LYMPH NODE ASPIRATION
|
|
|
- Hugo Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LYMPH NODE ASPIRATION CLINICAL AND HEMATOLOGIC OBSERVATIONS IN 11 PATIENTS* MAURICE MORRISON, M.D., A. A. SAMWICK, M.D., JOSHUA RUBINSTEIN, M.D., MELVIN STICH, M.D., AND LEO LOEYVE, M.D. From the Jewish Hospital of Brooklyn, the Jeioish Sanitarium and Hospital for Chronic Diseases, the Beth El Hospital and the Brooklyn Cancer Institute, Brooklyn, A T eio York Lymph node aspiration has become an important adjunct to the study of lymphadenopathies. 1 ' 3 " Si 8> 1 The procedure is of great value for the diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease, lymphosarcoma, leukemia and infectious mononucleosis. An aspiration may be repeated at intervals thus furnishing a guide to the effect of treatment. This procedure may also obviate the necessity of surgical excision of a node for biopsy. The most detailed recent study of the subject is the treatise by Tage Strange of Copenhagen. 9 The present report is based on our experiences in 11 patients with biopsy of tissue aspirated from lymph nodes. MATERIAL AND METHODS The diagnoses are indicated in Table 1. In addition to lymph node aspiration, other studies included those of peripheral blood and bone marrow, biopsy of splenic tissue obtained by puncture 6 or surgical removal of the spleen, and of surgically removed lymph nodes, and necropsy. The apparatus required includes a 2-gauge needle, a dry syringe and an alcohol sponge. No anesthetic is necessary. The operator grasps the node securely between the thumb and index finger of the left hand. He pierces the node, aspirates the tissue rapidly and then promptly withdraws the needle. He then makes a smear of the aspirate on a clean slide for staining with Wright's stain. ILLUSTRATIVE CASES 1. Myelogenous leukemia. (Fig. 5). A. B., a woman, age 5, was admitted to the hospital with pallor, fever, extreme adenopathy and ascites. The spleen extended four fingerbreadths below the left costal margin and the liver, three fingerbreadths below the right costal margin. The clinical picture favored a diagnosis of chronic lymphatic leukemia or Hodgkin's disease because of the collar of enlarged lymph nodes about the neck and the extreme enlargement of the nodes in the cervical, axillary and inguinal regions. The peripheral blood study determined the true nature of the process and tissue aspirated from the lymph node and spleen was confirmatory. The unusual feature was the striking lymph node involvement in a patient with myelogenous leukemia in a pre-agonal state. 2. Chronic lymphatic leukemia. (Figs. 3 and 4). A. G., a woman, age 62, represented a typical instance of chronic lymphatic leukemia in an older person. The lymphoblasts were prominent with a predominance of Grumel6e cells. This feature usually indicates either that the patient is entering an acute phase, or that x-ray therapy has induced in the patient a tendency to lymphoblastic "left shift". The presence of the Grumel6e cell serves to eliminate the diagnosis of lymphosarcoma. At times, this distinction is difficult. It may be stated that, as pointed out by Strunge, the characteristic Grumel<5e cell is present in pre- * Aided by a grant from the Jacques Loewe Research Foundation, New York, New York. Received for publication, July 19, Downloaded from on 11 May 218
2 256 MORRISON ET AL. ponderant numbers only in lymphatic leukemia. In acute lymphatic leukemia or after radiation therapy, lymphoblasts with characteristic nucleoli overshadow the presence of Grumel^e cells. 3. Lymphosarcoma. (Fig. 2). M. Y., a woman, age 39, was admitted with pallor and ecehymoses. On examination, lymphadenopathy and an enlarged spleen were found. The peripheral blood showed no evidence of the disease. The bone marrow showed an eosinophilia of 1 per cent. The latter finding suggested the possibility of Hodgkin's disease but the lymph node aspirate revealed the presence of lymphosarcoma cells. A biopsy had resulted in a diagnosis of lymphadenitis. In view of this discrepancy, the pathologist reviewed the original section and found evidence in it of lymphosarcoma. 