SEED HAEMATOLOGY. The blast cell a diagnostic heavyweight SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT NOVEMBER 2016
|
|
|
- Claud Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT NOVEMBER 2016 SEED HAEMATOLOGY The blast cell a diagnostic heavyweight Causes and cytological manifestations Blast cells are described as precursor cells with the ability to preserve themselves by dividing and to further differentiate. Under pathological conditions, blast cells can be mobilised from the bone marrow into the peripheral blood circulation. In adults, this represents an alarming finding that can indicate both reactive and malignant diseases such as leukaemia. Therefore the detection of blast cells in the peripheral blood is considered extremely important, and great responsibility is placed on the investigating laboratory. As well as information on the physiology, this article describes the possible causes of the release of blast cells into the blood, the characteristics by which they can be identified and how further diagnosis is carried out. Development, maturation and regulation Haematopoietic precursor cells develop from the pluripotent embryonic stem cells as a result of numerous development stages. In the bone marrow, these cells are referred to as blast cells ( blastós is the Greek word for germ, bud, sprout or shoot). For their further development, they are committed to one specific line (erythropoiesis, granulopoiesis, monopoiesis, thrombopoiesis and lymphopoiesis). Asymmetrical replication, as shown in Fig. 1, allows blast cells to form both identical daughter cells (replication) and to differentiate to form mature blood cells. Fig. 1 Asymmetrical replication (example erythropoiesis) A mature cell is developed after several differentiation stages, involving gradual condensation of the nuclear chromatin. While blast cells have a homogeneous chromatin, the nucleus shows chromatin clumping in the mature cells. The nucleus-plasma relation also drops (see Fig. 2) Blast cell Nuclear chromatin fine, homogeneous Nucleus-plasma relation % Maturation Fig. 2 Schematic illustration: blast cell / mature cell Mature cell Nuclear chromatin clumped Nucleus-plasma relation %
2 2 Bone marrow barrier Blast cells and other immature cells of haematopoiesis are captured in the bone marrow due to their size and adhesion properties, and do not enter the blood stream. This mechanism is referred to as the bone marrow barrier. A disruption of this bone marrow barrier is associated with a leucoerythroblastic blood picture. Definition of leucoerythroblastic blood picture The peripheral blood shows a left shift of the granulopoiesis towards promyelocytes and myeloblasts and the presence of nucleated red blood cells. Physiological blast cells These are medium to large cells (14 18 μm*) with the specific characteristics of the nucleus and cytoplasm described in Table 1. With leukaemia, blast cells can have a significantly changed appearance. What all blast cells have in common is the finely and evenly distributed, light nuclear chromatin. Blast cells in the peripheral blood, causes and cytological appearance A shift of blast cells into the peripheral blood occurs physiologically only in neonates. The reason for this is the extramedullary haematopoiesis that still exists at the time of birth. In adults, the presence of blast cells in the peripheral blood is a serious finding. Essentially, it is important to differentiate between a reactive and a leukaemic appearance of blast cells. Examples are shown in Table 2. The extent of the influx of blast cells can be used to differentiate between a reactive and a malignant picture, as can the composition of the other cell populations. Blood count values and clinical data are also helpful. Table 2 Diagnostic reasons for the presence of blast cells in the peripheral blood Table 1 Diagnostic characteristics of physiological blast cells Nucleus Shape: Nucleus-plasma relation: % Nucleoli: one to several (may not be visible) Finely distributed nucleic chromatin, no clumping Narrow (constituting 5 30 % of the cell) Basophilic Not granulated ** * Exception: megakaryoblast 150 μm ** Leukaemic blast cells may be granulated Reactive Severe bacterial infections, sepsis Treatment with growth factors (G-CSF) Regeneration after chemotherapy Viral infections (mononucleosis) Bone marrow carcinosis Malignant Acute leukaemias (AML, ALL, AUL) Myeloproliferative neoplasia (CML, PMF) Myelodysplastic syndromes (RAEB 1 and 2) MDS/MPN overlap syndrome (CMML 1 and 2) Aggressive lymphoma of the B cell and T cell lines Blast cells using May-Gruenwald stain [7] Image 1 Proerythroblast; size μm, nucleusplasma relation 70 %, deeply basophilic cytoplasm, Golgi zone Image 2 Myeloblast; size μm, nucleusplasma relation 80 %, light basophilic cytoplasm Image 3 Lymphoblast; size μm, nucleusplasma relation 90 %, narrow cytoplasm medium basophilic Image 4 Monoblast; size μm, nucleusplasma relation 70 %, nucleic lobulation +/, basophilic cytoplasm Image 5 Megakaryoblast; size up to 150 μm, nucleus-plasma relation 80 %, deeply basophilic cytoplasm, vacuoles +/ Fig. 3 Physiological blast cell types
