Epidemiology. Bis vivit qui bene vivit
|
|
|
- Dominic Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Epidemiology Bis vivit qui bene vivit
2 What is Epidemiology? Epidemiology, literally translated from Greek, means "the study of [a] people". Epidemiology is the study of how a disease is distributed in a population and of the factors that influence or determine this distribution.
3 Objectives of Epidemiology - determine the extent of disease in a population - study the natural history and prognosis of a disease - characterise the aetiology of a disease - identify risk factors or protective factors - evaluate preventive and therapeutic measures - provide the foundation for developing public policy and regulatory decisions
4 Historical Examples Edward Jenner ( ) - smallpox survivors were immune to the disease - variolation, the administration of material from infected people, was common (dangerous) practice - cowpox (mild form of smallpox) was found in milkmaids, who never contracted smallpox - pus from cowpox-infected patient was used to perform the first successful smallpox vaccination - miasmatic theory of cholera: cloud of disease close to earth, with lower altitudes more susceptible than higher ones - house to house survey of where cholera deaths obtained their water - proof of contagious nature and transmission pathways John Snow ( )
5 Point Prevalence Morbidity Measures Prevalence (π) proportion of affected individuals present in a population at a specific time point mathematically: probability π t that an individual randomly drawn at a specific time point is affected Period Prevalence proportion of affected individuals present in a population during a specific time period mathematically: probability π d that a randomly drawn individual is, or has been, affected during a specific time period
6 Period and Point Prevalence time 30 years period prevalence 4 ˆd π = = point prevalence 3 ˆt π = =
7 Confidence Interval The number X of diseased individuals in a sample of size n follows a Bin(n,π) distribution. KI: πˆ ± t1 α/2,n 1 π ˆ (1 πˆ) n yields a confidence interval for the estimate of π. Example: 20 diseased among 35 probands πˆd = = 95%KI: ± 2.04 = 0.57 ±
8 Morbidity Measures Incidence Proportion (γ), "Risk" A: number of new cases in a population at risk that occur during a specified time period N: number of individuals at risk during a specified time period γ = A N mathematically: probability (or risk) that an unaffected, randomly chosen individual gets affected during the time period of interest
9 Incidence Proportion time T: 30 years 3 ˆ γ = =
10 Morbidity Measures Incidence Rate (γ), "Risk" N: number of individuals at risk during time period A: number of new cases arising during time period T i : time units spent under risk by the i th individual γ = A N i = 1 Ti mathematically: (time) rate at which unaffected, randomly chosen individuals get affected
11 Incidence Rate time T: 30 years 3 γˆ = = incidents per person-year
12 Prevalence and Incidence D: disease duration 1-π γ prevalence pool π 1 E(D) expected prevalence pool inflow γ ( 1 π) t expected prevalence pool outflow 1 π t E(D)
13 Prevalence and Incidence In a stable, closed population (i.e. without migration into, or out of, the population) γ ( 1 π) t = 1 π t E(D) so that 1 π π = γ E(D) Through causing longer disease duration, improved medical care may increase the disease burden to society in the form of an increased prevalence.
14 Typhus Pediculus humanus Rickettsia prowazekii In the German population, the incidence rate of typhus is per year. The average disease duration is approximately one month. 1 π π = γ E(D) = = In the German population, approximately =14 cases of typhus are to be expected at any point in time.
15 Prevalence and Incidence Problems - ambiguous or incorrect diagnoses, latency - identification of highly selected cases from hospital admissions (severity, policy) - bad recording of cases (incomplete, missing) - variable diagnostic standards (temporal, regional) - ambiguous definition of population base (medical, ethnic, social) - temporal changes of disease patterns (spatial, phenotypical)
16 Effect Measures Relative Risk (ρ) Let a population be stratified into two strata (e.g. "exposed", "not exposed") with corresponding incidence rates or proportions ("risks") γ e and γ n during the observational period. ρ = γ γ e n is called the 'relative risk' under exposure. ρ>1: "risk factor", ρ<1: "protective"
17 Relative Risk (ρ) exposed not exposed time 30 years 5/ ˆ ρ = = = 2/
18 Clinical Trials Types of Epidemiological Studies Experimental (Interventional) - performed on single diseased individuals in a clinical setting - evaluation of therapeutic measures (e.g. drugs) Field Trials Assignment of Exposure by Investigator - performed on single non-diseased individuals in the field - evaluation of preventive measures (e.g. vaccination) Community Interventions - performed on groups of non-diseased individuals - evaluation of preventive measures (e.g. water treatment)
19 not exposed exposed Archetypal Experimental Study time
20 Cohort Studies Types of Epidemiological Studies - performed prospectively on non-diseased individuals of known exposure status, disease incidences are recorded Case-Control Studies Non-Experimental (Observational) Assignment of Exposure by Nature - performed retrospectively on individuals of known disease status, exposure status is recorded Cross-Sectional (Prevalence) Studies - performed retrospectively on the whole population or on a representative sample, disease and exposure is recorded
21 Archetypal Observational Study time
22 The Framingham Study Objective To identify the common factors or characteristics that contribute to cardiovascular disease (CVD) by following its development over a long period of time in a large group of participants who had not yet developed overt symptoms of CVD or suffered a heart attack or stroke. Design In 1948, 5209 men and women between the ages of 30 and 62 were recruited from Framingham, Massachusetts (representing 2/3 of the adult population). In 1971, another sample of 5135 men and women was established, comprising the offspring of the original cohort and their spouses.
23 The Framingham Study Results Careful monitoring of the Framingham Study population has led to the identification of the major CVD risk factors - high blood pressure - high blood cholesterol - smoking - obesity - diabetes - physical inactivity and critical information upon related factors such as age, gender, and psychosocial issues. The Framingham study has produced approximately 3500 articles in leading medical journals.