4. Giant follicular lymphoblastoma. M. A., a woman, age 53, was admitted to the hospital because of enlarged axillary and inguinal nodes. Lymph node aspiration revealed cells suggesting lymphosarcoma. Biopsy of a lymph node showed giant lymphfollicular lymphoblastoma. TABLE 1 DIAGNOSES IX 11 PATIENTS FROM WHOM LYMPH NODE TISSUE WAS ASPIRATED LEUKEMIA Acute myeloblastic 3 Chronic myelocytic 1 Monocytic 2 Chronic lymphatic 19 Chronic lymphatic, terminal (acute phase) 1 Stem cell 1 ' -LYMPHOSARCOMA Lymphosarcoma (small cell type) 12 Follicular lymphoblastoma 2 HODGKIN'S DISEASE 15 METASTATIC CANCER 7 INFECTIONS Tuberculosis 3 Boeck's sarcoidosis 1 Hepatitis, infectious 1 Infectious mononucleosis 5 Lymphadenitis 11 ANEMIAS Congenital hemolytic icterus 1 Cooley's anemia 1 MISCELLANEOUS CONDITIONS Lipoid dystrophy 1 Chondroma 1 Cirrhosis of liver 1 ASPIRATED TISSUE INADEQUATE FOR DIAGNOSIS Hodgkin's disease. (Fig. 1). S. D., a man, age 35, was admitted to the hospital with pain in the chest, fever, and generalized adenopathy. A lymph node aspiration revealed evidence of Hodgkin's disease, i.e., Reed-Sternberg cells, monocytoid cells, pleomorphism and eosinophilia. Some time later a biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. 6. Metastatic cancer. (Figs. 7 and S). A: B., a woman, age 64, was admitted to the hospital because of carcinoma of the breast with axillary nodes. Lymph node aspiration confirmed the diagnosis. All figures were made from material aspirated from lymph nodes. FIG. 1 (upper left). Dorothy-Reed cell in Hodgkin's disease. X 98. FIG. 2 (upper right). "Lymphosarcoma" cell (Patient M. Y.). Notice large cells with scant cytoplasm. These do not have appearance of Grumel<5e cells. X 13. FIG. 3 (lower left). Grumel(5e cell from Patient A. G. with chronic lymphatic leukemia. Note checkerboard appearance of nucleoplasm and occasional lymphoblast. X 13. FIG. 4 (lower right). Patient A. G. with chronic lymphatic leukemia. Grumel6e cell, enlarged. X 3. Downloaded from on 11 May 218
3 &t if/ «/ ti% m. % /^.A*"" F I G S Downloaded from on 11 May 218 'HI *
4 258 MORRISON ET AL. 7. Infectious mononucleosis. (Fig. 6). E. L., a male college student, age 19, was admitted to the hospital with two months' history of enlarged firm, nontender, discrete nodes in the cervical, axillary, inguinal and occipital regions. There was no evidence of enlargement of the nodes in the mediastinum. The liver and spleen were not enlarged. Cells suggestive of infectious mononucleosis were seen in the peripheral blood and in tissue aspirated from a node. 8. Lymphadenitis. B. S., a man, age 59, was admitted to the hospital with an enlarged cervical lymph node. The liver and spleen were foundto be enlarged. Clinically a diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease was suggested. The peripheral blood and bone aspiration'were noncontributory. Biopsy of a lymph node showed lymphadenitis, an occasional polymorphonuclear neutrophil, but no lymphoblasts, Crumel<?e or Reed-Sternberg cells. DISCUSSION. Progress has been made within recent years in developing methods for the diagnosis of a number of blood dyscrasias. In Hodgkin's disease, lymphosarcoma, giant follicular lymphoblastoma, and metastatic cancer in the nodes, often no definite diagnosis can be made on hematolqgjc.yfindings. At times the answer is found only on biopsy or necropsy. Lymph-node aspiration is therefore a helpful diagnostic method. In addition, certain instances of infectious mononucleosis difficult of diagnosis and leukemia are recognized after study of tissue aspirated from a lymph node. Some conditions, such as tuberculosis, Boeck's sarcoidosis and metastatic cancer require further experience with the method of biopsy of tissue aspirated from lymph nodes. ' - As will be noted in Table 1, approximately SO per cent of the patients studied had leukemia, lymphosarcoma, Hodgkin's disease;' lymphadenitis or metastatic cancer. There were also 5 patients with infectious mononucleosis and 3 with tuberculosis. Five of the patients were children, the youngest being four months old and the oldest eight years old. Table 2 offers a brief description of the cell type; the frequency of occurrence and the specific condition where these cells are found. Based upon the morphologic character of these elements, we set down tentative hematologic criteria for lymph node aspiration in different conditions (Table 3). In Table 4, one notes that lymph node aspiration provided the means for making the correct diagnosis most often in