AN OPERATION FOR HIATUS HERNIA WITH SHORT OESOPHAGUS
|
|
|
- Margery Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax (1957), 12, 181. AN OPERATION FOR HIATUS HERNIA WITH SHORT OESOPHAGUS BY J. LEIGH COLLIS From tile Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birminghan The patient with a hiatus hernia and a markedly short oesophagus presents a problem for which there is not at present a generally accepted line of treatment. There are gross macroscopic changes in the oesophagus and they tend to give rise to severe pain and dysphagia. The shortening of the oesophagus makes the problem unsuitable for treatment by the standard operations for hiatus hernia, while some of the suggested treatments, such as oesophago-jejunostomy, are so formidable that they are unsuitable for the frail and often aged subjects. Anatomical and physiological investigations which were published in 1954 led me to refashion my operative technique for the problem of hiatus hernia generally (Collis, Kelly, and Wiley, 1954). These investigations and the experience with the modified technique demonstrated certain points which seemed to have a special bearing on the difficult problem of the patient with a short oesophagus. Evidence was put forward in that paper to show that some infants with a hiatus hernia lose their symptoms before they lose the radiologically demonstrable hiatus hernia. It was suggested that this was due to the development of tone in the crural fibres so that gross reflux from the stomach below the diaphragm is controlled. The small amount of reflux which remains is sufficient to allow fluid to enter the gastric pouch above the diaphragm, but the force of the reflux is weak and can be controlled by the sphincter action at the cardia. If these children are followed up, it will be seen that further complete power to control reflux at the hiatus will usually be developed and when this is effected the hernia will in most cases remain reduced. This reduction does not always take place, but if the control at the hiatus is good the condition is very difficult to demonstrate radiologically and can only be shown at oesophagoscopy. This state of affairs is often referred to as a gastric-lined oesophagus. (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MARCH 29, 1957) This situation holds dangers for the patients in later life, but is compatible with many years of either symptom-free existence or a state of only trivial trouble. It seemed reasonable to wonder if something along similar lines could not be arranged for patients with established short oesophagus and free reflux. The essential part of the refashioned operation described in 1954 was that an acute angle of implantation between the stomach and the oesophagus should be formed. This is effected by suturing the two limbs of the right crus above and in front of the oesophagus. As a result of this, the point around which the oesophago-gastric junction angulates is lowered, with the effect that the angle automatically becomes more acute. The operative technique was fully described and it is only necessary to add that it has continued to give good results. The point of particular importance here is that the operation was used on some cases in which the oesophagus was short, and as a result the cardia could not be returned to the hiatus. The results in this group were not perfect, but it was clear that in many cases reflux could be controlled and symptomatic relief given. The weakness of this procedure was a technical one, in that there was too much bulk tissue occupying the oesophageal hiatus, so that a satisfactory angle between the stomach above the diaphragm and that below could not be produced. The suggestion that is now being made is that gastric tissue can be used to form the connecting tube between the lower end of the short oesophagus and the main body of the stomach within the abdomen. In view of the possible disadvantages of the use of this tissue it is desirable to have a clear knowledge of the physiological secretions of the part involved. In 1934 Berger described a careful study of the distribution of the parietal cells of the stomach which are the
2 182 J. LEIGH COLLIS FRc..-Fhis diagram is taken from the paper by Berger. The inaltl bodv of the stomacih is shaded black and is rich in parietal cells whicih produce HCI. Relatise to this thie shaded area at thie calrdia only has 50(). of the parietal cells. main source of hydrochloric acid. Fig. I is reproduced ftronm Berger's paper to show the arrangement. From this it will be seen that the area adjacent to the cardia has only a limited supply but that milost ot the lesser curve is well supplied. A series of sections was made from gastric tissue to confirm this statement. Another important work on this subject was produced by Billenkamp in He made a special study of the magenstrasse in 1 5 different species, including man, and he found that the mucosa of this area was thinner in man than other parts of the stomach and that it was practically devoid of peptic glands. It would seem that the area of the cardia and lesser curve has a definite power of producing acid bitt that it is deficient in its power to produce pepsin. GENERAL PLAN or OPERATION In view of the experience from congenital defects in this area and the work of Berger (1934) and Billenkamp (1929), it seems reasonable to pit forward a plan for using a gastric connecting link between the short oesophagus above and the main body of the stomach below the diaphragm, provided that certain precautions are taken. First, it is necessary to use onlv gastric tissule of the magenstrasse. Secondly, an cffective Xalve action must be obtained so that reflulx is prevented from the main body of the stomach into the cotinecting link and oesophagus above. Thirdly. it seems desirable that as narrow a tube of stomach as possible is used so that the amount ol gastric secretion should be minimal. TECHNIQUE OF OPERAT ION The patient is placed on his right side xith his whole body rotated a little backwards. An abdomino-thoracic incision is made froimi the iinibilicus to the edge of the trapzzitls along the line of the seventh or eighth