24 Risk and Odds Odds = 1 Risk Risk "The risk of catching a viral flue this winter is 0.20." one affected among five at risk "The odds of catching a viral flue this winter is 0.25." one affected for every four non-affected
25 Horse Race Betting "Old Mule" payoff odds 1:5 1:10 1:50 1:200 fair poor poor poor good fair poor poor good good fair poor good good good fair
26 Effect Measures Odds Ratio (OR) OR = γ γ e n /(1 /(1 γ γ e n ) ) If risks γ e and γ n are "sufficiently small" for the chosen time unit, i.e. of the order a few percent, then OR = γ γ e n /(1 /(1 γ γ e n ) ) γ γ e n = ρ
27 Odds Ratio (OR) exposed not exposed time 10 years time unit: 10 years 2 / 8 OR = = 1/ /10 ρˆ = = 1/
28 Odds Ratio (OR) not exposed exposed time 30 years time unit: 30 years 5/5 5/10 OR = = 4.00 ρˆ = = /8 2/10
29 Which Effect Measure? Cohort Studies (Relative Risk) affected not affected total exposed a b a+b not exposed c d total a+c b+d c+d n a a A e n and + b Ne c + d Nn a/(a c/(c + + b) d) = ˆγ ˆγ e n c = ρˆ A
30 Which Effect Measure? Case-Control Studies (Odds Ratio) affected not affected total exposed a b a+b not exposed c d total a+c b+d c+d n a c A A e n and b d N N e n A A e n a/c b/d (N e A /An A )/(N e A )... ˆγ ˆγ n /(1 ˆγ /(1 ˆγ e e e = = = n n n ) ) OR
31 Effect Measures Confidence Intervals ρ ˆ = a/(a c/(c + + b) d) OR = a/c b/d σˆ ln( ρ ) = 1 a a 1 + b + 1 c c 1 + d 1 a 1 b 1 c σˆ ln( OR) = d confidence intervals for the natural logarithms ln( ˆ) ρ ± z 1 σˆ α/2 ln( ρ) ln( OR) ± α/2 z 1 σˆ ln(or)
32 Cohort Study affected not affected total exposed not exposed total a/(a + b) 10/150 a/c 10/5 ρˆ = = = 2.00 OR = = = c/(c + d) 5/150 b/d 140/145 95% CI: % CI:
33 Case-Control Study affected not affected total exposed not exposed total a/c 100/50 OR = = = b/d 140/ % CI: a/(a + b) 100/240 ˆ ρ = = = c/(c + d) 50/
34 Which Effect Measure? Case-control studies do not normally allow the estimation of relative risks. An odds ratio provides a good approximation of the relative risk for a disease if the incidence rate (over the chosen time unit) is small.
35 Attributable Risk Aetiological Fraction Q: Which incidences are due to the exposure? A: This question cannot be answered on the basis of epidemiological data alone. E.g. many smokers will get lung cancer from causes other than tobacco smoke (e.g. asbestos, radiation, chance).
36 Attributable Risk Rate Fraction Q: What proportion of the risk under exposure is due to the exposure? AR = γ e γ γ e n = ρ ρ 1 assesses the excess risk in an individual.
37 Attributable Risk (AR) γ e,males = 0.50 γ n,males = 0.20 γ e,females = 0.08 γ n,females = 0.02 ρ = 0.50/ ρ = 0.08/ males = females = AR males = = 0.60 AR females = = Although the disease risk of exposed males is much higher than the disease risk of exposed females, the AR is higher in females because their relative risk is higher.
38 Population Attributable Risk Excess Fraction Q: What proportion of the incidences in the population is attributable to the exposure? PAR = γ γ γ n = f e fe ( ρ 1) ( ρ 1) + 1 γ: general incidence, f e : exposure frequency assesses the excess morbidity in a population.
39 Population Attributable Risk (PAR) γ e,males = 0.50 γ n,males = 0.20 γ e,females = 0.08 γ n,females = 0.02 ρ = 0.50/ ρ = 0.08/ males = females = f e,males = 0.20 f e,females = PAR males = = 0.23 PAR females = = Although the AR is higher in females than in males, the PAR's are the same because males are exposed more frequently than females.
40 Summary - Epidemiology is the science that studies the distribution of diseases and of their causal factors in populations. -The major morbidity measures used in epidemiology are the prevalence, i.e. the disease frequency, and the incidence, i.e. the occurrence rate of new cases. -Epidemiological studies can be either interventional or observational. In terms of their timing, studies can be of prospective or retrospective design. -The effect of an exposure upon disease risk can be measured by the relative risk or the odds ratio. -(Observational, retrospective) case-control studies do not allow the estimation of relative risks, only of odds ratios.
41 Appendix Standardisation Let a population be stratified into k strata (e.g. age, gender) with incidence rates γ 1,...,γ k. Let s 1,...,s k be "standard" person-times, e.g. in a reference population. γ S = k s γ i= 1 i i k s i= 1 i is called the 'standardised incidence rate'.
42 Appendix: Sex-Specific Incidence Rates population females males a Σt i ˆγ f a Σt i ˆγ m y y y y ˆ1 γ = 10/300 = ˆ2 γ = 11/600 = y -1 y -1
43 Appendix: Sex-Specific Incidence Rates population females males a Σt i ˆγ f a Σt i ˆγ m y y y y y -1 ˆ1 γ = 10/300 = ˆ2 γ = 11/600 = y -1 s female =150 s male =100 ˆγ 1, S = ( ) /250 = ˆγ 2, S = ( ) /250 = y -1 y -1
44 Appendix: Collapsing of Relative Risks γ e,males = 0.50 γ n,males = 0.20 γ e,females = 0.08 γ n,females = relative risk overall females 2.5 males proportion of males
45 Appendix: Collapsing of Odds Ratios γ e,males = 0.50 γ n,males = 0.20 γ e,females = 0.08 γ n,females = females odds ratio overall males proportion of males
Logistic Regression Predicting the Chances of Coronary Heart Disease. Multivariate Solutions
 Logistic Regression Predicting the Chances of Coronary Heart Disease Multivariate Solutions What is Logistic Regression? Logistic regression in a nutshell: Logistic regression is used for prediction of
Logistic Regression Predicting the Chances of Coronary Heart Disease Multivariate Solutions What is Logistic Regression? Logistic regression in a nutshell: Logistic regression is used for prediction of
Using Epidemiology to Identify the Cause of Disease: Cohort study
 Using Epidemiology to Identify the Cause of Disease: Cohort study Sakda Arj-ong Vallipakorn, M.D., MSICT., MSIS., PhD.(Clinical Epidemiology) Pediatrics, Pediatric Cardiology Emergency Medicine, Pediatric
Using Epidemiology to Identify the Cause of Disease: Cohort study Sakda Arj-ong Vallipakorn, M.D., MSICT., MSIS., PhD.(Clinical Epidemiology) Pediatrics, Pediatric Cardiology Emergency Medicine, Pediatric
1 Case Control Studies
 Statistics April 11, 2013 Debdeep Pati 1 Case Control Studies 1. Case-control (retrospective) study: Select cases, Select controls, Compare cases and controls 2. Cutaneous melanoma (Autier, 1996). 420
Statistics April 11, 2013 Debdeep Pati 1 Case Control Studies 1. Case-control (retrospective) study: Select cases, Select controls, Compare cases and controls 2. Cutaneous melanoma (Autier, 1996). 420
Trial Designs. Professor Peter Cameron
 Trial Designs Professor Peter Cameron OVERVIEW Review of Observational methods Principles of experimental design applied to observational studies Population Selection Looking for bias Inference Analysis
Trial Designs Professor Peter Cameron OVERVIEW Review of Observational methods Principles of experimental design applied to observational studies Population Selection Looking for bias Inference Analysis
An Introduction to Epidemiology
 An Introduction to Epidemiology Wei Liu, MPH Biostatistics Core Pennington Biomedical Research Center Baton Rouge, LA Last edited: January, 14 th, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.................................................................
