambridge Research & Instrumentation April 29, 2010 Seeing life in a new light 1 Digital Pathology Today Acquisition, storage, dissemination, remote
Molecular Characterization of Breast Cancer: The Clinical Significance
 Molecular Characterization of : The Clinical Significance Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville
Molecular Characterization of : The Clinical Significance Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
Gaining New Insights Through IF Multiplexed Staining and Analysis. Tyna Hope, Ph.D. P.Eng Biomarker Imaging Research Laboratory October 5, 2017
 Gaining New Insights Through IF Multiplexed Staining and Analysis Tyna Hope, Ph.D. P.Eng Biomarker Imaging Research Laboratory Assessing more from Tissue Sections Gaps with More Common Methods Most common
Gaining New Insights Through IF Multiplexed Staining and Analysis Tyna Hope, Ph.D. P.Eng Biomarker Imaging Research Laboratory Assessing more from Tissue Sections Gaps with More Common Methods Most common
Welcome. Nanostring Immuno-Oncology Summit. September 21st, FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Welcome Nanostring Immuno-Oncology Summit September 21st, 2017 1 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Agenda 4:00-4:30
Welcome Nanostring Immuno-Oncology Summit September 21st, 2017 1 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Agenda 4:00-4:30
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant
 Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES. 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH)
 INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH) Biopsy-Indications Diffuse/multifocal lesions (neoplastic, inflammatory, etc) Etiology of the
INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH) Biopsy-Indications Diffuse/multifocal lesions (neoplastic, inflammatory, etc) Etiology of the
Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment with Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
 Q: How is the strength of recommendation determined in the new molecular testing guideline? A: The strength of recommendation is determined by the strength of the available data (evidence). Strong Recommendation:
Q: How is the strength of recommendation determined in the new molecular testing guideline? A: The strength of recommendation is determined by the strength of the available data (evidence). Strong Recommendation:
Question 1 A. ER-, PR-, HER+ B. ER+, PR+, HER2- C. ER-, PR+, HER2- D. ER-, PR-, HER2- E. ER-, PR+, HER2+
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Question 1 The tumor depicted on the next slide
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Question 1 The tumor depicted on the next slide
Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Pathology Dept.
 Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Pathology Dept. Judith Sandbank M.D. Pathology Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center ISRAEL jsandbank@asaf.health.gov.il 2 nd IBDC, 9 th February, 2012 Pathology as
Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Pathology Dept. Judith Sandbank M.D. Pathology Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center ISRAEL jsandbank@asaf.health.gov.il 2 nd IBDC, 9 th February, 2012 Pathology as
HER2 FISH pharmdx TM Interpretation Guide - Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 FISH pharmdx TM Interpretation Guide - Breast Cancer For In Vitro Diagnostic Use FDA approved as an aid in the assessment of patients for whom Herceptin TM (trastuzumab) treatment
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 FISH pharmdx TM Interpretation Guide - Breast Cancer For In Vitro Diagnostic Use FDA approved as an aid in the assessment of patients for whom Herceptin TM (trastuzumab) treatment
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Abstract. Background. Objective
 Molecular epidemiology of clinical tissues with multi-parameter IHC Poster 237 J Ruan 1, T Hope 1, J Rheinhardt 2, D Wang 2, R Levenson 1, T Nielsen 3, H Gardner 2, C Hoyt 1 1 CRi, Woburn, Massachusetts,
Molecular epidemiology of clinical tissues with multi-parameter IHC Poster 237 J Ruan 1, T Hope 1, J Rheinhardt 2, D Wang 2, R Levenson 1, T Nielsen 3, H Gardner 2, C Hoyt 1 1 CRi, Woburn, Massachusetts,
Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the. Subtypes. Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy
 Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Classification of Molecular Subtypes Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy We know it is many diseases Breast cancer is
Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Classification of Molecular Subtypes Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy We know it is many diseases Breast cancer is
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Differential diagnosis of HCC
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Quest for an Ideal Immunohistochemical Panel Sanjay Kakar, MD UCSF Differential diagnosis of HCC Hepatocellular lesions Adenoma, FNH, HG dysplasia Adenocarcinoma CholangioCA, metastasis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Quest for an Ideal Immunohistochemical Panel Sanjay Kakar, MD UCSF Differential diagnosis of HCC Hepatocellular lesions Adenoma, FNH, HG dysplasia Adenocarcinoma CholangioCA, metastasis
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Quality Indicators - Anatomic Pathology- HSC/STC Jul-Sep 2 nd Qtr. Apr-Jun 1 st Qtr
 Eastern Health Volume 86 Page 001 CIHRT Exhibit P-3595 Page 1 INDICATOR Financial Overtime Hours / FTE Workload Increase - FTE equivalent Workload Quality Indicators - Anatomic Pathology- HSC/STC TOTAL
Eastern Health Volume 86 Page 001 CIHRT Exhibit P-3595 Page 1 INDICATOR Financial Overtime Hours / FTE Workload Increase - FTE equivalent Workload Quality Indicators - Anatomic Pathology- HSC/STC TOTAL
Recent advances in breast cancers
 Recent advances in breast cancers Breast cancer is a hetrogenous disease due to distinct genetic alterations. Similar morphological subtypes show variation in clinical behaviour especially in response
Recent advances in breast cancers Breast cancer is a hetrogenous disease due to distinct genetic alterations. Similar morphological subtypes show variation in clinical behaviour especially in response
Barriers to Understanding
 Behind the Scenes: The Critical Importance of Cancer Cell Pathology and the Pathologist Sherry T. Emery, M.D., Chief of Pathology Northeast Health System Barriers to Understanding Questions for 2010 What
Behind the Scenes: The Critical Importance of Cancer Cell Pathology and the Pathologist Sherry T. Emery, M.D., Chief of Pathology Northeast Health System Barriers to Understanding Questions for 2010 What
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Finite-element analysis of cell cluster dynamics in different cluster trap architectures. (a) Cluster-Chip (b) Filter (c) A structure identical to the Cluster-Chip except that one
Supplementary Figure 1 Finite-element analysis of cell cluster dynamics in different cluster trap architectures. (a) Cluster-Chip (b) Filter (c) A structure identical to the Cluster-Chip except that one
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer
 Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Figure S4. 15 Mets Whole Exome. 5 Primary Tumors Cancer Panel and WES. Next Generation Sequencing
 Figure S4 Next Generation Sequencing 15 Mets Whole Exome 5 Primary Tumors Cancer Panel and WES Get coverage of all variant loci for all three Mets Variant Filtering Sequence Alignments Index and align
Figure S4 Next Generation Sequencing 15 Mets Whole Exome 5 Primary Tumors Cancer Panel and WES Get coverage of all variant loci for all three Mets Variant Filtering Sequence Alignments Index and align
October Billing and compliance. Coagulation. Immunohistochemistry. Immunology. Referral testing ICD 10
 October 2015 Billing and compliance ICD 10 Coagulation Processing, transport and stability changes for multiple coagulation tests Immunohistochemistry IHC stain updates Immunology Lyme Western Blot testing
October 2015 Billing and compliance ICD 10 Coagulation Processing, transport and stability changes for multiple coagulation tests Immunohistochemistry IHC stain updates Immunology Lyme Western Blot testing
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology. Report. Key Questions. Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help:
 Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
TEST MENU BY SPECIALTY
 1 TEST MENU BY SPECIALTY Breast Pathology Surgical excisions, needle core biopsies, and plastic surgery accepted from all sites Assessment of margins Axillary lymph node dissections Sentinel lymph nodes
1 TEST MENU BY SPECIALTY Breast Pathology Surgical excisions, needle core biopsies, and plastic surgery accepted from all sites Assessment of margins Axillary lymph node dissections Sentinel lymph nodes