rib The chest and abdomen are opened bv resection ot onie otother of these ribs. It is found desirable to remove a segment of the costal margin. The incision in the diaphragm should be made as tailaterally as possible so as to minimize the nulimbet of filaments of the phrenic nerve which are CLut. For the same reason it should only be taken to ai point half an inch short of the central tendoin. [his is important to ensure generally good function in the diaphragm after this operation. A small amount of lateral weakness is not a disadvantage. The mediastinum is dissected so as to demonstrate the short oesophagus and stomach pouch. In sonie cases it will be found that so muich extrt. length of oesophagus can be obtained by this dissection to effect a standard plastic repair. When this cannot be achieved the gastric pouch is carefully cleared of vascular attachments so that its surface is smooth and clean. In order to do this it is useful to be able to inspect the stomach from below and to bring extra stomach up into the chest. When this stage is completed the anaesthetist passes a No. 9 (English gauge) stomach tube from the mouth into the intra-abdominal part ot the stomach. Parker-Kerr clamps are then applied as shown in Fig. 3. The distal ends of these clamps are brouiiht as close as possible to the simall stomach tube and lesser curve. The object of this is to make certain that the tube of stomach at this point will be as narrow as possible. The stomach is incised between the clamps and the free cuff sewn up before the clamps are removed. After removing the clamps the suture line is invaginated. The position now is as shown in Fig. 4. The part of the stomach pouch to the left is now returned below the diaphragm and has the effect of enlarging the fundus. Above the diaphragm a portion of the pouch remains which will from now on be referred to as the "connecting tube."
3 HI/A T(S H/ERVNIA FIG. 2.-This is a diagrammatic representation of the condition under consideration. A hiatus hernia is present with a short oesophagus. A broad neck of gastric tissue occupies the diaphragmatic hiatus. AFTEf' DIV/S/ON ANVD SLSUTURF FIG. 4.-This shows the position after the clamps have been removed and the stomach incised. The pouch of the hiatus hernias now been divided into two parts. First there is the part along the lesser curve which is the connecting tube, and secondly there is the part to the left which is going to be given back to the fundus. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 September Downloaded from POS/ TION/ FOR CLAMPS LOWER PART RE TURNVED TO ABDOMENV FIG. 3.-The parallel dark lines show the position in which the clamps FIG. 5.-The oesophagus and the connecting tube only remain above are placed. The lower end of the clamp is brought as close as the diaphragm. Only a narrow neck of gastric tissue is now in possible to the lesser curve. When the clamps are on, the the diaphragmatic hiatus. Around this narrow tube a satisgastric pouch is divided by them into two halves. factory plastic repair of the fibres of the right crus can be performed. on 14 June 2018 by guest. Protected by
4 The last phase of the operation is the plastic repair as described earlier in Thorax (Collis, Kelly, and Wiley, 1954). It is done from below the diaphragm. The under surface of the fibres of the right crus are dissected clean of everything except peritoneum, which is carefully preserved. The limbs of the right crus are now sutured together above and in front of the connecting tube. This produces an acute angle between the connecting tube and the main body of the stomach. As the diaphragm is closed the stomach is included in two of the stitches in order to retain the connecting tube and oesophagus in position. The chest and abdomen are closed with intercostal drainage for 48 hours. RESULTS Fig. 6 is a typical example of the type of case for which this operation has been done. Fig. 7 shows the same case after gastroplasty. The connecting tube can be seen. A good angle of implantation into the stomach had been produced and no regurgitation could be induced at barium swallow examination. The operation has been carried out on nine patients between April, 1955, and September, Seven were women and two were men. Their ages were between 50 and 70 in seven of the patients. The other two were aged 31 and 37 years. All had gross symptoms. Dysphagia was prominent in seven patients and one had had many oesophagoscopies for dilatation. At oesophagoscopy oesophagitis was marked in all cases, with ulceration noted in five. The oesophageal length was between 29 and 34 cm. It is to be noted that the grossest forms of short oesophagus have not been treated this way so far. After operation one of the patients who was apparently making good progress died with a coronary thrombosis. He was aged 67. In the first case, in a woman aged 31, reflux was not satisfactorily controlled, and although she is improved her condition is not considered satisfactory. The post-operative result in the other seven is excellent. A check barium swallow has been done in all of these between eight and 12 months from operation and in six no reflux could be produced. In one only slight reflux occurred. At the same period after operation these patients were also checked by oesophagoscopy and the complete absence of oesophagitis and stricture was noted. No patient has required post-operative oesophagoscopy and dilatation. This is in spite of the previous dilatations required in one case. It is to be noted that in the immediate post-operative period marked dysphagia was present in most patients and that FIG. 6.-This is a barium swallow film to show the type of case for which the operation has been done, i.e., an irreducible hiatus hernia with a short oesophagus. There is marked narrowing at the cardia and the patient had gross dysphagia. FIG. 7.-This is the same patient as shown in Fig. 6. A gastroplasty has now been performed. The connecting tube can clearly be seen with the cardia in about the same position as before operation. It is to be noted that the narrowing at the cardia has gone and this is in spite of no post-operative dilatation.