Hodgkin's disease, lymphosarcoma, lymphadenitis and metastatic cancer. In contrast, study of the peripheral blood alone was diagnostic in' lymphatic leukemia and infectious mononucleosis. In our study, information was obtained by concomitant aspirations of the spleen in 15 of 19 patients with lymphatic leukemia, in each of our 12 patients with lymphosarcoma, in three of our 15 subjects with Hodgkin's disease and in one of our patients with giant follicular lymphoblastoma. The question arises: will the diagnosis sometimes be overlooked in biopsy of FIG. 5 (upper left). Patient A. B. with myelosis of lymph node in late chronic myelogenous leukemia. Note myelocytes and myeloblasts. X 1. FIG. 6 (upper right). Patient A. W. Large cells of infectious mononucleosis. X 25. FIG. 7 (lower left). Clusters of malignant cells within a lymph node. X 55. FIG.-8 (lower right). Same as Figure 7. X 11. Downloaded from on 11 May 218
5 FIGS. 5-S 259 Downloaded from on 11 May 218
6 26 MORRISON ET AL. aspirated tissue when the conventional biopsy would be more revealing? We have never found this to be true. The same objection was raised in 1938 concerning the feasibility of biopsy of aspirated bone marrow as compared to that of biopsy of trephined bone marrow. 2 In time, it was found that each method has its place. Furthermore, bone marrow aspiration has become almost indispensable in hematology. We predict that similarly lymph node aspiration will prove of great value in replacing or supplementing surgical biopsy in the hematologic study of the TABLE 2 DESCRIPTION OF CELL TYPES NOTED IN TISSUE ASPIRATED FROM LYMPH NODES CELL TYPE FREQUENCY OCCURRENCE DESCRIPTION 1. Small lymphocvte 2. Large lvmphocvte 3. Reticulum cell 4. Syncytial cell 5. llcmoeytoblast 6. Grumelee cell* 7. Lymphoblast 8. Infectious mononucleosis cell. Myeloblast 1. Monocytoid cell 11. Ervthroid elements S5% 15% Many Many Many Many Normal Normal Inflammations, lymphosarcoma Lymphatic leukemia Normal and inflam-. mations Infectious mononucleosis Myeloses Hodgkin's disease Extramedullar}' hematopoiesis; spent polycythemia; osteosclerotic anemia Same as peripheral blood Same as peripheral blood Large nucleus (2-3 times size of small lymphocyte) surrounded by irregular cytoplasmic processes Groups of reticulum cells in masses with a common bluish cytoplasmic background Large cell (4-5 times size of small lymphocyte) with large nucleus of fine texture with one or more nucleoli, surrounded by a deep basophilic cytoplasm (forerunner of lymphoid series) Lymphoid elements with "checkerboard" nucleus Lymphoid elements with nucleoli Large lymphoid elements with indented nucleus and bluish cytoplasm Same as peripheral blood Like monocytes in peripheral blood, occasionally with more than one nucleus Reed-Sternberg cells Same as peripheral blood and bone marrow * The term "Grumelee" is freely used by Tage Strunge in his monograph. 9 It is taken from the French language and literally means "clotted". It applies to a cell with a lymphocytic nucleus of mosaic appearance and a "checkerboard" configuration. lymphadenopathies. At any rate, cytologic study of material aspirated from the lymph node is meant to be an adjunct and not a substitute for histologic study. It is easier to convince a patient to have an aspiration for cytologic study or biopsy than to have him submit to the conventional surgical removal of a lymph node for biopsy. SUMMARY Lymph node aspiration is a relatively simple procedure and can often be repeated either for subsequent study or in determining the effect of treatment. Downloaded from on 11 May 218
7 LYMPH NODE ASPIRATION 261 TABLE 3 CHARACTERISTIC FINDINGS IN TISSUE ASPIRATED FROM LYMPH NODES I. HODGKIN'S DISEASE A. Dorothy Reed-Sternberg cells B. Increase in monocytoid cells C. Eosinophils D. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (1 to 5 per cent) E. Increase in large lymphoid cells. Ratio of small to large (S:L) lymphoid cells is 3:7 (normal S:L, 9:1). Reticulum cells II. LYMPHOSARCOMA A. Large lymphoid cells increased (S:L, 1:9). These cells have large nuclei, rare nucleoli and scant cytoplasm (no "checkerboard" appearance). B. Mitotic figures prominent C. hemocytoblast 111. LYMPHATIC LEUKEMIA A. Chronic 1. Small lymphoid cells (Grumel6e cells) increased (S:L, 9:1). These cells are medium-sized and have a "checkerboard" appearance. 