3 3 Reactive The proportion of blast cells detected in the peripheral blood in the case of a reactive event is comparatively low (< 5 %) and there tends to be a continuous left shift up to the myeloblast stage or a leucoerythroblastic blood picture as shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 5 Blast cells in the peripheral blood in AML Fig. 4 Leucoerythroblastic blood picture in pneumogenic sepsis Acute promyelocytic leukaemia with the presence of faggot cells (FAB type M3/M3V), as shown in Fig. 6, is of particular clinical importance. In this specific type, associated with chromosomal translocation t(15;17), a prompt diagnosis is of key importance due to coagulation complications and the need for a special therapy. There are also often reactive changes in the neutrophils, such as toxic granulation and vacuolisation. In the case of viral infections (e.g. mononucleosis), single blast cells may be released into the peripheral blood. These are lymphoblasts, corresponding to the T cell line, in immunophenotyping, more specifically T immunoblasts, and they are component parts of a generally reactive lymphocytic appearance. If cell morphology indicates haematological neoplasia, a defined step-wise haematological diagnostic analysis is carried out for further differentiation. Haematological neoplasia A lot of haematological neoplasias are associated with blast cells appearance in the peripheral blood. The underlying damage to clonal stem cells can result in an absence of cell maturation, with a subsequent influx of blast cells. The proportion of blast cells can vary greatly, as can the number of white blood cells, manifesting in either leucopenia or excessive leucocytosis. The highest proportion of blast cells is exhibited in acute leukaemia. The proportion of blast cells in the blood and/or bone marrow defined for acute leukaemia is 20 % according to the WHO classification 2008 [8]. As well as an increase in blast cells and low numbers of mature white blood cells still present, the intermediate forms are often absent in patients with acute leukaemia (leukaemic hiatus). Morphological details, such as Auer rods, prove the origin of the blast populations from the myeloid cell line. An example of blast cells from an acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is shown in Fig. 5. Fig. 6 AML M3 faggot cells, bone marrow Blast cell differentiation by a step-wise diagnostic approach The cytology from the blood and bone marrow with the quantification of the blast cells is the starting point for a step-wise haematological diagnostic approach. Myeloid characteristics by which blast cells are differentiated, such as Auer rods or granules, are used to distinguish between a myeloid and lymphatic form of leukaemia. Cytochemical stains, such as peroxidase (POX), are used for further classification of myeloid cells, and alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase (NAE) is used to detect monocytes and their precursor cells.
4 12 16 basophilic, no granulation, physiologic, AML, MDS, CML needle-shaped red inclusions (Auer rods), AML-M1, -M2, -M3, -M6, RAEB , nucleoli +/ abundant cytoplasm, fine granules +/, pseudopodia +/, monocytoid deep basophilic, flaky Golgi zone, (POX Ø, esterase Ø) AML-M reddish granules, Golgi zone Ø, AML, RAEB spherical red inclusions (Auer bodies), additionally Auer rods, AML-M1, -M2, -M6 Monoblast description: see to the left Promonocyte description: see to the right monocytoid undifferentiated blast, no granulation, cytoplasmic blebbing or pseudopodia, (POX Ø, esterase Ø) AML-M7 Bornbarch 1, Norderstedt, Germany Phone Fax In cooperation with: You will find your local Sysmex representative s address under Platelet phagocytosis oval dense, coarse, purple-red granulation, (POX ++, esterase Ø) AML-M /lobulated bundles of Auer rods, AML-M3 and -M3V, t(15;17) lobed, intermediate chromatin haemophagocytosis +/, intermediate chromatin coarse, round, eosinophilic and blue-purple granules, (chloroacetate esterase +) AML-M4 Eo, inv(16), t(16;16) often blurred blue-purple granulation, often vacuoles, (toluidine blue +) acute basophilic leukaemia Blasts with brown dye precipitates of varied density. Remark: All neutrophils from the promyelocyte stage on are POX (bi-)lobulated often fine reddish granulation, bundles of Auer rods +/, AML-M3V, t(15;17) Blast with precipitates of brown dye; diagnostic for monoblastic AML only in case of diffuse and strong staining. Nucleus with invaginated cytoplasm** Granulated cytoplasm. Crucial is the nucleus: fingerprint-like indentation; POX + AML with NPM1- and FLT3- mutations often blurred basophilic granules +/, (toluidine blue +) mast cell leukaemia * For pragmatic reasons, the abbreviations of FAB classification diagnoses have been used. The WHO classification equivalents are as follows: M0 AML with minimal differentiation; M1 AML without maturation; M2 AML with maturation; M3 acute promyelocytic leukaemia; M4 acute myelomonocytic leukaemia; M5 acute monoblastic and monocytic leukaemia; M6 acute erythroid leukaemia/proerythroblastic leukaemia; M7 acute megakaryoblastic leukaemia. ** Invagination of the POX + cytoplasm into the nucleus. Definition of the cup-like blast population: indentation zone 25% of