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Predictive PP1Ca binding region in BIG3 : 1,228 1,232aa (-KAVSF-) HEK293T cells *** *** *** KPL-3C cells - E E2 treatment time (h)
 Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
PD-L1 Analyte Control DR
 Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Product Introduction
 Product Introduction Product Codes: HCL026, HCL027 and HCL028 Contents Introduction to HER2 2 HER2 immunohistochemistry 3 Cell lines as controls 5 HER2 Analyte Control DR IHC 7 HER2 Analyte Control DR
Product Introduction Product Codes: HCL026, HCL027 and HCL028 Contents Introduction to HER2 2 HER2 immunohistochemistry 3 Cell lines as controls 5 HER2 Analyte Control DR IHC 7 HER2 Analyte Control DR
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010 January ; 19(1): 144 147. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.epi-09-0807. Feasibility Study for Collection
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010 January ; 19(1): 144 147. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.epi-09-0807. Feasibility Study for Collection
HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Assessment of Breast Cancer with Borderline HER2 Status Using MIP Microarray
 Assessment of Breast Cancer with Borderline HER2 Status Using MIP Microarray Hui Chen, Aysegul A Sahin, Xinyan Lu, Lei Huo, Rajesh R Singh, Ronald Abraham, Shumaila Virani, Bal Mukund Mishra, Russell Broaddus,
Assessment of Breast Cancer with Borderline HER2 Status Using MIP Microarray Hui Chen, Aysegul A Sahin, Xinyan Lu, Lei Huo, Rajesh R Singh, Ronald Abraham, Shumaila Virani, Bal Mukund Mishra, Russell Broaddus,
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS.
 NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
LN04 - Lymphoma Tissue Microarray
 Reveal Biosciences offers Histochemical Staining, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Whole Slide Imaging, and Quantitative Image Analysis on any TMA LN04 - Lymphoma Tissue Microarray
Reveal Biosciences offers Histochemical Staining, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Whole Slide Imaging, and Quantitative Image Analysis on any TMA LN04 - Lymphoma Tissue Microarray
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
Pepsin Solution ready-to-use
 SIE HABEN DIE VISION, WIR HABEN DIE SUBSTANZ. Pepsin Solution Single component Pepsin Solution: only one component refrigerator stable Pepsin is a commonly used digestive enzyme for immunohistochemical
SIE HABEN DIE VISION, WIR HABEN DIE SUBSTANZ. Pepsin Solution Single component Pepsin Solution: only one component refrigerator stable Pepsin is a commonly used digestive enzyme for immunohistochemical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Quality assurance and quality control in pathology in breast disease centers
 Quality assurance and quality control in pathology in breast disease centers Judith Sandbank M.D. Pathology Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center ISRAEL jsandbank@asaf.health.gov.il 1 st IBDC, 28 th January, 2011
Quality assurance and quality control in pathology in breast disease centers Judith Sandbank M.D. Pathology Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center ISRAEL jsandbank@asaf.health.gov.il 1 st IBDC, 28 th January, 2011
MT09 - Normal Human Tissue Microarray, FDA
 Reveal Biosciences offers Histochemical Staining, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Whole Slide Imaging, and Quantitative Image Analysis on any TMA MT09 - Normal Human Tissue Microarray,
Reveal Biosciences offers Histochemical Staining, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Whole Slide Imaging, and Quantitative Image Analysis on any TMA MT09 - Normal Human Tissue Microarray,
The Pathology of Neoplasia Part II
 The Pathology of Neoplasia Part II February 2018 PAUL BOGNER, MD A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R O F O N C O L O G Y P A T H O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O L O G Y Clinical goals of cancer pathology
The Pathology of Neoplasia Part II February 2018 PAUL BOGNER, MD A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R O F O N C O L O G Y P A T H O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O L O G Y Clinical goals of cancer pathology
Supplementary figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Flowchart of experimental procedures of in situ hybridization using ViewRNA technology.