An Introduction to Epidemiology Wei Liu, MPH Biostatistics Core Pennington Biomedical Research Center Baton Rouge, LA Last edited: January, 14 th, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.................................................................
Epidemiologic Study Designs. (RCTs)
 Epidemiologic Study Designs Epidemiologic Study Designs Experimental (RCTs) Observational Analytical Descriptive Case-Control Cohort + cross-sectional & ecologic Epidemiologic Study Designs Descriptive
Epidemiologic Study Designs Epidemiologic Study Designs Experimental (RCTs) Observational Analytical Descriptive Case-Control Cohort + cross-sectional & ecologic Epidemiologic Study Designs Descriptive
Welcome to this third module in a three-part series focused on epidemiologic measures of association and impact.
 Welcome to this third module in a three-part series focused on epidemiologic measures of association and impact. 1 This three-part series focuses on the estimation of the association between exposures
Welcome to this third module in a three-part series focused on epidemiologic measures of association and impact. 1 This three-part series focuses on the estimation of the association between exposures
observational studies Descriptive studies
 form one stage within this broader sequence, which begins with laboratory studies using animal models, thence to human testing: Phase I: The new drug or treatment is tested in a small group of people for
form one stage within this broader sequence, which begins with laboratory studies using animal models, thence to human testing: Phase I: The new drug or treatment is tested in a small group of people for
Is There An Association?
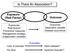 Is There An Association? Exposure (Risk Factor) Outcome Exposures Risk factors Preventive measures Management strategy Independent variables Outcomes Dependent variable Disease occurrence Lack of exercise
Is There An Association? Exposure (Risk Factor) Outcome Exposures Risk factors Preventive measures Management strategy Independent variables Outcomes Dependent variable Disease occurrence Lack of exercise
Public Health Strategies to Prevent Disease. HW: page 111 #1, 8-10, 14, 16
 Public Health Strategies to Prevent Disease HW: page 111 #1, 8-10, 14, 16 The Origin of Vaccines Smallpox is a highly contagious viral disease that results in a rash of blisters. This disease has now been
Public Health Strategies to Prevent Disease HW: page 111 #1, 8-10, 14, 16 The Origin of Vaccines Smallpox is a highly contagious viral disease that results in a rash of blisters. This disease has now been
Epidemiologic Measure of Association
 Measures of Disease Occurrence: Epidemiologic Measure of Association Basic Concepts Confidence Interval for population characteristic: Disease Exposure Present Absent Total Yes A B N 1 = A+B No C D N 2
Measures of Disease Occurrence: Epidemiologic Measure of Association Basic Concepts Confidence Interval for population characteristic: Disease Exposure Present Absent Total Yes A B N 1 = A+B No C D N 2
Answer keys for Assignment 4: Measures of disease frequency
 Answer keys for Assignment 4: Measures of disease frequency (The correct answer is underlined in bold text) 1. This statistic is used to estimate the risk of acquiring a disease. It may be measured as
Answer keys for Assignment 4: Measures of disease frequency (The correct answer is underlined in bold text) 1. This statistic is used to estimate the risk of acquiring a disease. It may be measured as
INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD.
 INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD. 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of this section, you will be able to: Provide a definition of epidemiology Describe the major types
INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD. 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of this section, you will be able to: Provide a definition of epidemiology Describe the major types
Epidemiology: Overview of Key Concepts and Study Design. Polly Marchbanks
 Epidemiology: Overview of Key Concepts and Study Design Polly Marchbanks Lecture Outline (1) Key epidemiologic concepts - Definition - What epi is not - What epi is - Process of epi research Lecture Outline
Epidemiology: Overview of Key Concepts and Study Design Polly Marchbanks Lecture Outline (1) Key epidemiologic concepts - Definition - What epi is not - What epi is - Process of epi research Lecture Outline
Study Design STUDY DESIGN CASE SERIES AND CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY DESIGN
 STUDY DESIGN CASE SERIES AND CROSS-SECTIONAL Daniel E. Ford, MD, MPH Vice Dean for Clinical Investigation Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Introduction to Clinical Research July 15, 2014 STUDY DESIGN Provides
STUDY DESIGN CASE SERIES AND CROSS-SECTIONAL Daniel E. Ford, MD, MPH Vice Dean for Clinical Investigation Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Introduction to Clinical Research July 15, 2014 STUDY DESIGN Provides
Sampling. (James Madison University) January 9, / 13
 Sampling The population is the entire group of individuals about which we want information. A sample is a part of the population from which we actually collect information. A sampling design describes
Sampling The population is the entire group of individuals about which we want information. A sample is a part of the population from which we actually collect information. A sampling design describes
Advanced IPD meta-analysis methods for observational studies
 Advanced IPD meta-analysis methods for observational studies Simon Thompson University of Cambridge, UK Part 4 IBC Victoria, July 2016 1 Outline of talk Usual measures of association (e.g. hazard ratios)
Advanced IPD meta-analysis methods for observational studies Simon Thompson University of Cambridge, UK Part 4 IBC Victoria, July 2016 1 Outline of talk Usual measures of association (e.g. hazard ratios)
Introduction to Epidemiology. Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi Community Health, first semester 2017/ 1018 Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan
 Introduction to Epidemiology Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi Community Health, first semester 2017/ 1018 Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan Lecture Contents. 1. Epidemiology defined. 2. The components of
Introduction to Epidemiology Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi Community Health, first semester 2017/ 1018 Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan Lecture Contents. 1. Epidemiology defined. 2. The components of
The Gender Divide Women, Men and Heart Disease February 2017
 The Gender Divide Women, Men and Heart Disease February 2017 Nandita S. Scott, MD FACC Co-Director MGH Heart Center Corrigan Women s Heart Health Program Massachusetts General Hospital Heart Disease For
The Gender Divide Women, Men and Heart Disease February 2017 Nandita S. Scott, MD FACC Co-Director MGH Heart Center Corrigan Women s Heart Health Program Massachusetts General Hospital Heart Disease For
Data that can be classified as belonging to a distinct number of categories >>result in categorical responses. And this includes:
 This sheets starts from slide #83 to the end ofslide #4. If u read this sheet you don`t have to return back to the slides at all, they are included here. Categorical Data (Qualitative data): Data that
This sheets starts from slide #83 to the end ofslide #4. If u read this sheet you don`t have to return back to the slides at all, they are included here. Categorical Data (Qualitative data): Data that
Risk Study. Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Definition
 Risk Study Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics What is Risk? Definition The probability of some untoward event The likelihood that people who are exposed to certain factors (risk factors)
Risk Study Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics What is Risk? Definition The probability of some untoward event The likelihood that people who are exposed to certain factors (risk factors)
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club. A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology. August, 2013
 Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Epidemiology overview
 Epidemiology overview Riris Andono Ahmad 1 Public Health Approach Surveillance: What is the problem? Problem Risk Factor Identification: What is the cause? Intervention Evaluation: What works? Implementation:
Epidemiology overview Riris Andono Ahmad 1 Public Health Approach Surveillance: What is the problem? Problem Risk Factor Identification: What is the cause? Intervention Evaluation: What works? Implementation:
The Late Pretest Problem in Randomized Control Trials of Education Interventions
 The Late Pretest Problem in Randomized Control Trials of Education Interventions Peter Z. Schochet ACF Methods Conference, September 2012 In Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, August 2010,
The Late Pretest Problem in Randomized Control Trials of Education Interventions Peter Z. Schochet ACF Methods Conference, September 2012 In Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, August 2010,
Research Methodology Workshop. Study Type
 Research Methodology Workshop Study Type What type of question? Frequency: how common is it? Aetiology: What caused this? Intervention: Does this intervention work? Diagnosis or test evaluation: How accurate
Research Methodology Workshop Study Type What type of question? Frequency: how common is it? Aetiology: What caused this? Intervention: Does this intervention work? Diagnosis or test evaluation: How accurate
Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies
 Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies Post-Graduate Course, Training in Research in Sexual Health, 24 Feb 05 Isaac M. Malonza, MD, MPH Department of Reproductive Health and Research
Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies Post-Graduate Course, Training in Research in Sexual Health, 24 Feb 05 Isaac M. Malonza, MD, MPH Department of Reproductive Health and Research
Appendix S1. List of Figures. List of Tables
 Appendix S1 List of Figures S1 Comparison of death rates in RealAge sample to US death rates...................... 1 S2 RealAge delta in California sample with full identifiers..........................
