Biological effects of extremely low radiation background conditions
|
|
|
- Antonia Blankenship
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biological effects of extremely low radiation background conditions Marie Davídková Dept. of Radiation Dosimetry Nuclear Physics Institute Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic
2
3 Development of new dosimetric methods for LET spectrometry (track-etched and semiconductor detectors) measurements in mixed radiation fields Monitoring of cosmic radiation in space and at mountain observatories for research on space weather aircraft and spacecraft crew dosimetry
4 Radioecology and radiocarbon dating Radiocarbon dating laboratory CRL (in cooperation with Archaeological Institute ASCR) Fossil fuel combustion and atmospheric 14 CO 2 and CO 2 Past environmental changes and 14 C 14 C in the vicinity of NPPs and in reference areas Low background liquid scintillation spectrometers QUANTULUS 1220 Sampling in the vicinity of NPP Temelín Monitoring of atmospheric 14 CO 2 Development of new analytical methods Theory of formation of liquid scintillation pulse spectra
5 Research on biological effects of radiation Radiation damage to DNA and DNA-protein complexes Biological effects of soft X rays and XUV Laser beam focusing lens Gas-puff orifice Samples Radiation therapy: - Induction of secondary cancers - Nuclear fragmentation TLD and PADC in proton beam
6 NPI rabiobiology program First experiments using human normal neonatal skin fibroblasts. Cells grown on a 2.5 μm mylar foil stretched on a plastic ring (Chemplex Industries, USA) In some cases cells were grown in T25 flasks or on glass covered petri dishes.
7 Cyclotron U-120M Isochronous cyclotron U-120M located in the NPI Current parameters of accelerated and extracted beams are: p+/ H : MeV, D+/ D : MeV, 3He+2: MeV, 4He+2: MeV
8 DSB induction and repair cyclotron U-120M 8
9 Proton Therapy Center Prague - Cyclotron IBA MeV PBS Pencil Beam Scanning mode First patient on
10 RBE of proton SOBP SOBP 1Gy: D (Gy) Survival RBE
11 Tandetron 4130 MC Installed in NPI in 2005 Accelerating ions of most of elements from H to Au with energies from MeV and intensities up to tens of μa. The main laboratory accessories are devices for material characterization by standard nuclear analytical techniques (RBS, RBS-channeling, ERDA, ERDA-TOF, PIXE, PIGE, and Ion-Microprobe with 1 μm lateral resolution) and for high-energy implantation. 3 fluencies of 2 MeV protons beginning end mean approx.dose samples protons/s 22min, 32x32mm Gy Gy Gy Gy At the Tandetron facility, the cells were irradiated on 5 mm Mylar foils, because of the low range of the protons and alpha particles. Special holder has been installed for the movement of the sample.
12 Micronuclei Micronuclei formation in human neonatal fibroblasts at first division after irradiation by 30 MeV proton beam A) proton scanning pristine beam, B) broad fixed beam. At least 1000 cells was scored and calculated %BNC from total cells, %BNC with MN from total BNC, and MNC with MN from total MNC. Proportion of binuclear cells reflects the cell division capacity, which decreases with increasing dose. Percent of binuclear cells with micronuclei was increasing with increasing absorbed dose (* - P<0.05, ** - P<0.01, *** - P<0.001).