2. Large lymphoid elements (rare) 3. No polymorphonuclear neutrophils B. Acute 1. Few Omnicide cells 2. Preponderance of lymphoblasts with nucleoli 3. Rare mitotic figure C. Subacute 1. Grumelde cells and lymphoblasts equal in number lv. r MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA A. Chronic, myelocytes (9 per cent of the cells) B.' Acute, myelocytes (9 per cent of the cells) V. LYMPHADENITIS, IRRITATIVE A. Ratio of small to large lymphoid elements (S:L, S:2) B. Moderate number of polymorphonuclear neutrophils C. hemocytoblast D. Rare eosinophil VI. LYMPHADENITIS, INFECTIOUS (PURULENT) A. Many polymorphonuclear neutrophils, degenerated, "toxic" B. Many smudged cells VII. INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS A. Large cells with indented nucleus and abundant basophilic cytoplasm B. Lymphoblasts (rare) C. No polymorphonuclear neutrophils VIII. NODE WITH METASTATIC CANCER A. Clusters of atypical cells B. Mitotic figures IX. GIANT FOLLICULAR LYMPHOBLASTOMA (Same as lymphosarcoma with addition of occasional monocytoid and small lymphoid cells) TABLE 4 COMPARATIVE DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF STUDIES OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD, BONE MARROW AND LYMPH NODE ASPIRATION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHADENOPATHY NO. OF BLOOD STUDIES PER CENT OK CORRECT DIAGNOSES NO. OF BONE MARROW STUDIES PER CENT OF CORRECT DIAGNOSES NO. OF LYMPH NODE STUDIES PER CENT OF CORRECT DIAGNOSES Hodgkin's disease Lymphosarcoma Infectious mononucleosis Lymphadenitis Metastatic cancer Lymphatic leukemia S3 SO Downloaded from on 11 May 218
8 262 MORRISON ET Ah. Aspiration of material from enlarged lymph nodes will often provide diagnostic hematologic data in Hodgkin's disease, lymphosarcoma, lymphadenitis and metastatic cancer. A description is given of type cells encountered in material aspirated from enlarged nodes. Criteria are given for the diagnosis of enlargement of lymph nodes, based on cells found in the aspirate. REFERENCES 1. BOVER, G. F.: El Diagnostico por la Punsion Ganglionar. Valencia: Editorial Sabre, CUSTEH, R. P.: An Atlas of the Blood and Bone Marrow. Philadelphia: W.B.Saunders Company, 1949, p FORKNER, C. E.: Material from lymph nodes of man. Studies on living and fixed cells withdrawn from lymph nodes of man. Arch. Int. Med., 4: , MARTIN, H. E., AND ELLIS, E. B.: Biopsv bv needle puncture and aspiration. Ann. Surg.; 92: , MARTIN, H. E., AND ELLIS, E. B.: Aspiration biopsy. Surg., Gynec. and Obst., 59: , MORRISON, M.: An analysis of the blood picture in 1 cases of malignancy. J. Lab. and Clin. Med., 17: , MORRISON, M., SAMWICK, A. A., RUBINSTEIN, J., MORRISON, H., AND LOEWE, L.: Splenic aspiration. J. A. M. A., 146: , PAVLOVSKY, A.: La Ponction Ganglionar: Su Conticucion al Diagnostico Clinicoquirurgico de las Affeciones Ganglionares. Buenos Aires: Thesis, 1934, 82 pp. 9. STRUNGE, T.: La Ponction des Ganglions Lymphatiques. Copenhagen: Ejnar Munksgaard, 1944, 137 pp. 1. TEMPKA, T., AND KUBICZEK, M.: Normal and pathological lymphadenograin in the light of own research. Acta med. Scandinav., 131: , Downloaded from on 11 May 218
Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue
 CONTENTS Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue White blood cells and lymph nodes Quantitative disorder of white blood cells Reactive lymphadenopathies Infectious lymphadenitis Tumor metastasis
CONTENTS Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue White blood cells and lymph nodes Quantitative disorder of white blood cells Reactive lymphadenopathies Infectious lymphadenitis Tumor metastasis
Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue
 Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul, M.D. Department of Pathology and Forensic Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Naresuan University CONTENTS White blood cells and lymph
Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul, M.D. Department of Pathology and Forensic Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Naresuan University CONTENTS White blood cells and lymph
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Infections and nonmicrobial inflammatory stimuli can cause leukocytosis (as seen in Lab 1) as well as lymph node enlargement (lymphadenopathy).