Appendix S1 List of Figures S1 Comparison of death rates in RealAge sample to US death rates...................... 1 S2 RealAge delta in California sample with full identifiers..........................
W e have previously described the disease impact
 606 THEORY AND METHODS Impact numbers: measures of risk factor impact on the whole population from case-control and cohort studies R F Heller, A J Dobson, J Attia, J Page... See end of article for authors
606 THEORY AND METHODS Impact numbers: measures of risk factor impact on the whole population from case-control and cohort studies R F Heller, A J Dobson, J Attia, J Page... See end of article for authors
University of Wollongong. Research Online. Australian Health Services Research Institute
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Health Services Research Institute Faculty of Business 2011 Measurement of error Janet E. Sansoni University of Wollongong, jans@uow.edu.au Publication
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Health Services Research Institute Faculty of Business 2011 Measurement of error Janet E. Sansoni University of Wollongong, jans@uow.edu.au Publication
Vocabulary. Bias. Blinding. Block. Cluster sample
 Bias Blinding Block Census Cluster sample Confounding Control group Convenience sample Designs Experiment Experimental units Factor Level Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population
Bias Blinding Block Census Cluster sample Confounding Control group Convenience sample Designs Experiment Experimental units Factor Level Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population
3. Factors such as race, age, sex, and a person s physiological state are all considered determinants of disease. a. True
 / False 1. Epidemiology is the basic science of public health. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: CNIA.BOYL.17.2.1 - Define epidemiology. 2. Within the field of epidemiology, the term distribution refers to the relationship
/ False 1. Epidemiology is the basic science of public health. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: CNIA.BOYL.17.2.1 - Define epidemiology. 2. Within the field of epidemiology, the term distribution refers to the relationship
Stratified Tables. Example: Effect of seat belt use on accident fatality
 Stratified Tables Often, a third measure influences the relationship between the two primary measures (i.e. disease and exposure). How do we remove or control for the effect of the third measure? Issues
Stratified Tables Often, a third measure influences the relationship between the two primary measures (i.e. disease and exposure). How do we remove or control for the effect of the third measure? Issues
Page down (pdf converstion error)
 1 of 6 2/10/2005 7:57 PM Weekly August6, 1999 / 48(30);649-656 2 of 6 2/10/2005 7:57 PM Achievements in Public Health, 1900-1999: Decline in Deaths from Heart Disease and Stroke -- United States, 1900-1999
1 of 6 2/10/2005 7:57 PM Weekly August6, 1999 / 48(30);649-656 2 of 6 2/10/2005 7:57 PM Achievements in Public Health, 1900-1999: Decline in Deaths from Heart Disease and Stroke -- United States, 1900-1999
Causal Association : Cause To Effect. Dr. Akhilesh Bhargava MD, DHA, PGDHRM Prof. Community Medicine & Director-SIHFW, Jaipur
 Causal Association : Cause To Effect Dr. MD, DHA, PGDHRM Prof. Community Medicine & Director-SIHFW, Jaipur Measure of Association- Concepts If more disease occurs in a group that smokes compared to the
Causal Association : Cause To Effect Dr. MD, DHA, PGDHRM Prof. Community Medicine & Director-SIHFW, Jaipur Measure of Association- Concepts If more disease occurs in a group that smokes compared to the
Key causes of preventable deaths in New Zealand In a population of 10,000 New Zealanders, every year there will be about:
 Preventive care - Chronic Disease Management in primary care: a population perspective Rod Jackson University of Auckland New Zealand (22/11/8) Key causes of preventable deaths in New Zealand In a population
Preventive care - Chronic Disease Management in primary care: a population perspective Rod Jackson University of Auckland New Zealand (22/11/8) Key causes of preventable deaths in New Zealand In a population
Chapter 02. Basic Research Methodology
 Chapter 02 Basic Research Methodology Definition RESEARCH Research is a quest for knowledge through diligent search or investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new
Chapter 02 Basic Research Methodology Definition RESEARCH Research is a quest for knowledge through diligent search or investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new
Outline. Introduction to Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. History of epidemiology
 Outline Introduction to Epidemiology Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/Travis County Health & Human Services Department Define History Basis of epidemiology Objectives of epidemiology Causal inference
Outline Introduction to Epidemiology Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/Travis County Health & Human Services Department Define History Basis of epidemiology Objectives of epidemiology Causal inference
Vaccine Efficacy, Effectiveness and Impact. G. HANQUET, KCE, 9 September 2017
 Vaccine Efficacy, Effectiveness and Impact G. HANQUET, KCE, 9 September 2017 RvB - CA, 16/09/2014 Outline The confusion Vaccine effects Methodologies Challenges Implications for decision making 2 Life
Vaccine Efficacy, Effectiveness and Impact G. HANQUET, KCE, 9 September 2017 RvB - CA, 16/09/2014 Outline The confusion Vaccine effects Methodologies Challenges Implications for decision making 2 Life
Modern Epidemiology A New Computational Science
 Modern Epidemiology A New Computational Science Facilitating Epidemiological Research through Computational Tools Armin R. Mikler Computational Epidemiology Research Laboratory Department of Computer Science
Modern Epidemiology A New Computational Science Facilitating Epidemiological Research through Computational Tools Armin R. Mikler Computational Epidemiology Research Laboratory Department of Computer Science
Infectious disease modeling
 Infectious disease modeling Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson) Infectious disease
Infectious disease modeling Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4500, Spring 2017 M. Macauley (Clemson) Infectious disease
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems 1 S C I E N C E 8 Scientific investigation leads to new knowledge about body systems and new medical applications. 2 S E C T I O N 4. 0 1 Developing a Theory for Disease 3 T O
