CD5~ Small B-Cell Leukemias Are Rarely Classifiable as Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
|
|
|
- Bernadette Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hematopathology / CD5- LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS CD5~ Small B-Cell Leukemias Are Rarely Classifiable as Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Jane C. Huang, M D, William G. Finn, M D, Charles L. Goolsby, PhD, Daina Variakojis, M D, and Do Ann C. Peterson, M D Key Words: CD5~; Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; Leukemic phase of non-hodgkin lymphoma; Splenic marginal zone lymphoma Expression of the CD5 antigen by neoplastic cells often is considered a diagnostic criterion for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). However, published series frequently include a number ofcd5~ cases. We studied the spectrum ofcd5~ B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders presenting with leukemic involvement and reassessed the prevalence ofcd5~ BCLL. We immunophenotyped 192 cases of clonal, small lymphocytic, B-cell disorders involving peripheral blood or bone marrow. Of these, 41 CD5~ cases were further analyzed, correlating the immunophenotypic findings with pathologic material and clinical data. Only 3 CDS' cases were classified as CD5~ B-CLL. These 3 cases had features unusual for B-CLL, including ight surface immunoglobulin expression, ight CD20 expression, and absence ofcd23 expression (2 cases) or Richter syndrome (1 case). The remainder of the CDS' cases consisted of hairy cell leukemia, hairy cell variant, prolymphocytic leukemia, follicular center cell lymphoma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL), small lymphocytic lymphoma with marrow fiosis, and lymphoma, not further classified. Eight cases remained unclassified, but some displayed features of SMZL. CD5~ lymphoproliferative disorders of peripheral blood or bone marrow are unlikely to be CLL and often are classified more appropriately as non-hodgkin lymphoma in the leukemic phase. B-cell small lymphocytic leukemias are a heterogeneous group of diseases. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is by far the most common, but other disorders such as prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL), hairy cell leukemia, and leukemic phase of non-hodgkin lymphoma are also included in this group.' The various leukemic small B-cell disorders traditionally have been distinguished by morphologic and cytochemical features, but immunophenotyping has greatly aided the classification process. For example, CD5, a pan T-cell marker found in a subset of B lymphocytes, is characteristically expressed by CLL and mantle cell lymphoma but is generally absent in other B-cell neoplasms.2 In fact, the presence of CD5 is often a diagnostic criterion for CLL.3 Nevertheless, several published studies of CLL include a subpopulation of CD5" cases, as high as 36%.4~9 CD5" B-cell lymphocytic proliferations presenting in peripheral blood or bone marrow are less common than those expressing CD5 and may pose a diagnostic dilemma, particularly in patients without previous diagnoses. The objectives of this study were to characterize the spectrum of CD5", clonal Bcell, small lymphocytic disorders presenting in peripheral blood or bone marrow and to determine the prevalence of CD5~ B-cell CLL within this group of CD5" disorders. Materials and Methods From January 1993 to June 1997, from the files of the Flow Cytometry Laboratory at rthwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago, 111, we identified 192 cases of clonal B-cell disorders presenting in peripheral blood or bone marrow. All cases demonstrated clonality by surface light chain restriction on B lymphocytes (CD19, CD20). Cases with prior lymph node or tissue diagnosis were excluded from the study. Of the 192 cases, 41 were CD5". The immunophenotypic features of 123 Abstract
2 Huang et al / CD5- LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS these 41 cases were then correlated with all available morphologic studies and clinical history. Immunophenotyping by Flow Cytometry CD5 expression was ascertained by 2- or 3-color flow cytometric analysis with antibodies against CD5 and CD 19. Lack of CD5 expression on CD 19 cells was determined by comparison with the negative or nonreactive populations and, in some cases, with appropriate negative isotype Morphologic Evaluations Wright-stained peripheral blood smears were reviewed on all 41 CD5 cases. In addition to the bone marrow biopsy specimens in 32 cases, lymph node biopsy specimens in 8 cases and splenectomy specimens in 6 cases were reviewed. Cases were classified by consensus among 4 of us (J.C.H., W.G.F, D.V., L.C.P) at a multiheaded microscope, using diagnostic criteria according to the French-American-British guidelines2 and the Revised European-American Lymphoma classification." If tissue sections were not available, a case was classified as a splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) after clinicopathologic correlation, requiring compatible peripheral blood and bone marrow morphologic features,212 immunophenotypic findings, 13 and clinical data (ie, presence of splenomegaly). Clinical History and Follow-Up Presenting symptoms and physical findings, as well as additional laboratory and radiologic tests and available 2 1. : -. - E 4» " i * : >.* * ( x. '.!' *?* "" -.. ' " i i nil ' i Ml K Figure I I A, Dim or weak expression of surface immunoglobulin (sig). B, Bright/strong expression of sig. 124 Two- or 3-color immunophenotyping (combinations of antibodies labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate, phycoerythrin, or phycoerythrin-cyanin 5) was performed as previously described,10 using various combinations of antibodies against the following antigens: CD5, CD 10, CD lie, CD 19, CD20, CD22, CD23, CD25, and K and X. light chains. Antibodies reactive to CD22 and CD23 were purchased from Immunotech (Westwood, Me); C D l l c and CD25 from Becton Dickinson (San Jose, Calif); a CD19-K-X combination from DAKO (Carpinteria, Calif); and CD5, CD 10, K, X, CD 19, and CD20 from Coulter Cytometry (Kendall, Fla). The peripheral blood or bone marrow specimens were prepared by a slightly modified protocol of the standard RBC Q Prep (Coulter Cytometry) lysis technique in which cells are washed after RBC lysis followed by the addition of antibodies and the fixation step. The immunophenotypic analyses were performed on a Coulter Epics Profile or Coulter XL flow cytometer, using 550-nm, 600-nm, and 650nm dichroic filters with 525-nm (fluorescein isothiocyanate) bandpass, 585-nm (phycoerythrin) bandpass, and 670-nm bandpass (phycoerythrin-cyanin 5) optical filters. controls (IgG2a) to measure the extent of nonspecific binding. For CD20 and surface immunoglobulin (sig), semiquantitative intensity of staining also was evaluated and was classified as ight or, representing high or low density of surface antigens, respectively. Strong or ight staining was noted if the fluorescence of the positive population did not overlap with that of the negative or nonreactive cell population, and weak or staining was noted if the intensity of staining in the positive group overlapped with the negative group I Figure II.