5 OPERATION FOR HIATUS HERNIA WITH SHORT OESOPHAGUS APHRAGM -- FIG. 8.-The incision has been made and the wound opened. The incision in the diaphragm is shown, and it will be seen that it stops short of the edge of the central tendon. N \" FIG. 9.-The mediastirnsm has now been dissected to show the stomach pouch and cardia.
6 186 J. LEIGH COLLIS FIG. 10.-The small stomach tube is now in position and the Parker-Kerr clamps have been placed on the stomach pouch. The tips of these clamps are brought as close as possible to the lesser curve. *Nii - -ts *~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1, %.''; ' ri;'i! j;i, ;1 hu " :1! - " r. % o 1..E:
7 Fic,. 12.-The clamps have been removed and the double layer of inv aginating suittures has been inserted. The gastric pouch has now been divided into two parts. To the right is the connecting tube and to the left is the part which will be retturned bclow the diaphragni to acid to the suize of the fundus. COIVNECTING TUBE Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 September Downloaded from FG-.13.-Only the connecting tube now. remains aboe thedeiaphragm-n. It I ies in the nmedias-niuin a ndl gives extra I ength to t he oesophagus so that the plastic repair at The hiatus ws ill be able to fte doren witliout tfznsion. Ft The diaphragrmi is nows retracted upwsards so thlatl the plastic repair of the hiatus cani be done frorti the tinder surface. A ltong line o1f -Liitiires has becin placed beisccrn the vtso limtlbs ot the right1 Lruis. above and in front tlf the stubstitutec for the kiesophaguls. the coinniiecting tutbe. Bv doing this the voint arolund w.uhich the gut anglilates is lowered by the sutjurc line. The fundils with hailf of the gastric poluch added to it is secn on the 1et on 14 June 2018 by guest. Protected by
8 188 it often continued for three weeks from operation. Some slight difficulty in swallowing was often present after this, but in all cases it steadily improved. Some degree of immediate postoperative dysphagia is regarded as desirable and it is felt that if it is not present the operation has not been done properly. Only one major post-operative complication occurred. This was a left subphrenic abscess with a leak from the suture line. The whole condition subsided spontaneously with drainage of the pus. The improvement of the general health of these patients has been remarkable and has resulted in their suffering less from other coexistent diseases. One patient had suffered for many years from narcolepsy and another from Parkinsonism. The symptoms of both conditions have become remarkably less. J. LEIGH COLLIS CONCLUSIONS The operation, which is called gastroplasty, is of considerable magnitude, but is still much smaller than oesophago-jejunostomy, and is well tolerated even by old and weak patients. It leaves the digestive arrangements near normal and there is no problem afterwards with nutrition. Excellent results have been obtained in seven patients, but the unsatisfactory state in the first case must be taken as a warning of the need to narrow the connecting tube sufficiently so that a really good angle of implantation can be obtained. The procedure has not been used on the very short oesophagi where the cardia is in the region of the aortic arch or above. The reason for this is conservatism, and it is felt that results justify its use for these also. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 September Downloaded from Attention has been drawn to the spontaneous relief of dysphagia after this operation. By this it is intended to suggest that many strictures which are generally believed to be fibrous are in fact mainly produced by reflex spasm. In these cases when the irritation of reflux has been removed and the oesophagitis has subsided the dysphagia will no longer be present. While putting this forward as an observed fact it is fully appreciated that in some strictures fibrous change is present and it is anticipated that oesophagoscopy may well have to be done for dilatation in some cases in the future. SUMMARY An operation is described for the condition of hiatus hernia with short oesophagus. The method involves the use of a small portion of stomach as a connecting link between the oesophagus above and the main body of the stomach below the diaphragm. The results of the use of the procedure in nine patients are described. The operation is referred to as a gastroplasty. I am particularly indebted to Dr. J. C. A. Raison, of the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Warwick, for help in this work. My thanks are also due to Mr. L. Dee, clinical photographer to the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham. REFERENCES Berger, E. H. (1934). Amer. J. Anat., 54, 87. Billenkamp, H. (1929). Beilr. path. Anal., 82, 475. Collis, J. L., Kelly, T. D., and Wiley, A. M. (1954). Thorax, 9, 175. on 14 June 2018 by guest. Protected by