the nuclear surface, 10% of blasts show goblet-shaped, usually light indentations. If cup-like blasts are identified, mutation analysis of NMP1 and FLT3 should be performed. Copyright 2014 Universitätsklinikum Aachen AÖR, Klinik für Onkologie, Hämatologie und Stammzelltransplantation Authors: Prof. Dr. med. Roland Fuchs, Reinhild Herwartz, Klinik für Onkologie, Hämatologie und Stammzelltransplantation, Universitätsklinikum Aachen SEED HAEMATOLOGY The blast cell a diagnostic heavyweight 4 Table 3 Progenitor markers Progenitor markers CD34 HLA-DR CD117 CD10 TdT Immunophenotyping is a key component of the step-wise diagnostic approach. This allows antigens to be detected on the cell surface or in the cell cytoplasm. Progenitor markers (Table 3) are of key importance for detecting blast cells, which are expressed as precursor cells at a defined time. As these mature, the antigens are lost and are replaced by other markers. In combination with line-specific markers, which are only expressed by one specific cell line (e. g. CD19 for B cells), the blast cells can be accurately classified in terms of their maturity and cell lines. Cells that express the antigen Haematopoietic precursor cells, capillary endothelial cells Progenitor cells of all lines, especially myeloblasts Haematopoietic precursor cells B cell and T cell precursor cells, stromal cells of the bone marrow Lymphatic progenitor cell marker, especially of the T cell line This does not, however, in any way reduce the importance of morphology, as this remains the initial method, allowing a prompt and reliable filter and gatekeeping function/setting of the further course. The abnormal blood smears are filtered by the laboratory staff in the central or specialist haematology laboratory, and the pathological findings are passed on, so that the haematological step-wise diagnostics can be set in motion. Added to this is the need for an integrated finding, taking into account all applied diagnostic methods. Blast cells in picture and text An overview of the physiologically and pathologically occurring blast cells is shown on the Sysmex blast cell poster and the complementing chart, which were developed in cooperation with the Clinic of Oncology/Haematology and Stem Cell Transplantation at the University Hospital of Aachen (Fig. 7). You are welcome to request a copy from your local Sysmex representative. Blasts myeloid Cytogenetics / molecular genetics represent another important diagnostic tool. By combining various methods, chromosomal aberrations that are relevant for therapeutic Myeloblast Granulated blast Abnormal promyelocyte Blasts, POX-positive and prognostic reasons can be detected at a cytogenetic or molecular biological level. As part of a comprehensive investigation to record all changes (aberrations) in the genome, Blast with Auer rods Blast with Auer rods and Auer bodies Faggot cell (M3) Lobulated blast (M3V) a karyogram is produced, which separates all chromosome pairs. The fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and the Monoblast Monoblast (1), promonocyte (2) 2 1 Promonocyte Blast, esterase positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are used to selectively detect specific mutations. Monocytoid blast (M4) Monocytoid blast (M5B) Abnormal eosinophil (M4 Eo) Cup-like blast At the end of these step-wise diagnostic investigations, a final assessment should be made, taking into account all methods, to deliver an integrated finding. Concluding remarks Methodology developments in haematological diagnostics now allows the disease types to be much more accurately diagnosed and classified than was possible in the times of FAB classification. Abnormal proerythroblast (M6) Common cytologic features Nucleus Shape: Nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio: 70 90% Chromatin: predominantly regularly distributed, not clumped, not condensed Varying numbers of nucleoli; may be hidden by chromatin Sysmex Europe GmbH Abnormal megakaryoblast (M7) Basophilic Reddish granulation +/ Auer rods +/ ; when +, evident for: AML, if blasts 20% RAEB-2, if blasts <20% Basophilic blast Quantification of blasts <1% in PB and <5% in BM: in MDS: RA, RCMD +/ ring sideroblasts <5% in PB and 5 9% in BM: RAEB % in PB and 10 19% in BM: RAEB-2 20% in PB and/or BM: acute leukaemia Universitätsklinikum Aachen Klinik für Onkologie, Hämatologie und Stammzelltransplantation Pauwelsstraße 30, Aachen, Germany Phone info@ukaachen.de Mast cell blast Fig. 7 Overview of various physiological and pathological blast cells available as a wall poster or A4 chart from your Sysmex representative ZE EN.N.03/14