3 Hematopathology / ORIGIL ARTICXE follow-up, were obtained from the patients' physicians or medical charts. Results 10-i 8 8tl 6- HCL* CLL PLL FCL LPL SMZL NHL' UNC Figure 21 Distribution of the 41 CD5" B-cell disorders by diagnosis. The asterisk indicates 5 cases of HCL and 1 case of HCL variant; the dagger, 1 case of small lymphocytic lymphoma with marrow fiosis, and 2 cases of NHL, not otherwise specified. HCL = hairy cell leukemia; CLL = chronic lymphocytic leukemia; PLL = prolymphocytic leukemia; FCL = follicular center cell lymphoma; LPL = lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma; SMZL = splenic marginal zone lymphoma; NHL = other non-hodgkin lymphoma; UNC = unclassified. The 41 CD5" cases included 26 men and 15 women with a median age of 63 years (range, years). All cases presented with peripheral blood or bone marrow involvement. Clinical and laboratory data for the patients are shown in ITable II, as are the complete immunophenotypic results. IFigure 21 shows the overall distribution of the cases by diagnosis. Five cases were classified as hairy cell leukemia, 1 as hairy cell leukemia-variant, 3 as CLL, and 2 as PLL. Lymphomas with leukemic involvement included 9 cases of follicular center cell lymphoma, 4 of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, 6 of SMZL, 1 of small lymphocytic lymphoma with bone marrow fiosis, and 2 of lymphoma, not otherwise classified. Eight cases were unclassified. Five cases showed morphologic features characteristic of hairy cell leukemia in peripheral blood and bone marrow, and the malignant cells were positive for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase.14 The immunophenotypic profile was also typical of hairy cell leukemia with coexpression of CD 19 and CD lie, as well as CD 19 and CD25. The morphologic features of the peripheral blood, bone marrow, and spleen specimens from the patient with hairy cell leukemia variant (patient 6) were similar to hairy cell leukemia except for the prominent nucleoli in many of the lymphoid cells. Immunophenotyping of the patient's peripheral blood specimen revealed expression of CD1 lc but absence of CD25. Only 3 of the 41 cases were classified as CLL. All 3 were elderly patients with peripheral absolute lymphocytosis and clinical evidence of organ involvement at the time of diagnosis (Table 1). In 2 of the 3 patients (patient 7 and 8), circulating lymphocytes were small and monotonous appearing with coarsely condensed chromatin and scant cytoplasm. The bone marrow pattern of involvement was diffuse in patient 8 and interstitial in patient 7. The lymphocytes in the bone marrow appeared uniform in size and appearance with coarse chromatin. However, the immunophenotypic profile was not typical for CLL.10 Specifically, in addition to the CD5 negativity, slg and CD20 expression were ight, and CD23 was negative in both cases. The peripheral blood lymphocytes in the third patient with CLL (patient 9) were mostly small to medium-sized with condensed chromatin but admixed with occasional prolymphocytes. In addition, the patient had 2 lymph node biopsy specimens showing histologic features of CLL with many proliferation centers I Image II. However, a bone marrow biopsy specimen that was obtained at the same time as the second lymph node biopsy showed large cell transformation, consistent with Richter syndrome. Immunophenotyping was performed on the second lymph Image I I A low-power view of the lymph node biopsy specimen from patient 9 shows diffuse effacement of nodal architecture with pale-appearing areas (H&E, x64). The pale areas represent proliferation centers rich in prolymphocytes (inset, H&E, x1,000), characteristic of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. AmJCIinPathol 1999;111:
4 Huang et al / CD5^ LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS Table II Clinical and Immunophenotypic Features of 41 Cases of CD5" B-Cell Disorders Immunophenotype Clinical Features Patient./ Sex/Age (y) ALC Lymphadenopathy Hepatosplenomegaly 21) 23 Hairy cell leukemia 1/M/ /M/38 3/M/50 4/M/48 5/M/48 6/M/60* X- X- X- X- X- X Chronic lymphocytic leukemia 7/F/ /M/ /M/ K- K- Small lymphocytic lymphoma 10/M/ Prolymphocytic leukemia /M/78 12/M/ X- K- Follicular center cell lymphoma 13/M/ /M/ /F/ /M/ /F/ /F/ /F/75 20/F/ /M/ X- X- K- X- X- K- K- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma /F/60 23/M/ /F/ /M/ K- K- X- K- Splenic marginal 26/M/82 27/M/50 28/F/83 29/F/60 30/F/89 31/M/63 X- X- X- X- K- bi n-hodgkin lymphoma 32/F/ /M/ bi Unclassified 34/M/68 35/F/82 36/M/83 37/F/69 38/M/66 39/F/47 40/M/53 41/M/73 K- K- X- K- X- X- X- zone lymphoma Ik *h ALC = absolute lymphocyte count (xl09/l); sig = surface immunoglobulin; = not available; X = lambda light chain; = ight; - = negative; = positive; = not done; K = kappa light chain. * The diagnosis is HCL variant. 126
5 Hematopathology / ORIGIL ARTICLE the lymph node biopsy specimen in 1. Patient 22 did not have a serum paraprotein, but the other 3 patients had a monoclonal IgM protein. The lymphoma cells expressed CD22 in 3 of 3 cases and CD1 lc in 2 of 4 cases, but did not express CD23 in 3 of 3 cases or CD 10 in 4 of 4 cases. Six cases were classified as SMZL. All 6 patients presented with splenomegaly, and 2 of them had lymphadenopathy. All 6 had involvement of the peripheral blood and bone marrow at the time of diagnosis. In 3 of the cases, the lymphocytes had heterogeneous morphologic features llmage 31. A minority of the cells had coarsely condensed chromatin and scant cytoplasm. Other lymphocytes had distinct eccentric Two patients had PLL; absolute lymphocyte counts were between 28 and 30 x 109/L. The peripheral blood lymphocytes showed a single prominent nucleolus with chromatin condensation around the periphery. In both cases, the disease involved the bone marrow focally with an interstitial pattern of involvement. A splenectomy specimen from 1 patient confirmed the diagnosis of PLL. One of the patients with PLL had a limited immunophenotype, but lymphocytes in both patients were CD5" and expressed ight slg. Peripheral blood and bone marrow involvement by non-hodgkin lymphoma constituted the majority of the CD5~ cases. Nine cases were classified as follicular center cell lymphoma. All 9 of these cases had bone marrow involvement. Six of the 9 cases of follicular center cell lymphoma had elevated peripheral blood lymphocyte counts. Five cases with peripheral blood involvement showed variable proportions of deeply cleaved lymphocytes with scant cytoplasm. The cleaved lymphocytes constituted approximately 40% to 90% of the lymphoid cells. However, the circulating lymphocytes in the sixth patient with peripheral blood involvement (patient 21) were similar to CLL llmage 21 with rare to absent cleaved cells. The bone marrow biopsy specimen, similar to all others in this group, contained characteristic paratrabecular lymphoid aggregates. The diagnosis was confirmed by a subsequent lymph node biopsy in this and 3 other cases and by a subsequent splenectomy in 1 case. The immunophenotypes were variable, but all were CD5 and ight CD20. CD 10 expression was seen in 4 of 9 cases. All 4 cases of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma involved the bone marrow, and 1 case (patient 24) also had peripheral blood involvement. The peripheral blood lymphocytes in patient 24 were morphologically mature-appearing. An interstitial or nodular pattern of bone marrow involvement was seen. Subsequent tissue examination showed lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma in spleen sections in 2 cases and in llmage 21 The peripheral blood lymphocytes from patient 21 displayed round nuclei with condensed chromatin, resembling chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes. However, bone marrow and lymph node biopsies confirmed a follicular lymphoma (Wright stain, x1,200). node biopsy specimen and not on the bone marrow specimen. Except for the lack of CD5 expression, the findings were typical for CLL. The lymphocytes expressed weak slg and CD20 and were positive for CD23. Patient 10 had a small lymphocytic lymphoma in the bone marrow specimen that was characterized by uniform small lymphocytes with round nuclei, condensed chromatin, and scant cytoplasm. The malignant lymphoid infiltrates were interstitial and nodular; none was paratrabecular. The morphologic features were compatible with CLL, but the patient did not have peripheral blood lymphocytosis. Only the bone marrow was immunophenotyped. Except for the lack of CD5 expression, the clonal B-cell population showed slg, CD20, and CD23 expression, features typical for CLL. Image 31 Peripheral blood lymphocytes from 3 of the 6 patients with splenic marginal zone lymphoma displayed a spectrum of morphologic appearances, including lymphocytes with irregular cytoplasmic borders (left), plasmacytoid lymphocytes (middle), and cleaved lymphocytes (right) (Wright stain, x1,200)
