160 A. Shiraishi et al. ms, TE: 9 ms, excitations: 1, FA: 30, FOV: 25 cm, matrix: 256~256, slice thickness: 3 4 mm, no gap) with fat saturation. The c
|
|
|
- Leon Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol.2, No.4, p , 2003 MAJOR PAPER Extension of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: Histopathological Association with MR Imaging and Mammography Akihiko SHIRAISHI 1 *, Yoshihisa KUROSAKI 1, Tadayuki MAEHARA 1, Masaru SUZUKI 2, and Masafumi KUROSUMI 3 1 Department of Radiology, Juntendo University School of Medicine Hongo, Bunkyo ku, Tokyo , Japan Departments of 2 Radiology and 3 Clinical Pathology, Saitama Cancer Center (Received August 28, 2003; Accepted December 17, 2003) The purpose of this study is to evaluate the capability of breast MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and mammography in determining tumor extent and the detectability of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) in association with histopathological features. Thirty women with breast cancer underwent 3D dynamic MRI.Twelve women had pure DCIS and 18 women had DCIS with microinvasion.we analyzed the results of preoperative MRI and mammography with histopathologic results, retrospectively.the mean lesion size was 55.1 mm from the histopathologic results. Twenty six lesions were detected through the MRI (a sensitivity of 86.7z).MRI depicted eight lesions without mammographically detected microcalciˆcation.in seven cases, MRI showed tumor extent accurately compared with mammography, and the combined diagnosis improved the accuracy of evaluating tumor extent.mri can complement mammography in guiding surgical treatment of DCIS by providing better assessment of the extent of the lesion. Keywords: breast, magnetic resonance imaging, mammography, ductal carcinoma in situ, diagnosis Introduction Because of its easy availability, low cost, and ability to detect microcalciˆcations, mammography is currently the imaging modality of ˆrst choice for breast evaluation.ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) accounts for 15z 20z of all detected breast cancers and 25z 56z of clinically occult cancers detected with mammography; it is found in 16z of asymptomatic women at autopsy. 1,2 Clustered microcalciˆcation is the most common mammographic feature of DCIS and is found in 85z 90z of cases. 3 However, the several limitations of mammography are well documented, including di culties in the assessment of dense breasts and the evaluation of DCIS without microcalciˆcation. Recently, breast conservation surgery has become an increasingly common treatment for DCIS. Accurate evaluation of the tumor extent is important for breast conserving treatment of DCIS. 4 Advanced breast MRI techniques are gaining *Corresponding author, Phone: { , Fax: { , E mail: asiraisi med.juntendo.ac.jp ground as adjuncts to mammography, although questions remain about their usefulness in imaging of in situ carcinomas.we evaluate the capability of breast MRI and mammography regarding lesion detectability and the extent of DCIS association with histopathologic features. Materials and Methods MRI studies were reviewed in thirty histologically veriˆed lesions (12 pure DCIS and 18 DCIS with microinvasive foci).the patients ranged in age from 34 to 70 years (average, 49.8 years). Nineteen of 30 lesions were treated with mastectomy, and 11 lesions were treated with breast conserving surgery. Mammography and MRI were performed within four weeks of surgery. Imaging technique The MRI examinations were performed with two dišerent 1.5T systems (Gyroscan, ACS NT, Philips; VISART, Toshiba).On both systems, a breast surface coil was used with the patient in the prone position.the entire single breast was imaged with a 3D spoiled gradient echo sequence (TR:
2 160 A. Shiraishi et al. ms, TE: 9 ms, excitations: 1, FA: 30, FOV: 25 cm, matrix: 256~256, slice thickness: 3 4 mm, no gap) with fat saturation. The coronal dynamic series comprised four scan times: before and 2, 6, 10 min after intravenous injection of 0.1 mmolwkg Gd DTPA. MPR (multiplanar reconstruction) images were obtained with parasagittal images after examination. In the mammographic examinations, magniˆcation and Wor spot compression views were obtained in addition to the standard oblique and craniocaudal projections (Mammorex, MGS 110B Toshiba). Pathological resection and method In breast conserving surgery, the received material is prepared as 5 mm thick slices throughout the nipple margin to the distal end to evaluate the tumor extent precisely. In cases where mastectomy was performed, a 5 mm sliced section was obtained in parallel to the line passing through the nipple and the tumor. The tumor diameter was estimated by pathologists through tumor extent mapping with the results of the microscopic examination. Imaging analysis MRI and mammography examinations were separately evaluated by two radiologists (AS, MS) with extensive experience in breast MR imaging