13 Deterministic and stochastic effects of IR Deterministic effects develop due to cell killing by high dose radiation, appear above a given threshold dose, which is considerably higher than doses from natural radiation or from occupational exposure at normal operation, the severity of the effect depends on the dose, at a given high dose the effect is observed in severe form in all exposed cells, at higher doses the effect cannot increase. 100% 0% Deterministic effects Stochastic effects Dose Stochastic effects develop due to mutation effects of low dose radiation, the threshold dose is not known accurately; it is observed that cancer of different location appears above different dose ranges, the severity of the effect does not depend on the dose, but the frequency of the appearance of the (probabilistic) effect in the exposed population group is dose dependent, (in most cases) linearly increasing with the dose. - Cancer, stroke, hearth, gastrointestinal and respiratory diseases
14 Radiation damage at cellular level Stochastic effects of radiation are related to DNA damage and thus to effects at cellular level The processing and misrepair of radiation induced DSB and complex DNA damages are principally responsible for chromosome/gene alterations that manifest as chromosome aberrations and somatic cell mutations Mutations: from point mutations in single genes to deletions that encompass several physically linked genes Radiation induced spectrum of mutations differs from spontaneous mutations, mutations induced by UV and many chemical mutagens
15 Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) The probes: repetitive and "unique" sequences. Targets: Metaphase chromosomes Interphase nuclei Extended chromatin fibers Entire Cells/RNA Tissue sections FISH applies fluorescently labeled DNA probes to detect gene or chromosome abnormalities that are generally beyond the resolution of routine cytogenetics. The DNA is first denatured. The fluorescently labeled probe is added and hybridizes with the sample DNA at the target site as it reanneals back into a double helix. The probe signal can be seen through a fluorescent microscope. (nucleolus organizing region)
16 Chromosome aberrations detected by FISH Reciprocal Exchanges (RE) Complex Exchanges (CE) translocation dicentric tricentric centric ring insertion Incomplete Exchanges (IE) Breaks Can be transferred to offspring, others are lethal incomplete translocation incomplete dicentrics terminal and interstitial deletions
17 Dose-effect relationship Current understanding of mechanisms and quantitative data on dose and time-dose relationships support a linear dose response at low doses (i.e., LNT) for total cancer risk (ICRP 99 - Low-dose Extrapolation of Radiation-related Cancer Risk, 2005 ) Cancer risk Dose (Gy)
18 Microbeam irradiations Track-etch plastic showing single hits by 3MeV protons, spaced at 20 micrometer intervals. Gray Cancer Institute, report precision sub-micron up to several microns - up to cells per hour - X and g rays, electrons, ions up to argon nuclei
19 By-stander effects Up to the early 1990 s: important biological effects are produced only very close neighborhood of the tracks and within cell nucleus; Cellular responses induced via bystander effect include chromosomal aberrations, mutations, cell death, apoptosis, malignant transformation and genomic instability. 1-30% of nonirradiated cells found in different cell systems and signaling mechanism appear to be involved (role of cytokines, ROS = reactive oxygen species)
20 Bystander signals COX2 - cyclooxygenase 2 DR5 - death receptor 5 IL interleukin JNK - Jun N-terminal kinase NO - nitric oxide NOS2 - NO synthase 2 ROS - reactive oxygen species TGFb transforming growth factor b TGFbR - TGFb receptor TNFa - tumor necrosis factor a TRAIL - TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Prise and O Sullivan, Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 351, 2009, copyright 2009 Through gap junctions and the cytokine signals into the extracellular matrix. In vivo: macrophages may be important mediators, which release bystander signals affecting nonirradiated cells. Cytokine-mediated signaling, signal transduction through MAPKs and nuclear factor kb alongside the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
21 Mutation frequency Risk? Dose (Gy)
22 Adaptive response and bystander effect Adaptive response = pre-exposing cell to a low priming dose appear to protect these cells from the deleterious effects of second, larger dose Sawant et al., Radiat. Res. 156, 177, 2001
23 Adaptive response Both in vivo and in vitro Humans and animals In normal and tumour cells For different endpoints: chromosomal aberrations, micronuclei formation, gene mutations, cell killing Doses in the range mgy, decline above 200 mgy, disappear above 500 mgy Hypothesis: enhance DNA repair ability and cellular antioxydant activity Adaptive response and apoptosis possibly constitute a complementary defense mechanism Cancer risk? Dose (Gy)
24 Genomic instability Observed in number of different cellular systems whereby radiation exposure induces a type of instability in individual cells that is transmitted to their progeny leading to a persistent enhancement in the rate at which genetic changes arise in the descendants of irradiated cells after many generations of replication Radiation diverse endpoints: large-scale chromosomal rearrangements, deletions and aberrations, gene amplification (extra copies of specific DNA segments), aneuploidy (wrong number of chromosomes), micronucleus formation and gene mutation. The capacity of radiation to induce genomic instability depends to a large extent on radiation quality or linear energy transfer (LET) and dose. There appears to be a low dose threshold effect with low LET, beyond which no additional genomic instability is induced. Low doses of both high and low LET radiation are capable of inducing this phenomenon.