6 Huang et al / CDS- LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS nucleoli and loosely condensed chromatin. Cytoplasmic irregularities imparting a villous appearance were occasionally present but were not a consistent feature. Occasional plasmacytoid lymphocytes and rare cleaved cells were seen. In contrast, the other 3 patients with SMZL (patients 26-28) had uniform monomorphous lymphocytes with abundant cytoplasm and frequent nucleoli. Eight cases were not classified. In 6 of the 8 unclassified cases, peripheral blood smears were the material available for review. The peripheral lymphocytes were not morphologically acceptable for CLL, but some resembled the lymphocytes in the SMZL cases. The lymphocytes were heterogeneous in 3 cases; many lymphocytes had eccentric nucleoli, and occasional plasmacytoid cells and small mature lymphocytes were present. The other 5 cases had more homogeneous lymphocytes with abundant cytoplasm and visible to prominent nucleoli. The immunophenotypic results included the following: ight slg expression Image 41 Photomicrograph of spleen from patient 31, who had splenic marginal zone lymphoma (H&E, x200). 128 Discussion Although CD5 expression in B-cell CLL is well documented 3 and is recognized in recent classification systems," 15 a number of cases reported as CLL or CLL variants are CD5".4"9'16,17 CD5" CLL, despite its persistence in diagnostic hematology, represented fewer than 2% of the 192 B-cell leukemias in the current study. Furthermore, each of the 3 cases classified as CD5 CLL had unusual features. Two patients had morphologic features of CLL in blood and bone marrow specimens, but the immunophenotypic findings were unusual for CLL with ight slg, ight CD20 expression, and absence of CD23. The third patient with CLL showed large cell transformation in the bone marrow specimen (Richter syndrome), despite lymph node histologic features and an immunophenotype typical for CLL except for the absence of CD5 expression. The majority of the CD5" small B-cell disorders in the present study represented non-hodgkin lymphoma in the leukemic phase, including follicular center cell lymphoma and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. Six cases were classified as SMZL, a provisional entity in the Revised European-American Lymphoma classification." In 3 of these cases, the peripheral blood lymphocytes had heterogeneous morphologic features. The other 3 cases displayed distinctive uniform lymphocyte morphologic features, with abundant cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei with coarse chromatin and small nucleoli. These cells in the latter 3 cases displayed morphologic features previously ascribed to a subtype of CLL 18 and were similar to the C D l l c B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorder described by Hanson et al.19 About half of the 14 patients in the series reported by Hanson et al19 were CD5", and some of these patients subsequently underwent splenectomies that revealed SMZL (Curtis Hanson, MD, personal communication by phone; summer 1996). The CDllc disorders and SMZL overlap, but the exact relationship is unknown. The bone marrow was focally involved by lymphoma in 5 of the 6 cases of SMZL. All 5 cases had focal, nonparatrabecular lymphoid infiltrates, but paratrabecular aggregates also were seen in 2 cases. In contrast, the sixth patient (patient 31) had diffuse bone marrow involvement. The lymphocytes in the bone marrow contained moderate amounts of cytoplasm, resulting in well-spaced nuclei. A lymph node biopsy and subsequent splenectomy I Image 41 in this patient confirmed the diagnosis of a SMZL. In addition to the CD5 negativity, slg expression was ight in 4 of 6 cases; CD20 expression was ight in 5 of 6 cases; CD23 was negative in 5 of 6 cases; CD22 was expressed in all 6 cases; and CD1 lc was positive in 3 of 6 cases. in 7 of 8 cases, ight CD20 in 8 of 8 cases, CD23" in 7 of 7, CD22 in 7 of 7 cases, CD 10" in 7 of 7 cases, CD1 lc in 3 of 8 cases, and CD25 in 7 of 8 cases. The 2 remaining patients had leukemic involvement by non-hodgkin lymphoma that could not be further subclassified. Patient 32 had no peripheral blood absolute lymphocytosis, but the bone marrow contained a small B-cell lymphoma with fiosis. Patient 33 had extensive disease with involvement of peripheral blood, bone marrow, spleen, liver, lymph nodes, pleural cavity, and cereospinal fluid. The lymph node morphologic features for patient 33 were suggestive of mantle cell lymphoma, but cytogenetic and molecular data did not confirm the bcl-\ translocation.
7 H e m a t o p a t h o l o g y / ORIGIL ARTICLE Published series of CLL report varying incidences of CD5" CLL, ranging from 0% to 36%. 4 " 10 We propose 2 causes for this variability. First, different studies have used different criteria to determine the status of CD5 expression. Expression of CD5 in CLL is heterogeneous and forms a spectrum of variable densities, similar to CD20 and slg expression.20 The status of CD5 expression in the present study was evaluated by comparing the surface fluorescence intensity of the clonal B-cell population with the intensity of the negative or nonreactive population and with appropriate negative isotype controls. Although this method is sensitive, the possibility of extremely low-density expression of CD5 could not be excluded. True absence of expression may be determined by molecular methods, such as the detection of CDS messenger R.21 Second, judging from the data we report, it is likely that many cases reported as CD5" CLL represent specific nonhodgkin lymphomas in the leukemic phase. This is difficult to confirm, since the diagnosis of CLL is based primarily on peripheral blood morphologic features and immunophenotype, and additional studies are not always undertaken. However, half of the cases in 1 report of follicular lymphoma in the leukemic phase were originally referred to as CLL.22 Furthermore, published reports associate atypical features with CD5~ CLL, including higher incidence of organomegaly, shorter survival, more advanced stage of disease, and atypical morphologic features.6'9,17'23 Finally, many reported cases of atypical CLL are associated with characteristics of nonhodgkin lymphoma, including the presence of circulating small cleaved lymphocytes and characteristic cytogenetic features, such as the t(14;18).17 In view of our findings and those of other investigators, we conclude that CD5" CLL is rare and is often more appropriately classified as non-hodgkin lymphoma in the leukemic phase. It follows, therefore, that CD5" B-cell leukemias presenting as CLL warrant a more extensive clinical and laboratory evaluation before a definitive diagnosis is made. Only after a non-hodgkin lymphoma or other chronic leukemic disorders have been excluded should a diagnosis of CD5~ CLL be considered. From the rthwestern University Medical School, Chicago, Illinois. Address reprint requests to Dr Peterson: Wesley Pavilion, Room 393, 250 E Superior St, Chicago, IL References 1. Kroft SH, Finn WG, Peterson LC. The pathology of the chronic lymphoid leukemias. Blood Rev. 1995;9: Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel M-T, et al. Proposals for the classification of chronic (mature) B and T lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Pathol. 1989;42: Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, et al. National Cancer Institute-sponsored working group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1996;87: Batata A, Shen B. Immunophenotyping of subtypes of Bchronic (mature) lymphoid leukemia: a study of 242 cases. Cancer. 1992;70: Geisler CH, Larsen JK, Hansen NE, et al. Prognostic importance of flow cytometric immunophenotyping of 540 consecutive patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1991;78: Kurec AS, Threatte GA, Gottlieb AJ, et al. Immunophenotypic subclassification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Br J Haematol. 1992;81: Matutes E, Owusu-Ankomah K, Morilla R, et al. The immunological profile of B-cell disorders and proposal of a scoring system for the diagnosis of CLL. Leukemia. 1994;8: De Rossi G, Mauro FR, Lo Coco F, et al. CD5 negative lymphocytosis mimicking typical B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia: description of 26 cases. uv Rev Fr Hematol. 