and mammography. The reviewers were unaware of the histopathologic results. The consensus of the two radiologists as present was considered positive. In mammography, mass lesions, asymmetric opacities, architectural distortion, and malignant microcalciˆcations were considered positive ˆndings. MRI ˆndings were considered to be positive for tumorifafocalareaofenhancement,compared with normal breast tissue, was seen after contrast administration; the ˆndings were interpreted as negative if no enhancement was seen or if dišuse and uniform enhancement of the breast parenchyma was seen. We analyzed the preoperative MRI and mammography for tumor detectability and tumor extent, and the greater lesion size between mammographyandmriwasselectedinacombined diagnosis. The tumor size was measured as the maximal diameter in each modality, and we evaluated the accuracy of demonstrated tumor extent. For lesions detected in both modalities, we determined the dišerence in size between the imaging and histopathologic results as follows: within 10 mm, mm, and more than 20 mm. We also evaluated size discrepancy as a percentage: the dišerence in size divided by the actual size of the specimen. Results Of 30 lesions, the mean lesion size was 55.1 mm from the histopathologic results. MRI depicted 26 lesions (a sensitivity of 86.7z), mammography depicted 23 lesions (a sensitivity of 76.7z), and 22 lesions were detected with both modalities. Of the 26 lesions detected by MRI, four lesions without dense breast could not be depicted with mammography. In eight cases, mammography did not detect microcalciˆcations. All lesions in these eight cases were identiˆed with MRI. In one case, a lesion was identiˆed with mammography as a clustered microcalciˆcation, although no abnormality was detected with MRI. Three lesions (less than 10 mm in two lesions incidentally detected with microscopic examination and 20 mm in one lesion detected with ultrasound) were not detected with either modality. For lesions detected with both modalities, the mean histopathological tumor size was 40.9 mm (ranging from 10 to 90 mm). With MRI, the tumor size was underestimated or overestimated within 10mm in 13 cases. MRI overestimated tumor size by more than 20 mm in one case; in this case, proliferative ˆbrocystic change was found around the malignant lesion histologically. In seven cases, MRI underestimated tumor size by more than 20 mm. MRI could not show the microscopic extent of the tumor. Mammography evaluated tumor size with a distinction range within 10 mm in 10 cases. In seven cases, mammography underestimated tumor size by more than 20 mm. In seven cases, MRI was superior to mammography, and in three cases mammography was more accurate than MRI in evaluating the tumor extent. In the diagnoses combining MRI and mammography, the distinction range was more than 20 mm in four cases if the greater size was selected. (Table 1 shows the results demonstrating tumor extent.) MRI evaluated the percentage discrepancy within 20z in 12 cases. (Table 2 shows the percentage discrepancy in size.) Discussion Breast MRI has recently evolved, and many studies have documented the improvements in diagnostic performance, showing a higher sensitivity to invasive carcinoma than is provided with mammography. 5 7 The use of MRI as an adjunct to mammography resulted in an increase in diagnostic accuracy.anearlysteepincreaseinsignalintensity followed by a decrease or plateau in signal intensity has been reported as a sign of malignancy, and a continuous increase in signal intensity is regarded Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
3 Extension of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ 161 Table 1. DiŠerence in tumor extent between imaging and specimen 0 Å10 mm mm»21 mm Å10 mm mm»21 mm underestimation overestimation 8 (18 MRI 2 (9.1z) 8 (36.4z) 3 (13.6z) 6 (27.3z) 3 (13.6z) 0 0 mammography 1 (4.5z) 7 (31.8z) 3 (13.6z) 7 (31.8z) 3 (13.6z) 0 1 (4.5z) MRI{mammography 2 (9.1z) (36.4z) 4.2z) 3 (13.6z) 4 (18.2z) 0 1 (4.5z) MRI{mammography: combined evaluation with MRI and mammography Table 2. DiŠerence in size divided by actural size of specimen 0 20z 21 40z 41 60z 61 80z z 100zº MRI mammography as a sign of benignity. 8 Various authors reported MR ˆndings of DCIS; however, the evaluation of DCIS with MRI is reported to be limited. The reported sensitivities of MRI for the detection of DCIS have varied widely, ranging from 40z to 100z 9 13 ; moreover, there have been reports of false negative cases with variable size tumors. 5,14 16 DCIS demonstrates a variable enhancement pattern with MRI. Some investigators have identiˆed relatively slowly enhancing cancers and rapidly enhancing benign lesions. 17 DCIS shows clumped or linear enhancement along the ductal pattern. The ductal pattern is important in the diagnosis of DCIS. However, ˆbrocystic changes show clumped enhancement as well as DCIS, and the enhancement is sometimes delayed, suggesting benignity. 