A REVIEW OF SURGICAL RESULTS IN HIATUS HERNIA
 Thorax (1961), 16, 114. A REVIEW OF SURGICAL RESULTS IN HIATUS HERNIA BY J. LEIGH COLLIS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In 1954 a paper was published (Collis, Kelly, and Wiley) which described
Thorax (1961), 16, 114. A REVIEW OF SURGICAL RESULTS IN HIATUS HERNIA BY J. LEIGH COLLIS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In 1954 a paper was published (Collis, Kelly, and Wiley) which described
RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH
 Thorax (1956), 11, 275. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH BY From tile United Leeds Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1956) This is a preliminary report describing
Thorax (1956), 11, 275. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH BY From tile United Leeds Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1956) This is a preliminary report describing
Observations on oesophageal length
 Thorax (1976), 31, 284. Observations on oesophageal length G. J. KALLOOR, A. H. DESHPANDE, and J. LEIGH COLLIS The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Kalloor, G. J., Deshpande, A. H., and Leigh Colfis,
Thorax (1976), 31, 284. Observations on oesophageal length G. J. KALLOOR, A. H. DESHPANDE, and J. LEIGH COLLIS The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Kalloor, G. J., Deshpande, A. H., and Leigh Colfis,
Reflux after cardiomyotomy
 Gut, 1965, 6, 80 FRANK ELLIS AND F. L. COLE From the Departments of Surgery and Radiology, Guy's Hospital, London EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS A series of 56 patients with achalasia of the cardia included 16 with
Gut, 1965, 6, 80 FRANK ELLIS AND F. L. COLE From the Departments of Surgery and Radiology, Guy's Hospital, London EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS A series of 56 patients with achalasia of the cardia included 16 with
A review of the management of 100 cases of
 Thorax (1972), 27, 599. A review of the management of 100 cases of benign stricture of the oesophagus S. RAPTIS' and D. MEARNS MILNE Thoracic Unit, Frenchay Hospital One hundred cases of benign stricture
Thorax (1972), 27, 599. A review of the management of 100 cases of benign stricture of the oesophagus S. RAPTIS' and D. MEARNS MILNE Thoracic Unit, Frenchay Hospital One hundred cases of benign stricture
Innervation of the diaphragm and its practical aspects in surgery
 Innervation of the diaphragm and its practical aspects in surgery ROBERT SCOTT' From Stobhill General Hospital, Glasgow N.J Thorax (1965), 20, 357. Older French anatomists speak of the formation vena cava,
Innervation of the diaphragm and its practical aspects in surgery ROBERT SCOTT' From Stobhill General Hospital, Glasgow N.J Thorax (1965), 20, 357. Older French anatomists speak of the formation vena cava,
CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS. By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead
 CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead THE purpose of this short paper is twofold: first, to report a condition which
CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead THE purpose of this short paper is twofold: first, to report a condition which
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction. of the esophagogastric junction at. Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D.
 Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
ANATOMY OF THE CRURA OF THE DIAPHRAGM AND
 Thorax (1954), 9, 175. ANATOMY OF THE CRURA OF THE DIAPHRAGM AND THE SURGERY OF HIATUS HERNIA BY J. LEIGH COLLIS, T. D. KELLY, AND A. M. WILEY From the Queen Eiizabeth Hospital, Birmningham PART 1: ANATOMY
Thorax (1954), 9, 175. ANATOMY OF THE CRURA OF THE DIAPHRAGM AND THE SURGERY OF HIATUS HERNIA BY J. LEIGH COLLIS, T. D. KELLY, AND A. M. WILEY From the Queen Eiizabeth Hospital, Birmningham PART 1: ANATOMY
LATE RESULTS IN TRANSTHORACIC
 Thorax (1951), 6, 316. LATE RESULTS IN TRANSTHORACIC HERNIOTOMIES BY TYGE CL. GERTZ, J. E. P. M. REGOUT, AND GREGERS THOMSEN From the Department of Thoracic Surgery and Radiology, the University Hospital,