1993;35:45M Salomon-Nguyen F, Valensi F, Merle-Beral H, et al. A scoring system for classification of CD5" B CLL versus CD5 B CLL and B PLL. Leuk Lymphoma. 1995; 16:445^ Finn WG, Thangavelu M, Yelavarthi KK, et al. Karyotype correlates with peripheral blood morphology and immunophenotype in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am ] CUnPathoi 1996;105: Han-is NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, et al. A revised EuropeanAmerican classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994;84: Melo JV, Hegde U, Parreira A, et al. Splenic B cell lymphoma with circulating villous lymphocytes: differential diagnosis of B cell leukaemias with large spleens. J Clin Pathol. 1987;40: Matutes E, Morilla R, Owusu-Ankomah K, et al. The immunophenotype of splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes and its relevance to the differential diagnosis with other B-cell disorders. Blood. 1994;83: Paoletti M, Bitter MA, Varan JW. Hairy cell leukemia: morphologic, cytochemical, and immunologic features. Clin LabUed. 1988;8: Jaffe ES, Berard CW, Dibold J, et al. Society for Hematopathology Program: Proposed World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Am J SurgPathol. 1997;21: The CD5" B-cell disorders were often difficult to classify accurately based solely on analysis of peripheral blood. In some cases, the diagnosis of lymphoma was reached after the absence of CD5 expression prompted further clinical and laboratory evaluation. For example, the peripheral lymphocytes of 1 patient (patient 21) morphologically resembled CLL (Image 2), but immunophenotyping revealed the lack of CD5 expression. A subsequent bone marrow biopsy revealed paratrabecular lymphoid infiltrates, and a subsequent lymph node biopsy was diagnostic of follicular small cleaved cell lymphoma. Cytogenetic study also revealed the characteristic t(14;18) in this case.
8 Huang et al / CD5" LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS 16. Maloum K, Davi F, Magnac C, et al. Analysis of VH gene expression in CD5 and CD5~ B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1995;86: Matutes E, Oscier D, Garcia-Marco J, et al. Trisomy 12 defines a group of CLL with atypical morphology: correlation between cytogenetic, clinical and laboratory features in 544 patients. Br j Haematol. 1996;92: Peterson LC, Bloomfield CD, Sundberg RD, et al. Morphology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its relationship to survival. Am J Med. 1975;59: Hanson CA, Gribbin TE, Schnitzer B, et al. CDllc (Leu-M5) expression characterizes a B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorder with features of both chronic lymphocytic leukemia and hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 1990;76: Kay NE, Peterson L. Heterogeneity of CD5 memane expression on B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leu/c Lymphoma. 1991;5: Gignac SM, Buschle M, Hoffand AV, et al. Down-regulation of CD5 mr in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by differentiation-inducing agents. Eur] Immunol. 1990;20; Melo JV, Robinson DSF, de Oliveira MP, et al. Morphology and immunology of circulating cells in leukemic phase of follicular lymphoma. ] Clin Pathol. 1988;41: Criel A, Wlodarska 1, Meeus P, et al. Trisomy 12 is uncommon in typical chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Br J Haematol. 1994;87: Am J Clin Pathol 1999,111:
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Clinical and Laboratory Features of CD5- Negative Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.901781 Received: 2016.10.01 Accepted: 2016.10.24 Published: 2017.05.05 Clinical and Laboratory Features of CD5- Negative Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Authors Contribution:
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.901781 Received: 2016.10.01 Accepted: 2016.10.24 Published: 2017.05.05 Clinical and Laboratory Features of CD5- Negative Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Authors Contribution:
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY Original Article Mantle Cell Lymphoma Morphologic Findings in Bone Marrow Involvement JAY WASMAN, MD, 1 NANCY S. ROSENTHAL, MD,' AND DIANE C. FARHI, MD 2 Although mantle cell lymphoma (MCL),
HEMATOPATHOLOGY Original Article Mantle Cell Lymphoma Morphologic Findings in Bone Marrow Involvement JAY WASMAN, MD, 1 NANCY S. ROSENTHAL, MD,' AND DIANE C. FARHI, MD 2 Although mantle cell lymphoma (MCL),
Patterns of Lymphoid Neoplasia in Peripheral Blood. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Disclosure
 Patterns of Lymphoid Neoplasia in Peripheral Blood Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Disclosure Dr Baltrucki has received an honorarium for his participation as a faculty presenter in this
Patterns of Lymphoid Neoplasia in Peripheral Blood Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Disclosure Dr Baltrucki has received an honorarium for his participation as a faculty presenter in this
The patient had a mild splenomegaly but no obvious lymph node enlargement. The consensus phenotype obtained from part one of the exercise was:
 Case History An 86 year old male was admitted to hospital with chest infection. Haematological examination subsequently revealed the following: Hb- 11.0 g/dl; WBC- 67.1 x 10^9/l; PLT- 99 x10^9/l; RBC-
Case History An 86 year old male was admitted to hospital with chest infection. Haematological examination subsequently revealed the following: Hb- 11.0 g/dl; WBC- 67.1 x 10^9/l; PLT- 99 x10^9/l; RBC-
Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Study of 382 Patients
 Hematopathology / LYMPHOMAS WITH IGM PARAPROTEIN Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Study of 382 Patients Pei Lin, MD, 1 Suyang Hao, MD, 1* Beverly C. Handy, MD, 2 Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos,
Hematopathology / LYMPHOMAS WITH IGM PARAPROTEIN Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Study of 382 Patients Pei Lin, MD, 1 Suyang Hao, MD, 1* Beverly C. Handy, MD, 2 Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos,
Immunophenotyping in the diagnosis of chronic lymphoproliferative disorders
 J7 Clin Pathol 1994;47:871-875 871 L eaders~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.........;->:>> :*--:-- :- -::-*;:- --::- >:-:;-:: ::;...:::::...::::::::::*::;:;;::;::;::;;:;;:;;::;::;::;;:;;:;:::::::::::::::::: Task Force
J7 Clin Pathol 1994;47:871-875 871 L eaders~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.........;->:>> :*--:-- :- -::-*;:- --::- >:-:;-:: ::;...:::::...::::::::::*::;:;;::;::;::;;:;;:;;::;::;::;;:;;:;:::::::::::::::::: Task Force
Leukemic Phase of Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Blastoid Variant
 Hematopathology / LEUKEMIC BLASTOID MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Leukemic Phase of Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Blastoid Variant Timothy P. Singleton, MD, Margaret M. Anderson, MD, Charles W. Ross, MD, and Bertram Schnitzer,
Hematopathology / LEUKEMIC BLASTOID MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Leukemic Phase of Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Blastoid Variant Timothy P. Singleton, MD, Margaret M. Anderson, MD, Charles W. Ross, MD, and Bertram Schnitzer,
Immunophenotypic Profile of Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
 Hematopathology / IMMUNOPHENOTYPE OF LPL/WM Immunophenotypic Profile of Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Sergej Konoplev, MD, PhD, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos,
Hematopathology / IMMUNOPHENOTYPE OF LPL/WM Immunophenotypic Profile of Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Sergej Konoplev, MD, PhD, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos,
DETERMINATION OF A LYMPHOID PROCESS
 Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
CME/SAM. Abstract. Hematopathology / CD103 and CD123 in B-Cell Neoplasia
 Hematopathology / CD103 and CD123 in B-Cell Neoplasia Characteristic CD103 and CD123 Expression Pattern Defines Hairy Cell Leukemia Usefulness of CD123 and CD103 in the Diagnosis of Mature B-Cell Lymphoproliferative
Hematopathology / CD103 and CD123 in B-Cell Neoplasia Characteristic CD103 and CD123 Expression Pattern Defines Hairy Cell Leukemia Usefulness of CD123 and CD103 in the Diagnosis of Mature B-Cell Lymphoproliferative
Diagnostic Usefulness of CD23 and FMC-7 Antigen Expression Patterns in B-Cell Lymphoma Classification
 Hematopathology / AND ANTIGEN EXPRESSION IN B-CELL LYMPHOMA CLASSIFICATION Diagnostic Usefulness of and Antigen Expression Patterns in B-Cell Lymphoma Classification Diana P. Garcia, MD, 1* Michele T.