11 Therefore, if the ductal pattern is not identiˆed, DCIS is often indistinguishable from a benign lesion with MRI. The cure rate of DCIS with mastectomy is approximately 100z. Currently, demand for breast conservation treatment is increasing. Harris et al. describe lumpectomy and radiation therapy as reasonable for a DCIS within 3 cm in size. 18 Rosner et al. demonstrated that patients who underwent wedge resection had equivalent outcomes to those who underwent mastectomy for DCIS. 19 Therefore, accurate evaluation of the tumor extent is important when breast conservation treatment is considered. Mammography can demonstrate most DCIS lesions, but a more accurate imaging assessment of lesion extent is necessary for successful breast conservation. The extent of DCIS cannot always be accurately predicted with mammography. 20,21 The tumor extent is often underestimated with mammography. 22 As for size determination of breast cancer with MRI, several previous reports are available. 23,24 They concluded that MRI provided greater accuracy than did mammography in determining tumor size. Boetes et al. demonstrated with eight DCIS lesions that, while the size of the invasive part was correctly estimated, the DCIS component was underestimated by more than 1 cm in all patients. 12 However, little data is available for DCIS. In our study group, the detectability of DCIS was higher with MRI than with mammography. Microcalciˆcations and the microscopic extent of the lesions are not depicted with MRI; therefore, MRI alone may be insu cient. One false negative case with MRI was correctly diagnosed as a malignancy with mammography. Because MRI was able to depict DCIS without microcalciˆcations (Fig. 1), a combined evaluation would increase the sensitivity compared with a single modality. One 15 mm lesion was not identiˆed with MRI, suggesting that tumor size alone is not responsible for false negative results. We considered that mammography is able to depict lesions if microcalciˆcation exists, and that demonstration with MRI is related not only to lesion size, but also to the amount of tumor cells and the signal behavior of contrast enhancement. We analyzed the histologic results and the preoperative MRI results regarding tumor extent for DCIS. MRI in addition to mammography improved the diagnostic accuracy of evaluating tumor extent and reduced the number of cases in which the tumor margin was underestimated by more than 20 mm. In our hospital, surgeons have a policy of maintaining a 20 mm surgical margin for breast conservative surgery. Our results suggest that MRI is helpful for preoperatively evaluating tumor extent in DCIS. However, the presence of Vol. 2 No. 4, 2003
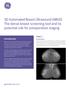
4 162 A. Shiraishi et al. Fig year old woman with bloody nipple discharge Mediolateral oblique mammogram of the right (a) and left (b) breasts shows no deˆnite mass and malignant calciˆcations. Dynamic studies of coronal images (c) before and at (d) 2,(e) 6, and(f) 10 min after injection of Gd DTPA show clumped enhancement in the upper inner quadrant of the left breast. (g) TheMPRimage demonstrates linear enhancements toward the nipple in a ductal pattern,corresponding to a DCIS. ˆbrocystic changes reduces the diagnostic value. If there is only dišuse or patchy enhancement without linear fashion with MRI,histological examination is necessary in the cases where mammography depicted no malignant calciˆcations. In conclusion,mri improves lesion detectability and accuracy when evaluating tumor extent and it is able to depict DCIS without microcalciˆcations. Acknowledgments We wish to thank T. Ohtsuka,K. Ishiguri,and the technicians of the Saitama Cancer Center for their invaluable assistance. References 1. Stomper PC,Margolin FR. Ductal carcinoma in situ: the mammographer's perspective. AJR 1994; 162: Ores SG,Schnall MD,Newman RW,et al. MR imaging guided localization and biopsy of breast lesions: initial experience. Radiology 1994; 193: Evans AJ,Wilson ARM,Burrell HC,et al. Mammographic features of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) present on previous mammography. Clinic Radiol 1999; 54: Elliott RL,Haynes AE,Bolin JA,et al. Stereotaxic needle localization and biopsy of occult breast lesions: ˆrst year's experience. Am Surg 1992; 58: Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