Unit B: Cells and Systems 1 S C I E N C E 8 Scientific investigation leads to new knowledge about body systems and new medical applications. 2 S E C T I O N 4. 0 1 Developing a Theory for Disease 3 T O
Vascular Diseases. Overview: Selected Slides
 Vascular Diseases Overview: Selected Slides Total deaths and change in vascular death rates
Vascular Diseases Overview: Selected Slides Total deaths and change in vascular death rates
S160 #15. Comparing Two Proportions, Part 3 Odds Ratio. JC Wang. March 15, 2016
 S60 #5 Comparing Two Proportions, Part 3 JC Wang March 5, 206 Outline Odds Odds 2 JC Wang WMU) S60 #5 S60, Lecture 5 2 / The odds that an event occurs is Odds = Odds Probability that event occurs Probability
S60 #5 Comparing Two Proportions, Part 3 JC Wang March 5, 206 Outline Odds Odds 2 JC Wang WMU) S60 #5 S60, Lecture 5 2 / The odds that an event occurs is Odds = Odds Probability that event occurs Probability
Cohort studies. Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva Nguyen Thi My Huong, MD PhD WHO/RHR/SIS
 Cohort studies Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2012 Nguyen Thi My Huong, MD PhD WHO/RHR/SIS OUTLINE Overview Definitions Study design Basic measures Advantages and disadvantages
Cohort studies Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2012 Nguyen Thi My Huong, MD PhD WHO/RHR/SIS OUTLINE Overview Definitions Study design Basic measures Advantages and disadvantages
Confounding, Effect modification, and Stratification
 Confounding, Effect modification, and Stratification Tunisia, 30th October 2014 Acknowledgment: Kostas Danis Takis Panagiotopoulos National Schoool of Public Health, Athens, Greece takis.panagiotopoulos@gmail.com
Confounding, Effect modification, and Stratification Tunisia, 30th October 2014 Acknowledgment: Kostas Danis Takis Panagiotopoulos National Schoool of Public Health, Athens, Greece takis.panagiotopoulos@gmail.com
Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Management Making a Difference
 Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Management Making a Difference Norman Sharpe March 2014 Numbers and age-standardised mortality rates from all causes, by sex, 1950 2010 Death rates halved Life expectancy
Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Management Making a Difference Norman Sharpe March 2014 Numbers and age-standardised mortality rates from all causes, by sex, 1950 2010 Death rates halved Life expectancy
Chapter 2. Epidemiological and Toxicological Studies
 Chapter 2 Epidemiological and Toxicological Studies Introduction Epidemiological and toxicological studies seek to determine the cause of a particular illness or disease. Etiology is the study of causes.
Chapter 2 Epidemiological and Toxicological Studies Introduction Epidemiological and toxicological studies seek to determine the cause of a particular illness or disease. Etiology is the study of causes.
Study Designs in Epidemiology
 Study Designs in Epidemiology Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi, BDS, MPH, DrPH First semester 2017/ 2018 Department of Family and Community Medicine School of Medicine/ The University of Jordan Epidemiologic Study
Study Designs in Epidemiology Dr. Sireen Alkhaldi, BDS, MPH, DrPH First semester 2017/ 2018 Department of Family and Community Medicine School of Medicine/ The University of Jordan Epidemiologic Study
History and aims of immunisation. Dr Anna Clarke Department of Public Health Dr. Steevens Hospital Dublin 8
 History and aims of immunisation Dr Anna Clarke Department of Public Health Dr. Steevens Hospital Dublin 8 Objectives To examine the history of immunisation To explain the aim of immunisation To develop
History and aims of immunisation Dr Anna Clarke Department of Public Health Dr. Steevens Hospital Dublin 8 Objectives To examine the history of immunisation To explain the aim of immunisation To develop
ADENIYI MOFOLUWAKE MPH APPLIED EPIDEMIOLOGY WEEK 5 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT APRIL
 ADENIYI MOFOLUWAKE MPH 510 - APPLIED EPIDEMIOLOGY WEEK 5 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT APRIL 4 2013 Question 1: What makes the first study a case-control study? The first case study is a case-control study because
ADENIYI MOFOLUWAKE MPH 510 - APPLIED EPIDEMIOLOGY WEEK 5 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT APRIL 4 2013 Question 1: What makes the first study a case-control study? The first case study is a case-control study because
8/10/2012. Education level and diabetes risk: The EPIC-InterAct study AIM. Background. Case-cohort design. Int J Epidemiol 2012 (in press)
 Education level and diabetes risk: The EPIC-InterAct study 50 authors from European countries Int J Epidemiol 2012 (in press) Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most common chronic
Education level and diabetes risk: The EPIC-InterAct study 50 authors from European countries Int J Epidemiol 2012 (in press) Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most common chronic
Biostatistics and Epidemiology Step 1 Sample Questions Set 1
 Biostatistics and Epidemiology Step 1 Sample Questions Set 1 1. A study wishes to assess birth characteristics in a population. Which of the following variables describes the appropriate measurement scale
Biostatistics and Epidemiology Step 1 Sample Questions Set 1 1. A study wishes to assess birth characteristics in a population. Which of the following variables describes the appropriate measurement scale
Protecting the gains: what changes are needed to prevent a reversal of the downward CVD mortality trend?
 Protecting the gains: what changes are needed to prevent a reversal of the downward CVD mortality trend? Abstract 117 Jesse D Ortendahl 1, Allison L Diamant 2, Peter P Toth 3, Dasha Cherepanov 1, Amanda
Protecting the gains: what changes are needed to prevent a reversal of the downward CVD mortality trend? Abstract 117 Jesse D Ortendahl 1, Allison L Diamant 2, Peter P Toth 3, Dasha Cherepanov 1, Amanda
Gender Identity and Expression. Week 8
 Gender Identity and Expression Week 8 1 Objectives 1. Describe research methods for studying gender identity and expression as they relate to health 2. Identify some key health disparities in relation
Gender Identity and Expression Week 8 1 Objectives 1. Describe research methods for studying gender identity and expression as they relate to health 2. Identify some key health disparities in relation
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Clair C, Rigotti NA, Porneala B, et al. Association of smoking cessation and weight change with cardiovascular disease among people with and without diabetes. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.1644.