Hematopathology / AND ANTIGEN EXPRESSION IN B-CELL LYMPHOMA CLASSIFICATION Diagnostic Usefulness of and Antigen Expression Patterns in B-Cell Lymphoma Classification Diana P. Garcia, MD, 1* Michele T.
Flow Cytometric Analysis of Surface Light Chain Expression Patterns in B-Cell Lymphomas Using Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies
 Hematopathology / Light Chain Expression in B-NHLs Flow Cytometric Analysis of Surface Light Chain Expression Patterns in B-Cell Lymphomas Using Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies Pedro Horna, MD, Horatiu
Hematopathology / Light Chain Expression in B-NHLs Flow Cytometric Analysis of Surface Light Chain Expression Patterns in B-Cell Lymphomas Using Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies Pedro Horna, MD, Horatiu
WHO Classification. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small T-cell granular lymphocytic leukemia
 Blood Malignancies-II Prof. Dr. Herman Hariman, a Ph.D, SpPK (KH). Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. of Clinical Pathology, School of Medicine, University of North Sumatra WHO classification
Blood Malignancies-II Prof. Dr. Herman Hariman, a Ph.D, SpPK (KH). Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. of Clinical Pathology, School of Medicine, University of North Sumatra WHO classification
Comparative Study of Marginal Zone Lymphoma Involving Bone Marrow
 Hematopathology / MARGINAL ZONE LYMPHOMA INVOLVING BONE MARROW Comparative Study of Marginal Zone Lymphoma Involving Bone Marrow Sara A. Kent, MD, Daina Variakojis, MD, and LoAnn C. Peterson, MD Key Words:
Hematopathology / MARGINAL ZONE LYMPHOMA INVOLVING BONE MARROW Comparative Study of Marginal Zone Lymphoma Involving Bone Marrow Sara A. Kent, MD, Daina Variakojis, MD, and LoAnn C. Peterson, MD Key Words:
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology. Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport
 From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Hematopathology / HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF SPLENIC SMALL B-CELL LYMPHOMAS
 Hematopathology / HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF SPLENIC SMALL B-CELL LYMPHOMAS Histopathologic Features of Splenic Small B-Cell Lymphomas A Study of 42 Cases With a Definitive Diagnosis by the World Health
Hematopathology / HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF SPLENIC SMALL B-CELL LYMPHOMAS Histopathologic Features of Splenic Small B-Cell Lymphomas A Study of 42 Cases With a Definitive Diagnosis by the World Health
Case Report Primary Hairy Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma of the Breast: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Volume 2014, Article ID 497027, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/497027 Case Report Primary Hairy Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma of the Breast: A Case Report and Review of
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Volume 2014, Article ID 497027, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/497027 Case Report Primary Hairy Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma of the Breast: A Case Report and Review of
Immunophenotypic Variations in Hairy Cell Leukemia
 Hematopathology / IMMUNOPHENOTYPIC VARIATIONS IN HCL Immunophenotypic Variations in Hairy Cell Leukemia Yi-Hua Chen, MD, 1* Martin S. Tallman, MD, 2 Charles Goolsby, PhD, 1 and LoAnn Peterson, MD 1 Key
Hematopathology / IMMUNOPHENOTYPIC VARIATIONS IN HCL Immunophenotypic Variations in Hairy Cell Leukemia Yi-Hua Chen, MD, 1* Martin S. Tallman, MD, 2 Charles Goolsby, PhD, 1 and LoAnn Peterson, MD 1 Key
Flow cytometric evaluation of endoscopic biopsy specimens from patients with gastrointestinal tract B-cell lymphoma: a preliminary report
 Jichi Medical University Journal Flow cytometric evaluation of endoscopic biopsy specimens from patients with gastrointestinal tract B-cell lymphoma: a preliminary report Satoko Oka,, Kazuo Muroi,, Kazuya
Jichi Medical University Journal Flow cytometric evaluation of endoscopic biopsy specimens from patients with gastrointestinal tract B-cell lymphoma: a preliminary report Satoko Oka,, Kazuo Muroi,, Kazuya
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Critical Analysis and Diagnostic Usefulness of Limited Immunophenotyping of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas by Flow Cytometry
 Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC IMMUNOPHENOTYPING IN B-CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Critical Analysis and Diagnostic Usefulness of Limited Immunophenotyping of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas by Flow Cytometry
Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC IMMUNOPHENOTYPING IN B-CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Critical Analysis and Diagnostic Usefulness of Limited Immunophenotyping of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas by Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometric analysis of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders
 Flow cytometric analysis of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders David M. Dorfman, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Objectives Review
Flow cytometric analysis of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders David M. Dorfman, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Objectives Review
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo
 Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Diagnosis of lymphoid neoplasms has been
 Iranian Journal of Pathology (2007)2 (1), 1-61 Review Article Mehdi Nassiri Dep. of Pathology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, USA Abstract Correct diagnosis and classification of
Iranian Journal of Pathology (2007)2 (1), 1-61 Review Article Mehdi Nassiri Dep. of Pathology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, USA Abstract Correct diagnosis and classification of
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation
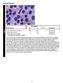 BMD-02 Cell Identification Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Erythrocyte precursor, normal 228 95.8 Educational Erythrocyte, normal 7 3.0 Educational Erythrocyte precursor with megaloblastic
BMD-02 Cell Identification Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Erythrocyte precursor, normal 228 95.8 Educational Erythrocyte, normal 7 3.0 Educational Erythrocyte precursor with megaloblastic
Pathology #07. Hussein Al-Sa di. Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib. Mature B-Cell Neoplasm. 0 P a g e
 Pathology #07 Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Hussein Al-Sa di Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib 0 P a g e Thursday 18/2/2016 Our lecture today (with the next 2 lectures) will be about lymphoid tumors This is a little bit long
Pathology #07 Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Hussein Al-Sa di Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib 0 P a g e Thursday 18/2/2016 Our lecture today (with the next 2 lectures) will be about lymphoid tumors This is a little bit long
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
LYMPHOMAS an overview of some subtypes of NHLs
 One of the confusing aspects of the lymphoid neoplasms concerns the use of the descriptive terms "leukemia" and "lymphoma." LYMPHOMAS an overview of some subtypes of NHLs Leukemia is used for lymphoid
One of the confusing aspects of the lymphoid neoplasms concerns the use of the descriptive terms "leukemia" and "lymphoma." LYMPHOMAS an overview of some subtypes of NHLs Leukemia is used for lymphoid
Immunopathology of Lymphoma
 Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113)
 Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the CLL Post-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the CLL Post-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Levels of expression of CD19 and CD20 in chronic B cell leukaemias
 364 Academic Department of Haematology and Cytogenetics, The Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, London SW3, UK E Matutes N Farahat R Morilla D Catovsky Department of Internal Medicine,
364 Academic Department of Haematology and Cytogenetics, The Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research, London SW3, UK E Matutes N Farahat R Morilla D Catovsky Department of Internal Medicine,
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this talk.