25 Conclusions Chromosome aberrations and somatic cell mutations suggest linear dose-effect relationship at low dose region. There exist the by-stander effect, adaptive response and genomic instability which may influence the nature of dose response relationship at low doses and low doserates. Dose response at low doses of ionizing radiation is at present uncertain and a simple extrapolation from high doses may not be appropriate. Cancer risk? Dose (Gy) The better understanding of the mechanisms for these phenomena, the extent to which they are active in vivo and how they are interrelated is necessary before they can be confirmed as factors to be included in the estimation of potential risk to the human population of exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation.
26 Cell response to extremely low levels of IR Gran Sasso National Laboratory INFN, Italy Adopted from Nature 485, 435, 2012
27 First radiobiology experiments in LNGS (1992-3) yeast cells (Saccharomyces cereuisiae D7) 120 generations - 4 msv in ISS, 0.6 msv in LNGS - cells treated by different concentrations of metyl methasulfonate (MMS, an alkylating agent and a carcinogen ) Satta et al. Mutation Research 347, , 1995 Induction of Ade-2 reciprocal recombinants or aberrant has been followed (single event of crossing-over at the Ade-2 locus provokes formation of a twin spot red-pink colonies, other recombinational rearrangements lead to red, pink or sectored colonies). Mitotic intergenic recombination is a signature of DNA damage cells cultivated at extremely low radiation background lose their ability to deal with DNA damage
28 LNGS vs ISS human lymphoblastoid TK6 cells Carbone et al. Radiat. Environ Biophys. 48, 189, increase in micronuclei formation after 2 Gy X-rays cells cultivated at extremely low radiation background lose their ability to deal with DNA damage - decrease of antioxidant enzymatic activity after 6 months growth at the ISS and LNGS - SOD - superoxide dismutase - CAT - catalase - SE-GPx - selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase
29 Collaboration perspectives Underground Laboratory Modane (Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane, LSM) CNRS/IN2P3 (LSM), France (1700 m underground) Adopted from
30 Future perspectives Further decrease of natural radiation background level in the Underground Laboratory in Modane, France investigate the mechanisms involved in low dose radiation response of human/rodent cell cultures kept in conditions of extremely low levels of background ionizing radiation or in reference background radiation laboratories: changes of the cell cycle regulation, cell proliferation and stability of the genome, gene expression of stress response enzymes The main outcome of the project shall be determination of mechanisms regulated by low radiation doses which are necessary for physiological functioning and ability to cope with DNA damage.
31 Thank you for your attention
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons
 Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc.
 Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE
 COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation
 The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Edouard Azzam New Jersey Medical School Newark, USA Two phenomena have been recently implicated
The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Edouard Azzam New Jersey Medical School Newark, USA Two phenomena have been recently implicated
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology
 The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Determination of Radon Concentration in Some Types of Cigarettes
 Determination of Radon Concentration in Some Types of Cigarettes Tarfa.H.Alsheddi 1, Amal Mohamed 2 and Shaffa.Al.Mansour 3 1 Department of physics, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia. 2 Department of
Determination of Radon Concentration in Some Types of Cigarettes Tarfa.H.Alsheddi 1, Amal Mohamed 2 and Shaffa.Al.Mansour 3 1 Department of physics, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia. 2 Department of
María José Mesa López
 María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
A. Incorrect! All the cells have the same set of genes. (D)Because different types of cells have different types of transcriptional factors.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program
 U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
What is radiation quality?