 Supplementary figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Flowchart of experimental procedures of in situ hybridization using ViewRNA technology. Supplementary figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2. Evidence for existence
Supplementary figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Flowchart of experimental procedures of in situ hybridization using ViewRNA technology. Supplementary figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2. Evidence for existence
GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BREAST PATHOLOGY
 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BREAST PATHOLOGY LEVEL: PGY2, PGY3, PGY5 A number of these rotations are introductory in nature, as they are major subspecialties, and are followed by two more blocks in PGY-3, during
GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BREAST PATHOLOGY LEVEL: PGY2, PGY3, PGY5 A number of these rotations are introductory in nature, as they are major subspecialties, and are followed by two more blocks in PGY-3, during
Reviewer's report. Version: 1 Date: 24 May Reviewer: Cathy Moelans. Reviewer's report:
 Reviewer's report Title: Validation of HER2 testing with core needle biopsy specimens from primary breast cancers in terms of interobserver reproducibility and concordance with surgically resected specimens
Reviewer's report Title: Validation of HER2 testing with core needle biopsy specimens from primary breast cancers in terms of interobserver reproducibility and concordance with surgically resected specimens
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Pathology. AGO e. V. in der DGGG e.v. sowie in der DKG e.v.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
Supplemental Table 1 Molecular Profile of the SCLC Cell Line Panel
 Supplemental Table 1 Molecular Profile of the SCLC Cell Line Panel p53 RB Myc Cell Line Mutation A Mutation A Amplification B COR-L103 C p.y234c p.d584e L-Myc NCI-H526 p.s33_splice None N-Myc NCI-H1048
Supplemental Table 1 Molecular Profile of the SCLC Cell Line Panel p53 RB Myc Cell Line Mutation A Mutation A Amplification B COR-L103 C p.y234c p.d584e L-Myc NCI-H526 p.s33_splice None N-Myc NCI-H1048
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Files for Zehir, Benayed et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Sample
Supplementary Files for Zehir, Benayed et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Sample
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC
 Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
It s not a four legged animal anymore. Disclosure
 It s not a four legged animal anymore Parminder Singh, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division hematology and oncology No disclosures Disclosure 1 Four legged animal which use the tips of their toes,
It s not a four legged animal anymore Parminder Singh, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division hematology and oncology No disclosures Disclosure 1 Four legged animal which use the tips of their toes,
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Deciphering the biology that drives response to immunotherapy
 Deciphering the biology that drives response to immunotherapy Phenoptics TM Quantitative Pathology Platform Trent Norris, Field Application Scientist September 15, 2016 HUMAN HEALTH ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
Deciphering the biology that drives response to immunotherapy Phenoptics TM Quantitative Pathology Platform Trent Norris, Field Application Scientist September 15, 2016 HUMAN HEALTH ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
Central Pathology Review and Tissue MicroArrays. Dr Lisa Storer Children s Brain Tumour Research Centre Nottingham
 Central Pathology Review and Tissue MicroArrays Dr Lisa Storer Children s Brain Tumour Research Centre Nottingham What is a tissue microarray? Tissue microarrays (TMAs) consist of paraffin blocks in which
Central Pathology Review and Tissue MicroArrays Dr Lisa Storer Children s Brain Tumour Research Centre Nottingham What is a tissue microarray? Tissue microarrays (TMAs) consist of paraffin blocks in which
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data
 Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Immunohistochemistry in Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors. Sahar Rassi Zankoul, MD
 Immunohistochemistry in Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors Sahar Rassi Zankoul, MD Introduction Bone tumors represent a wide variety of tumors of various origins and malignant potentials. These different tumor
Immunohistochemistry in Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors Sahar Rassi Zankoul, MD Introduction Bone tumors represent a wide variety of tumors of various origins and malignant potentials. These different tumor