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. Mixed follicular and paracortical hyperplasia. Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
PhenoPath. Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 PhenoPath Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA C urrent diagnosis of B cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) is based on the 2008 WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
PhenoPath Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA C urrent diagnosis of B cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) is based on the 2008 WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome)
 Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Synonyms Crow-Fukase syndrome Multicentric Castleman disease Takatsuki syndrome Acronym coined by Bardwick POEMS Scheinker,
Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Synonyms Crow-Fukase syndrome Multicentric Castleman disease Takatsuki syndrome Acronym coined by Bardwick POEMS Scheinker,
, , 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia FISH Panel. Impact on Diagnosis
 Hematopathology / CLL, FISH, AND 14Q32 TRANSLOCATIONS Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia FISH Panel Impact on Diagnosis Beverly P. Nelson, MD, 1 Rohit Gupta, MD, 1 Gordon W. Dewald, PhD, 2 Sarah F. Paternoster,
Hematopathology / CLL, FISH, AND 14Q32 TRANSLOCATIONS Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia FISH Panel Impact on Diagnosis Beverly P. Nelson, MD, 1 Rohit Gupta, MD, 1 Gordon W. Dewald, PhD, 2 Sarah F. Paternoster,
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow
 The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
accumulation the blood, marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen.
 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia accumulation of mature-appearing appearing lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. CLL cells are: monoclonal l B lymphocytes that express CD19. CD5, and
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia accumulation of mature-appearing appearing lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. CLL cells are: monoclonal l B lymphocytes that express CD19. CD5, and
Prepared by: Dr.Mansour Al-Yazji
 C L L CLL Prepared by: Abd El-Hakeem Abd El-Rahman Abu Naser Ahmed Khamis Abu Warda Ahmed Mohammed Abu Ghaben Bassel Ziad Abu Warda Nedal Mostafa El-Nahhal Dr.Mansour Al-Yazji LEUKEMIA Leukemia is a form
C L L CLL Prepared by: Abd El-Hakeem Abd El-Rahman Abu Naser Ahmed Khamis Abu Warda Ahmed Mohammed Abu Ghaben Bassel Ziad Abu Warda Nedal Mostafa El-Nahhal Dr.Mansour Al-Yazji LEUKEMIA Leukemia is a form
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA
 FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
Frequency of additional clonal populations detected by high sensitivity flow cytometry in patients with hairy cell leukemia
 J Hematopathol (2012) 5:123 130 DOI 10.1007/s12308-012-0137-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of additional clonal populations detected by high sensitivity flow cytometry in patients with hairy cell leukemia
J Hematopathol (2012) 5:123 130 DOI 10.1007/s12308-012-0137-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of additional clonal populations detected by high sensitivity flow cytometry in patients with hairy cell leukemia
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype. Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital
 Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
CME/SAM. Olga Pozdnyakova, MD, PhD, 1 Svetlana Kondtratiev, MD, 1,2 Betty Li, MS, 1 Karry Charest, 1 and David M. Dorfman, MD, PhD 1.
 Hematopathology / New Mastocytosis Flow Cytometry Approach High-Sensitivity Flow Cytometric Analysis for the Evaluation of Systemic Mastocytosis Including the Identification of a New Flow Cytometric Criterion
Hematopathology / New Mastocytosis Flow Cytometry Approach High-Sensitivity Flow Cytometric Analysis for the Evaluation of Systemic Mastocytosis Including the Identification of a New Flow Cytometric Criterion
Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation
 Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Test Utilization: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
 Test Utilization: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Initial Evaluation Diagnostic Criteria Selection of Tests for Prognosis Response to Therapy Challenges Assessment for persistent disease Paul J. Kurtin, M.D.
Test Utilization: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Initial Evaluation Diagnostic Criteria Selection of Tests for Prognosis Response to Therapy Challenges Assessment for persistent disease Paul J. Kurtin, M.D.
HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor I. Description of the rotation: During this rotation, the resident will gain
HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor I. Description of the rotation: During this rotation, the resident will gain
A Practical Guide To Diagnose B-Cell Lymphomas on FNAs. Nancy P. Caraway, M.D.