 What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
The application of 1.6 MeV proton microbeam to investigate radiation-induced bystander effect in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell line
 The application of 1.6 MeV proton microbeam to investigate radiation-induced bystander effect in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell line Elena LAGZDINA, Mindaugas GASPARIŪNAS, Rita PLUKIENĖ, Artūras PLUKIS,
The application of 1.6 MeV proton microbeam to investigate radiation-induced bystander effect in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell line Elena LAGZDINA, Mindaugas GASPARIŪNAS, Rita PLUKIENĖ, Artūras PLUKIS,
LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Radiation Effects in Life Sciences
 Radiation Effects in Life Sciences oocyte eggs in uterus spermatheca gonad Quality of Radiation Biological Effects Applications of SSD in Life sciences Nanodosimetry Particle Microscope (pct) vulva Radiation
Radiation Effects in Life Sciences oocyte eggs in uterus spermatheca gonad Quality of Radiation Biological Effects Applications of SSD in Life sciences Nanodosimetry Particle Microscope (pct) vulva Radiation
FISH and PNA-FISH. FISH and PNA-FISH. Stochastic effect. Radiation and cancer. 1) chromosome 2) FISH 3) PNA-FISH. Chromosome translocations.
 BIODOSIMETRY IN THE 21 st CENTURY Training Meeting HICARE in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency Hiroshima, Japan, June 10-14, 2013. FISH and FISH and Satoshi Tashiro Research Institute
BIODOSIMETRY IN THE 21 st CENTURY Training Meeting HICARE in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency Hiroshima, Japan, June 10-14, 2013. FISH and FISH and Satoshi Tashiro Research Institute
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage
 Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam
 Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Two-Dimensional Thermoluminescence Dosimetry System for Proton Beam Quality Assurance
 Two-Dimensional Thermoluminescence Dosimetry System for Proton Beam Quality Assurance Jan Gajewski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Kraków, Poland German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany Existing
Two-Dimensional Thermoluminescence Dosimetry System for Proton Beam Quality Assurance Jan Gajewski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Kraków, Poland German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany Existing
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle
 CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
HUMAN LUNG CANCER RISKS FROM RADON PART II INFLUENCE FROM COMBINED ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER EFFECTS A MICRODOSE ANALYSIS
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 9 Issue 4 Article 8 12-2011 HUMAN LUNG CANCER RISKS FROM RADON PART II INFLUENCE FROM COMBINED ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER EFFECTS A MICRODOSE ANALYSIS
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 9 Issue 4 Article 8 12-2011 HUMAN LUNG CANCER RISKS FROM RADON PART II INFLUENCE FROM COMBINED ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER EFFECTS A MICRODOSE ANALYSIS
INTRODUCTION Many researchers have found strong positive correlation between b increase in incidence of chromosome aberrations and the impact of small
 COMPARATIVE CYTOGENETIC ANALYSIS OF CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS AND PREMATURE CENTROMERE DIVISION IN PERSONS EXPOSED TO RADIONUCLIDES Dubravka Jovičić 1, Boban Rakić 2, Tanja Vukov 3, Jelena Pajić 2, Snežana
COMPARATIVE CYTOGENETIC ANALYSIS OF CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS AND PREMATURE CENTROMERE DIVISION IN PERSONS EXPOSED TO RADIONUCLIDES Dubravka Jovičić 1, Boban Rakić 2, Tanja Vukov 3, Jelena Pajić 2, Snežana
HEALTH RISKS FROM EXPOSURE TO FAST NEUTRONS. Prof. Marco Durante
 HEALTH RISKS FROM EXPOSURE TO FAST NEUTRONS Prof. Marco Durante Risk from neutrons Risk from exposure to fission spectrum neutrons has been extensively studied in the 60 s at nuclear reactors using animal
HEALTH RISKS FROM EXPOSURE TO FAST NEUTRONS Prof. Marco Durante Risk from neutrons Risk from exposure to fission spectrum neutrons has been extensively studied in the 60 s at nuclear reactors using animal
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Chapter 7. What is Radiation Biology? Ionizing Radiation. Energy Transfer Determinants 09/21/2014
 Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Characterization and implementation of Pencil Beam Scanning proton therapy techniques: from spot scanning to continuous scanning
 Characterization and implementation of Pencil Beam Scanning proton therapy techniques: from spot scanning to continuous scanning Supervisors Prof. V. Patera PhD R. Van Roermund Candidate Annalisa Patriarca
Characterization and implementation of Pencil Beam Scanning proton therapy techniques: from spot scanning to continuous scanning Supervisors Prof. V. Patera PhD R. Van Roermund Candidate Annalisa Patriarca
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
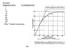 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
 RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation
 EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2006 Report Volume II Scientific Annexes C, D and E EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations
EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2006 Report Volume II Scientific Annexes C, D and E EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations
The use of radiation microbeams to investigate the bystander effect in cells and tissues
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 580 (2007) 446 450 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima The use of radiation microbeams to investigate the bystander effect in cells and tissues M. Folkard
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 580 (2007) 446 450 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima The use of radiation microbeams to investigate the bystander effect in cells and tissues M. Folkard
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model
 Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure
 Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
NEUTRONS. 1. Exposure Data
 NEUTRONS 1. Exposure Data Exposure to neutrons can occur from the nuclear fission reactions usually associated with the production of nuclear energy, from cosmic radiation in the natural environment and
NEUTRONS 1. Exposure Data Exposure to neutrons can occur from the nuclear fission reactions usually associated with the production of nuclear energy, from cosmic radiation in the natural environment and
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function. Ch. 8
 Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Assistant Professor Department of Therapeutic Radiology Yale University School of Medicine
 A Mechanism-Based Approach to Predict Relative Biological i Effectiveness and the Effects of Tumor Hypoxia in Charged Particle Radiotherapy David J. Carlson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Therapeutic
A Mechanism-Based Approach to Predict Relative Biological i Effectiveness and the Effects of Tumor Hypoxia in Charged Particle Radiotherapy David J. Carlson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Therapeutic
Radiation Health Effects
 Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
The Promise and Pitfalls of Mechanistic Modeling in Radiation Oncology
 The Promise and Pitfalls of Mechanistic Modeling in Radiation Oncology Robert D. Stewart, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology University of Washington School of Medicine Department of Radiation
The Promise and Pitfalls of Mechanistic Modeling in Radiation Oncology Robert D. Stewart, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology University of Washington School of Medicine Department of Radiation
Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection
 1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FACR, FAAPM Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Adjunct Assistant Professor (Radiology) GWU School
1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FACR, FAAPM Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Adjunct Assistant Professor (Radiology) GWU School
Radiation physics and radiation protection. University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Chromosome Abnormalities
 Chromosome Abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities vs. molecular mutations Simply a matter of size Chromosomal abnormalities are big errors Two types of abnormalities 1. Constitutional problem present
Chromosome Abnormalities Chromosomal abnormalities vs. molecular mutations Simply a matter of size Chromosomal abnormalities are big errors Two types of abnormalities 1. Constitutional problem present
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Possible Consequences of Inhomogeneous Suborgan Distribution of Dose and the Linear No-Threshold Dose-Effect Relationship
 Possible Consequences of Inhomogeneous Suborgan Distribution of Dose and the Linear No-Threshold Dose-Effect Relationship Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy Centre for Energy Research, Hungarian Academy of
Possible Consequences of Inhomogeneous Suborgan Distribution of Dose and the Linear No-Threshold Dose-Effect Relationship Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy Centre for Energy Research, Hungarian Academy of
CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
 CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION Ron Mitchel Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River,
CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION Ron Mitchel Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River,
C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than. O-Beam
 1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation. Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic
 Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) 2007 National Academy of Science National Research
Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) 2007 National Academy of Science National Research
A Commentary on: A History of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Low Dose Radiation Research Program: Dr. Antone L.