5 5 References [1] Bennett JM et al. (1976): Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) co-operative group. Br J Haematol 33 : [2] Fuchs R et al. (2013): Manual Hämatologie. Nora-Verlag. (book in German) [3] Fuchs R et al. (2002): Akute myeloische Leukämie. UNI-MED Verlag AG, Bremen. (book in German) [4] Haferlach T et al. (2011): Labordiagnostik in der Hämatologie Vom Symptom zur Diagnose. Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag, Cologne. (publication in German) [5] Jaffe ES et al. (2011): Tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. IARC Press, Lyon. [6] Murphy K et al. (2009): Janeway Immunologie, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg. (book in German) [7] Binder T et al. (2012): Pappenheim-Färbung: Beschreibung einer hämatologischen Standardfärbung Geschichte, Chemie, Durchführung, Artefakte und Problemlösungen. J Lab Med 36(5) : (abstract in English, publication in German) [8] Swerdlow SH et al. (ed.) (2008): WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, fourth edition. IARC Press, Lyon. Authors Reinhild Herwartz Biomedical specialist analyst for haematology University Hospital RWTH Aachen Clinic for Oncology/Haematology and Stem Cell Transplantation Prof. Dr. med. Roland Fuchs University Hospital RWTH Aachen Clinic for Oncology/Haematology and Stem Cell Transplantation Design and specifications may be subject to change due to further product development. Changes are confirmed by their appearance on a newer document and verification according to its date of issue. Copyright 2016 Sysmex Europe GmbH Sysmex Europe GmbH Bornbarch 1, Norderstedt, Germany Phone Fax info@sysmex-europe.com You will find your local Sysmex representative s address under EN.N.10/16
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Formation of Blood Cells
 Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material
 Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Acute myeloid leukemia. M. Kaźmierczak 2016
 Acute myeloid leukemia M. Kaźmierczak 2016 Acute myeloid leukemia Malignant clonal disorder of immature hematopoietic cells characterized by clonal proliferation of abnormal blast cells and impaired production
Acute myeloid leukemia M. Kaźmierczak 2016 Acute myeloid leukemia Malignant clonal disorder of immature hematopoietic cells characterized by clonal proliferation of abnormal blast cells and impaired production
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY
 HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY Failure of terminal differentiation Failure of differentiated cells to undergo apoptosis Failure to control growth Neoplastic stem cell FAILURE OF TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION
HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY Failure of terminal differentiation Failure of differentiated cells to undergo apoptosis Failure to control growth Neoplastic stem cell FAILURE OF TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and
 Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities Acute Myeloid Leukemia with recurrent cytogenetic Abnormalities -t(8;21)(q22;q22)(aml/eto) -inv(16) or t(16;16) -t(15;17) -11q23 Acute Myeloid
Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities Acute Myeloid Leukemia with recurrent cytogenetic Abnormalities -t(8;21)(q22;q22)(aml/eto) -inv(16) or t(16;16) -t(15;17) -11q23 Acute Myeloid
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED
 Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL LEUKEMIA FORMS CHAPTER 16A REVISED: DECEMBER 2017
 LEUKEMIA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Leukemia studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any leukemia study. Please refer
LEUKEMIA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Leukemia studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any leukemia study. Please refer
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
Myeloid neoplasms. Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories:
 Myeloid neoplasms Note: Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories: 1. AML : Acute myeloid leukemia(stem cell with myeloid
Myeloid neoplasms Note: Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories: 1. AML : Acute myeloid leukemia(stem cell with myeloid
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Chapter 10 Bone Marrow
 Chapter 10 Bone Marrow Contents Red Bone Marrow... 188 Hemopoiesis... 189 Early Steps in Hemopoiesis... 190 Late Steps in Hemopoiesis... 190 Yellow Bone Marrow... 197 Guide to Practical Histology: Bone
Chapter 10 Bone Marrow Contents Red Bone Marrow... 188 Hemopoiesis... 189 Early Steps in Hemopoiesis... 190 Late Steps in Hemopoiesis... 190 Yellow Bone Marrow... 197 Guide to Practical Histology: Bone
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Chapter 21 Outline. General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements
 Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
Morfologia normale e patologica
 Morfologia normale e patologica Gina Zini Centro di Ricerca ReCAMH Dpt. Ematologia Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma EMATOLOGIA DI LABORATORIO: percorsi diagnostici e obiettivi clinici. Milano 11-12
Morfologia normale e patologica Gina Zini Centro di Ricerca ReCAMH Dpt. Ematologia Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma EMATOLOGIA DI LABORATORIO: percorsi diagnostici e obiettivi clinici. Milano 11-12
Pathology. #11 Acute Leukemias. Farah Banyhany. Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16
 35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer
 Bone marrow Is a soft connective tissue occupies the medullary cavity of long bones and all the spaces between the trabeculae of spongy bone. It accounts for approximately 5% of the body weight in humans.