Thorax (1951), 6, 316. LATE RESULTS IN TRANSTHORACIC HERNIOTOMIES BY TYGE CL. GERTZ, J. E. P. M. REGOUT, AND GREGERS THOMSEN From the Department of Thoracic Surgery and Radiology, the University Hospital,
The Combined Collis-Nissen Operation: Early Assessment of Reflwx Control
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The Combined Collis-Nissen Operation: Early Assessment of Reflwx Control Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Jay S. Orringer, M.D. ABSTRACT This report summarizes the clinical experience with
ORIGINAL ARTICLES The Combined Collis-Nissen Operation: Early Assessment of Reflwx Control Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Jay S. Orringer, M.D. ABSTRACT This report summarizes the clinical experience with
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
Diffuse oesophageal spasm
 Diffuse oesophageal spasm Thorax (1966), 21, 511. D. R. CRADDOCK, A. LOGAN, AND P. R. WALBAUM From the Incoordination of muscular contraction is sometimes seen in the apparently healthy oesophagus, but
Diffuse oesophageal spasm Thorax (1966), 21, 511. D. R. CRADDOCK, A. LOGAN, AND P. R. WALBAUM From the Incoordination of muscular contraction is sometimes seen in the apparently healthy oesophagus, but
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Anatomical course of an oesophago-gastroduodeno-jejunal duplication
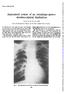 Thorax (1965), 20, 248 Anatomical course of an oesophago-gastroduodeno-jejunal duplication DONALD BARLOW From the Hospitals for Diseases of the Chest (London Chest Hospital) An electrician's mate aged
Thorax (1965), 20, 248 Anatomical course of an oesophago-gastroduodeno-jejunal duplication DONALD BARLOW From the Hospitals for Diseases of the Chest (London Chest Hospital) An electrician's mate aged
Intrathoracic fundoplication for reflux stricture
 Thorax 1983;38:36-40 Intrathoracic fundoplication for reflux stricture associated with short oesophagus K MOGHISSI From the Humberside Cardiothoracic Surgical Centre, Castle Hill Hospital, Cottingham,
Thorax 1983;38:36-40 Intrathoracic fundoplication for reflux stricture associated with short oesophagus K MOGHISSI From the Humberside Cardiothoracic Surgical Centre, Castle Hill Hospital, Cottingham,
Compression of the oesophagus by the aorta1
 Thorax (1969), 24, 32. Compression of the oesophagus by the aorta1 I. K. R. McMILLAN AND I. HYDE From the Wessex Cardiac and Thoracic Centre, Southampton Chest Hospital Compression of the lower dorsal
Thorax (1969), 24, 32. Compression of the oesophagus by the aorta1 I. K. R. McMILLAN AND I. HYDE From the Wessex Cardiac and Thoracic Centre, Southampton Chest Hospital Compression of the lower dorsal
approach suffer from mild dyspepsia and never seek treatment. The increasing frequency with which this
 Thorax (1966), 21, 295. Surgical treatment of hiatal hernia, with particular reference to the transthoracic subdiaphragmatic approach S. ZELLOS' From the Regional Cardiothoracic Unit, Newcastle UpOlt Tyne
Thorax (1966), 21, 295. Surgical treatment of hiatal hernia, with particular reference to the transthoracic subdiaphragmatic approach S. ZELLOS' From the Regional Cardiothoracic Unit, Newcastle UpOlt Tyne
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017?
 AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas, NV October 28, 2017 Session VIII: Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017? James D.
AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas, NV October 28, 2017 Session VIII: Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017? James D.
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
CASE REPORTS. Giant Esophagus. An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy
 CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
SURGERY LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
Achalasia is a primary esophageal motility disorder of unknown
 Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy for Achalasia Andrew Pierre, MD, MSc Achalasia is a primary esophageal motility disorder of unknown etiology. Pathologically, it is characterized by loss of ganglion cells in
Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy for Achalasia Andrew Pierre, MD, MSc Achalasia is a primary esophageal motility disorder of unknown etiology. Pathologically, it is characterized by loss of ganglion cells in
Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition
 22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
GIT RADIOLOGY. Water-soluble contrast media (e.g. gastrograffin) are the other available agents.which doesn t cause inflammatory peritonitis..