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
PHARMACOGENETICS OF BREAST CANCER
 PHARMACOGENETICS OF BREAST CANCER MALGORZATA JAREMKO, PhD Mount Sinai School of Medicine, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Outlines Breast cancer therapeutic situation Pharmacogenetics of antiestrogen
PHARMACOGENETICS OF BREAST CANCER MALGORZATA JAREMKO, PhD Mount Sinai School of Medicine, Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Outlines Breast cancer therapeutic situation Pharmacogenetics of antiestrogen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Incorporating pharmacodynamic, response and patient selection biomarkers. Paul Elvin PhD Chief Translational Science Officer Aptus Clinical
 Incorporating pharmacodynamic, response and patient selection biomarkers Paul Elvin PhD Chief Translational Science Officer Aptus Clinical 22 Oncology drug development Biomarkers key for: Strong hypothesis
Incorporating pharmacodynamic, response and patient selection biomarkers Paul Elvin PhD Chief Translational Science Officer Aptus Clinical 22 Oncology drug development Biomarkers key for: Strong hypothesis
A NEW VISION IN THE DIAGNOSTIC/PROGNOSIS OF CANCER USING QUANTITATIVE. Prof. Antonio Ferrer-Montiel
 A NEW VISION IN THE DIAGNOSTIC/PROGNOSIS OF CANCER USING QUANTITATIVE BIOLOGY Prof. Antonio Ferrer-Montiel QUANTITATIVE BIOLOGY: A NECESSITY Objective measures Quantitative ranking Subjective bias elimination
A NEW VISION IN THE DIAGNOSTIC/PROGNOSIS OF CANCER USING QUANTITATIVE BIOLOGY Prof. Antonio Ferrer-Montiel QUANTITATIVE BIOLOGY: A NECESSITY Objective measures Quantitative ranking Subjective bias elimination
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Product Introduction. Product Codes: HCL029, HCL030 and HCL031. Issue
 Product Introduction Product Codes: HCL029, HCL030 and HCL031 Issue 1. 180510 Contents Introduction to Estrogen Receptor 2 ER immunohistochemistry 3 Quality control 5 Cell lines as controls 6 Estrogen
Product Introduction Product Codes: HCL029, HCL030 and HCL031 Issue 1. 180510 Contents Introduction to Estrogen Receptor 2 ER immunohistochemistry 3 Quality control 5 Cell lines as controls 6 Estrogen
Expanded View Figures
 Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer
 Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
PRESAGE CIVO: A NOVEL PLATFORM FOR PRECISION ONCOLOGY & DRUG DEVELOPMENT
 PRESAGE : A NOVEL PLATFORM FOR PRECISION ONCOLOGY & DRUG DEVELOPMENT DECEMBER 2017 Presage Biosciences, Inc. 2017. All rights reserved. Presage Proprietary Biosciences, information. Inc. 2017. All rights
PRESAGE : A NOVEL PLATFORM FOR PRECISION ONCOLOGY & DRUG DEVELOPMENT DECEMBER 2017 Presage Biosciences, Inc. 2017. All rights reserved. Presage Proprietary Biosciences, information. Inc. 2017. All rights
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets
 2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets Lee H. Chen Bioinformatics and Biostatistics
2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets Lee H. Chen Bioinformatics and Biostatistics
I. Diagnosis of the cancer type in CUP
 Latest Research: USA I. Diagnosis of the cancer type in CUP II. Outcomes of site-specific therapy of the cancer type in CUP a. Prospective clinical trial b. Retrospective clinical trials 1 Latest Research:
Latest Research: USA I. Diagnosis of the cancer type in CUP II. Outcomes of site-specific therapy of the cancer type in CUP a. Prospective clinical trial b. Retrospective clinical trials 1 Latest Research:
Utility of Adequate Core Biopsy Samples from Ultrasound Biopsies Needed for Today s Breast Pathology
 Utility of Adequate Core Biopsy Samples from Ultrasound Biopsies Needed for Today s Breast Pathology Ugur Ozerdem, M.D. 1 Abstract Background: There is a paradigm shift in breast biopsy philosophy. In
Utility of Adequate Core Biopsy Samples from Ultrasound Biopsies Needed for Today s Breast Pathology Ugur Ozerdem, M.D. 1 Abstract Background: There is a paradigm shift in breast biopsy philosophy. In
Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis
 5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering
 nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Surgical Pathology Lab of the Future. Thomas M. Grogan, M.D. Professor of Pathology, University of Arizona Founder, Ventana Medical Systems, Inc.
 Surgical Pathology Lab of the Future Thomas M. Grogan, M.D. Professor of Pathology, University of Arizona Founder, Ventana Medical Systems, Inc. 28 April 2010 Objective Demonstrate how the next generation
Surgical Pathology Lab of the Future Thomas M. Grogan, M.D. Professor of Pathology, University of Arizona Founder, Ventana Medical Systems, Inc. 28 April 2010 Objective Demonstrate how the next generation