 A Commentary on: A History of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Low Dose Radiation Research Program: 1998 2008 Dr. Antone L. Brooks 1 1. Retired, Washington State University 1 6802 West 13 th
A Commentary on: A History of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Low Dose Radiation Research Program: 1998 2008 Dr. Antone L. Brooks 1 1. Retired, Washington State University 1 6802 West 13 th
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Dose-Response Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University
 Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University Outline Bystander effects and genomic instability In vivo relevance and evidence The fish model
Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University Outline Bystander effects and genomic instability In vivo relevance and evidence The fish model
Ionizing Radiation. Michael J. Vala, CHP. Bristol-Myers Squibb
 Ionizing Radiation Michael J. Vala, CHP Bristol-Myers Squibb michael.vala@bms.com 732-227-5096 2013 American Industrial Hygiene Association, New Jersey Section, Inc. Course Objectives At the end of this
Ionizing Radiation Michael J. Vala, CHP Bristol-Myers Squibb michael.vala@bms.com 732-227-5096 2013 American Industrial Hygiene Association, New Jersey Section, Inc. Course Objectives At the end of this
Applications of Particle Accelerators
 Applications of Particle Accelerators Prof. Rob Edgecock STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory EMMA Accelerator at Daresbury Laboratory Applications >30000 accelerators in use world-wide: 44% for radiotherapy
Applications of Particle Accelerators Prof. Rob Edgecock STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory EMMA Accelerator at Daresbury Laboratory Applications >30000 accelerators in use world-wide: 44% for radiotherapy
CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS
 10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned. Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago
 The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
Radiation Protection
 2007 CERN Accelerator School (The bases of) Radiation Protection Marco Silari CERN, Geneva, Switzerland M. Silari Radiation Protection 21.09.2007 1 Introduction To tell you in one hour all about radiation
2007 CERN Accelerator School (The bases of) Radiation Protection Marco Silari CERN, Geneva, Switzerland M. Silari Radiation Protection 21.09.2007 1 Introduction To tell you in one hour all about radiation
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology
 Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Advances in biological dosimetry
 Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Importance of Radiation Dosimetry standards in preclinical radiobiology studies
 Importance of Radiation Dosimetry standards in preclinical radiobiology studies Ceferino Obcemea Radiation Research Program National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, USA CIRMS 2018 No financial conflict
Importance of Radiation Dosimetry standards in preclinical radiobiology studies Ceferino Obcemea Radiation Research Program National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, USA CIRMS 2018 No financial conflict
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
Application of the Commission's Recommendations for the Protection of People in
 ICRP Publication 127 ICRP Publication 126 ICRP Publication 125 ICRP Publication 124 ICRP Publication 123 ICRP Publication 122 ICRP Publication 121 ICRP Publication 120 ICRP 2011 Proceedings Radiological
ICRP Publication 127 ICRP Publication 126 ICRP Publication 125 ICRP Publication 124 ICRP Publication 123 ICRP Publication 122 ICRP Publication 121 ICRP Publication 120 ICRP 2011 Proceedings Radiological
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
Lecture -2- Environmental Biotechnology
 Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Medical- and Radiation Physics Research at Surrey
 Medical- and Radiation Physics Research at Surrey D.A. Bradley Department of Physics Centre for Nuclear and Radiation Physics University of Surrey Guildford United Kingdom * d.a.bradley@surrey.ac.uk Topic
Medical- and Radiation Physics Research at Surrey D.A. Bradley Department of Physics Centre for Nuclear and Radiation Physics University of Surrey Guildford United Kingdom * d.a.bradley@surrey.ac.uk Topic
ICRP 128 ICRP ICRP ICRP 1928
 ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 1928 ICRP ICRP ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 129 ICRP 128 Radiological Protection in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Radiation Dose to Patients from Radiopharmaceuticals: A Compendium of Current
ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 1928 ICRP ICRP ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 129 ICRP 128 Radiological Protection in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Radiation Dose to Patients from Radiopharmaceuticals: A Compendium of Current
Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach. R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham
 Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch, AECL, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River
Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch, AECL, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River
An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013)
 ISCN 2013 An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013) Editors Lisa G. Shaffer Jean McGowan-Jordan Michael Schmid Recommendations of the International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic
ISCN 2013 An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013) Editors Lisa G. Shaffer Jean McGowan-Jordan Michael Schmid Recommendations of the International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis
 Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Radioactivity. Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radioactivity Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation Studies of impact of ionizing radiation on the human body - Hiroshima - US-Japanese teams medical tests, autopsies, human organ analysis, on-site
Radioactivity Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation Studies of impact of ionizing radiation on the human body - Hiroshima - US-Japanese teams medical tests, autopsies, human organ analysis, on-site
INFLUENCE OF CELL ENVIRONMENT ON MICRONUCLEATION IN CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY CELLS. A Dissertation NATALIA GENNADIEVNA MEDVEDEVA
 INFLUENCE OF CELL ENVIRONMENT ON MICRONUCLEATION IN CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY CELLS A Dissertation by NATALIA GENNADIEVNA MEDVEDEVA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial
INFLUENCE OF CELL ENVIRONMENT ON MICRONUCLEATION IN CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY CELLS A Dissertation by NATALIA GENNADIEVNA MEDVEDEVA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in vitro
 Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25:195-199 Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in
Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25:195-199 Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in
Advances in Radiobiological Studies Using a Microbeam
 J. Radiat. Res., 50: Suppl., A7-A12 (2009) Advances in Radiobiological Studies Using a Microbeam Tom K. HEI 1,2,3 *, Leslie K. BALLAS 2, David J. BRENNER 1,3 and Charles R. GEARD 1 Microbeam/3D human tissues/arabidopsis/bystander
J. Radiat. Res., 50: Suppl., A7-A12 (2009) Advances in Radiobiological Studies Using a Microbeam Tom K. HEI 1,2,3 *, Leslie K. BALLAS 2, David J. BRENNER 1,3 and Charles R. GEARD 1 Microbeam/3D human tissues/arabidopsis/bystander
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment
 Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are group of very unstable compounds that
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are group of very unstable compounds that
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting
 BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW
 RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW PILLALAMARRI ILA Earth Atmospheric & Planetary Sciences Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 IAP
RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW PILLALAMARRI ILA Earth Atmospheric & Planetary Sciences Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 IAP
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy
 Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation
 J. RADIAT. RES., 40: SUPPL., 53 59 (1999) Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation RICHARD C. MILLER 1 *, STEPHEN A. MARINO 1, STEWART G. MARTlN 2, KENSHI KOMATSU 3, CHARLES
J. RADIAT. RES., 40: SUPPL., 53 59 (1999) Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation RICHARD C. MILLER 1 *, STEPHEN A. MARINO 1, STEWART G. MARTlN 2, KENSHI KOMATSU 3, CHARLES
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Ionizing Radiation. Nuclear Medicine
 Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1
 J. Radiat. Res., 47: Suppl., B19 B24 (2006) Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1 Christian STREFFER* Genomic instability/malformation/transgenerational
J. Radiat. Res., 47: Suppl., B19 B24 (2006) Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1 Christian STREFFER* Genomic instability/malformation/transgenerational
Direct evidence for a bystander effect of ionizing radiation in primary human fibroblasts
 doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2000.1665, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com Direct evidence for a bystander effect of ionizing radiation in primary human fibroblasts OV Belyakov,
doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2000.1665, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com Direct evidence for a bystander effect of ionizing radiation in primary human fibroblasts OV Belyakov,
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research
 Mutation Research 659 (2008) 211 220 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/reviewsmr Community address: www.elsevier.com/locate/mutres