 LAB 5: LYMPHOID TISSUE AND SKIN The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the lymphoid tissue and skin. The lymphoid organs include the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Abnormalities in the lymph
LAB 5: LYMPHOID TISSUE AND SKIN The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the lymphoid tissue and skin. The lymphoid organs include the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Abnormalities in the lymph
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA. April 16, 2008
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN
 LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC LYMPHADENOPATHY.
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE
 Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
CHAPTER:4 LEUKEMIA. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY 8/12/2009
 LEUKEMIA CHAPTER:4 1 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Leukemia A group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of
LEUKEMIA CHAPTER:4 1 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Leukemia A group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY: A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN LYMPHADENOPTHY
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Mahesh S Patil and Anand A S, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Mahesh S Patil and Anand A S, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center
 LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
BLASTIC CRISIS AND MYELOFIBROSIS SIMULTANEOUS COMPLICATIONS IN A CASE OF CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 BLASTIC CRISIS AND MYELOFIBROSIS SIMULTANEOUS COMPLICATIONS IN A CASE OF CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 151 To 153 Khalid Hassan ( Department of Pathology (Haematology)
BLASTIC CRISIS AND MYELOFIBROSIS SIMULTANEOUS COMPLICATIONS IN A CASE OF CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 151 To 153 Khalid Hassan ( Department of Pathology (Haematology)
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
DETERMINATION OF A LYMPHOID PROCESS
 Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material
 Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
MARROW BIOPSY. not be neglected. An increase of fat globules may. in hyperplasia. The smears are stained with
 478 STERNAL MARROW BIOPSY BY E. NEUMARK, M.B., B.S.(Lond.) Lecturer in Pathology, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London Sternal puncture has become established as a useful diagnostic aid since its
478 STERNAL MARROW BIOPSY BY E. NEUMARK, M.B., B.S.(Lond.) Lecturer in Pathology, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London Sternal puncture has become established as a useful diagnostic aid since its
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/24 Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study K Florence, K Suresh, K Lavanya Department
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/24 Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study K Florence, K Suresh, K Lavanya Department
FNACasaDiagnosticToolintheEvaluationofLymphadenopathyATertiaryHospitalExperience
 Global Journal of Medical Research: C Microbiology and Pathology Volume 14 Issue 7 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Global Journal of Medical Research: C Microbiology and Pathology Volume 14 Issue 7 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Bio& 242 Unit 3 / Lecture 1
 Bio& 242 Unit 3 / Lecture 1 Major Functions of Blood The body contains 4 to 6 liters of blood with an average ph of 7.35 to 7.45. Functions include: Transport Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones,
Bio& 242 Unit 3 / Lecture 1 Major Functions of Blood The body contains 4 to 6 liters of blood with an average ph of 7.35 to 7.45. Functions include: Transport Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones,
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points
 Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points Koh Liang Piu Department of Hematology-Oncology National University Cancer Institute National University Health System Objectives of this talk: 1. To provide some useful
Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points Koh Liang Piu Department of Hematology-Oncology National University Cancer Institute National University Health System Objectives of this talk: 1. To provide some useful
Title. Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date DOI. Doc URL.
 Title PLASMACYTOID CELLS OF CANINE PERIPHERAL BLOOD IN ELE Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date 1970-09 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.18.3.125
Title PLASMACYTOID CELLS OF CANINE PERIPHERAL BLOOD IN ELE Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date 1970-09 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.18.3.125
A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease
 A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease R. M. CROSS J. clini. Path. (1968), 21, 0-10 From the Royal Air Force Institute ofpathology and Tropical Medicine, Halton, Buckinghamshire
A clinicopathological study of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease R. M. CROSS J. clini. Path. (1968), 21, 0-10 From the Royal Air Force Institute ofpathology and Tropical Medicine, Halton, Buckinghamshire
, , 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
ISPUB.COM. A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHOD
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice
 Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice Stephen S. Raab, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Eastern Health and Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John s, NL and University of Washington,
Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice Stephen S. Raab, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Eastern Health and Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John s, NL and University of Washington,
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 37/Aug 21, 2014 Page 9580
 THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
Groin lymph node icd 10
 Groin lymph node icd 10 Search ICD - 10 coding challenge: Removal of lymph is admitted now for superficial groin dissection of sentinel lymph node. the ICD - 10 diagnosis code for the. ICD - 10 : R59.1
Groin lymph node icd 10 Search ICD - 10 coding challenge: Removal of lymph is admitted now for superficial groin dissection of sentinel lymph node. the ICD - 10 diagnosis code for the. ICD - 10 : R59.1
COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY
 CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Chapter 46. Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder
 Chapter 46 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Components of the Blood Red
Chapter 46 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Components of the Blood Red
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and
 Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2.
 Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Dept. of Anat., Yamaguchi Med. School, Ube (Director: Prof. B. OSOGOE and Assist. Prof. K. AWAYA).
 Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 18, n. 4 (January 1960). P. 479-487. Dept. of Anat., Yamaguchi Med. School, Ube (Director: Prof. B. OSOGOE and Assist. Prof. K. AWAYA). A Quantitative Study of the Plasma Cell Population
Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 18, n. 4 (January 1960). P. 479-487. Dept. of Anat., Yamaguchi Med. School, Ube (Director: Prof. B. OSOGOE and Assist. Prof. K. AWAYA). A Quantitative Study of the Plasma Cell Population
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Percutaneous Aspiration Biopsy of Lymph Nodes
 Percutaneous Aspiration Biopsy of Lymph Nodes WILLIAM L BETSILL, JR., M.D., AND STEVEN I. HAJDU, M.D. Betsill, William L., and Hajdu, Steven I.: Percutaneous aspiration biopsy of lymph nodes. Am J Clin
Percutaneous Aspiration Biopsy of Lymph Nodes WILLIAM L BETSILL, JR., M.D., AND STEVEN I. HAJDU, M.D. Betsill, William L., and Hajdu, Steven I.: Percutaneous aspiration biopsy of lymph nodes. Am J Clin
HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor I. Description of the rotation: During this rotation, the resident will gain
HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor I. Description of the rotation: During this rotation, the resident will gain
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Pathology of the Lymphoid System
 Pathology of the Lymphoid System Learning Objectives: Define lymphadenitis and enumerate its types. Briefly describe the morphological appearance of reactive lymph node. Describe the microscopic picture
Pathology of the Lymphoid System Learning Objectives: Define lymphadenitis and enumerate its types. Briefly describe the morphological appearance of reactive lymph node. Describe the microscopic picture
Pathology #07. Hussein Al-Sa di. Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib. Mature B-Cell Neoplasm. 0 P a g e
 Pathology #07 Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Hussein Al-Sa di Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib 0 P a g e Thursday 18/2/2016 Our lecture today (with the next 2 lectures) will be about lymphoid tumors This is a little bit long
Pathology #07 Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Hussein Al-Sa di Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib 0 P a g e Thursday 18/2/2016 Our lecture today (with the next 2 lectures) will be about lymphoid tumors This is a little bit long
Lymphatic System Disorders
 Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphomas Malignant neoplasms involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes Specific causes not identified // Higher risk in adults who received radiation during childhood
Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphomas Malignant neoplasms involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes Specific causes not identified // Higher risk in adults who received radiation during childhood
FNA of Thyroid. Toward a Uniform Terminology With Management Guidelines. NCI NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference
 FNA of Thyroid NCI NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference Toward a Uniform Terminology With Management Guidelines Thyroid Thyroid FNA Cytomorphology NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference
FNA of Thyroid NCI NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference Toward a Uniform Terminology With Management Guidelines Thyroid Thyroid FNA Cytomorphology NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference
Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol
 Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol Cells derived from the bone marrow that mature and take part in cellular immune reactions are called lymphocytes. When lymphocytes undergo transformation and
Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol Cells derived from the bone marrow that mature and take part in cellular immune reactions are called lymphocytes. When lymphocytes undergo transformation and
THE incidence of cancer of the prostate gland among men who have symptoms
 PROSTATE GLAND BIOPSY EUGENE F. POUTASSE, Department of Urology M.D. THE incidence of cancer of the prostate gland among men who have symptoms of bladder neck obstruction is about one out of five. The
PROSTATE GLAND BIOPSY EUGENE F. POUTASSE, Department of Urology M.D. THE incidence of cancer of the prostate gland among men who have symptoms of bladder neck obstruction is about one out of five. The
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine
 International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 616832, 20 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.616832 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013 A. L. Hemalatha, Nishtha Batra, Deepthi.