 A Practical Guide To Diagnose B-Cell Lymphomas on FNAs Nancy P. Caraway, M.D. Major Factors Impacting Dx Lymphomas on Small Bxs Classification systems Immunophenotyping by multiprobe flow cytometry and
A Practical Guide To Diagnose B-Cell Lymphomas on FNAs Nancy P. Caraway, M.D. Major Factors Impacting Dx Lymphomas on Small Bxs Classification systems Immunophenotyping by multiprobe flow cytometry and
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies
 Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma
 Frequency of Lymphoid Neoplasms Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma Stephen Hamilton-Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus University Hospital B-cell neoplasms 88% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Frequency of Lymphoid Neoplasms Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma Stephen Hamilton-Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus University Hospital B-cell neoplasms 88% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA. April 16, 2008
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Tres
 Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
Tel: Fax: Received: 25, Jul, 2014 Accepted: 16, Dec, 2014
 IJHOSCR International Journal of Hematology- Oncology and Stem Cell Research Original Article T-cell/Natural killer-cell neoplasms presenting as leukemia- Case series from single tertiary care center Shano
IJHOSCR International Journal of Hematology- Oncology and Stem Cell Research Original Article T-cell/Natural killer-cell neoplasms presenting as leukemia- Case series from single tertiary care center Shano
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD. Parts 2 and 3
 HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Parts 2 and 3 NEOPLASTIC LYMPHOID DISEASES Introduction o The bone marrow is the source of all cells in the
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Parts 2 and 3 NEOPLASTIC LYMPHOID DISEASES Introduction o The bone marrow is the source of all cells in the
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Reactive and Neoplastic Lymphocytosis
 Reactive and Neoplastic Lymphocytosis Koranda A. Walsh, VMD, BS Assistant Professor, Clinical Pathobiology University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine PLEASE NOTE: These notes are meant as
Reactive and Neoplastic Lymphocytosis Koranda A. Walsh, VMD, BS Assistant Professor, Clinical Pathobiology University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine PLEASE NOTE: These notes are meant as
Bone Marrow Involvement in Malignant Lymphomas (Non-Hodgkin ' s) Eman Sadiq Jalal MSc
 MSc Abstract: Background: Bone marrow biopsies are taken routinely in the initial investigation of patients with non-hodgkin, s lymphomas to estimate the progression of disease at time of presentation
MSc Abstract: Background: Bone marrow biopsies are taken routinely in the initial investigation of patients with non-hodgkin, s lymphomas to estimate the progression of disease at time of presentation
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Morphology and immunology of circulating cells in leukaemic phase of follicular lymphoma
 J Clin Pathol 1988;41:951-959 Morphology and immunology of circulating cells in leukaemic phase of follicular lymphoma JUNIA V MELO, DANIELE S F ROBINSON, MARIA P DE OLIVEIRA, I W THOMPSON,* I A LAMPERT,*
J Clin Pathol 1988;41:951-959 Morphology and immunology of circulating cells in leukaemic phase of follicular lymphoma JUNIA V MELO, DANIELE S F ROBINSON, MARIA P DE OLIVEIRA, I W THOMPSON,* I A LAMPERT,*
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228
 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
B-cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Blood and Bone Marrow
 B-cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Blood and Bone Marrow Sanam Loghavi, MD Department of Hematopathology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosures I have no
B-cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Blood and Bone Marrow Sanam Loghavi, MD Department of Hematopathology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosures I have no
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Clinicopathologic Study of 26 Cases
 Hematopathology / CLL/SLL WITH IGM PARAPROTEIN Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Clinicopathologic Study of 26 Cases C. Cameron Yin, MD, PhD, 1 Pei
Hematopathology / CLL/SLL WITH IGM PARAPROTEIN Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Clinicopathologic Study of 26 Cases C. Cameron Yin, MD, PhD, 1 Pei
CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1364 CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting Sakthi Sankari S 1 *, Arjunan A 2, Bhuvaneswari M.G. 2, Sindhuja
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1364 CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting Sakthi Sankari S 1 *, Arjunan A 2, Bhuvaneswari M.G. 2, Sindhuja
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
T he translocation t(11;14)(q13;q32) and cyclin D1 overexpression
 940 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of cyclin D1 in B cell lymphoproliferative disorders by flow cytometry P Jain, G M Giustolisi, S Atkinson, M O Elnenaei, R Morilla, K Owusu-Ankomah, F Rafiq-Mohammed, E Matutes,
940 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of cyclin D1 in B cell lymphoproliferative disorders by flow cytometry P Jain, G M Giustolisi, S Atkinson, M O Elnenaei, R Morilla, K Owusu-Ankomah, F Rafiq-Mohammed, E Matutes,
Collected: , PM Sent: , PM Received: , PM Preliminary: , PM. Notification Status: COMPREHENSIVE DIAGNOSIS
 PATIENT Name:HIPAA, Compliant DOB: 03-25-1945 (60 yr) ID#: xxx-xx-0000 Sex: M Tel: xxx-xxx-xxxx SPECIMEN Your No:WS05-xxxx Case No:C05-00xxx Req. No:Txxxxx Collected: 06-08-05, PM Sent: 06-09-05, PM Received:
PATIENT Name:HIPAA, Compliant DOB: 03-25-1945 (60 yr) ID#: xxx-xx-0000 Sex: M Tel: xxx-xxx-xxxx SPECIMEN Your No:WS05-xxxx Case No:C05-00xxx Req. No:Txxxxx Collected: 06-08-05, PM Sent: 06-09-05, PM Received:
Many of the hematolymphoid disorders are derived
 REVIEW ARTICLE Practical Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: A Review of Useful Antibodies for Diagnosis Ji Lu, MD and Karen L. Chang, MD Abstract: This review article offers some useful panels of
REVIEW ARTICLE Practical Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: A Review of Useful Antibodies for Diagnosis Ji Lu, MD and Karen L. Chang, MD Abstract: This review article offers some useful panels of
Case Presentation No. 075
 Case Presentation No. 075 Session 4. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cristina Montalvo, MD Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
Case Presentation No. 075 Session 4. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cristina Montalvo, MD Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
Pathology of the Lymphoid System
 Pathology of the Lymphoid System Learning Objectives: Define lymphadenitis and enumerate its types. Briefly describe the morphological appearance of reactive lymph node. Describe the microscopic picture
Pathology of the Lymphoid System Learning Objectives: Define lymphadenitis and enumerate its types. Briefly describe the morphological appearance of reactive lymph node. Describe the microscopic picture
Outlines. Disclosures. Updates on B-cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Blood and Bone Marrow
 Updates on B-cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Blood and Bone Marrow Sa A, Wang MD Jeffrey L. Jorgensen, MD, PhD Department of Hematopathology, UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston,
Updates on B-cell Chronic Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Blood and Bone Marrow Sa A, Wang MD Jeffrey L. Jorgensen, MD, PhD Department of Hematopathology, UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston,
Utility of CD200 immunostaining in the diagnosis of primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma: comparison with MAL, CD23, and other markers
 & 2012 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/12 $32.00 1637 Utility of CD200 immunostaining in the diagnosis of primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma: comparison with MAL, CD23, and other markers
& 2012 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/12 $32.00 1637 Utility of CD200 immunostaining in the diagnosis of primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma: comparison with MAL, CD23, and other markers
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43
 ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach
 Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
5/16/2018 HEMATOPATHOLOGY FOR CYTOPATHOLOGISTS HEMATOPATHOLOGY FOR C CYTOPATHOLOGISTS I HAVE NOTHING TO C DISCLOSE
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY FOR C CYTOPATHOLOGISTS Kathryn Lindsey, MD McKee Cytology Symposium HEMATOPATHOLOGY FOR C CYTOPATHOLOGISTS Kathryn Lindsey, MD McKee Cytology Symposium I HAVE NOTHING TO C DISCLOSE Kathryn
HEMATOPATHOLOGY FOR C CYTOPATHOLOGISTS Kathryn Lindsey, MD McKee Cytology Symposium HEMATOPATHOLOGY FOR C CYTOPATHOLOGISTS Kathryn Lindsey, MD McKee Cytology Symposium I HAVE NOTHING TO C DISCLOSE Kathryn
Corrigenda. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (revised 4th edition): corrections made in second print run
 Corrigenda WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (revised 4th edition): corrections made in second print run In addition to corrections of minor typographical errors, corrections
Corrigenda WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (revised 4th edition): corrections made in second print run In addition to corrections of minor typographical errors, corrections
CCND1-IGH Fusion-Amplification and MYC Copy Number Gain in a Case of Pleomorphic Variant Mantle Cell Lymphoma
 AJCP /CASE REPORT CCND1-IGH Fusion-Amplification and MYC Copy Number Gain in a Case of Pleomorphic Variant Mantle Cell Lymphoma Yuan Miao, MD, 1,2 Pei Lin, MD, 1 Wei Wang, MD, 1 L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD,
AJCP /CASE REPORT CCND1-IGH Fusion-Amplification and MYC Copy Number Gain in a Case of Pleomorphic Variant Mantle Cell Lymphoma Yuan Miao, MD, 1,2 Pei Lin, MD, 1 Wei Wang, MD, 1 L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD,
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016. Clinical History
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Case Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
 Case 148 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology Robert P Hasserjian Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA Clinical history
Case 148 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology Robert P Hasserjian Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA Clinical history
Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
 Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
11/8/2018 DISCLOSURES. I have NO Conflicts of Interest to Disclose. UTILTY OF DETECTING PATTERNS
 Bharat N. Nathwani, M.D. City of Hope Medical Center Professor, Director of Pathology Consultation Services, 1500 East Duarte Road, Duarte, California, 91010 DISCLOSURES -------------------------------------------------------
Bharat N. Nathwani, M.D. City of Hope Medical Center Professor, Director of Pathology Consultation Services, 1500 East Duarte Road, Duarte, California, 91010 DISCLOSURES -------------------------------------------------------
FINALIZED SEER SINQ S NOVEMBER 2011
 : 20110133 Multiple primaries/heme & Lymphoid Neoplasms: A patient was diagnosed 7/31/08 with DLBCL (9680/3) (biopsy left supraclav. node), stage IIIB. Treated with chemo. 10/14/10 biopsy right supraclav.