5 Extension of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Soderstrom CE, Harms SE, Copit DS, et al. Threedimensional RODEO breast MR imaging of lesions containing ductal carcinoma in situ. Radiology 1996; 201: Elvecrog EL, Lechner MC, Nelson MT. Nonpalpable breast lesions: correlation of stereotaxic largecore needle biopsy and surgical biopsy results. Radiology 1993; 188: Bone B, Aspelin P, Bronge L, et al. Sensitivity and speciˆcity of MR mammography with histopathological correlation in 250 breasts. Acta Radiologica 1996; 37: Baudu LD, Murakami J, Murayama S, et al. Breast lesions: correlation of contrast medium enhancement patterns on MR images with histopathologic ˆndings and tumor angiogenesis. Radiology 1996; 200: Fryberg ER, Bland KI. Overview of the biology and management of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer 1994; 74: Heywang SH. Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. Invest Radiol 1994; 29: Orel SG, Schnall MD, LiVolsi VA, et al. Suspicious breast lesions: MR imaging with radiologic pathologic correlation. Radiology 1994; 190: BoetesC,BarentzJO,MusRD,etal.MRcharacterization of suspicious breast lesions with a gadolinium enhanced turbo FLASHsubtraction technique. Radiology 1994; 193: Gilles R, Meunier M, Lucidarme O, et al. Clustered breast microcalciˆcations: evaluation by dynamic contrast enhanced subtraction MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1996; 20(1): Fobben ES, Rubin CZ, Kalisher L, et al. Breast MR imaging with commercially available technique: radiologic pathologic correlation. Radiology 1995; 196: Gilles R, Guinebretiere J, Lucidarme O, et al. Non palpable breast tumors: diagnosis with contrastenhanced subtraction dynamic MR imaging. Radiology 1994; 191: Stomper PC, Connolly JL. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: correlation between mammographic calciˆcation and tumor subtype. AJR 1992; 159: Holland R, Hendriks JHCL, Verbeek ALM, et al. Extent, distribution, and mammographic Whistological distribution of breast ductal carcinoma in situ. Lancet 1990; 335: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Veronesi U, et al. Breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1992; 327: RosnerD,BedwaniRN,VenaJ,etal.Noninvasive breast carcinoma: results of a national survey by the American College of Surgeons. Ann Surg 1980; 192: Gilles R, Zafrani B, Guinebretiere JM, et al. Ductal carcinoma in situ: MR imaging histopathologic correlation. Radiology 1995; 196: StomperPC,HermanS,KlippensteinDL,etal. Suspect breast lesions: ˆndings at dynamic gadolinium enhanced MR imaging correlated with mammographic and pathologic features. Radiology 1995; 197: Boetes C, Mus RDM, Holland R, et al. Breast tumors: comparative accuracy of MR imaging relative to mammography and US for demonstrating extent. Radiology 1995; 197: Boetes C, Strijik SP, Holland R, et al. Falsenegative MR imaging of malignant breast tumors. Eur Radiol 1997; 7: Westerhof JP, Fischer U, Moritz JD, et al. MR imaging of mammographically detected clustered microcalciˆcations: is there any value? Radiology 1998; 207: Vol. 2 No. 4, 2003
MRI of the Breast for the Detection and Assessment of the Size of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
 MRI of the Breast for the Detection and Assessment of the Size of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Do Youn Kim, MD 1 Woo Kyung Moon, MD 1 Nariya Cho, MD 1 Eun Sook Ko, MD 1 Sang Kyu Yang, MD 1 Jeong Seon Park,
MRI of the Breast for the Detection and Assessment of the Size of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Do Youn Kim, MD 1 Woo Kyung Moon, MD 1 Nariya Cho, MD 1 Eun Sook Ko, MD 1 Sang Kyu Yang, MD 1 Jeong Seon Park,
Breast Cancers Not Detected at MRI: Review of False-Negative Lesions
 Women s Imaging Original Report Shimauchi et al. MRI-Occult Breast s Women s Imaging Original Report WOMEN S IMAGING Breast s Not Detected at MRI: Review of False-Negative Lesions Akiko Shimauchi 1 Sanaz
Women s Imaging Original Report Shimauchi et al. MRI-Occult Breast s Women s Imaging Original Report WOMEN S IMAGING Breast s Not Detected at MRI: Review of False-Negative Lesions Akiko Shimauchi 1 Sanaz
Invited. Challenges to Interpretation of Breast MRI
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:821 829 (2001) Review Invited Challenges to Interpretation of Breast MRI Karen Kinkel, MD,* and Nola M. Hylton, PhD This review describes the current knowledge
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:821 829 (2001) Review Invited Challenges to Interpretation of Breast MRI Karen Kinkel, MD,* and Nola M. Hylton, PhD This review describes the current knowledge
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Breast Cancers Not Detected at MRI: Review of False-Negative Lesions
 Women s Imaging Original Report Shimauchi et al. MRI-Occult Breast s Women s Imaging Original Report WOMEN S IMAGING Akiko Shimauchi 1 Sanaz A. Jansen 1 Hiroyuki Abe 1 Nora Jaskowiak 2 Robert A. Schmidt
Women s Imaging Original Report Shimauchi et al. MRI-Occult Breast s Women s Imaging Original Report WOMEN S IMAGING Akiko Shimauchi 1 Sanaz A. Jansen 1 Hiroyuki Abe 1 Nora Jaskowiak 2 Robert A. Schmidt
DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation.
 DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation. Poster No.: C-1560 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. B. Ibrahim, P. Morris, S. ANANDAN; Burlington, MA/US Keywords:
DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation. Poster No.: C-1560 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. B. Ibrahim, P. Morris, S. ANANDAN; Burlington, MA/US Keywords:
Clinical Practice Guideline for the Indications for Use of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 CIHRT Exhibit P-2595 Page 1 Question: Clinical Practice Guideline for the Indications for Use of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Eastern Health Breast Disease Site Group What are the current indications
CIHRT Exhibit P-2595 Page 1 Question: Clinical Practice Guideline for the Indications for Use of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Eastern Health Breast Disease Site Group What are the current indications
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions with T2*-Weighted First Pass Perfusion Imaging
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions with T2*-Weighted First Pass Perfusion
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions with T2*-Weighted First Pass Perfusion
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks
 Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications?
 Original Article Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications? Shinya Yamamoto, Takashi Chishima Department of Breast Surgery, Yokohama Rosai Hospital, Yokohama 222-0036,
Original Article Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications? Shinya Yamamoto, Takashi Chishima Department of Breast Surgery, Yokohama Rosai Hospital, Yokohama 222-0036,
MRI Occult Invasive Breast Cancer
 MRI Occult Invasive Breast Cancer Poster No.: C-1573 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Patel, N. Chhaya, K. Stafford, B. Holloway, D. Tsukagoshi, A. Malhotra; London/ Keywords: Cancer,
MRI Occult Invasive Breast Cancer Poster No.: C-1573 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Patel, N. Chhaya, K. Stafford, B. Holloway, D. Tsukagoshi, A. Malhotra; London/ Keywords: Cancer,
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Breast MRI Update. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
ROLE OF MRI IN SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER. B.Zandi Professor of Radiology
 ROLE OF MRI IN SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER B.Zandi Professor of Radiology Introduction In the USA, Breast Cancer is : The Most Common Non-Skin Cancer The Second Leading cause of
ROLE OF MRI IN SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER B.Zandi Professor of Radiology Introduction In the USA, Breast Cancer is : The Most Common Non-Skin Cancer The Second Leading cause of
Breast Cancer Imaging
 Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Role of MRI in breast cancer management
 REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will identify appropriate uses of magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging tests in the management of breast cancer Louie Enriquez, MD Radiology Imaging
REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will identify appropriate uses of magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging tests in the management of breast cancer Louie Enriquez, MD Radiology Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice
 Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32: (2010)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32:1117 1123 (2010) Original Research Peripheral Hyperintense Pattern on T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Breast Carcinoma: Correlation With Early Peripheral
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32:1117 1123 (2010) Original Research Peripheral Hyperintense Pattern on T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Breast Carcinoma: Correlation With Early Peripheral
Department of Radiology, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung 404, Taiwan 2
 Journal of Oncology Volume 2010, Article ID 431341, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2010/431341 Clinical Study Characterization of Pure Ductal Carcinoma In Situ on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging: Do Nonhigh
Journal of Oncology Volume 2010, Article ID 431341, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2010/431341 Clinical Study Characterization of Pure Ductal Carcinoma In Situ on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging: Do Nonhigh
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation
 Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
3D Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS): The dense breast screening tool and its potential role for preoperative staging
 3D Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS): The dense breast screening tool and its potential role for preoperative staging Introduction Breast cancer is by far the most common cancer amongst women across Europe,
3D Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS): The dense breast screening tool and its potential role for preoperative staging Introduction Breast cancer is by far the most common cancer amongst women across Europe,
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008
 Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008 Breast Cancer Most common cancer in American women 180,000 new cases per year Second most common cause of cancer death 44,000
Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008 Breast Cancer Most common cancer in American women 180,000 new cases per year Second most common cause of cancer death 44,000
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Electrical impedance scanning of the breast is considered investigational and is not covered.
 ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Medical Policy Title: Electrical Impedance Scanning of the Breast Document: ARB0127 Administered by: Public Statement:
ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Medical Policy Title: Electrical Impedance Scanning of the Breast Document: ARB0127 Administered by: Public Statement:
Computerized Segmentation and Classification of Breast Lesions Using Perfusion Volume Fractions in Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI
 28 International Conference on BioMedical Engineering and Informatics Computerized Segmentation and Classification of Breast Lesions Using Perfusion Volume Fractions in Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI Sang
28 International Conference on BioMedical Engineering and Informatics Computerized Segmentation and Classification of Breast Lesions Using Perfusion Volume Fractions in Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI Sang
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy for Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast
 1 Angela Kempen February Case Study February 22, 2012 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy for Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast History of Present Illness: JE is a 45 year-old Caucasian female who underwent
1 Angela Kempen February Case Study February 22, 2012 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy for Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast History of Present Illness: JE is a 45 year-old Caucasian female who underwent
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Female Breast
 January 2002 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Female Breast Its Role, Indication, Technique & Future. Christian Zechmann, Heidelberg Medical School Year, IV Dr. Introduction Breast cancer is the most
January 2002 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Female Breast Its Role, Indication, Technique & Future. Christian Zechmann, Heidelberg Medical School Year, IV Dr. Introduction Breast cancer is the most
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors
 Breast Cancer Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors JMAJ 45(6): 258 264, 2002 Tokiko ENDO Director of the Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast masses include the
Breast Cancer Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors JMAJ 45(6): 258 264, 2002 Tokiko ENDO Director of the Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast masses include the
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS
 Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS Poster No.: C-0412 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Breast H. G. Toonen, R. Mann, H. Huisman, J. Veltman, C. Boetes; Nijmegen/NL
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS Poster No.: C-0412 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Breast H. G. Toonen, R. Mann, H. Huisman, J. Veltman, C. Boetes; Nijmegen/NL
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography
 Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Breast Health and Imaging Glossary
 Contact: Lorna Vaughan HerSpace Breast Imaging & Biopsy Associates 300 State Route 35 South W. Long Branch, NJ 07764 732-571-9100, ext. 104 lorna@breast-imaging.com Breast Health and Imaging Glossary Women
Contact: Lorna Vaughan HerSpace Breast Imaging & Biopsy Associates 300 State Route 35 South W. Long Branch, NJ 07764 732-571-9100, ext. 104 lorna@breast-imaging.com Breast Health and Imaging Glossary Women
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a complementary
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:460 467 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 BREAST IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of breast MRI in planning the surgical treatment of breast cancer Gökhan Duygulu, Ayşenur
Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:460 467 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 BREAST IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of breast MRI in planning the surgical treatment of breast cancer Gökhan Duygulu, Ayşenur
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Comparison of Mammography, Ultrasonography, and MRI in the Evaluation of Disease Extent
 Article ID: WMC005222 ISSN 2046-1690 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Comparison of Mammography, Ultrasonography, and MRI in the Evaluation of Disease Extent Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Hak