 GIT RADIOLOGY Imaging techniques-general principles: Contrast examinations: Barium sulphate is the best contrast for GIT (with good mucosal coating & excellent opacification & being inert); but is contraindicated
GIT RADIOLOGY Imaging techniques-general principles: Contrast examinations: Barium sulphate is the best contrast for GIT (with good mucosal coating & excellent opacification & being inert); but is contraindicated
The Physician as Medical Illustrator
 The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
THE CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL SYNDROME IN CHILDHOOD
 THE CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL SYNDROME IN CHILDHOOD The term 'cardio-oesophageal syndrome' is used to cover all infants and children with incompetence of the cardia. Ninety-three instances of the syndrome have
THE CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL SYNDROME IN CHILDHOOD The term 'cardio-oesophageal syndrome' is used to cover all infants and children with incompetence of the cardia. Ninety-three instances of the syndrome have
Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis
 Thorax (1970), 5, 459. Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis D. A. K. WOODWARD1 Oesophageal Laboratory, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham 15 The variability
Thorax (1970), 5, 459. Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis D. A. K. WOODWARD1 Oesophageal Laboratory, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham 15 The variability
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
THE NATURAL EVOLUTION OF HIATAL HERNIAS
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 143. THE NATURAL EVOLUTION OF HIATAL HERNIAS BY EMILIO ROVIRALTA From Instituto Policlinico, Barcelona, Spain (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MAY 1, 1963) Observations made over
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 143. THE NATURAL EVOLUTION OF HIATAL HERNIAS BY EMILIO ROVIRALTA From Instituto Policlinico, Barcelona, Spain (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MAY 1, 1963) Observations made over
The anti-reflux mechanism after cardiomyotomy'
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 569-573 The anti-reflux mechanism after cardiomyotomy' R LOBELLO,2 D A W EDWARDS,3 J W P GUMMER, AND M STEKELMAN From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, the
Thorax, 1978, 33, 569-573 The anti-reflux mechanism after cardiomyotomy' R LOBELLO,2 D A W EDWARDS,3 J W P GUMMER, AND M STEKELMAN From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, the
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Medical Illustration PLME 0400
 Introduction to Medical Illustration PLME 0400 October 17 From sketch to narrative From Sketch to Sketch: Point of view Degree of detail Visible and invisble parts Landmarks : Plan your moves The IKEA
Introduction to Medical Illustration PLME 0400 October 17 From sketch to narrative From Sketch to Sketch: Point of view Degree of detail Visible and invisble parts Landmarks : Plan your moves The IKEA
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease Information Sheet
 Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease Information Sheet Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease This sheet gives you information about Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease & Fundoplication Surgery What is gastro-oesophageal
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease Information Sheet Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease This sheet gives you information about Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease & Fundoplication Surgery What is gastro-oesophageal
Gastroplasty with Partial or Total Plication for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Manometric and ph-metric Postoperative Studies
 Gastroplasty with Partial or Total Plication for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Manometric and ph-metric Postoperative Studies Francisco Paris, M.D., Manuel Tomas-Ridocci, M.D., Adolfo Benages, M.D., Angel G.
Gastroplasty with Partial or Total Plication for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Manometric and ph-metric Postoperative Studies Francisco Paris, M.D., Manuel Tomas-Ridocci, M.D., Adolfo Benages, M.D., Angel G.
Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation
 Thorax (1972), 27, 353. Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, R. W. GIRDWOOD, G. H. WOOLER, and M. I. IONESCU Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
Thorax (1972), 27, 353. Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, R. W. GIRDWOOD, G. H. WOOLER, and M. I. IONESCU Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
Complications of Intrathoraac Nissen Fundoplication
 Complications of Intrathoraac Nissen Fundoplication Kamal A. Mansour, M.D., Harry G. Burton, M.D., Joseph I. Miller, Jr., M.D., and Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT This report details our experience
Complications of Intrathoraac Nissen Fundoplication Kamal A. Mansour, M.D., Harry G. Burton, M.D., Joseph I. Miller, Jr., M.D., and Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT This report details our experience
Selective vagotomy of the canine oesophagusa
 Thorax (1976), 31, 185. Selective vagotomy of the canine oesophagusa model for the treatment of hiatal hernia Surgical Unit, M. H. EDWARDS University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff Edwards, M. H. (1976). Thorax,
Thorax (1976), 31, 185. Selective vagotomy of the canine oesophagusa model for the treatment of hiatal hernia Surgical Unit, M. H. EDWARDS University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff Edwards, M. H. (1976). Thorax,
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD
 Esophagus Anatomy/Physiology Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD Manometry Question 50 years old female with chest pain and dysphagia. Manometry
Esophagus Anatomy/Physiology Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD Manometry Question 50 years old female with chest pain and dysphagia. Manometry
James Paget University Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Hiatus hernia. Patient Information
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
The left thoracoabdominal incision provides excellent
 Left Thoracoabdominal Incision Sudhir Sundaresan The left thoracoabdominal incision provides excellent exposure for operations dealing with the distal esophagus or proximal stomach. It is particularly
Left Thoracoabdominal Incision Sudhir Sundaresan The left thoracoabdominal incision provides excellent exposure for operations dealing with the distal esophagus or proximal stomach. It is particularly
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Oesophagus Esophagus. Symptoms of esophageal disease: Surgical Anatomy.