Mutation Research 659 (2008) 211 220 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/reviewsmr Community address: www.elsevier.com/locate/mutres
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells
 The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
UQ X-ray Safety Training Module
 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module 23 January 2018, v2 1 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module Course Overview: This training module has been developed for workers at the University of Queensland, and forms part
UQ X-ray Safety Training Module 23 January 2018, v2 1 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module Course Overview: This training module has been developed for workers at the University of Queensland, and forms part
Are non-targeted effects important in radiation protection? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour McMaster University Canada
 Are non-targeted effects important in radiation protection? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour McMaster University Canada Non-targeted radiation effects Inter-animal/plant signaling Effects in neighbouring
Are non-targeted effects important in radiation protection? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour McMaster University Canada Non-targeted radiation effects Inter-animal/plant signaling Effects in neighbouring
III. Proton-therapytherapy. Rome SB - 5/5 1
 Outline Introduction: an historical review I Applications in medical diagnostics Particle accelerators for medicine Applications in conventional radiation therapy II III IV Hadrontherapy, the frontier
Outline Introduction: an historical review I Applications in medical diagnostics Particle accelerators for medicine Applications in conventional radiation therapy II III IV Hadrontherapy, the frontier
The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE
 The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE Andrea Ottolenghi, Klaus Trott, Giorgio Baiocco, Vere Smyth Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy On behalf of the ANDANTE project MELODI
The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE Andrea Ottolenghi, Klaus Trott, Giorgio Baiocco, Vere Smyth Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy On behalf of the ANDANTE project MELODI
SOURCES AND EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION
 SOURCES AND EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes VOLUME II: EFFECTS UNITED
SOURCES AND EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes VOLUME II: EFFECTS UNITED
Space Radiation Risks for Long. Duration Missions Edward Semones
 Space Radiation Risks for Long Duration Missions Edward Semones Radiation Health Officer Space Life Sciences Directorate Johnson Space Center Presented to the American Astronautical Society November 16,
Space Radiation Risks for Long Duration Missions Edward Semones Radiation Health Officer Space Life Sciences Directorate Johnson Space Center Presented to the American Astronautical Society November 16,
Neutrons. ρ σ. where. Neutrons act like photons in the sense that they are attenuated as. Unlike photons, neutrons interact via the strong interaction
 Neutrons Neutrons act like photons in the sense that they are attenuated as I = I 0 e μx where Unlike photons, neutrons interact via the strong interaction μ = The cross sections are much smaller than
Neutrons Neutrons act like photons in the sense that they are attenuated as I = I 0 e μx where Unlike photons, neutrons interact via the strong interaction μ = The cross sections are much smaller than
Acquisition of Radiation Resistant Ability in Non- Irradiated Cells by Secreted Factors from Low Dose Irradiated Cells
 Nagoya University Acquisition of Radiation Resistant Ability in Non- Irradiated Cells by Secreted Factors from Low Dose Irradiated Cells Jun Kumagai a *, Akane Oohashi b and Genro Kashino c a Institute
Nagoya University Acquisition of Radiation Resistant Ability in Non- Irradiated Cells by Secreted Factors from Low Dose Irradiated Cells Jun Kumagai a *, Akane Oohashi b and Genro Kashino c a Institute
VICH GL23: Studies to evaluate the safety of residues of veterinary drugs in human food: genotoxicity testing
 6 November 2014 EMA/CVMP/VICH/526/2000 Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) VICH GL23: Studies to evaluate the safety of residues of veterinary drugs in human food: genotoxicity testing
6 November 2014 EMA/CVMP/VICH/526/2000 Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) VICH GL23: Studies to evaluate the safety of residues of veterinary drugs in human food: genotoxicity testing
Multistep Carcinogenesis
 Multistep Carcinogenesis M.Rosemann, Institute for Radiation Biology Helmholtz Center Munich, Research Centre for Health and Environment The Hallmarks of Cancer D.Hanahan, Cell 2011 The Hallmarks of Cancer
Multistep Carcinogenesis M.Rosemann, Institute for Radiation Biology Helmholtz Center Munich, Research Centre for Health and Environment The Hallmarks of Cancer D.Hanahan, Cell 2011 The Hallmarks of Cancer
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