: 20110133 Multiple primaries/heme & Lymphoid Neoplasms: A patient was diagnosed 7/31/08 with DLBCL (9680/3) (biopsy left supraclav. node), stage IIIB. Treated with chemo. 10/14/10 biopsy right supraclav.
Lack of Surface Immunoglobulin Light Chain Expression by Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping Can Help Diagnose Peripheral B-Cell Lymphoma
 Hematopathology / SURFACE IMMUNOGLOBULIN LIGHT CHAIN NEGATIVE PERIPHERAL B-CELL LYMPHOMA Lack of Surface Immunoglobulin Light Chain Expression by Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping Can Help Diagnose Peripheral
Hematopathology / SURFACE IMMUNOGLOBULIN LIGHT CHAIN NEGATIVE PERIPHERAL B-CELL LYMPHOMA Lack of Surface Immunoglobulin Light Chain Expression by Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping Can Help Diagnose Peripheral
Hyperplasia of Mantle/Marginal Zone B Cells With Clear Cytoplasm in Peripheral Lymph Nodes A Clinicopathologic Study of 35 Cases
 Hematopathology / HYPERPLASIA OF MANTLE/MARGINAL ZONE B CELLS WITH CLEAR CYTOPLASM Hyperplasia of Mantle/Marginal Zone B Cells With Clear Cytoplasm in Peripheral Lymph Nodes A Clinicopathologic Study of
Hematopathology / HYPERPLASIA OF MANTLE/MARGINAL ZONE B CELLS WITH CLEAR CYTOPLASM Hyperplasia of Mantle/Marginal Zone B Cells With Clear Cytoplasm in Peripheral Lymph Nodes A Clinicopathologic Study of
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy. Faizi Ali, MD
 88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
Morphometric Characterization of Small Cell Lymphocytic Lymphoma
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2014; 4(79): 179-183 10.1515/arsm-2015-0002 Chisoi Anca 1, Aşchie Mariana 2, Poinăreanu I. 2 Morphometric Characterization of Small Cell Lymphocytic Lymphoma 1 Spitalul Clinic Judetean
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2014; 4(79): 179-183 10.1515/arsm-2015-0002 Chisoi Anca 1, Aşchie Mariana 2, Poinăreanu I. 2 Morphometric Characterization of Small Cell Lymphocytic Lymphoma 1 Spitalul Clinic Judetean
Significant CD5 Expression on Normal Stage 3 Hematogones and Mature B Lymphocytes in Bone Marrow
 Hematopathology / CD5 Expression on Normal B Cells Significant CD5 Expression on Normal Stage 3 Hematogones and Mature B Lymphocytes in Bone Marrow Franklin S. Fuda, DO, Nitin J. Karandikar, MD, PhD, and
Hematopathology / CD5 Expression on Normal B Cells Significant CD5 Expression on Normal Stage 3 Hematogones and Mature B Lymphocytes in Bone Marrow Franklin S. Fuda, DO, Nitin J. Karandikar, MD, PhD, and
Flow Cytometric Analysis of CD5+ B Cells A Frame of Reference for Minimal Residual Disease Analysis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
 Hematopathology / CD5+ -CELL NLYSIS Y FLOW CYTOMETRY Flow Cytometric nalysis of CD5+ Cells Frame of Reference for Minimal Residual Disease nalysis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Ritu Gupta, MD, 1 Paresh
Hematopathology / CD5+ -CELL NLYSIS Y FLOW CYTOMETRY Flow Cytometric nalysis of CD5+ Cells Frame of Reference for Minimal Residual Disease nalysis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Ritu Gupta, MD, 1 Paresh
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 06 Page June 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x An Indolent Natural Killer Cell Leukemia Presenting with Bilateral Ankle Arthritis and Low Grade Fever Abstract Author Subhash Chandra
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x An Indolent Natural Killer Cell Leukemia Presenting with Bilateral Ankle Arthritis and Low Grade Fever Abstract Author Subhash Chandra
Follicular Lymphoma: the WHO
 Follicular Lymphoma: the WHO and the WHERE? Yuri Fedoriw, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Director of Hematopathology University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC Disclosure
Follicular Lymphoma: the WHO and the WHERE? Yuri Fedoriw, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Director of Hematopathology University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC Disclosure
Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7100-7104 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001717 Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case Jenny
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7100-7104 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001717 Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case Jenny
Role of Immunotyping in Chronic Lymphocytosis: Review of the Natural History of the Condition in 145 Adult Patients
 Subject Review Role of Immunotyping in Chronic Lymphocytosis: Review of the Natural History of the Condition in 145 Adult Patients AYALEW TEFFERI, M.D., Division of Hematology and Internal Medicine; CHIN-YANG
Subject Review Role of Immunotyping in Chronic Lymphocytosis: Review of the Natural History of the Condition in 145 Adult Patients AYALEW TEFFERI, M.D., Division of Hematology and Internal Medicine; CHIN-YANG
Symptomatic Massive Splenomegaly in Persistent Polyclonal B- cell Lymphocytosis Requiring Splenectomy
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 1 (2015) Issue 3 Symptomatic Massive Splenomegaly in Persistent Polyclonal B- cell Lymphocytosis Requiring Splenectomy Shanel B. Bhagwandin, DO*,
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 1 (2015) Issue 3 Symptomatic Massive Splenomegaly in Persistent Polyclonal B- cell Lymphocytosis Requiring Splenectomy Shanel B. Bhagwandin, DO*,
Blood Cell Identification: 2011-B Mailing: Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
 Please Note: To view the Figures and Images contained within this education activity in color, access the electronic version of the reading. CASE HISTORY This peripheral blood smear is from a 51-year-old
Please Note: To view the Figures and Images contained within this education activity in color, access the electronic version of the reading. CASE HISTORY This peripheral blood smear is from a 51-year-old