Bone marrow Is a soft connective tissue occupies the medullary cavity of long bones and all the spaces between the trabeculae of spongy bone. It accounts for approximately 5% of the body weight in humans.
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab
 Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Hematopoiesis. BHS Liège 27/1/2012. Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne
 Hematopoiesis BHS Liège 27/1/2012 Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne Hematopoiesis: definition = all the phenomenons to produce blood cells Leukocytes = White Blood Cells Polynuclear = Granulocytes Platelet
Hematopoiesis BHS Liège 27/1/2012 Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne Hematopoiesis: definition = all the phenomenons to produce blood cells Leukocytes = White Blood Cells Polynuclear = Granulocytes Platelet
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD. Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS
 HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS Introduction: o Myeloid neoplasms are divided into three major categories: o Acute
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS Introduction: o Myeloid neoplasms are divided into three major categories: o Acute
HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE
 Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
Hematopoie)c System. Kris)ne Kra2s, M.D.
 Hematopoie)c System Kris)ne Kra2s, M.D. Hematopoie)c System Lecture Objec)ves Describe the developmental stages of erythropoiesis. Describe the developmental stages of granulopoiesis. Describe the differences
Hematopoie)c System Kris)ne Kra2s, M.D. Hematopoie)c System Lecture Objec)ves Describe the developmental stages of erythropoiesis. Describe the developmental stages of granulopoiesis. Describe the differences
2 nd step do Bone Marrow Study If possible both the aspiration and
 Blood Malignancies-I Prof. Herman Hariman,SpPK a (KH). Ph.D.(U.K) Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. Clinpath, FK-USU First do the Full Blood Count Hb, WBCS, Platelets Morphology!! Such as blasts,
Blood Malignancies-I Prof. Herman Hariman,SpPK a (KH). Ph.D.(U.K) Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. Clinpath, FK-USU First do the Full Blood Count Hb, WBCS, Platelets Morphology!! Such as blasts,
What is MDS? Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Classification & Risk Stratification
 What is MDS? Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Classification & Risk Stratification Rami Komrokji, MD Clinical Director Malignant Hematology Moffitt Cancer Center Normal Blood and Bone Marrow What is MDS Myelodysplastic
What is MDS? Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Classification & Risk Stratification Rami Komrokji, MD Clinical Director Malignant Hematology Moffitt Cancer Center Normal Blood and Bone Marrow What is MDS Myelodysplastic
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Megakaryocyte or Precursor, Normal
 Precursor, Normal SYNONYMS none VITAL STATISTICS size...20-160 µm in diameter N:C ratio...varible, depending on maturation of cell; early forms have a high N:C rato which decreases as cell matures and
Precursor, Normal SYNONYMS none VITAL STATISTICS size...20-160 µm in diameter N:C ratio...varible, depending on maturation of cell; early forms have a high N:C rato which decreases as cell matures and
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
 Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
r). SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER nnmlbih UNIVERSITY Sophia Blaauw INSTRUCTIONS FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
 r). nnmlbih UNIVERSITY OF SCIEFICE nnd TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
r). nnmlbih UNIVERSITY OF SCIEFICE nnd TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
Ordering Physician CLIENT,CLIENT. Collected REVISED REPORT
 HPWET Hematopathology Consultation, MML Embed Client Hematopathology Consult REVISED INAL DIAGNOSIS Interpretation Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and biopsies, bilateral iliac crests: 1. Normocellular
HPWET Hematopathology Consultation, MML Embed Client Hematopathology Consult REVISED INAL DIAGNOSIS Interpretation Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and biopsies, bilateral iliac crests: 1. Normocellular
Bone Marrow Pathology. Part 1. R.S. Riley, M.D., Ph.D.
 Bone Marrow Pathology Part 1 R.S. Riley, M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Pathology Bone marrow basics Red cell diseases White cell diseases Other diseases Bone Marrow Pathology Bone marrow basics Hematopoiesis
Bone Marrow Pathology Part 1 R.S. Riley, M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Pathology Bone marrow basics Red cell diseases White cell diseases Other diseases Bone Marrow Pathology Bone marrow basics Hematopoiesis
MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES. Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman
 MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman BONE MARROW ASPIRATION Sites Sternum Anterior or posterior iliac spines Aspiration from
MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman BONE MARROW ASPIRATION Sites Sternum Anterior or posterior iliac spines Aspiration from
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Henry Moon lecture May 2007 Outline Definition Conceptual overview; pathophysiologic mechanisms Incidence,
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Henry Moon lecture May 2007 Outline Definition Conceptual overview; pathophysiologic mechanisms Incidence,
Primary myelofibrosis
 - It s a bone marrow fibrosis Primary myelofibrosis - It's type of myeloproliferative disease i.e. neoplastic proliferation of mature cell of myloid linage. - Its similar to chronic myloid leukemia (CML).