Article ID: WMC005222 ISSN 2046-1690 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Comparison of Mammography, Ultrasonography, and MRI in the Evaluation of Disease Extent Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Hak
Feasibility of MRI-guided large-core-needle biopsy of suspiscious breast lesions at 3T
 Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 1639 1644 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1310-0 BREAST Nicky H. G. M. Peters Carla Meeuwis Chris J. G. Bakker Willem P. Th. M. Mali Arancha M. Fernandez-Gallardo Richard van Hillegersberg
Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 1639 1644 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1310-0 BREAST Nicky H. G. M. Peters Carla Meeuwis Chris J. G. Bakker Willem P. Th. M. Mali Arancha M. Fernandez-Gallardo Richard van Hillegersberg
BREAST MRI. VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece
 BREAST MRI VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece Breast ΜR Imaging (MRM) Breast MR imaging is an extremely powerful diagnostic tool, that when used in
BREAST MRI VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece Breast ΜR Imaging (MRM) Breast MR imaging is an extremely powerful diagnostic tool, that when used in
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI BREAST CANCER. The incidence of getting breast cancer is 1:19 in Malaysia
 Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay
 CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
Throughout this policy, bracketed numbers link topics across multiple sections according to the indication numbers in the following list.
 Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Page: 1 of 33 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Description Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast
Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Page: 1 of 33 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast Description Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI
 Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation
 Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection
 Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis
 Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions A. Zulfiqar, MMed* v. Param, DMRD** F.A. Meah, FRACS* s. Nair, FRCS** M.A. Siti-Aishah, DCP* A. N orizan, DCP** * Departments of Radiology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions A. Zulfiqar, MMed* v. Param, DMRD** F.A. Meah, FRACS* s. Nair, FRCS** M.A. Siti-Aishah, DCP* A. N orizan, DCP** * Departments of Radiology,
Positive and Negative Predictive Values of BI-RADS}-MRI Descriptors for Focal Breast Masses
 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 7 15, 2006 MAJOR PAPER Positive and Negative Predictive Values of BI-RADS}-MRI Descriptors for Focal Breast Masses Mitsuhiro TOZAKI*, Takao IGARASHI,
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 7 15, 2006 MAJOR PAPER Positive and Negative Predictive Values of BI-RADS}-MRI Descriptors for Focal Breast Masses Mitsuhiro TOZAKI*, Takao IGARASHI,
Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy using computer-aided 3.0 T- MRI guidance: diagnostic performance in 173 lesions
 Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy using computer-aided 3.0 T- MRI guidance: diagnostic performance in 173 lesions Poster No.: C-2870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Pozzetto, L. Camera,
Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy using computer-aided 3.0 T- MRI guidance: diagnostic performance in 173 lesions Poster No.: C-2870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Pozzetto, L. Camera,
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Breast Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
BI-RADS CATEGORIZATION AND BREAST BIOPSY categorization in the selection of appropriate breast biopsy technique is also discussed. Patients and method
 Original Article Positive Predictive Value of BI-RADS Categorization in an Asian Population Yah-Yuen Tan, Siew-Bock Wee, Mona P.C. Tan and Bee-Kiang Chong, 1 Departments of General Surgery and 1Diagnostic
Original Article Positive Predictive Value of BI-RADS Categorization in an Asian Population Yah-Yuen Tan, Siew-Bock Wee, Mona P.C. Tan and Bee-Kiang Chong, 1 Departments of General Surgery and 1Diagnostic
Role of Breast MRI in the Preoperative Evaluation of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
 Women s Imaging Original Research Schell et al. Preoperative Breast MRI Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Amy M. Schell 1 Kari Rosenkranz 2 Petra J. Lewis 3 Schell AM, Rosenkranz K, Lewis
Women s Imaging Original Research Schell et al. Preoperative Breast MRI Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Amy M. Schell 1 Kari Rosenkranz 2 Petra J. Lewis 3 Schell AM, Rosenkranz K, Lewis
Breast MRI: Friend or Foe?