Supplementary Online Content Clair C, Rigotti NA, Porneala B, et al. Association of smoking cessation and weight change with cardiovascular disease among people with and without diabetes. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.1644.
Section 3.2, Vaccinations, explores how and who discovered vaccines.
 Curriculum links: D5, D6, D7, R4 PSE: (1a), (1e). Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes Section 3.2, Vaccinations, explores how and who discovered vaccines. In this is
Curriculum links: D5, D6, D7, R4 PSE: (1a), (1e). Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes Section 3.2, Vaccinations, explores how and who discovered vaccines. In this is
Chapter 2 Epidemiology. Multiple Choice Questions
 Medical Sociology 13th Edition Cockerham TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/medical-sociology-13th-editioncockerham-test-bank/ Medical Sociology 13th Edition Cockerham SOLUTIONS
Medical Sociology 13th Edition Cockerham TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/medical-sociology-13th-editioncockerham-test-bank/ Medical Sociology 13th Edition Cockerham SOLUTIONS
Risk Factors for NCDs
 Risk Factors for NCDs Objectives: Define selected risk factors such as; tobacco use, diet, nutrition, physical activity, obesity, and overweight Present the epidemiology and significance of the risk factors
Risk Factors for NCDs Objectives: Define selected risk factors such as; tobacco use, diet, nutrition, physical activity, obesity, and overweight Present the epidemiology and significance of the risk factors
Diabetes. Ref HSCW 024
 Diabetes Ref HSCW 024 Why is it important? Diabetes is an increasingly common, life-long, progressive but largely preventable health condition affecting children and adults, causing a heavy burden on health
Diabetes Ref HSCW 024 Why is it important? Diabetes is an increasingly common, life-long, progressive but largely preventable health condition affecting children and adults, causing a heavy burden on health
Scientific Method in Vaccine History
 Student Name: Student Recording Sheet 1 The Scientific Method Scientific Method in Vaccine History 1. Why is there no single model of the scientific method? The scientific method is a way of asking questions.
Student Name: Student Recording Sheet 1 The Scientific Method Scientific Method in Vaccine History 1. Why is there no single model of the scientific method? The scientific method is a way of asking questions.
Supplemental tables/figures
 Supplemental tables/figures Table S:Baseline variables included in calculation of QRISK and Framingham scores Ethnicity (European, Indian Pakistani, Bangladeshi, Black African, Black Caribbean) QRISK Age,
Supplemental tables/figures Table S:Baseline variables included in calculation of QRISK and Framingham scores Ethnicity (European, Indian Pakistani, Bangladeshi, Black African, Black Caribbean) QRISK Age,
Infectious Disease Surveillance in NZ. Michael Baker Department of Public Health, University of Otago, Wellington
 Infectious Disease Surveillance in NZ Michael Baker Department of Public Health, University of Otago, Wellington michael.baker@otago.ac.nz Outline Current best practice High quality surveillance of specific
Infectious Disease Surveillance in NZ Michael Baker Department of Public Health, University of Otago, Wellington michael.baker@otago.ac.nz Outline Current best practice High quality surveillance of specific
Dylan Small Department of Statistics, Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania. Based on joint work with Paul Rosenbaum
 Instrumental variables and their sensitivity to unobserved biases Dylan Small Department of Statistics, Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania Based on joint work with Paul Rosenbaum Overview Instrumental
Instrumental variables and their sensitivity to unobserved biases Dylan Small Department of Statistics, Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania Based on joint work with Paul Rosenbaum Overview Instrumental
Introduction, Summary, and Conclusions
 Chapter 1 Introduction, Summary, and Conclusions David M. Burns, Lawrence Garfinkel, and Jonathan M. Samet Cigarette smoking is the largest preventable cause of death and disability in developed countries
Chapter 1 Introduction, Summary, and Conclusions David M. Burns, Lawrence Garfinkel, and Jonathan M. Samet Cigarette smoking is the largest preventable cause of death and disability in developed countries
Low-Carbohydrate Diets and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-based Cohort Study and Pooling Prospective Studies
 Low-Carbohydrate Diets and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-based Cohort Study and Pooling Prospective Studies Mohsen Mazidi 1, Niki Katsiki 2, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis 3, Maciej Banach
Low-Carbohydrate Diets and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-based Cohort Study and Pooling Prospective Studies Mohsen Mazidi 1, Niki Katsiki 2, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis 3, Maciej Banach
Analyzing diastolic and systolic blood pressure individually or jointly?
 Analyzing diastolic and systolic blood pressure individually or jointly? Chenglin Ye a, Gary Foster a, Lisa Dolovich b, Lehana Thabane a,c a. Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster
Analyzing diastolic and systolic blood pressure individually or jointly? Chenglin Ye a, Gary Foster a, Lisa Dolovich b, Lehana Thabane a,c a. Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY
 IP THE INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY EXECUTIVE SUMMARIES IP THE INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM 61 NEW CAVENDISH STREET, LONDON, W1M 8AR SWITCHBOARD : 0171-467 7100 FAX : DIRECT LINE 0171-255 1472
IP THE INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY EXECUTIVE SUMMARIES IP THE INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM 61 NEW CAVENDISH STREET, LONDON, W1M 8AR SWITCHBOARD : 0171-467 7100 FAX : DIRECT LINE 0171-255 1472
Statistical Fact Sheet Populations
 Statistical Fact Sheet Populations At-a-Glance Summary Tables Men and Cardiovascular Diseases Mexican- American Males Diseases and Risk Factors Total Population Total Males White Males Black Males Total
Statistical Fact Sheet Populations At-a-Glance Summary Tables Men and Cardiovascular Diseases Mexican- American Males Diseases and Risk Factors Total Population Total Males White Males Black Males Total
Reflection Questions for Math 58B
 Reflection Questions for Math 58B Johanna Hardin Spring 2017 Chapter 1, Section 1 binomial probabilities 1. What is a p-value? 2. What is the difference between a one- and two-sided hypothesis? 3. What
Reflection Questions for Math 58B Johanna Hardin Spring 2017 Chapter 1, Section 1 binomial probabilities 1. What is a p-value? 2. What is the difference between a one- and two-sided hypothesis? 3. What
Cohort studies. Training course in research methodology and research protocol development Geneva Nguyen Thi My Huong, MD PhD WHO/RHR/SIS
 Cohort studies Training course in research methodology and research protocol development Geneva 2018 Nguyen Thi My Huong, MD PhD WHO/RHR/SIS OUTLINE Overview Definitions Study design Basic measures Advantages
Cohort studies Training course in research methodology and research protocol development Geneva 2018 Nguyen Thi My Huong, MD PhD WHO/RHR/SIS OUTLINE Overview Definitions Study design Basic measures Advantages
Dr. Alongkone Phengsavanh University of Health Sciences Vientiane, Laos
 Dr. Alongkone Phengsavanh University of Health Sciences Vientiane, Laos Epidemiology: Epi = upon Demos = people Logy = study of Epidemiology is a discipline that describes, quantifies, and postulates causal
Dr. Alongkone Phengsavanh University of Health Sciences Vientiane, Laos Epidemiology: Epi = upon Demos = people Logy = study of Epidemiology is a discipline that describes, quantifies, and postulates causal
Part 1. An Ran Chen MY Camp 2 nd Round 2012
 Part 1 In the lecture, Professor Tom Körner focuses on the various mathematical ideas used to understand the spread of infectious diseases, focussing especially on Small pox. These are as follow: 1. Using
Part 1 In the lecture, Professor Tom Körner focuses on the various mathematical ideas used to understand the spread of infectious diseases, focussing especially on Small pox. These are as follow: 1. Using
Anatomy of Medical Studies: Part I. Emily D Agostino Epidemiology and Biostatistics CUNY School of Public Health at Hunter College
 Anatomy of Medical Studies: Part I!! Emily D Agostino Epidemiology and Biostatistics CUNY School of Public Health at Hunter College I. Standard format of a Medical Study Abstract (quick overview: what
Anatomy of Medical Studies: Part I!! Emily D Agostino Epidemiology and Biostatistics CUNY School of Public Health at Hunter College I. Standard format of a Medical Study Abstract (quick overview: what
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection in the world.