- It s a bone marrow fibrosis Primary myelofibrosis - It's type of myeloproliferative disease i.e. neoplastic proliferation of mature cell of myloid linage. - Its similar to chronic myloid leukemia (CML).
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms
 Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
DETERMINATION OF A LYMPHOID PROCESS
 Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Cell sorting: A bridge between morphology and flow cytometry. Pr François Mullier, Pr Bernard Chatelain July 19th, 2013
 Cell sorting: A bridge between morphology and flow cytometry Pr François Mullier, Pr Bernard Chatelain July 19th, 2013 1 CELL SORTING: PRINCIPLES D.Davies CELL SORTING: PRINCIPLES Aims Efficiency Purity
Cell sorting: A bridge between morphology and flow cytometry Pr François Mullier, Pr Bernard Chatelain July 19th, 2013 1 CELL SORTING: PRINCIPLES D.Davies CELL SORTING: PRINCIPLES Aims Efficiency Purity
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES
 MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra university hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences Key Features ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Cytopenias
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra university hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences Key Features ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Cytopenias
Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study
 Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCY
 HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCY Reference Compulsory reading Haematology at Glance 2 nd ed. Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Chapters: 20 to 31 Pages: 46 to 69 Pathogenesis of Haematological Malignancy Figure (a)
HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCY Reference Compulsory reading Haematology at Glance 2 nd ed. Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Chapters: 20 to 31 Pages: 46 to 69 Pathogenesis of Haematological Malignancy Figure (a)
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Terri Boyer 17 th October 2006 Overview Disease information: Aetiology of ALL proposed theory, contributing factors Symptoms Complications Diagnostic approaches - morphology
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Terri Boyer 17 th October 2006 Overview Disease information: Aetiology of ALL proposed theory, contributing factors Symptoms Complications Diagnostic approaches - morphology
4. TEXTBOOK: ABUL K. ABBAS. ANDREW H. LICHTMAN. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY. 5 TH EDITION. Chapter 2. pg
 LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
Normal Blood and Bone Marrow Populations
 4 CHAPTER 4 Normal Blood and Bone Marrow Populations It is essential to have a sound understanding of the nature and immunophenotypic characteristics of the normal cell populations encountered in bone
4 CHAPTER 4 Normal Blood and Bone Marrow Populations It is essential to have a sound understanding of the nature and immunophenotypic characteristics of the normal cell populations encountered in bone
Hematopathology Case Study
 www.medfusionservices.com Hematopathology Case Study CV3515-14 JUNE Clinical Presentation: Clinical Information: A 42 year old male with history of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) presents with an elevated
www.medfusionservices.com Hematopathology Case Study CV3515-14 JUNE Clinical Presentation: Clinical Information: A 42 year old male with history of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) presents with an elevated
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure
 Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure I am receiving an honorarium from Sysmex for today s presentation. 1 Determining the Etiology for
Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure I am receiving an honorarium from Sysmex for today s presentation. 1 Determining the Etiology for
Blood & Blood Formation
 Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Agriculture, Romania 2 Municipal Clinical Emergency Hospital from Timisoara, Gheorghe Dima Street, no. 5, Romania
 MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES IN BLOOD CELLS IN ACUTE LEUKAEMIA IN HUMANS NOTE 2. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES OF FIGURATIVE ELEMENTS BLOOD AND BONE MARROW IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE LEUKAEMIA SUSPICION Olga-Alina
MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES IN BLOOD CELLS IN ACUTE LEUKAEMIA IN HUMANS NOTE 2. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES OF FIGURATIVE ELEMENTS BLOOD AND BONE MARROW IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE LEUKAEMIA SUSPICION Olga-Alina
BCR-ABL1 positive Myeloid Sarcoma Nicola Austin
 BCR-ABL1 positive Myeloid Sarcoma Nicola Austin Cytocell UK & Ireland User Group Meeting Jesus College, Cambridge 4 th - 5 th April 2017 Myeloid Sarcoma WHO Classification Tumours of Haematopoietic and
BCR-ABL1 positive Myeloid Sarcoma Nicola Austin Cytocell UK & Ireland User Group Meeting Jesus College, Cambridge 4 th - 5 th April 2017 Myeloid Sarcoma WHO Classification Tumours of Haematopoietic and
INFECTION/ INFLAMMATION
 HAEMATOLOGY OCTOBER 2017* WHITE PAPER INFECTION/ INFLAMMATION Novel haematological parameters for rapidly monitoring the immune system response Patients with inflammatory disease are common on hospital
HAEMATOLOGY OCTOBER 2017* WHITE PAPER INFECTION/ INFLAMMATION Novel haematological parameters for rapidly monitoring the immune system response Patients with inflammatory disease are common on hospital
Myelodysplastic scoring system with flow cytometry. G Detry B Husson
 Myelodysplastic scoring system with flow cytometry G Detry B Husson Myelodysplastic syndroms Clonal haematopoietic stem cell disease characterized by dysplasia in one or more of the myeloid cell lines
Myelodysplastic scoring system with flow cytometry G Detry B Husson Myelodysplastic syndroms Clonal haematopoietic stem cell disease characterized by dysplasia in one or more of the myeloid cell lines
Hematology 101. Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD
 Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Peripheral Blood Smear: Diagnostic Clues and Algorithms
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias
 Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
LEUCOGNOST. Diagnostic-systems for the detection of leukaemias and myeloproliferative diseases. Focussing your hematology targets.