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 616832, 20 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.616832 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013 A. L. Hemalatha, Nishtha Batra, Deepthi.
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (of T cell lineage)
 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (of T cell lineage) Definition T-cell lymphoma comprised of large cells with abundant cytoplasm and pleomorphic, often horseshoe-shaped nuclei CD30+ Most express cytotoxic
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (of T cell lineage) Definition T-cell lymphoma comprised of large cells with abundant cytoplasm and pleomorphic, often horseshoe-shaped nuclei CD30+ Most express cytotoxic
What is a hematological malignancy? Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies. Etiology of hematological malignancies. Leukemias
 Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies Cancer of the formed elements of the blood What is a hematological malignancy? A hematologic malignancy is a malignancy (or cancer) of any of the formed elements
Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies Cancer of the formed elements of the blood What is a hematological malignancy? A hematologic malignancy is a malignancy (or cancer) of any of the formed elements
HIV AND LYMPHADENOPATHY
 HIV AND LYMPHADENOPATHY Sagren Naidoo Research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of
HIV AND LYMPHADENOPATHY Sagren Naidoo Research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation
 Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation HIHIM 409 WBC count RBC count WBC differential Hemoglobin (HGB) Hematocrit (HCT) % of volume occupied by RBCs CBC Red cell indices Mean cell volume (MCV) average
Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation HIHIM 409 WBC count RBC count WBC differential Hemoglobin (HGB) Hematocrit (HCT) % of volume occupied by RBCs CBC Red cell indices Mean cell volume (MCV) average
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3
 PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
Pathology. #11 Acute Leukemias. Farah Banyhany. Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16
 35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Lymphoma Read with the experts
 Lymphoma Read with the experts Marc Seltzer, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Director, PET-CT Course American College of Radiology Learning Objectives Recognize
Lymphoma Read with the experts Marc Seltzer, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Director, PET-CT Course American College of Radiology Learning Objectives Recognize
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy.
 November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
Pathology of the Lymphoid System
 Pathology of the Lymphoid System Learning Objectives: Define lymphadenitis and enumerate its types. Briefly describe the morphological appearance of reactive lymph node. Describe the microscopic picture
Pathology of the Lymphoid System Learning Objectives: Define lymphadenitis and enumerate its types. Briefly describe the morphological appearance of reactive lymph node. Describe the microscopic picture
Whole Blood. Lab 29A. Blood. Plasma. Whole Blood. Formed Elements. Plasma: Fluid component. Formed elements: Cells and fragments
 Whole Blood Lab 29A. Blood Plasma: Fluid component Water (90%) Dissolved plasma proteins Other solutes Formed elements: Cells and fragments RBCs (carry Oxygen) WBCs (immunity) Platelets (cell fragments
Whole Blood Lab 29A. Blood Plasma: Fluid component Water (90%) Dissolved plasma proteins Other solutes Formed elements: Cells and fragments RBCs (carry Oxygen) WBCs (immunity) Platelets (cell fragments
Fine-Needle Aspiration and Cytologic Findings of Surgical Scar Lesions in Women With Breast Cancer
 148 Fine-Needle Aspiration and Cytologic Findings of Surgical Scar Lesions in Women With Breast Cancer Ehud Malberger, DMD, FIAC,* Yeouda Edoute, MD, PhD,t Osnaf Toledano, MD,* and Dov Sapir, MDS Benign
148 Fine-Needle Aspiration and Cytologic Findings of Surgical Scar Lesions in Women With Breast Cancer Ehud Malberger, DMD, FIAC,* Yeouda Edoute, MD, PhD,t Osnaf Toledano, MD,* and Dov Sapir, MDS Benign
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
A Look at the Lymphoid System Rose Raskin, DVM, PhD, DACVP Purdue University West Lafayette, IN
 A Look at the Lymphoid System Rose Raskin, DVM, PhD, DACVP Purdue University West Lafayette, IN The lymphoid organs commonly biopsied include the peripheral and internal lymph nodes, spleen, and occasionally
A Look at the Lymphoid System Rose Raskin, DVM, PhD, DACVP Purdue University West Lafayette, IN The lymphoid organs commonly biopsied include the peripheral and internal lymph nodes, spleen, and occasionally
Cytology for the Endocrinologist. Nicole Massoll M.D
 Cytology for the Endocrinologist Nicole Massoll M.D Objectives Discuss slide preperation Definitions of adequacy ROSE (Rapid On-Site Evaluation) Thyroid Cytology Adequacy Nicole Massoll M.D. University