 Esophagus Surgical Anatomy. The esophagus is a muscular tube 25 cm long occupying the posterior mediastinum and extending from the cricopharyngeal sphincter to the cardia of the stomach 2 cm of this tube
Esophagus Surgical Anatomy. The esophagus is a muscular tube 25 cm long occupying the posterior mediastinum and extending from the cricopharyngeal sphincter to the cardia of the stomach 2 cm of this tube
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Reflux Control Following Gastroplasty
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Reflux Control Following Gastroplasty Robert D. Henderson, M.B.,.F.R.C.S.(C) ABSTRACT A Belsey gastroplasty was performed on 135 patients, 132 of whom were available for follow-up. Despite
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Reflux Control Following Gastroplasty Robert D. Henderson, M.B.,.F.R.C.S.(C) ABSTRACT A Belsey gastroplasty was performed on 135 patients, 132 of whom were available for follow-up. Despite
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Hiatal hernias may be classified. hiatal hernia DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION. This article is the first in a twopart series about these somewhat
 paraesophagealh hiatal hernia Leslie K Browder, MD, and Alex G Little, MD DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION Hiatal hernias may be classified as four types. The most common, Type I, may present as gastroesophageal
paraesophagealh hiatal hernia Leslie K Browder, MD, and Alex G Little, MD DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION Hiatal hernias may be classified as four types. The most common, Type I, may present as gastroesophageal
High peptic stricture of the oesophagus
 High peptic stricture of the oesophagus JAMES S. DAVIDSON Bradford Royal Infirmary Thorax (1976), 31, 1. Davidson, J. S. (1976). Thorax, 31, 1-14. High peptic sticture of the oesophagus. Fifty-seven patients
High peptic stricture of the oesophagus JAMES S. DAVIDSON Bradford Royal Infirmary Thorax (1976), 31, 1. Davidson, J. S. (1976). Thorax, 31, 1-14. High peptic sticture of the oesophagus. Fifty-seven patients
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Kelly procedure. How does the urinary system work? What is a Kelly procedure and why does my child need one?
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Kelly procedure This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the Kelly procedure used
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Kelly procedure This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the Kelly procedure used
Paraesophageal Hernia
 Paraesophageal Hernia Inderpal (Netu) S. Sarkaria, M.D. Vice Chairman, Clinical Affairs Director, Robotic Thoracic Surgery Co-Director, Esophageal and Lung Surgery Institute Speaker/Education: Intuitive
Paraesophageal Hernia Inderpal (Netu) S. Sarkaria, M.D. Vice Chairman, Clinical Affairs Director, Robotic Thoracic Surgery Co-Director, Esophageal and Lung Surgery Institute Speaker/Education: Intuitive
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Muscles of the Core. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS
 Muscles of the Core PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Intercostal Muscles Run between the ribs Provide shape and movement for chest wall External intercostals: aid in both quiet (passive) and forced
Muscles of the Core PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Intercostal Muscles Run between the ribs Provide shape and movement for chest wall External intercostals: aid in both quiet (passive) and forced
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
gastric epithelia Lower oesophagus lined with intestinal and LEON ABRAMS AND DONALD HEATH burning pain in the epigastrium and he was
 Thorax (1965), 20, 66. Lower oesophagus lined with intestinal and gastric epithelia LEON ABRAMS AND DONALD HEATH From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, and the Department
Thorax (1965), 20, 66. Lower oesophagus lined with intestinal and gastric epithelia LEON ABRAMS AND DONALD HEATH From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham, and the Department
TWO CASES OF UNILATERAL PARALYSIS OF THE DIAPHRAGM IN THE NEWBORN TREATED SURGICALLY BY
 '1 I,1 Thorax (1954), 9, 248 TWO CASES OF UNILATERAL PARALYSIS OF THE DIAPHRAGM IN THE NEWBORN TREATED SURGICALLY BY From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY
'1 I,1 Thorax (1954), 9, 248 TWO CASES OF UNILATERAL PARALYSIS OF THE DIAPHRAGM IN THE NEWBORN TREATED SURGICALLY BY From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY
e-anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 April 2016
 e-anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Web: www.ranzcr.edu.au Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au ABN 37 000 029 863 CASE
e-anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Web: www.ranzcr.edu.au Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au ABN 37 000 029 863 CASE
was a contributory factor. Agreeing with Harrington as to the site of the bleeding, small but repeated blood losses were said to occur by
 Anaemia and hiatus hernia: Thorax (1067), 2±,?3. experience in 450 patients COLIN W. 0. WINDSOR AND J. LEIGH COLLIS From the United Birmingham Hospitals Since a correlation between hiatus hernia and anaemia
Anaemia and hiatus hernia: Thorax (1067), 2±,?3. experience in 450 patients COLIN W. 0. WINDSOR AND J. LEIGH COLLIS From the United Birmingham Hospitals Since a correlation between hiatus hernia and anaemia
Hiatus hernia and heartburn
 Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD*
 HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD* BY J. H. JOHNSTON From the Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool The first description of a hiatus hernia was probably that of Bright (1836), who recorded the autopsy of
HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD* BY J. H. JOHNSTON From the Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool The first description of a hiatus hernia was probably that of Bright (1836), who recorded the autopsy of
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
and Gastro-oesophageal Reflux What symptoms might I expect?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Heartburn and Gastro-oesophageal Reflux www.corecharity.org.uk Why does reflux happen? Does reflux always cause symptoms?
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Heartburn and Gastro-oesophageal Reflux www.corecharity.org.uk Why does reflux happen? Does reflux always cause symptoms?