 LEUCOGNOST Diagnostic-systems for the detection of leukaemias and myeloproliferative diseases Focussing your hematology targets. LEUCOGNOST LEUCOGNOST ALPA Cytochemical staining for the differentiation
LEUCOGNOST Diagnostic-systems for the detection of leukaemias and myeloproliferative diseases Focussing your hematology targets. LEUCOGNOST LEUCOGNOST ALPA Cytochemical staining for the differentiation
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Introduction to Haematology. Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria
 Introduction to Haematology Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria Suggested reading Haematology at a Glance Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Second Edition Published by Blackwell
Introduction to Haematology Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria Suggested reading Haematology at a Glance Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Second Edition Published by Blackwell
Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY
 Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY DISCLOSURES NONE Learning objectives To review the rules of BMA evaluation To review the main issues
Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY DISCLOSURES NONE Learning objectives To review the rules of BMA evaluation To review the main issues
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228
 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms with Defined Molecular Abnormalities
 WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms with Defined Molecular Abnormalities Robert W. McKenna, M.D. 1/2009 WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms (4th Edition)--2008 Incorporates new information that
WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms with Defined Molecular Abnormalities Robert W. McKenna, M.D. 1/2009 WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms (4th Edition)--2008 Incorporates new information that
Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia"
 Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia" Hoelzer, D.,l, Harriss, E. B.l, Kurrle, E.l, Schmücker, H.l, Hellriegel,
Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia" Hoelzer, D.,l, Harriss, E. B.l, Kurrle, E.l, Schmücker, H.l, Hellriegel,
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia with molecular abnormalities SH
 Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia with molecular abnormalities SH2017-0351 Madhu P. Menon MD,PhD, Juan Gomez MD, Kedar V. Inamdar MD,PhD and Kristin Karner MD Madhu P Menon, MD, PhD Henry Ford Hospital Patient
Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia with molecular abnormalities SH2017-0351 Madhu P. Menon MD,PhD, Juan Gomez MD, Kedar V. Inamdar MD,PhD and Kristin Karner MD Madhu P Menon, MD, PhD Henry Ford Hospital Patient
Blood Cell Identification: 2011-B Mailing: Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
 Please Note: To view the Figures and Images contained within this education activity in color, access the electronic version of the reading. CASE HISTORY This peripheral blood smear is from a 51-year-old
Please Note: To view the Figures and Images contained within this education activity in color, access the electronic version of the reading. CASE HISTORY This peripheral blood smear is from a 51-year-old
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY. White Blood Cells (WBC) Dr Nervana Mostafa
 BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY White Blood Cells (WBC) Dr Nervana Mostafa 1 Lecture content. 1 Eosinophils and Basophilophils formation, maturation and function. 2. 3. 4. 5 Monocytes and macrophage formation, maturation
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY White Blood Cells (WBC) Dr Nervana Mostafa 1 Lecture content. 1 Eosinophils and Basophilophils formation, maturation and function. 2. 3. 4. 5 Monocytes and macrophage formation, maturation
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Types
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Types Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Types Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis
 Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Objectives are to: Identify the developmental cells of erythropoiesis
Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Objectives are to: Identify the developmental cells of erythropoiesis
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
HSCT MANAGEMENT WHITE PAPER. Managing stem cell apheresis effectively
 HAEMATOLOGY JANUARY 2017 WHITE PAPER HSCT MANAGEMENT Managing stem cell apheresis effectively Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a treatment that
HAEMATOLOGY JANUARY 2017 WHITE PAPER HSCT MANAGEMENT Managing stem cell apheresis effectively Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a treatment that
Table 1: biological tests in SMD
 Table 1: biological tests in SMD Tests Mandatory Recommended Under validation Morphology Marrow aspirate Marrow biopsy 1 Iron staining Quantification of dysplasia WHO 2008 Classification Cytogenetics Conventional
Table 1: biological tests in SMD Tests Mandatory Recommended Under validation Morphology Marrow aspirate Marrow biopsy 1 Iron staining Quantification of dysplasia WHO 2008 Classification Cytogenetics Conventional