 Hi. I m Kristina Dahlstrom, an instructor in the Department of Head and Neck Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. My lecture today will be on the epidemiology of oropharyngeal
Hi. I m Kristina Dahlstrom, an instructor in the Department of Head and Neck Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. My lecture today will be on the epidemiology of oropharyngeal
Penelitian IKM/Epidemiologi. Contact: Blog: suyatno.blog.undip.ac.id Hp/Telp: /
 Penelitian IKM/Epidemiologi Oleh : Suyatno, Ir. MKes Contact: E-mail: suyatnofkmundip@gmail.com Blog: suyatno.blog.undip.ac.id Hp/Telp: 08122815730 / 024-70251915 Epidemiologic Study Designs I. Experimental
Penelitian IKM/Epidemiologi Oleh : Suyatno, Ir. MKes Contact: E-mail: suyatnofkmundip@gmail.com Blog: suyatno.blog.undip.ac.id Hp/Telp: 08122815730 / 024-70251915 Epidemiologic Study Designs I. Experimental
Heart Disease and Stroke in New Mexico. Facts and Figures: At-A-Glance
 Heart Disease and Stroke in New Mexico Facts and Figures: At-A-Glance December H e a r t D i s e a s e a n d S t r o k e Heart disease and stroke are the two most common conditions that fall under the
Heart Disease and Stroke in New Mexico Facts and Figures: At-A-Glance December H e a r t D i s e a s e a n d S t r o k e Heart disease and stroke are the two most common conditions that fall under the
Missing data. Patrick Breheny. April 23. Introduction Missing response data Missing covariate data
 Missing data Patrick Breheny April 3 Patrick Breheny BST 71: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/39 Our final topic for the semester is missing data Missing data is very common in practice, and can occur
Missing data Patrick Breheny April 3 Patrick Breheny BST 71: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/39 Our final topic for the semester is missing data Missing data is very common in practice, and can occur
You can t fix by analysis what you bungled by design. Fancy analysis can t fix a poorly designed study.
 You can t fix by analysis what you bungled by design. Light, Singer and Willett Or, not as catchy but perhaps more accurate: Fancy analysis can t fix a poorly designed study. Producing Data The Role of
You can t fix by analysis what you bungled by design. Light, Singer and Willett Or, not as catchy but perhaps more accurate: Fancy analysis can t fix a poorly designed study. Producing Data The Role of
Socioeconomic status and the 25x25 risk factors as determinants of premature mortality: a multicohort study of 1.7 million men and women
 Socioeconomic status and the 25x25 risk factors as determinants of premature mortality: a multicohort study of 1.7 million men and women (Lancet. 2017 Mar 25;389(10075):1229-1237) 1 Silvia STRINGHINI Senior
Socioeconomic status and the 25x25 risk factors as determinants of premature mortality: a multicohort study of 1.7 million men and women (Lancet. 2017 Mar 25;389(10075):1229-1237) 1 Silvia STRINGHINI Senior
Differences that occur by gender, race or ethnicity, education or income, disability, geographic location, or sexual orientation. Healthy People 2010
 Differences that occur by gender, race or ethnicity, education or income, disability, geographic location, or sexual orientation. Healthy People 2010 Health Inequalities: Measureable differences in health
Differences that occur by gender, race or ethnicity, education or income, disability, geographic location, or sexual orientation. Healthy People 2010 Health Inequalities: Measureable differences in health
Types of Biomedical Research
 INTRODUCTION & MEASUREMENT IN CLINICAL RESEARCH Sakda Arj Ong Vallipakorn, MD MSIT, MA (Information Science) Pediatrics, Pediatric Cardiology Emergency Medicine, Ped Emergency Family Medicine Section of
INTRODUCTION & MEASUREMENT IN CLINICAL RESEARCH Sakda Arj Ong Vallipakorn, MD MSIT, MA (Information Science) Pediatrics, Pediatric Cardiology Emergency Medicine, Ped Emergency Family Medicine Section of
The Current Pediatric Oncology Landscape
 The Current Pediatric Oncology Landscape An Imperative for Change Smita Bhatia, MD, MPH UAB Department of Pediatrics at Children s Hospital of Alabama Five-year Observed Survival Rates for Two Time Periods,
The Current Pediatric Oncology Landscape An Imperative for Change Smita Bhatia, MD, MPH UAB Department of Pediatrics at Children s Hospital of Alabama Five-year Observed Survival Rates for Two Time Periods,
Smoking decreases the duration of life lived with and without cardiovascular disease: a life course analysis of the Framingham Heart Study
 European Heart Journal (24) 25, 49 45 Clinical research Smoking decreases the duration of life lived with and without cardiovascular disease: a life course analysis of the Framingham Heart Study Abdullah
European Heart Journal (24) 25, 49 45 Clinical research Smoking decreases the duration of life lived with and without cardiovascular disease: a life course analysis of the Framingham Heart Study Abdullah
HEALTH PROMOTION AND CHRONIC DISEASE PREVENTION PROGRAM OREGON STATE OF THE HEART AND STROKE REPORT 2001 PREPARED BY.