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY
 Tennyson Centre Suite 19 520 South Road Kurralta Park SA 5037 P 08 8292 2399 F 08 8292 2388 admin@urologicalsolutions.com.au www.urologicalsolutions.com.au Darwin Private Hospital Suite 5 Rocklands Drive
Tennyson Centre Suite 19 520 South Road Kurralta Park SA 5037 P 08 8292 2399 F 08 8292 2388 admin@urologicalsolutions.com.au www.urologicalsolutions.com.au Darwin Private Hospital Suite 5 Rocklands Drive
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead
 IRRADIATION INJURIES OF THE PERINEUM By R. L. B. BEARE, F.R.C.S. The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead MISGUIDED radiotherapy has in the past caused much misery, and continues to do so, although
IRRADIATION INJURIES OF THE PERINEUM By R. L. B. BEARE, F.R.C.S. The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead MISGUIDED radiotherapy has in the past caused much misery, and continues to do so, although
On the relationship between gastric ph and pressure
 Gut, 1979, 20, 59-63 On the relationship between gastric ph and pressure in the normal human lower oesophageal sphincter M. D. KAYE1 From the Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine, University of
Gut, 1979, 20, 59-63 On the relationship between gastric ph and pressure in the normal human lower oesophageal sphincter M. D. KAYE1 From the Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine, University of
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
A video demonstration of the Li s anastomosis the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma
 Surgical Technique A video demonstration of the the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma Yan Zheng*, Yin Li*, Zongfei Wang, Haibo Sun, Ruixiang Zhang
Surgical Technique A video demonstration of the the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma Yan Zheng*, Yin Li*, Zongfei Wang, Haibo Sun, Ruixiang Zhang
Embryology, anatomy and physiology of the oesophagus. Sarah Forsyth
 Embryology, anatomy and physiology of the oesophagus Sarah Forsyth Embryology Basics Endoderm forms scaffolding of GIT Endoderm forms the lining of the yolk sac Derivative of foregut Wk 4 - Foregut develops
Embryology, anatomy and physiology of the oesophagus Sarah Forsyth Embryology Basics Endoderm forms scaffolding of GIT Endoderm forms the lining of the yolk sac Derivative of foregut Wk 4 - Foregut develops
GEOFFREY H. Leeds WOOLER. The coronary ligament surrounds the bare area of
 Thorax (1956), 11, 21 1. SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS BY GEOFFREY H. Leeds The term subphrenic abscess denotes infection occurring in the region bounded by the diaphragm above, and by the transverse meso-colon,
Thorax (1956), 11, 21 1. SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS BY GEOFFREY H. Leeds The term subphrenic abscess denotes infection occurring in the region bounded by the diaphragm above, and by the transverse meso-colon,
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
show-n to give off a branch, and sometimes two or three branches, to
 THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
2 Paraesophageal Hiatus Hernia
 2 Paraesophageal Hiatus Hernia Luigi Bonavina Pearls and Pitfalls Paraesophageal (type II) hiatus hernia represents a distinct anatomic and clinic entity requiring a unique therapeutic strategy, and is
2 Paraesophageal Hiatus Hernia Luigi Bonavina Pearls and Pitfalls Paraesophageal (type II) hiatus hernia represents a distinct anatomic and clinic entity requiring a unique therapeutic strategy, and is
AND TECHNIC. GEORGE CRILE, Jr., M.D. Division of Surgery
 SUBDIAPHRAGMATIC VAGOTOMY; AND TECHNIC INDICATIONS GEORGE CRILE, Jr., M.D. Division of Surgery The principle of vagotomy as described by Dragstedt 1 has been widely accepted in the treatment of peptic
SUBDIAPHRAGMATIC VAGOTOMY; AND TECHNIC INDICATIONS GEORGE CRILE, Jr., M.D. Division of Surgery The principle of vagotomy as described by Dragstedt 1 has been widely accepted in the treatment of peptic
Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1-
 Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Nissen Hiatal Hernia Rep& Problems of Recurrence &d. Continued Symptoms. R. D. Henderson, M.B.
 Nissen Hiatal Hernia Rep& Problems of Recurrence &d R. D. Henderson, M.B. Continued Symptoms ABSTRACT The standard Nissen operation is the most effective method of reflux control. However, the procedure
Nissen Hiatal Hernia Rep& Problems of Recurrence &d R. D. Henderson, M.B. Continued Symptoms ABSTRACT The standard Nissen operation is the most effective method of reflux control. However, the procedure
Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats
 Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats I. Gastrostomy tube A. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement Supplies for PEG tube placement: Supplies and equipment for general anesthesia
Placing PEG and Jejunostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats I. Gastrostomy tube A. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement Supplies for PEG tube placement: Supplies and equipment for general anesthesia
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