Myeloproliferative Disorders - D Savage - 9 Jan 2002
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
The patient had a mild splenomegaly but no obvious lymph node enlargement. The consensus phenotype obtained from part one of the exercise was:
 Case History An 86 year old male was admitted to hospital with chest infection. Haematological examination subsequently revealed the following: Hb- 11.0 g/dl; WBC- 67.1 x 10^9/l; PLT- 99 x10^9/l; RBC-
Case History An 86 year old male was admitted to hospital with chest infection. Haematological examination subsequently revealed the following: Hb- 11.0 g/dl; WBC- 67.1 x 10^9/l; PLT- 99 x10^9/l; RBC-
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES: A diagnosis often missed
 MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES: A diagnosis often missed D R. EMMA W YPKEMA C O N S U LTA N T H A E M AT O L O G I S T L A N C E T L A B O R AT O R I E S THE MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES DEFINITION The Myelodysplastic
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES: A diagnosis often missed D R. EMMA W YPKEMA C O N S U LTA N T H A E M AT O L O G I S T L A N C E T L A B O R AT O R I E S THE MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES DEFINITION The Myelodysplastic
Adult Acute leukemia. Matthew Seftel. August
 Adult Acute leukemia Matthew Seftel August 21 2007 mseftel@cancercare.mb.ca Principles 3 cases Diagnosis and classification of acute leukemia (AL) Therapy Emergencies Remission induction BMT Complications
Adult Acute leukemia Matthew Seftel August 21 2007 mseftel@cancercare.mb.ca Principles 3 cases Diagnosis and classification of acute leukemia (AL) Therapy Emergencies Remission induction BMT Complications
Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points
 Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points Koh Liang Piu Department of Hematology-Oncology National University Cancer Institute National University Health System Objectives of this talk: 1. To provide some useful
Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points Koh Liang Piu Department of Hematology-Oncology National University Cancer Institute National University Health System Objectives of this talk: 1. To provide some useful
Usefulness of NEUT-X determination in routine diagnostic procedures: application to myelodysplastic syndromes. F. Cymbalista.
 Usefulness of NEUT-X determination in routine diagnostic procedures: application to myelodysplastic syndromes F. Cymbalista Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are common malignant disorders with a poor prognosis.
Usefulness of NEUT-X determination in routine diagnostic procedures: application to myelodysplastic syndromes F. Cymbalista Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are common malignant disorders with a poor prognosis.
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz
 Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Blood Cell Identification Graded
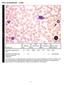 Blood Cell Identification Graded BCK/BCP-11 BCK BCP Referees Participants Participants Performance Identification No. % No. % No. % Evaluation Neutrophil, segmented or band Neutrophil with Pelger-Huët
Blood Cell Identification Graded BCK/BCP-11 BCK BCP Referees Participants Participants Performance Identification No. % No. % No. % Evaluation Neutrophil, segmented or band Neutrophil with Pelger-Huët
Case Presentation No. 075
 Case Presentation No. 075 Session 4. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cristina Montalvo, MD Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
Case Presentation No. 075 Session 4. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cristina Montalvo, MD Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43
 ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
Proper Slide Preparation
 Hematology Essentials: A Foundation for WBC Review Using Case Studies Christine Hinz, MS, MLS(ASCP) CM Proper Slide Preparation smooth, homogenous film 1/2 to 3/4 the slide length straight feather edge
Hematology Essentials: A Foundation for WBC Review Using Case Studies Christine Hinz, MS, MLS(ASCP) CM Proper Slide Preparation smooth, homogenous film 1/2 to 3/4 the slide length straight feather edge
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow
 The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
Leukaemia Laboratory diagnosis. Dr. D.Aruna chaithanya, I yr PG(Pathology),KIMS.
 Leukaemia Laboratory diagnosis Dr. D.Aruna chaithanya, I yr PG(Pathology),KIMS. Leukemia Stem cell disorder characterized by a malignant neoplastic proliferation and accumulation of immature hematopoietic
Leukaemia Laboratory diagnosis Dr. D.Aruna chaithanya, I yr PG(Pathology),KIMS. Leukemia Stem cell disorder characterized by a malignant neoplastic proliferation and accumulation of immature hematopoietic
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 20-year-old female with sickle cell disease who presents with bilateral leg pain for 3 days. She is scheduled to have bilateral hip and leg
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 20-year-old female with sickle cell disease who presents with bilateral leg pain for 3 days. She is scheduled to have bilateral hip and leg