 Breast MRI: Friend or Foe? UCSF Postgraduate Course May 18, 2013 Cheryl Ewing, MD Clinical Professor of Surgery UCSF Department of Surgery APPLEGATE HAS DOUBLE MASTECTOMY IN CANCER SCARE DIAGNOSED WITH
Breast MRI: Friend or Foe? UCSF Postgraduate Course May 18, 2013 Cheryl Ewing, MD Clinical Professor of Surgery UCSF Department of Surgery APPLEGATE HAS DOUBLE MASTECTOMY IN CANCER SCARE DIAGNOSED WITH
Breast Cancer Screening Clinical Practice Guideline. Kaiser Permanente National Breast Cancer Screening Guideline Development Team
 NATIONAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Breast Cancer Screening Clinical Practice Guideline Kaiser Permanente National Breast Cancer Screening Guideline Development Team This guideline is informational only.
NATIONAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Breast Cancer Screening Clinical Practice Guideline Kaiser Permanente National Breast Cancer Screening Guideline Development Team This guideline is informational only.
Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
 Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 450 454, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088 Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 450 454, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088 Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium. Sat Nov 12 th 2016
 Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Mammography. What is Mammography? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography
 Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
New subtraction algorithms for evaluation of lesions on dynamic contrast-enhanced MR mammography
 Eur Radiol (2002) 12:3018 3022 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1335-0 BREAST Byung Gil Choi Hak Hee Kim Euy Neyng Kim Bum-soo Kim Ji-Youn Han Seung-Schik Yoo Seog Hee Park New subtraction algorithms for evaluation
Eur Radiol (2002) 12:3018 3022 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1335-0 BREAST Byung Gil Choi Hak Hee Kim Euy Neyng Kim Bum-soo Kim Ji-Youn Han Seung-Schik Yoo Seog Hee Park New subtraction algorithms for evaluation
Abstract. Available online commentary review reports primary research
 Available online http://breast-cancer-research.com/content/3/1/055 Primary research Comparison of written reports of mammography, sonography and magnetic resonance mammography for preoperative evaluation
Available online http://breast-cancer-research.com/content/3/1/055 Primary research Comparison of written reports of mammography, sonography and magnetic resonance mammography for preoperative evaluation
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings
 Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Breast MR biopsy. I Thomassin-Naggara, A.Jalaguier-Coudray, J Chopier
 Breast MR biopsy I Thomassin-Naggara, A.Jalaguier-Coudray, J Chopier Background EUSOBI When a radiologist perform a MR breast imaging he has to be able to realize or to be apart of a network who is able
Breast MR biopsy I Thomassin-Naggara, A.Jalaguier-Coudray, J Chopier Background EUSOBI When a radiologist perform a MR breast imaging he has to be able to realize or to be apart of a network who is able
The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes
 The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes Connie Lehman MD PhD Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director of Breast Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Opportunities New technology provides
The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes Connie Lehman MD PhD Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director of Breast Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Opportunities New technology provides
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors
 Eur Radiol (2011) 21:2475 2483 DOI 10.1007/s00330-011-2210-7 BREAST Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors Christian Sohns & Martin Scherrer
Eur Radiol (2011) 21:2475 2483 DOI 10.1007/s00330-011-2210-7 BREAST Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors Christian Sohns & Martin Scherrer
Imaging-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Introduction 1. Executive Summary 5
 Roman_pages 20-09-2005 21:01 Pagina IX Table of contents Introduction 1 Executive Summary 5 1. Epidemiological guidelines for quality assurance in breast cancer screening 15 1.10 Introduction 17 1.20 Local
Roman_pages 20-09-2005 21:01 Pagina IX Table of contents Introduction 1 Executive Summary 5 1. Epidemiological guidelines for quality assurance in breast cancer screening 15 1.10 Introduction 17 1.20 Local
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