 OREGON STATE OF THE HEART AND STROKE REPORT 2001 PREPARED BY THE OREGON DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN SERVICES HEALTH SERVICES HEALTH PROMOTION AND CHRONIC DISEASE PREVENTION PROGRAM www.healthoregon.org/hpcdp Contents
OREGON STATE OF THE HEART AND STROKE REPORT 2001 PREPARED BY THE OREGON DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN SERVICES HEALTH SERVICES HEALTH PROMOTION AND CHRONIC DISEASE PREVENTION PROGRAM www.healthoregon.org/hpcdp Contents
Epidemiological Model of HIV/AIDS with Demographic Consequences
 Advances in Applied Mathematical Biosciences. ISSN 2248-9983 Volume 5, Number 1 (2014), pp. 65-74 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Epidemiological Model of HIV/AIDS with
Advances in Applied Mathematical Biosciences. ISSN 2248-9983 Volume 5, Number 1 (2014), pp. 65-74 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Epidemiological Model of HIV/AIDS with
BLY1AP. General Certificate of Secondary Education March Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology) BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology)
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education March 2008 SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology) BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology)
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education March 2008 SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology) BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology)
CHAPTER 3 METHOD AND PROCEDURE
 CHAPTER 3 METHOD AND PROCEDURE Previous chapter namely Review of the Literature was concerned with the review of the research studies conducted in the field of teacher education, with special reference
CHAPTER 3 METHOD AND PROCEDURE Previous chapter namely Review of the Literature was concerned with the review of the research studies conducted in the field of teacher education, with special reference
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Inohara T, Xian Y, Liang L, et al. Association of intracerebral hemorrhage among patients taking non vitamin K antagonist vs vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants with in-hospital
Supplementary Online Content Inohara T, Xian Y, Liang L, et al. Association of intracerebral hemorrhage among patients taking non vitamin K antagonist vs vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants with in-hospital
Before Statement After
 CHAPTER 17 Immunity and Disease LESSON 1 Diseases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 17 Immunity and Disease LESSON 1 Diseases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
EPI 200C Final, June 4 th, 2009 This exam includes 24 questions.
 Greenland/Arah, Epi 200C Sp 2000 1 of 6 EPI 200C Final, June 4 th, 2009 This exam includes 24 questions. INSTRUCTIONS: Write all answers on the answer sheets supplied; PRINT YOUR NAME and STUDENT ID NUMBER
Greenland/Arah, Epi 200C Sp 2000 1 of 6 EPI 200C Final, June 4 th, 2009 This exam includes 24 questions. INSTRUCTIONS: Write all answers on the answer sheets supplied; PRINT YOUR NAME and STUDENT ID NUMBER
NOVEL BIOMARKERS AS RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
 NOVEL BIOMARKERS AS RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Amy Alman, PhD Assistant Professor of Epidemiology College of Public Health University of South Florida Causation is a concept central to epidemiology
NOVEL BIOMARKERS AS RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Amy Alman, PhD Assistant Professor of Epidemiology College of Public Health University of South Florida Causation is a concept central to epidemiology
sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify
![sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify](/thumbs/80/80506400.jpg) BE.104 Spring Epidemiology: Test Development and Relative Risk J. L. Sherley Agent X? Cause Health First, Some definitions Morbidity = Mortality = sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify death Easy
BE.104 Spring Epidemiology: Test Development and Relative Risk J. L. Sherley Agent X? Cause Health First, Some definitions Morbidity = Mortality = sickness, disease, [toxicity] Hard to quantify death Easy
How do we know that smoking causes lung cancer?
 How do we know that smoking causes lung cancer? Seif Shaheen Professor of Respiratory Epidemiology Centre for Primary Care and Public Health Blizard Institute Barts and The London School of Medicine and
How do we know that smoking causes lung cancer? Seif Shaheen Professor of Respiratory Epidemiology Centre for Primary Care and Public Health Blizard Institute Barts and The London School of Medicine and
Introduction to Epidemiology. January 21, 2015 Fresno State University Paul K. Mills, Ph.D., M.P.H.
 Introduction to Epidemiology January 21, 2015 Fresno State University Paul K. Mills, Ph.D., M.P.H. Epidemiology The study of the distribution and determinants of disease in human populations. Distribution-how
Introduction to Epidemiology January 21, 2015 Fresno State University Paul K. Mills, Ph.D., M.P.H. Epidemiology The study of the distribution and determinants of disease in human populations. Distribution-how
115 remained abstinent. 140 remained abstinent. Relapsed Remained abstinent Total
 Chapter 10 Exercises 1. Intent-to-treat analysis: Example 1 In a randomized controlled trial to determine whether the nicotine patch reduces the risk of relapse among smokers who have committed to quit,
Chapter 10 Exercises 1. Intent-to-treat analysis: Example 1 In a randomized controlled trial to determine whether the nicotine patch reduces the risk of relapse among smokers who have committed to quit,
Case-control studies. Hans Wolff. Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire. WHO- Postgraduate course 2007 CC studies
 Case-control studies Hans Wolff Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire Hans.Wolff@hcuge.ch Outline Case-control study Relation to cohort study Selection of controls Sampling
Case-control studies Hans Wolff Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire Hans.Wolff@hcuge.ch Outline Case-control study Relation to cohort study Selection of controls Sampling
HIGH LEVELS OF PREVENTABLE CHRONIC DIEASE, INJURY AND MENTAL HEALTH PROBLEMS
 HIGH LEVELS OF PREVENTABLE CHRONIC DIEASE, INJURY AND MENTAL HEALTH PROBLEMS Let s look at CANCER AS A WHOLE. What is the nature of the problem? Well, cancer is the growth of cells within the body. We
HIGH LEVELS OF PREVENTABLE CHRONIC DIEASE, INJURY AND MENTAL HEALTH PROBLEMS Let s look at CANCER AS A WHOLE. What is the nature of the problem? Well, cancer is the growth of cells within the body. We
Module 2: Fundamentals of Epidemiology Issues of Interpretation. Slide 1: Introduction. Slide 2: Acknowledgements. Slide 3: Presentation Objectives
 Slide 1: Introduction Issues of of Interpretation in in Epidemiologic Studies Developed through APTR Initiative to Enhance Prevention and Population Health Developed Education through in collaboration
Slide 1: Introduction Issues of of Interpretation in in Epidemiologic Studies Developed through APTR Initiative to Enhance Prevention and Population Health Developed Education through in collaboration
PhD Course in Biostatistics
 PhD Course in Biostatistics Univ.-Prof. DI Dr. Andrea Berghold Institute for Medical Informatics, Statistics and Documentation Medical University of Graz andrea.berghold@medunigraz.at Content Introduction
PhD Course in Biostatistics Univ.-Prof. DI Dr. Andrea Berghold Institute for Medical Informatics, Statistics and Documentation Medical University of Graz andrea.berghold@medunigraz.at Content Introduction