Cytology for the Endocrinologist Nicole Massoll M.D Objectives Discuss slide preperation Definitions of adequacy ROSE (Rapid On-Site Evaluation) Thyroid Cytology Adequacy Nicole Massoll M.D. University
An Uncommon Presentation of Large B-cell Lymphoma of the kidney A Case Report and Literature Review
 An Uncommon Presentation of Large B-cell Lymphoma of the kidney A Case Report and Literature Review CHRISTOPHER ADILETTA M.D., AJAZ SHAWL M.D. ST. JOSEPH S HEALTH, SYRACUSE, NY Our Patient Case We present
An Uncommon Presentation of Large B-cell Lymphoma of the kidney A Case Report and Literature Review CHRISTOPHER ADILETTA M.D., AJAZ SHAWL M.D. ST. JOSEPH S HEALTH, SYRACUSE, NY Our Patient Case We present
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies
 Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Study of advantages and disadvantages of bone marrow trephine biopsy over bone marrow aspiration
 Original article: Study of advantages and disadvantages of bone marrow trephine biopsy over bone marrow aspiration 1 Dr. Smita Bhadekar *, 2 Dr.Sunita Patil 1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pathology, BJGMC,
Original article: Study of advantages and disadvantages of bone marrow trephine biopsy over bone marrow aspiration 1 Dr. Smita Bhadekar *, 2 Dr.Sunita Patil 1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pathology, BJGMC,
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Lách
 Lách Lách Lách Lách Splenogonadal fusion. Splenic tissue is attached to testicular tissue. Pseudocyst (false or secondary cyst). A, Outer aspect. Pseudocyst (false or secondary cyst). B, Inner surface.
Lách Lách Lách Lách Splenogonadal fusion. Splenic tissue is attached to testicular tissue. Pseudocyst (false or secondary cyst). A, Outer aspect. Pseudocyst (false or secondary cyst). B, Inner surface.
Low grade High grade , immune suppression chronic persistent inflammation viruses B-symptoms
 We've one category for lymphoid neoplasm which is the lymphoma in contrast to that of myeloid which has three categories; acute myeloid leukemias, myeloproliferative & myelodysplastic disorders. Lymphoma
We've one category for lymphoid neoplasm which is the lymphoma in contrast to that of myeloid which has three categories; acute myeloid leukemias, myeloproliferative & myelodysplastic disorders. Lymphoma
Case # year old man with a 2 cm right kidney mass
 Case # 4. 52 year old man with a 2 cm right kidney mass Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 Diagnosis: Negative/Non-diagnostic Normal kidney tissue Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the kidney is performed
Case # 4. 52 year old man with a 2 cm right kidney mass Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 Diagnosis: Negative/Non-diagnostic Normal kidney tissue Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the kidney is performed
Understanding your diagnosis. Dr Graham Collins Consultant Haemtologist Oxford University Hospitals
 Understanding your diagnosis Dr Graham Collins Consultant Haemtologist Oxford University Hospitals Common questions I get asked What is lymphoma? What subtype do I have and what does that mean? What are
Understanding your diagnosis Dr Graham Collins Consultant Haemtologist Oxford University Hospitals Common questions I get asked What is lymphoma? What subtype do I have and what does that mean? What are
LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES Identify etiology and epidemiology for leukemia and lymphoma. Discuss common types of leukemia. Distinguish
LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES Identify etiology and epidemiology for leukemia and lymphoma. Discuss common types of leukemia. Distinguish
Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms. Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University
 Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University What is an integrated approach? What is an integrated approach? Incorporating all diagnostic
Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University What is an integrated approach? What is an integrated approach? Incorporating all diagnostic
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
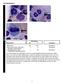 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL LEUKEMIA FORMS CHAPTER 16A REVISED: DECEMBER 2017
 LEUKEMIA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Leukemia studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any leukemia study. Please refer
LEUKEMIA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Leukemia studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any leukemia study. Please refer
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED
 Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Megakaryocyte or Precursor, Normal
 Precursor, Normal SYNONYMS none VITAL STATISTICS size...20-160 µm in diameter N:C ratio...varible, depending on maturation of cell; early forms have a high N:C rato which decreases as cell matures and
Precursor, Normal SYNONYMS none VITAL STATISTICS size...20-160 µm in diameter N:C ratio...varible, depending on maturation of cell; early forms have a high N:C rato which decreases as cell matures and
